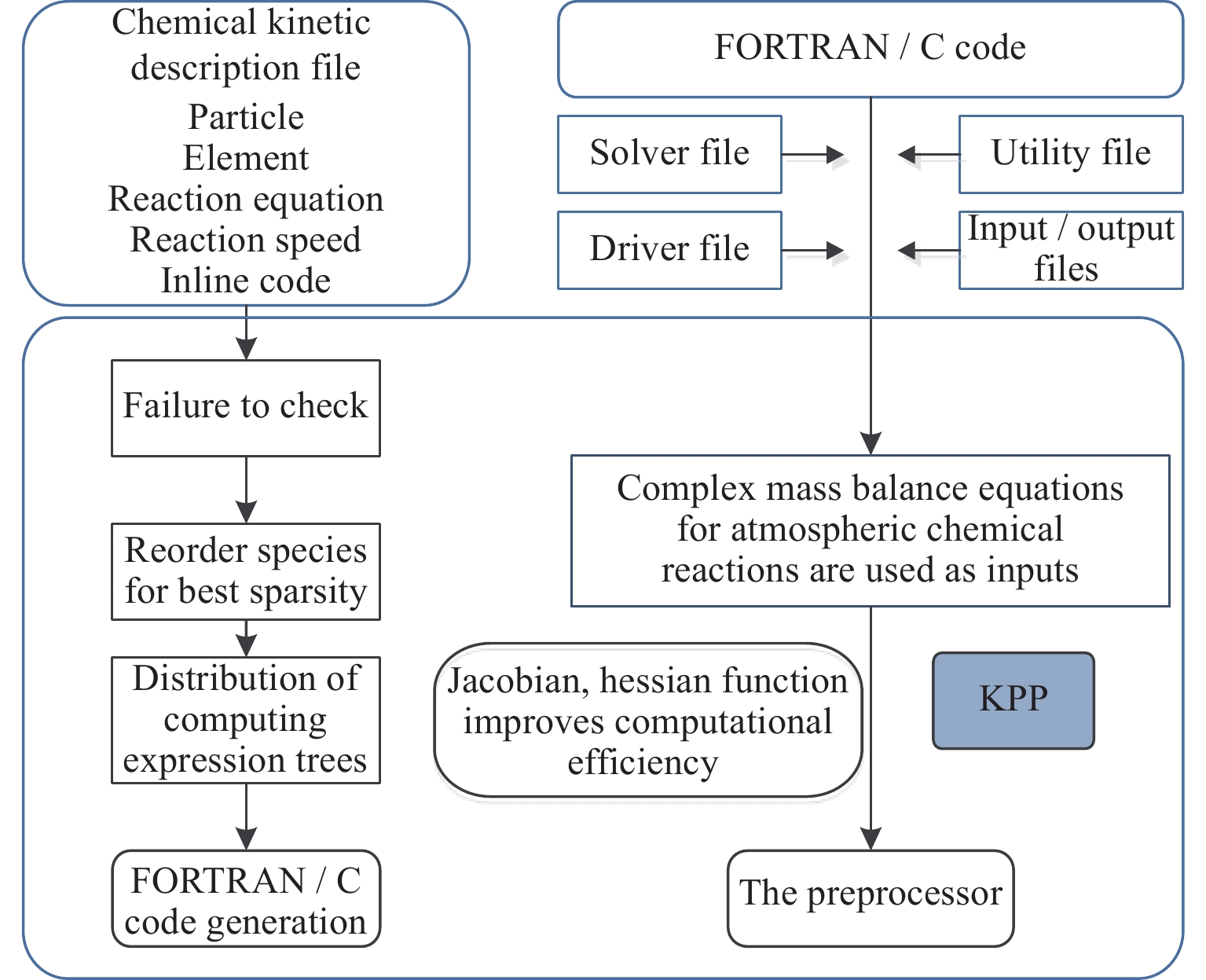
Computer-aided Chemical Kinetic Modeling in Near Space
-
摘要:
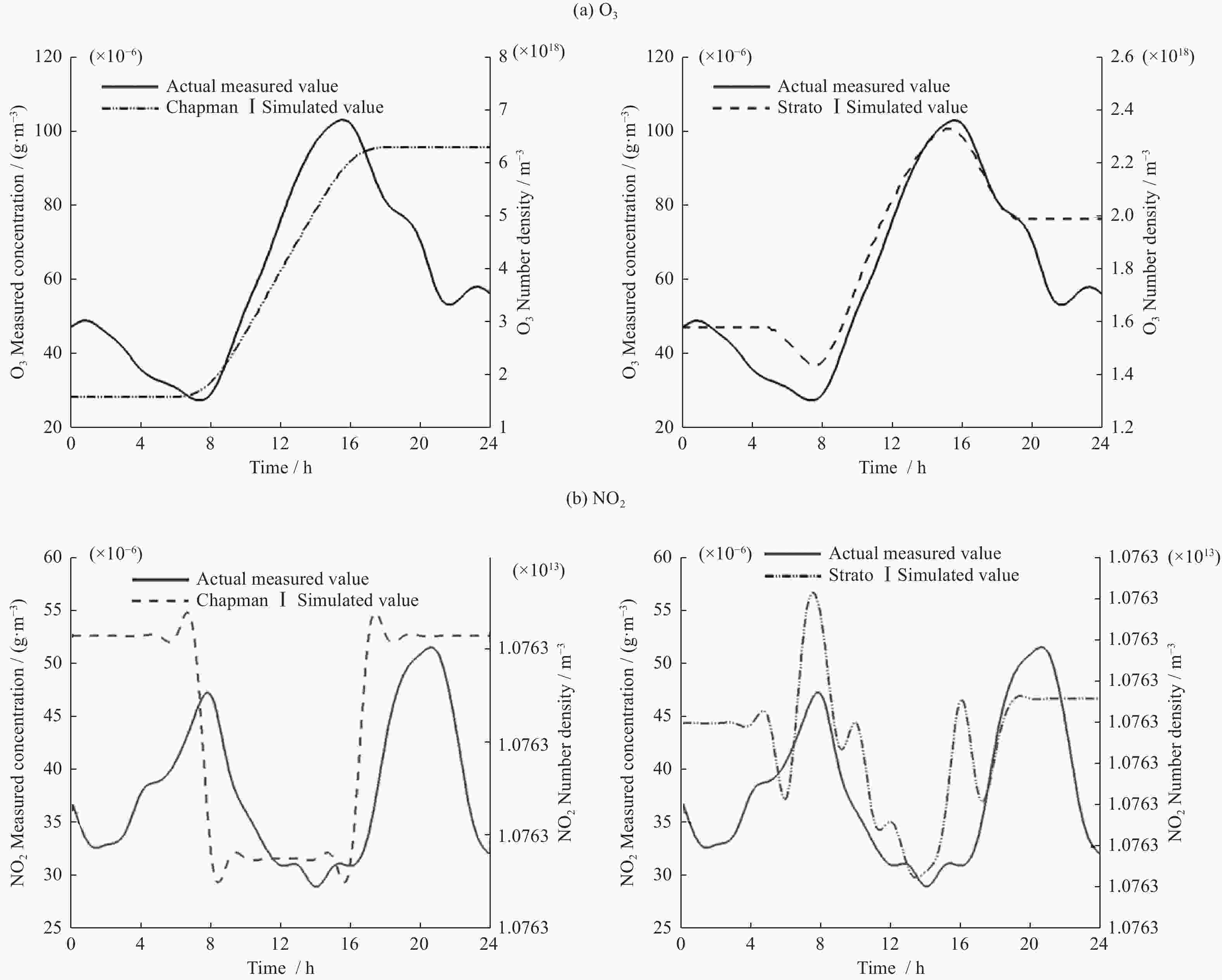
围绕临近空间大气化学过程数值模拟计算问题,以平流层大气4个典型光化学系统为例,运用化学动理学预处理(KPP)工具,对不同复杂度的光化学反应质量平衡方程体系进行预处理,快速建立各系统化学动理学方程组的代数表示;针对模型中的大刚性ODE方程组,选取6种不同的数值计算方案(rodas,ros3,ros4,rosenbrock,sdirk,seulex) , 实现ODE方程组的离散表示,并自动生成所需计算代码。在此基础上,开展平流层光化学过程数值模拟试验,重点考察了:各数值计算方案的计算效率和计算稳定性;各系统主要化学成分随着时间的演化规律;光化学系统复杂度对各模型主要成分变化的影响。模拟结果显示:KPP工具能有效应对临近空间大气化学反应系统复杂度的增长,缩短大气化学模型建模与检验周期,为临近空间大气化学过程研究提供有效技术支撑。
Abstract:As the typical processes in stratospheric photochemical reactions, four systems with different complicities in mass balance equations are selected as the bench mark cases, to show the efficiency and convenience for application of the Chemical Kinetics Preprocess (KPP) tool in Near Space chemical modelings. Focusing on the large rigid ODE equations in the model, six different numerical calculation schemes are selected (rodas, ros3, ros4, rosenbrock, sdirk, seulex), to realize the discrete representation of ODE equations, and automatically generate the required calculation code. On this basis, the numerical simulation experiments of stratospheric photochemical processes are carried out, focusing on: (i) the computational efficiency and stability of the numerical calculation schemes; (ii) the evolution of main chemical components of each system with time; (iii) the influence of the complexity of the photochemical system on the changes of the main components of each model. Simulation results show that the KPP tool can effectively cope with the increase of the complexity of atmospheric chemical reaction system in adjacent space, shorten the modeling and testing period of atmospheric chemical model, and provide effective technical support for the research of the atmospheric chemical process in adjacent space.
-
Key words:
- Near space /
- Atmospheric chemistry /
- KPP /
- Numerical Simulation
-
表 1 平流层中的单分子、双分子和三分子光化学反应
Table 1. Single, bimolecular and trimolecular chemical reactions in the stratosphere
反应方程式 反应速率 1 O3+hv = O+O2 6.120×10–4 J 2 O3+O = 2O2 8.0×10–12 e(–2060/T) 3 H + OH +N2 = H2O + N2 1.38×10–24×(1/T)2.6 表 2 Chapman Ⅰ模型的化学反应方程式
Table 2. Chemical reaction equation of Chapman Ⅰ model
反应方程式 反应速率 O2+hv = 2O 2.643×10–10 J 3 O2+O = O3 8.018×10–17 O3+hv = O+O2 6.120×10–4 J O3+O = 2O2 1.576×10–15 NO+O3 = NO2+O2 6.062×10–15 NO2+O = NO+O2 1.069×10–11 表 3 Chapman Ⅰ模型中各成分初始体积分数
Table 3. Initial volume fraction of each component in Chapman Ⅰ model
O O2 O3 NO NO2 8.159×10–9 0.209 6.560×10–6 1.075×10–8 2.759×10–9 表 4 Chapman Ⅱ模型的化学反应方程式
Table 4. Chemical reaction equation of Chapman Ⅱ model
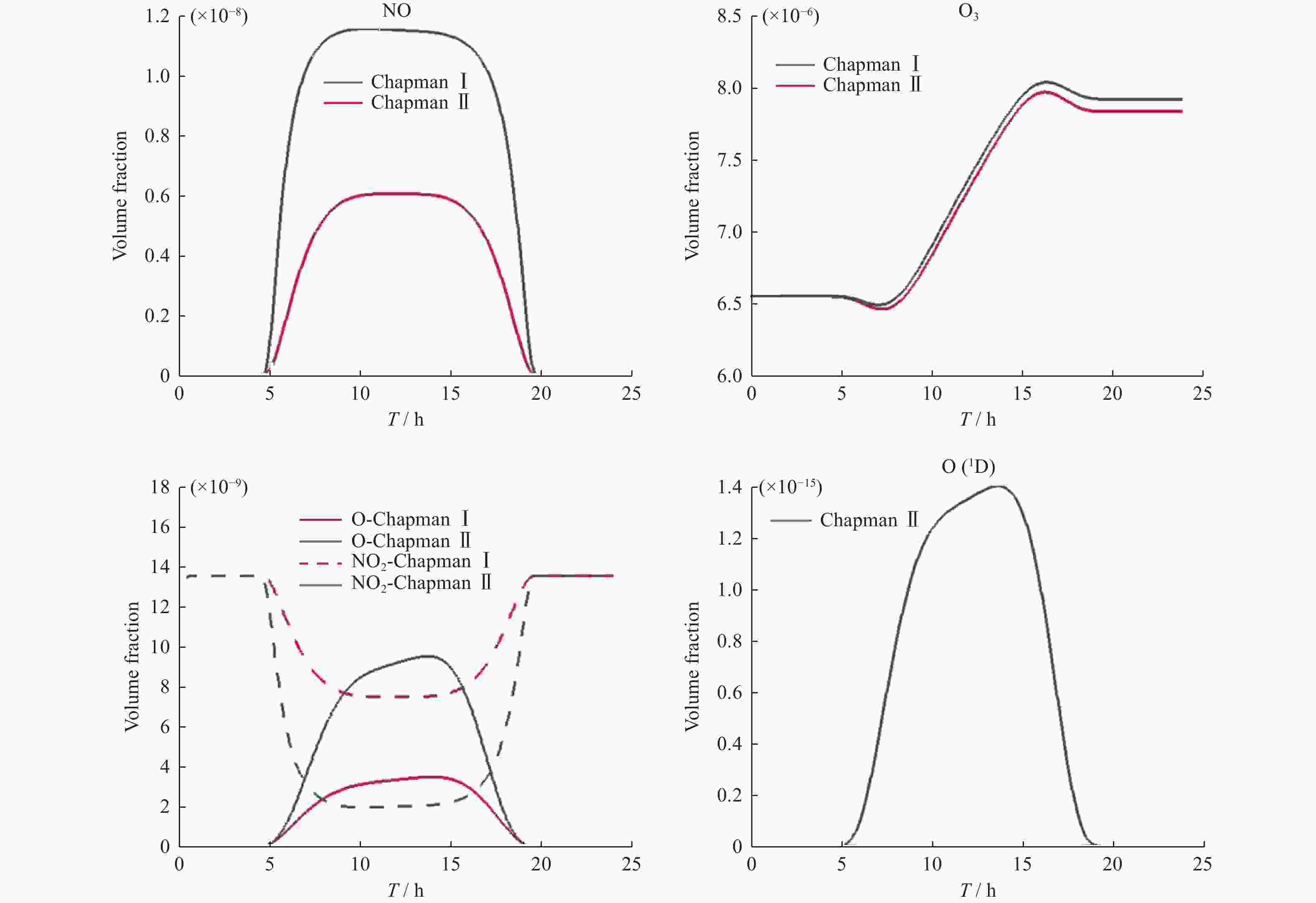
反应方程式 反应速率 1 O2+hv=2O 2.643×10–10 J 3 2 O2+O=O3 8.018×10–17 3 O3+hv=O+O2 6.120×10–4 J 4 O3+O=2O2 1.576×10–15 5 NO+O3=NO2+O2 6.062×10–15 6 NO2+O=NO+O2 1.069×10–11 7 O3+hv=O(1D)+O2 1.070×10–3 J 2 8 O(1D)+M=O+M 7.110×10–11 9 O(1D)+O3=2O2 1.200×10–10 10 NO2+hv=NO+O 1.289×10–2 J 表 5 各求解器计算Chapman模型效率(单位 s)
Table 5. Each solver calculates the efficiency of the Chapman model (Unit s)
ros3 rosenbrock ros4 sdirk seulex rodas ChapmanⅠ模型 0.029 0.027 0.037 0.03 0.025 0.025 ChapmanⅡ模型 0.03 0.032 0.029 0.03 0.027 0.023 表 6 各求解器计算Chapman模型误差值
Table 6. Each solver calculates the error value of the Chapman model
ros3 rosenbrock ros4 sdirk seulex rodas ChapmanⅠ模型(×10–13) 6.195 3.481 3.846 3.075 14.178 2.996 ChapmanⅡ模型(×10–13) 4.712 2.918 3.559 2.680 11.994 2.586 表 7 各求解器计算Strato模型效率(单位 s)
Table 7. Each solver calculates the efficiency of the Strato model (Unit s)
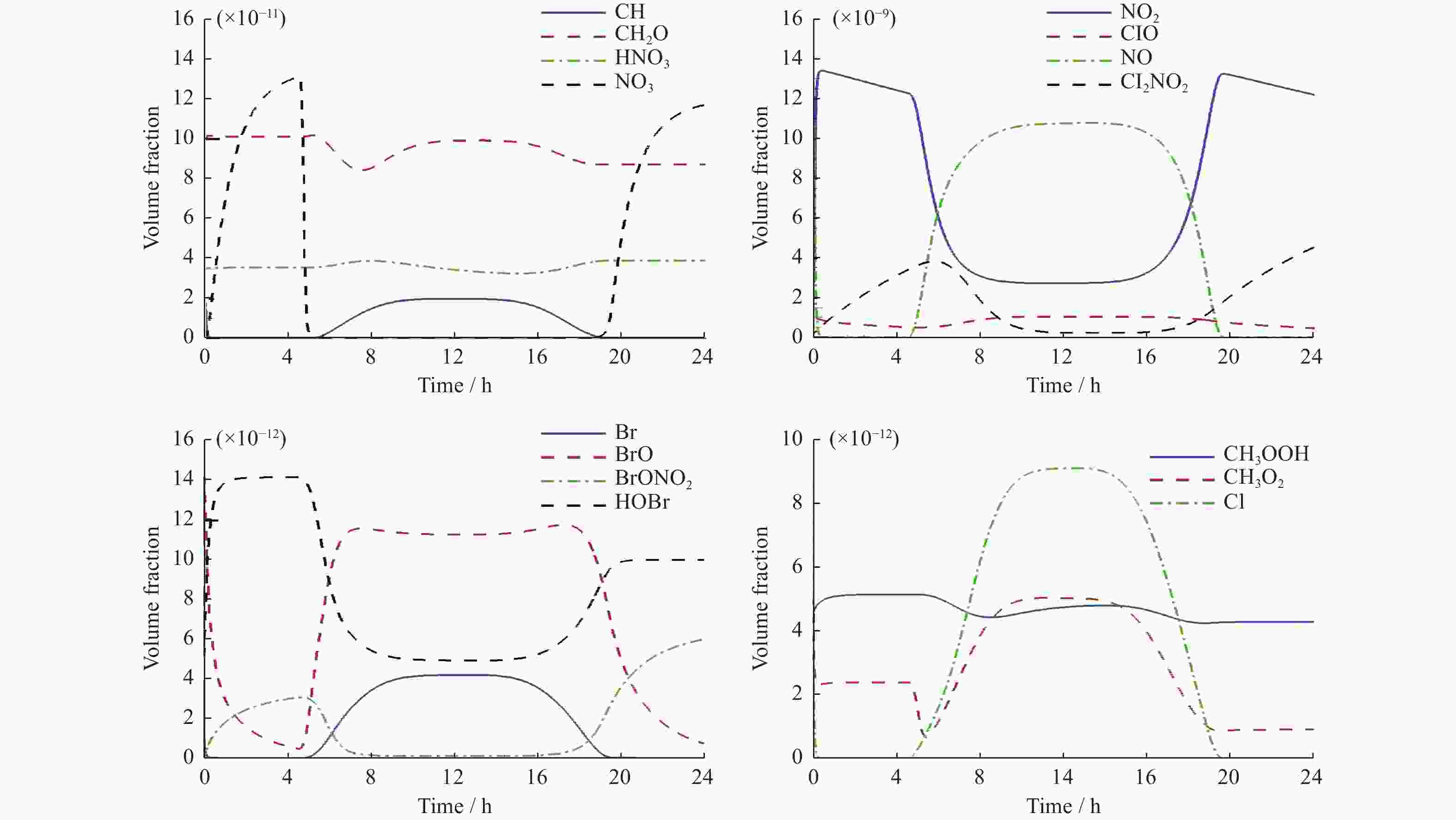
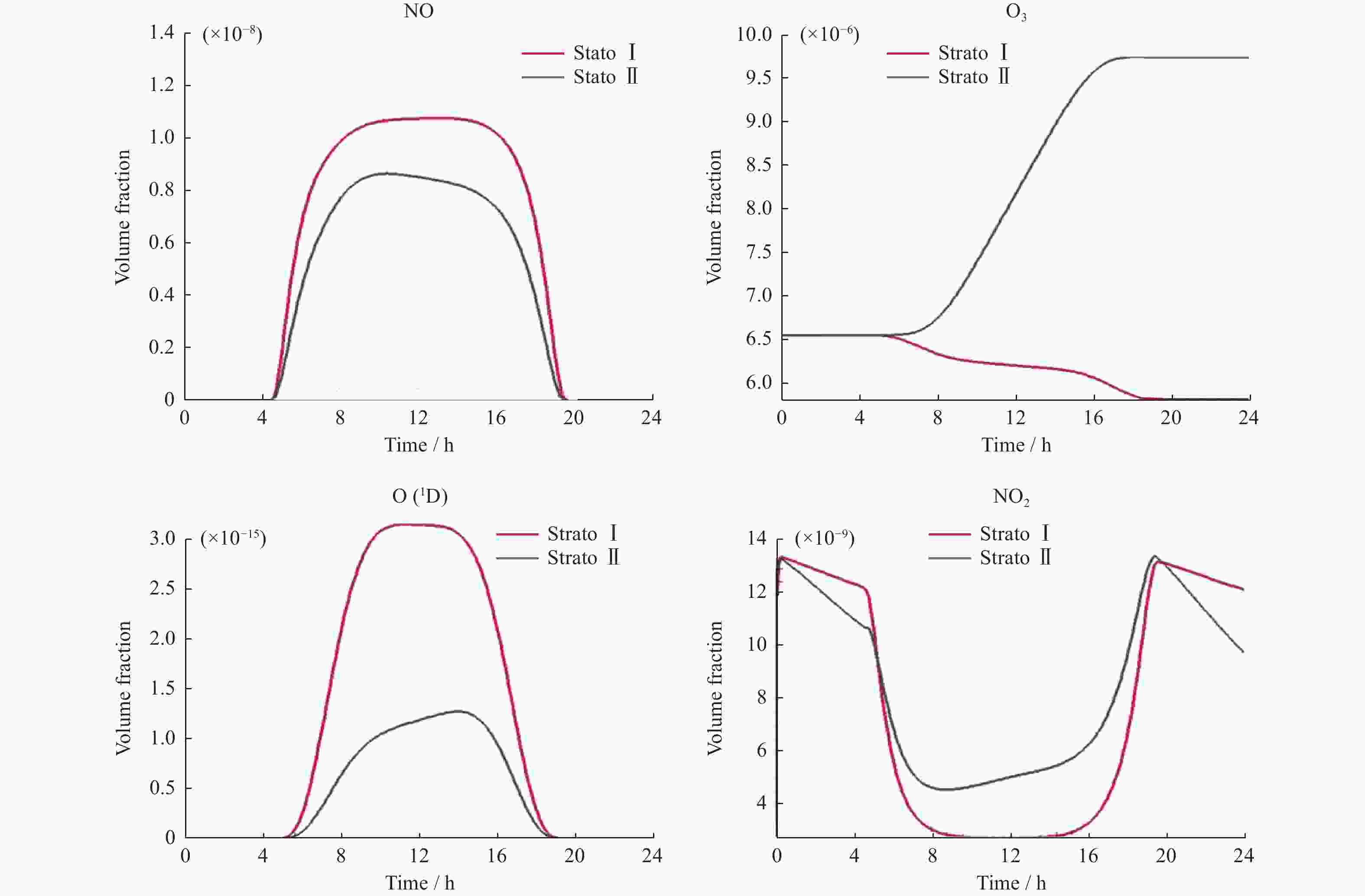
ros3 rosenbrock ros4 sdirk seulex rodas StratoⅠ模型 0.088 0.081 0.086 0.085 0.085 0.091 StratoⅡ模型 0.100 0.105 0.099 0.094 0.105 0.108 表 8 各求解器计算Strato模型误差值
Table 8. Each solver calculates the error value of the Strato model
ros3 rosenbrock ros4 sdirk seulex rodas StratoⅠ模型(×10–11) 8.9809 8.9985 8.9806 8.9803 8.9994 8.9797 StratoⅡ模型(×10–13) 1.6525 3.4438 1.6432 1.6033 3.5338 1.5614 -
[1] BRASSEUR G P, SOLOMON SUSAN. Aeronomy of the Middle Atmosphere: Chemistry and Physics of the Stratosphere and Mesosphere[M]. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, 2005: 25-32 [2] REES M H. Physics and Chemistry of the Upper Atmosphere[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1989: 49-64 [3] 马鹏里, 张强, 杨兴国, 等. 大气化学研究进展—臭氧、气溶胶研究综述[J]. 干旱气象, 2003(4): 66-70MA Pengli, ZHANG Qiang, YANG Xingguo, et al. Research progress of atmospheric chemistry- review of ozone and aerosol research[J]. Dry Meteorology, 2003(4): 66-70 [4] 王明星. 大气化学[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 1999: 10-13WANG Mingxing. Atmospheric Chemistry[M]. Beijng: Meteorological Press, 1999: 10-13 [5] 肖存英. 临近空间大气动力学特性研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院研究生院(空间科学与应用研究中心), 2009XIAO Cunying. Study on Atmospheric Dynamics in Near Space[D]. Beijing: Graduate School of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Center for Space Science and Applied Research), 2009 [6] 王振亚, 李海洋, 周士康. 平流层中臭氧耗减化学研究进展[J]. 科学通报, 2001, 46(8): 619-625 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2001.08.002WANG Zhenya, LI Haiyang, ZHOU Shikang. Advances in ozone depletion chemistry in the stratosphere[J]. Science Bulletin, 2001, 46(8): 619-625 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2001.08.002 [7] 徐晓斌, 葛宝珠, 林伟立. 臭氧生成效率(OPE)相关研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2009, 24(008): 845-853XU Xiaobin, GE Baozhu, LIN Weili. Progress in the research of Ozone Production Efficiency (OPE)[J]. Advances in Geoscience, 2009, 24(008): 845-853 [8] 贾龙, 葛茂发, 徐永福, 等. 大气臭氧化学研究进展[J]. 化学进展, 2006, 018(011): 1565-1574JIA Long, GE Maofa, XU Yongfu, et al. Advances in atmospheric ozone chemistry[J]. Chemical Progress, 2006, 018(011): 1565-1574 [9] 刘春红, 杨培才, 曾庆存. 平流层臭氧均相光化学系统的非线性特性——对Clx和NOx排放强度变化的响应[J]. 中国科学(D辑:地球科学), 1997(05): 475-480LIU Chunhong, YANG Peicai, ZENG Qingcun. Nonlinear characteristics of stratospheric ozone homogeneous photochemical system-response to Clx and NOx emission intensity changes[J]. hinese Science (part D:Geoscience) , 1997(05): 475-480 [10] 范志强. 临近空间大气环境探测资料分析研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科技大学, 2018FAN Zhiqiang. Analysis and Study of Atmospheric Environment Detection Data in Near Space[D]. Changsha: University of National Defense Science and Technology, 2018 [11] CHAPMAN S A. Theory of upper atmospheric ozone[J]. Memoirs of The Royal Meteorological Society, 1930, 3: 103-125 [12] BRASSEUR G P, JACOB D J. Modeling of Atmospheric Chemistry[M]. Cambridge : Cambridge University Press, 2017: 34-45 [13] DESMOND J H. Modeling and Simulating Chemical Reactions[M]. New York: Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 2008 [14] NICHOLAS J H. The Princeton Companion to Applied Mathmatics[M]. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2015 [15] 田文寿, 张敏, 舒建川. 中层大气模式的应用及发展前景[J]. 地球科学进展, 2009, 24(03): 252-261 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2009.03.004TIAN Wenshou, ZHANG Min, SHU Jianchuan. Application and development prospect of mesosphere model[J]. Advances in Geoscience, 2009, 24(03): 252-261 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2009.03.004 [16] 毕云. 平流层水汽与甲烷的分布和变化及其气候效应的研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2009BI Yun. Study on the Distribution and Variation of Stratospheric Water Vapor and Methane and Their Climatic Effects[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2009 [17] 潘晨. 利用WACCM4模式对平流层大气组成的模拟研究[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2013PAN Chen. Simulation of Stratospheric Atmospheric Composition Using WACCM4 Model[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Engineering, 2013 [18] 潘晨, 朱彬, 施春华, 等. SD-WACCM模式对平流层化学组分的模拟研究[J]. 气象科学, 2015, 35(01): 9-16PAN Chen, ZHU Bin, SHI Chunhua, et al. Simulation study of stratospheric chemical composition by SD-WACCM model[J]. Meteorological Sciences, 2015, 35(01): 9-16 [19] 刘宁微, 马建中, 伍湘君, 等. 两个模式对平流层温度模拟的比较与分析[J]. 大气科学学报, 2017, 40(06): 721-728LIU Ningwei, MA Jianzhong, WU Xiangjun, et al. Comparison and analysis of two models for stratospheric temperature simulation[J]. Journal of atmospheric science, 2017, 40(06): 721-728 [20] 徐寄遥, 马瑞平, SMITH A K. 光化-动力耦合重力波模式及其应用——Ⅰ. 模式的建立[J]. 中国科学(A辑), 2001(S1): 142-148XU Jiyao, MA Ruiping, SMITH A K. Photochemical-dynamic coupled gravity wave model and its application- I. The establishment of the model[J]. Chinese Science (Series A) , 2001(S1): 142-148 [21] 徐寄遥, 马瑞平, SMITH A K. 光化-动力耦合重力波模式及其应用——Ⅱ. 稳定传播的重力波对中层顶区化学成分分布的影响[J]. 中国科学(A辑), 2001(S1): 149-156XU Jiyao, MA Ruiping, SMITH A K. Photochemical-dynamic coupled gravity wave model and its application- Ⅱ. Effect of stably propagating gravity waves on chemical composition distribution in the mesopause region[J]. Chinese Science (Series A) , 2001(S1): 149-156 [22] 王体健, 李宗恺. 不同方案求解非线性化学动力学方程组的比较[J]. 应用气象学报, 1996, 7(04): 466-472WANG Tijian, LI Zongkai. Comparison of different schemes for solving nonlinear chemical kinetic equations[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 1996, 7(04): 466-472 [23] 王体健, 孙照渤. 一种非线性大气化学动力学方程组的新算法[J]. 南京气象学院学报, 1998, 021(003): 398-404WANG Shijian, SUN Zhaobo. A new algorithm for nonlinear atmospheric chemical kinetic equations[J]. Journal of Nanjing Institute of Meteorology, 1998, 021(003): 398-404 [24] 张欣, 王体健, 沈凡卉, 等. 非线性大气化学动力学方程组数值解法的比较[J]. 气象科学, 2010, 30(04): 427-437 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0827.2010.04.001ZHANG Xin, WANG Tijian, SHEN Fanhui, et al. Comparison of numerical solutions of nonlinear atmospheric chemical kinetic equations[J]. Meteorological Sciences, 2010, 30(04): 427-437 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0827.2010.04.001 [25] 芮守娟. 关中地区臭氧浓度变化特征及其形成过程的数值模拟[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2019RUI Shoujuan. Numerical Simulation of Ozone Concentration Change and Its Formation Process in Guanzhong Area[D]. Xian: Chang'an University, 2019 [26] DAMIAN-IORDACHE V. KPP-Chemistry Simulation Development Environment[D]. Iowa: The University of Iowa, 1996 [27] DAMIAN V, SANDU A, DAMIAN M, et al. The kinetic preprocessor KPP-a software environment for solving chemical kinetics[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2002, 26(11): 1567-1579 [28] SANDU A, VERWER J G, BLOM J G, et al. Benchmarking stiff ODE solvers for atmospheric chemistry problems II: Rosenbrock solvers[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 1997, 31(20): 3459-3472 doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(97)83212-8 [29] 楼晟荣. 大气环境中OH自由基反应活性的检测技术[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2012LOU Shengrong. Detection of Reaction Activity of OH Free Radicals in Atmospheric Environment[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2012 [30] 林秀, 王智民, 韩基新. 大气中臭氧的存在形式及环保对策[J]. 黑龙江大学自然科学学报, 2003(03): 118-122 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7011.2003.03.029LIN Xiu, WANG Zhimin, HAN Jixin. The existing forms of ozone in the atmosphere and environmental protection countermeasures[J]. Journal of Natural Science of Heilongjiang University, 2003(03): 118-122 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7011.2003.03.029 [31] HWANG D Y, MEBEL A M. Ab initio study on the reaction mechanism of ozone with the chlorine atom[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 1998, 109(24): 10847-10852 doi: 10.1063/1.477781 [32] WOFSY S C, MCELROY M B, YUNG Y L. The chemistry of atmospheric bromine[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2013, 2(6): 215-218 -
-





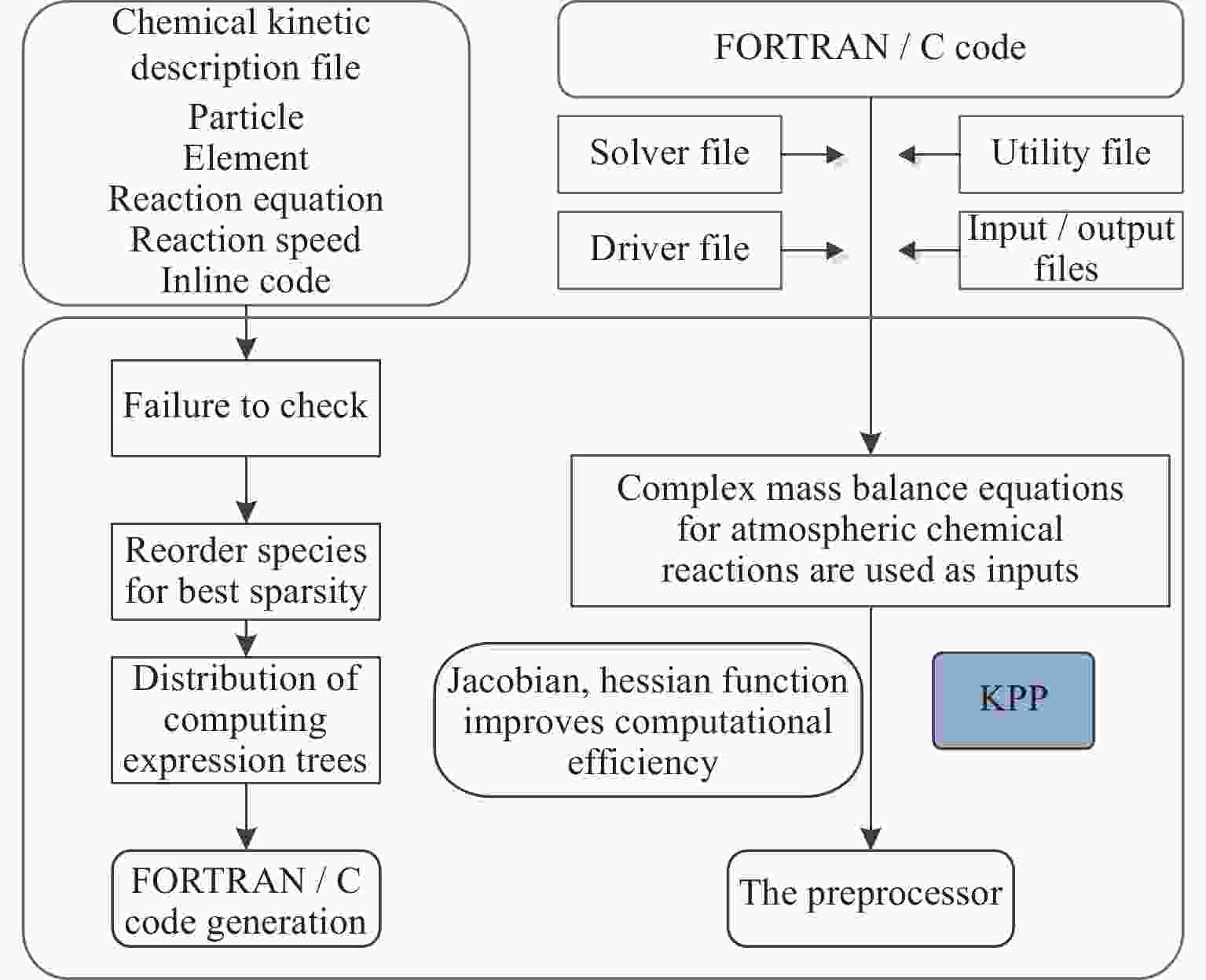
 下载:
下载: