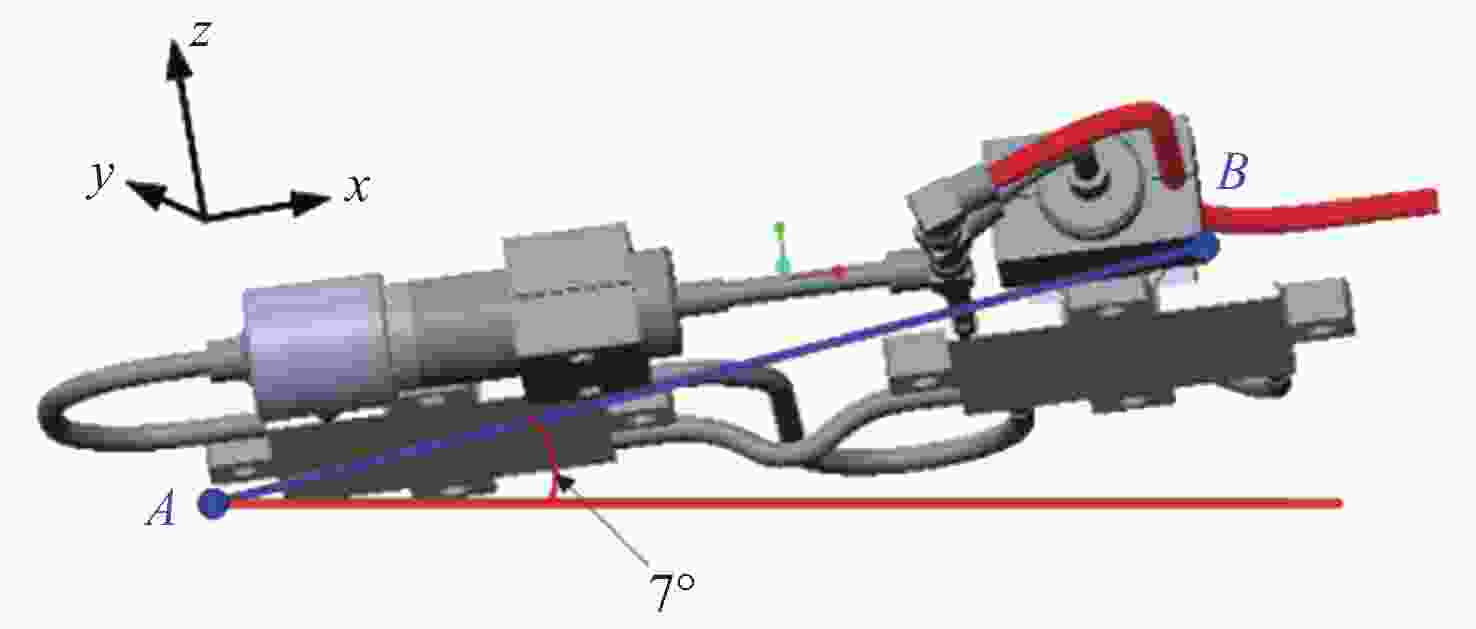
Investigation on Performance Difference of 35 K Cryogenic Heat Transfer System in Ground and Space Environment
-
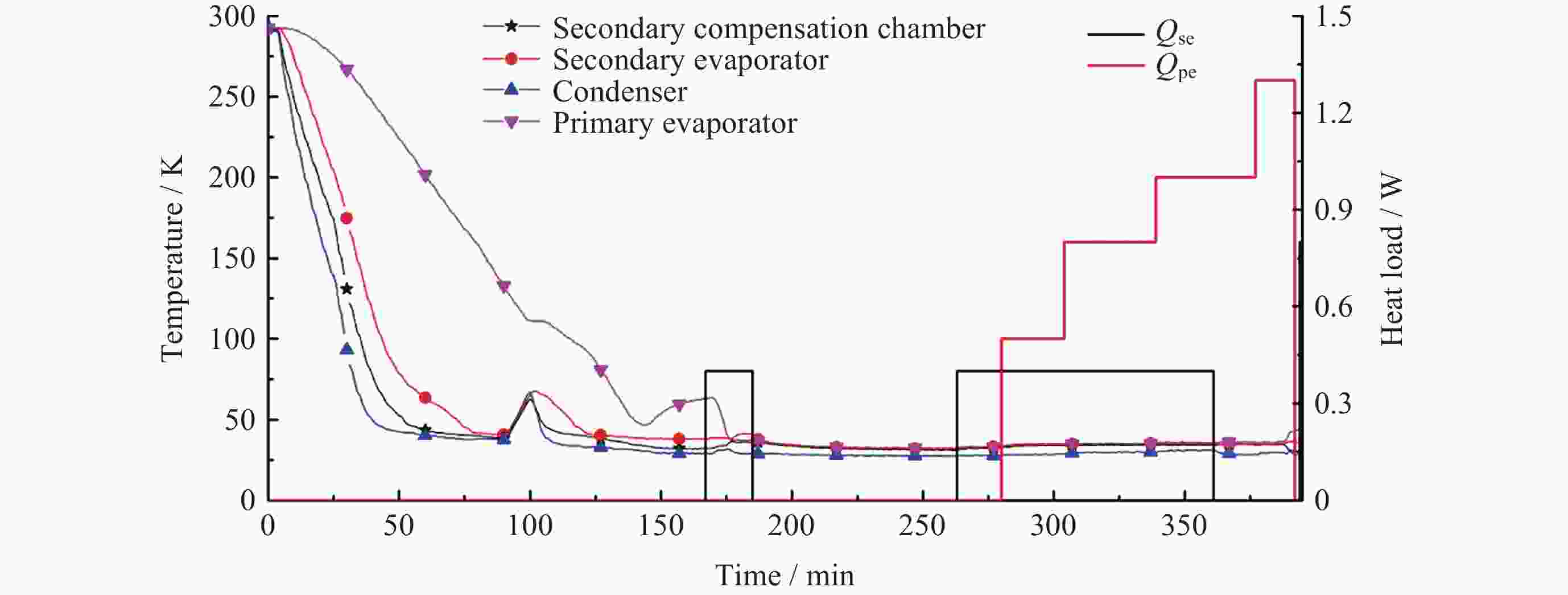
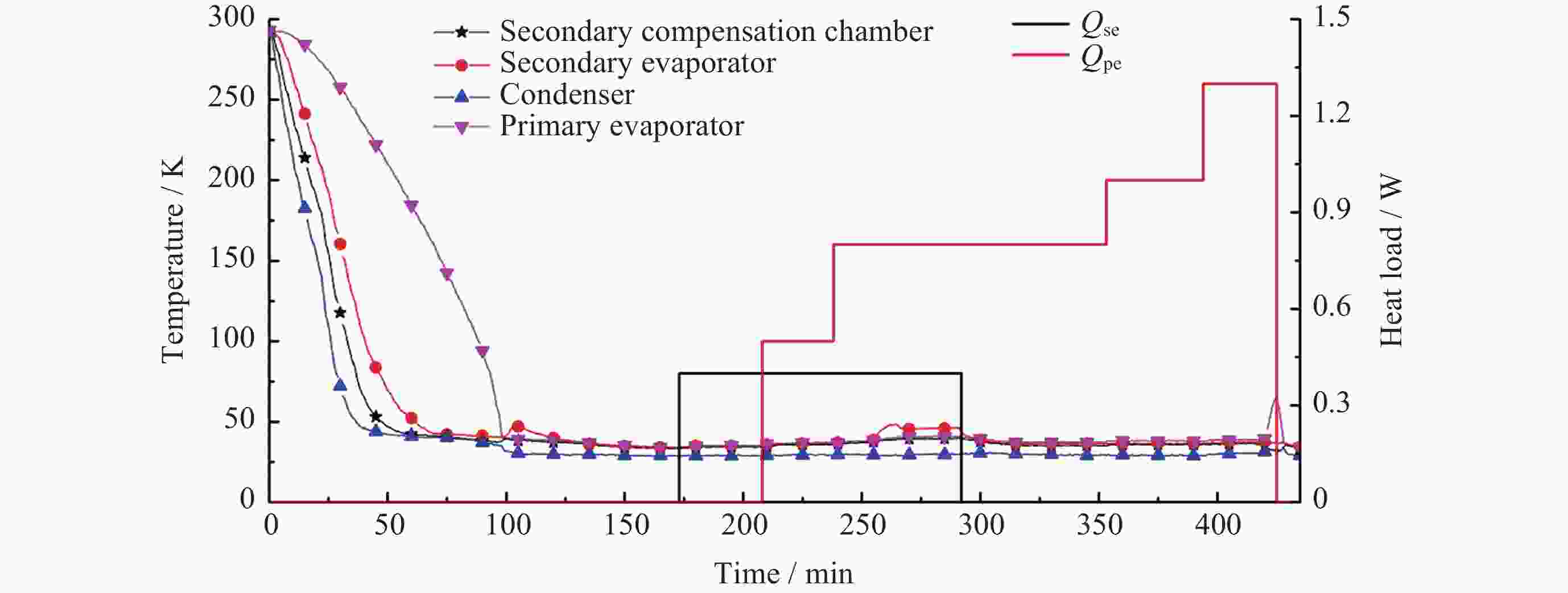
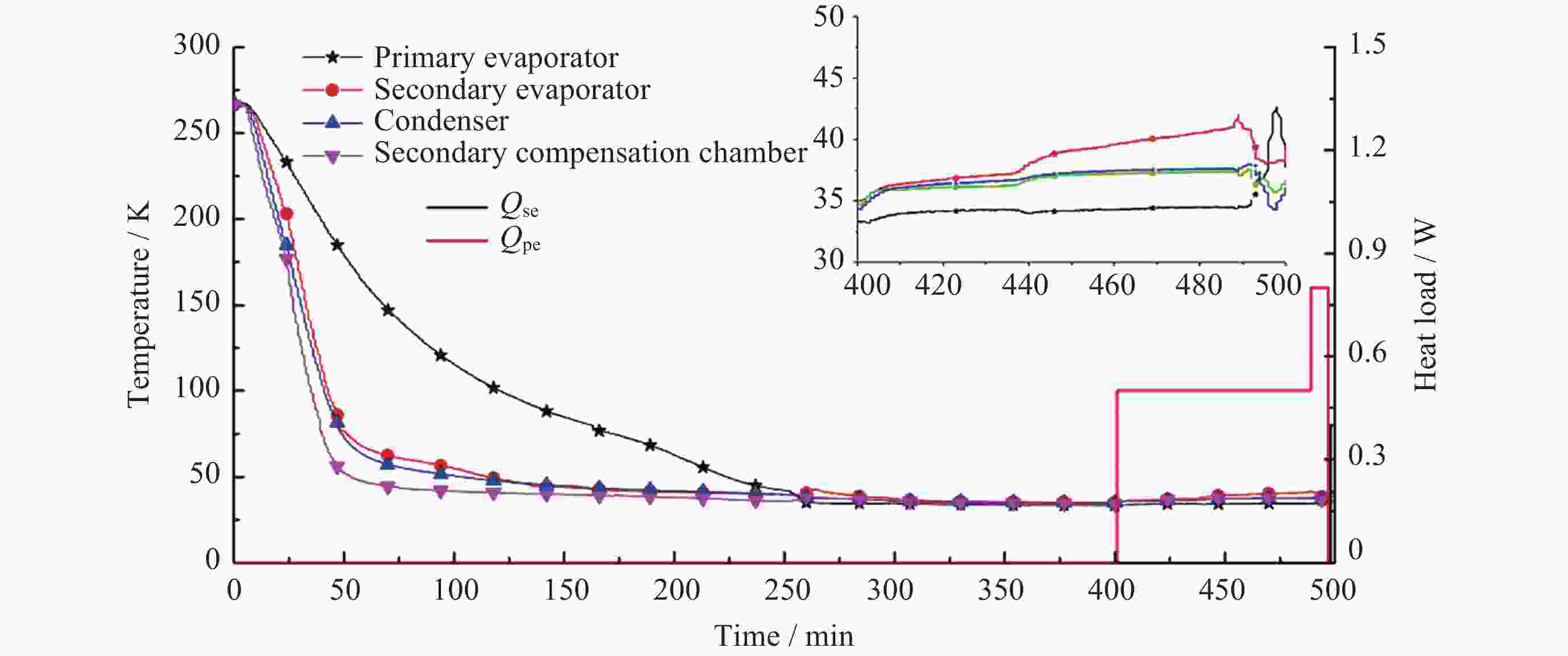
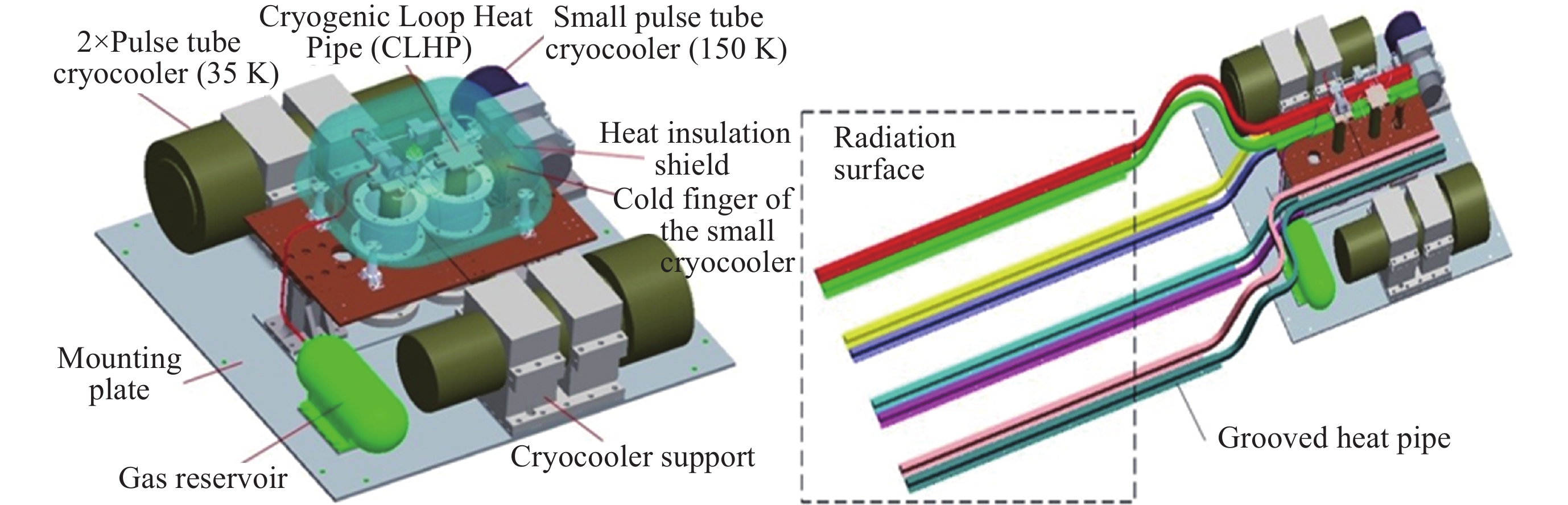
摘要: 为了解决空间红外探测系统的深低温散热问题, 保证红外探测器的低温工作环境, 基于脉冲管制冷机和深冷环路热管, 设计研制了一套35 K温区的深低温获取与热传输集成系统. 该系统由一套35 K温区氖工质深冷环路热管、两台35 K温区脉冲管制冷机、一台150 K温区脉冲管制冷机、隔热冷屏、测温/加热组件、控制系统等组成. 完成了地面单机级、整星级热真空测试, 并于2020年完成空间飞行测试. 在地面单机试验中开展了水平姿态和逆重力恶劣姿态下的传热测试, 保证了空间微重力下必定能稳定工作; 整星级测试验证了系统在卫星平台散热工况下的工作特性, 空间飞行测试获得了系统的空间微重力下的工作性能. 本文分析了系统在上述不同阶段的热性能, 包括超临界启动特性, 稳态运行性能等, 验证了相关设计的正确性, 重点对比了不同阶段的性能差异, 分析其可能的原因.Abstract: In order to solve the problem of cryogenic heat dissipation of space infrared detection system and ensure its cryogenic operating environment, an integrated system of cryogenic acquisition and heat transfer in 35 K temperature range was designed and developed based on pulse tube cooler and cryogenic loop heat pipe. The system consists of a neon cryogenic loop heat pipe, two sets of pulse tube cooler in 35 K temperature range, one pulse tube cooler in 150 K temperature range, thermal insulation screen, temperature measurement / heating components, control system. It has completed ground single-level and satellite-level thermal vacuum tests, and completed space flight tests in 2020. Heat transfer tests under horizontal attitude and anti-gravity conditions were carried out in the ground stand-alone test to ensure that the system could work stably in space microgravity. The whole-satellite test verified the working characteristics of the system under the heat dissipation condition of the satellite platform, and the space flight test obtained the working performance of the system under space microgravity. This paper introduces the thermal performance of the system in different stages, including supercritical start-up characteristics, steady-state operation performance, etc. The results have verified the correctness of relevant design, and this paper focuses on comparing the performance differences in different stages, and analyzes the possible reasons.
-
表 1 深冷环路热管结构参数
Table 1. Structure parameters of the cryogenic loop heat pipe
部件名称 结构参数 参数值 主蒸发器 壳体外径/内径 ×长度 /mm 13/11×50 毛细芯外径/内径 ×长度/mm 11/4×40 次蒸发器 壳体外径/内径 ×长度/mm 13/11×35 毛细芯外径/内径 ×长度/mm 11/4×37 主传输管线 液体管线外径/内径 ×长度/mm 3/2×600 冷凝器管线外径/内径 ×长度/mm 2/1×700 蒸气管线外径/内径 ×长度/mm 3/2×700 次传输管线 液体管线外径/内径 ×长度/mm 3/2×700 冷凝器管线外径/内径 ×长度/mm 2/1×260 蒸气管线外径/内径 ×长度/mm 3/2×30 毛细芯 孔隙度/ (%) 55 最大孔径/ μm 0.5 储气室 体积/ mL 400 表 2 不同姿态下的稳态运行温度对比
Table 2. Comparison of steady-state operating temperature under different conditions
主载荷/次载荷 逆重力工作温度T6/K 水平工作温度T6/K 0.5 W/0.4 W 35.0 33.3 0.8 W/0.4 W 35.1 33.9 1.0 W/0 W 36.1 35.5 -
[1] JACO C, NGUYEN T, TWARD E. High capacity two-stage coaxial pulse tube cooler[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2008, 985(1): 530-537 [2] TANCHON J, TROLLIER T, TRIQUENEAUX S, et al. 20-50 K and 40-80 K pulse tube coolers: two candidates for a low temperature cooling chain[J]. Cryogenics, 2010, 50(1): 55-60 doi: 10.1016/j.cryogenics.2009.10.007 [3] WILSON K B, FRALICK C C, GEDEON D R, et al. Sunpower's CPT60 pulse tube cryocooler[M]//MILLER S D, ROSS JR R G. Cryocoolers 14. Boulder: International Cryocooler Conference, Inc, 2007: 123-132 [4] GUO Yuandong, LIN Guiping, BAI Lizhan, et al. Experimental study on the supercritical startup of cryogenic loop heat pipes with redundancy design[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2016, 118: 353-363 doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2016.04.022 [5] PEREIRA H, HAUG F, SILVA P, et al. Cryogenic loop heat pipes for the cooling of small particle detectors at CERN[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2010, 1218(1): 1039-1046 [6] HOANG T T, O’CONNELL T A, KU J, et al. Performance demonstration of hydrogen advanced loop heat pipe for 20-30K cryocooling of far infrared sensors[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 5904, Cryogenic Optical Systems and Instruments XI. San Diego, USA: SPIE, 2005: 590410 [7] BUGBY D, MARLAND B, STOUFFER C, et al. Across-gimbal and miniaturized cryogenic loop heat pipes[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2003, 654(1): 218-226 [8] 郭元东. 15~40 K温区深冷环路热管技术的理论与实验研究[D]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学, 2019GUO Yuandong. Theoretical and Experimental Investigation of Cryogenic Loop Heat Pipe Technology Operating in 15~40 K[D]. Beijing: Beihang University, 2019 [9] HE Falong, DU Wangfang, ZHAO Jianfu, et al. Numerical simulation on the effects of component layout orientation on the performance of a neon-charged cryogenic loop heat pipe[J]. Microgravity Science and Technology, 2020, 32(2): 179-188 doi: 10.1007/s12217-019-09761-3 [10] GUO Yuandong, LIN Guiping, HE Jiang, et al. Experimental analysis of operation failure for a neon cryogenic loop heat pipe[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2019, 138: 96-108 doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2019.04.045 -
-




 郭元东:男, 1992年6月出生于河北省邢台市. 现为北京航空航天大学航空科学与工程学院副教授, 硕士生导师, 主要研究方向为航天器热控、热管、流动沸腾传热、微通道换热技术理论与实验研究. E-mail:
郭元东:男, 1992年6月出生于河北省邢台市. 现为北京航空航天大学航空科学与工程学院副教授, 硕士生导师, 主要研究方向为航天器热控、热管、流动沸腾传热、微通道换热技术理论与实验研究. E-mail: 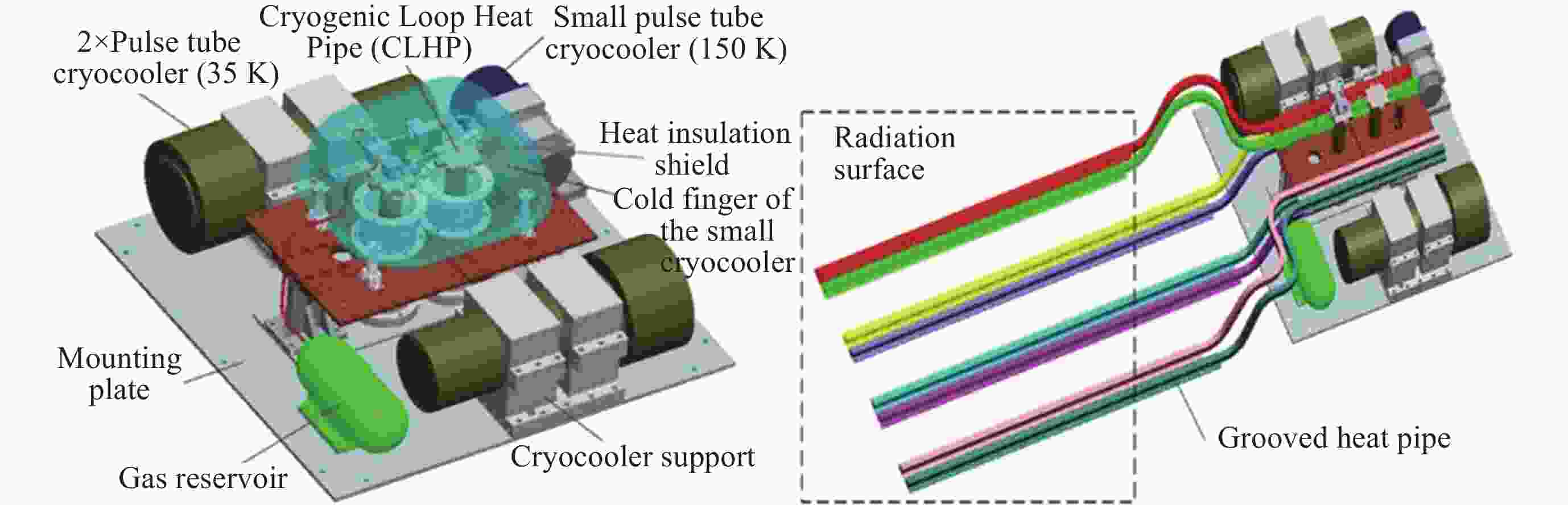
 下载:
下载: