Analyses for the Mechanism of Solar Radio Burst Interfering Satellite Navigation Signal and Influence Presentation
-
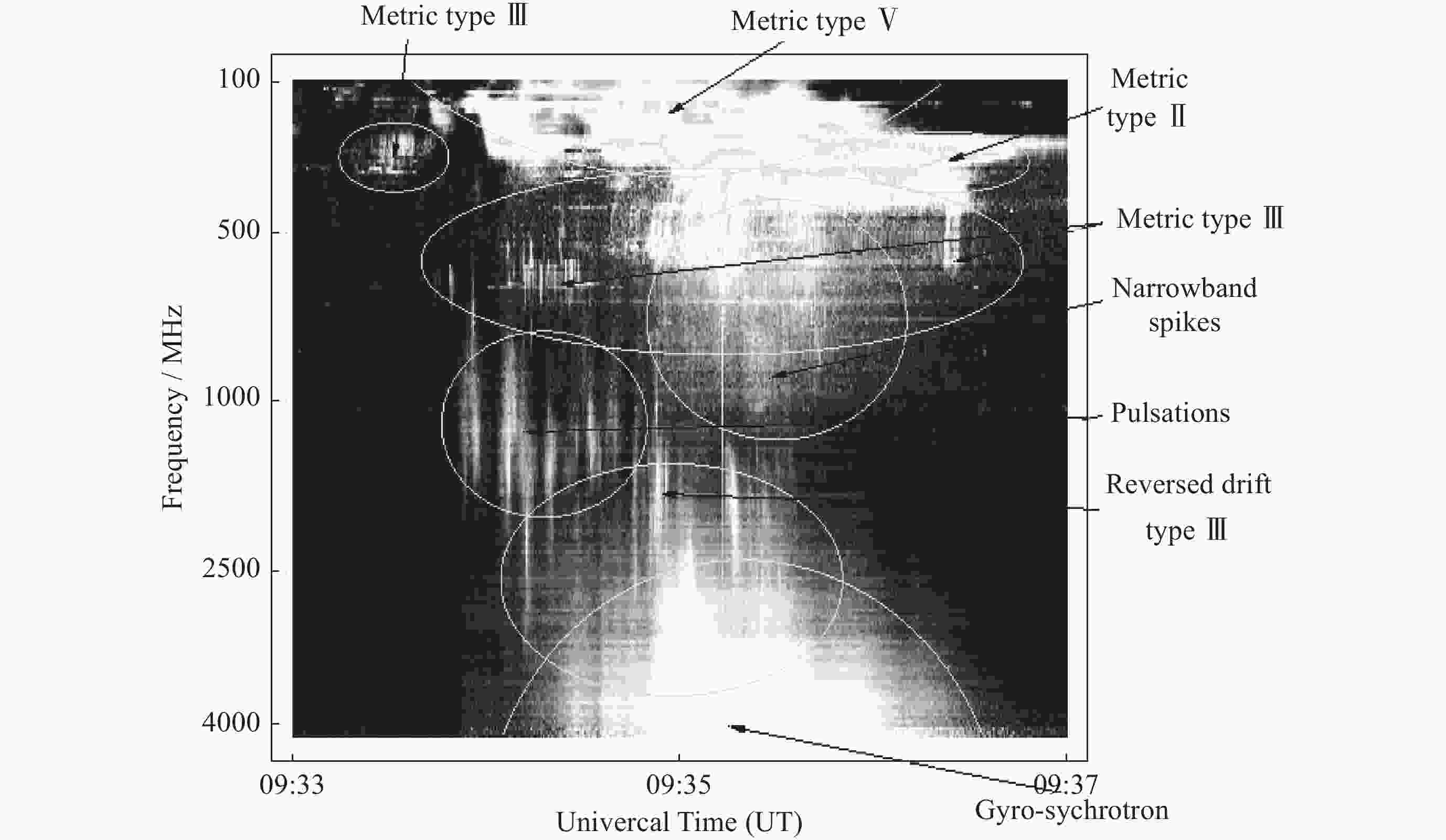
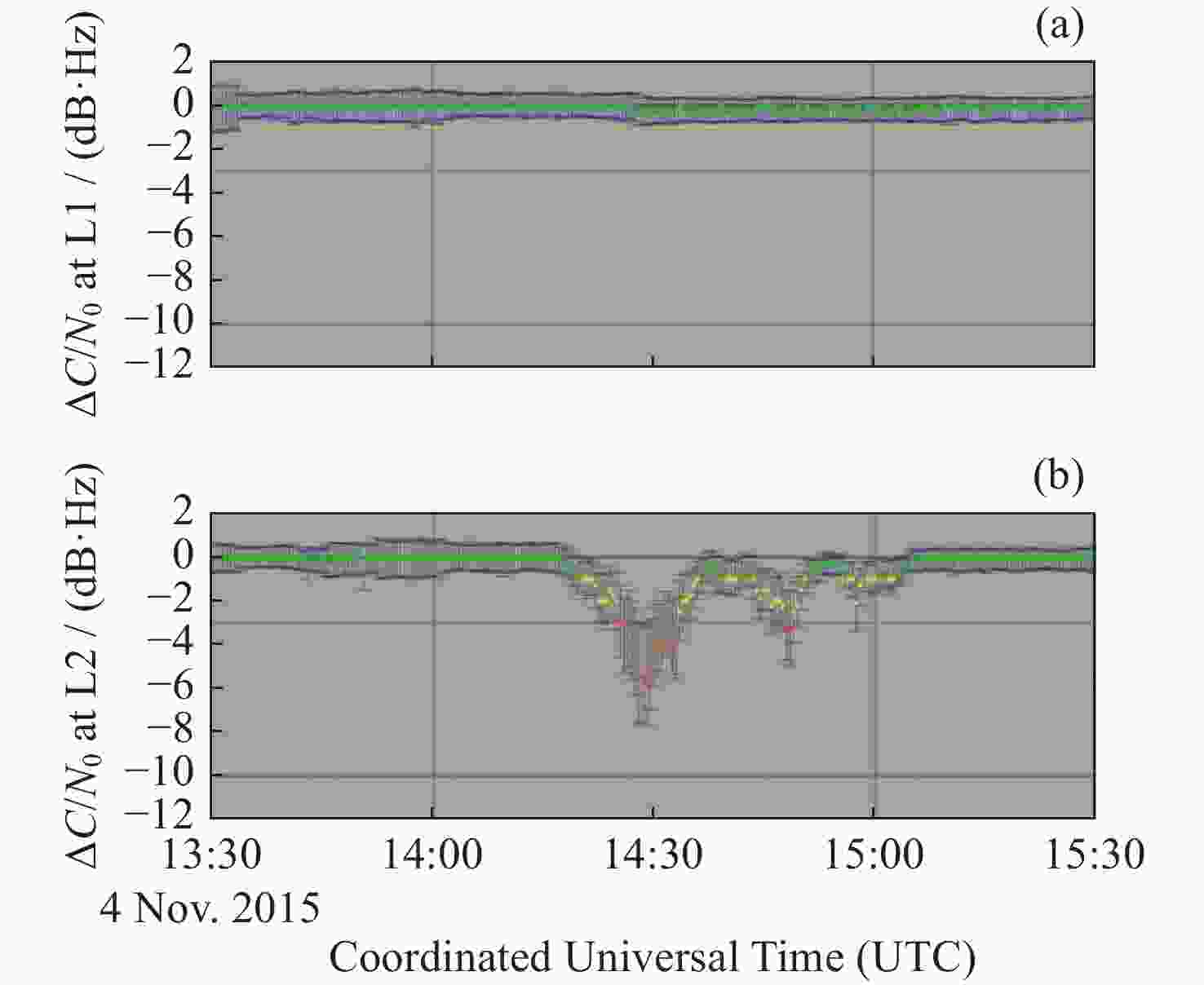
摘要: 太阳射电爆发是一种潜在的导航系统干扰因素。通过导航信号模型推导,分析了其干扰导航信号的机理,提出太阳射电爆发干扰导航通信的影响方程与太阳射电爆发流量、接收机性能以及太阳–天线高度角有关,其中太阳射电流量总功率与信号的信噪比下降呈正相关;同时受到太阳–天线高度角和有效面积的制约,又与接收机环路滤波器响应函数呈卷积关系。通过对2003年10月28日、2006年12月6日和2015年11月4日事件中GPS失锁情况分析,发现同一次事件中同一站点不同接收机的失锁率不同;同一次事件中不同纬度的接收机失锁率不同,以及在同一次事件中L波段(1~2 GHz)太阳射电爆发频谱不均匀的条件下,L1和L2频段信号的信噪比下降情况也不同。 从上述三个事件的观测表征验证了上述影响方程的分析正确性。Abstract: Solar radio bursts are a potential interference factor in navigation systems. From the navigation signal model is derived in this paper, the paper analyzes the solar radio burst interference mechanism of navigation signal, the interference effects exist three effects, namely with the solar radio burst flux, receiver performance, and the Angle of the Sun-navigation antenna height, synthesize the proposed the influence of solar radio burst interfere with communication navigation equation. It is concluded that the total integrated power of the solar burst flow in the navigation communication frequency band is positively correlated with the decrease of the signal to noise ratio of the communication signal, and is affected by the modulation of the height Angle of the sun-antenna and the effective area of the antenna, and has a convolution relationship with the response function of the loop filter of the navigation receiver. Then, this paper further analyzed the GPS lock-out signal during the solar radio bursts on 28 October 2003, 6 December 2006 and 4 November 2015. It is found that the loss-rate of different receivers at the same site is different in the same event (receiver performances effect). The loss-of-lock rate of the same receiver at different latitudes in the same event is different (Sun-antenna height Angle effect). In addition, under the condition of non-uniform spectrum of L-band (1~2 GHz) solar radio bursts in the same event (solar radio burst flow distribution effect), the decrease of signal to noise ratio of L1 and L2 band communication signals is also different. Therefore, the analytical correctness of the above influence equation is verified by the observation characterization of the above three events.
-
表 1 在太阳射电爆发流量为1000 sfu条件下的不同码元速率载噪比损失
Table 1. Noise ratio loss for different symbol rates when SRB flux reaches 1000 sfu
C/A码 P(Y)码 M码 Rc/MHz 1.023 10.23 5.115 通信带宽BW/MHz 2.046 20.46 10.23 PSRB/dBw –150 –140 –143 用户最低可解调接收功率/dBw –158.5 –161.5 –164.5 最大影响载噪比/dB 8.5 21.5 21.5 表 2 不同天线面积条件下流量为1000 sfu的太阳射电爆发引起的载噪比影响
Table 2. With the different effective area the SRB flux reaches 1000 sfu causing influences results
Ae/m2 0.005 0.001 0.0005 0.0001 PSRB/dBw –150 –157 –160 –167 C/A码/dB最低所需可解调接收功率条件下的载噪比影响 8.5 1.5 0 0 P(Y)码/dB 最低所需可解调接收功率条件下的载噪比影响 21.5 4.5 1.5 0 M码/dB最低所需可解调接收功率条件下的载噪比影响 21.5 7.5 4.5 0 表 3 2003年10月28日事件中接收机锁定率与接收机种类之间的关系
Table 3. Relationship between the phased lock loop and different receiver types during the event occurred on 28 October 2003
接收机型号 考察的
接收机数目最强阶段
锁定率次强阶段
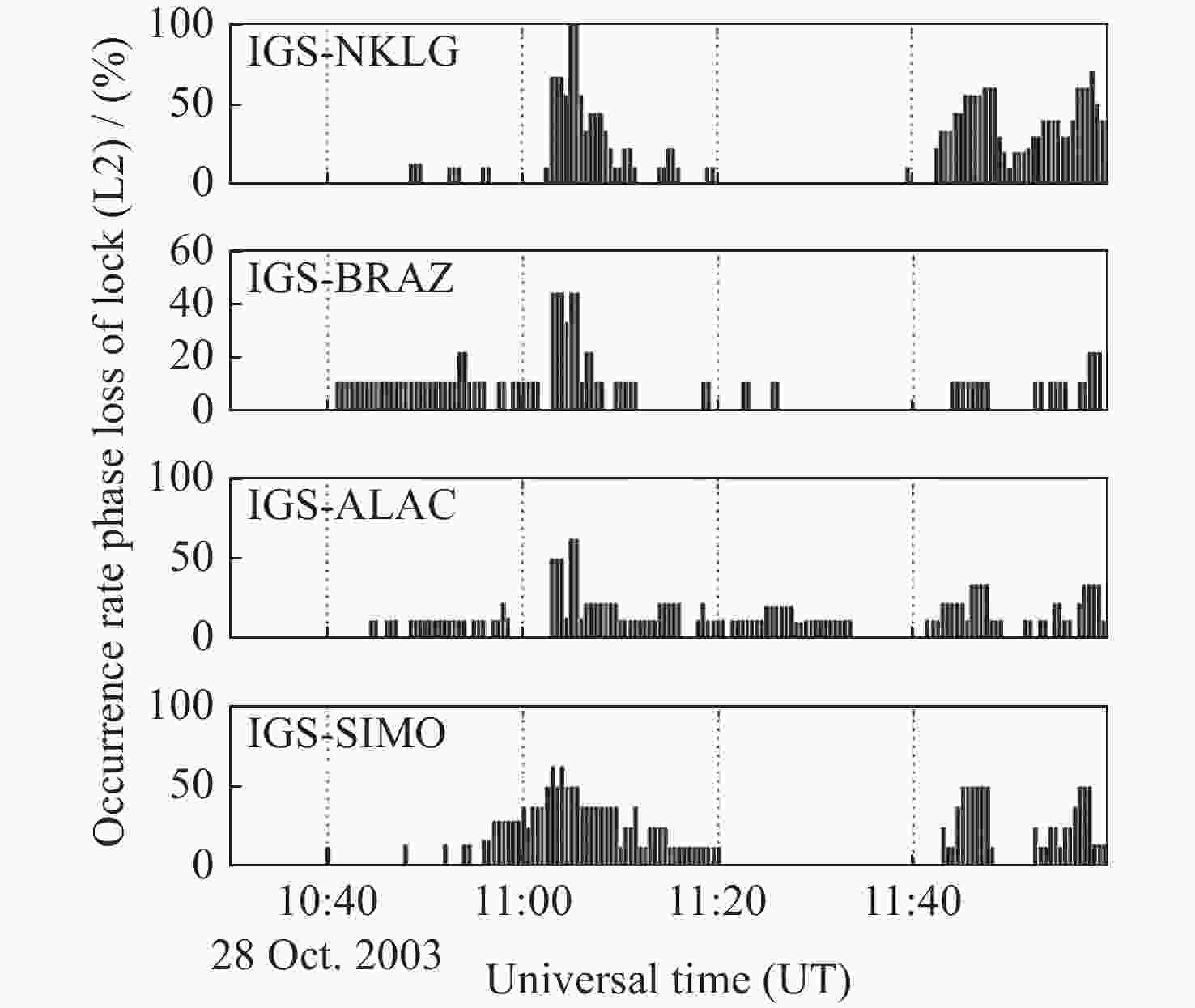
锁定率ASHTECH Z-XII3 43 11.62 2.33 ASHTECH UZ-12 12 8.33 0.00 ASHTECH Z18 11 27.27 18.18 TRIMBLE 4000 SSI 38 78.95 63.16 TRIMBLE 4700 9 22.22 22.22 TRIMBLE 4000 SSE 6 16.67 16.67 AOA SNR-8000 ACT 14 7.14 7.14 AOA BENCHMARK ACT 8 0.00 0.00 AOA ROGUE SNR-8000 8 75.00 75.00 JPS LEGACY 7 14.29 14.29 注 最强阶段时间11:02-11:12 UTC, 次强阶段时间11:42-12:00 UTC。 表 4 2003年10月28日事件中几个台站位置分布和失锁率情况
Table 4. Loss of lock present and the positions of several stations during the event occurred on 28 October 2003
台站名称 地理位置(经纬度) 当时太阳高度角 L2频点失锁率情况 IGS-NKLG 2.1°N,9.4°E 74°50′ 100% 影响最强 IGS-BRAZ 47.9°S,15.9°W 49°28′ 50%,持续时间较长 IGS-ALAC 38.2°N,0.3°W 37°59′ 50% IGS-SIMO 18.4°N,34.2°W 36°30′ 50% -
[1] HEY J S. Solar radiations in the 4~6 meter radio wave-length band[J]. Nature, 1946, 157(3976): 47-48 [2] LANZEROTTI L J, GARY D E, THOMSON D J, et al. Solar radio burst event (6 April 2001) and noise in wireless communications systems[J]. Bell Labs Technical Journal, 2002, 7(1): 159-163 doi: 10.1002/bltj.30 [3] CHEN Z Y, GAO Y, LIU Z Z. Evaluation of solar radio bursts’ effect on GPS receiver signal tracking within International GPS Service network[J]. Radio Science, 2005, 40(3): RS3012 [4] KINTNER JR P M, O’HANLON B, GARY D E, et al. Global Positioning System and solar radio burst forensics[J]. Radio Science, 2009, 44(1): RS0A08 [5] CARRANO C S, BRIDGWOOD C T, GROVES K M. Impacts of the December 2006 solar radio bursts on the performance of GPS[J]. Radio Science, 2009, 44(1): RS0A25 [6] YUE X, SCHREINER W S, KUO Y H, et al. The effect of solar radio bursts on the GNSS radio occultation signals[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2013, 118(9): 5906-5918 doi: 10.1002/jgra.50525 [7] 黄文耿, 阿尔察, 刘四清, 等. 2006年12月13日太阳射电暴对GPS观测的影响[J]. 空间科学学报, 2015, 35(6): 679-686 doi: 10.11728/cjss2015.06.679HUANG Wengeng, ERCHA A, LIU Siqing, et al. Effect of the 13 December 2006 solar radio burst on GPS observations[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2015, 35(6): 679-686 doi: 10.11728/cjss2015.06.679 [8] MARQUÉ C, KLEIN K L, MONSTEIN C, et al. Solar radio emission as a disturbance of aeronautical radionavigation[J]. Journal of Space Weather and Space Climate, 2018, 8: A42 doi: 10.1051/swsc/2018029 [9] 董亮, 闫小娟, 黄文耿, 等. 2015年11月4日太阳射电爆发干扰导航信号事件中的X射线先兆分析[J]. 天文研究与技术, 2021, 18(3): 294-300 doi: 10.14005/j.cnki.issn1672-7673.20210524.001DONG Liang, YAN Xiaojuan, HUANG Wengeng, et al. X-ray aura analysis of the solar radio burst interfering with navigation signal events on November 4, 2015[J]. Astronomical Research & Technology, 2021, 18(3): 294-300 doi: 10.14005/j.cnki.issn1672-7673.20210524.001 [10] SATO H, JAKOWSKI N, BERDERMANN J, et al. Solar radio burst events on 6 September 2017 and its impact on GNSS signal frequencies[J]. Space Weather, 2019, 17(6): 816-826 doi: 10.1029/2019SW002198 [11] YANG F, ZHU X F, CHEN X Y, et al. Intense L-band solar radio bursts detection based on GNSS carrier-to-noise ratio decrease over multi-satellite and multi-station[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(4): 1405 doi: 10.3390/s21041405 [12] 董亮. 太阳射电爆发干扰通信系统评估与预警方案的研究[D]. 昆明: 云南大学, 2016DONG Liang. The Assessment and Pre-alarm Methods Research for the Solar Radio Burst Events Interfering the Communication Systems[D]. Kunming: Yunnan University, 2016 [13] 董亮, 闫小娟, 黄文耿, 等. 太阳射电爆发对不同波段无线电信号影响分析[C]//第35届中国气象学会年会 S18 空间天气观测与业务的融合. 合肥: 中国气象学会, 2018: 12DONG Liang, YAN Xiaojuan, HUANG Wengeng, et al. Analysis of the influence of solar radio bursts on radio signals in different bands[C]//Proceedings of the 35 th National Meteorological Annual Meeting. Hefei: Chinese Meteorological Society, 2018: 12 [14] HUANG W G, AA E, SHEN H, et al. Statistical study of GNSS L-band solar radio bursts[J]. GPS Solutions, 2018, 22(4): 114 doi: 10.1007/s10291-018-0780-4 [15] NITA G M, GARY D E, LANZEROTTI L J, et al. The peak flux distribution of solar radio bursts[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2002, 570(1): 423-438 doi: 10.1086/339577 [16] 曹志刚, 钱亚生. 现代通信原理[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 1992Z. G Cao, Y. S Qian. Principles of Modern Communication[M]. Beijing, Tsinghua University Press, 1992 [17] KAPLAN E D, HEGARTY C J. GPS原理与应用[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2012KAPLAN E D, HEGARTY C J. Understanding GPS Principles and Applications[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2012 [18] KUMMER W H, GILLESPIE E S. Antenna measurements—1978[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1978, 66(4): 483-507 doi: 10.1109/PROC.1978.10940 -
-






 下载:
下载: