Estimation of Energy Input during Throat Aurora Processes
-
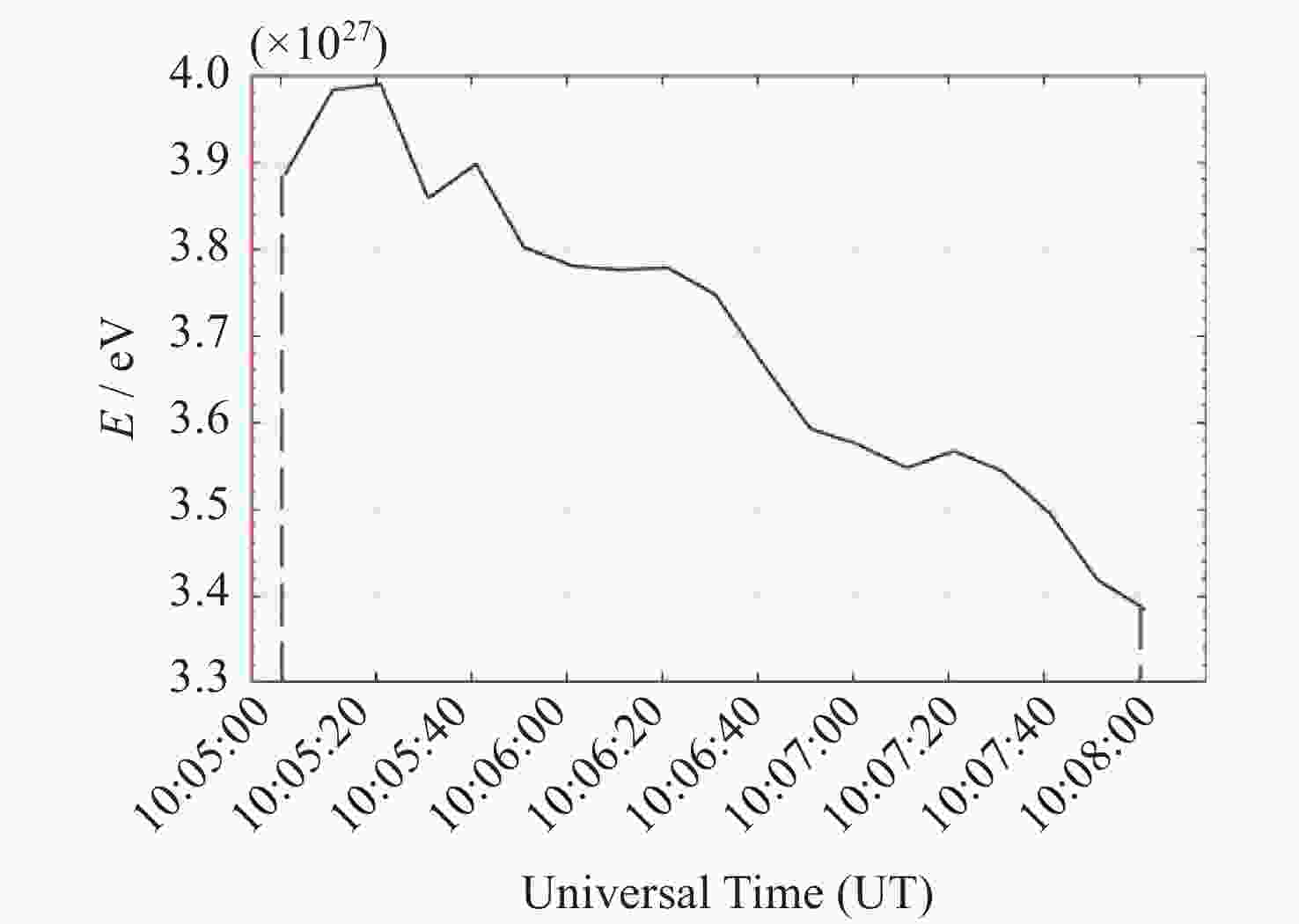
摘要: 喉区极光是一种只发生在磁正午附近的特殊分立极光, 具有明显的从分立极光卵赤道侧边界向低纬延伸的特征. 已有研究表明, 喉区极光对应于一种由磁重联导致的磁层顶局地凹陷. 磁重联是太阳风能量注入到地球磁层空间的重要方式之一, 但伴随喉区极光过程有多少能量传输进入电离层尚不明确. 利用2015年12月的地基全天空极光观测与经过电离层上方的卫星粒子共轭观测, 建立了极光强度与沉降电子能通量之间的相关关系. 在此基础上, 针对发生在2015年12月8日的一个典型喉区极光事件, 在综合考虑持续时间与空间尺度基础上, 估算出伴随该事件由电子携带的输入到电离层的总能量约为$ 1.07\times {10}^{11}\;\mathrm{J} $, 单位面积输入能量的平均功率约为$ 1.31\times {10}^{-4}\;\mathrm{W}\cdot {\mathrm{m}}^{-2} $, 对比以往研究中MHD模拟给出的通常情况下极隙区能量输入结果, 本文给出的喉区极光过程中能量输入的效率约为MHD模拟结果的两倍, 表明伴随喉区极光过程的能量输入非常可观, 可能引起局地空间天气效应.Abstract: The throat aurora is a kind of discrete auroras occurred around the Magnetic Local Noon (MLN). The discrete arc is almost vertical to the auroral oval and extends equatorward. Previous studies have shown that the throat auroral structure corresponds to the localized magnetopause indentations which are related to the particular magnetopause reconnection. As is known, magnetic reconnection is the important approach inputting energy of solar wind, so the research of energy input of throat aurora is key to understand this particular magnetopause reconnection. A new way to estimate the energy input by using all auroral events happened on December 2015 is built. A relational expression about auroral intensity and energy flux of electronic precipitation is set up by observations of both ground station and satellite. Estimating the total energy input of a typical throat auroral event which lasted three minutes and happened on 8 December 2015 by this relational expression, and the answer is about $ 1.07\times {10}^{11}\;\mathrm{J} $. And the average power of input energy per area is about $ 1.31\times {10}^{-4}\;\mathrm{W} \cdot {\mathrm{m}}^{-2} $. Compared with the usual polar gap energy input results given by MHD simulation in previous studies, the energy input efficiency of the throat auroral process given in this paper is about twice that of the MHD simulation results, which indicates that the energy input accompanying the throat auroral process is very considerable and may cause local space weather effects.
-
Key words:
- Throat aurora /
- Electron energy flux /
- Auroral intensity /
- Energy input power
-
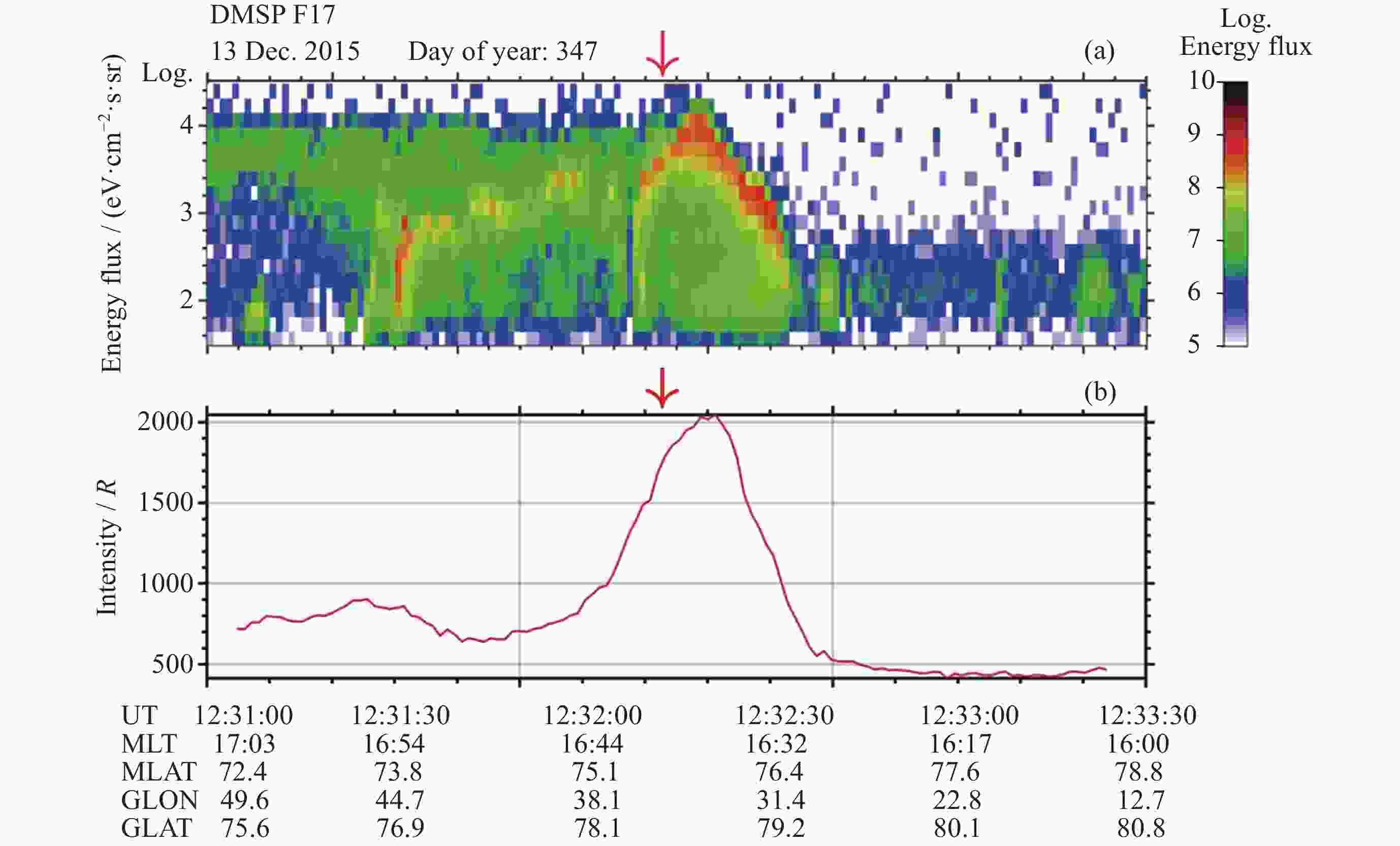
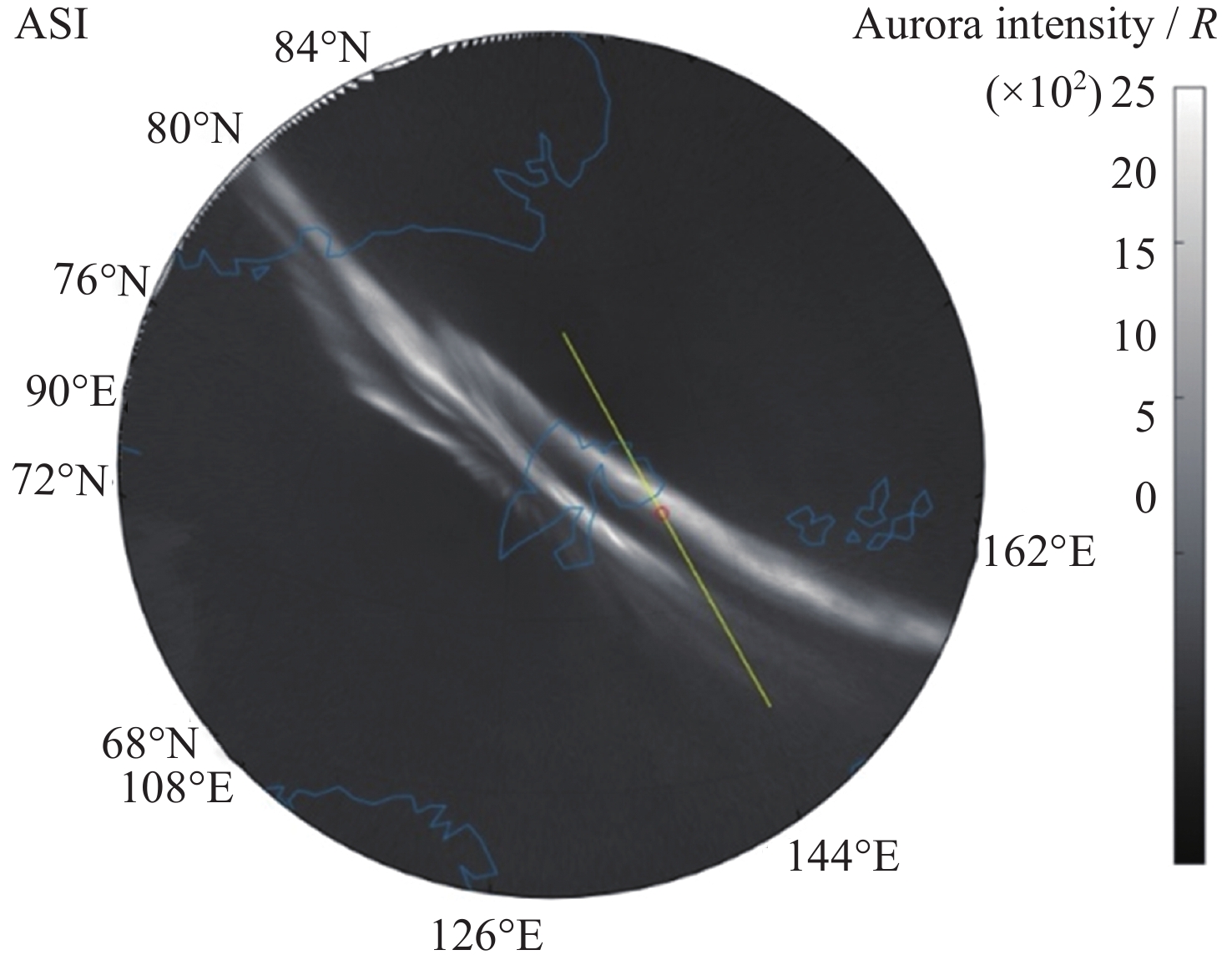
图 1 2015年12月13日12:32:10 UT地面极光观测和12:31:00 UT-12:33:30 UT时段的DMSP卫星粒子观测. DMSP卫星运动轨迹(黄线)叠加在地面极光观测中
Figure 1. Ground auroral observations happened on 13 December 2015 at 12:32:40 UT and DMSP-Satellite particle observations between 12:31:00 UT and 12:33:30 UT. The track of DMSP-Satellite is showed by yellow line on the ground auroral observations
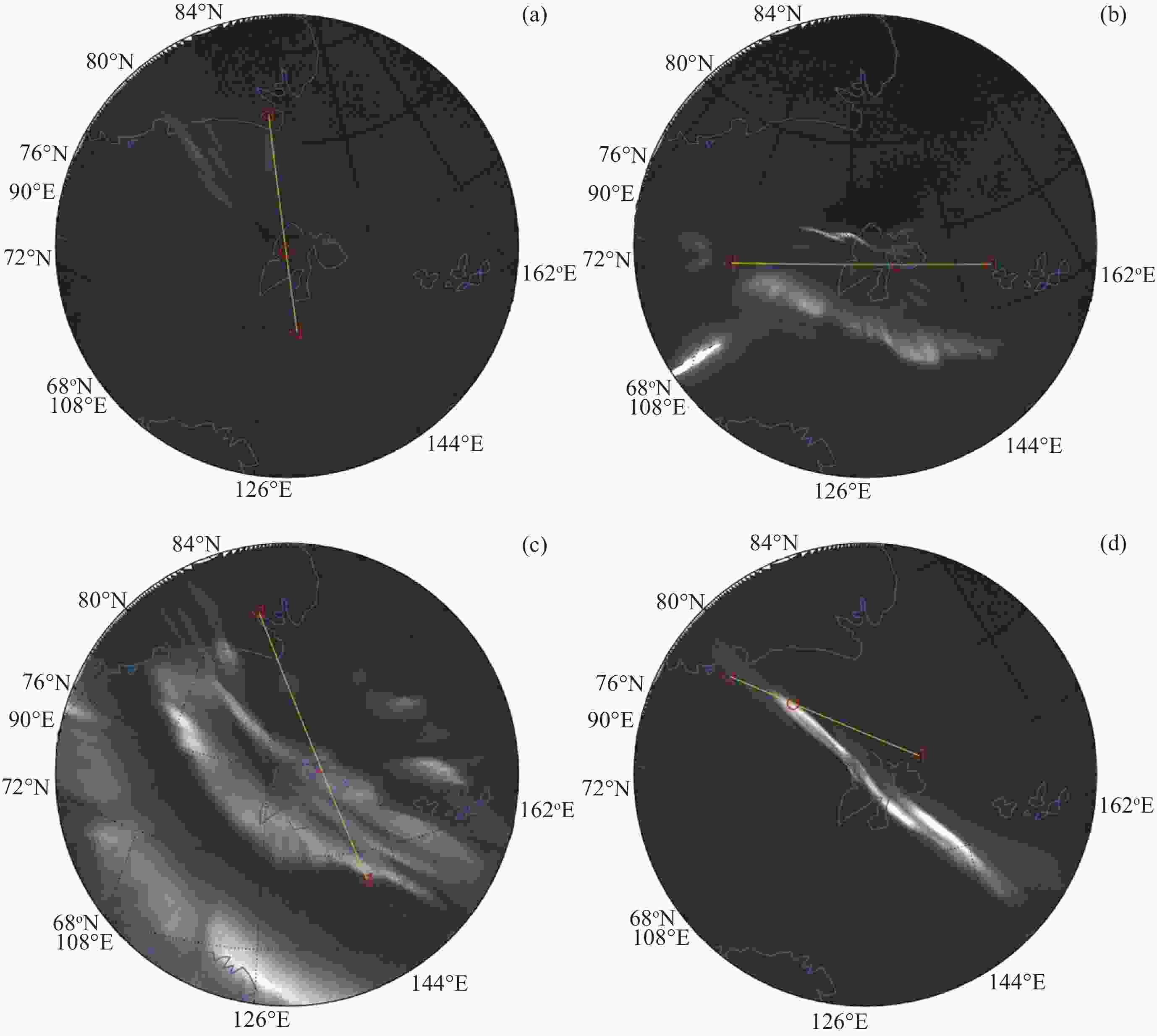
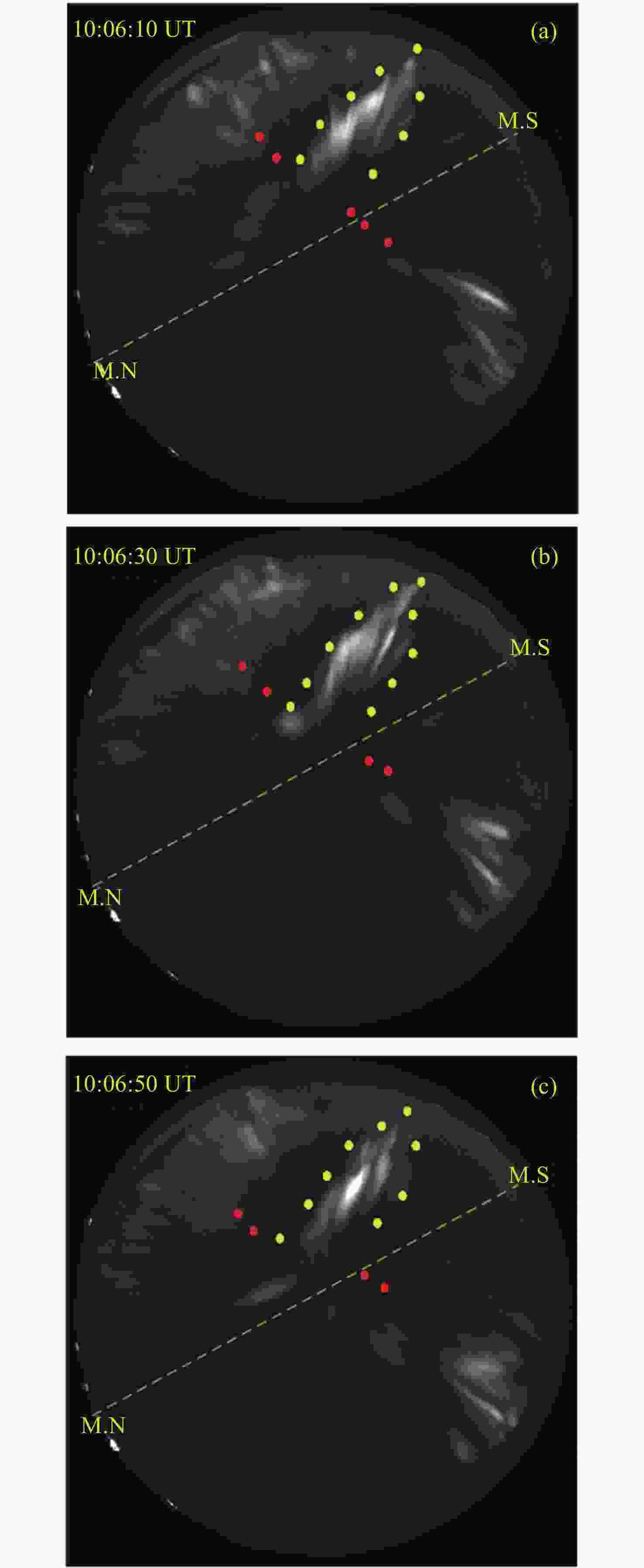
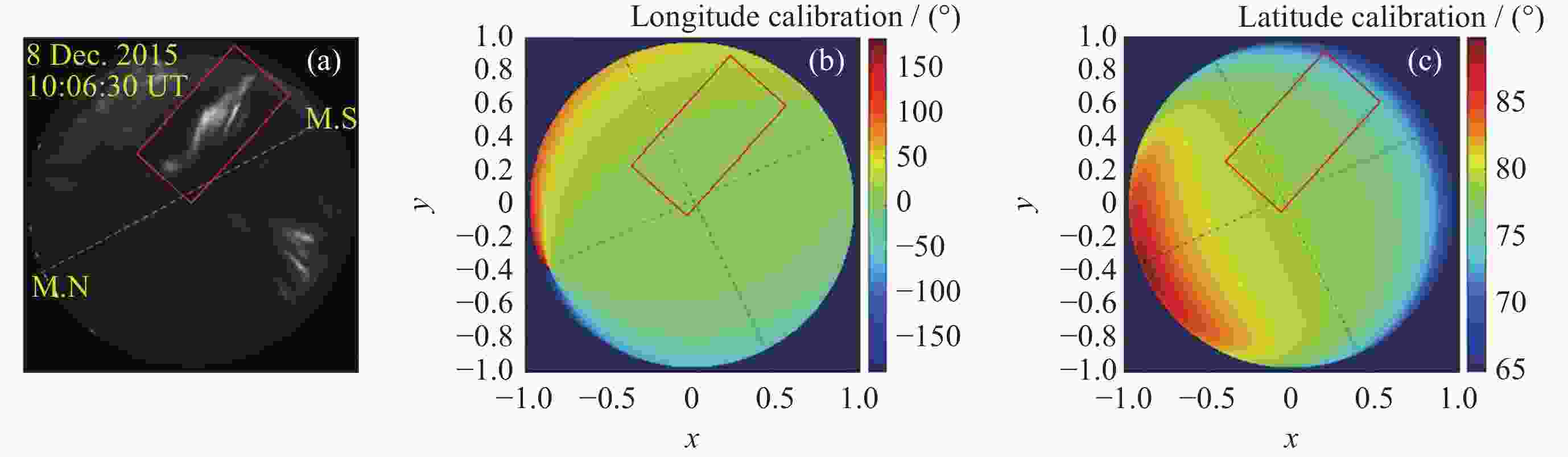
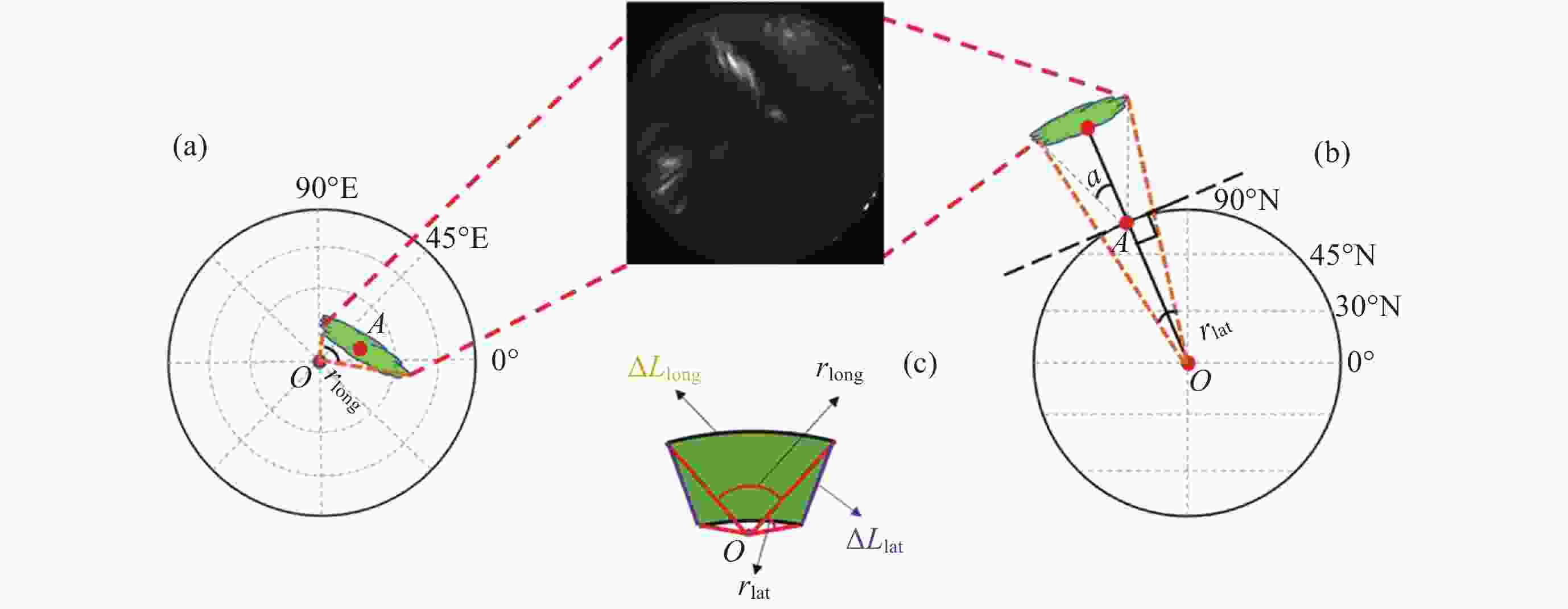
图 6 喉区极光样本事件的ASI观测. (a) ASI观测. (b)经度定标图. (c) 纬度定标图. 其中定标图原点表示图像中心, 整个ASI像素映射在–1~1的归一化网格点中
Figure 6. ASI observation of sample event of throat aurora. (a) The image of ASI observation. (b) Pseudo-color image for longitude calibration. (c) Pseudo-color image for latitude calibration. The origin of the calibration map represents the image center, the whole ASI pixel is mapped in the normalized grid point of –1~1
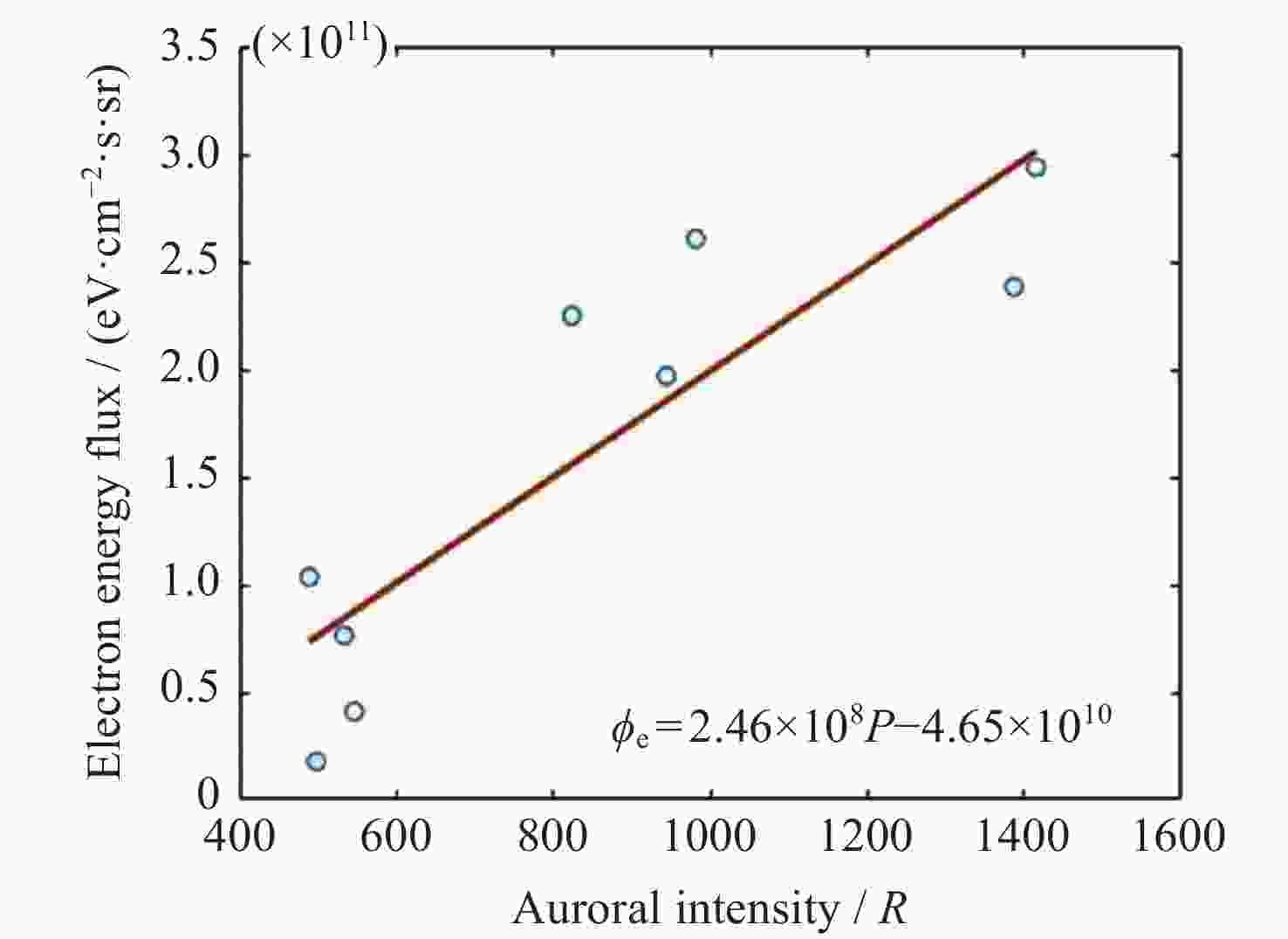
表 1 2015年12月数据得到的全部有效对应点以及相关参数信息
Table 1. Sample event data selected according to the criteria in December 2015
No. Satellite Date UT Electron energy flux / ($ \mathrm{e}\mathrm{V} \cdot {\mathrm{c}\mathrm{m}}^{-2} \cdot {\mathrm{s}}^{-1} $) Auroral intensity / R 1 F17 13 Dec. 2015 12:32:40 $ 2.939\times {10}^{11} $ 1415 2 F17 13 Dec. 2015 12:33:00 $ 2.607\times {10}^{11} $ 982 3 F17 14 Dec. 2015 13:59:20 $ 1.971\times {10}^{11} $ 944 4 F17 15 Dec. 2015 12:05:30 $ 2.250\times {10}^{11} $ 824 5 F17 16 Dec. 2015 11:53:10 $ 1.036\times {10}^{11} $ 489 6 F17 16 Dec. 2015 11:53:20 $ 1.788\times {10}^{10} $ 498 7 F17 16 Dec. 2015 11:53:40 $ 7.662\times {10}^{10} $ 533 8 F17 16 Dec. 2015 11:53:50 $ 4.121\times {10}^{10} $ 546 9 F18 13 Dec. 2015 10:56:00 $ 2.384\times {10}^{11} $ 1387 -
[1] CHAPMAN S, FERRARO V C A. A new theory of magnetic storms[J]. Nature, 1930, 126(3169): 129-130 doi: 10.1038/126129a0 [2] AXFORD W I, HINES C O. A unifying theory of high-latitude geophysical phenomena and geomagnetic storms[J]. Canadian Journal of Physics, 1961, 39(10): 1433-1464 doi: 10.1139/p61-172 [3] BIRN J, DRAKE J F, SHAY M A, et al. Geospace Environmental Modeling (GEM) magnetic reconnection challenge[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2001, 106(A3): 3715-3719 doi: 10.1029/1999JA900449 [4] SANDHOLT P E, FARRUGIA C J, MOEN J, et al. A classification of dayside auroral forms and activities as a function of interplanetary magnetic field orientation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1998, 103(A10): 23325-23345 doi: 10.1029/98JA02156 [5] 韩德胜, 胡泽骏, 陈相材, 等. 基于北极黄河站观测的日侧极光研究新进展[J]. 极地研究, 2018, 30(3): 235-250 doi: 10.13679/j.jdyj.20180020HAN Desheng, HU Zejun, CHEN Xiangcai, et al. Recent results obtained from dayside optical auroral observations at Yellow River station[J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2018, 30(3): 235-250 doi: 10.13679/j.jdyj.20180020 [6] MENG C I, MAUK B, MCILWAIN C E. Electron precipitation of evening diffuse aurora and its conjugate electron fluxes near the magnetospheric equator[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1979, 84(A6): 2545-2558 doi: 10.1029/JA084iA06p02545 [7] LOCKWOOD M. Relationship of dayside auroral precipitations to the open‐closed separatrix and the pattern of convective flow[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1997, 102(A8): 17475-17487 doi: 10.1029/97JA01100 [8] MENDE S B, FREY H U, ANGELOPOULOS V. Source of the dayside cusp aurora[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2016, 121(8): 7728-7738 doi: 10.1002/2016JA022657 [9] SHI R, LIANG J, HU Z J, et al. The potential role of modified electron acoustic wave and nonlinear mode coupling in mono-energetic aurora[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2023, 50(9): e2022GL102680 doi: 10.1029/2022GL102680 [10] FELDSTEIN Y I, ELPHINSTONE R D. Aurorae and the large-scale structure of the magnetosphere[J]. Journal of Geomagnetism and Geoelectricity, 1992, 44(12): 1159-1174 doi: 10.5636/jgg.44.1159 [11] HAN D S, CHEN X C, LIU J J, et al. An extensive survey of dayside diffuse aurora based on optical observations at Yellow River Station[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2015, 120(9): 7447-7465 doi: 10.1002/2015JA021699 [12] HAN D S, LIU J J, CHEN X C, et al. Direct evidence for throat aurora being the ionospheric signature of magnetopause transient and reflecting localized magnetopause indentations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2018, 123(4): 2658-2667 doi: 10.1002/2017JA024945 [13] QIU H X, HAN D S, WANG B Y, et al. In situ observation of a magnetopause indentation that is correspondent to throat aurora and is caused by magnetopause reconnection[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2022, 49(15): e2022GL099408 doi: 10.1029/2022GL099408 [14] HAN D S. Ionospheric polarization electric field guiding magnetopause reconnection: a conceptual model of throat aurora[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2019, 62(12): 2099-2105 doi: 10.1007/s11430-019-9358-8 [15] HAN D S, HIETALA H, CHEN X C, et al. Observational properties of dayside throat aurora and implications on the possible generation mechanisms[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2017, 122(2): 1853-1870 doi: 10.1002/2016JA023394 [16] 韩德胜, 邱荟璇, 石润. 喉区极光模型再考[J]. 地球与行星物理论评, 2022, 53(5): 605-612 doi: 10.19975/j.dqyxx.2022-036HAN Desheng, QIU Huixuan, SHI Run. Reconsideration on the concept model of throat aurora[J]. Reviews of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, 2022, 53(5): 605-612 doi: 10.19975/j.dqyxx.2022-036 [17] 李国君. 基于ASI的地球极隙区电离层投影边界定位与建模[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2021LI Guojun. Location and Modeling of the Ionospheric Projection Boundary of Earth’s Cusp Region Based on ASI[D]. Xi’an: Xidian University, 2021 [18] 丘琪, 杨惠根, 陆全明, 等. 日侧极光弧的发光强度与沉降电子能谱的相关关系[J]. 地球物理学报, 2017, 60(2): 489-498 doi: 10.6038/cjg20170204QIU Qi, YANG Huigen, LU Quanming, et al. Correlation between emission intensities in dayside auroral arcs and precipitating electron spectra[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2017, 60(2): 489-498 doi: 10.6038/cjg20170204 [19] LU J, ZHANG H X, WANG M, et al. Energy transfer across the magnetopause under radial IMF conditions[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2021, 920(1): 52 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/ac15f4 [20] CHEN X C, HAN D S, LORENTZEN D A, et al. Dynamic properties of throat aurora revealed by simultaneous ground and satellite observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2017, 122(3): 3469-3486 doi: 10.1002/2016JA023033 -
-





 范天舒:男, 1998年1月出生于内蒙古巴彦淖尔. 内蒙古师范大学硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为磁层物理. E-mail:
范天舒:男, 1998年1月出生于内蒙古巴彦淖尔. 内蒙古师范大学硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为磁层物理. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: