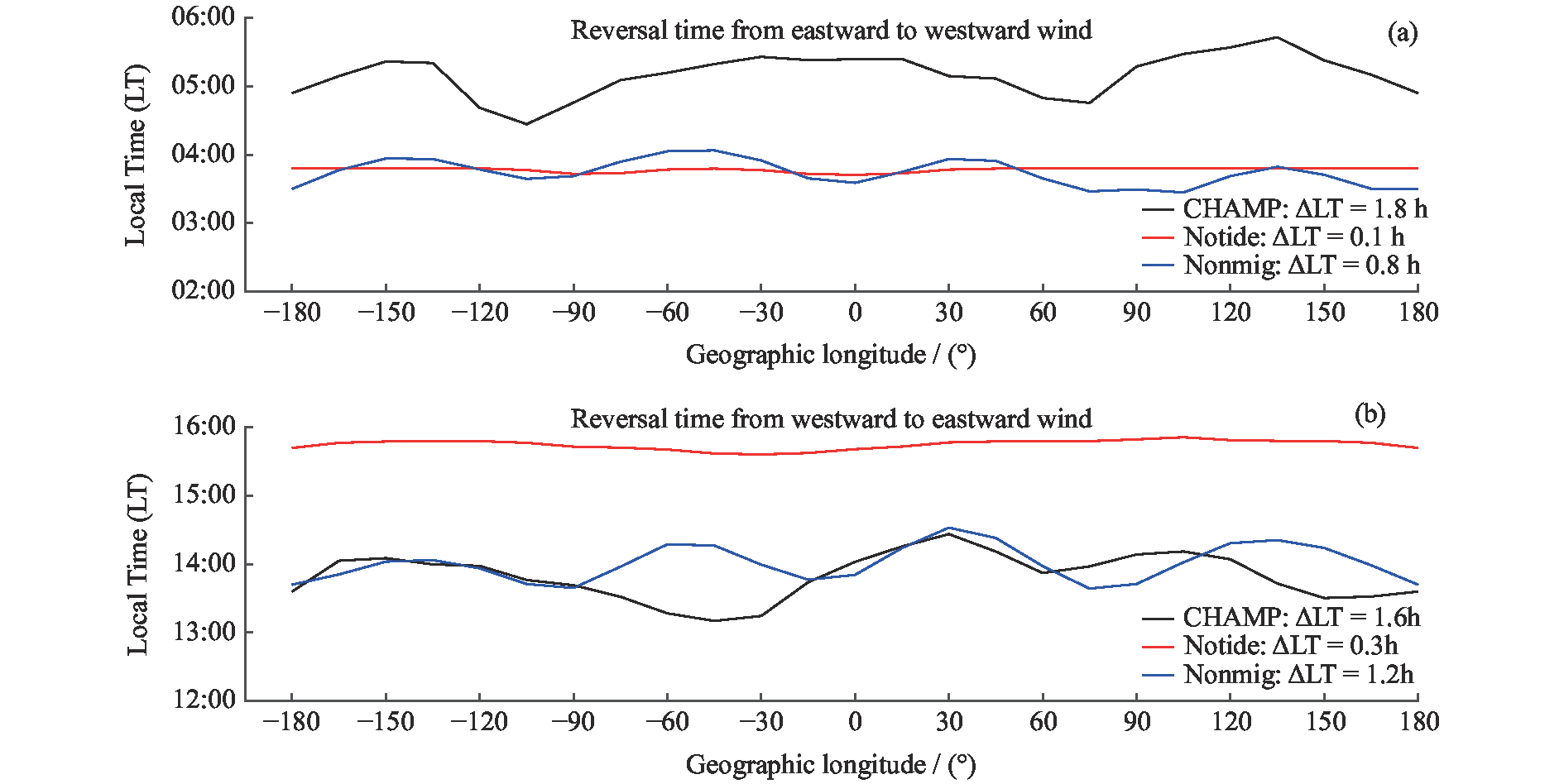
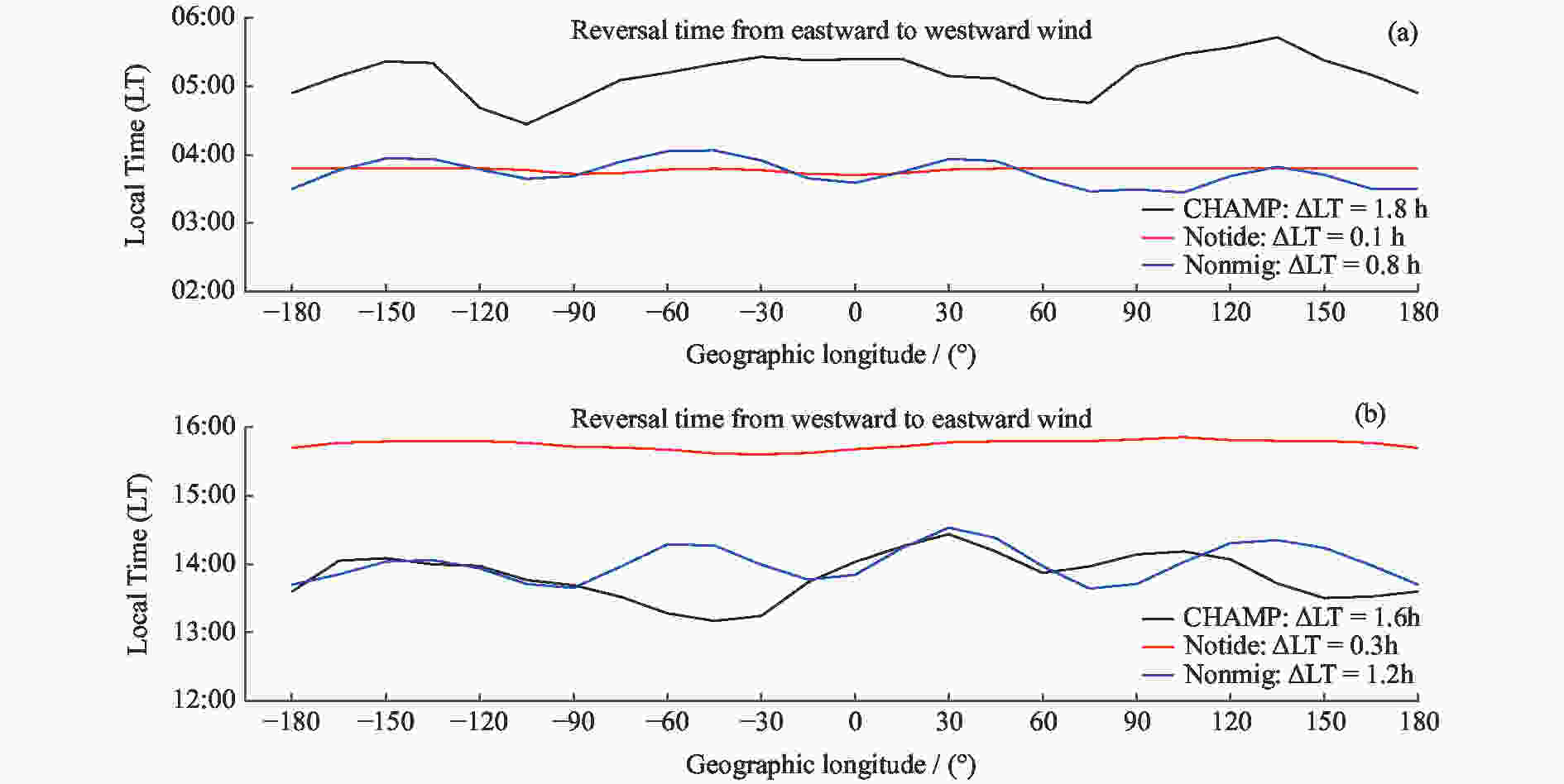
赤道地区热层纬向风反转时间和风速的经度分布差异
doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.02.210329039 cstr: 32142.14.cjss2022.02.210329039
Longitudinal Difference of Equatorial Thermospheric Zonal Wind’s Reversal Time and Speed
-
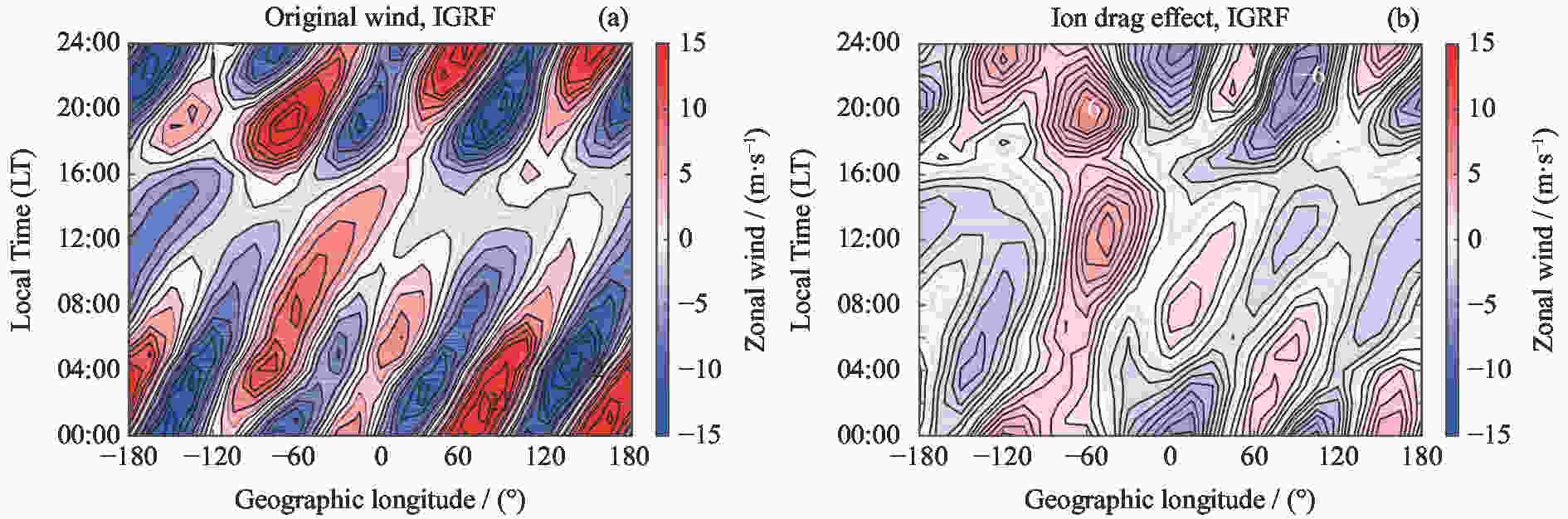
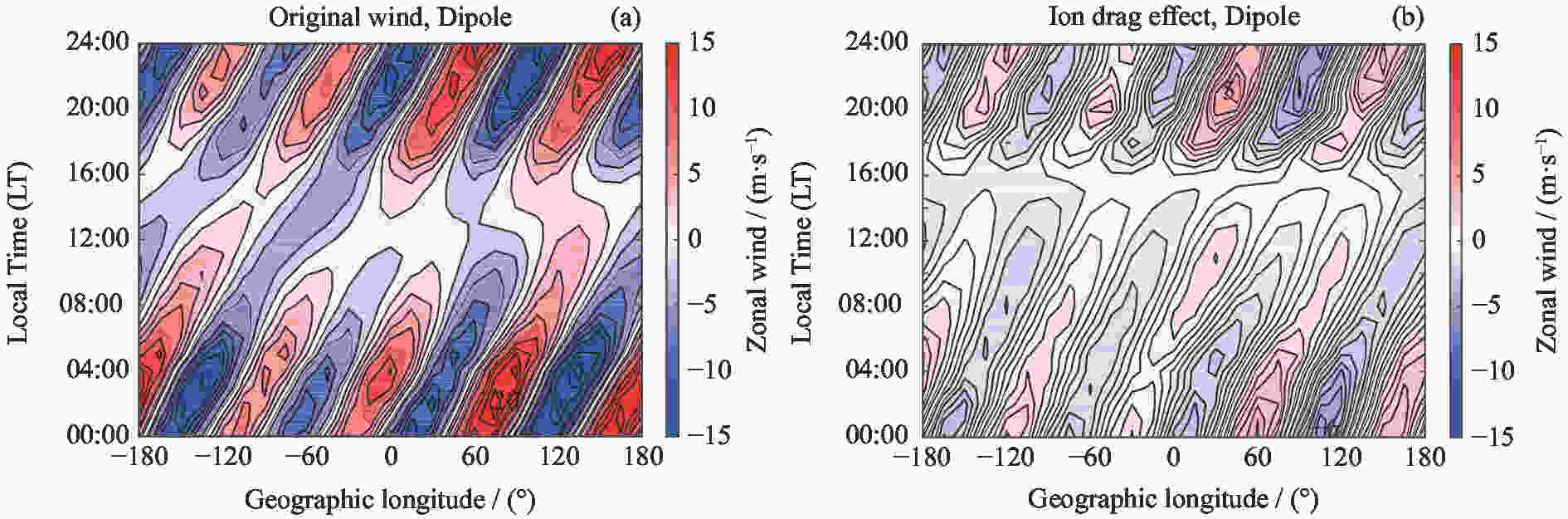
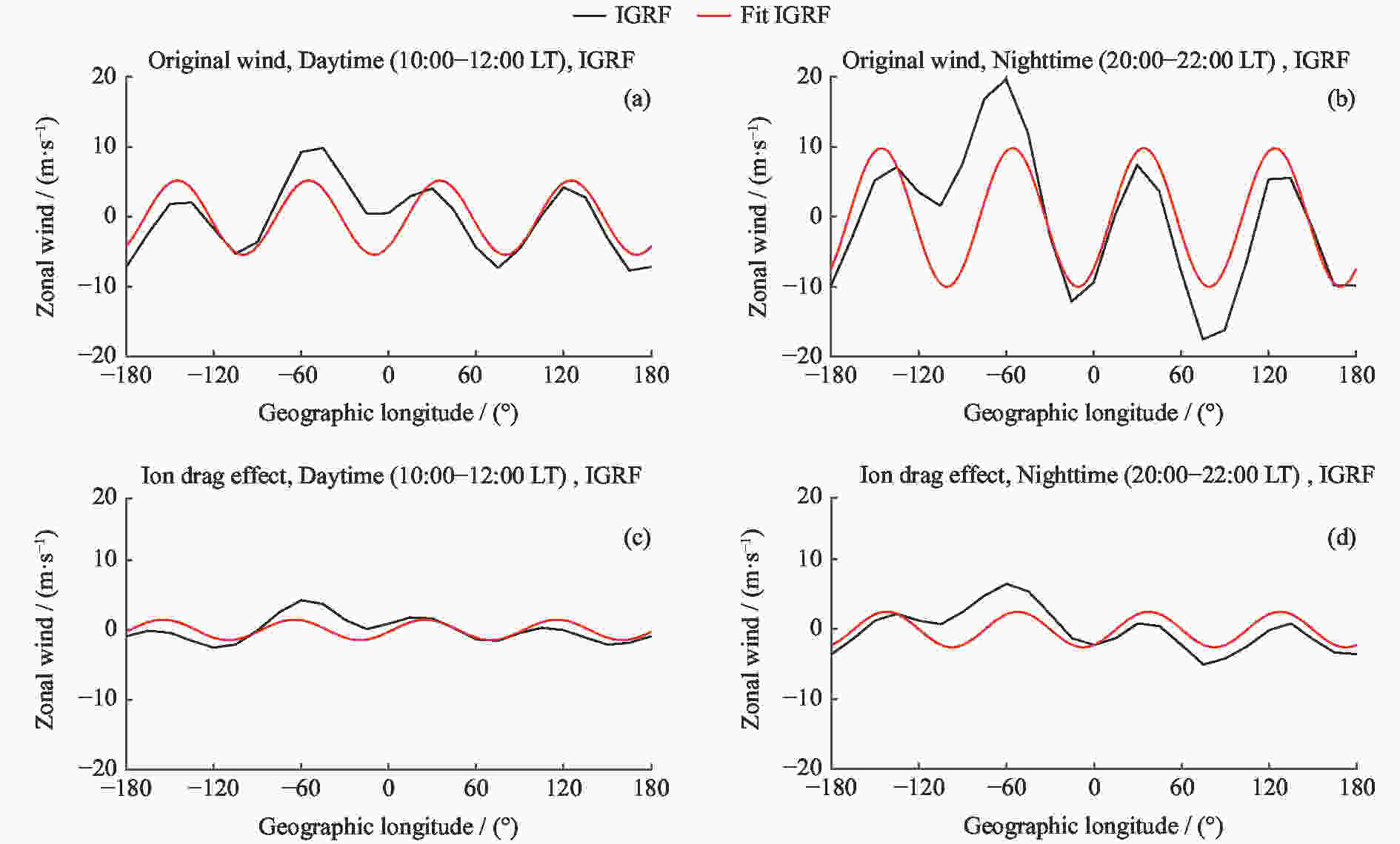
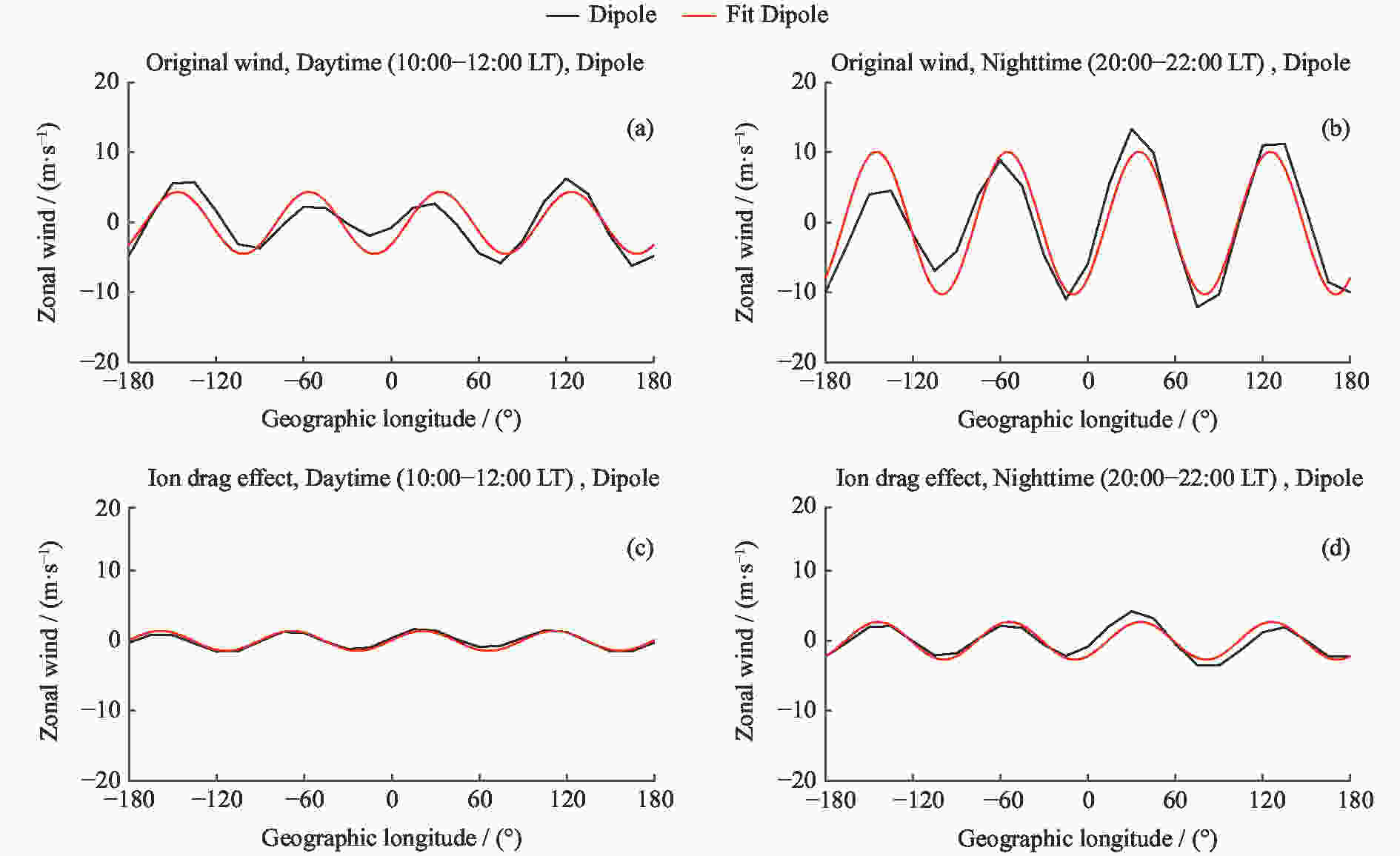
摘要: 使用CHAMP卫星观测资料和TIEGCM模拟数据,研究了太阳活动低年春秋分季节赤道地区热层纬向风的反转时间和风速在经度分布上的差异,重点分析了离子拖曳力在不同地磁场构型下对纬向风速地理经度分布的影响。研究发现,纬向风一般在清晨时段由东向转为西向,下午时段由西向转为东向,但反转时间存在明显的经度差异,最大经度差异可达1.8 h,这主要是由于低层大气非迁移潮汐波的影响。非迁移潮汐波使下午时段的风场反转时间提前约2 h,更符合卫星观测结果;但其对清晨时段风场反转时间的影响不明显,从而使模拟结果与观测结果有较大差异。纬向风的经度四波结构主要来源于低层大气潮汐,但离子拖曳力对不同地磁场构型下的纬向风四波结构有一定的影响。分析发现,除低层大气非迁移潮汐波的作用外,离子拖曳力对纬向风四波结构的贡献约为25%,白天时段的贡献高于夜晚时段,在理想偶极子磁场时的贡献高于真实地磁场。Abstract: Based on the Challenging Minisatellite Payload (CHAMP) satellite observations and Thermosphere Ionosphere Electrodynamics General Circulation Model (TIEGCM) simulations, the longitudinal variation of the reversal local time of the equatorial thermospheric zonal wind and its speed at equinoxes during solar minimum period are investigated. It is found that the zonal wind generally turns from eastward to the westward in the morning and from westward to the eastward in the afternoon. However, there are obvious longitudinal differences in the reversal time, with the maximum longitudinal difference of 1.8 h. This is mainly due to the upward-propagating non-migrating tide in the lower atmosphere. The tide can advance the reversal time about 2 h in the afternoon, which is more consistent with the observation. However, it has no obvious effect on the reversal time in the morning, which makes the simulation result different from the observation. The longitudinal wave-4 structure of the zonal wind mainly comes from the non-migrating tide, but the ion drag contributes to the wave-4 structure of the zonal wind. The quantitative analysis shows that the contribution of ion drag to the wave-4 structure is about 25%. The ion drag effect is larger in the daytime than the nighttime, and larger in the frame of the idea dipole field than the real IGRF field.
-
Key words:
- Longitudinal difference of zonal wind /
- Ion drag /
- CHAMP /
- TIEGCM
-
表 1 离子拖曳力对纬向风四波经度分布影响的定量分析结果
Table 1. Quantitative analysis of the influence of ion drag on the longitudinal variation of the zonal wind
10:00-12:00 LT 20:00-22:00 LT IGRF 26.4% 25.3% Dipole 31.1% 26.7% -
[1] RISHBETH H. Thermospheric winds and the F-region: a review[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Terrestrial Physics, 1972, 34(1): 1-47 doi: 10.1016/0021-9169(72)90003-7 [2] BLANC M, RICHMOND A D. The ionospheric disturbance dynamo[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1980, 85(A4): 1669-1686 doi: 10.1029/JA085iA04p01669 [3] HEDIN A E, SPENCER N W, KILLEEN T L. Empirical global model of upper thermosphere winds based on Atmosphere and Dynamics Explorer satellite data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1988, 93(A9): 9959-9978 doi: 10.1029/JA093iA09p09959 [4] LIEBERMAN R S, AKMAEV R A, FULLER-ROWELL T J, et al. Thermospheric zonal mean winds and tides revealed by CHAMP[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2013, 40(10): 2439-2443 doi: 10.1002/grl.50481 [5] LIU H X, WATANABE S, KONDO T. Fast thermospheric wind jet at the Earth’s dip equator[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2009, 36(8): L08103 [6] LIU H X, LÜHR H, WATANABE S, et al. Zonal winds in the equatorial upper thermosphere: decomposing the solar flux, geomagnetic activity, and seasonal dependencies[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2006, 111(A7): A07307 [7] MIYOSHI Y, FUJIWARA H, JIN H, et al. Numerical simulation of the equatorial wind jet in the thermosphere[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2012, 117(A3): A03309 [8] HÄUSLER K, LÜHR H, RENTZ S, et al. A statistical analysis of longitudinal dependences of upper thermospheric zonal winds at dip equator latitudes derived from CHAMP[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2007, 69(12): 1419-1430 doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2007.04.004 [9] OBERHEIDE J, FORBES J M, HÄUSLER K, et al. Tropospheric tides from 80 to 400 km: propagation, interannual variability, and solar cycle effects[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2009, 114(D1): D00I05 [10] HÄUSLER K, LÜHR H. Nonmigrating tidal signals in the upper thermospheric zonal wind at equatorial latitudes as observed by CHAMP[J]. Annales Geophysicae, 2009, 27(7): 2643-2652 doi: 10.5194/angeo-27-2643-2009 [11] HÄUSLER K, LÜHR H, HAGAN M E, et al. Comparison of CHAMP and TIME-GCM nonmigrating tidal signals in the thermospheric zonal wind[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2010, 115(D1): D00I08 [12] LÜHR H, HÄUSLER K, STOLLE C. Longitudinal variation of F region electron density and thermospheric zonal wind caused by atmospheric tides[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2007, 34(16): L16102 [13] LIN C H, WANG W, HAGAN M E, et al. Plausible effect of atmospheric tides on the equatorial ionosphere observed by the FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC: three-dimensional electron density structures[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2007, 34(11): L11112 doi: 10.1029/2007GL029265 [14] WANG H, ZHANG K D. Longitudinal structure in electron density at mid-latitudes: upward-propagating tidal effects[J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 2017, 69(1): 11 doi: 10.1186/s40623-016-0596-9 [15] LÜHR H, MAUS S, ROTHER M. Noon-time equatorial electrojet: its spatial features as determined by the CHAMP satellite[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2004, 109(A1): A01306 [16] LÜHR H, ROTHER M, HÄUSLER K, et al. The influence of nonmigrating tides on the longitudinal variation of the equatorial electrojet[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2008, 113(A8): A08313 [17] WANG H, ZHENG Z C, ZHANG K D, et al. Influence of nonmigrating tides and geomagnetic field geometry on the diurnal and longitudinal variations of the equatorial electrojet[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(6): e2019JA027631 [18] HARTMAN W A, HEELIS R A. Longitudinal variations in the equatorial vertical drift in the topside ionosphere[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2007, 112(A3): A03305 [19] ZHANG K D, WANG W B, WANG H, et al. The longitudinal variations of upper thermospheric zonal winds observed by the CHAMP satellite at low and midlatitudes[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2018, 123(11): 9652-9668 doi: 10.1029/2018JA025463 [20] REIGBER C, LÜHR H, SCHWINTZER P. CHAMP mission status[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2002, 30(2): 129-134 doi: 10.1016/S0273-1177(02)00276-4 [21] DROB D P, EMMERT J T, CROWLEY G, et al. An empirical model of the Earth’s horizontal wind fields: HWM07[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2008, 113(A12): A12304 [22] EMMERT J T, DROB D P, SHEPHERD G G, et al. DWM07 global empirical model of upper thermospheric storm-induced disturbance winds[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2008, 113(A11): A11319 [23] RICHMOND A D, RIDLEY E C, ROBLE R G. A thermosphere/ionosphere general circulation model with coupled electrodynamics[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1992, 19(6): 601-604 doi: 10.1029/92GL00401 [24] CHANG L C, LIN C H, LIU J Y, et al. Seasonal and local time variation of ionospheric migrating tides in 2007-2011 FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC and TIE-GCM total electron content[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2013, 118(5): 2545-2564 doi: 10.1002/jgra.50268 [25] WANG H, LÜHR H. Longitudinal variation in zonal winds at subauroral regions: possible mechanisms[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2016, 121(1): 745-763 doi: 10.1002/2015JA022086 [26] MAUTE A, RICHMOND A D, ROBLE R G. Sources of low-latitude ionospheric E × B drifts and their variability[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2012, 117(A6): A06312 [27] COLEY W R, HEELIS R A, SPENCER N W. Comparison of low-latitude ion and neutral zonal drifts using DE 2 data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physice, 1994, 99(A1): 341-348 doi: 10.1029/93JA02205 [28] KONDO T, RICHMOND A D, LIU H, et al. On the formation of a fast thermospheric zonal wind at the magnetic dip equator[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2011, 38(10): L10101 [29] LIU H X, WATANABE S. Seasonal variation of the longitudinal structure of the equatorial ionosphere: does it reflect tidal influences from below?[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2008, 113(A8): A08315 -
-







 下载:
下载: