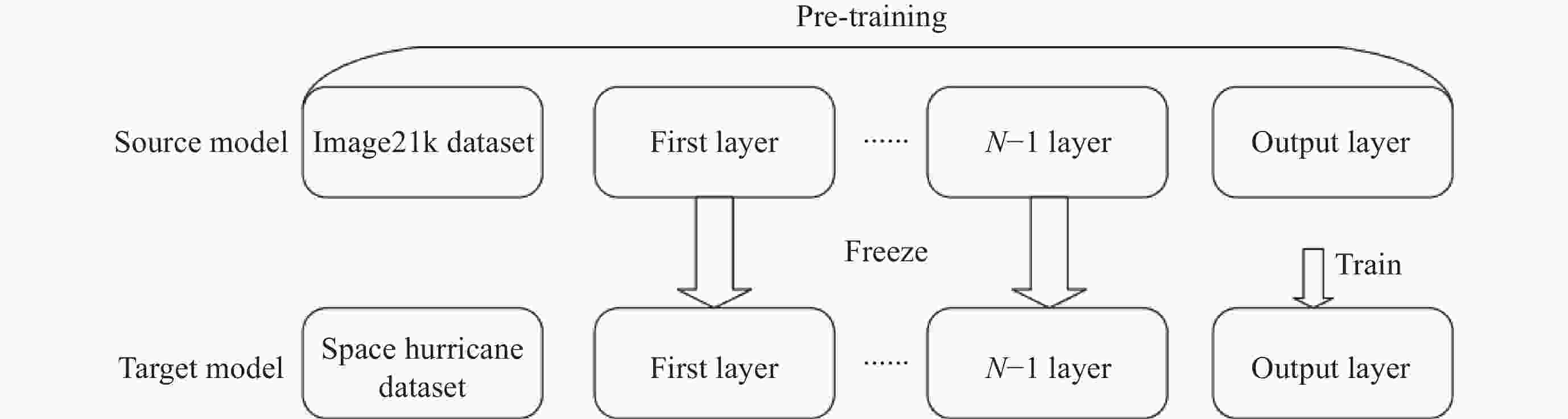
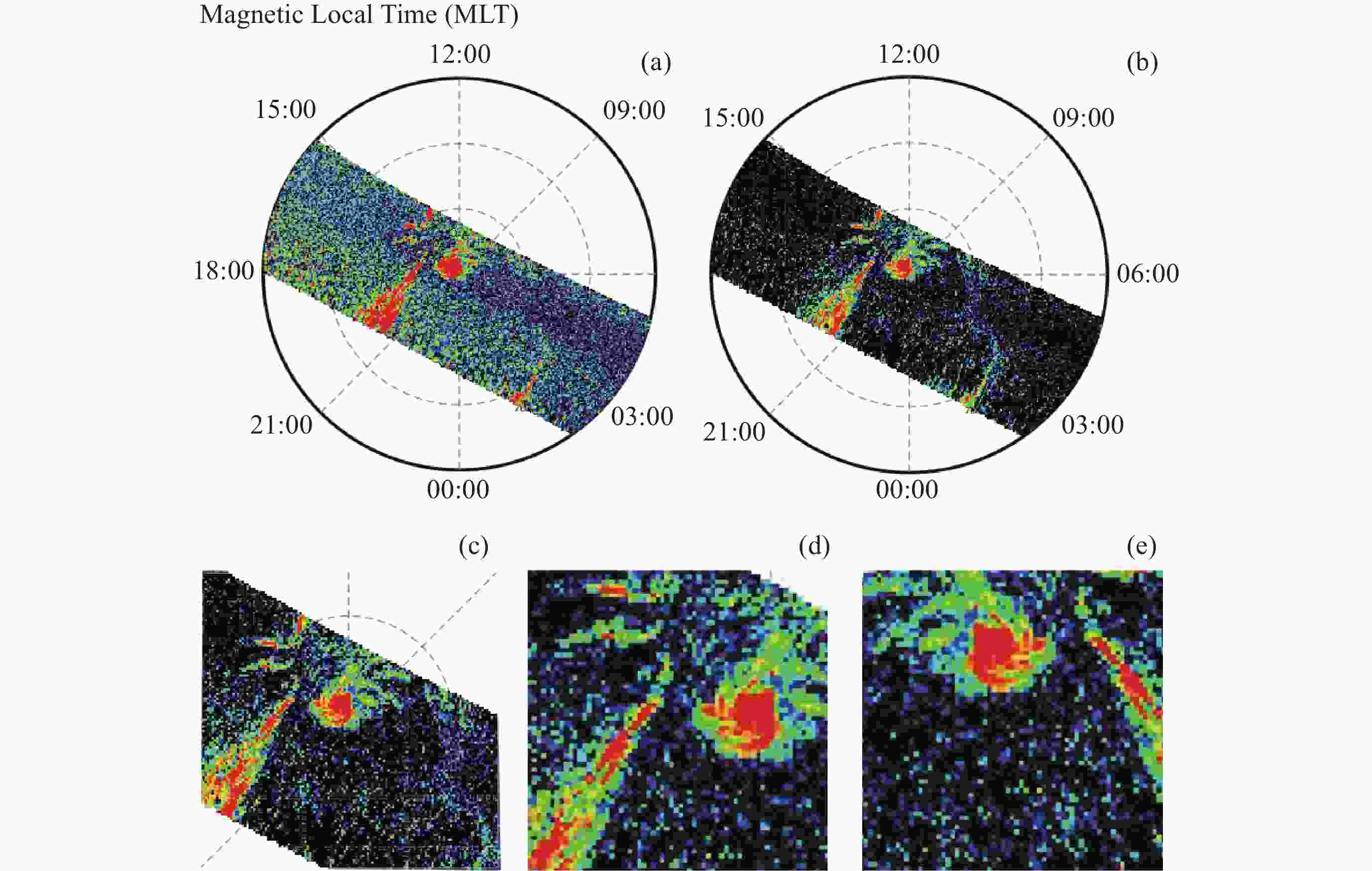
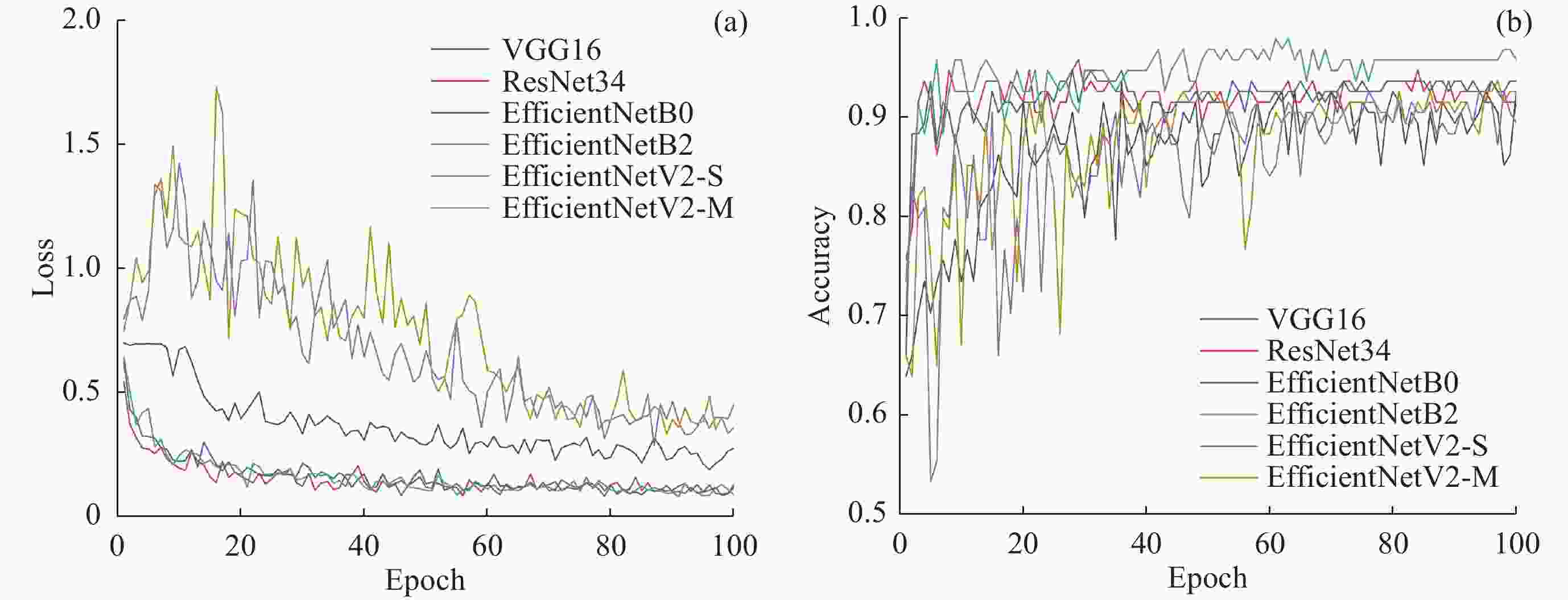
Automatic Identification of Space Hurricane Based on Transfer Learning
-
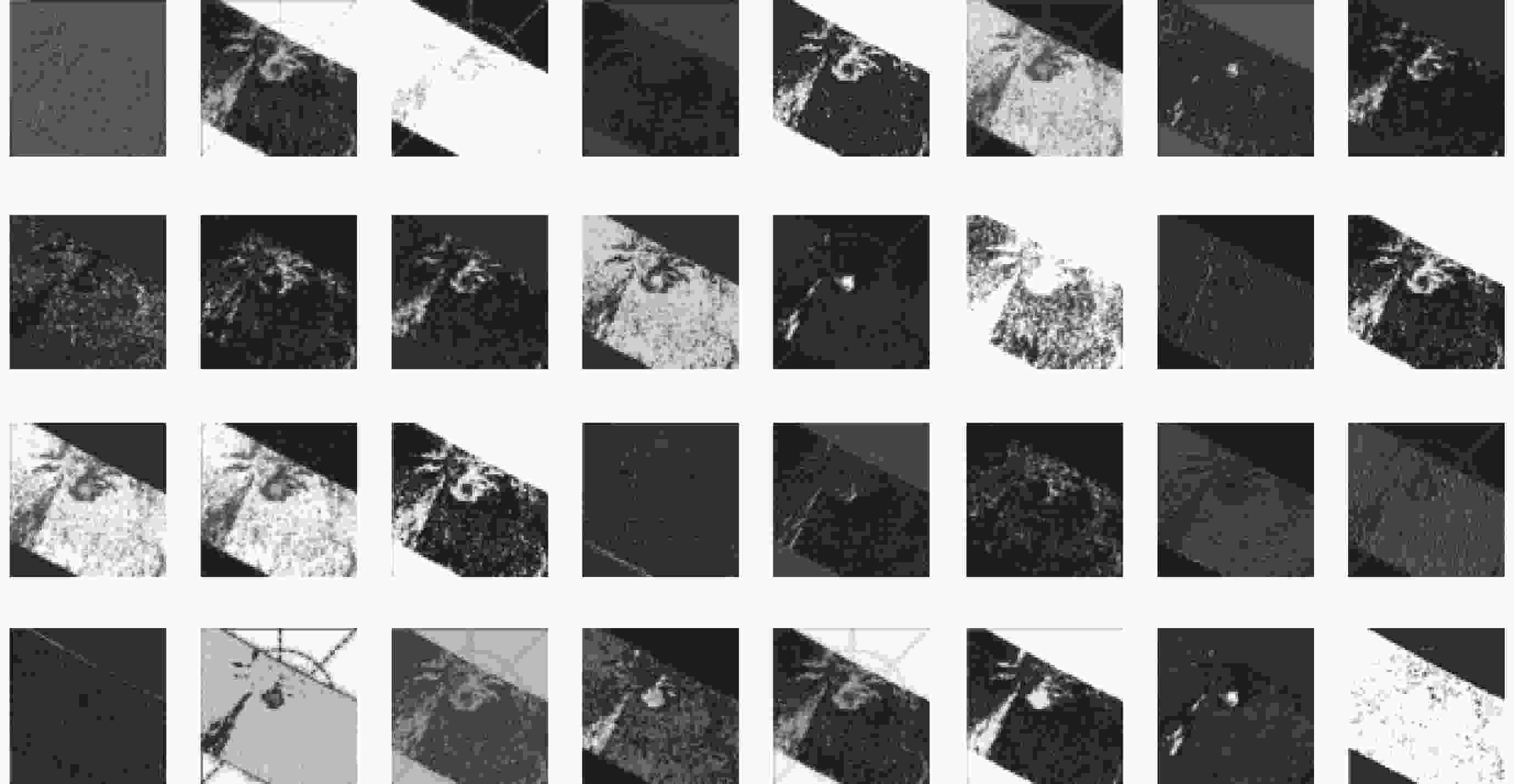
摘要: 太空台风是极盖区内一种新发现的大尺度亮斑状极光结构,直观表征了地磁平静期的一种堪比磁暴的太阳风能量注入现象,这更新了人们对太阳风–磁层–电离层耦合过程的认识,如何从海量星载极光数据中准确髙效识别出太空台风事件具有重要的科学意义。采用深度学习的方法,通过六种网络模型的对比,最终基于迁移学习和EfficientNetB2网络提出了一种太空台风自动识别方法。在2005-2021年美国国防气象卫星(Defense Meteorological Satellite Program,DMSP)上搭载的紫外光谱成像仪(Special Sensor Ultraviolet Spectrographic Imager,SSUSI)的观测数据中验证了该模型的有效性,识别准确率达到97.7%。研究结果表明,该方法可用于从海量星载极光观测数据中自动识别太空台风事件。
-
关键词:
- 太空台风 /
- 极光 /
- 迁移学习 /
- EfficientNetB2
Abstract: Space hurricane is a newly discovered large-scale and bright spot-like auroral structure in the polar cap region, which visually characterizes a solar wind energy injection phenomenon comparable to a magnetic storm during the geomagnetic calm period, this updates the understanding of the solar wind-magnetosphere-ionosphere coupling process, it is of great scientific importance to accurately and efficiently identify space hurricane events from the huge amount of auroral data. Deep learning is used, six networks are compared, and an automatic space hurricane identification method based on Transfer learning and EfficientNetB2 is proposed, validate the effectiveness of the model in DMSP/SSUSI observations from 2005 to 2021 with an accuracy of 97.7%. The results show that the method can be used to automatically identify Space hurricane events from a large amount of satellite-based auroral observation data.-
Key words:
- Space hurricane /
- Aurora /
- Transfer learning /
- EfficientNetB2
-
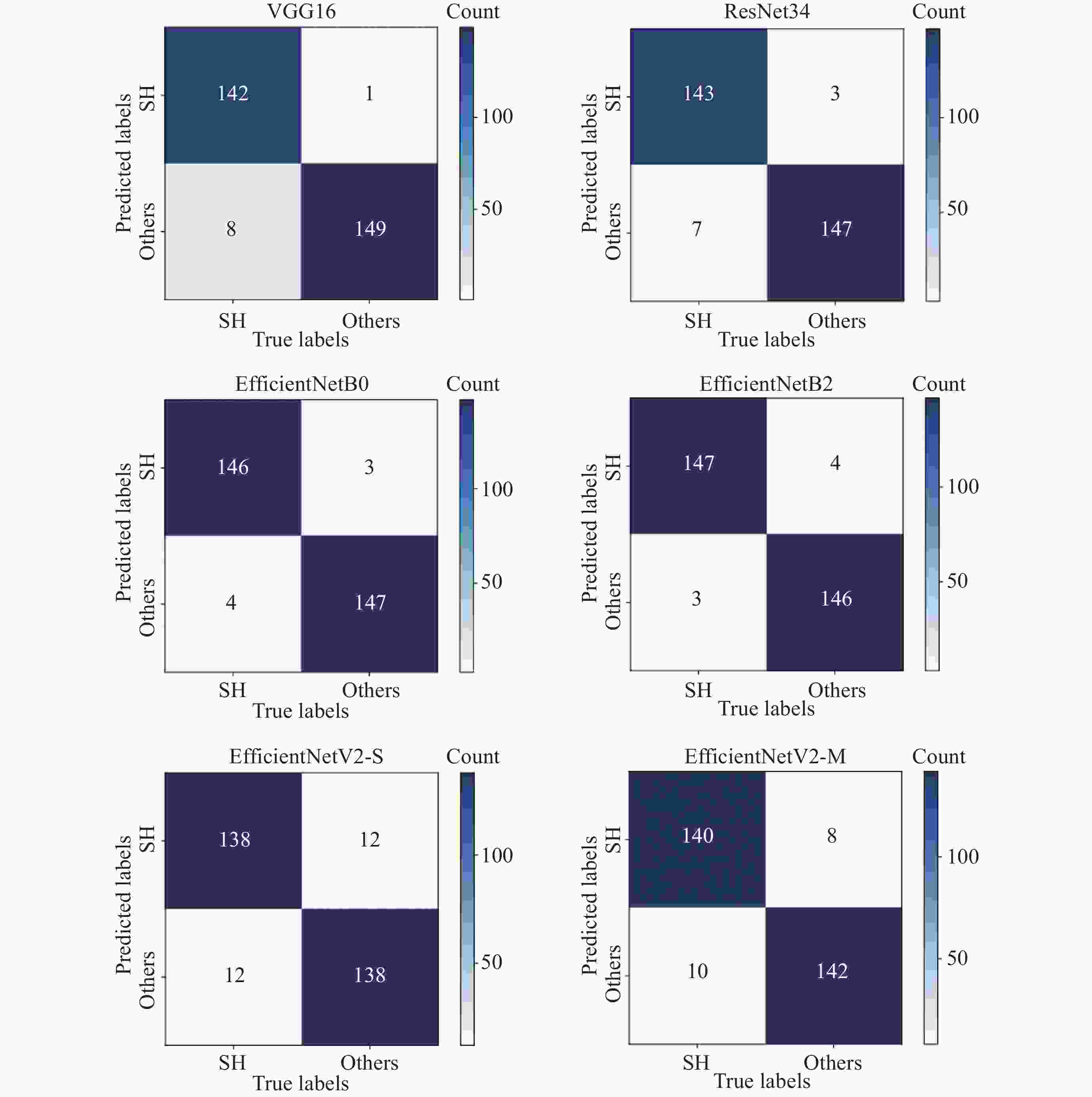
表 1 混淆矩阵
Table 1. Confusion matrix
Confusion matrix True labels 1 0 Predicted labels 1 n1 n2 0 n3 n4 表 2 6种模型测试集的评价指标
Table 2. Evaluation metrics of six models in the test set
Model name a p r s F1 VGG 0.9700 0.9930 0.9467 0.9933 0.9693 ResNet 0.9667 0.9795 0.9533 0.9800 0.9662 EfficientNetB0 0.9767 0.9799 0.9733 0.9800 0.9766 EfficientNetB2 0.9767 0.9735 0.9800 0.9733 0.9767 EfficientNetV2-S 0.9200 0.9200 0.9200 0.9200 0.9200 EfficientNetV2-M 0.9400 0.9459 0.9333 0.9467 0.9396 表 3 EfficientNetB0的体系结构
Table 3. Architecture of EfficientNetB0
Stage Operator Resolution Channels Layers 1 Conv3×3 224×224 32 1 2 MBConv1, k3×3 112×112 16 1 3 MBConv6, k3×3 112×112 24 2 4 MBConv6, k5×5 56×56 40 2 5 MBConv6, k3×3 28×28 80 3 6 MBConv6, k5×5 14×14 112 3 7 MBConv6, k5×5 14×14 192 4 8 MBConv6, k3×3 7×7 320 1 9 Conv1×1&Pooling&FC 7×7 1280 1 -
[1] FELDSHTEYN Y I. Some problems concerning the morphology of auroras and magnetic disturbances at high latitudes[J]. Geomagnetism Aeronomy, 1963, 3: 183-192 [2] FREY H U, IMMEL T J, LU G, et al. Properties of localized, high latitude, dayside aurora[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2003, 108(A4): 8008 doi: 10.1029/2002JA009332 [3] XING Z Y, ZHANG Q H, HAN D S, et al. Conjugate observations of the evolution of polar cap arcs in both hemispheres[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2018, 123(3): 1794-1805 [4] HAN D S, FENG H T, ZHANG H, et al. A new type of polar cap arc observed in the ~1500 MLT Sector: 1. Northern hemisphere observations[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2020, 47(20): e2020GL090261 [5] ZHANG Q H, ZHANG Y L, WANG C, et al. A space hurricane over the Earth’s polar ionosphere[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 1207 doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21459-y [6] SYRJÄSUO M T, DONOVAN E F. Diurnal auroral occurrence statistics obtained via machine vision[J]. Annales Geophysicae, 2004, 22(4): 1103-1113 doi: 10.5194/angeo-22-1103-2004 [7] LI Y C, JIANG N K. An aurora image classification method based on compressive sensing and distributed WKNN[C]//2018 IEEE 42 nd Annual Computer Software and Applications Conference (COMPSAC). Tokyo: IEEE, 2018: 347-354 [8] KIM S K, RANGANATH H S. Content-based retrieval of aurora images based on the Hierarchical Representation[C]//12 th International Conference on Advanced Concepts for Intelligent Vision Systems. Sydney: Springer, 2010: 249-260 [9] GONZALEZ R C. Deep convolutional neural networks (Lecture Notes)[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2018, 35(6): 79-87 doi: 10.1109/MSP.2018.2842646 [10] 佟欣, 邹自明, 白曦, 等. 喉区极光的机器识别[J]. 空间科学学报, 2021, 41(4): 654-666 doi: 10.11728/cjss2021.04.654TONG Xin, ZOU Ziming, BAI Xi, et al. Machine identification of throat aurora[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2021, 41(4): 654-666 doi: 10.11728/cjss2021.04.654 [11] CLAUSEN L B N, NICKISCH H. Automatic classification of auroral images from the Oslo Auroral THEMIS (OATH) data set using machine learning[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2018, 123(7): 5640-5647 doi: 10.1029/2018JA025274 [12] KVAMMEN A, WICKSTRØM K, MCKAY D, et al. Auroral image classification with deep neural networks[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(10): e2020JA027808 [13] DONAHUE J, JIA Y Q, VINYALS O, et al. DeCAF: a deep convolutional activation feature for generic visual recognition[C]//Proceedings of the 31 st International Conference on Machine Learning. Beijing: ACM, 2014: I-647-I-655 [14] 李彦枝, 陈昌红, 谢晓芳, 基于改进卷积神经网络的极光图像分类算法研究[J]. 南京邮电大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 39(6): 86-93LI Y Z, CHEN C H, XIE X F. Research on aurora image classification algorithm based on improved convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 39(6): 86-93 [15] SADO P, CLAUSEN L B N, MILOCH W J, et al. Transfer learning aurora image classification and magnetic disturbance evaluation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2022, 127(1): e2021JA029683 [16] Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition[J]. Computer Science, 2014. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.1409.1556 [17] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas: IEEE, 2016: 770-778 [18] TAN M X, LE Q. EfficientNet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the 36 th International Conference on Machine Learning. Long Beach: PMLR, 2019: 6105-6114 [19] TAN M X, LE Q. EfficientNetV2: smaller models and faster training[C]//Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning. ElectrNetwork: PMLR, 2021: 10096-10106 [20] LI H, PAN J K, ZENG H D, et al. Identification of specific substances in the FAIMS spectra of complex mixtures using deep learning[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(18): 6160 doi: 10.3390/s21186160 [21] PAN S J, YANG Q. A survey on transfer learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2010, 22(10): 1345-1359 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2009.191 -
-






 下载:
下载: