基于深度学习的太阳黑子Wilson山磁类型识别方法
doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.03.210107004 cstr: 32142.14.cjss2022.03.210107004
Recognition Method for Mount Wilson Magnetic Type of Sunspots Based on Deep Learning
-
摘要: 太阳黑子是太阳光球层中带有较强磁场的区域,通常是太阳爆发活动的源区。Wilson山磁分类是当前最为主流的太阳黑子分类方法之一,对研究太阳爆发有重要意义。利用2010-2017年间SDO/HMI成像仪观测到的720s_SHARP磁图和白光图数据,研究使用深度学习对太阳黑子群Wilson山磁分类的方法。实验结果表明,Xception网络在识别太阳黑子Wilson山磁类型上能取得最优的效果,其中对α类型黑子的F1得分为96.50%,β类为93.20%,其他类型的黑子为84.65%。
-
关键词:
- 太阳黑子 /
- Xception网络 /
- 深度学习 /
- Wilson山磁分类
Abstract: Sunspots are the regions with stronger magnetic field in the solar photosphere and most of solar eruptions occur in complex sunspot groups. Mount Wilson magnetic classification is one of the most popular sunspots classification methods, which is of great significance to the study of solar eruptions. In recent years, with the rapid development of China’s space industry, space physics research has entered the era of big data. Deep learning methods for processing space science data are springing up. In this study, based on the SDO/HMI SHARP continuum and magnetogram data during 2010-2017, we propose to apply deep learning for the image recognition of Mount Wilson magnetic type of sunspots. The results show that Xception has a productive performance in the identification of the sunspots magnetic types in solar active regions. The F1 score of sunspots group of α exceeds 96%, that of β is more than 93%, and that of other types is more than 84%.-
Key words:
- Sunspots /
- Xception network /
- Deep learning /
- Mount Wilson magnetic classification
-
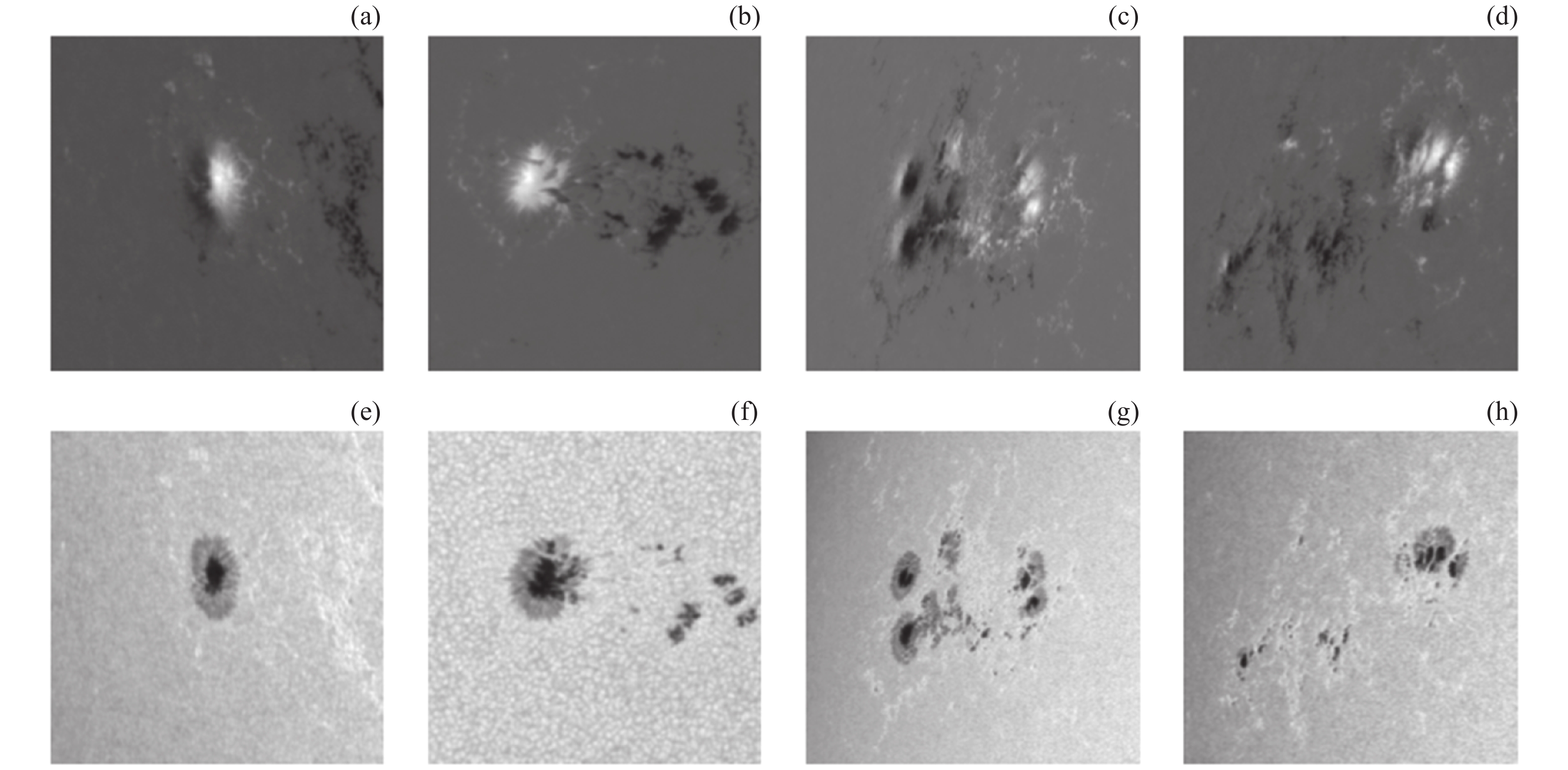
图 1 (a)为α类型的太阳黑子群磁场观测图像,(b)为β类型的太阳黑子群磁场观测图像,(c)和(d)为β-x类型太阳黑子群磁场观测图像,(e)为(a)相应的α类型太阳黑子群白光观测图像,(f)为(b)相应的β类型太阳黑子群白光观测图像,(g)和(h)为(c)和(d)相应的β-x类型太阳黑子群白光观测图像
Figure 1. (a) Magnetogram of sunspots group of α, (b) magnetogram of sunspots group of β, (c)(d) magnetograms of sunspots group of β-x, (e) the image of sunspots group of α corresponding to (a), (f) the image of sunspots group of β corresponding to (b), (g)(h) the images of sunspots group of β-x corresponding to (c)(d)
表 1 Wilson黑子磁类型分类
Table 1. Mount Wilson sunspots classification
类型 释义 α 单极黑子群 β 一个黑子群具有正负两种磁场极性,并且相反极性之间的划分界限简单明显 γ 与 β 类不同,该活动区较为复杂,这种类型的黑子群正负极性分布非常不规则 β-γ 此种类型的黑子群分布十分复杂,相反极性之间没有明显的边界 δ 在此类型的双极黑子群中,存在相反极性本影共用同一半影的情况,且其间距小于 2° β-δ 包含一个或多个 δ 黑子的 β 磁类型黑子群 β-γ-δ 包含一个或多个 δ 黑子的 β-γ 磁类型黑子群 γ-δ 包含一个或多个 δ 黑子的 γ 磁类型黑子群 表 2 训练、验证、测试集的分布
Table 2. Distribution of training, validation and test sets
磁类型(时间区间) α β β-x 训练集(2010年5月至2014年5月) 3767 5882 1926 验证集(2014年6月至2015年5月) 942 1471 481 测试集(2015年6月至2017年5月) 567 496 109 总计(2010年5月至2017年5月) 5276 7849 2516 表 3 二分类混淆矩阵
Table 3. Definition of confusion matrix on binary classification
名称 识别的 α 识别的非 α 真实的 α T F 真实的非 α N C 表 4 不同深度学习模型的F1分数(%)
Table 4. F1 score (%) of different classification methods
类型 α β β-x 数据扩充 × √ × √ × √ × √ × √ × √ TTA × × √ √ × × √ √ × × √ √ Xception 94.52 96.04 94.96 96.50 89.33 92.32 90.53 93.20 82.10 82.94 83.41 84.65 MobileNetV2 94.35 94.37 95.79 95.44 90.63 91.49 92.43 92.57 83.11 87.08 83.57 86.54 MobileNet 94.34 95.51 94.65 94.65 90.86 90.26 90.51 89.85 85.05 77.68 82.35 81.06 ResNet50 93.35 93.31 94.19 93.72 86.53 88.78 87.84 89.38 71.84 76.33 71.97 78.34 Inception ResNetV2 95.06 93.60 96.28 94.18 90.00 88.35 91.48 89.30 80.52 76.36 80.00 77.78 3层CNN8 69.64 – – – 64.90 – – – 64.54 – – – 白光Xception – – – 95.21 – – – 90.03 – – – 75.86 磁图Xception – – – 91.53 – – – 86.09 – – – 76.84 注 √和×分别表示有和没有使用数据扩充和TTA策略,其中在 α,β和 β-x 上F1分数最高的用黑体加粗表示。 -
[1] MCINTOSH P S, The classification of sunspot groups[J]. Solar Physics, 1990, 125(2): 251–267. [2] PADINHATTEERI S, HIGGINS P A, BLOOMFIELD D S, et al. Automatic detection of magnetic δ in sunspot groups[J]. Solar Physics, 2016, 291(1): 41-53 doi: 10.1007/s11207-015-0808-7 [3] FU Xiaona, LIAO Chengwu, BAI Xianyong, et al. A detection method for sunspots based on convolutional neural network LeNet-5[J]. Astronomical Research & Technology, 2018, 15(3): 340-346 [4] 李泠, 崔延美, 刘四清, 等. 太阳黑子自动识别与特征参量自动提取[J]. 空间科学学报, 2020, 40(3): 315-322 doi: 10.11728/cjss2020.03.315LI Ling, CUI Yanmei, LIU Siqing, et al. Automatic detection of sunspots and extraction of sunspot characteristic parameters[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2020, 40(3): 315-322 doi: 10.11728/cjss2020.03.315 [5] FANG Y H, CUI Y M, AO X Z. Deep learning for automatic recognition of magnetic type in sunspot groups[J]. Advances in Astronomy, 2019, 2019(123): 1-10 [6] HALE G E, ELLERMAN F, NICHOLSON S B, et al. The magnetic polarity of sun-spots[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 1919, 49: 153 doi: 10.1086/142452 [7] SAMMIS I, TANG F, ZIRIN H. The dependence of large flare occurrence on the magnetic structure of sunspots[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2000, 540(1): 583-587 doi: 10.1086/309303 [8] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas: IEEE, 2016: 770-778 [9] SZEGEDY C, LIU W, JIA Y Q, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[C]//Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Boston: IEEE, 2015: 1-9 [10] CHOLLET F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions [C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. Hawaii: IEEE, 2017: 1251-1258 [11] HOWARD A G, ZHU M L, CHEN B, et al. MobileNets: efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1704.04861, 2017 [12] SANDLER M, HOWARD A, ZHU M L, et al. MobileNetV2: inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City: IEEE, 2018: 4510-4520 [13] WANG G, LI W, OURSELIN S, et al. Automatic brain tumor segmentation using convolutional neural networks with test-time augmentation[C]//Proceedings of international MICCAI Brainlesion Workshop. Cham: Springer, 2018: 61-72 -
-






 下载:
下载: