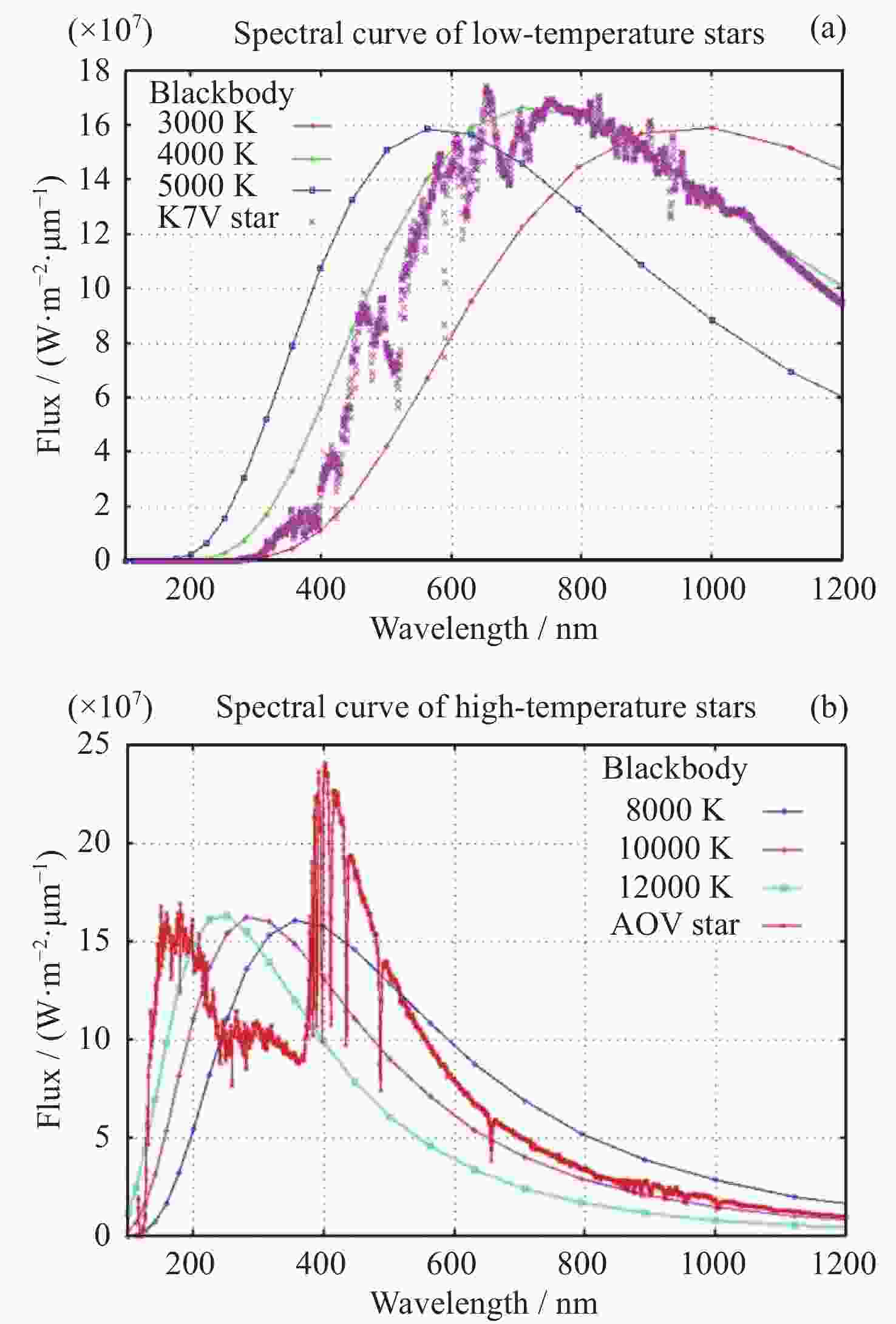
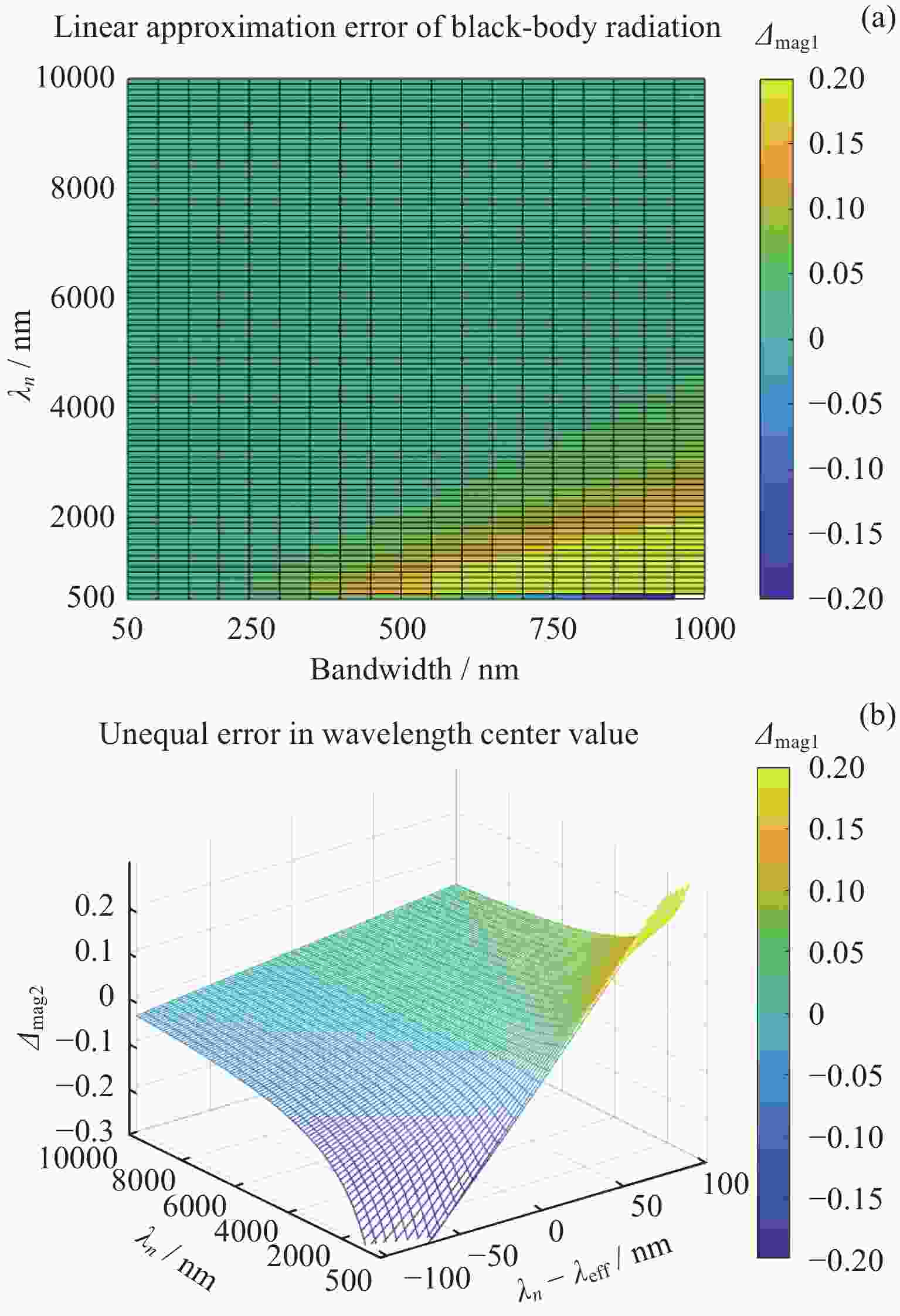
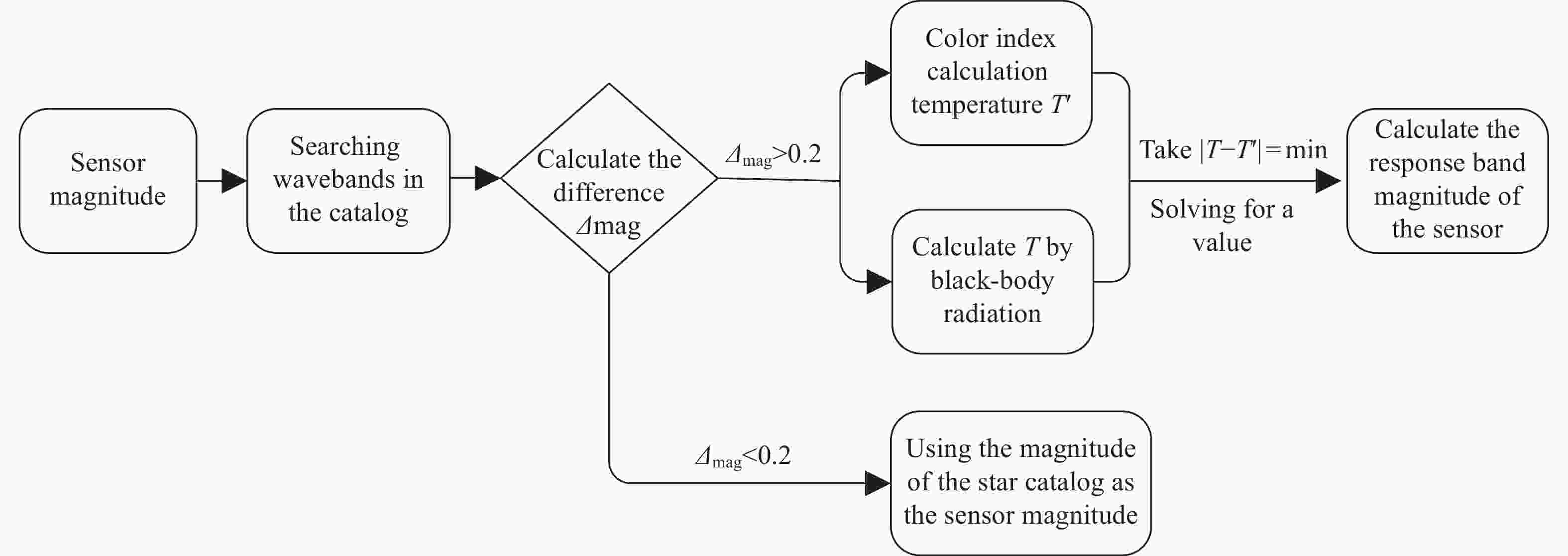
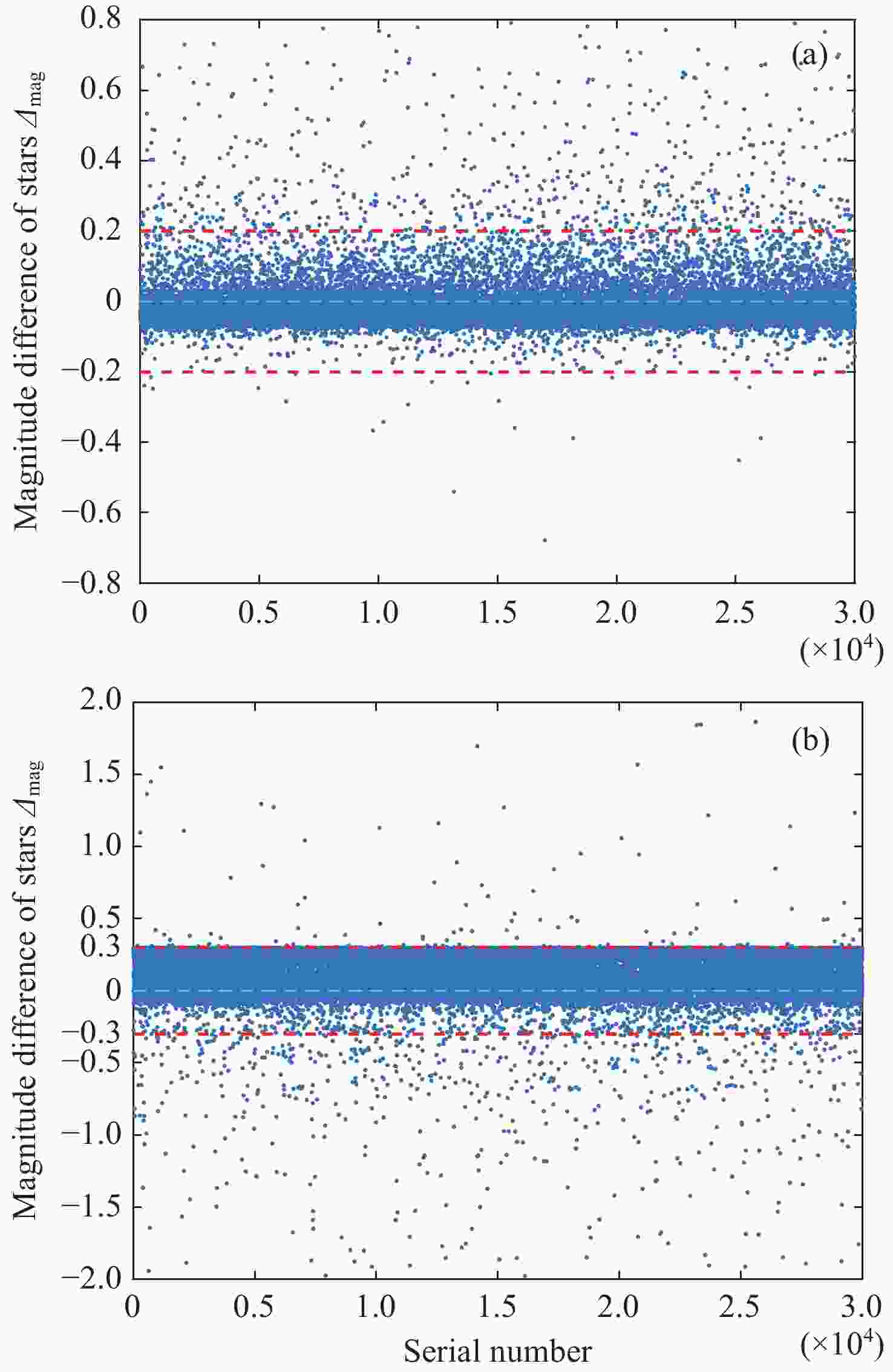
Calculation Method for Response Band Magnitude of Aerospace Sensors
-
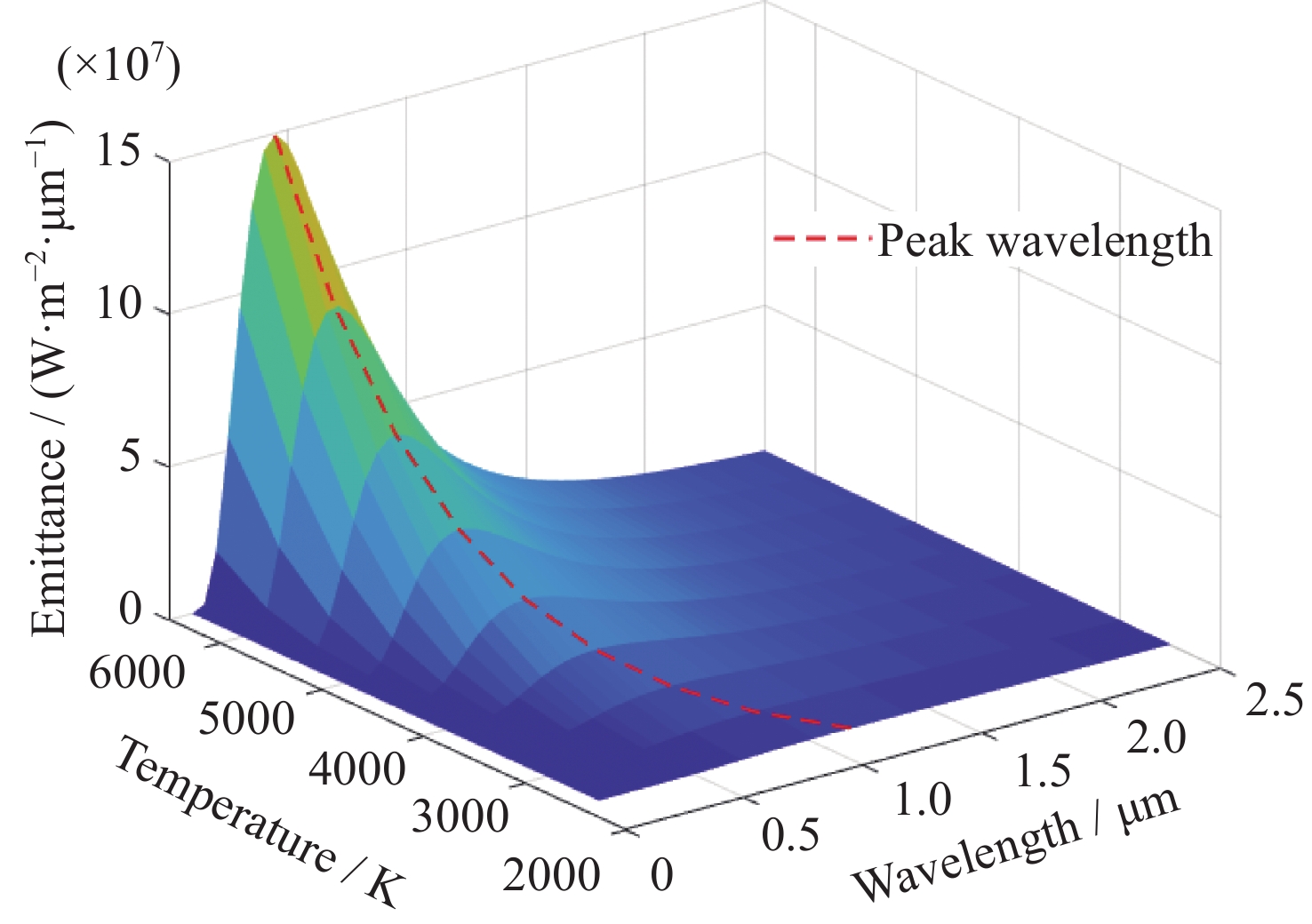
摘要: 精确的恒星星等信息是开展导航星表建立、航天器定姿、红外相机定标等工作的基础,现有公开星表涵盖测光波段不全且带宽普遍较窄,难以找到与任务传感器响应波段相匹配的星等信息。为此提出了一种基于恒星辐射光谱的传感器响应波段星等计算方法。该方法利用公开星表数据信息,建立星表测光波段与传感器响应波段星等差值模型,对星表星等与传感器响应波段星等差值进行估算;将色指数计算的恒星近似表面温度作为先验信息,在传感器响应波段区间进行普朗克方程求解,进而推算恒星在传感器响应波段的星等。星表数据计算验证表明,该方法具有较好的稳健性和适应性,对传感器响应波段星等推导精度为0.066等 (1δ),93.3%恒星推算误差优于0.2等,可满足导航星表建立、航天器定姿、红外相机定标等应用需求。Abstract: Accurate stellar magnitude information is the foundation for conducting navigation star catalog establishment, spacecraft attitude determination, infrared camera calibration, and other work. The existing public star catalogs do not cover all the photometry bands and the bandwidth is generally narrow, making it difficult to find magnitude information that matches the response bands of the mission sensors. A method for calculating the magnitude of sensor response bands based on stellar radiation spectra is proposed. This method utilizes publicly available catalog data information to establish a model for the magnitude difference between the photometry band of the catalog and the sensor response band, and estimates the magnitude difference between the catalog magnitude and the sensor response band. Using the approximate surface temperature of the star calculated by the color index as prior information, the Planck equation is solved in the sensor response band range to calculate the magnitude of the star in the sensor response band. The verification of star catalog data calculation shows that the method has good robustness and adaptability, and the star magnitude derivation accuracy of sensor response band is 0.066 magnitude (1δ), 93.3% of the star estimation error is better than 0.2 magnitude, which can meet the needs of navigation star catalog establishment, spacecraft attitude determination, infrared camera calibration, and other applications.
-
Key words:
- Magnitude /
- Color index /
- Sensors /
- Response band /
- Black-body radiation /
- Radiation flux
-
表 1 Johnson测光系统部分参数
Table 1. Partial parameters of Johnson photometry system
测光波段 U B V R I J H K 有效波长/μm 0.366 0.438 0.545 0.641 0.798 1.22 1.63 2.19 半波带宽/μm 0.066 0.094 0.088 0.138 0.149 0.213 0.307 0.390 0星等辐流量/(10–14 W·cm–2·μm–1) 417.5 632 363.1 217.7 112.6 31.47 11.38 3.961 表 2 同一恒星不同波段星等差异
Table 2. Different band magnitudes of the same star
恒星HIP编号 测光波段 B V R I J H 21479 7.32 5.87 5.06 4.39 –2.62 –3.73 32349 –1.46 –1.46 –1.46 –1.43 –1.36 –1.33 34444 2.69 1.91 1.43 1.05 0.77 0.54 78265 2.66 2.83 2.91 3.08 3.47 3.5 91262 0.03 0.03 0.07 0.10 –0.18 –0.03 表 3 部分星表测光波段数据
Table 3. Partial photometric band data of open star catalog
星表 滤光片 有效波长/μm 半波带宽/μm Hipparcos Hp 0.550 0.225 Tycho BT 0.420 0.075 VT 0.510 0.100 SDSS u 0.352 0.063 g 0.480 0.141 r 0.625 0.139 i 0.769 0.154 z 0.911 0.141 PAN-STARRS Ps1 g 0.484 0.105 Ps1 r 0.620 0.125 Ps1 w 0.629 0.256 Ps1 open 0.694 0.398 Ps1 i 0.753 0.121 Ps1 z 0.868 0.099 Ps1 y 0.963 0.064 2 MASS J 1.236 0.162 H 1.662 0.251 K 2.159 0.262 GAIA Gbp 0.504 0.233 G 0.585 0.420 Grp 0.769 0.284 WISE W1 3.353 0.663 W2 4.603 1.042 W3 11.561 5.506 W4 22.088 4.102 IRAS IRAS 12 μm 10.164 6.067 IRAS 25 μm 21.735 10.018 IRAS 60 μm 52.137 30.516 IRAS 100 μm 95.484 33.265 表 4 星表对应波段星等差值统计
Table 4. Magnitude differences of star catalogue for corresponding bands
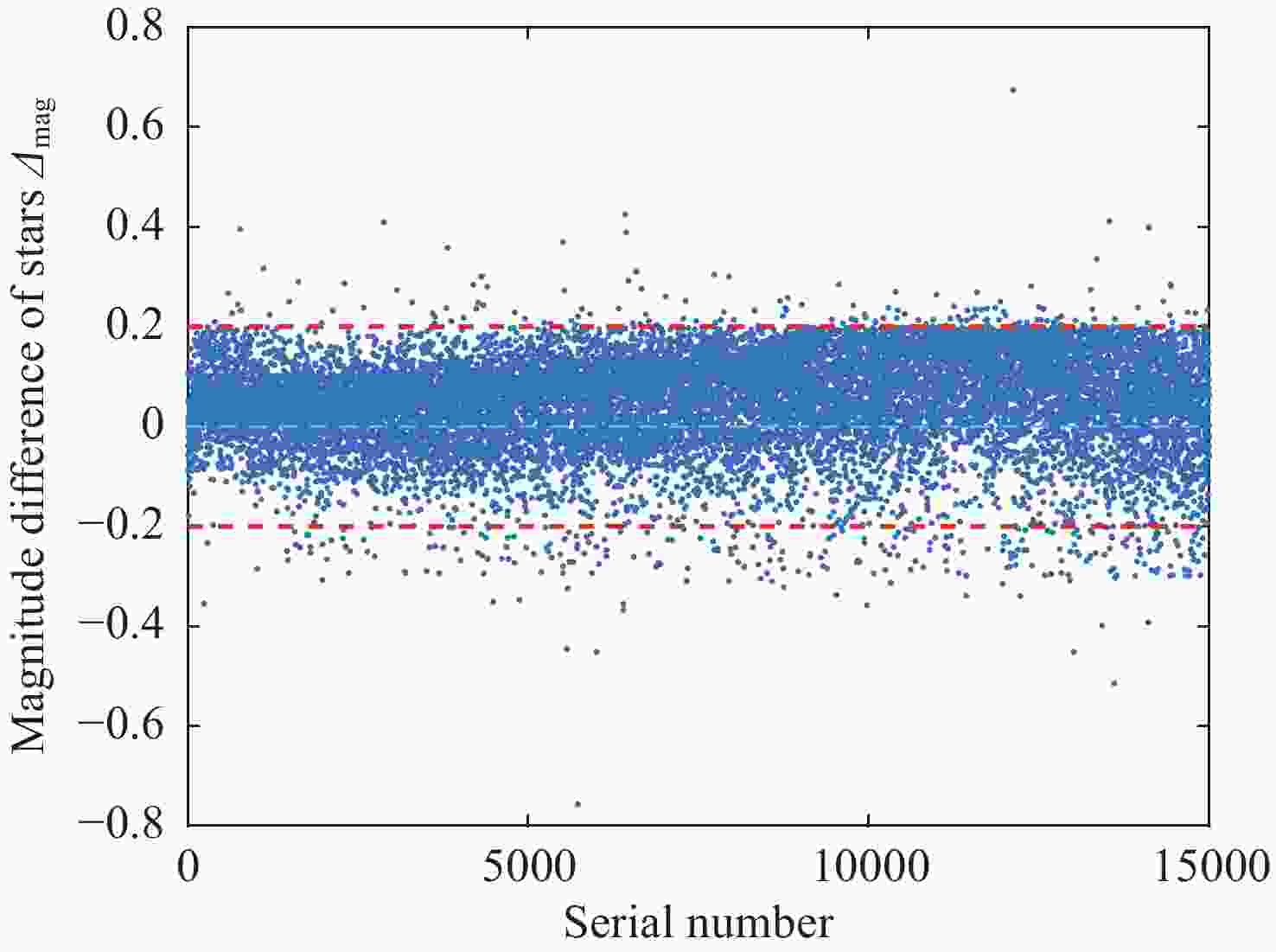
星等差值|Δmag| 0.05 0.05~0.1 0.1~0.2 0.2~0.3 <0.5 均值 方差 Hp与VT 62.7% 30.2% 4.3% 1.2% 99.7% 0.05 0.08 G与R 21.8% 16.6% 18.1% 36.9% 98.3% 0.16 0.15 -
[1] LU R, WU Y P. Estimation of stellar instrument magnitudes using synthetic photometry[C]//2019 IEEE Aerospace Conference. Big Sky: IEEE, 2019: 1-7 [2] 牟达, 李全勇, 董家宁. 地基红外系统探测空间目标红外星等的分析[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2011, 40(9): 1609-1613MU Da, LI Quanyong, DONG Jianing. Analysis on ground-based infrared detection system detecting the infrared magnitude of space targets[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2011, 40(9): 1609-1613 [3] WANG W J, WEI X G, LI J, et al. Guide star catalog generation for short-wave infrared (SWIR) All-Time star sensor[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2018, 89(7): 075003 doi: 10.1063/1.5023157 [4] LORENZO-OLIVEIRA D, DE MELLO G F P, DUTRA-FERREIRA L, et al. Fine structure of the age-chromospheric activity relation in solar-type stars: I. The Ca II infrared triplet: absolute flux calibration[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2016, 595: A11 [5] 张辉, 周向东, 汪新梅, 等. 近地空间全天时星敏感器技术现状及发展综述[J]. 航空学报, 2020, 41(8): 623719ZHANG Hui, ZHOU Xiangdong, WANG Xinmei, et al. Survey of technology status and development of all-time star sensors in near-earth space[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2020, 41(8): 623719 [6] 黄晨, 王建军, 高昕, 等. 红外星表在地基红外辐射测量系统中的应用[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2013, 42(11): 2901-2906 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2013.11.006HUANG Chen, WANG Jianjun, GAO Xin, et al. Application of infrared star catalog in ground-based infrared radiation measurement system[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2013, 42(11): 2901-2906 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2013.11.006 [7] MA Y, JIANG J, ZHANG G J. Stellar instrument magnitude estimation in infinite-dimensional space[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(3): 1422-1432 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2946836 [8] STRUNZ H C, BAKER T, ETHRIDGE D. Estimation of stellar instrument magnitudes[C]//Proceedings of the SPIE 1949, Space Guidance, Control, and Tracking. Orlando: SPIE, 1993: 228-235 [9] VAN DER BLIEK N S, BOUCHET P, HABING H J, et al. Standard stars for the Infrared Space Observatory, ISO[J]. Messenger, European Southern Observatory, Garching, Germany, 1992: 28-30 [10] BLACKWELL D E, LYNAS-GRAY A E. Determination of the temperatures of selected ISO flux calibration stars using the Infrared Flux Method[J]. Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series, 1998, 129(3): 505-515 doi: 10.1051/aas:1998202 [11] KRUZHILOV I S. Evaluation of instrument stellar magnitudes without recourse to data as to star spectral classes[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2012, 6(1): 063537 doi: 10.1117/1.JRS.6.063537 [12] KRUZHILOV I, KARELIN A, KNIAZEV V, et al. Calculating stellar magnitude to enhance guide star catalogs[J]. SPIE Newsroom, 2012 [13] 张婉莹, 王涛, 陈凡胜. 星上定标的观测恒星确定方法研究[J]. 中国空间科学技术, 2017, 37(3): 71-76ZHANG Wanying, WANG Tao, CHEN Fansheng. Research on determining methods of observed stellar in on-board radiometric calibration[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2017, 37(3): 71-76 [14] 王誉都, 孙小进, 张恒, 等. 利用多星表交叉外推恒星能量的方法[J]. 红外与毫米波学报, 2019, 38(4): 473-478WANG Yudu, SUN Xiaojin, ZHANG Heng, et al. A new approach for extrapolating star flux using cross-matching multiple catalogues[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2019, 38(4): 473-478 [15] SCHULMAN E, COX C V. Misconceptions about astronomical magnitudes[J]. American Journal of Physics, 1997, 65(10): 1003-1007 doi: 10.1119/1.18714 [16] COCHRAN A L. Spectrophotometry with a self-scanned silicon photodiode array. II. Secondary standard stars[J]. Astrophysical Journal, 1981, 45: 83-96 doi: 10.1086/190708 [17] BESSELL M S. Photometric systems[J]. International Astronomical Union Colloquium, 1993, 136: 22-39 doi: 10.1017/S025292110000734X [18] CASAGRANDE L, VANDENBERG D A. Synthetic stellar photometry – II. Testing the bolometric flux scale and tables of bolometric corrections for the Hipparcos/Tycho, Pan-STARRS1, SkyMapper, and JWST systems[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2018, 475(4): 5023-5040 doi: 10.1093/mnras/sty149 [19] MANN A W, VON BRAUN K. Revised filter profiles and zero points for broadband photometry[J]. Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, 2015, 127(948): 102-125 doi: 10.1086/680012 [20] BESSELL M S. The Hipparcos and Tycho photometric system passbands[J]. Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, 2000, 112(773): 961-965 doi: 10.1086/316598 [21] BILIR S, AK S, KARAALI S, et al. Transformations between 2 MASS, SDSS and BVRI photometric systems: bridging the near-infrared and optical[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2008, 384(3): 1178-1188 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2007.12783.x [22] APELLÁNIZ J M. A uniform set of optical/NIR photometric zero points to be used with CHORIZOS[OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: astro-ph/0609430, 2007 [23] ZOMBECK M V. Handbook of Space Astronomy and Astrophysics[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2006 [24] BESSELL M S, CASTELLI F, PLEZ B. Model atmospheres broad-band colors, bolometric corrections and temperature calibrations for O-M stars[J]. Astronomy and Astrophysics, 1998, 333: 231-250 [25] BESSELL M, MURPHY S. Spectrophotometric libraries, revised photonic passbands, and zero points for UBVRI, Hipparcos, and Tycho photometry[J]. Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, 2012, 124(912): 140 doi: 10.1086/664083 [26] BINNEY J, MERRIFIELD M, KING I R. Galactic astronomy[J]. Physics Today, 1999, 52(8): 64-65 [27] HUGHES D W. The introduction of absolute magnitude (1902-1922)[J]. Journal of Astronomical History and Heritage, 2006, 9(2): 173-179 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1440-2807.2006.02.06 [28] JOHNSON H L. Astronomical measurements in the infrared[J]. Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics, 1966, 4: 193-206 doi: 10.1146/annurev.aa.04.090166.001205 [29] BATTAT J. Working “with magnitudes and color indices,”[J]. Hardvard Technical Note https://www.cfa..edu/~dfabricant/huchra/ay145/magnitudes.pdf (May 2005) [30] HANSLMEIER A. State Variables of Stars[M]//HANSLMEIER A. Introduction to Astronomy and Astrophysics. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2023: 303-335 [31] PLANCK M. The Theory of Heat Radiation[M]. Philadelphia: Blakiston, 1914 [32] SICHEVSKIJ S G, MIRONOV A V, MALKOV O Y. Accuracy of stellar parameters determined from multicolor photometry[J]. Astrophysical Bulletin, 2014, 69(2): 160-168 doi: 10.1134/S1990341314020035 [33] MALKOV O, KOVALEVA D, SICHEVSKY S, et al. Statistical relations between stellar spectral and luminosity classes and stellar effective temperature and surface gravity[J]. Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2020, 20(9): 139 doi: 10.1088/1674-4527/20/9/139 [34] MICHAEL RICHMOND. Astronomical spectra, filters, and magnitudes[EB/OL].http://spiff.rit.edu/classes/phys440/ lectures/filters/filters.html. [35] WRIGHT E L, EISENHARDT P R M, MAINZER A K, et al. The wide-field infrared survey explorer (wise): mission description and initial on-orbit performance[J]. The Astronomical Journal, 2010, 140(6): 1868-1881 doi: 10.1088/0004-6256/140/6/1868 [36] KLEBE D, SEBAG J, BLATHERWICK R D, et al. All-sky mid-infrared imagery to characterize sky conditions and improve astronomical observational performance[J]. Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, 2012, 124(922): 1309-1317 doi: 10.1086/668866 [37] DAVENPORT J R A, IVEZIĆ Ž, BECKER A C, et al. The SDSS-2 MASS-WISE 10-dimensional stellar colour locus[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2014, 440(4): 3430-3438 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stu466 [38] 许春. 一种利用恒星进行遥感卫星辐射定标的方法[J]. 红外与毫米波学报, 2017, 36(5): 581-588 doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2017.05.012XU Chun. A flux calibration method for remote sensing satellites using star flux[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2017, 36(5): 581-588 doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2017.05.012 [39] 冉晓强, 汶德胜, 邱跃洪, 等. 一种新的多三角形星图识别算法[J]. 光子学报, 2009, 38(7): 1867-1871RAN Xiaoqiang, WEN Desheng, QIU Yuehong, et al. A novel multi-triangle star pattern recognition algorithm[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2009, 38(7): 1867-1871 [40] SHIRAHATA M, MATSUURA S, HASEGAWA S, et al. Calibration and performance of the AKARI far-infrared surveyor (FIS)—slow-scan observation mode for point-sources[J]. Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan, 2009, 61(4): 737-750 doi: 10.1093/pasj/61.4.737 [41] ROSHANIAN J, YAZDANI S, BEHESHT S B, et al. 2 MASS infrared star catalog data mining for use onboard a daytime star tracker[C]//2015 7 th International Conference on Recent Advances in Space Technologies (RAST). Istanbul: IEEE, 2015: 75-79 [42] WANG W J, WEI X G, LI J, et al. Optical parameters optimization for all-time star sensor[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(13): 2960 doi: 10.3390/s19132960 [43] PERRYMAN M, LINDEGREN L, KOVALEVSKY J, et al. The hipparcos catalogue[J]. Astronomy and Astrophysics, 1997, 323: L49-L52 [44] Hipparcos/Copenhagen/USNO Tycho-2 Catalog[EB/OL]. [2023-05-25]. http://tdc-www.harvard.edu/software/catalogs/tycho2.html [45] COLLABORATION G. VizieR online data catalog: Gaia DR2 (Gaia Collaboration, 2018)[J]. VizieR Online Data Catalog, 2018: I/345 [46] TUCKER D L, KENT S, RICHMOND M W, et al. The Sloan Digital Sky Survey monitor telescope pipeline[J]. Astronomische Nachrichten, 2006, 327(9): 821-843 doi: 10.1002/asna.200610655 [47] KAPLAN G H, BANGERT J, PUATUA W, et al. User’s Guide to NOVAS Version C3.0[M]. US Naval Observatory, 2009. [48] SKRUTSKIE M F, CUTRI R M, STIENING R, et al. The two micron all sky survey (2 MASS)[J]. The Astronomical Journal, 2006, 131(2): 1163-1183 doi: 10.1086/498708 -
-





 下载:
下载: