COSMIC Ionospheric Occultation Inversion Simulation and Constellation Optimization Research
-
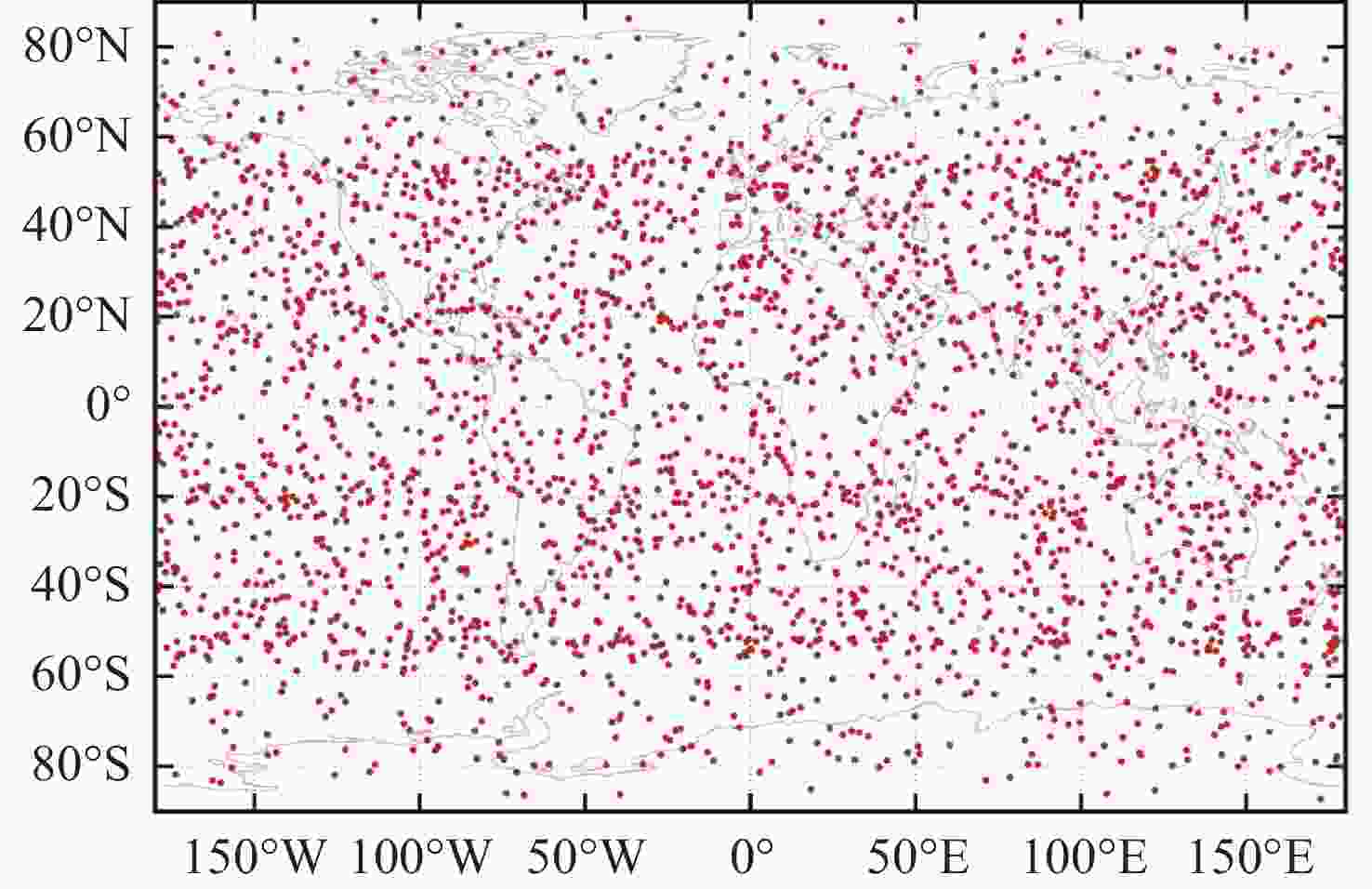
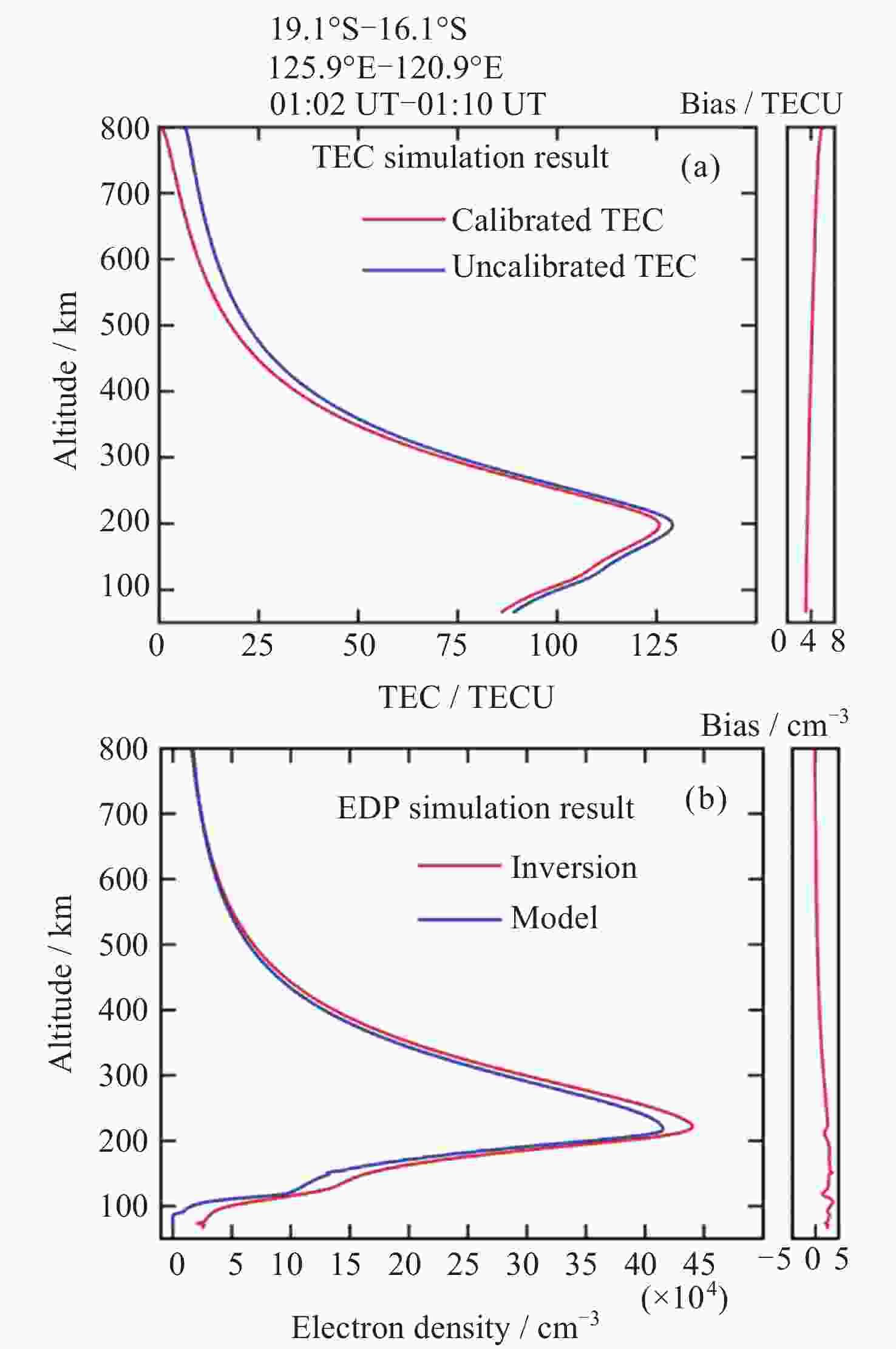
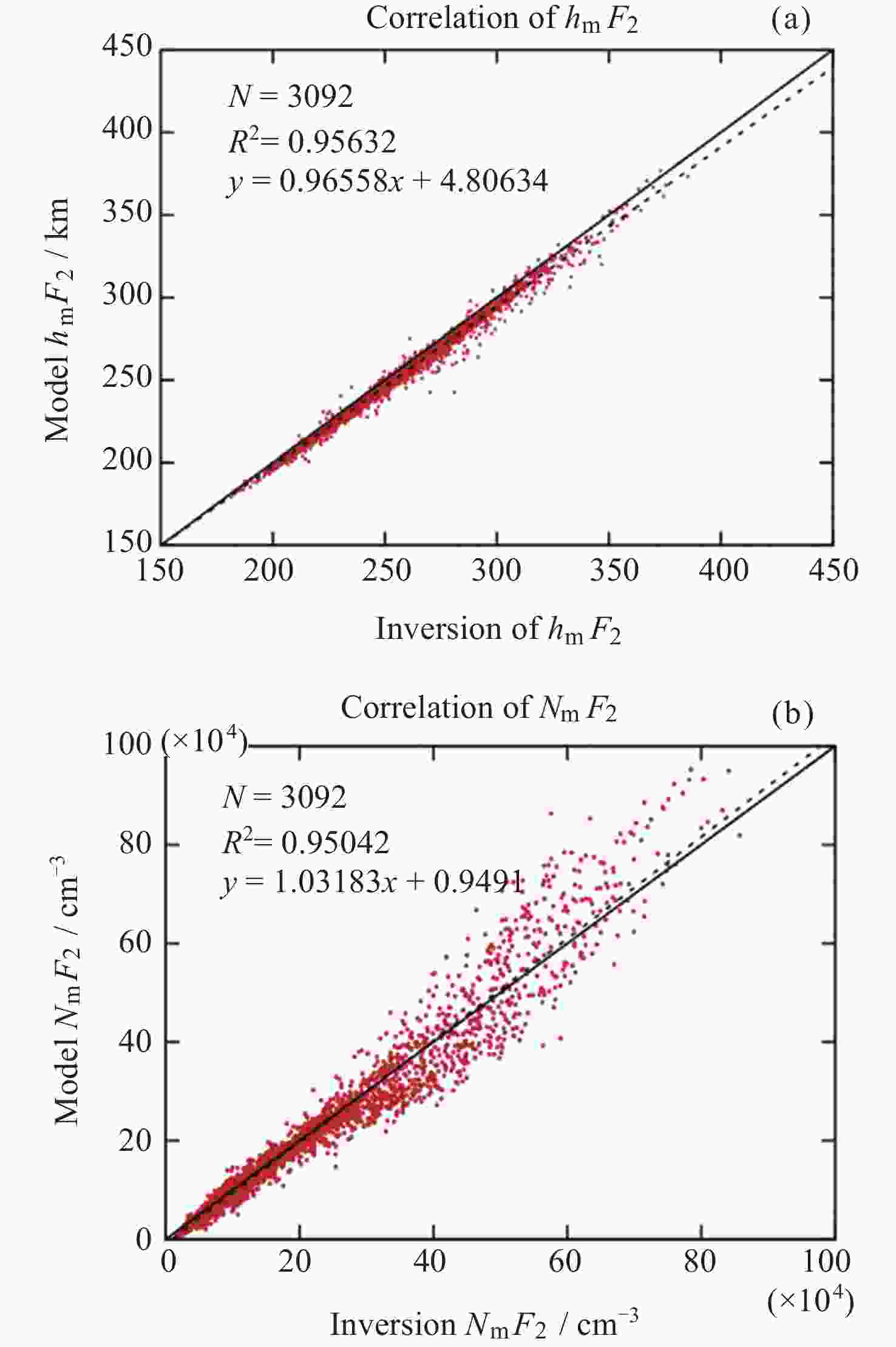
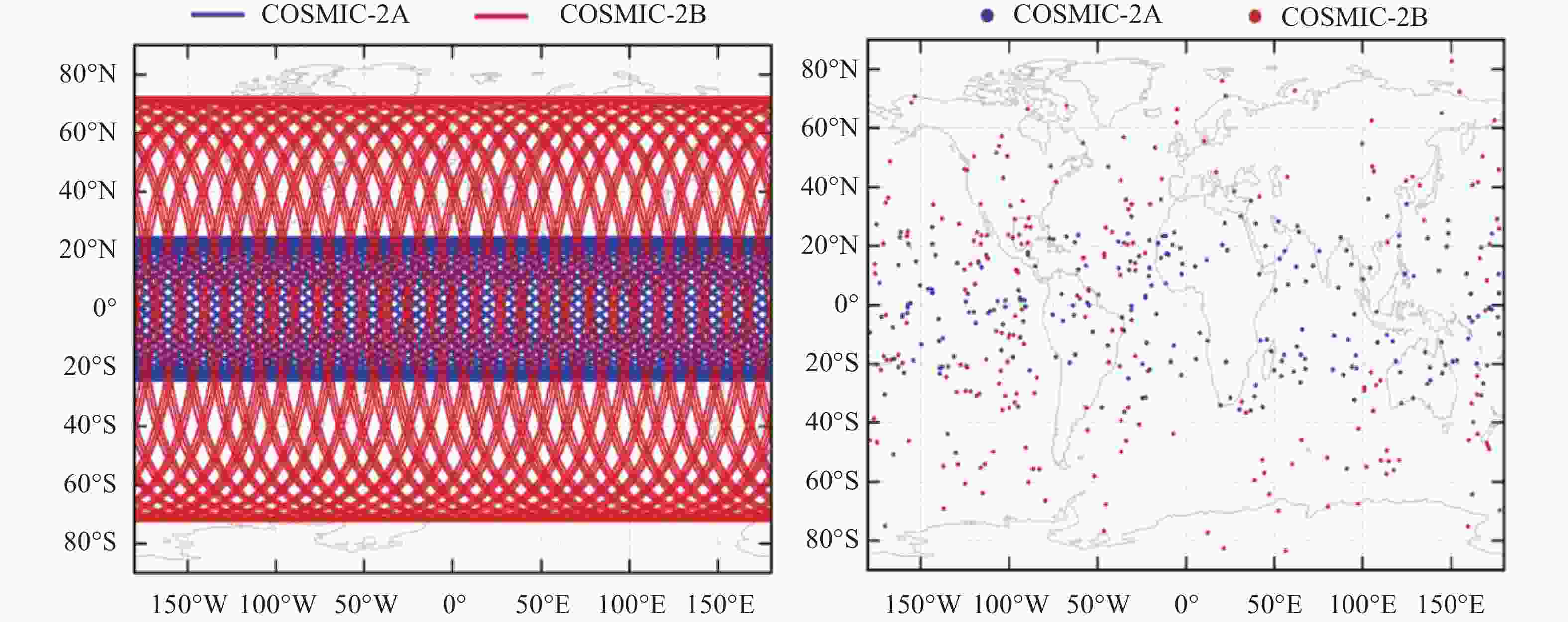
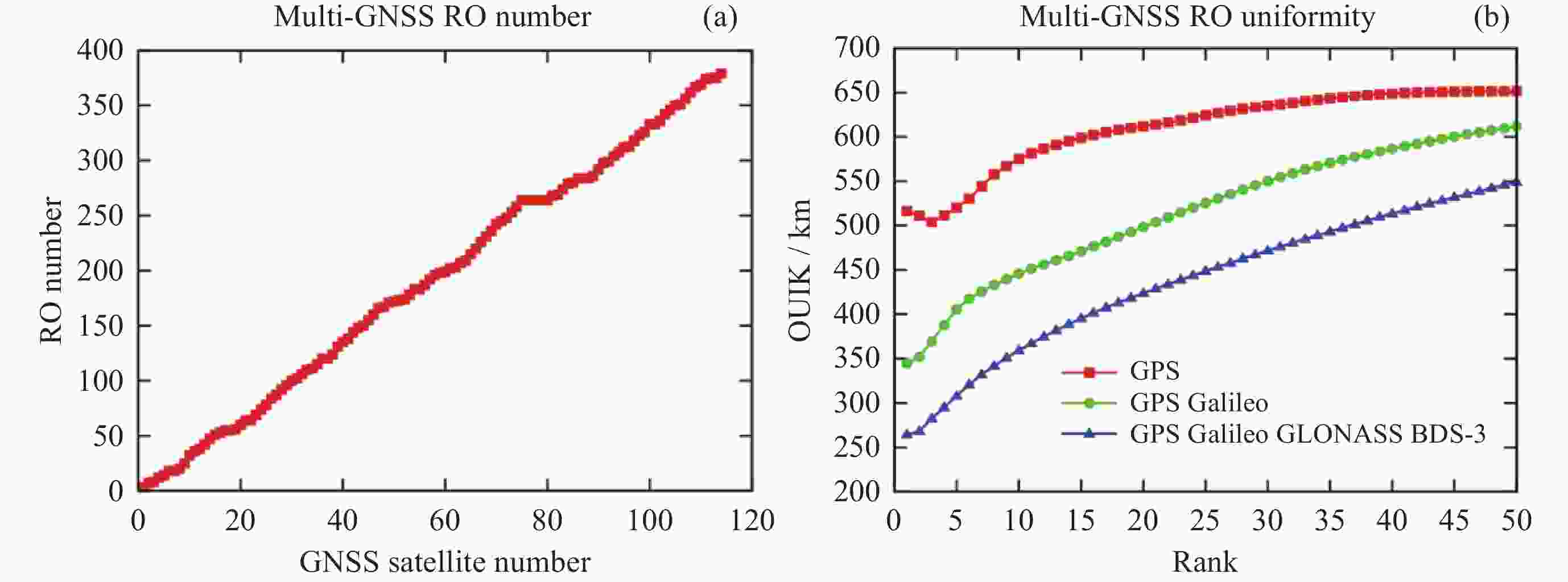
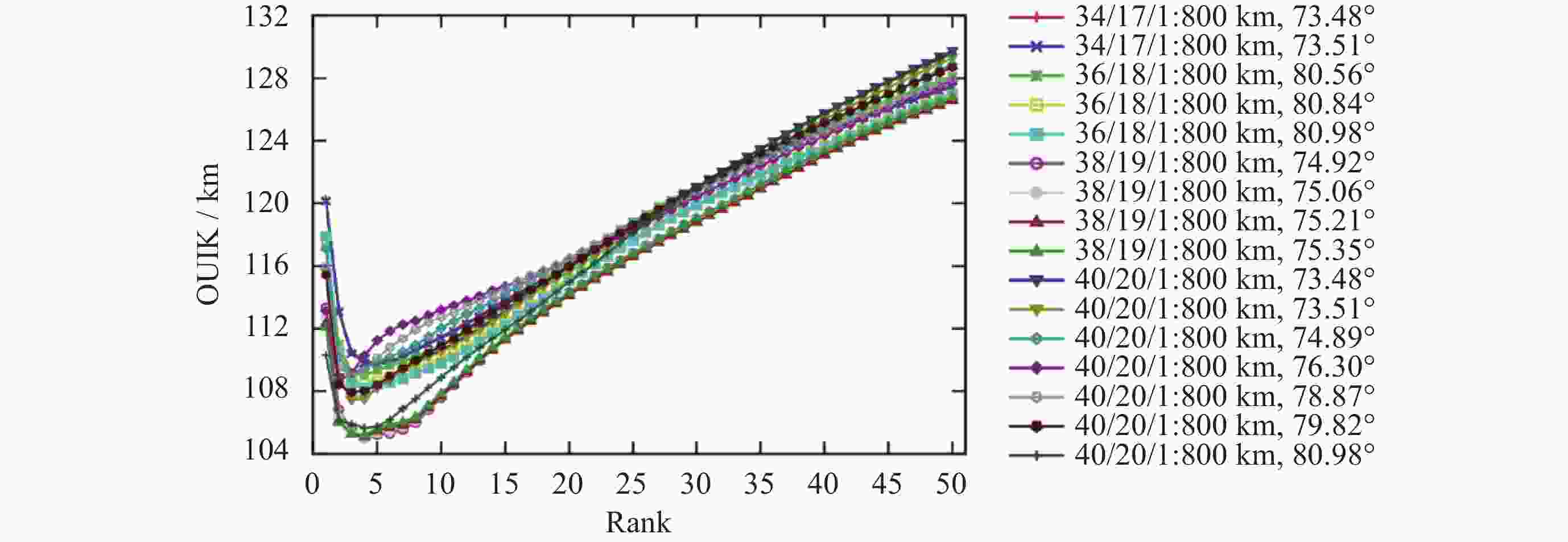
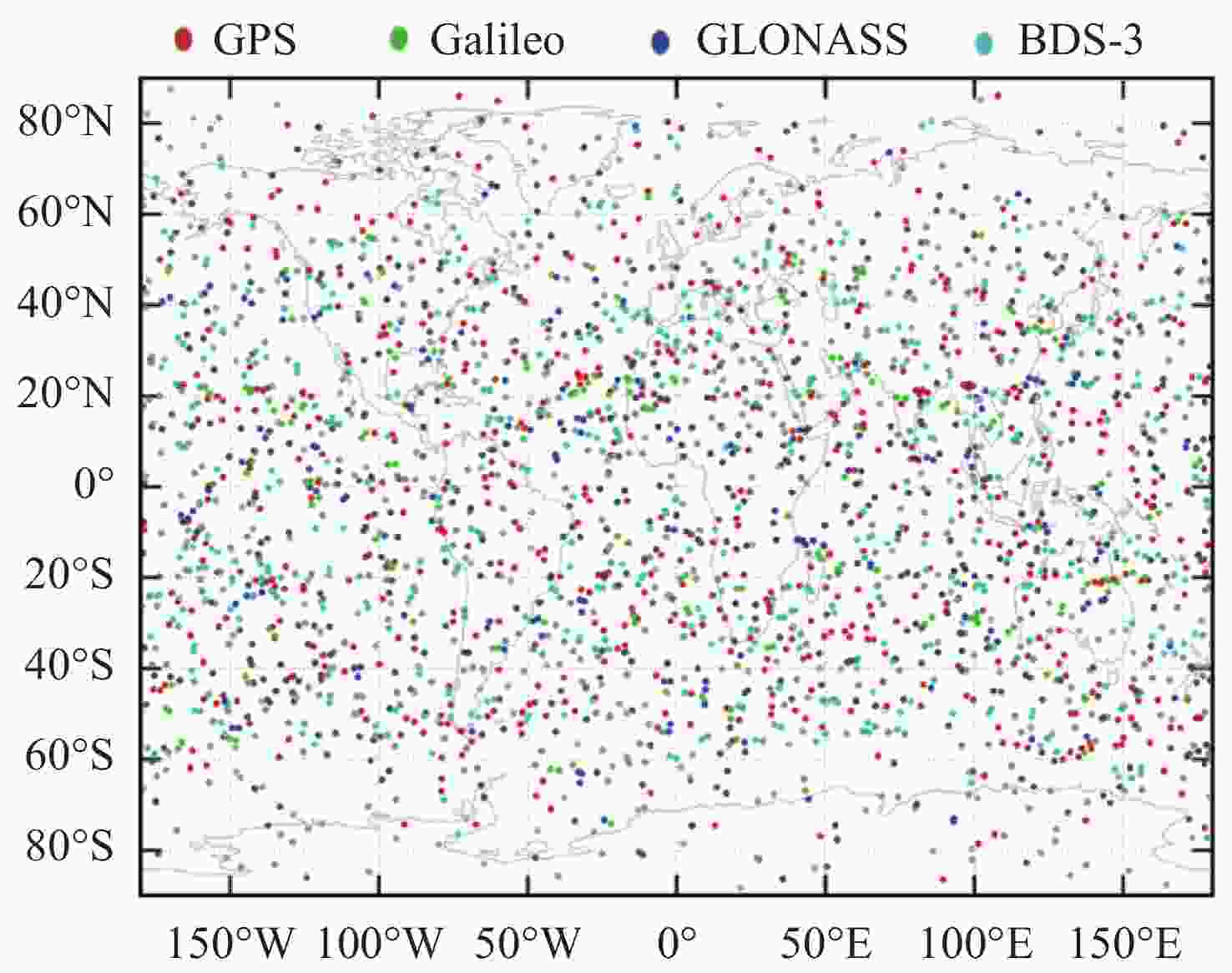
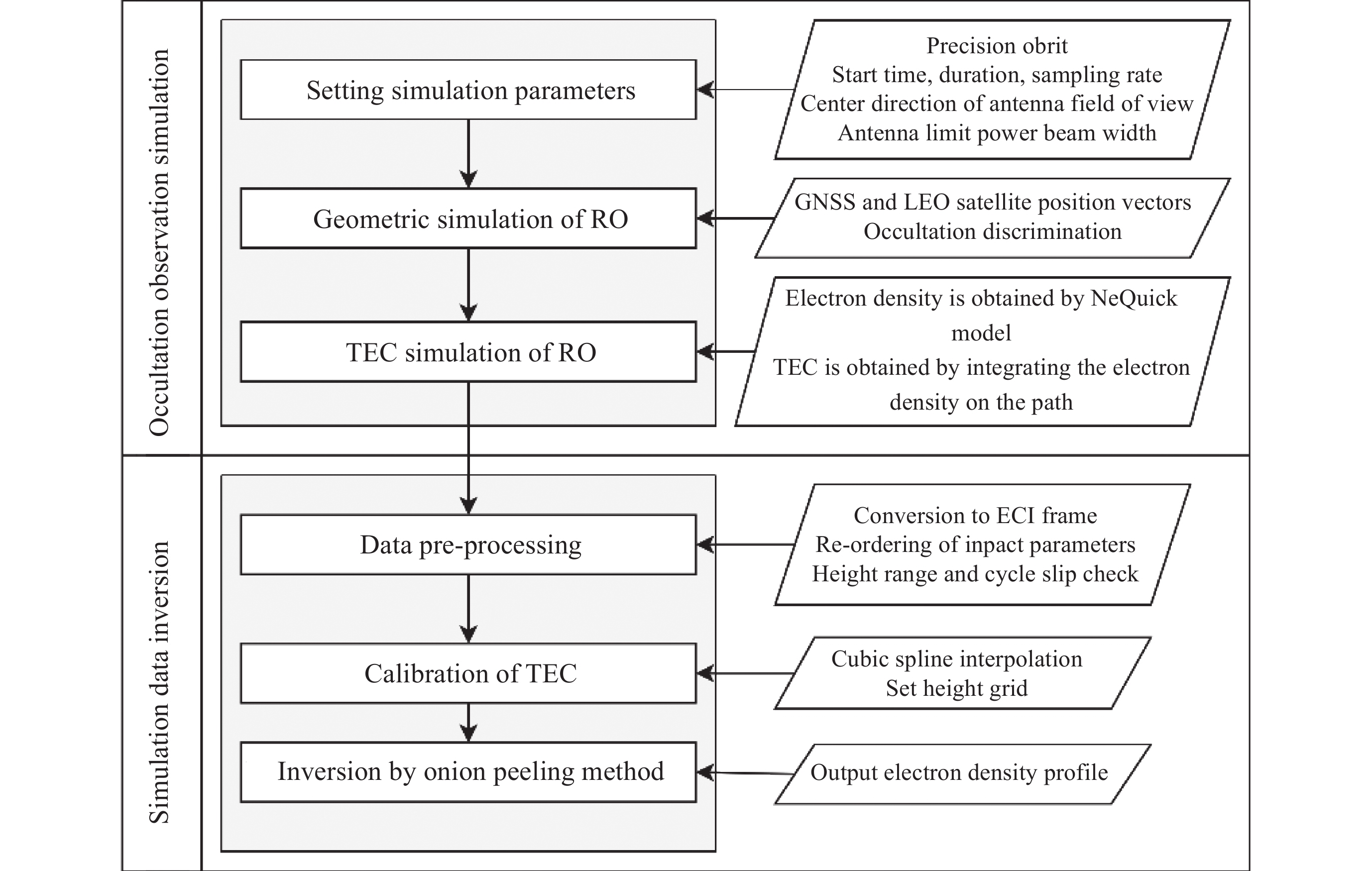
摘要: 基于卫星导航系统精密星历和NeQuick模型模拟COSMIC星座电离层掩星事件的几何过程和物理数据, 并采用改正TEC法和“洋葱分层”算法反演电离层三维电子密度. 模拟反演得到的电子密度廓线与模型变化趋势一致, 偏差较小. 电离层hmF2, NmF2的绝对误差分别为4.2 km和0.26×104 cm–3, 相对误差分别为1.66%和4.95%, 反演值与模型值的线性回归决定系数R2分别为0.956和0.950, 表明掩星反演模拟完整可靠、正确有效. 在几何模拟正确的基础上, 分析了COSMIC-2完全组网时的掩星观测性能及多系统GNSS对掩星数量及空间分布特征的影响. 为提高未来掩星事件的时效性及时空分布的均匀性, 提出了一种掩星分布均匀性指数, 并且通过非支配排序遗传算法实现掩星星座卫星总数、轨道面数、轨道倾角的最优确定.Abstract: Using precise GNSS ephemeris and the NeQuick model, we simulated the geometric process and physical data of COSMIC ionospheric Radio Occultation (RO), and inverted the three-dimensional electron density of the ionosphere using the calibrated TEC method and “onion layering” algorithm. The obtained electron density profile was found to be consistent with the model trend with small deviations. The absolute errors of ionospheric hmF2 and NmF2 were 4.2 km and 0.26×104 cm–3, respectively, with relative errors of 1.66% and 4.95%, respectively. The linear regression coefficient of determination R2 for the ionospheric hmF2 and NmF2 inversion results and model values were 0.956 and 0.950, respectively, indicating the completeness, correctness, and effectiveness of the occultation inversion simulation. Building on the correct geometric simulation, we analyzed the occultation observation performance of COSMIC-2 and the influence of multi-GNSS on the number and spatial distribution characteristics of occultation. It is found that the number of navigation satellites participating in the occultation observation is proportional to the occultation event, and the uniformity of the occultation distribution significantly improves with the increase in navigation satellites. To enhance the timeliness of future occultation events and the uniformity of their spatial and temporal distribution, the uniformity index of occultation distribution is proposed and improved the COSMIC-2B using a fast non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm to determine the optimal total number of occultation satellites, number of orbital planes, and orbital inclination. The optimal configuration of 38/19/1∶800 km, 75.21° was found, achieving the design goals of N≤40, F=1, h=800 km, 72°≤i<90°. With 106 satellites including GPS, Galileo, GLONASS, and BDS-3 in one hour, this configuration can observe 2675 occultation events with uniform spatial and temporal distribution.
-
Key words:
- COSMIC /
- Ionosphere /
- Occultation inversion /
- Simulation /
- Electron density
-
表 1 电离层峰值参数反演结果与NeQuick模型的对比
Table 1. Comparison of ionospheric peak parameter inversion results with NeQuick model
hmF2 NmF2 绝对误差均值 4.214 km 0.258×104 cm–3 绝对误差标准差 7.501 km 3.805×104 cm–3 相对误差均值 1.658% 4.950% 相对误差标准差 2.408% 17.968% 表 2 COSMIC-2星座设计
Table 2. COSMIC-2 constellation design
COSMIC-2 A COSMIC-2 B 卫星总数 6 6 (+1备用) 轨道面数 6 6 相邻轨道相位因子 1 1 轨道倾角 24° 72° 轨道高度 550 km 800 km 视场范围 沿轨方向45°半角锥 天底方向65°半角锥 -
[1] HAJJ G A, ROMANS L J. Ionospheric electron density profiles obtained with the Global Positioning System: Results from the GPS/MET experiment[J]. Radio Science, 1998, 33(1): 175-190 doi: 10.1029/97RS03183 [2] 黄栋, 黄城, 李金岭, 等. GPS无线电掩星技术监测地球大气[J]. 地球科学进展, 1997, 12(3): 217-223HUANG Dong, HUANG Cheng, LI Jinling, et al. Monitoring the Earth’s atmosphere with GPS radio occultation[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 1997, 12(3): 217-223 [3] 曾桢, 胡雄, 张训械, 等. 电离层GPS掩星观测反演技术[J]. 地球物理学报, 2004, 47(4): 578-583 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2004.04.005ZENG Zhen, HU Xiong, ZHANG Xunjie, et al. Inversion of ionospheric GPS occultation data[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2004, 47(4): 578-583 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2004.04.005 [4] 周义炎, 吴云, 乔学军, 等. GPS掩星技术和电离层反演[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2005, 25(2): 29-35 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5942.2005.02.005ZHOU Yiyan, WU Yun, QIAO Xuejun, et al. GPS occultation technique and ionospheric inversion[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2005, 25(2): 29-35 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5942.2005.02.005 [5] 吴小成. 电离层无线电掩星技术研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院研究生院, 2008WU Xiaocheng. Radio Occultation Technique for Ionosphere Detection[D]. Beijing: Graduate School of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2008 [6] 刘经南, 赵莹, 张小红. GNSS无线电掩星电离层反演技术现状与展望[J]. 武汉大学学报·信息科学版, 2010, 35(6): 631-635LIU Jingnan, ZHAO Ying, ZHANG Xiaohong. Current situation and expectation of inversion of ionospheric GNSS occultation[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2010, 35(6): 631-635 [7] KRANKOWSKI A, ZAKHARENKOVA I, KRYPIAK-GREGORCZYK A, et al. Ionospheric electron density observed by FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC over the European region and validated by ionosonde data[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2011, 85(12): 949-964 doi: 10.1007/s00190-011-0481-z [8] YUE X A, SCHREINER W S, KUO Y H, et al. Global 3-D ionospheric electron density reanalysis based on multisource data assimilation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Space Physics, 2012, 117(A9): A09325 [9] LIN C H, LIU J Y, CHENG C Z, et al. Three‐dimensional ionospheric electron density structure of the Weddell Sea Anomaly[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Space Physics, 2009, 114(A2): A02312 [10] 王也英, 符养, 杜晓勇, 等. 全球GNSS掩星计划进展[J]. 气象科技, 2009, 37(1): 74-78 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6345.2009.01.014WANG Yeying, FU Yang, DU Xiaoyong, et al. Advances in global GNSS occultation projects[J]. Meteorological Science and Technology, 2009, 37(1): 74-78 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6345.2009.01.014 [11] 吴小成, 胡雄, 宫晓艳, 等. 三维模式约束的电离层掩星反演方法[J]. 地球物理学报, 2008, 51(3): 618-625 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2008.03.002WU Xiaocheng, HU Xiong, GONG Xiaoyan, et al. Three dimensional model constrained inversion method for ionospheric occultation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2008, 51(3): 618-625 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2008.03.002 [12] WU X C, HU X, GONG X Y, et al. Analysis of inversion errors of ionospheric radio occultation[J]. GPS Solutions, 2009, 13(3): 231-239 doi: 10.1007/s10291-008-0116-x [13] YUE X A, SCHREINER W S, LEI J H, et al. Error analysis of Abel retrieved electron density profiles from radio occultation measurements[J]. Annales Geophysicae, 2010, 28(1): 217-222 doi: 10.5194/angeo-28-217-2010 [14] YUE X A, SCHREINER W S, ROCKEN C, et al. Evaluation of the orbit altitude electron density estimation and its effect on the Abel inversion from radio occultation measurements[J]. Radio science, 2011, 46(1): RS1013 [15] 孙方方. COSMIC掩星电子密度廓线反演及比较验证[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2018SUN Fangfang. The Retrieval and Comparative Validiation of COSMIC Radio Occultation Electron Density Profiles[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2018 [16] 赵世军, 孙学金, 朱有成, 等. LEO卫星轨道参数对GPS掩星数量和分布的影响[J]. 解放军理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2002, 3(2): 85-89ZHAO Shijun, SUN Xuejin, ZHU Youcheng, et al. Effect of LEO satellite’s orbit parameter on GPS occultation event’s number and distribution[J]. Journal of PLA University of Science and Technology, 2002, 3(2): 85-89 [17] 徐晓华, 李征航, 罗佳. 单颗LEO卫星轨道参数对GPS掩星事件分布和数量影响的模拟研究[J]. 武汉大学学报·信息科学版, 2005, 30(7): 609-612XU Xiaohua, LI Zhenghang, LUO Jia. Simulation of the impacts of single LEO satellite orbit parameters on the distribution and number of occultation events[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2005, 30(7): 609-612 [18] 徐晓华, 李征航, 罗佳. LEO星座参数对GPS掩星数量和时空分布影响的模拟研究[J]. 测绘学报, 2005, 34(4): 305-311 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1595.2005.04.005XU Xiaohua, LI Zhenghang, LUO Jia. Simulation research on the impact of LEO constellation’s parameters on the number and space-time distribution of GPS occultation events[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2005, 34(4): 305-311 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1595.2005.04.005 [19] 王先毅, 孙越强, 白伟华, 等. 北斗掩星事件数量与分布的模拟研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2013, 56(8): 2522-2530 doi: 10.6038/cjg20130803WANG Xianyi, SUN Yueqiang, BAI Weihua, et al. Simulation of number and distribution of Compass occultation events[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2013, 56(8): 2522-2530 doi: 10.6038/cjg20130803 [20] SCHREINER W S, SOKOLOVSKIY S V, ROCKEN C, et al. Analysis and validation of GPS/MET radio occultation data in the ionosphere[J]. Radio Science, 1999, 34(4): 949-966 doi: 10.1029/1999RS900034 [21] LEI J H, SYNDERGAARD S, BURNS A G, et al. Comparison of COSMIC ionospheric measurements with ground‐based observations and model predictions: preliminary results[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Space Physics, 2007, 112(A7): A07308 [22] 梁斌, 李成, 魏世隆. GNSS掩星大气探测星座设计与构型控制方法研究[M]. 北京: 中国宇航出版社, 2018: 5-8LIANG Bin, LI Cheng, WEI Shilong. Research on GNSS occultation atmospheric detection constellation design and configuration control method[M]. Beijing: China Astronautic Publishing House, 2018: 5-8 [23] POLI P, HEALY S B, RABIER F, et al. Preliminary assessment of the scalability of GPS radio occultations impact in numerical weather prediction[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2008, 35(23): L23811 [24] 梁斌, 王珏瑶, 李成, 等. 多GNSS掩星大气探测卫星星座设计[J]. 宇航学报, 2016, 37(3): 334-340LIANG Bin, WANG Jueyao, LI Cheng, et al. Design of multi-GNSS occultation sounding satellite constellation[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2016, 37(3): 334-340 [25] WANG J Y, LIANG B. 4-GNSS radio occultation satellite constellation design based on Dual-gate uniformity evaluation index[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part G: Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2017, 231 (1): 3-16 -
-





 许波波:男, 1999年10月出生于湖南省衡阳市. 现为河海大学测绘科学与技术系硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为GNSS电离层监测. E-mail:
许波波:男, 1999年10月出生于湖南省衡阳市. 现为河海大学测绘科学与技术系硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为GNSS电离层监测. E-mail: 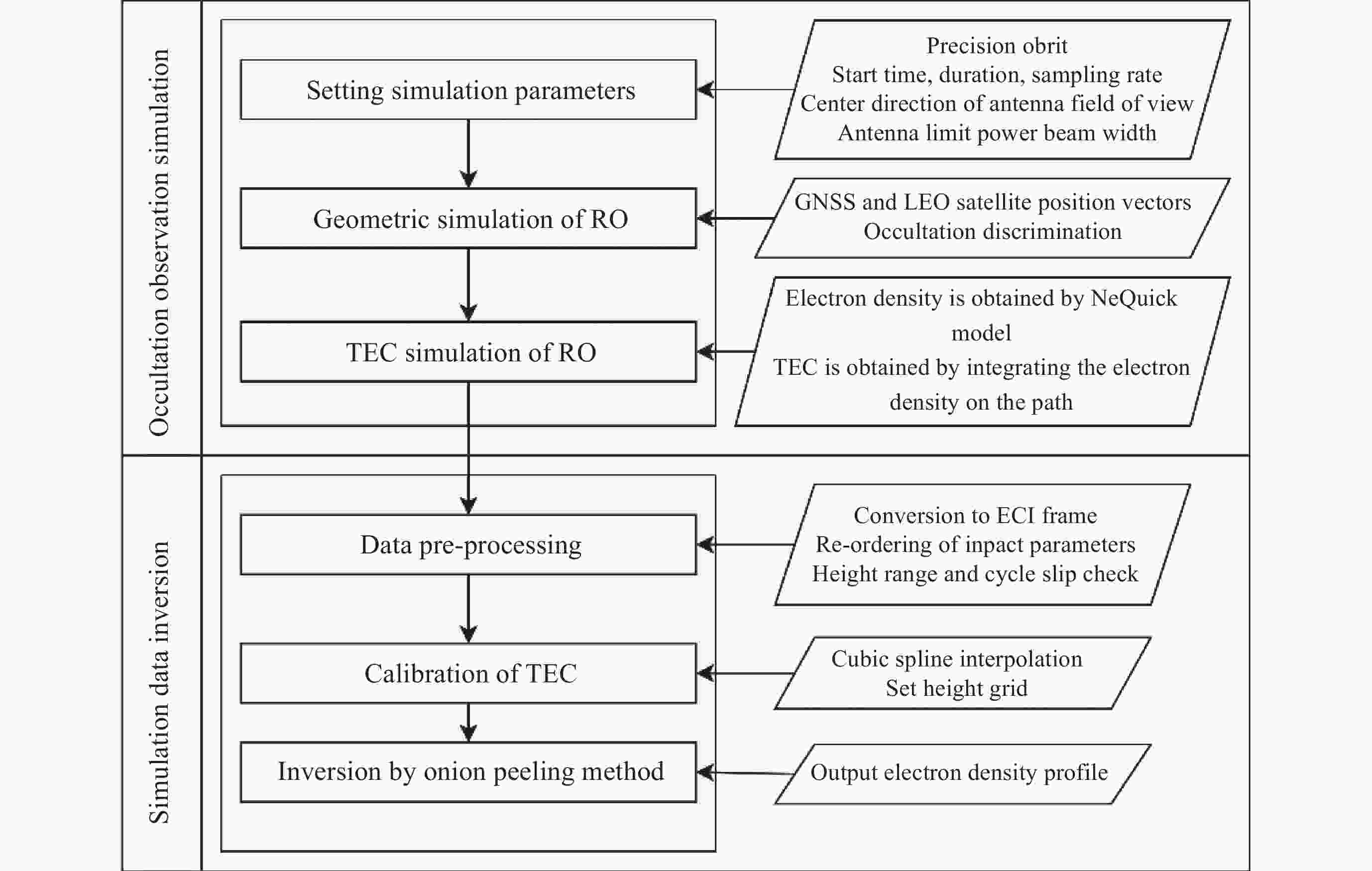
 下载:
下载: