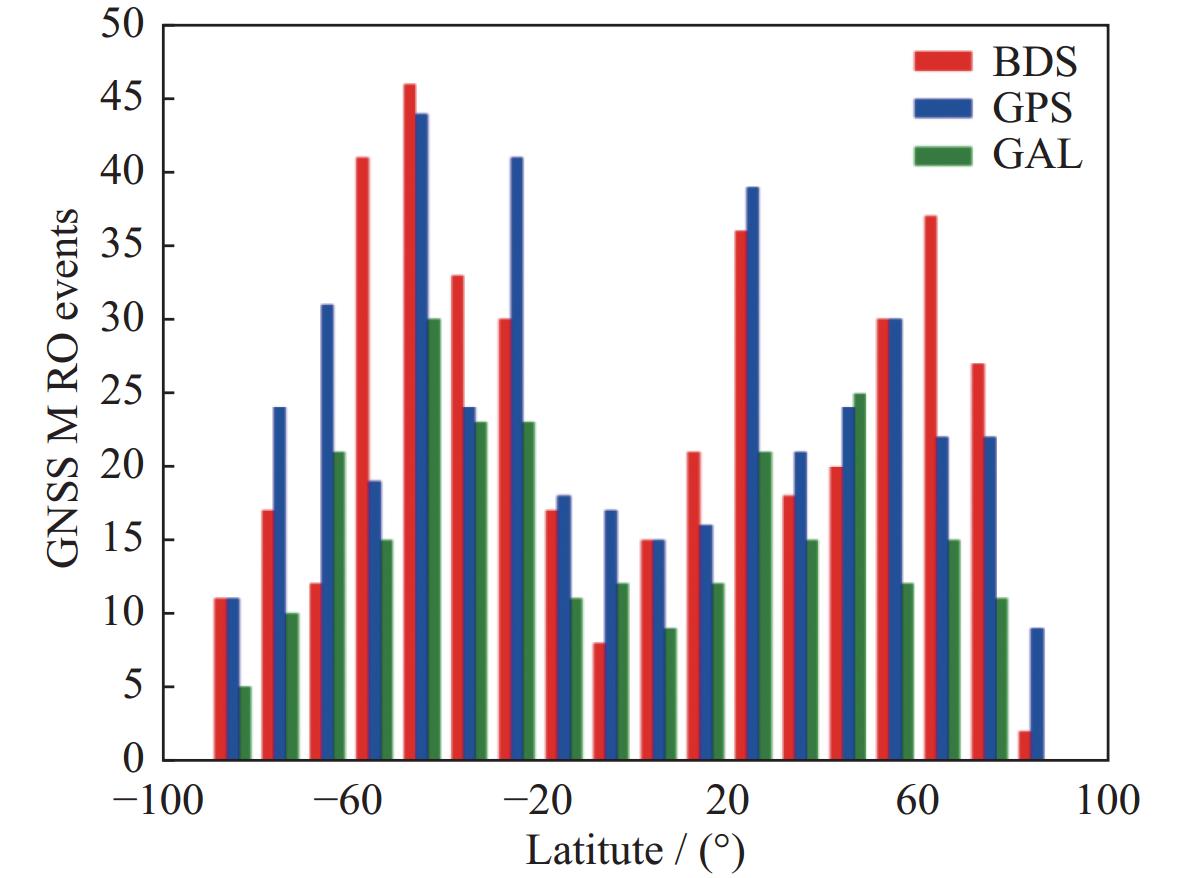
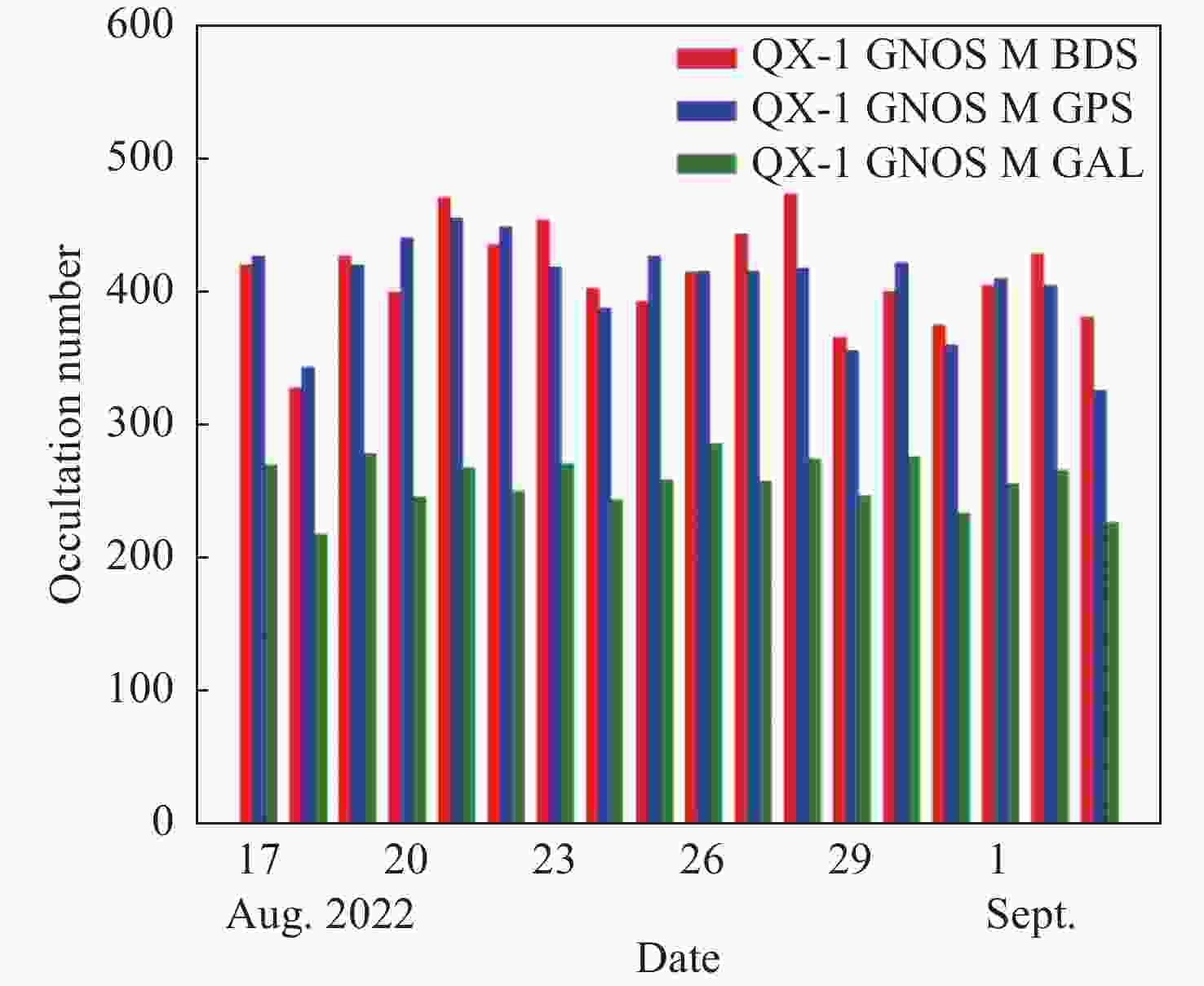
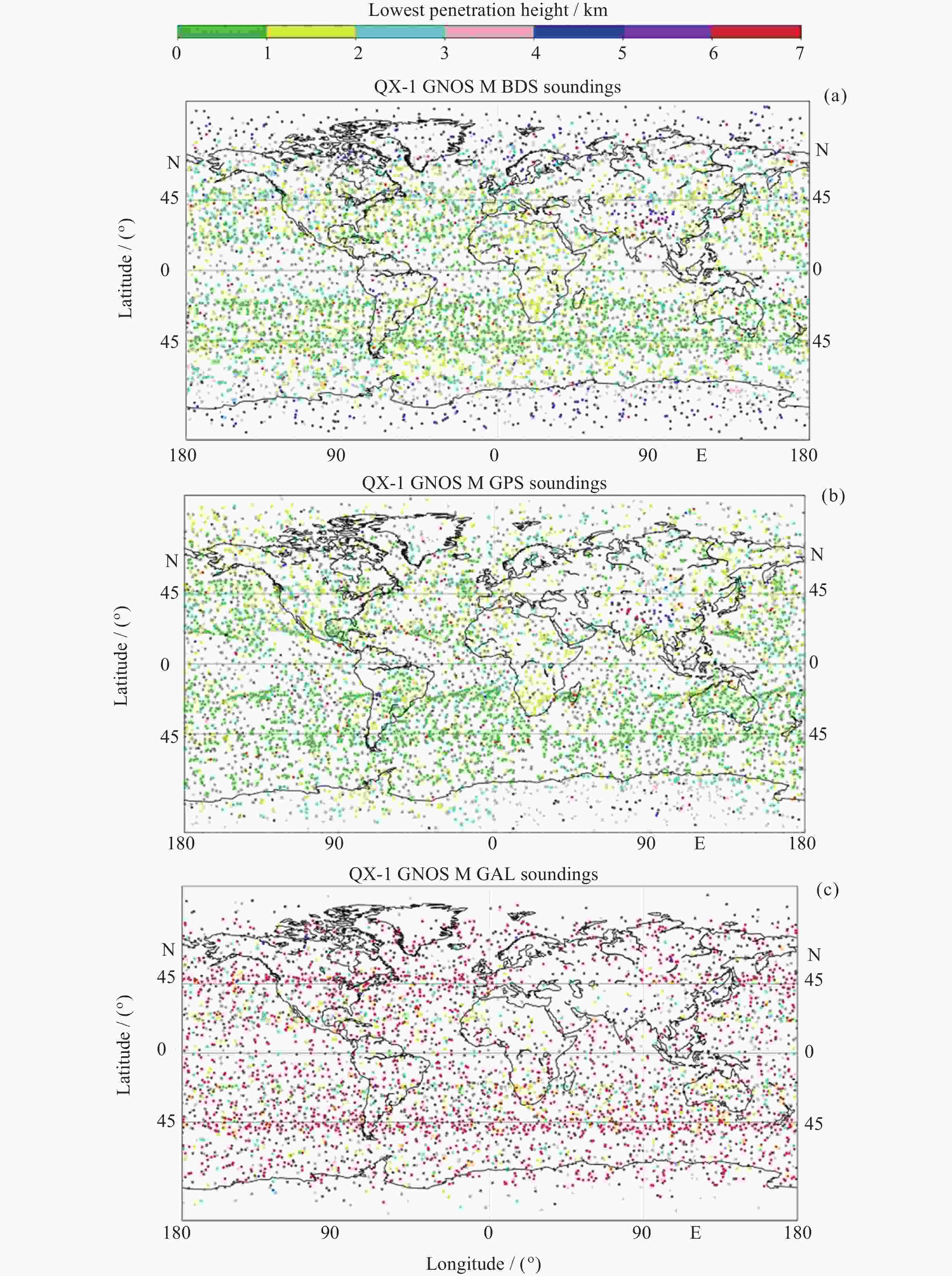
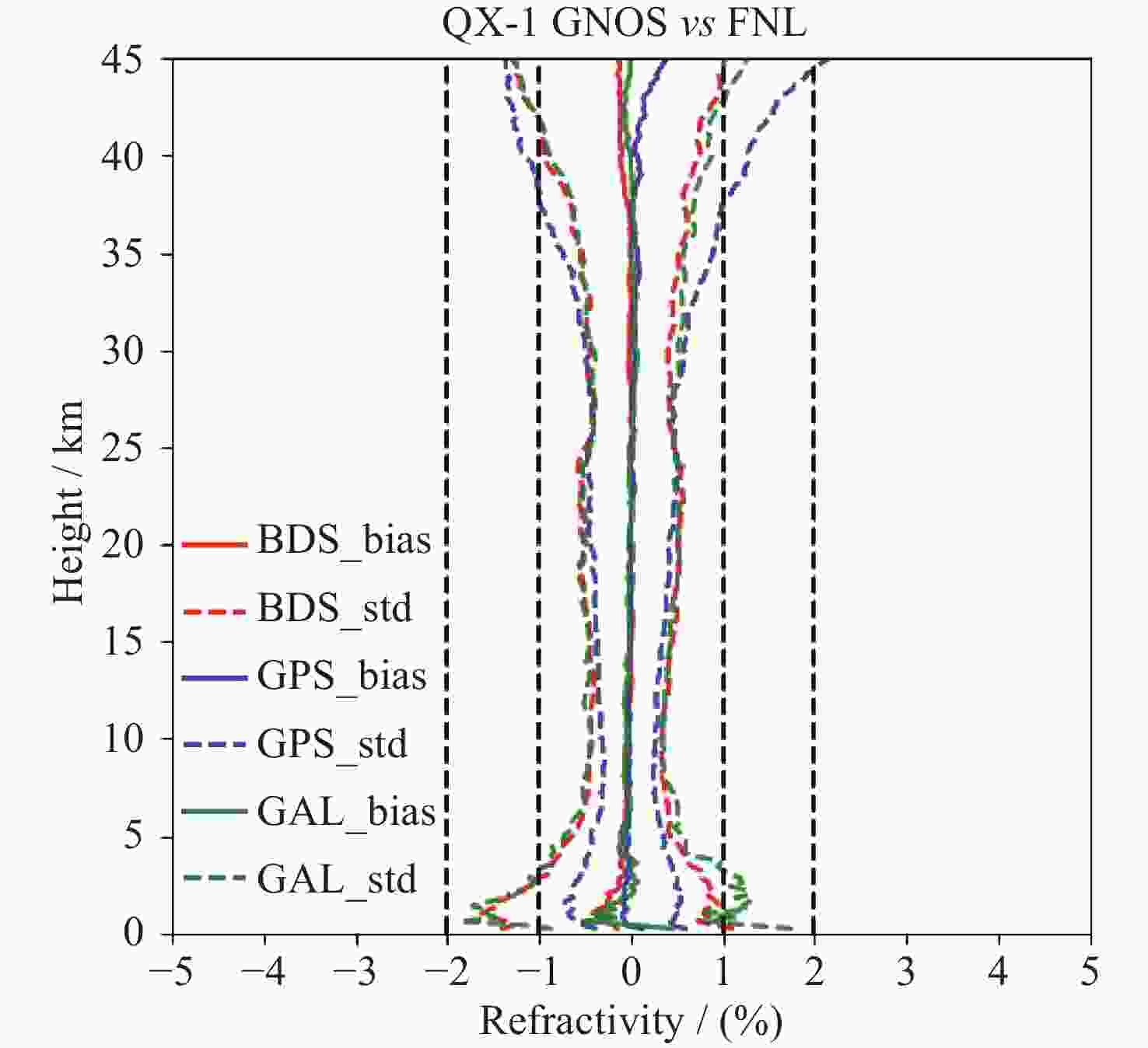
| [1] |
ROCKEN C, ANTHES R, EXNER M, et al. Analysis and validation of GPS/MET data in the neutral atmosphere[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 1997, 102(D25): 29849-29866 doi: 10.1029/97JD02400
|
| [2] |
WICERT J, BEYERLE G, KONIG R, et al. GPS radio occultation with CHAMP and GRACE: A first look at a new and promising satellite configuration for global atmospheric sounding[J]. Annales Geophysicae: Atmospheres, Hydrospheres and Space Sciences, 2005, 23(3): 653-658
|
| [3] |
仇通胜. 基于北斗三号的无线电掩星接收机信号处理关键技术研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2021. DOI: 10.27562/d.cnki.gkyyz.2021.000015QIU Tongsheng. Study on Key Technique of Signal Processing for BDS-3 Based Radio Occultation Receiver[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2021. DOI: 10.27562/d.cnki.gkyyz.2021.000015
|
| [4] |
ANTHES R A, BERNHARDT P A, CHEN Y, et al. The COSMIC/FORMOSAT-3 Mission: Early results[J]. Bulle tin of the American Meteorological Society, 2008, 89(3): 313-334 doi: 10.1175/BAMS-89-3-313
|
| [5] |
KUO Y H, SCHREINER W S, WANG J, et al. Comparison of GPS radio occultation soundings with radiosondes[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2005, 32(5). DOI: 10.1029/2004GL021443
|
| [6] |
SCHREINER W S, WEISS J P, ANTHES R A, et al. COSMIC‐2 radio occultation constellation: first results[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2020, 47(4): e2019GL086841 doi: 10.1029/2019GL086841
|
| [7] |
IURII C, IRINA Z, JOHN B, et al. Accuracy assessment of the quiet-time ionospheric F2 peak parameters as derived from COSMIC-2 multi-GNSS radio occultation measurements[J]. Journal of Space Weather and Space Climate, 2021, 11
|
| [8] |
LI Y, KIRCHENGAST G, SCHERLLIN-PIRSCHER B, et al. Dynamic statistical optimization of GNSS radio occultation bending angles: Advanced algorithm and performance analysis[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2015, 8(8): 3447-3465 doi: 10.5194/amt-8-3447-2015
|
| [9] |
BAI W H, SUN Y Q, DU Q F, et al. An introduction to the FY3 GNOS instrument and mountain-top tests[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2014, 7(6): 1817-1823 doi: 10.5194/amt-7-1817-2014
|
| [10] |
SUN Y Q, BAI W H, LIU C L, et al. The FengYun-3C radio occultation sounder GNOS: a review of the mission and its early results and science applications[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2018, 11(10): 5797-5811 doi: 10.5194/amt-11-5797-2018
|
| [11] |
WEI J D, LI Y ZHANG K F, et al. An evaluation of Fengyun-3C radio occultation atmospheric profiles over 2015-2018[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(13): 2116 doi: 10.3390/rs12132116
|
| [12] |
LIU Z Y, SUN Y Q, BAI W H, et al. Validation of preliminary results of thermal tropopause derived from FY-3C GNOS data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(9): 1139 doi: 10.3390/rs11091139
|
| [13] |
王树志, 朱光武, 白伟华, 等. 风云三号C星全球导航卫星掩星探测仪首次实现北斗掩星探测[J]. 物理学报, 2015, 64(8): 089301 doi: 10.7498/aps.64.089301WANG Shuzhi, ZHU Guangwu, BAI Weihua, et al. For the first time Fengyun-3C satellite-global navigation satellite system occultation sounder achieved spaceborne BeiDou system radio occultation[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2015, 64(8): 089301 doi: 10.7498/aps.64.089301
|
| [14] |
LIAO M, ZHANG P, YANG G L, et al. Preliminary validation of the refractivity from the new radio occultation sounder GNOS/FY-3C[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2016, 9(2): 781-792 doi: 10.5194/amt-9-781-2016
|
| [15] |
廖蜜, 张鹏, 刘健, 等. 风云卫星的掩星干大气温度廓线精准度特征[J]. 应用气象学报, 2023, 34(3): 270-281LIAO Mi, ZHANG Peng, LIU Jian, et al. Accuracy and stability of radio occultation dry temperature profiles from Fengyun satellite[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 2023, 34(3): 270-281
|
| [16] |
刘艳, 孟祥广, 白伟华, 等. FY-3D卫星的北斗掩星分布特征与误差特性[J]. 空间科学学报, 2022, 42(3): 476-484 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.03.210208019LIU Yan, MENG Xiangguang, BAI Weihua, et al. Analysis of Beidou Radio Occultation Data from FY-3D Satellite[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2022, 42(3): 476-484 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.03.210208019
|
| [17] |
HUANG F X, XIA J M, YIN C, et al. Assessment of FY-3E GNOS II GNSS-R global wind product[J]. IEEE Jour nal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2022, 15: 7899-7912. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3205331
|
| [18] |
杨光林, 孙越强, 白伟华, 等. 风云三号C星GNOS北斗掩星电离层探测初步结果[J]. 空间科学学报, 2019, 39(1): 36-45 doi: 10.11728/cjss2019.01.036YANG Guanglin, SUN Yueqiang, BAI Weihua, et al. Beidou navigation satellite system sounding of the ionosphere from FY-3C GNOS: preliminary results[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2019, 39(1): 36-45 doi: 10.11728/cjss2019.01.036
|
| [19] |
DU Q F, SUN Y Q, BAI W H, et al. The on-orbit performance of FY-3D GNOS[C]//International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Yokohama: IEEE, 2019: 7669-7671
|
| [20] |
ZHANG H, HUANGFU J, WANG X, et al. Comparative analysis of Binhu and Cosmic-2 radio occultation data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(19): 4958 doi: 10.3390/rs14194958
|
| [21] |
BEYERLE G, SCHMIDT T, MICHALAK G, et al. GPS radio occultation with GRACE: Atmospheric profiling utilizing the zero difference technique[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2005, 32(13): L13806
|





 刘智勇 男, 1982年出生于黑龙江省哈尔滨市, 现为武汉大学遥感信息工程学院在读博士研究生, 工程师, 主要从事资源与环境、遥感卫星图像智能处理等领域工作. E-mail:
刘智勇 男, 1982年出生于黑龙江省哈尔滨市, 现为武汉大学遥感信息工程学院在读博士研究生, 工程师, 主要从事资源与环境、遥感卫星图像智能处理等领域工作. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: