BDS/GPS对流层延迟估计及对精密单点定位的影响
doi: 10.11728/cjss2024.01.2022-0051 cstr: 32142.14.cjss2024.01.2022-0051
BDS/GPS Zenith Tropospheric Delay Estimation and Its Effect on Precise Point Positioning
-
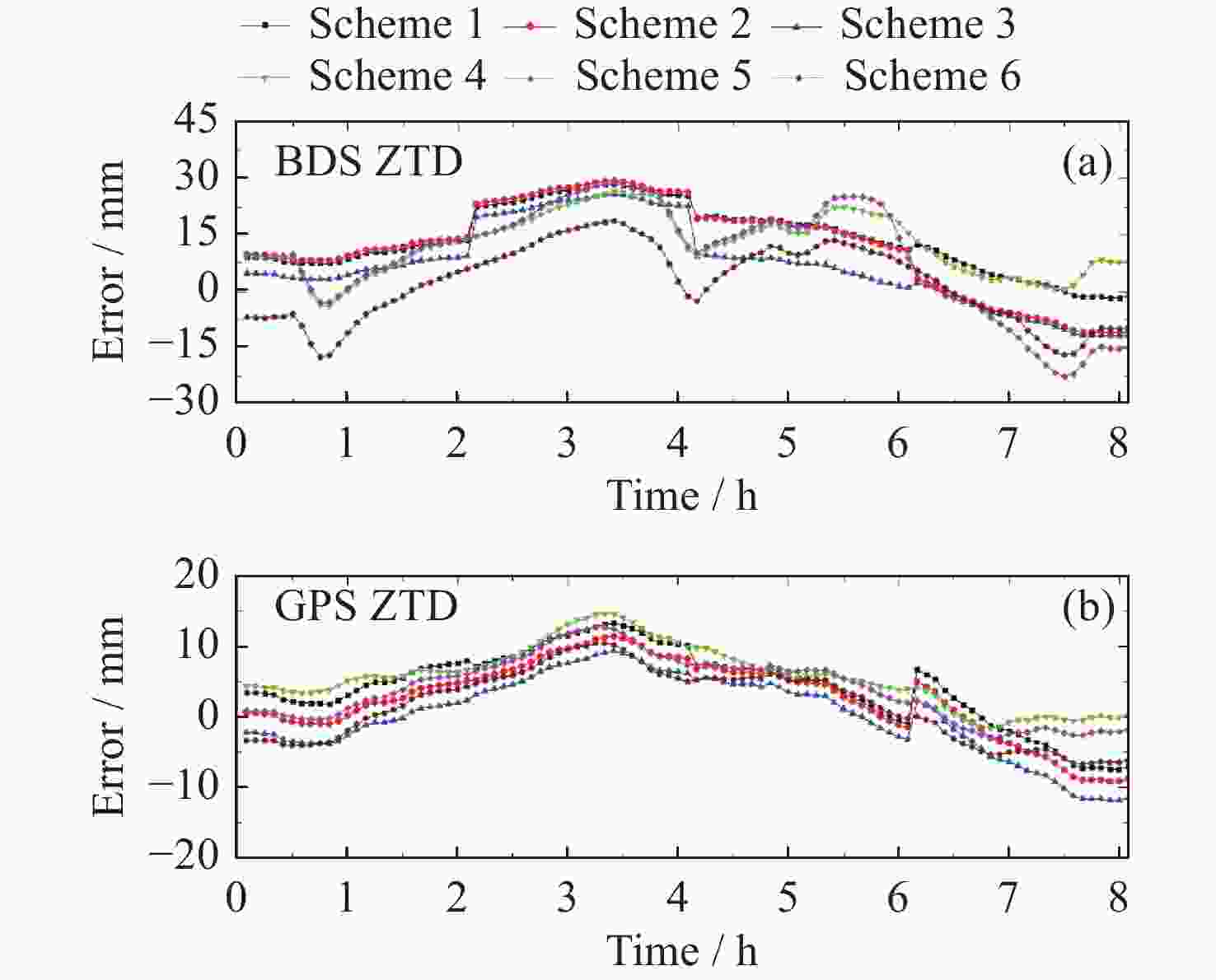
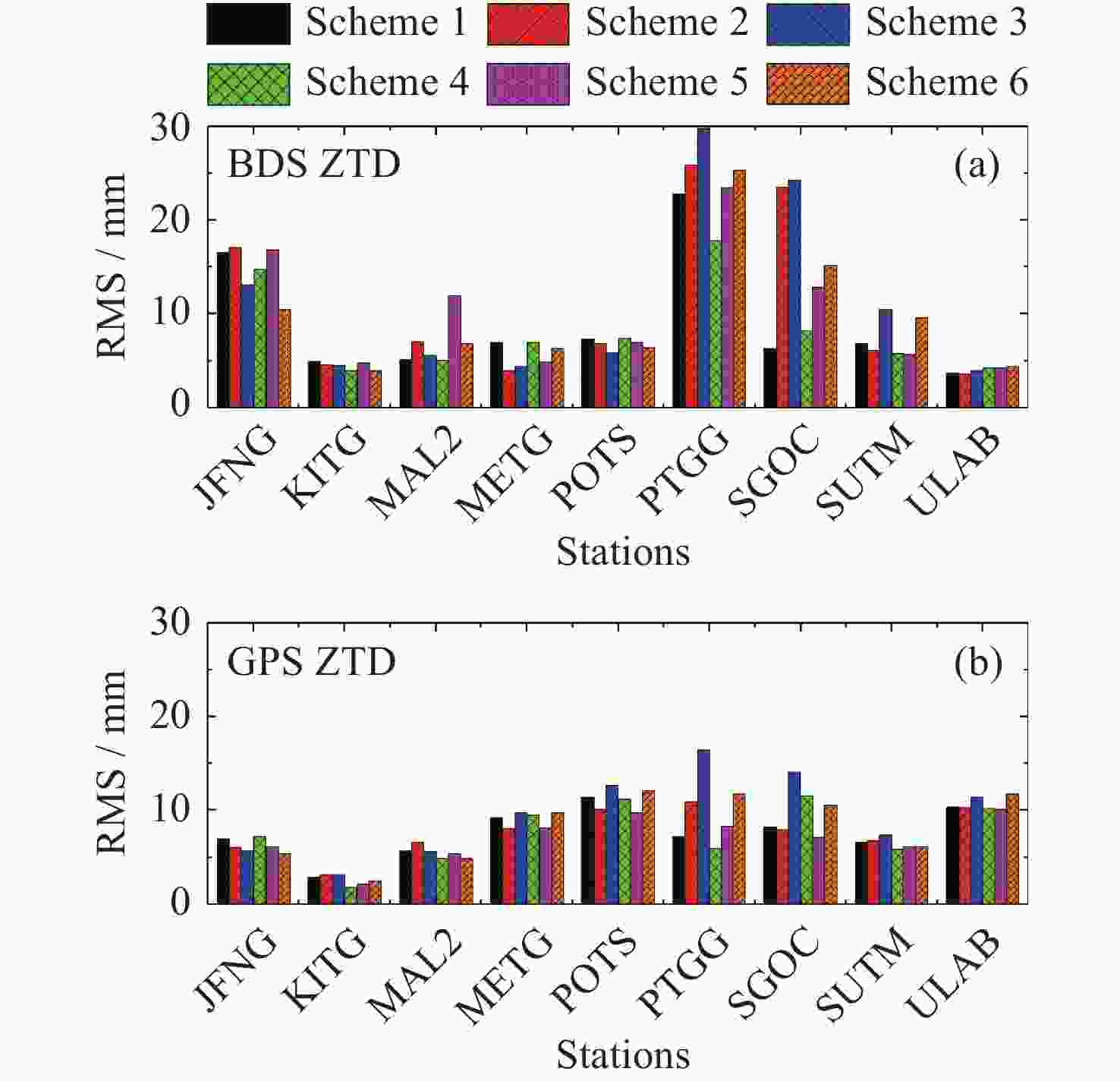
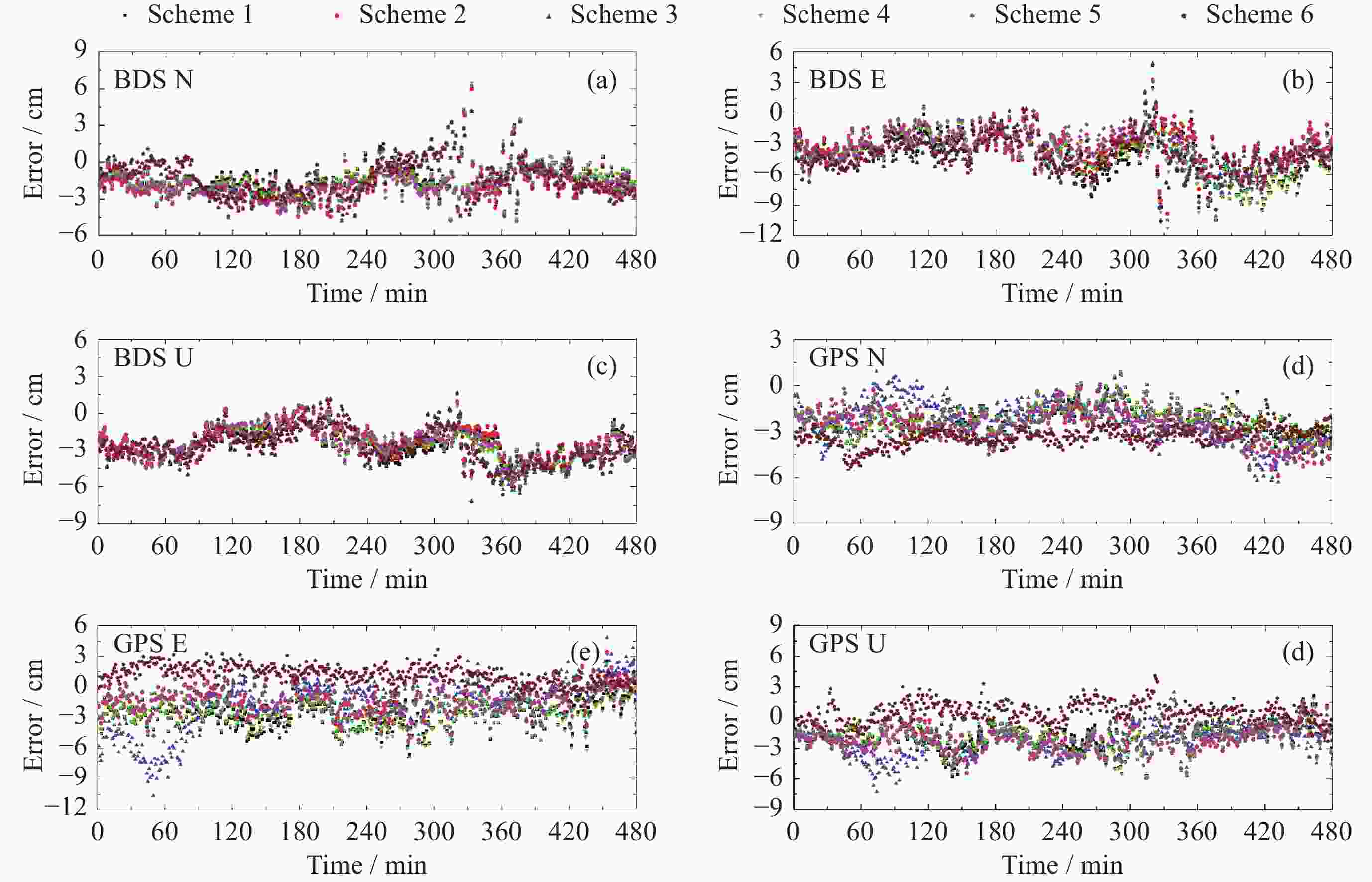
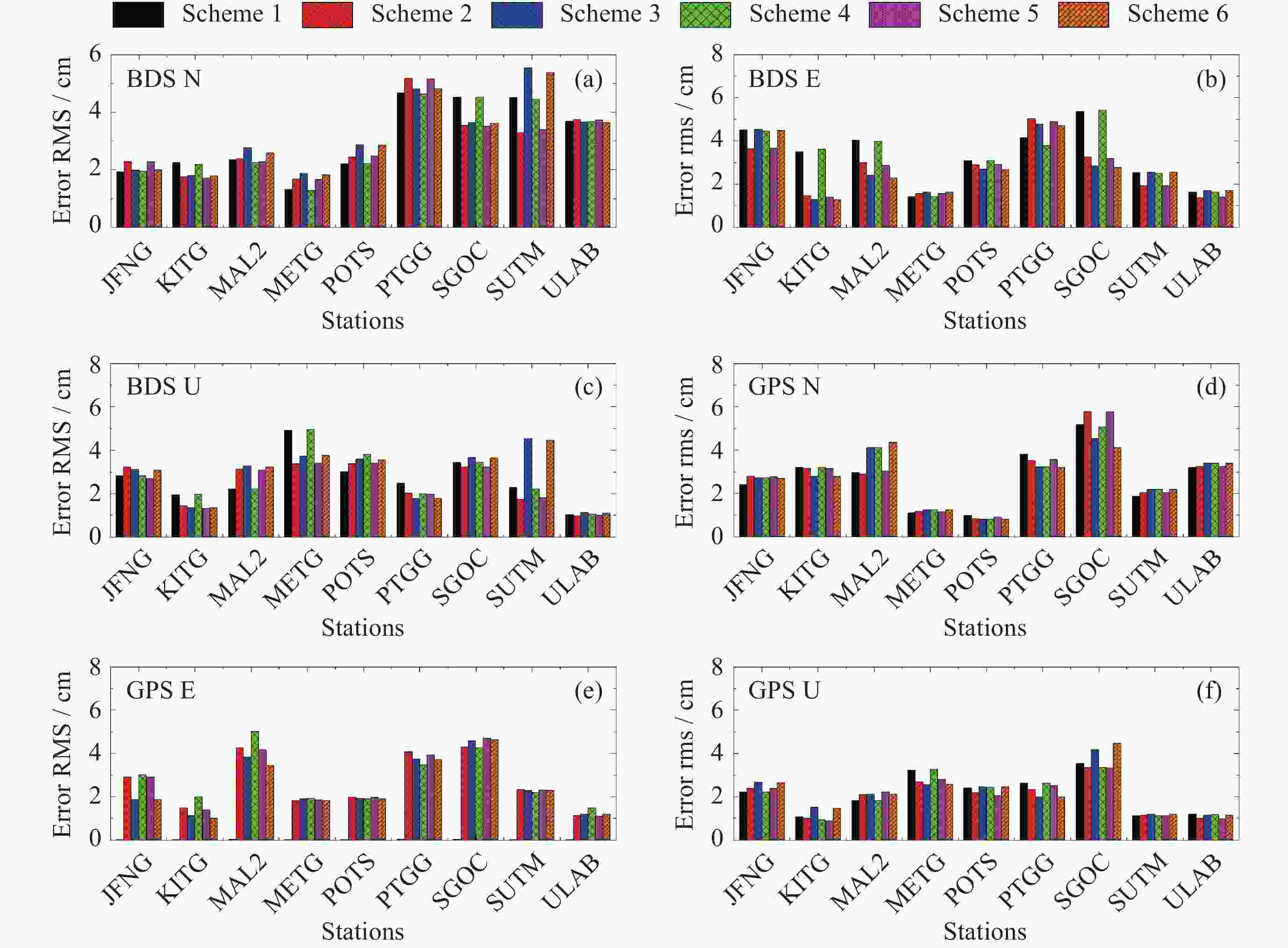
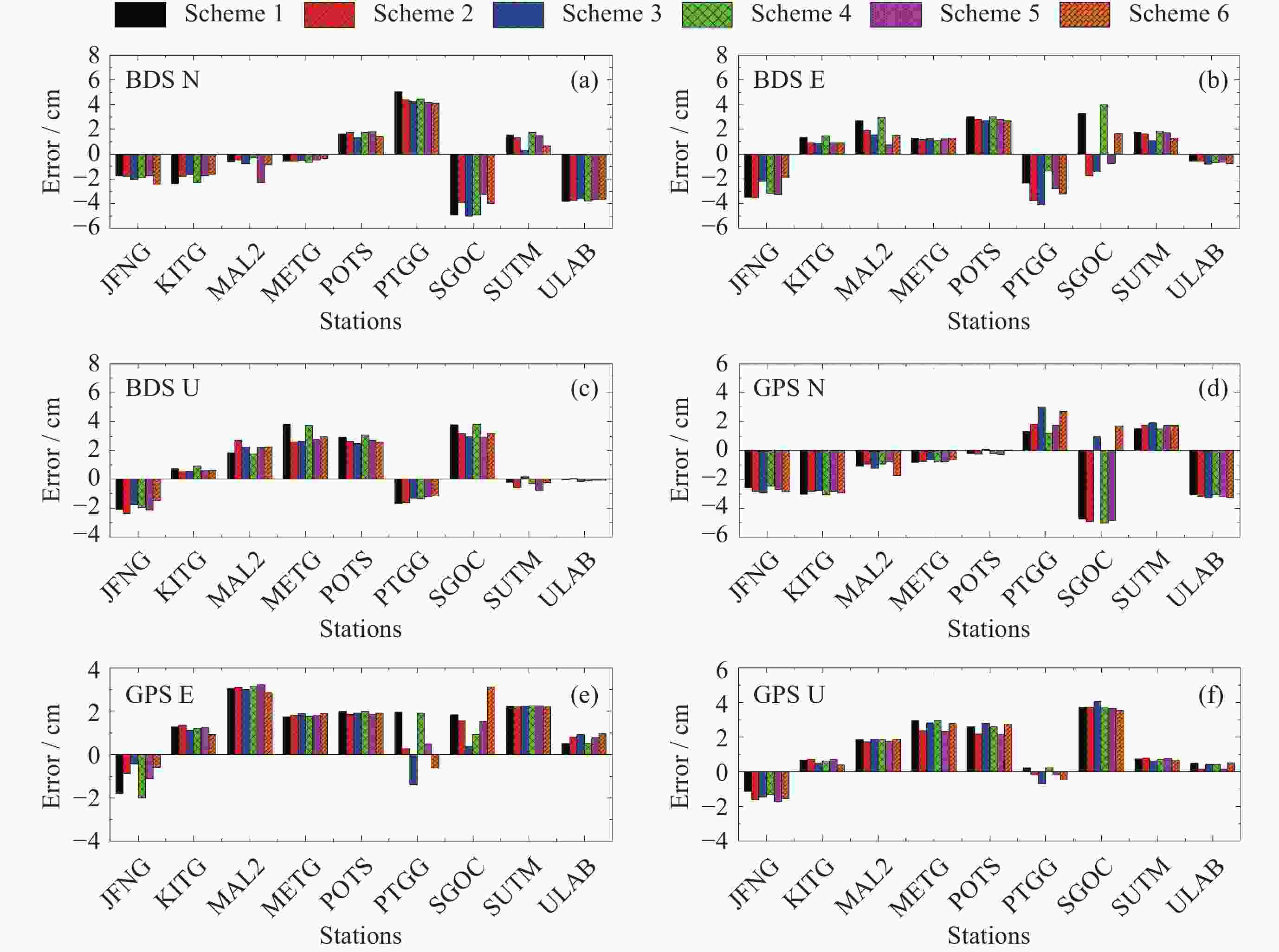
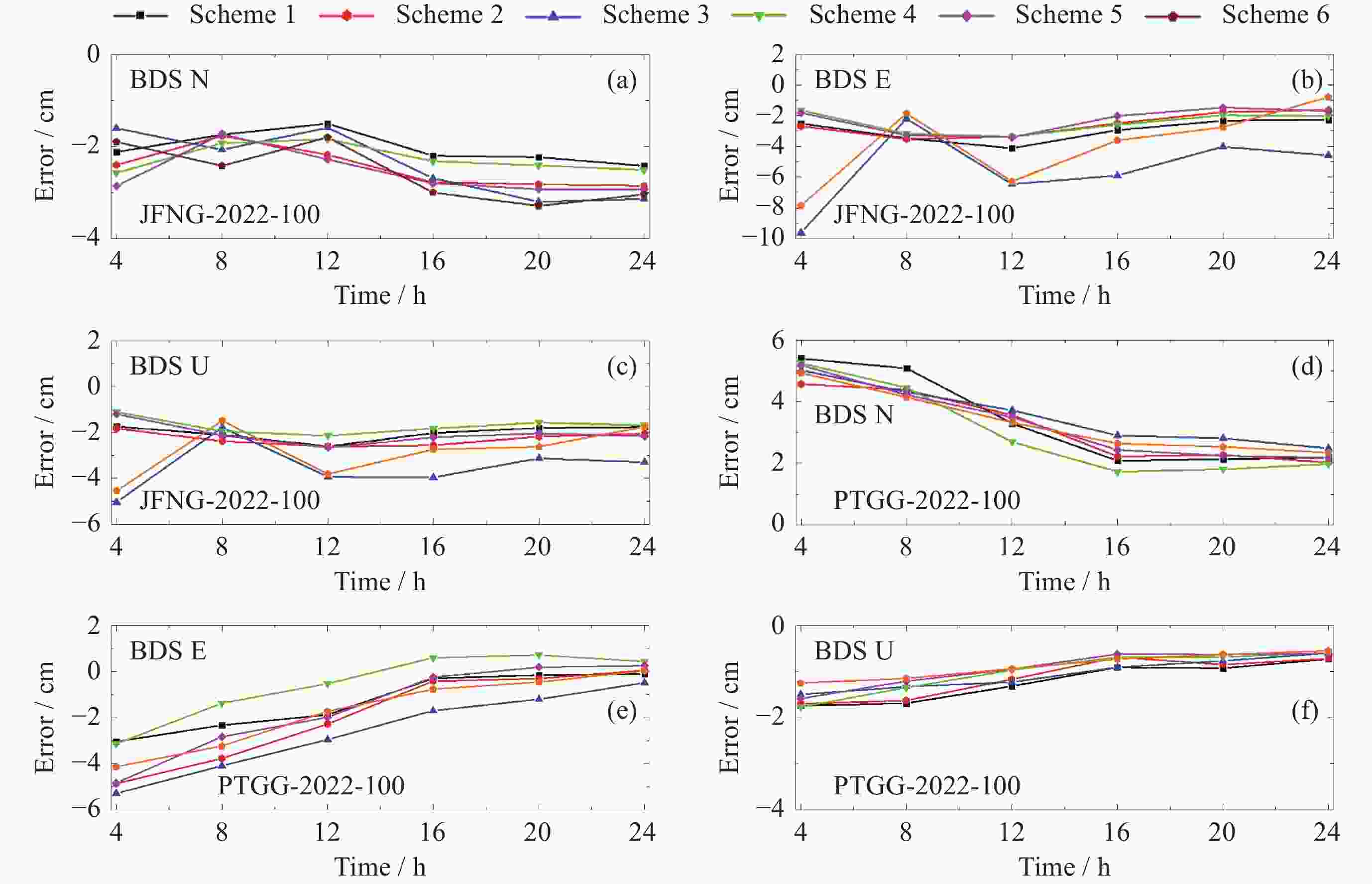
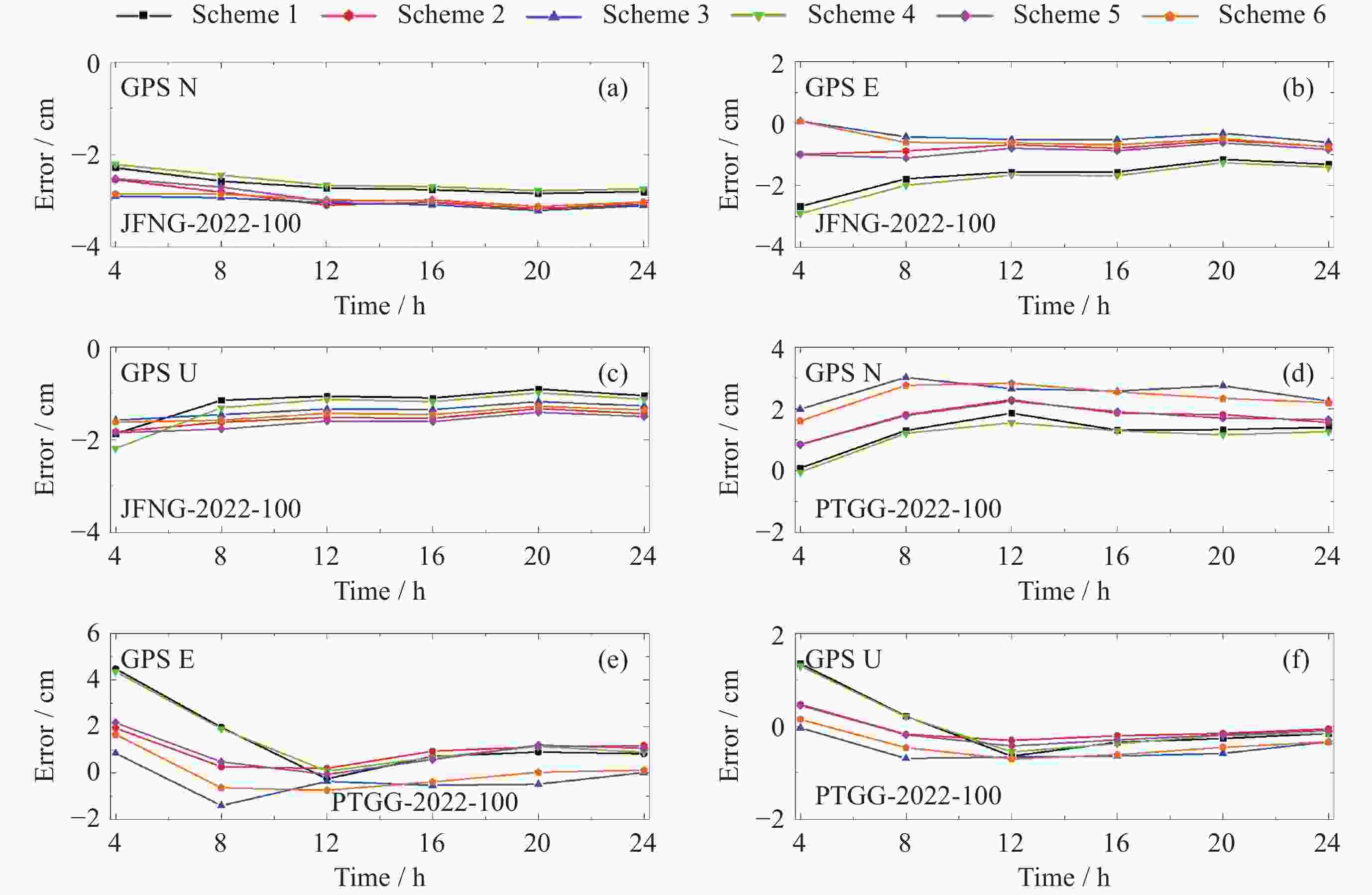
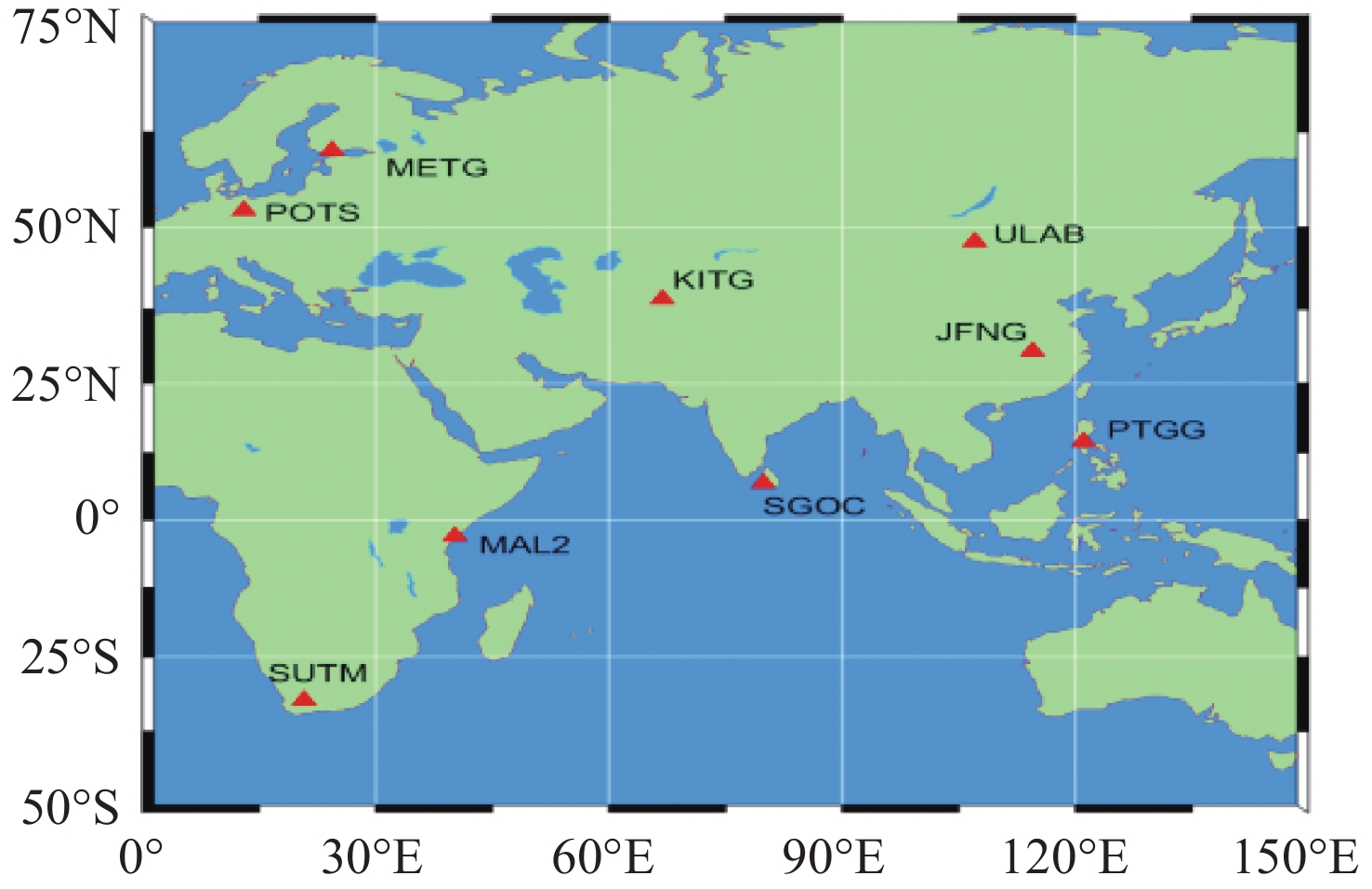
摘要: 针对对流层湿延迟参数估计及水平梯度处理策略对精密单点定位影响的问题, 以9个多系统实验网实测数据为基础, 设计了6种对流层延迟处理方案并进行实验. 实验结果表明, 观测时长在8 h时段内, BDS/GPS定位模式下, 对流层延迟的水平梯度处理不宜采用随机游走模型; 采用随机游走估算对流层湿延迟参数, 且不估算或使用分段常数处理水平梯度的策略相对占优. 动静态精密单点定位结果显示, BDS/GPS采用分段常数或随机游走进行对流层湿延迟参数估算和分段常数处理水平梯度的策略相对占优, 采用随机游走处理水平梯度的策略稍弱. 总体而言, BDS较GPS估算的对流层延迟及定位精度稍弱; 海洋周边6种方案解算结果差异较内陆站大. 静态精密单点定位模式下, 随着观测时长的增加, 6种方案定位误差趋势趋于一致, 误差大小基本在2 cm内, 观测时长大于12 h时, 随机游走估算对流层湿延迟参数和不考虑水平梯度的处理策略整体较优.Abstract: The influence of zenith wet delay parameter estimation and horizontal troposphere gradient processing strategy on precise point positioning is studied, Six zenith tropospheric delay processing schemes were designed and experimented on the basis of the measured data from nine Multi-GNSS Experiment stations. The experimental results show that, during the 8 h observation period, it is not suitable to use the random walk model to deal with the horizontal troposphere gradient of the zenith wet delay in the BDS/GPS Precise Point Positioning mode; and the strategies of estimating the zenith wet delay parameter by random walk and handling the horizontal troposphere gradient without estimating or using the piecewise constant are relatively advantageous. The results of the dynamic and static precise point positioning show that the BDS/GPS strategy of estimating the zenith wet delay parameter and processing the horizontal troposphere gradient with piecewise constant or random walk is relatively superior, while the strategy of processing the horizontal troposphere gradient with random walk is slightly weaker. Overall, the zenith tropospheric delay and precise point positioning accuracy estimated by BDS is slightly weaker than that by GPS; the differences in the results of the six schemes around the ocean are larger than those of the inland stations. In the static Precise Point Positioning mode, with the increase of observation time, the trend of Precise Point Positioning errors of the six schemes tends to be the same, and the error size is basically within 2 cm. When the observation time is longer than 12 h, the strategy of estimating the zenith wet delay parameter by random walk and not considering the horizontal troposphere gradient is better overall.
-
表 1 对流层延迟参数估计与处理策略
Table 1. Parameters’ estimation and data processing strategies of ZTD
方案 对流层湿延迟参数解算 对流层水平梯度处理策略 标注 方案1 PWC NO PWC-NO 方案2 PWC PWC PWC-PWC 方案3 PWC RW PWC-RW 方案4 RW NO RW-NO 方案5 RW PWC RW-PWC 方案6 RW RW RW-RW 注 NO代表不考虑HTG. 表 2 精密单点定位参数估计及其处理策略设置
Table 2. Models and data processingstrategies of PPP
处理方式 参数 处理策略 数据处理 观测值 L1和L2消电离层组合 采样间隔 30 s 卫星截止高度角 15° 参数估计 最小二乘法 定位模式 动态/静态 误差处理 卫星轨道 WHU精密星历 卫星钟差 WHU精密钟差 地球自转参数 WHU ERP 海洋潮模型 模型改正 相位偏差 WHU偏差 相位缠绕 模型改正 参数估计 对流层投影函数 VMF3 ZWT估算模式 PCW/RW HTG估算模式 PCW/RW/NO PWC时长 2 h 模糊度 不固定 接收机钟差 高斯白噪声 -
[1] 朱明晨, 胡伍生, 王来顺. GPT2w模型在中国区域的精度检验与分析[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2019, 44(9): 1304-1311ZHU Mingchen, HU Wusheng, WANG Laishun. Accuracy test and analysis for GPT2w model in China[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(9): 1304-1311 [2] WANG N B, LI Z S, LI M, et al. GPS, BDS and Galileo ionospheric correction models: an evaluation in range delay and position domain[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2018, 170: 83-91 doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2018.02.014 [3] LIU Z, CHEN X H, LIU Q. Estimating zenith tropospheric delay based on GPT2w model[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 139258-139263 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2931984 [4] 李薇, 袁运斌, 欧吉坤, 等. 全球对流层天顶延迟模型IGGtrop的建立与分析[J]. 科学通报, 2012, 57 (15): 1317-1325LI Wei, YUAN Yunbin, OU Jikun, et al. A new global zenith tropospheric delay model IGGtrop for GNSS applications[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57 (17): 2132-2139 [5] 姚宜斌, 张豹, 严凤, 等. 两种精化的对流层延迟改正模型[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(5): 1492-1501 doi: 10.6038/cjg20150503YAO Yibin, ZHANG Bao, YAN Feng, et al. Two new sophisticated models for tropospheric delay corrections[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(5): 1492-1501 doi: 10.6038/cjg20150503 [6] SCHÜLER T. The TropGrid2 standard tropospheric correction model[J]. GPS Solutions, 2014, 18(1): 123-131 doi: 10.1007/s10291-013-0316-x [7] BÖHM J, MÖLLER G, SCHINDELEGGER M, et al. Development of an improved empirical model for slant delays in the troposphere (GPT2w)[J]. GPS Solutions, 2015, 19(3): 433-441 doi: 10.1007/s10291-014-0403-7 [8] 姚宜斌, 曹娜, 许超钤, 等. GPT2模型的精度检验与分析[J]. 测绘学报, 2015, 44(7): 726-733YAO Yibin, CAO Na, XU Chaoqian, et al. Accuracy assessment and analysis for GPT2[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2015, 44(7): 726-733 [9] 高兴旺, 李付岗, 张秋昭, 等. 大型桥梁桥塔监测的GNSS相对对流层延迟估计[J]. 测绘科学, 2021, 46(2): 42-47,70GAO Xingwang, LI Fugang, ZHANG Qiuzhao, et al. GNSS relative tropospheric delay estimation for large bridge pylon monitoring[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2021, 46(2): 42-47,70 [10] 刘宁, 张永志, 熊永良. GPS参考站对流层湿延迟近实时估计的三步滤波算法[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2015, 40(7): 918-923LIU Ning, ZHANG Yongzhi, XIONG Yongliang. A three-step Kalman filter algorithm for near real-time estimating tropospheric wet delay on GPS reference stations[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2015, 40(7): 918-923 [11] YANG X, CHANG G B, WANG Q X, et al. An adaptive Kalman filter based on variance component estimation for a real-time ZTD solution[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Geophysica, 2019, 54(1): 89-121 doi: 10.1007/s40328-019-00247-7 [12] 范昊鹏, 孙中苗, 袁明泽, 等. 利用气象数据计算局部对流层湿延迟的方法[J]. 测绘科学, 2019, 44(9): 139-145FAN Haopeng, SUN Zhongmiao, YUAN Mingze, et al. Method of calculating accurate tropospheric wet delay for local area by meteorological data[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2019, 44(9): 139-145 [13] LI B F, FENG Y M, SHEN Y Z, et al. Geometry-specified troposphere decorrelation for subcentimeter real-time kinematic solutions over long baselines[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 2010, 115(B11): B11404 [14] 曹文涛, 郭际明, 谢翔, 等. 对流层水平梯度对PPP的影响[J]. 测绘通报, 2014(2): 13-15,25CAO Wentao, GUO Jiming, XIE Xiang, et al. Influence of horizontal gradients on precise point positioning[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2014(2): 13-15,25 [15] 范昊鹏, 孙中苗, 张丽萍, 等. 顾及映射函数误差的对流层延迟两步估计法[J]. 测绘学报, 2019, 48(3): 286-294 doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2019.20180306FAN Haopeng, SUN Zhongmiao, ZHANG Liping, et al. A two-step estimation method of troposphere delay with consideration of mapping function errors[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2019, 48(3): 286-294 doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2019.20180306 [16] LI X, HUANG G W, ZHANG Q, et al. A new GPS/BDS tropospheric delay resolution approach for monitoring deformation in super high-rise buildings[J]. GPS Solutions, 2018, 22(3): 90 doi: 10.1007/s10291-018-0752-8 [17] BOCK O, DOERFLINGER E. Atmospheric modeling in GPS data analysis for high accuracy positioning[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Part A: Solid Earth and Geodesy, 2001, 26 (6/7/8): 373-383 [18] MEINDL M, SCHAER S, HUGENTOBLER U, et al. Tropospheric gradient estimation at CODE: results from global solutions[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, 2004, 82(1B): 331-338 [19] 李黎, 匡翠林, 朱建军, 等. 水平梯度和映射函数对PPP对流层延迟估计的影响分析[J]. 工程勘察, 2011, 39(5): 52-56,60LI Li, KUANG Cuilin, ZHU Jianjun, et al. Influence analysis of horizontal gradients and mapping functions on tropospheric delay estimation[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, 2011, 39(5): 52-56,60 [20] 许华冠, 程宗颐. GPS精密定位中对流层折射参数估计方法的比较分析[J]. 中国科学院上海天文台年刊, 1997, 18: 95-102XU Huaguan, CHENG Zongyi. The comparison and analysis of the parameter estimation methods for tropospheric refraction on GPS precise positioning[J]. Annals of Shanghai Observatory Academia Sinica, 1997, 18: 95-102 [21] GENG J H, CHEN X Y, PAN Y X, et al. PRIDE PPP-AR: an open-source software for GPS PPP ambiguity resolution[J]. GPS Solutions, 2019, 23(91): 1-10 [22] 魏二虎, 刘学习, 王凌轩. BDS/GPS组合精密单点定位精度分析与评价[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2018, 43(11): 1654-1660WEI Erhu, LIU Xuexi, WANG Lingxuan, et al. Analysis and assessment of BDS/GPS combined precise point positioning accuracy[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2018, 43(11): 1654-1660 -
-





 邓标:男, 1981年9月出生于安徽省亳州市. 现为滁州学院地理信息与旅游学院高级工程师, 主要研究方向为GNSS数据处理与精密工程测量.E-mail:
邓标:男, 1981年9月出生于安徽省亳州市. 现为滁州学院地理信息与旅游学院高级工程师, 主要研究方向为GNSS数据处理与精密工程测量.E-mail: 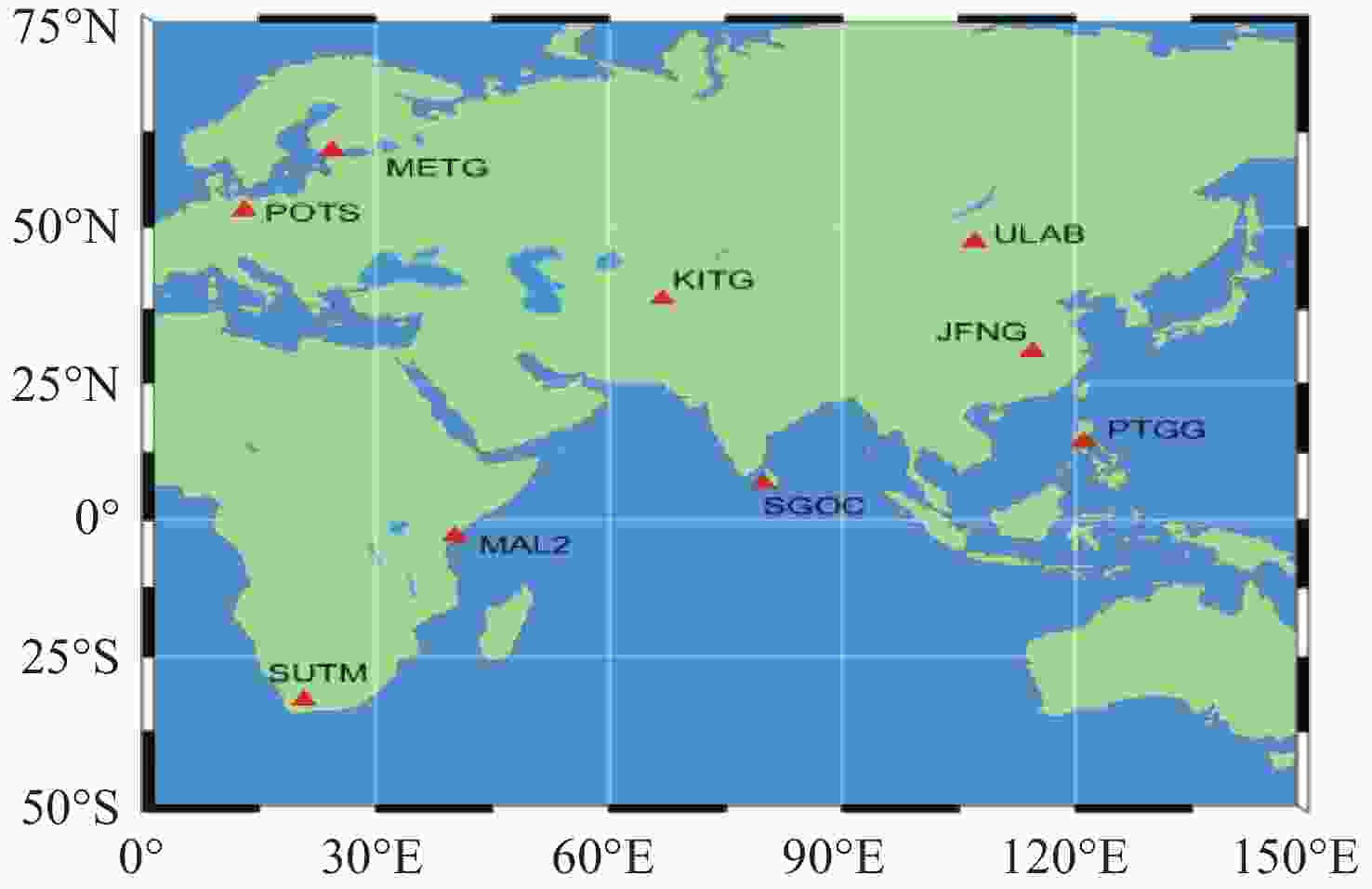
 下载:
下载: