Method of Spacecraft Maneuver Detection Based on Two-line Elements
-
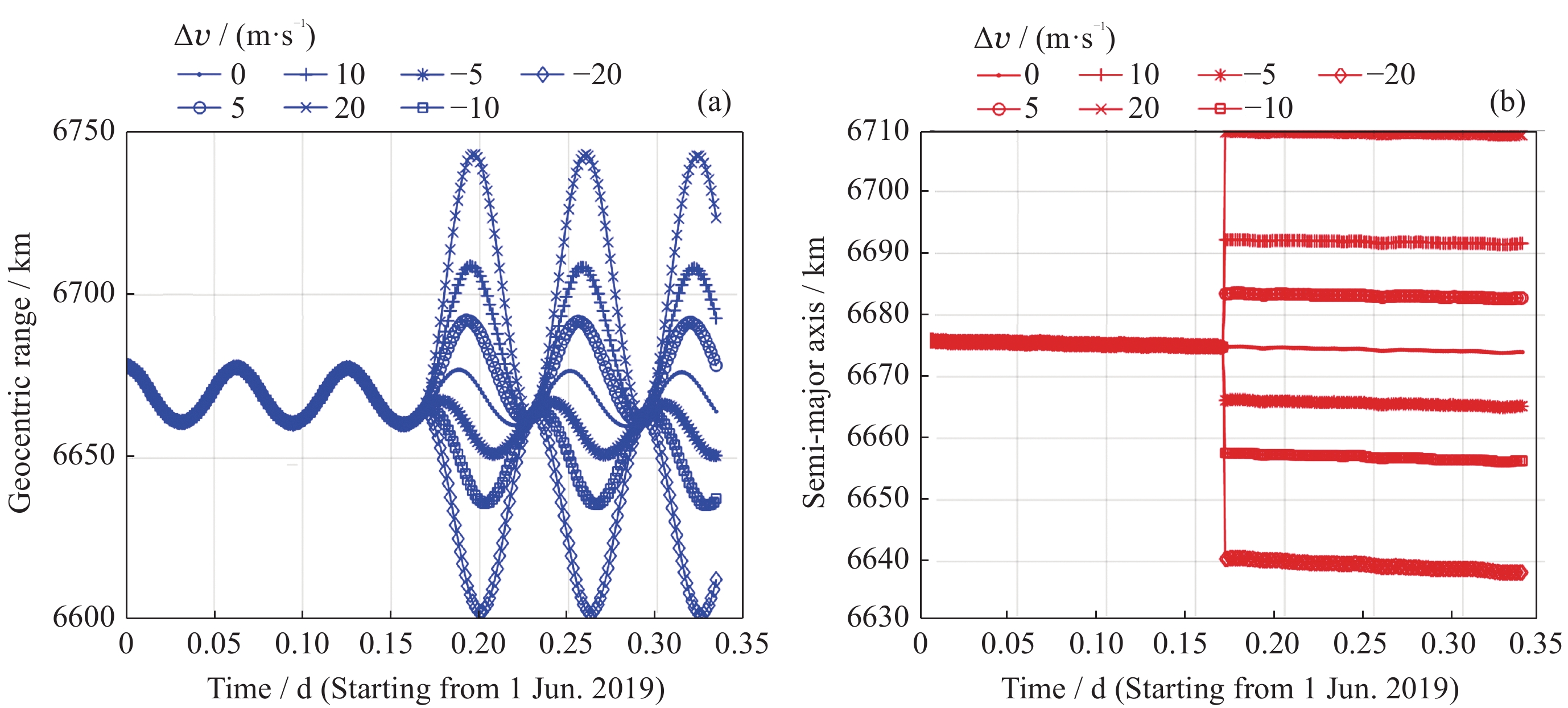
摘要: 由于不同功能的航天器承担的任务不尽相同、轨道亦不相同等原因, 航天器不时需要变轨机动以确保完成任务. 对于非合作航天器, 其可能的变轨信息预先未知且难以预测, 故需要准确快速判断航天器的变轨事件, 以及时调整轨道探测策略. 由于美国公布的双行根数具有来源稳定、更新频率快和容易获取等特点, 本文结合航天器轨道动力学及变轨控制的特点, 提出了基于TLE双行根数的航天器变轨机动检测方法, 通过检测半长轴的变化量和相对距离最小值实现了在轨航天器轨道面内机动的检测. 以METOP-A1和IRNSS 1G两个航天器在2019年6-9月的TLE根数为例, 说明使用该方法开展机动检测的操作流程和步骤. 同时大量仿真计算结果表明, 该方法能够有效解决航天器在轨运行过程中面内机动时间和半长轴改变量的检测以及多次变轨识别的问题, 检测精度与TLE根数自身精度及机动量大小相关.Abstract: Due to the missions and orbit types of different spacecraft are quite different, orbit maneuvers must be conducted by spacecraft irregularly to ensure that they could complete their tasks successfully. For the non-cooperative spacecraft, their possible orbit maneuvers are usually unknown and very difficult to predict in advance, so it is necessary to identify possible orbit maneuver events in order to adjust spacecraft detection strategy in time. Two-Line Element (TLE for short) published by the USA, has the advantages of stable source, fast update frequency and easy acquisition, so it is proper to carry out the research on the method of spacecraft maneuver detection based on TLE. According to laws of operation and orbit control of spacecraft, this paper proposed a method based on TLE to detect maneuver events, which happened in the orbit plane of spacecraft, by checking and comparing the changes in semi-major axis and minimum ranges between two TLEs. The TLEs, from June, 2019 to September, 2019, of two spacecraft, METOP-A1 and IRNSS 1G, were taken for example to demonstrate the operating procedures and steps of maneuver detection using this method. Then, a large number of TLEs were generated by simulation, and on the basis, some calculations of maneuver detection were conducted correspondingly. From the statistical result, it could be found that the deviation of maneuver detection results was influenced by the own precision of TLEs and the amplitude of changes in semi-major axis. This method could effectively solve the problem of detecting the time and changes in semi-major axis of in-plane maneuvers, and identifying multiple maneuvers, so its effectiveness and usability was fully proved.
-
Key words:
- Two-line elements /
- Spacecraft /
- Orbit maneuver /
- Maneuver detection
-
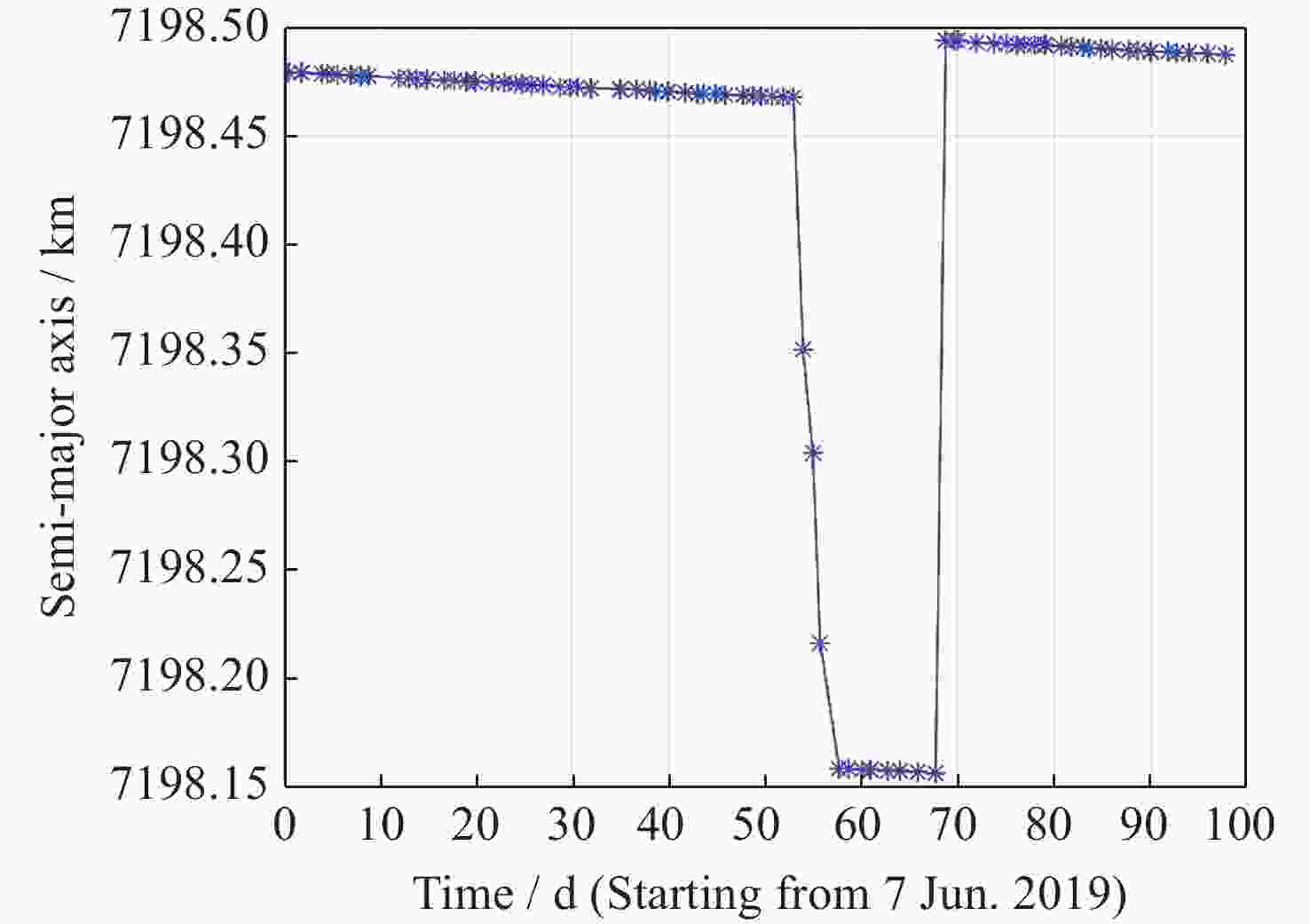
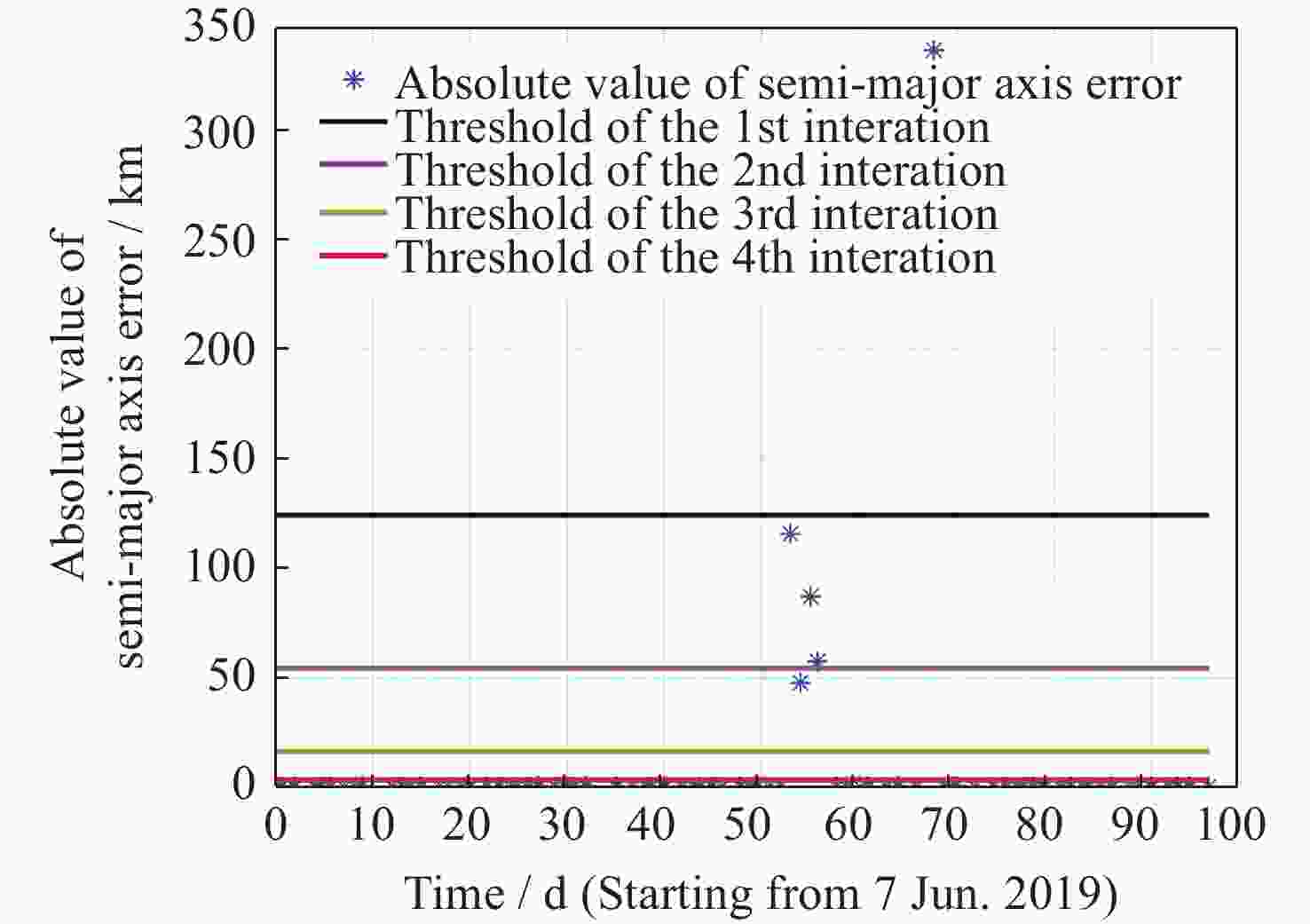
表 1 目标29499变轨筛选门限迭代过程结果
Table 1. Iteration process of maneuver detection threshold of target 29499
Iterations $ \Delta \bar a $/m $ {\sigma _{\bar a}} $/m $ {\delta _a} $/m 1 7.7 39.8 127.1 2 3.9 17.3 55.7 3 1.0 5.2 16.7 4 0.47 1.1 3.6 表 2 目标29499半长轴跳变筛选结果
Table 2. Detection result of change in semi-major axis of target 29499
No. TLE Maneuver time
(BJT)Change in semi-major
axis/mMinimum range/m Confirmed 1 TLE1~TLE2 31 Jul. 2019 04:16:15.2 –57.0 49.7 No 2 TLE2~TLE3 31 Jul. 2019 17:39:47.9 –58.3 102.8 No 3 TLE3~TLE4 1 Aug. 2019 06:50:50.0 –47.9 62.1 No 4 TLE4~TLE5 2 Aug. 2019 07:36:47.7 –144.6 227.3 No 5 TLE5~TLE6 14 Aug. 2019 20:16:43.2 336.5 55.9 Yes 表 3 目标29499相对距离最小值判断结果
Table 3. Judging result of minimum range of target 29499
No. TLE Maneuver time
(BJT)Change in semi-major
axis/mMinimum range/m Confirmed 1 TLE1~TLE3 1 Aug. 2019 10:58:19.3 115.3 142.2 No 2 TLE1~TLE4 31 Jul. 2019 16:39:47.7 163.2 243.2 No 3 TLE1~TLE5 1 Aug. 2019 11:03:23.9 307.8 46.8 Yes 4 TLE2~TLE4 1 Aug. 2019 03:26:20.7 106.2 170.3 No 5 TLE2~TLE5 1 Aug. 2019 18:00:20.0 250.9 382.3 No 6 TLE3~TLE5 2 Aug. 2019 01:19:04.5 192.6 131.1 No 表 4 目标29499变轨分析结果
Table 4. Maneuver detection result of target 29499
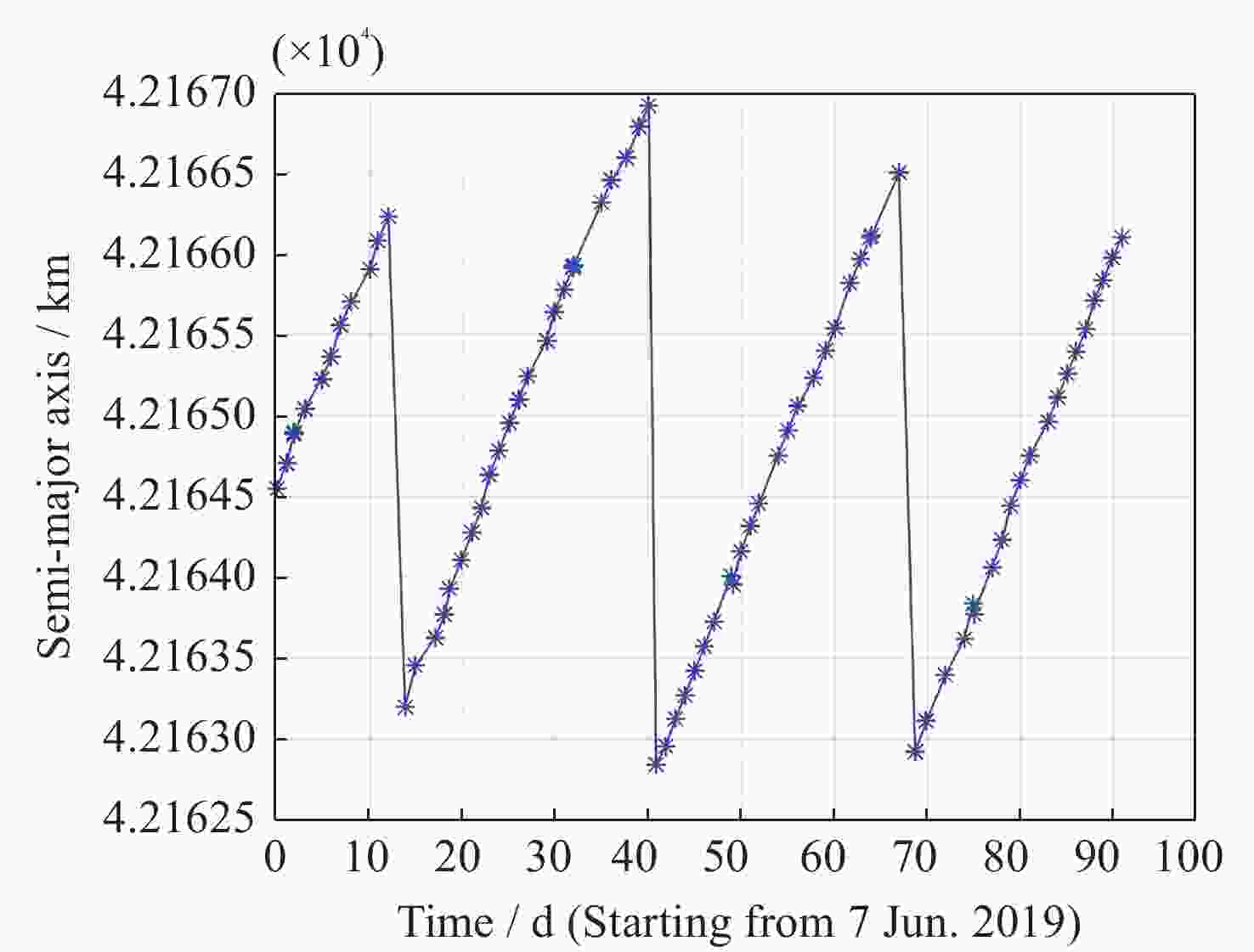
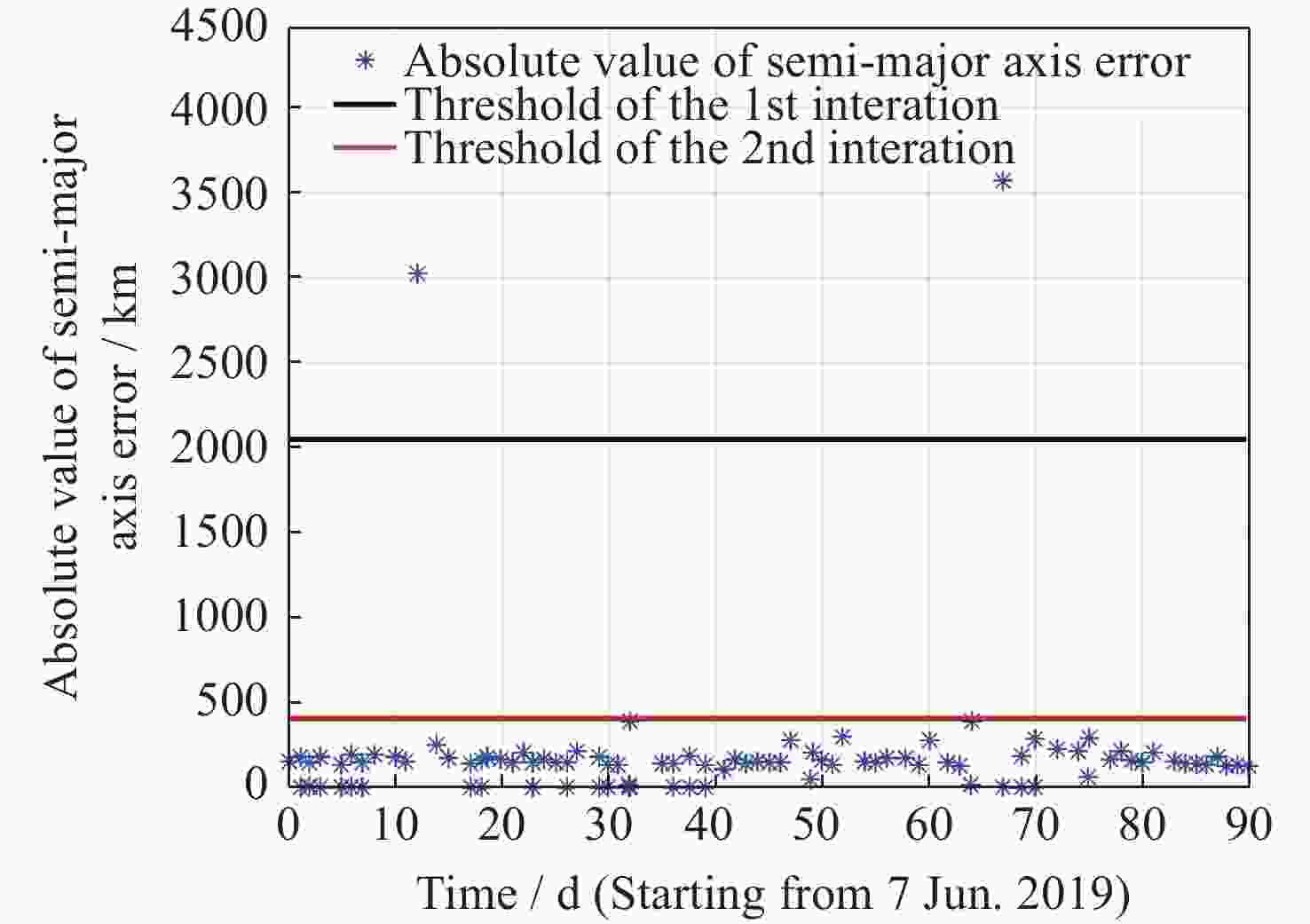
No. Maneuver time (BJT) Change in semi-major axis/m 1 1 Aug. 2019 11:03:23.9 307.8 4 14 Aug. 2019 20:16:43.2 336.5 表 5 目标41469变轨筛选门限迭代过程
Table 5. Iteration process of maneuver detection threshold of target 41469
Iterations $ \Delta \bar a $/m $ {\sigma _{\bar a}} $/m $ {\delta _a} $/m 1 304.7 676.6 2334.5 2 174.7 70.4 385.8 表 6 目标41469变轨分析结果
Table 6. Maneuver detection result of target 41469
No. TLE Maneuver time
(BJT)Change in semi-major
axis/mMinimum range/m Confirmed 1 TLE1~TLE2 2019-06-21 14:50:25.5 –3278.1 642.3 Yes 2 TLE2~TLE3 2019-07-17 15:09:50.1 –4248.1 621.8 Yes 3 TLE3~TLE4 2019-08-14 23:44:26.4 –3810.2 595.0 Yes 表 7 仿真航天器机动变轨检测变差(低轨)
Table 7. Deviation of maneuver detection result of simulated spacecraft (LEO)
Altitude of simulated spacecraft <500 km 500~1000 km 1000~2000 km Deviation of maneuver detection results Error of change in semi-major axis/(%) Error of maneuver time/h Error of change
in semi-major axis/(%)Error of maneuver time/h Error of change
in semi-major axis/(%)Error of maneuver time/h Theoretical maneuver <20 m 68.3 5.5 54.1 3.2 50.3 2.7 20~100 m 38.9 3.7 30.6 1.0 28.4 0.8 >100 m 14.2 1.2 12.5 0.5 8.7 0.3 表 8 仿真航天器机动变轨检测变差(高轨)
Table 8. Deviation of maneuver detection result of simulated spacecraft (HEO)
Altitude of simulated spacecraft 2000~10000 km >10000 km Deviation of maneuver
detection resultsError of change in
semi-major axis/(%)Error of maneuver time/h Error of change in
semi-major axis/(%)Error of maneuver time/h Theoretical maneuver <1000 m 10 0.8 8.8 0.8 1~10 km 1.8 0.2 2.5 0.5 >10 km 0.5 0.1 0.1 0.05 -
[1] 崔文, 张炜, 李海晶, 等. 一种基于TLE根数的在轨航天器变轨检测方法: 中国, CN202010153120.0[P]. 2020-03-04CUI Wen, ZHANG Wei, LI Haijing, et al. A method of satellite maneuver examination based on TLE: China, CN202010153120.0[P]. 2020-03-04 [2] 刘磊. 空间目标轨道机动探测研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2019LIU Lei. Research on Orbital Maneuver Detection of Space Objects[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2019 [3] 王扬洋, 林彬, 杨夏, 等. 空间临近目标行为辨识方法[J]. 中国空间科学技术, 2021, 41(6): 63-71WANG Yangyang, LIN Bin, YANG Xia, et al. Behavior identification of space adjacent targets[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2021, 41(6): 63-71 [4] SONG W D, WANG R L, WANG J. A simple and valid analysis method for orbit anomaly detection[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2012, 49(2): 386-391 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2011.10.007 [5] 张涛涛, 白显宗, 郝嘉, 等. 基于预报偏差的LEO航天器轨道异常检测[J]. 中国空间科学技术, 2012, 32(5): 40-46, 68 doi: 10.3780/j.issn.1000-758X.2012.05.007ZHANG Taotao, BAI Xianzong, HAO Jia, et al. LEO spacecraft orbit anomaly detection based on prediction dispersion[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2012, 32(5): 40-46, 68 doi: 10.3780/j.issn.1000-758X.2012.05.007 [6] 于大腾, 王华, 尤岳, 等. 不完备轨道信息下的LEO轨道面内机动检测方法[J]. 宇航学报, 2013, 34(3): 314-319YU Dateng, WANG Hua, YOU Yue, et al. A new in-plane maneuver detection method for incomplete orbit information of LEO spacecraft[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2013, 34(3): 314-319 [7] 徐明, 白雪, 彭娜, 等. 一种基于聚类分析的航天器相对轨道机动侦测方法和系统: 中国, 202210624323.2[P]. 2022-09-06XU Ming, BAI Xue, PENG Na, et al. A method and system for detecting relative orbital maneuver of spacecraft based on cluster analysis: China, 202210624323.2[P]. 2022-09-06 [8] 杨震, 李泽越, 罗亚中, 等. 一种航天器轨道机动逆向移动滑窗检测方法、装置和设备: 中国, 202210311812.2[P]. 2022-07-22YANG Zhen, LI Zeyue, LUO Yazhong, et al. A method, device and equipment for detecting reverse-moving sliding windows of spacecraft orbital maneuvers: China, 202210311812.2[P]. 2022-07-22 [9] 刘林, 汤靖师. 卫星轨道理论与应用[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2015LIU Lin, TANG Jingshi. Satellite Orbit Theory and Applications[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2015 [10] CLARK R, LEE R. Parallel processing for orbital maneuver detection[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2020, 66(2): 444-449 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2020.04.010 [11] 王荣兰, 刘卫, 刘四清, 等. 一种基于TLE数据的轨道异常分析方法[J]. 空间科学学报, 2014, 34(2): 208-213 doi: 10.11728/cjss2014.02.208WANG Ronglan, LIU Wei, LIU Siqing, et al. An orbital anomaly analysis method based on TLE data[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2014, 34(2): 208-213 doi: 10.11728/cjss2014.02.208 [12] VALLADO A D, CRAWFORD P. SGP4 orbit determination[C]//AIAA/AAS Astrodynamics Specialist Conference and Exhibit. Honolulu: American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2008: 1630-1658 [13] WEI D, ZHAO C Y. An accuracy analysis of the SGP4/SDP4 model[J]. Chinese Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2010, 34(1): 69-76 doi: 10.1016/j.chinastron.2009.12.009 [14] 韦栋, 赵长印. SGP4/SDP4模型精度分析[J]. 天文学报, 2009, 50(3): 332-339 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5245.2009.03.010WEI Dong, ZHAO Changyin. Analysis on the accuracy of the SGP4/SDP4 model[J]. Acta Astronomica Sinica, 2009, 50(3): 332-339 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5245.2009.03.010 [15] 程昊文. 航天器轨道理论在空间目标编目管理中的应用[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2012CHENG Haowen. The Application of Satellite Orbit Theory in Maintaining the Space Object Catalog[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2019 -
-




 崔文:男, 1986年10月出生于湖北省潜江市. 高级工程师, 主要研究方向为航天器轨道计算及机动检测分析. E-mail:
崔文:男, 1986年10月出生于湖北省潜江市. 高级工程师, 主要研究方向为航天器轨道计算及机动检测分析. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: