Analysis of Beidou Radio Occultation Data from FY-3D Satellite
-
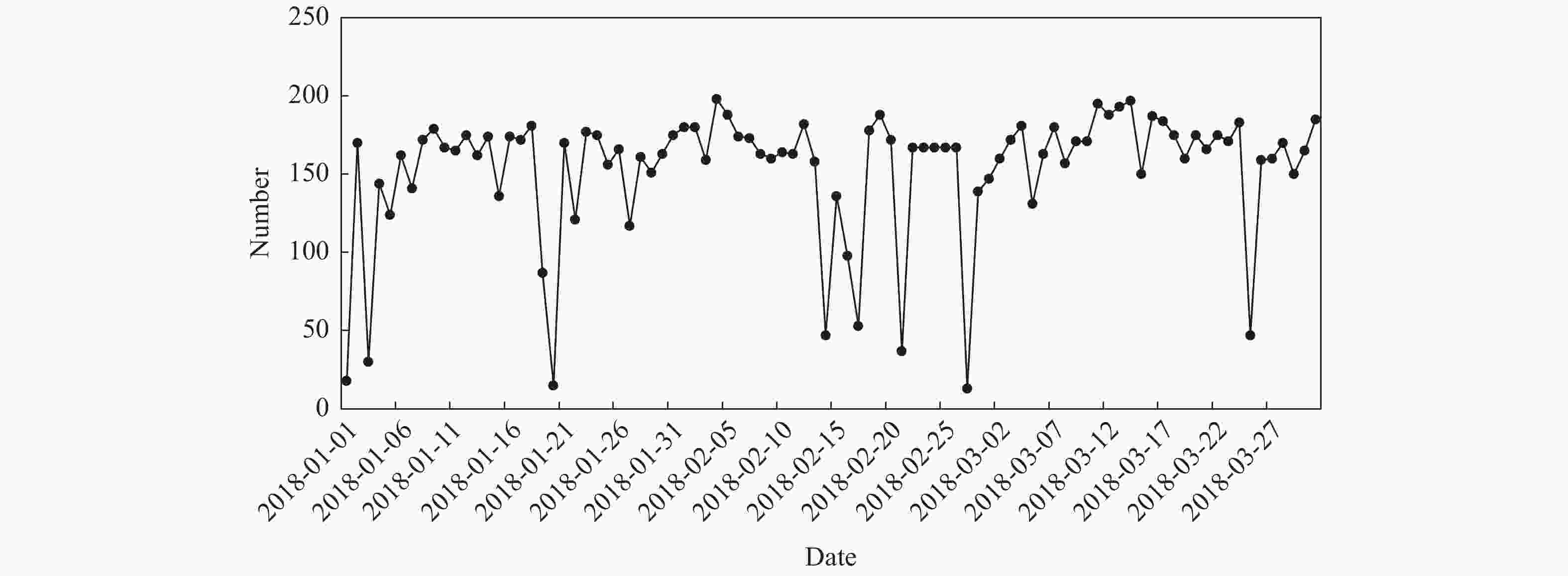
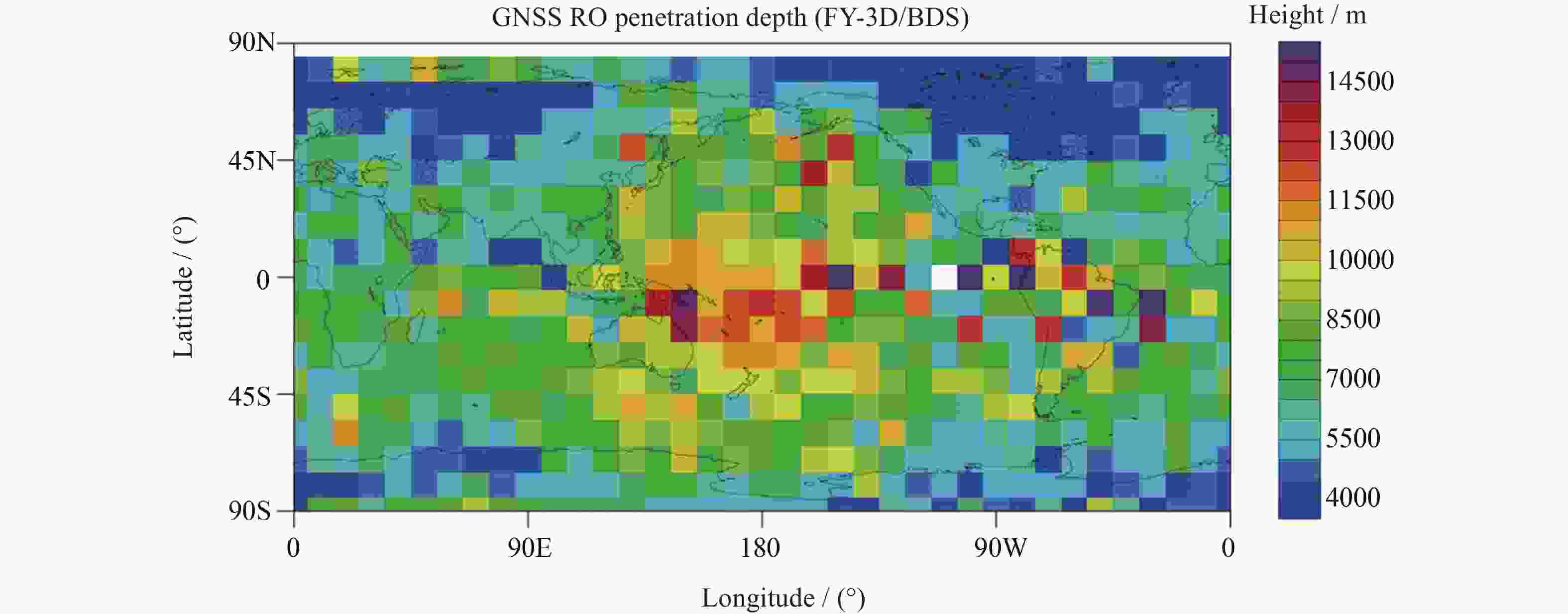
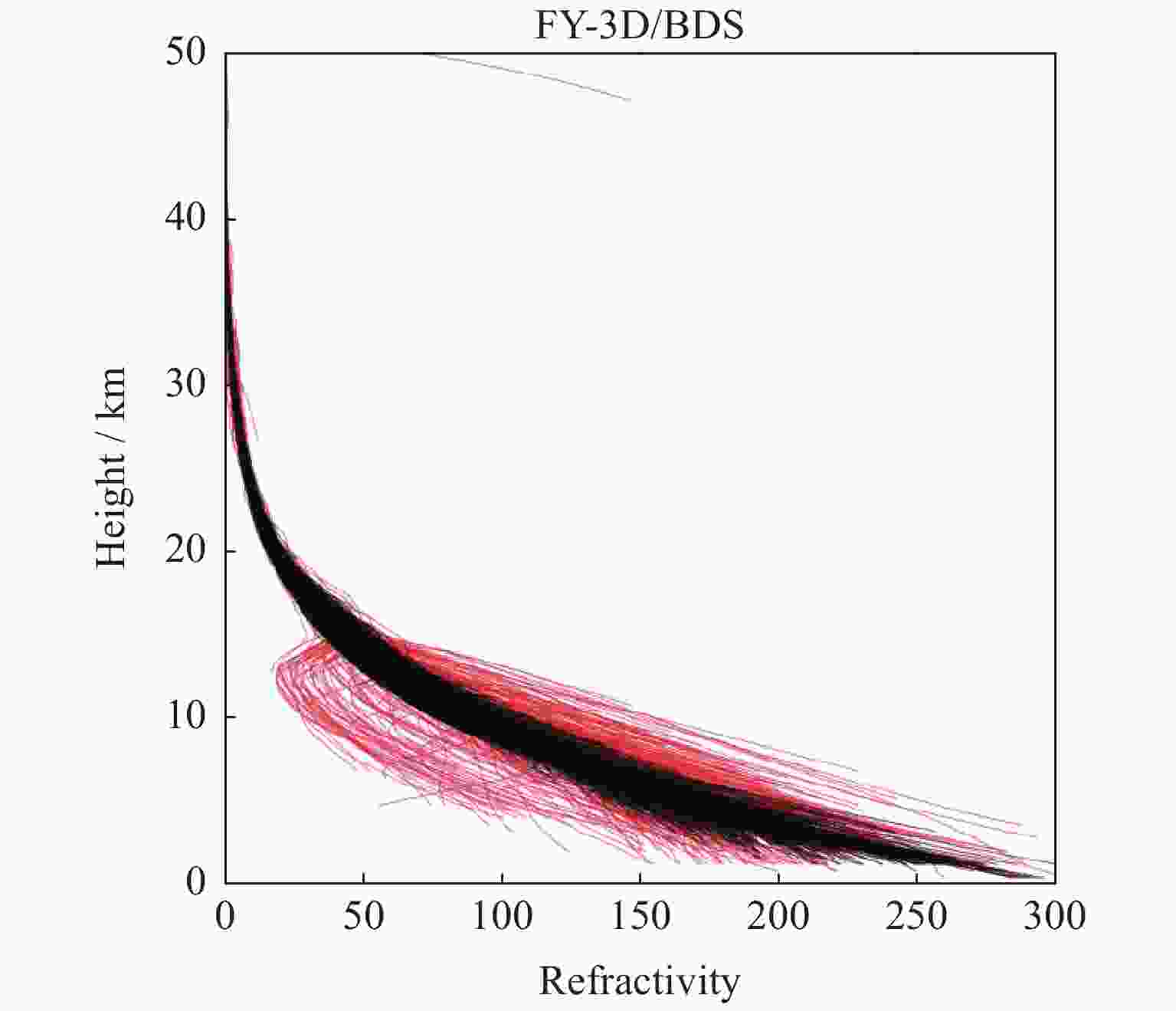
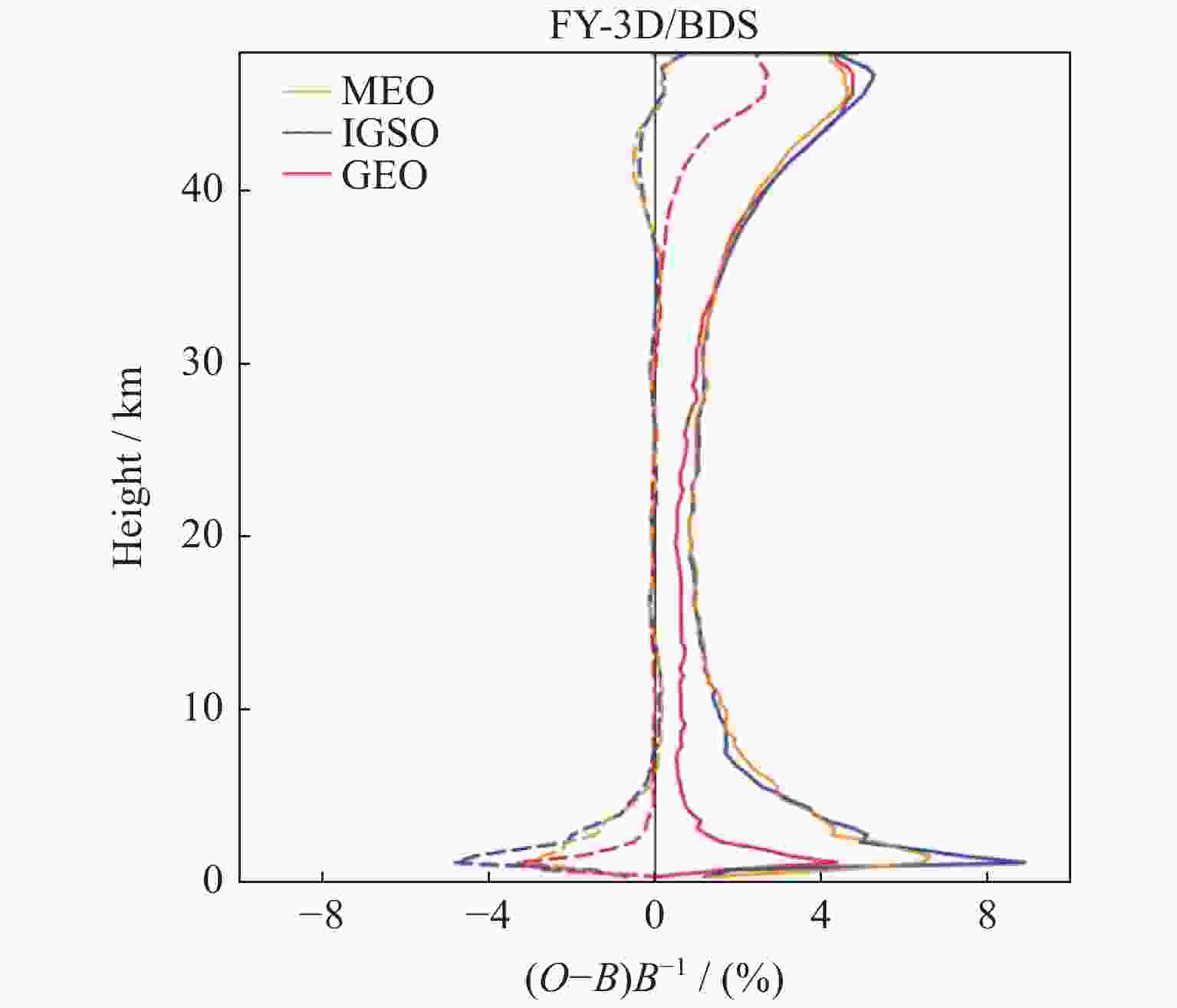
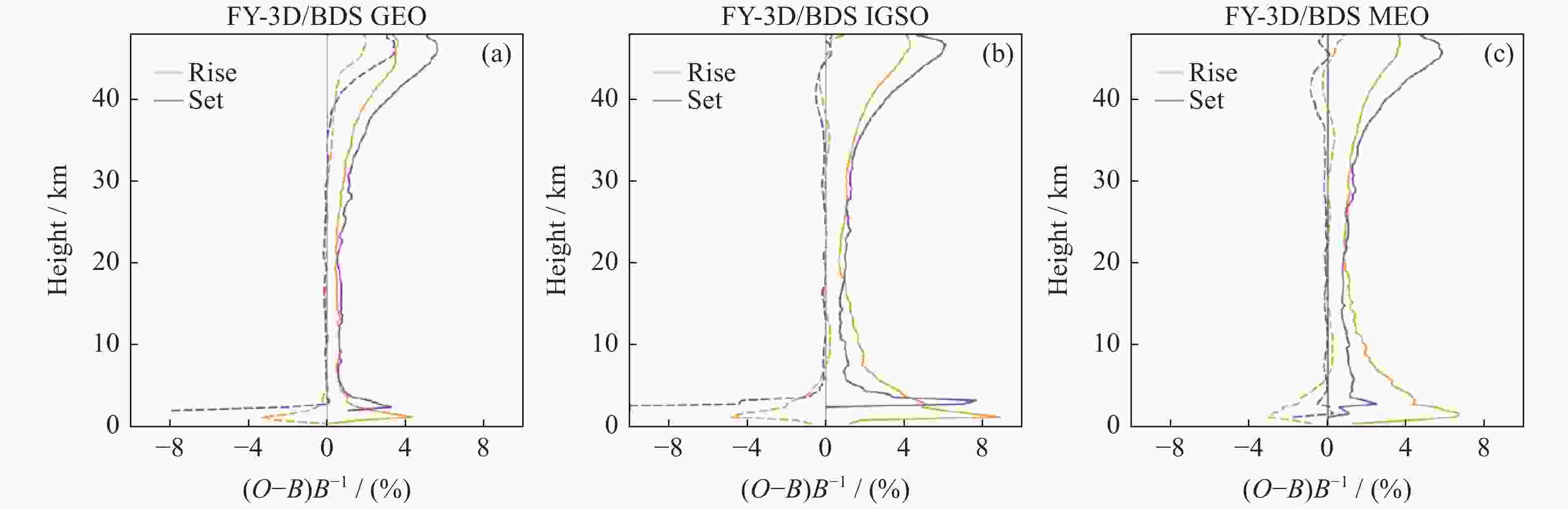
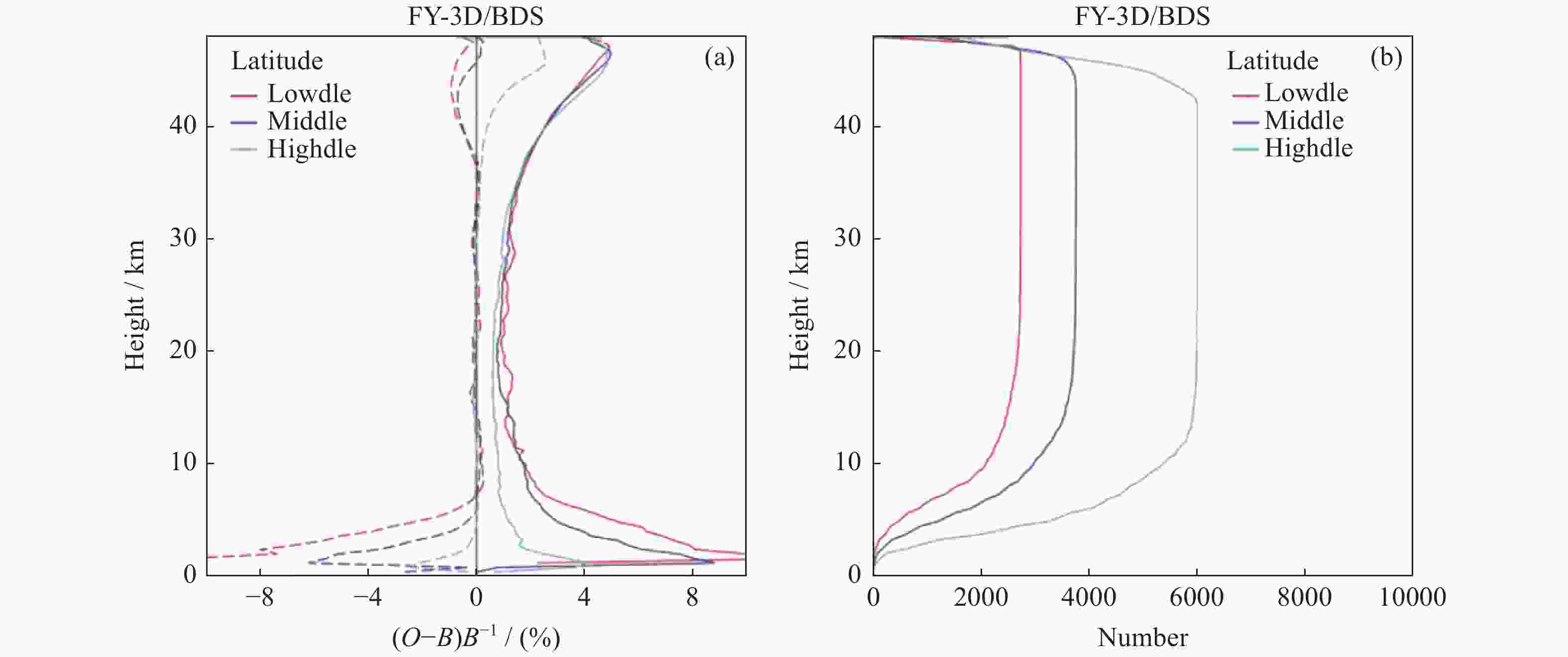
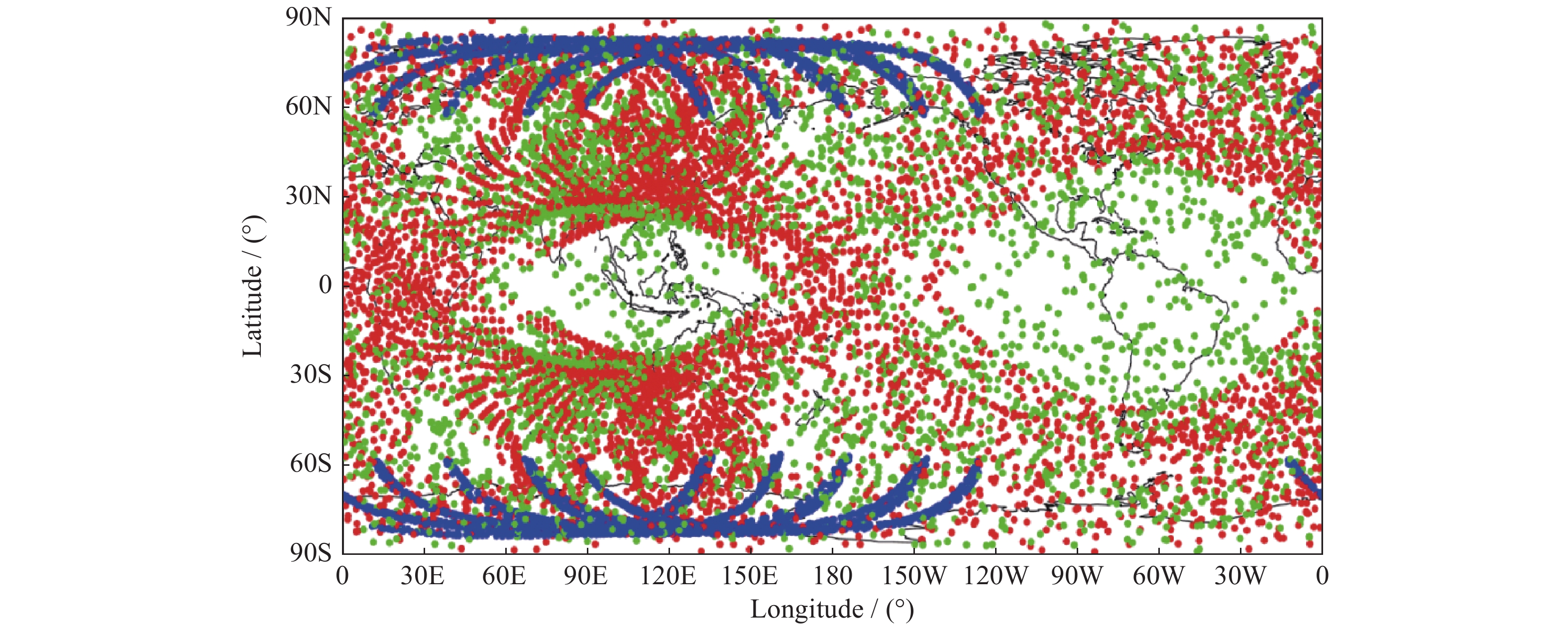
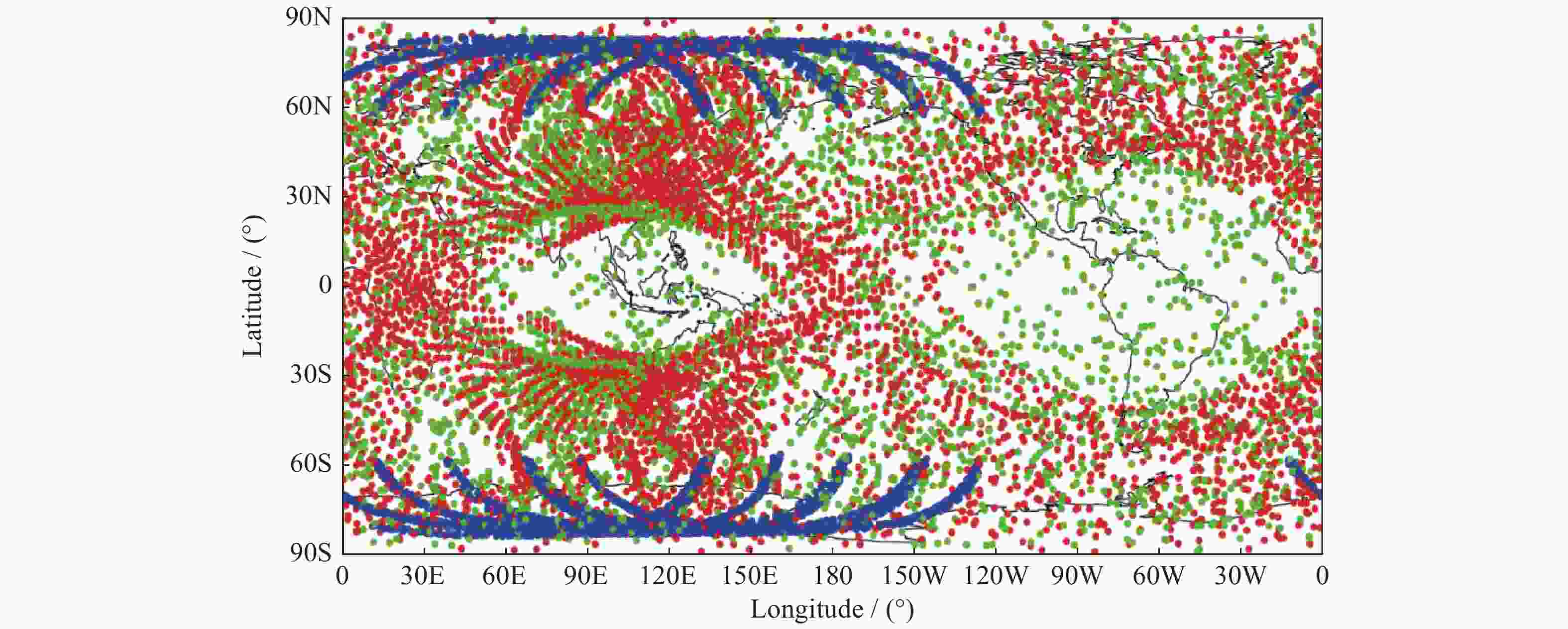
摘要: 利用2018年1-3月FY-3D卫星的掩星折射率数据,研究了北斗导航卫星系统的掩星分布特点、数据精度以及误差统计特征。北斗导航卫星系统同步静止轨道掩星沿卫星轨道呈弧状分布在南北两极地区,倾斜轨道掩星在东西半球低纬度地区分别形成一小一大两个空洞,中地球轨道掩星则全球均匀分布。北斗掩星折射率数据精度在探测核心区域,即12~32 km范围内,与ERA5再分析资料计算的折射率相比,平均偏差的标准差约为1.5%,在核心区外,标准差从1.5%逐渐增大到6%。静止轨道掩星的平均偏差在高层略大于倾斜轨道和中地球轨道掩星。下降掩星在20 km以上区域的标准差大于上升掩星,20 km以下区域小于上升掩星。高纬地区北斗掩星标准差最小,低纬地区最大,对流层中下层尤其明显。分析结果表明,北斗掩星的数据精度和误差特征与GPS掩星数据相似。Abstract: Based on the Beidou radio occultation refractivity data of FY-3D satellite from January to March in 2018, the distribution characteristics of Beidou occultation, data accuracy and statistical characteristics of errors are studied. The Beidou Geostationary Orbit (GEO) occultation is distributed arc-shaped along the satellite orbit in the northern and southern polar regions, the Inclined Geo-Synchronous Orbit (IGSO) occultation forms one large and one small cavity respectively in the low latitude areas of the eastern and western hemispheres to form two cavities, and the Middle-Earth Orbit (MEO) occultation is distributed uniformly around the world. The accuracy of the Beidou occultion refractivity is within the range of 12~32 km in the core area. Compared with the ERA5 reanalysis data, the standard deviation of the average deviation is about 1.5%. In the range of height below 12 km and above 35 km, the standard deviation gradually increases from 1.5% to 6%. The deviation of GEO occultation over 35 km is slightly larger than that of IGSO and MEO occultation, but the standard deviation is smaller than that of these two types of occultation. The standard deviation of the descending occultation above 20 km is higher than that of the ascending occultation, but the area below 20 km is less than that of the ascending occultation. The standard deviation of the Beidou occultation is the smallest in high latitudes, followed by that in low latitudes and the largest in middle latitudes, especially in the middle and lower troposphere. The accuracy and error characteristics of the Beidou radio occultation data are consistent with the GPS radio occultation data, indicating that the Earth atmosphere occultation detection does not depend on the satellite navigation system.
-
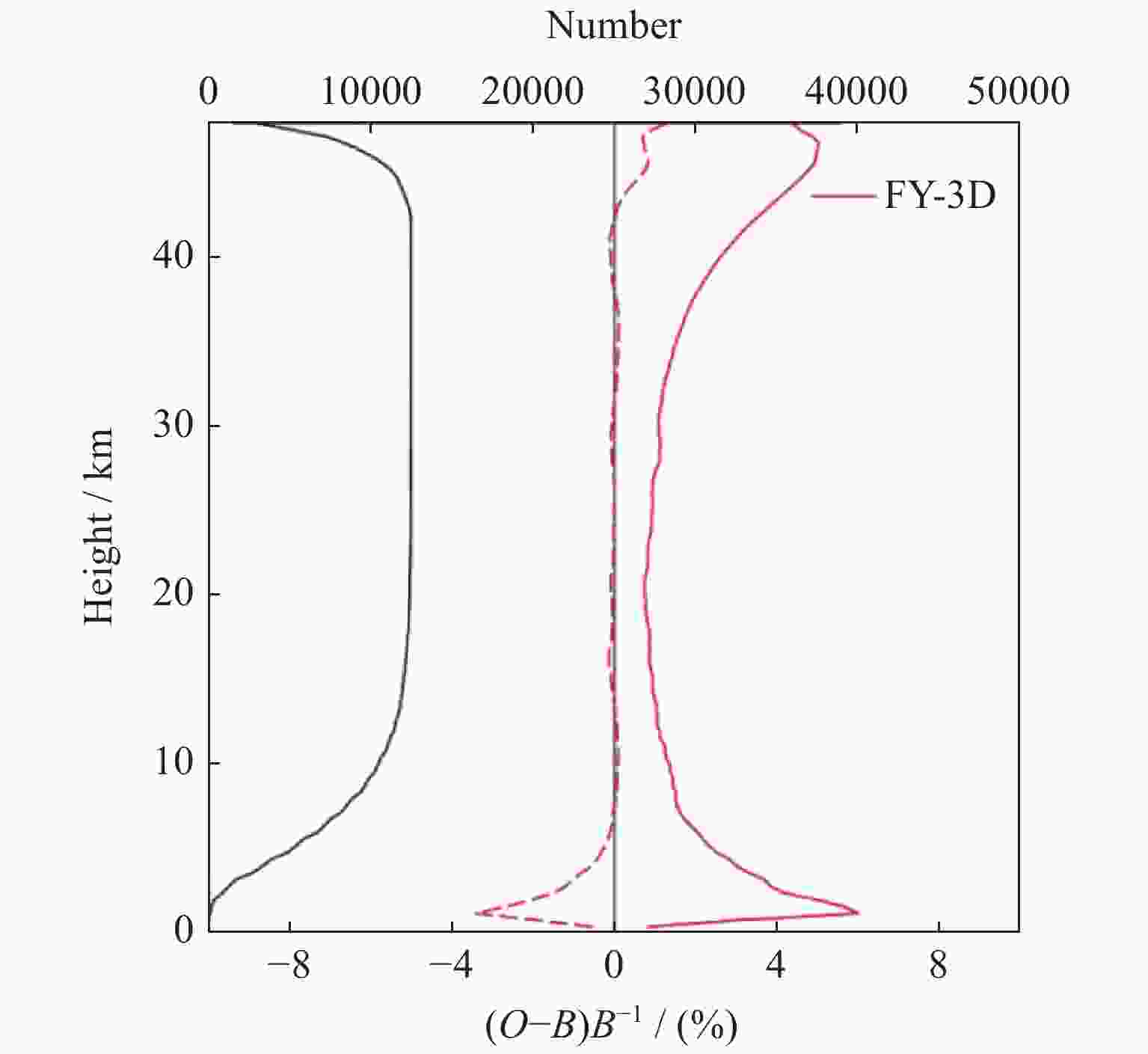
图 5 观测总数(黑实线)以及折射率观测与ERA5再分析资料计算的折射率平均偏差(红虚线)和标准差(红实线)。O表示观测折射率,B表示ERA5计算的折射率
Figure 5. Mean bias (red dashed line) and standard deviation (red solid line) of refractivity compared with ERA5 reanalysis, and the number (black solid line). O stands for observation refractivity, and B stands for the refractivity based on ERA5 reanalysis
表 1 不同轨道的GNOS北斗掩星数量和占比
Table 1. Number and proportion of GNOS Beidou RO in different orbits
轨道类型 全球 东半球 西半球 GEO IGSO MEO GEO IGSO MEO GEO IGSO MEO 掩星数量 4038 5292 3768 3412 3591 2224 626 1701 1544 占比/(%) 31 40 29 26 27 17 5 13 12 -
[1] KURSINSKI E R, HAJJ G A, SCHOFIELD J T, et al. Observing Earth’s atmosphere with radio occultation measurements using the global positioning system[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 1997, 102(D19): 23429-23465 doi: 10.1029/97JD01569 [2] ANTHES R A. Exploring Earth's atmosphere with radio occultation: contributions to weather, climate and space weather[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2011, 4(6): 1077-1103 doi: 10.5194/amt-4-1077-2011 [3] WARE R, EXNER M, FENG D, et al. GPS sounding of the atmosphere from low earth orbit: preliminary results[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 1996, 77(1): 19-40 doi: 10.1175/1520-0477(1996)077<0019:GSOTAF>2.0.CO;2 [4] ROCKEN C, ANTHES R, EXNER M, et al. Analysis and validation of GPS/MET data in the neutral atmosphere[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 1997, 102(D25): 29849-29866 doi: 10.1029/97JD02400 [5] WICKERT J, REIGBER C, BEYERLE G, et al. Atmosphere sounding by GPS radio occultation: first results from CHAMP[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2001, 28(17): 3263-3266 doi: 10.1029/2001GL013117 [6] HAJJ G A, DE LA TORRE JUÁREZ M, IJIMA B A, et al. GPS radio occupations coming of age: spacecraft launches add two new instruments for climate monitoring[J]. Eos, Transactions American Geophysical Union, 2002, 83(4): 37 doi: 10.1029/2002EO000028 [7] TAPLEY B D, BETTADPUR S, WATKINS M, et al. The gravity recovery and climate experiment: mission overview and early results[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2004, 31(9): L09607 doi: 10.1029/2004GL019920 [8] ANTHES R A, BERNHARDT P A, CHEN Y, et al. The COSMIC/FORMOSAT-3 mission: early results[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2008, 89(3): 313-334 doi: 10.1175/BAMS-89-3-313 [9] LOISELET M, STRICKER N, MENARD Y, et al. GRAS-Metop ’s GPS-based atmospheric sounder[J]. ESA Bulletin, 2000, 102: 38-44 [10] VON ENGELN A, HEALY S, MARQUARDT C, et al. Validation of operational GRAS radio occultation data[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2009, 36(17): L17809 doi: 10.1029/2009GL039968 [11] BI Y M, YANG Z D, ZHANG P, et al. An introduction to China FY3 radio occultation mission and its measurement simulation[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2012, 49(7): 1191-1197 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2012.01.014 [12] BAI W H, SUN Y Q, DU Q F, et al. An introduction to the FY3 GNOS instrument and mountain-top tests[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2014, 7(6): 1817-1823 doi: 10.5194/amt-7-1817-2014 [13] SUN Y Q, BAI W H, LIU C L, et al. The FengYun-3 C radio occultation sounder GNOS: a review of the mission and its early results and science applications[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2018, 11(10): 5797-5811 doi: 10.5194/amt-11-5797-2018 [14] ANTHES R, SCHREINER W. Six new satellites watch the atmosphere over Earth’s equator[J]. Eos, Transactions American Geophysical Union, 2019: 100 doi: 10.1029/2019EO131779 [15] SCHREINER W S, WEISS J P, ANTHES R A, et al. COSMIC-2 radio occultation constellation: first results[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2020, 47(4): e2019GL086841 doi: 10.1029/2019GL086841 [16] WANG X Y, SUN Y Q, DU Q F, et al. GNOS-Radio occultation sounder on board of Chinese FY3 satellites[C]//Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Quebec City, QC, Canada: IEEE, 2014 [17] 廖蜜, 张鹏, 毕研盟, 等. 风云三号气象卫星掩星大气产品精度的初步检验[J]. 气象学报, 2015, 73(6): 1131-1140 doi: 10.11676/qxxb2015.072LIAO Mi, ZHANG Peng, BI Yanmeng, et al. A preliminary estimation of the radio occultation products accuracy from the Fengyun-3 C meteorological satellite[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2015, 73(6): 1131-1140 doi: 10.11676/qxxb2015.072 [18] 王树志, 朱光武, 白伟华, 等. 风云三号C星全球导航卫星掩星探测仪首次实现北斗掩星探测[J]. 物理学报, 2015, 64(8): 089301 doi: 10.7498/aps.64.089301WANG Shuzhi, ZHU Guangwu, BAI Weihua, et al. For the first time Fengyun-3 C satellite-global navigation satellite system occultation sounder achieved spaceborne Bei Dou system radio occultation[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2015, 64(8): 089301 doi: 10.7498/aps.64.089301 [19] LIAO M, ZHANG P, YANG G L, et al. Preliminary validation of the refractivity from the new radio occultation sounder GNOS/FY-3 C[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2016, 9(2): 781-792 doi: 10.5194/amt-9-781-2016 [20] LIAO M, HEALY S, ZHANG P. Processing and quality control of FY-3 C GNOS data used in numerical weather prediction applications[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2019, 12(5): 2679-2692 doi: 10.5194/amt-12-2679-2019 [21] WEI J D, LI Y, ZHANG K F, et al. An evaluation of Fengyun-3 C radio occultation atmospheric profiles over 2015–2018[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(13): 2116 doi: 10.3390/rs12132116 [22] BAI W D, SUN Y Q, XIA J M, et al. Validation results of maximum S4 index in F-layer derived from GNOS on FY3 C satellite[J]. GPS Solutions, 2019, 23(1): 19 doi: 10.1007/s10291-018-0807-x [23] 杨光林, 孙越强, 白伟华, 等. 风云三号C星GNOS北斗掩星电离层探测初步结果[J]. 空间科学学报, 2019, 39(1): 36-45 doi: 10.11728/cjss2019.01.036YANG Guanglin, SUN Yueqiang, BAI Weihua, et al. Beidou navigation satellite system sounding of the ionosphere from FY-3 C GNOS: preliminary results[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2019, 39(1): 36-45 doi: 10.11728/cjss2019.01.036 [24] BORMANN N, DUNCAN D, ENGLISH S, et al. Growing operational use of FY-3 data in the ECMWF system[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2021, 38(8): 1285-1298 doi: 10.1007/s00376-020-0207-3 [25] CULVERWELL I D, LEWIS H W, OFFILER D, et al. The radio occultation processing package, ROPP[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2015, 8(4): 1887-1899 doi: 10.5194/amt-8-1887-2015 -
-





 下载:
下载: