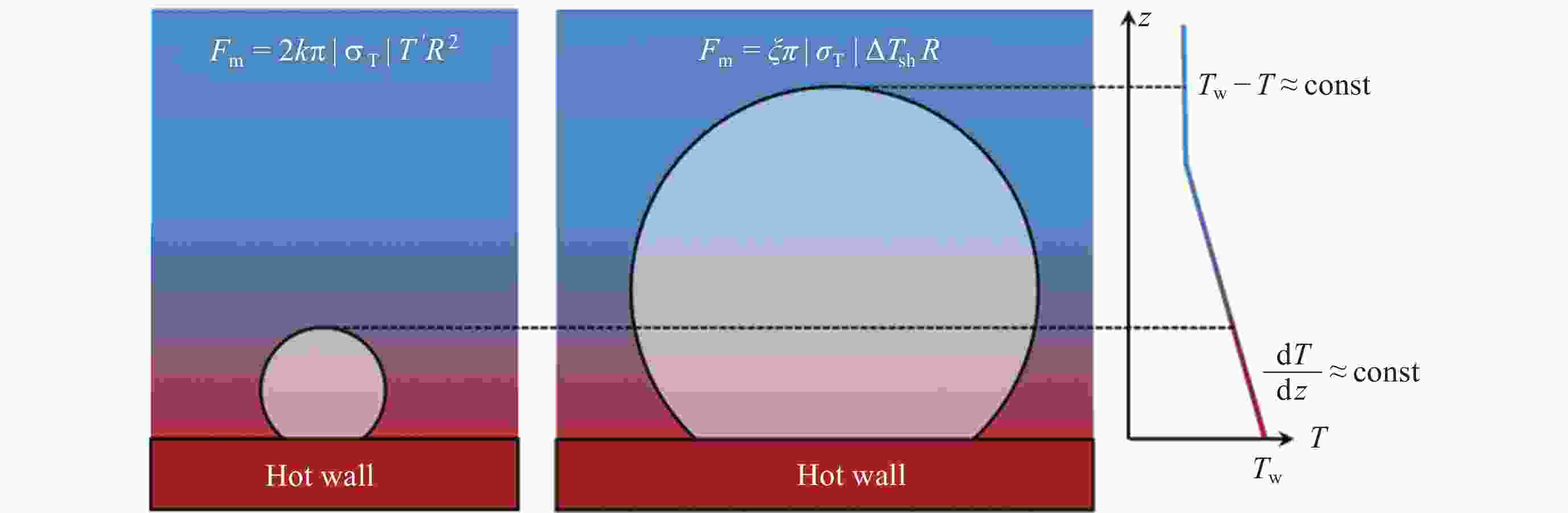
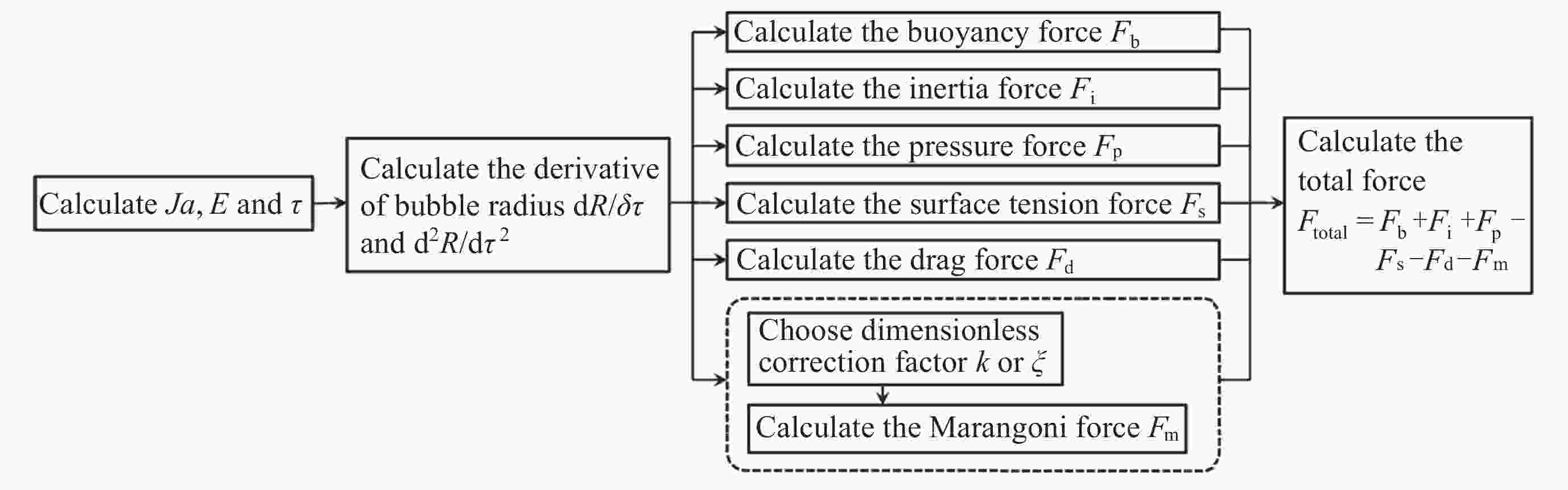
微重力下火箭推进系统液氧贮箱内气泡脱离半径研究
doi: 10.11728/cjss2024.01.2023-0003 cstr: 32142.14.cjss2024.01.2023-0003
On Bubble Departure Radius in Liquid Oxygen Tank of Rocket Propulsion System under Microgravity
-
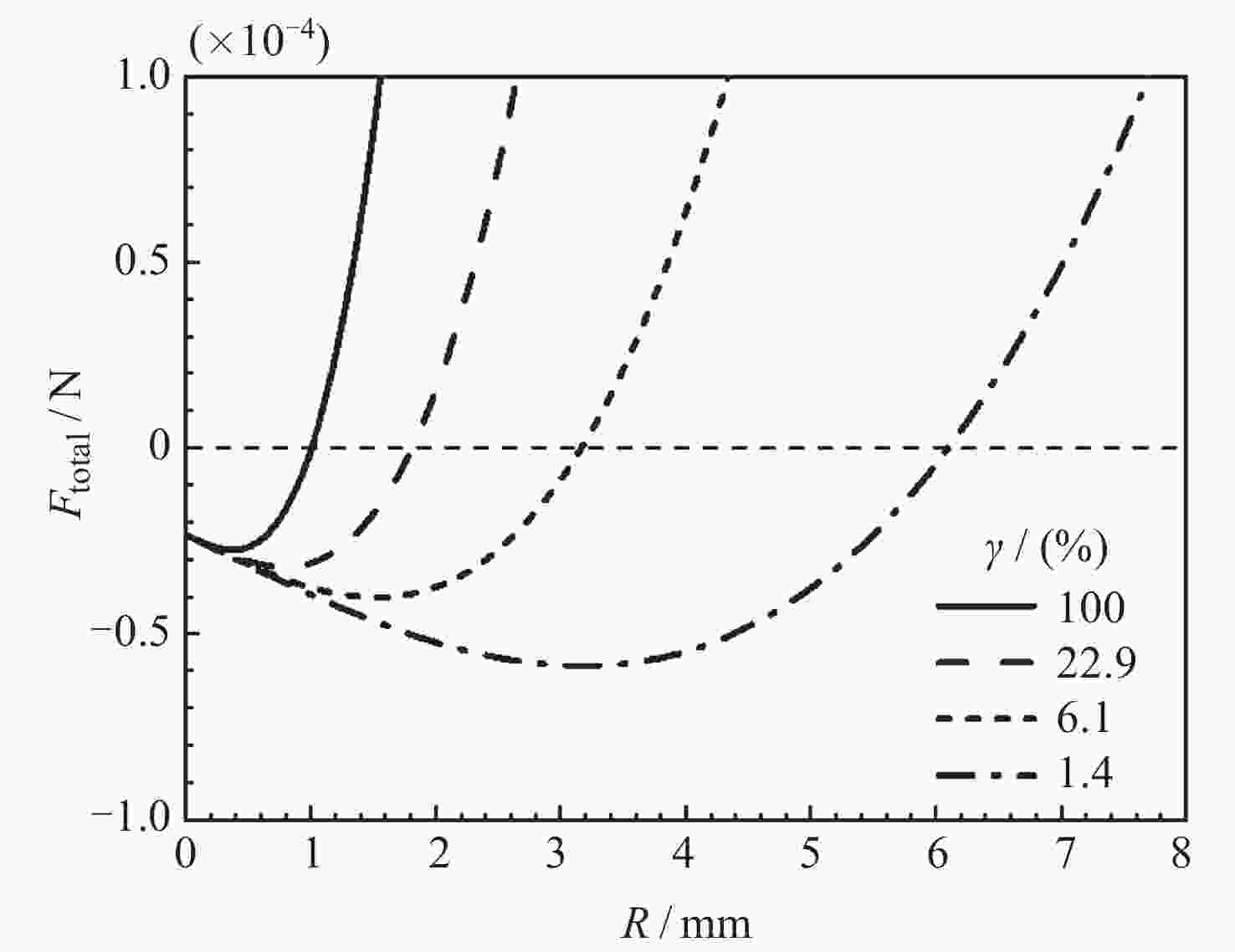
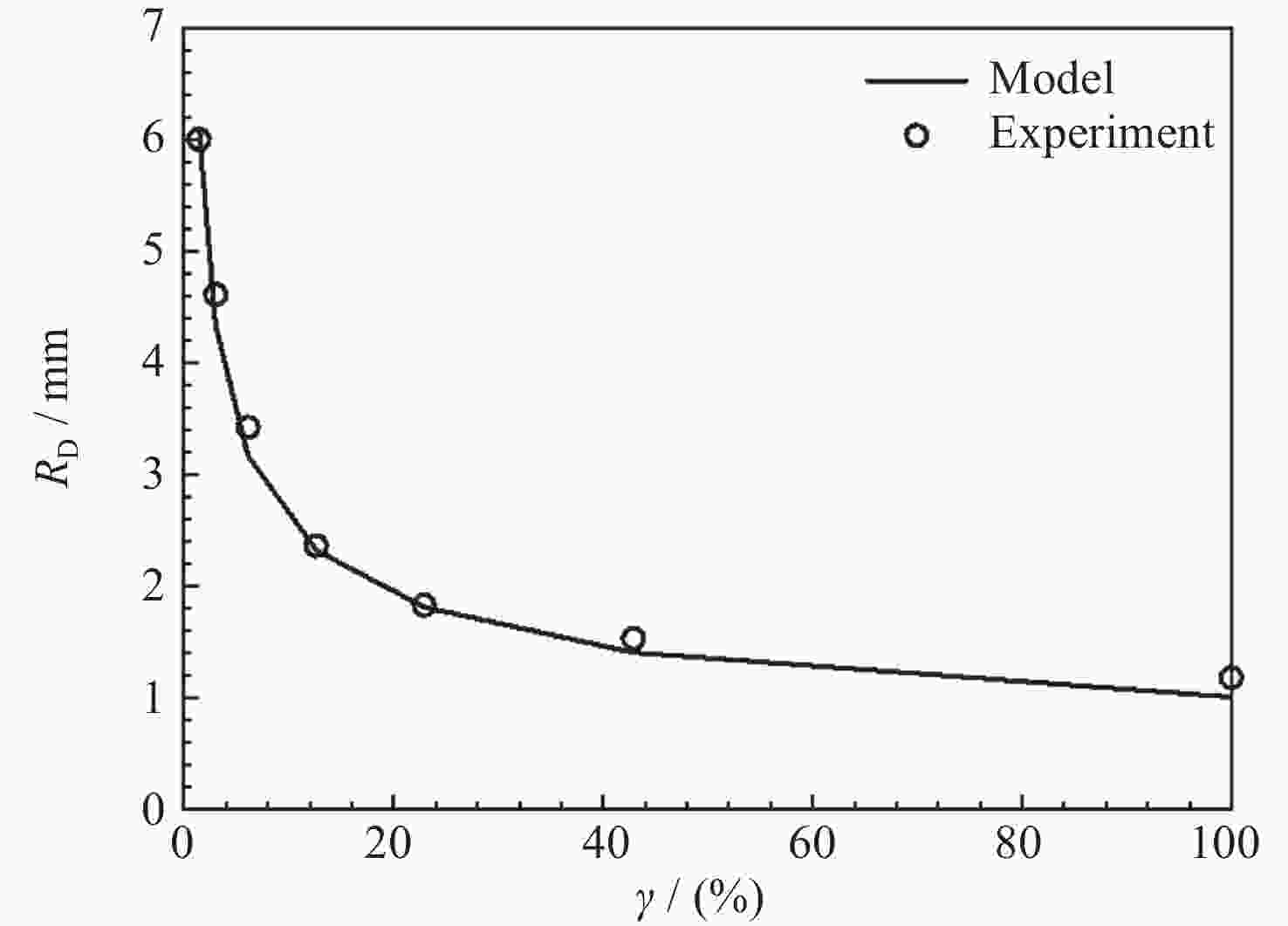
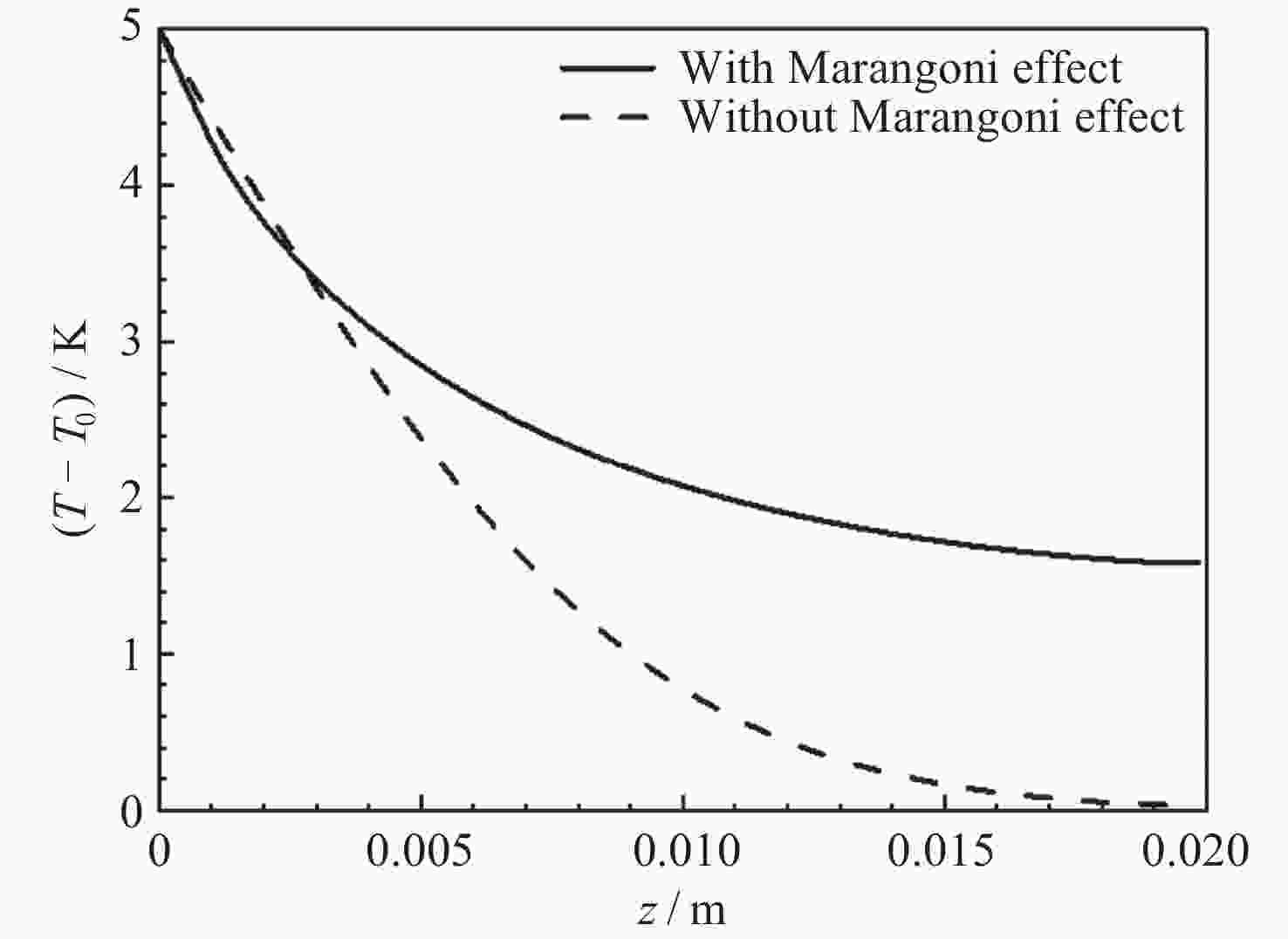
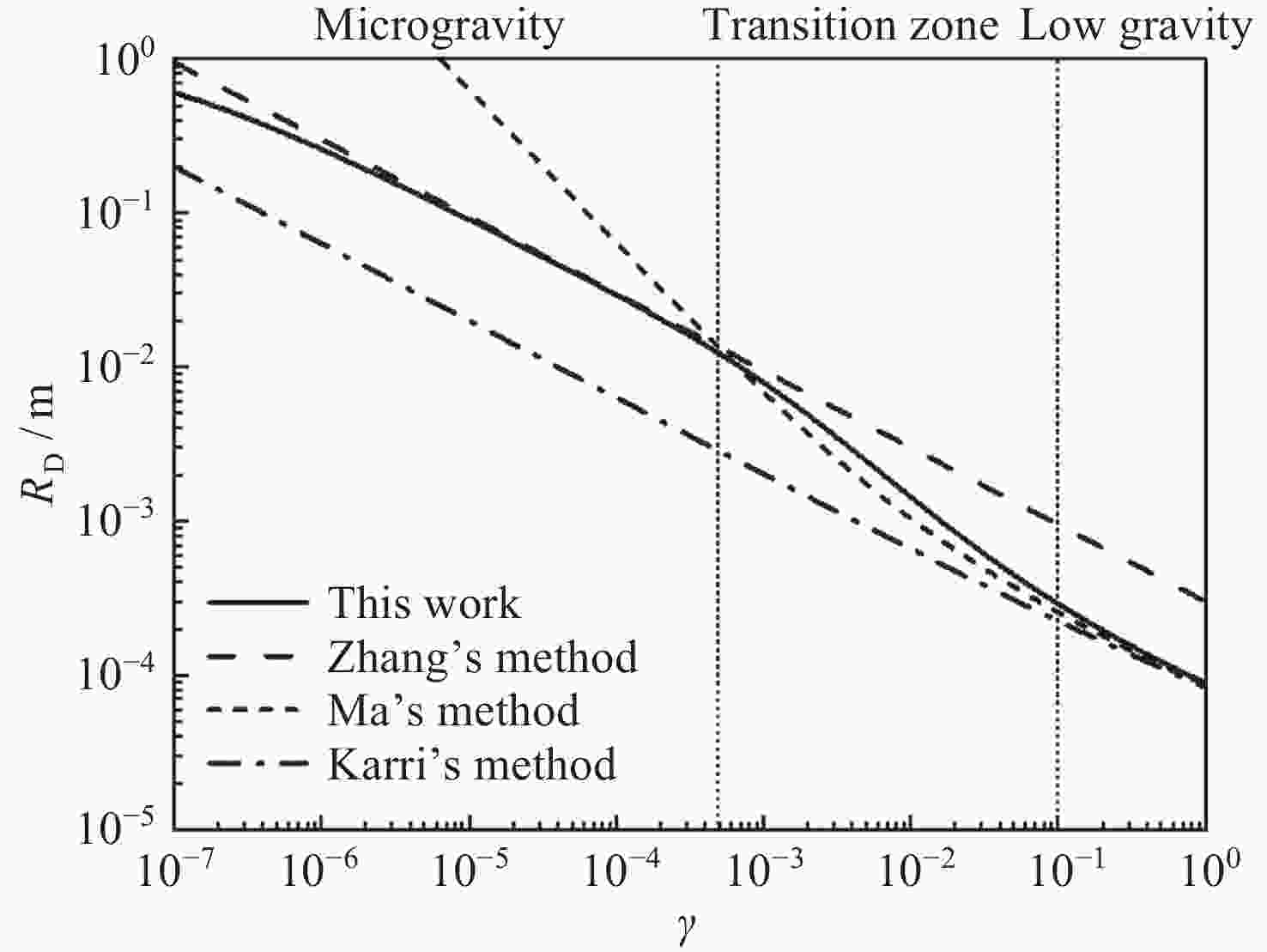
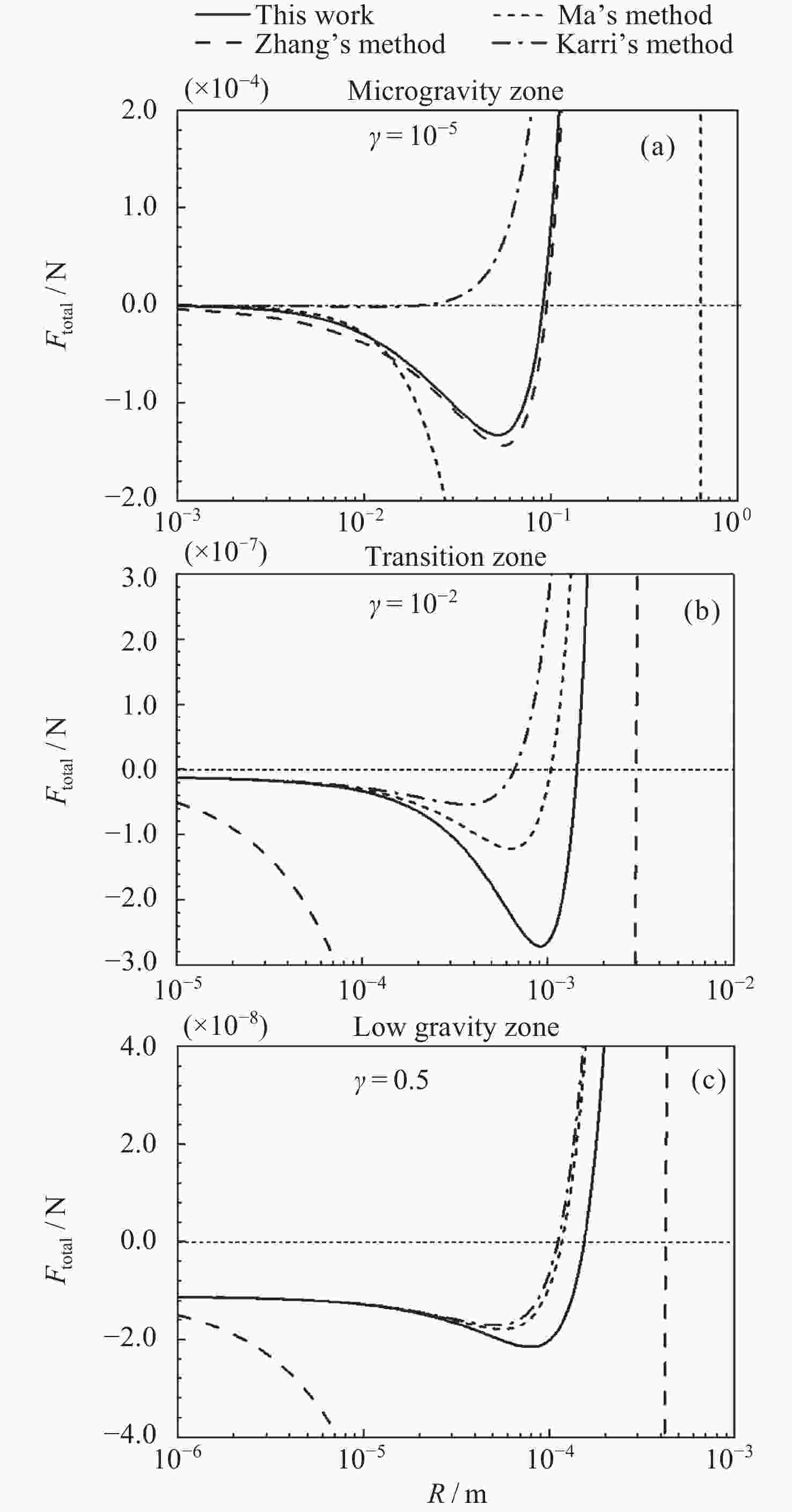
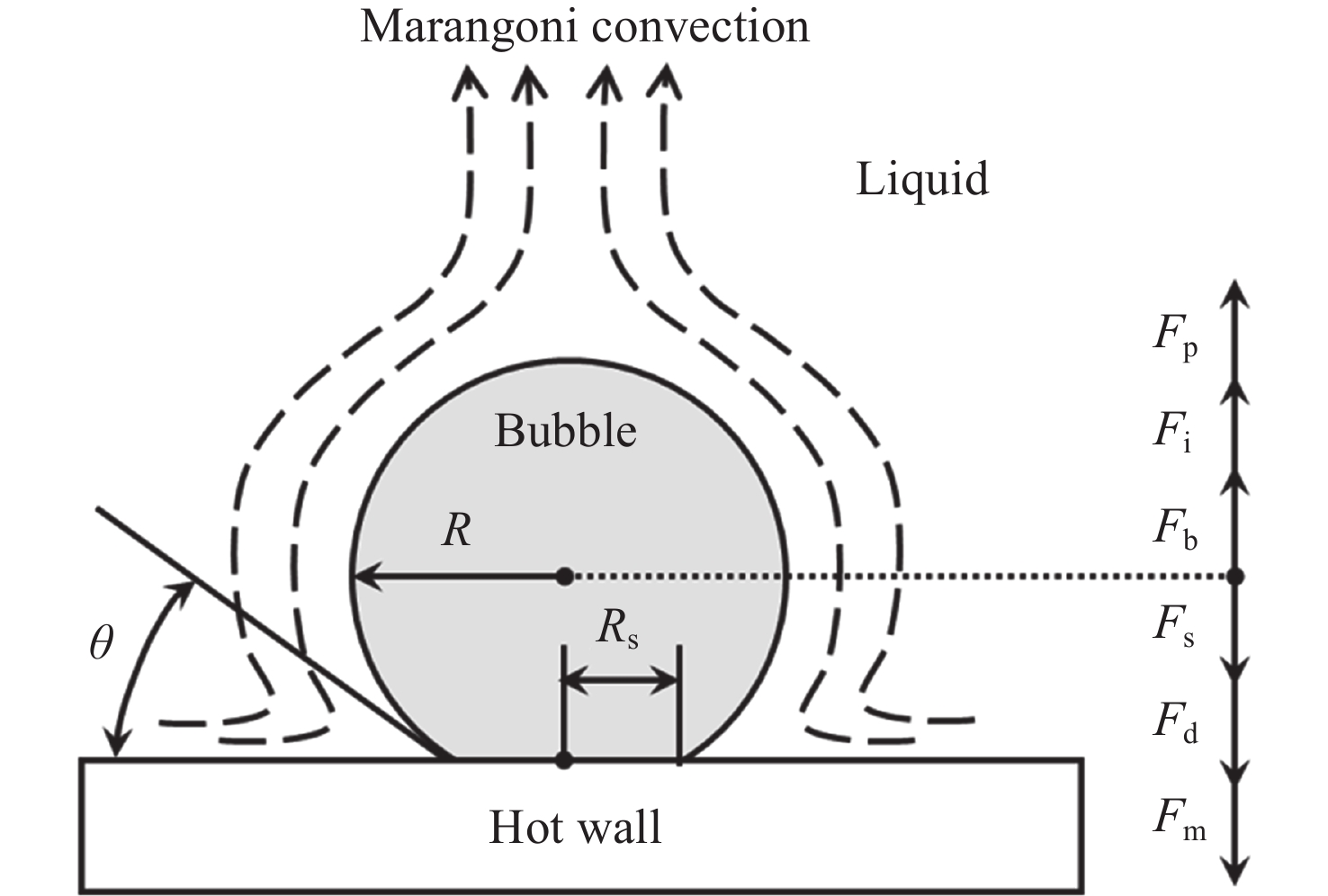
摘要: 研究微重力下液氧贮箱内气泡脱离半径是运载火箭推进系统推进剂在轨沸腾与换热计算的基础. 与常重力和低重力环境不同, 微重力下Marangoni效应变得突出. 为了求解气泡脱离半径, 构建包含浮力、惯性力、压差力、表面张力、黏性阻力和Marangoni力的气泡动力学模型. 针对现有Marangoni力计算公式适用范围狭窄的问题, 依托数值仿真方法, 拟合得到了更精确的修正因子计算公式, 进而扩充了Marangoni力计算模型的适用范围. 使用运载火箭液氧贮箱常规工作压力0.3 MPa下的饱和液氧物性参数, 计算得到气泡所受合力随半径的变化关系以及气泡脱离半径随重力的变化关系. 结果表明, 气泡的脱离行为可以由微重力区、过渡区和低重力区三个区域来划分. 微重力区内可以形成厘米级甚至米级的大气泡, 而低重力区内只能形成0.1 mm级的小气泡. 相比之前的模型, 本文模型可以同时适用于三个区, 更全面地揭示了微重力下液氧贮箱内的气泡脱离特性, 可以为液氧贮箱换热特性分析提供理论支撑.Abstract: Studying the bubble departure radius in the liquid oxygen tank under microgravity is the basis for the propellant boiling and heat transfer calculation of the launch vehicle propulsion system in orbit. Unlike regular or low gravity environments, the Marangoni effect becomes essential in microgravity. To calculate the bubble departure radius, Firstly, a bubble dynamics model is developed, including buoyancy, inertia, pressure, surface tension, drag, and Marangoni forces. Secondly, to solve the problem of the narrow application range of the existing Marangoni force formulas, a more accurate correction factor is fitted by numerical simulation. Consequently, the Marangoni force model is extended. Finally, using the physical parameters of saturated liquid oxygen at 0.3 MPa, a conventional working pressure for the liquid oxygen tank of the launch vehicle, the change of the total force with the radius and the departure radius with gravity are calculated, respectively. The results show that bubbles' departure behavior can be divided into three zones: microgravity zone, transition zone, and low gravity zone. The microgravity zone can form large bubbles of a centimeter or even meter scale, while the low gravity zone can only form tiny bubbles of 0.1 mm scale. Compared with the previous models, the model in this work can be applied to all three zones. Therefore, it comprehensively reveals the bubble departure characteristics in the liquid oxygen tank under microgravity. It can also provide theoretical support for analyzing the heat transfer characteristics in the liquid oxygen tank.
-
Key words:
- Microgravity /
- Liquid oxygen tank /
- Pool boiling /
- Bubble dynamics /
- Marangoni effect /
- Bubble departure radius
-
表 1 饱和状态下水的物性(1 atm)
Table 1. Physical properties of water in the saturated state (1 atm)
参数名称 符号 数值 液相密度/(kg·m–3) $ {\rho _{\text{l}}} $ 958.37 气相密度/(kg·m–3) $ {\rho _{\text{g}}} $ 0.59766 液相比热容/(kJ·kg–1·K–1) $ {c_{{\text{p,l}}}} $ 4.2156 液相热扩散系数/ (m2·s–1) $ {a_{\text{l}}} $ 1.6808×10–7 汽化潜热/(kJ·kg–1) $ {h_{{\text{fg}}}} $ 2256.5 表面张力系数/(mN·m–1) $ \sigma $ 58.917 液相动力黏度/(Pa·s) $ {\mu _{\mathrm{l}}} $ 0.00028166 接触角[3]/(o) $ \theta $ 45 表 2 仿真边界条件
Table 2. Simulation boundary conditions
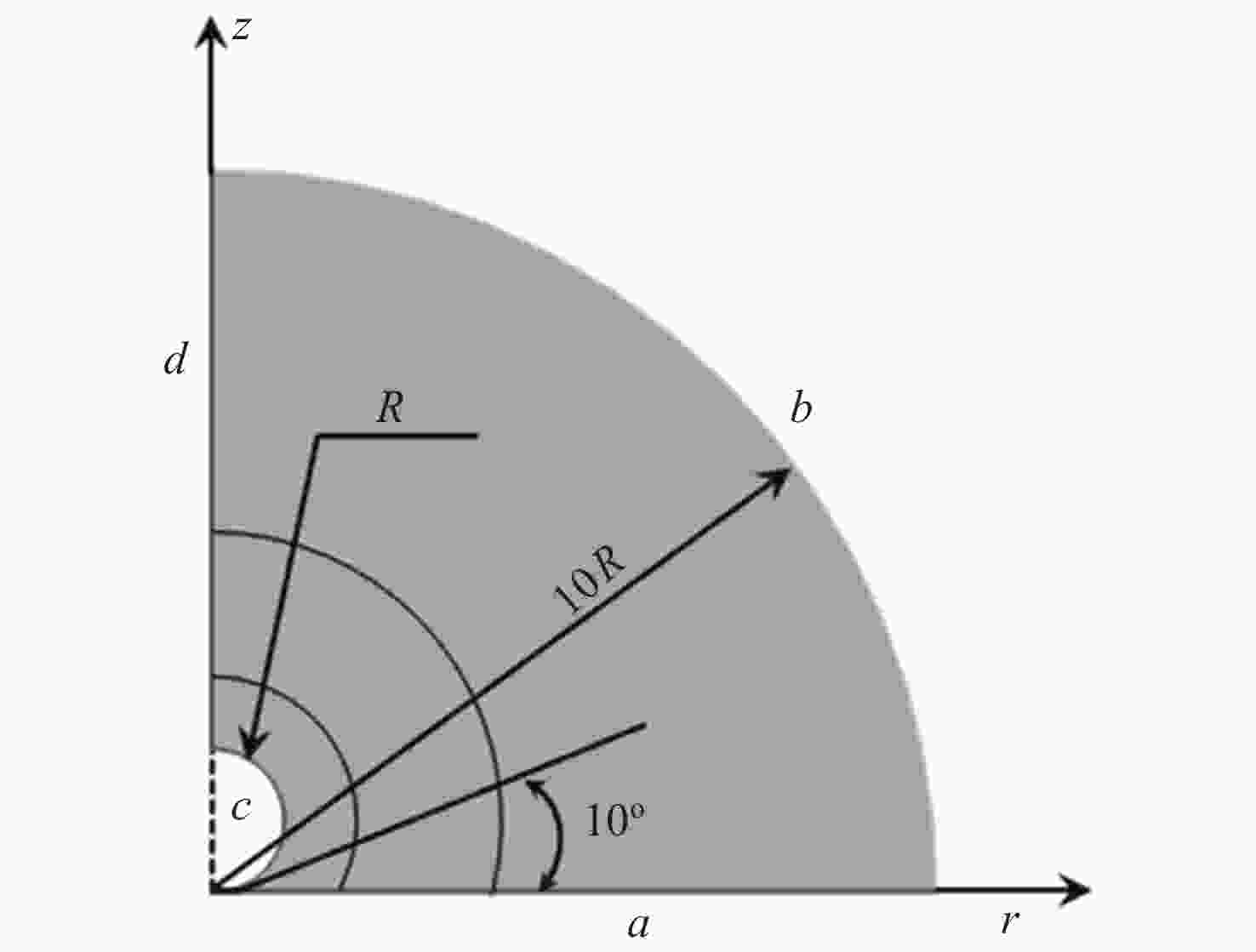
编号 流体力学条件 传热学条件 说明 a 无滑移壁面 温度 贮箱壁面 ${\boldsymbol{u}} = 0$ $T = {T_{\text{w}}}$ b 压力出口 绝热 仿真外边界 $p = {p_{{\text{ref}}}} = 0$ $ \left( {{\lambda _{\text{l}}}\nabla T} \right) \cdot {\boldsymbol{n}} = 0 $ c 滑移壁面 马氏效应 气泡表面 ${\boldsymbol{u}} \cdot {\boldsymbol{n}} = 0$ $ \left( { - p{\boldsymbol{I}} + {\boldsymbol{\tau }}} \right){\boldsymbol{n}} = {\sigma _{\text{T}}}{\nabla _{\text{t}}}T $ d — — 对称轴 表 3 饱和状态下液氧的物性(0.3 MPa)
Table 3. Physical properties of saturated liquid oxygen (0.3 MPa)
参数名称 符号 数值 液相密度/(kg·m–3) $ {\rho _{\text{l}}} $ 1080.1 气相密度/(kg·m–3) $ {\rho _{\text{g}}} $ 12.170 液相比热容/(kJ·kg–1·K–1) $ {c_{{\text{p,l}}}} $ 1.7487 液相热扩散系数/(m2·s–1) $ {a_{\text{l}}} $ 7.0734×10–8 汽化潜热/(kJ·kg–1) $ {h_{{\text{fg}}}} $ 200.20 表面张力系数/(mN·m–1) $ \sigma $ 10.265 液相动力黏度/(Pa·s) $ {\mu _{\mathrm{l}}} $ 0.00014552 接触角[15]/(o) $ \theta $ 10 温度/K $ {T_0} $ 102.2 表 4 表面张力温度系数[13]
Table 4. Surface tension temperature coefficient
温度/K 表面张力系数/(mN·m–1) 表面张力温度系数/(mN·m–1·K–1) 101 10.512 –0.24 103 10.032 表 5 网格无关性验证
Table 5. Mesh independence verification
网格序号 单元总数(×103) 气泡顶部过热度/K 相对偏差/(%) 1 3.4 0.2978 4.42 2 5.7 0.3024 6.03 3 8.6 0.2911 2.07 4 12.1 0.2852 — 表 6 仿真所得马氏力随气泡半径的变化
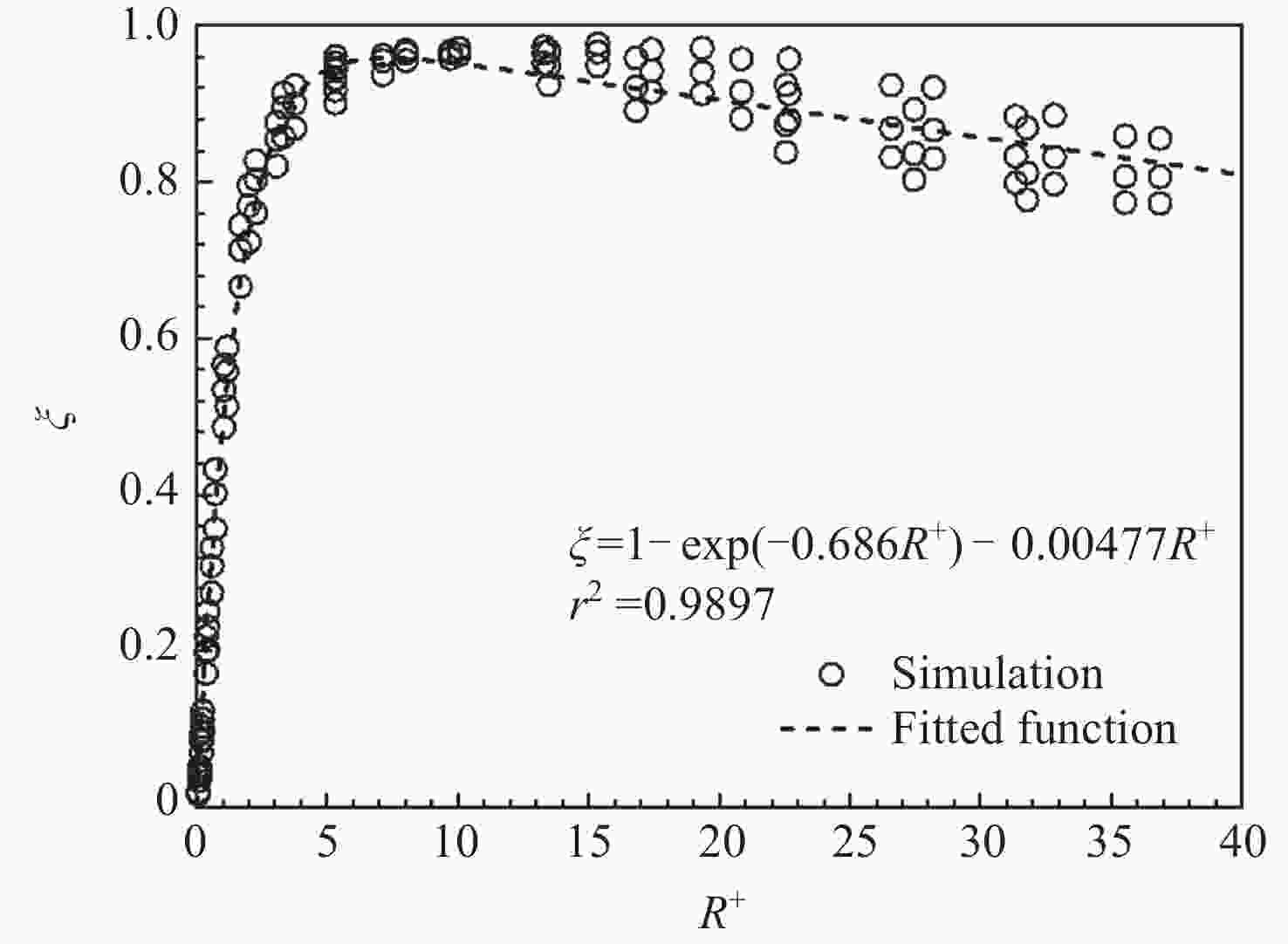
Table 6. Change of Marangoni force with bubble Radius obtained from simulation
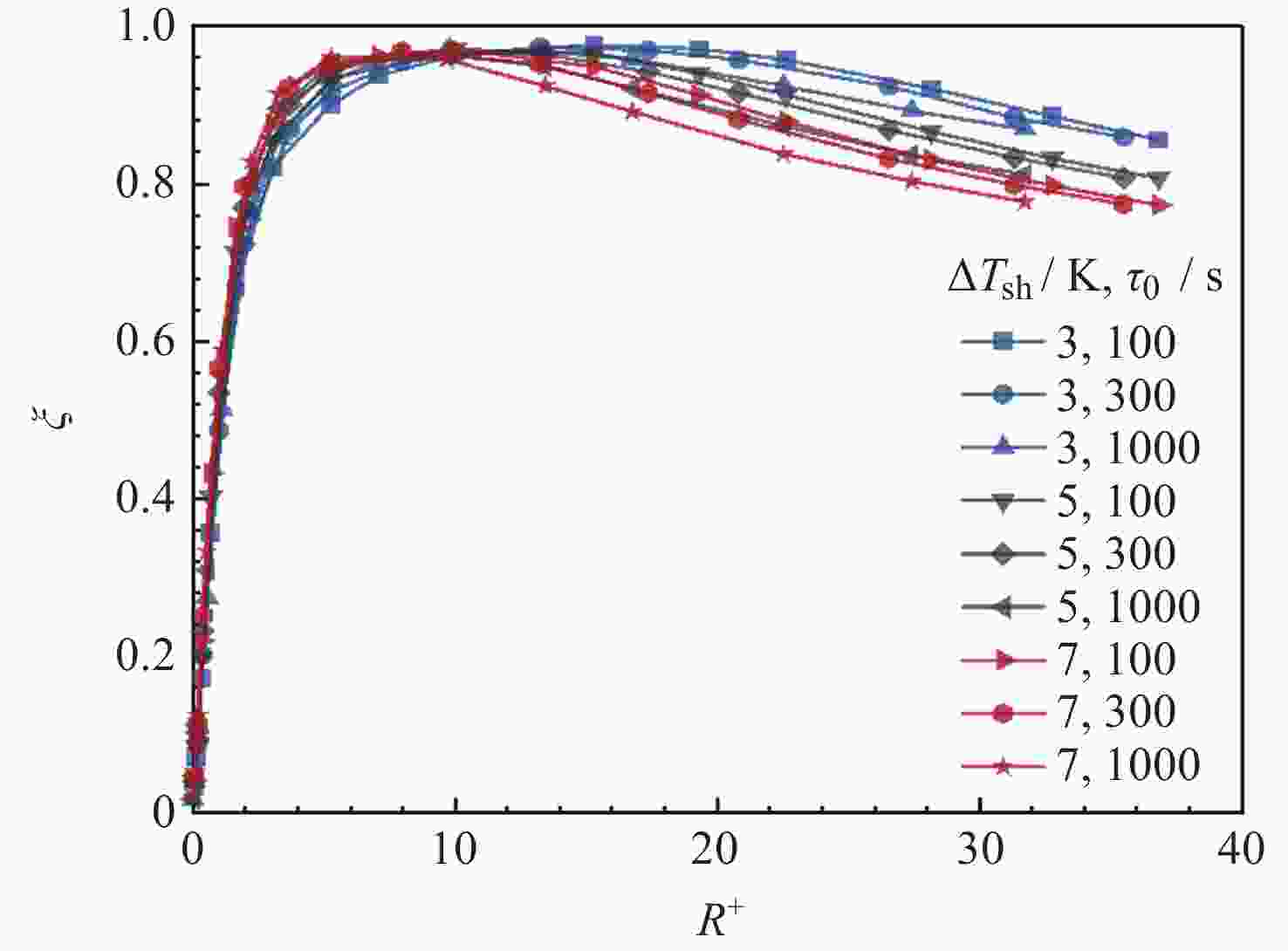
R /mm R+ 马氏力Fm/N 修正因子ξ 0.5 0.1081 7.7174×10–8 0.0409 1 0.2153 3.8843×10–7 0.1030 2 0.4271 1.7431×10–6 0.2312 5 1.0428 1.0067×10–5 0.5341 10 2.0098 2.9000×10–5 0.7693 20 3.7600 6.7864×10–5 0.9001 30 5.3174 1.0660×10–4 0.9426 50 8.0163 1.8185×10–4 0.9647 100 13.2935 3.6385×10–4 0.9651 150 17.4053 5.3273×10–4 0.9421 200 20.8566 6.9017×10–4 0.9154 300 26.5871 9.8190×10–4 0.8682 400 31.3604 1.2557×10–3 0.8327 500 35.5285 1.5211×10–3 0.8070 -
[1] ZHANG N, CHAO D F. Models for enhanced boiling heat transfer by unusual Marangoni effects under microgravity conditions[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 1999, 26(8): 1081-1090 doi: 10.1016/S0735-1933(99)00099-8 [2] YAN Chunjie, ZHENG Yongyu, Yang Qi, et al. Deformation characteristics of gas-liquid interface in cryogenic propellant tank under microgravity environment[J]. Vacuum and Cryogenics, 2022, 28(3): 285-290 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7086.2022.03.006 [3] KARRI S R. Dynamics of bubble departure in microgravity[J]. Chemical Engineering Communications, 1988, 70(1): 127-135 doi: 10.1080/00986448808940623 [4] SIEGEL R, KESHOCK E G. Effects of reduced gravity on nucleate boiling bubble dynamics in saturated water[J]. Aiche Journal, 1964, 10(4): 509-517 doi: 10.1002/aic.690100419 [5] YOUNG N O, GOLDSTEIN J S, BLOCK M J. The motion of bubbles in a vertical temperature gradient[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1959, 6(3): 350-356 doi: 10.1017/S0022112059000684 [6] LIU Gang, ZHAO Jianfu, WAN Shixin, et al. Bubble departure diameter in microgravity pool boiling[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2008, 29(1): 93-95 [7] ZHANG Y, WEI J, XUE Y, et al. Bubble dynamics in nucleate pool boiling on micro-pin-finned surfaces in microgravity[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2014, 70: 172-182 doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2014.04.074 [8] MA Yuan, SUN Peijie, LI Peng, et al. Investigation on the boiling bubble departure behavior of cryogenic fluid in microgravity[J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 2018, 52(9): 89-94 [9] 易天浩, 陈超越, 雷作胜, 等. 微重力池沸腾中的气泡和传热行为数值模拟[J]. 空间科学学报, 2019, 39(4): 469-477 doi: 10.11728/cjss2019.04.469YI Tianhao, CHEN Chaoyue, LEI Zuosheng, et al. Numerical simulation of bubble dynamics and heat transfer during pool boiling in microgravity[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2019, 39(4): 469-477 doi: 10.11728/cjss2019.04.469 [10] BEER H, BORROW P, BEST R. Nucleate boiling: bubble growth and dynamics[M]// Hahne E. Heat Transfer in Boiling. New York: Academic Press, 1977: 21-52 [11] MIKIC B B, ROHSENOW W M, GRIFFITH P. On bubble growth rates[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1970, 13(4): 657-666 doi: 10.1016/0017-9310(70)90040-2 [12] WAGNER W, PRUß A. The IAPWS formulation 1995 for the thermodynamic properties of ordinary water substance for general and scientific use[J]. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 2002, 31(2): 387-535 doi: 10.1063/1.1461829 [13] LEMMON E W, BELL I H, HUBER M L, et al. NIST standard reference database 23: reference fluid thermodynamic and transport properties-refprop, version 10.0 [EB/OL]. (2022-01-27)[2022-05-31]. https://doi.org/10.18434/T4/1502528 [14] STRAUB J. Boiling Heat Transfer and Bubble Dynamics in Microgravity[M]. Advances in Heat Transfer, Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2001: 35, 57-172 [15] LI Z, ZHU Z, LIU Q, et al. Simulating propellant reorientation of vehicle upper stage in microgravity environment[J]. Microgravity Science and Technology, 2013, 25(4): 237-241 doi: 10.1007/s12217-013-9351-z [16] YANG Shiming, Tao Wenquan. Numerical Heat Transfer[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2001 [17] STEWART R B, JACOBSEN R T, WAGNER W. Thermodynamic properties of oxygen from the triple point to 300 K with pressures to 80 MPa[J]. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 1991, 20(5): 917-1021 doi: 10.1063/1.555897 [18] LEE D J. Bubble departure radius under microgravity[J]. Chemical Engineering Communications, 1992, 117(1): 175-189 doi: 10.1080/00986449208936065 [19] LI Jing, ZHAO Jianfu, YAN Na, et al. Bubble behavior in microgravity pool boiling[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2008(3): 439-442 [20] ZHENG Yao, CHANG Huawei, CHEN Hong, et al. Bubble departure characteristics during liquid hydrogen flow boiling under microgravity[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2021, 52(5): 1666-1672 -
-





 李文韬:男, 1999年7月出生于陕西省汉中市, 现为北京航空航天大学在读博士生, 主要研究方向为微重力下气泡动力学、多物理场耦合数值仿真等. E-mail:
李文韬:男, 1999年7月出生于陕西省汉中市, 现为北京航空航天大学在读博士生, 主要研究方向为微重力下气泡动力学、多物理场耦合数值仿真等. E-mail: 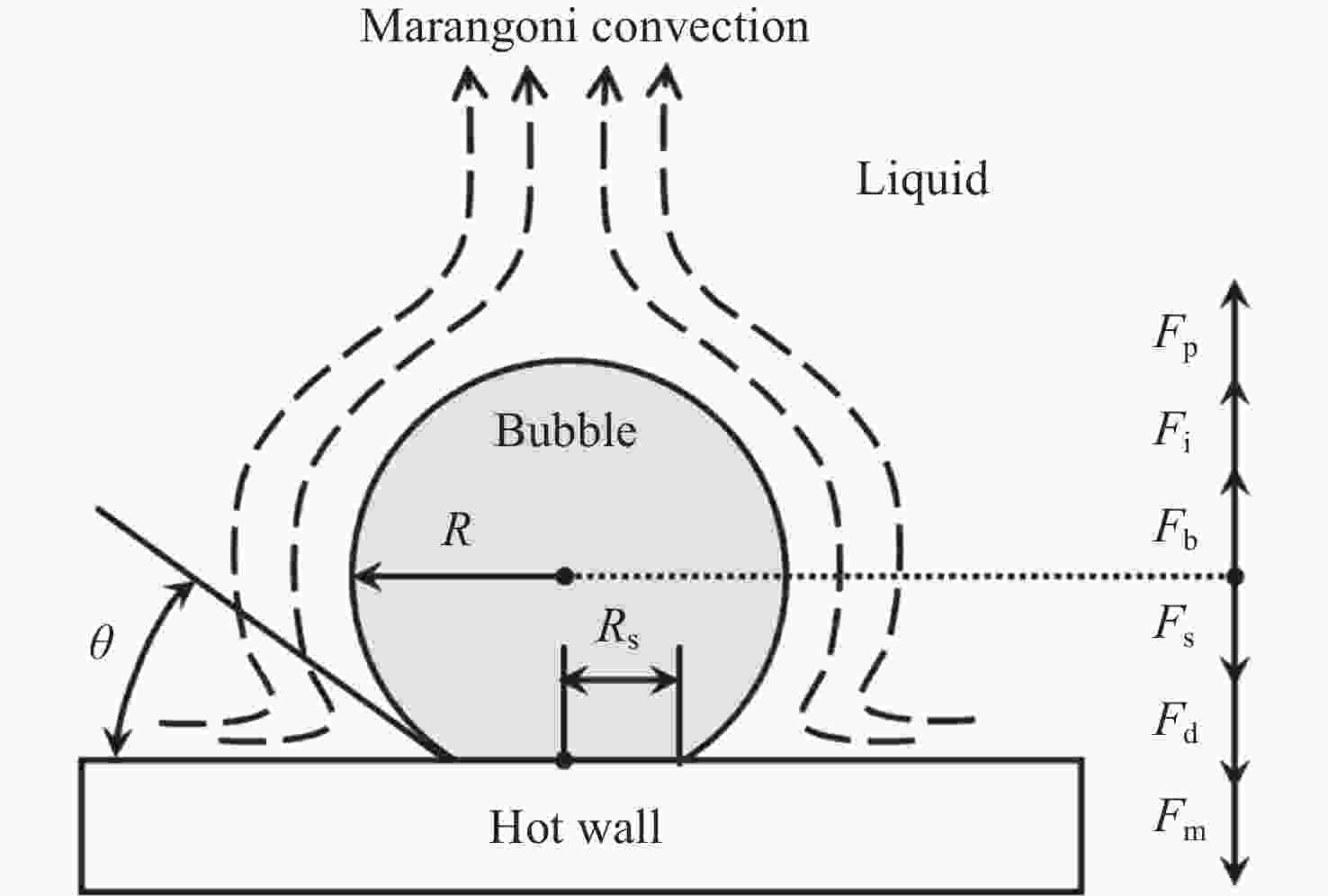
 下载:
下载: