FY3D/GNOS大气掩星探测温度与TIMED/SABER探测温度和NRLMSISE00 模式温度的比较
doi: 10.11728/cjss2024.03.2023-0072 cstr: 32142.14.cjss2024.03.2023-0072
Comparison of FY3D/GNOS Atmospheric Occultation Detection Temperature with TIMED/ SABER Temperature and NRLMSISE00 Model Temperature
-
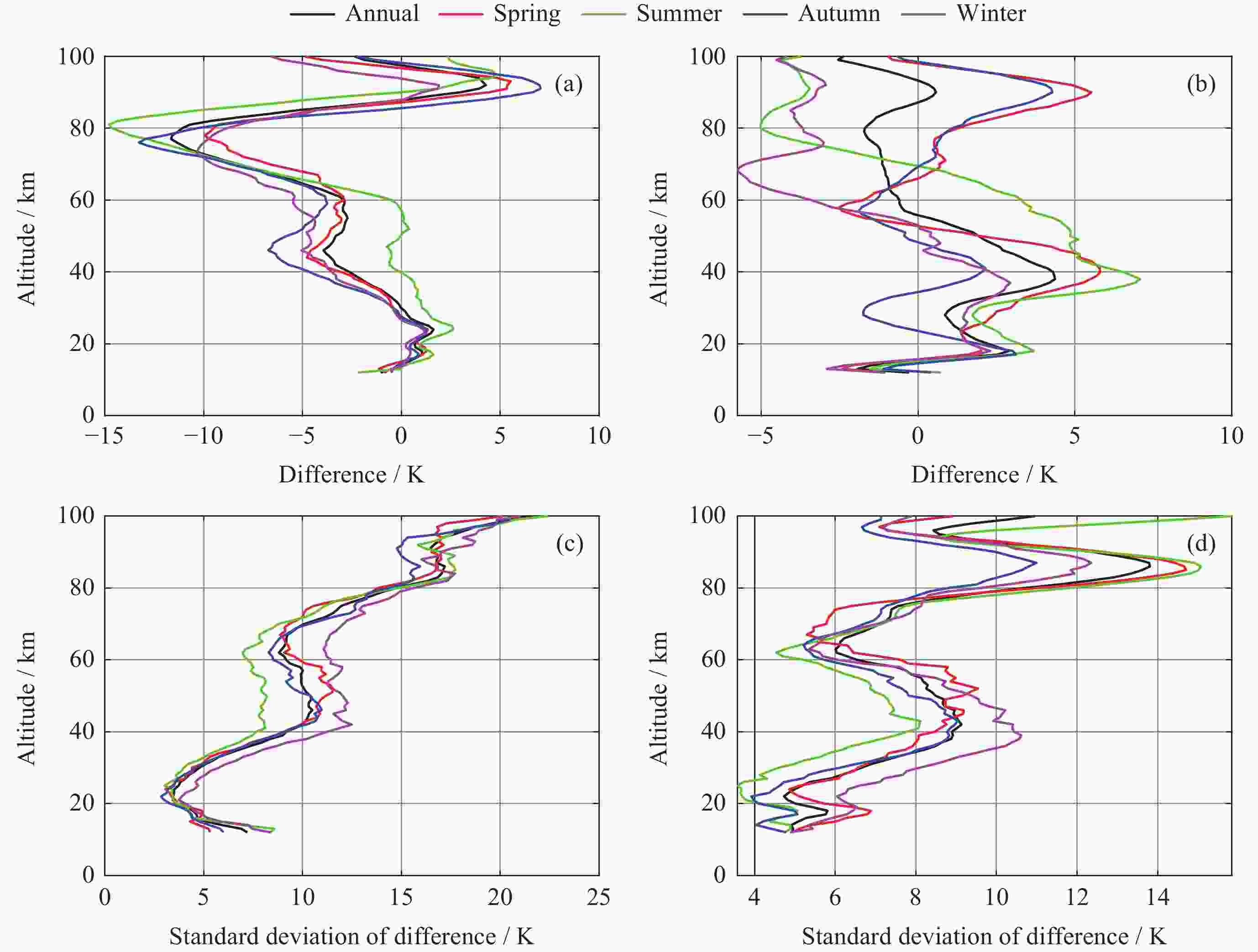
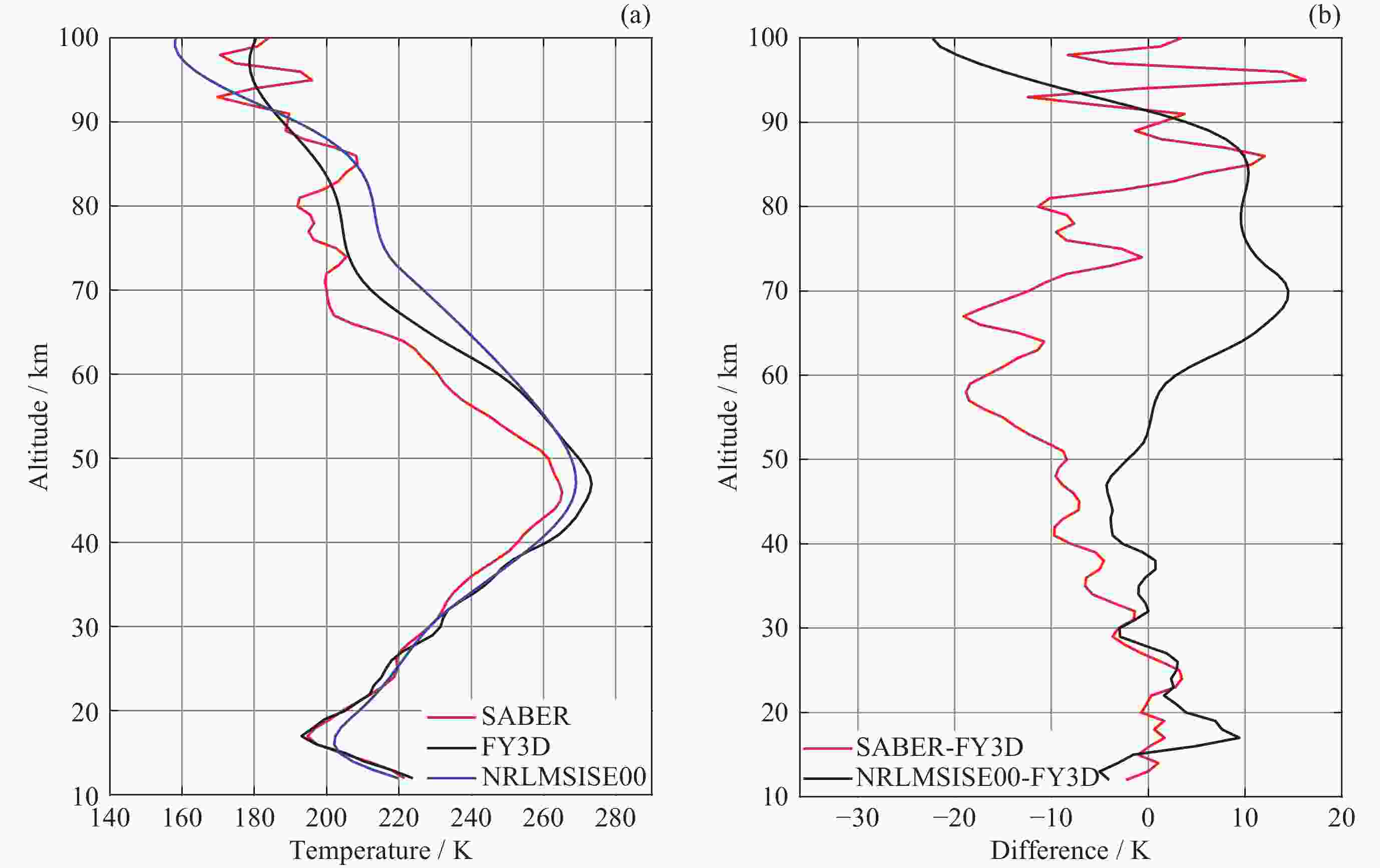
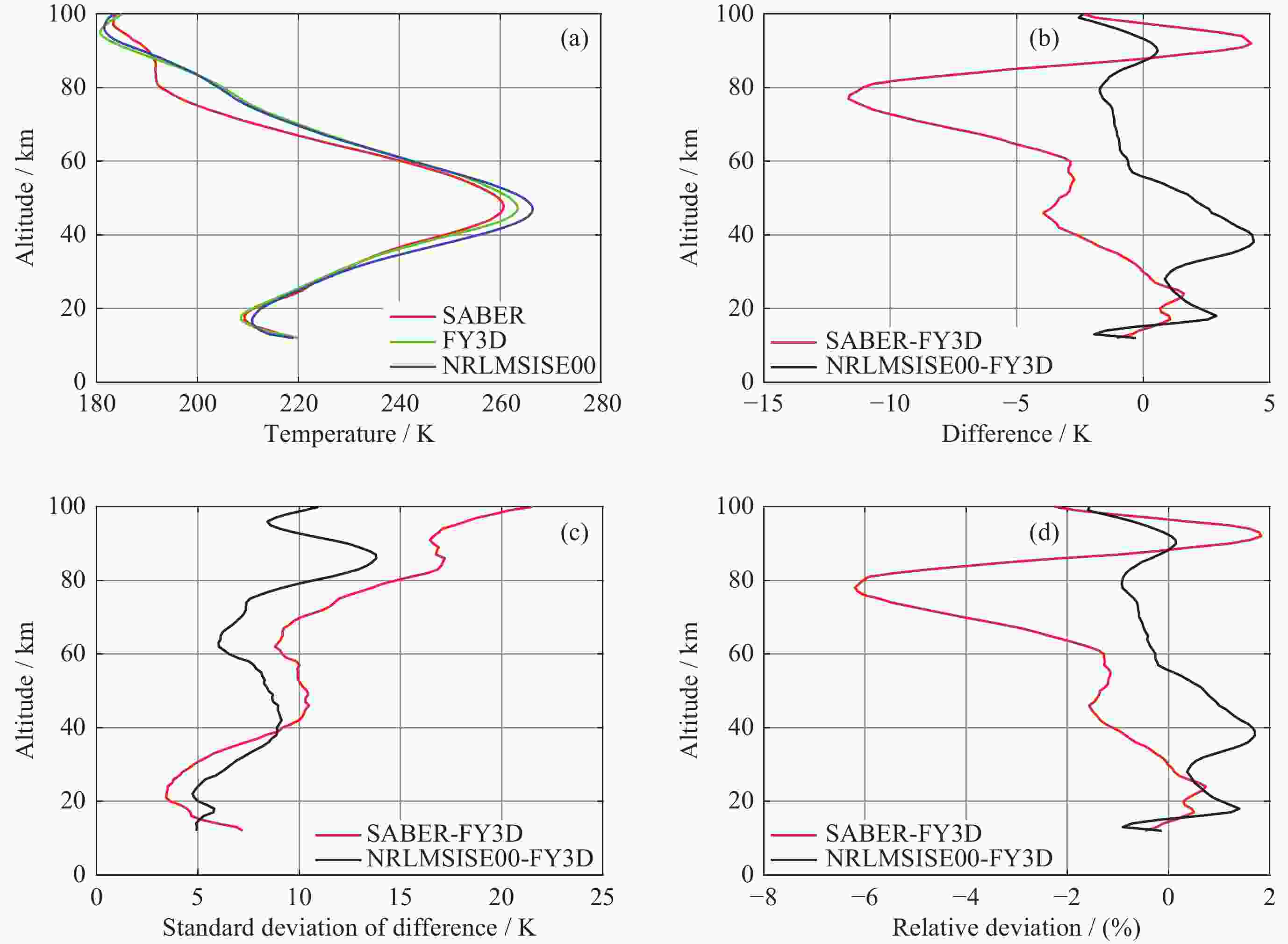
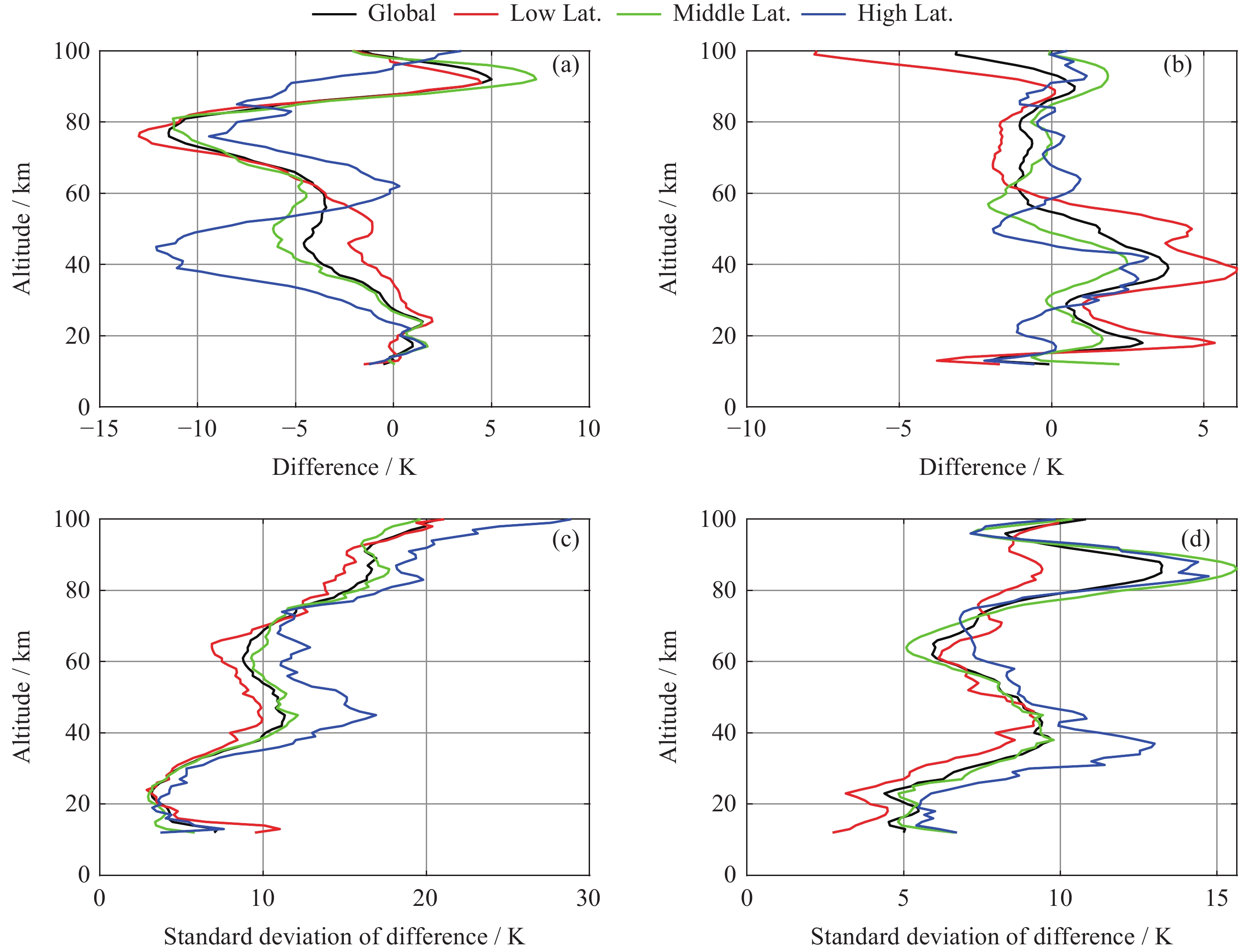
摘要: 大气温度数据的精确探测对于研究中高层大气的结构特征和动力学过程具有重要意义. 利用2019年1月至2021年12月共3年的FY3D掩星观测数据, 借助TIMED/SABER探测数据和NRLMSISE00大气模式数据, 对12~100 km范围内的大气温度数据进行比较. 统计分析SABER-FY3D温度偏差(TSABER–TFY3D)和NRLMSISE00-FY3D温度偏差(TNRLMSISE00–TFY3D)及其随纬度、季节的分布和南北半球的差异. 结果显示, 三种温度数据随高度变化趋势是大体一致的, SABER-FY3D温度偏差在12~30 km高度范围内为正偏差(0~1.8 K), 随高度升高, 温度偏差从30 km处的0 K增加到77 km处的$ - $11.6 K. NRLMSISE00-FY3D温度偏差在平流层为正偏差(0~4.4 K), 在中间层和低热层为负偏差($ - $2~0 K). 两种温度偏差随纬度和季节都存在明显的变化特征. 60 km以下, SABER-FY3D温度偏差在低纬地区较小($ - $3.8~1.8 K), 高纬地区较大($ - $12~1.6 K), 夏季较小($ - $0.5~2.2 K), 冬季较大($ - $6.2~1 K); NRLMSISE00-FY3D温度偏差正好相反, 在高纬地区较小($ - $1.6~2.4 K), 低纬地区较大($ - $3.9~6.1 K), 冬季较小($ - $2~2.2 K), 夏季较大($ - $1.3~7.1 K). 两类月平均温度偏差的零偏差线所在高度在南北半球均存在春夏季节较高, 秋冬季节较低的特征. 冬季40~60 km高度区域内, 北半球的SABER-FY3D平均温度负偏差比南半球的明显.
-
关键词:
- FY3D大气掩星温度 /
- 温度偏差 /
- 季节变化 /
- 纬度变化
Abstract: The accurate detection of atmospheric temperature is of great significance for studying the structural characteristics and dynamic processes of the middle and upper atmosphere. The GNOS (Global Navigation Satellite System Occultation Sounder) mounted on the FY3D has been carrying out atmospheric sounding since 15 November 2017. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the atmospheric temperature data products of the FY3D satellite. This study was conducted to comparatively analyze the atmospheric temperature data within the range of 12~100 km based on FY3D occultation observation data for 3 years from January 2019 to December 2021, with the aid of TIMED/SABER detection data and NRLMSISE00 atmospheric model data. The SABER-FY3D temperature deviation (TSABER–TFY3D) and NRLMSISE00-FY3D temperature deviation (TNRLMSISE00–TFY3D) and their distribution with latitude, season, and the difference between the northern and southern hemispheres were analyzed. The results show that the three sets of temperature data have generally consistent trend with change in height. SABER-FY3D temperature deviation is positive (0~1.8 K) in the altitude range of 12~30 km, and as the altitude increases, the temperature deviation increases from 0 K at 30 km to $ - $11.6 K at 77 km. NRLMSISE00-FY3D temperature deviation is positive (0~4.4 K) in the stratosphere, and negative ($ - $2~0 K) in the mesosphere and low thermosphere. Both temperature deviations show significant variations with latitude and season. Below 60 km, SABER-FY3D temperature deviation is smaller in the low-latitude region ($ - $3.8~1.8 K) and larger in the high-latitude region ($ - $12~1.6 K), smaller in summer ($ - $0.5~2.2 K) and larger in winter ($ - $6.2~1 K); NRLMSISE00-FY3D temperature deviation is just the opposite, smaller in the high-latitude region ($ - $1.6~2.4 K) and larger in the low-latitude ($ - $3.9~6.1 K), smaller in winter ($ - $2~2.2 K),, and larger in summer($ - $1.3~7.1 K). The zero deviation lines of the two types of monthly average temperature deviations show characteristics of being higher in spring and summer and lower autumn and winter in both hemispheres. In the winter, in the altitude region of 40~60 km, the negative deviation of the SABER-FY3D average temperature in the northern hemisphere is more obvious than that in the southern hemisphere. -
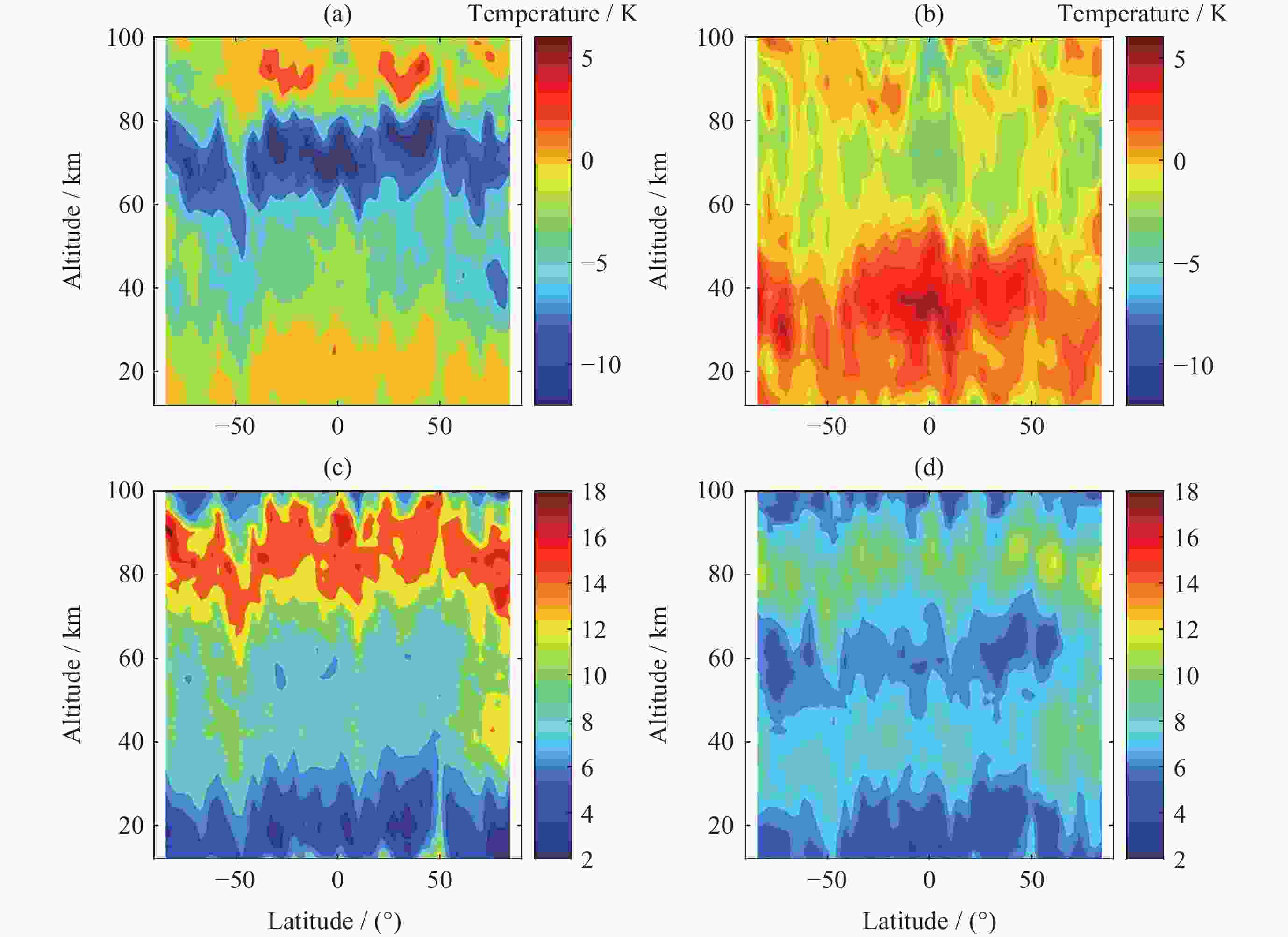
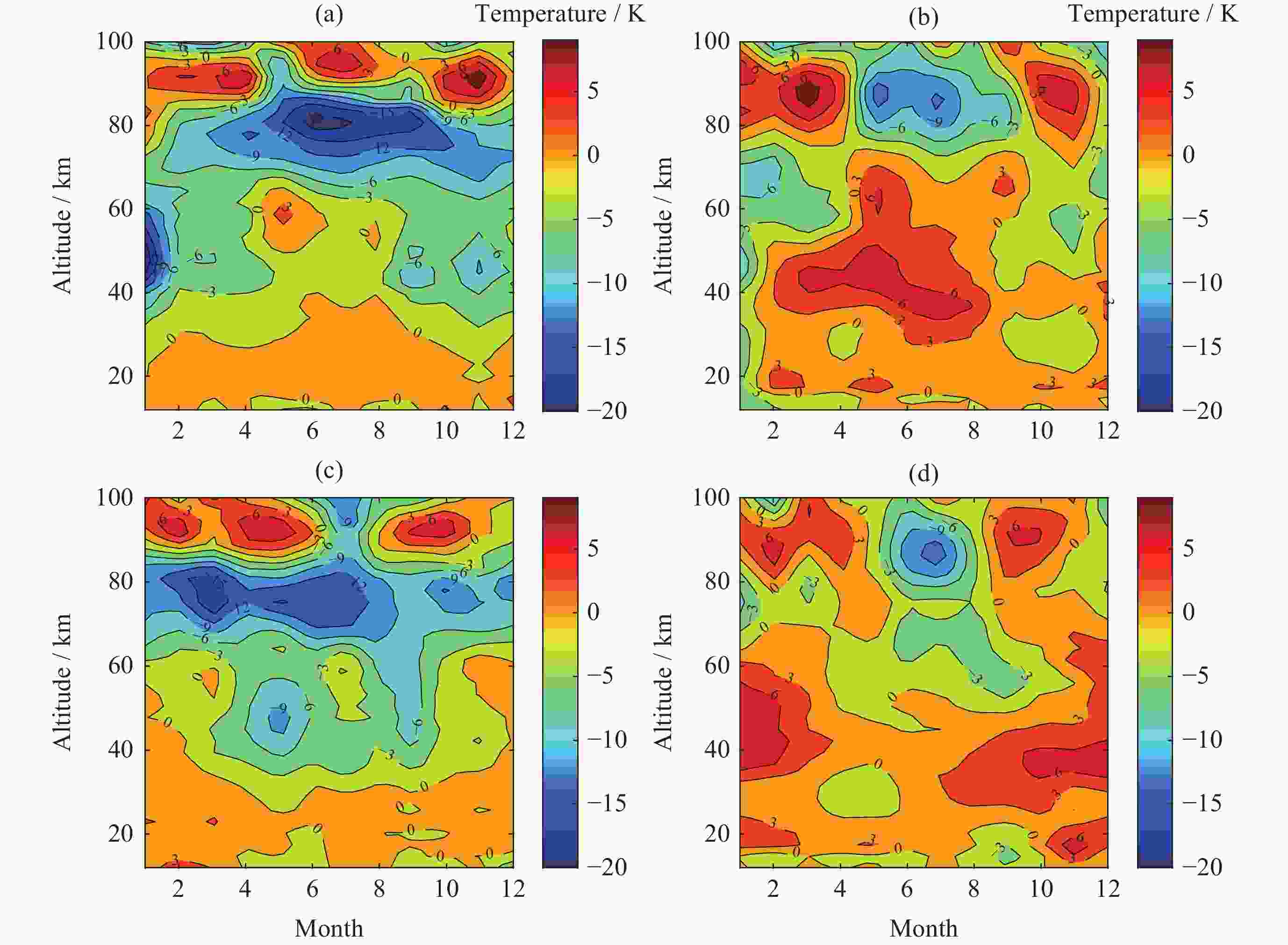
图 7 北半球SABER-FY3D(a)和NRLMSISE00-FY3D(b)月平均温度偏差以及南半球SABER-FY3D(c)和NRLMSISE00-FY3D(d)月平均温度偏差随月份和高度变化
Figure 7. Monthly mean temperature difference in the northern hemisphere of SABER-FY3D (a) and NRLMSISE00-FY3D (b) with month and altitude. Monthly mean temperature difference in the southern hemisphere of SABER-FY3D (c) and NRLMSISE00-FY3D (d) with month and altitude
表 1 纬度和季节划分标准
Table 1. Latitude and seasonal criteria
分类 北半球 南半球 纬度 低纬 0°-30°N 30°S-0° 中纬 30°-60°N 60°-30°S 高纬 60°-90°N 90°-60°S 季节 春季 3-5月 9-11月 夏季 6-8月 12-2月 秋季 9-11月 3-5月 冬季 12-2月 6-8月 表 2 FY3D/GNOS与TIMED/SABER匹配数据分布情况
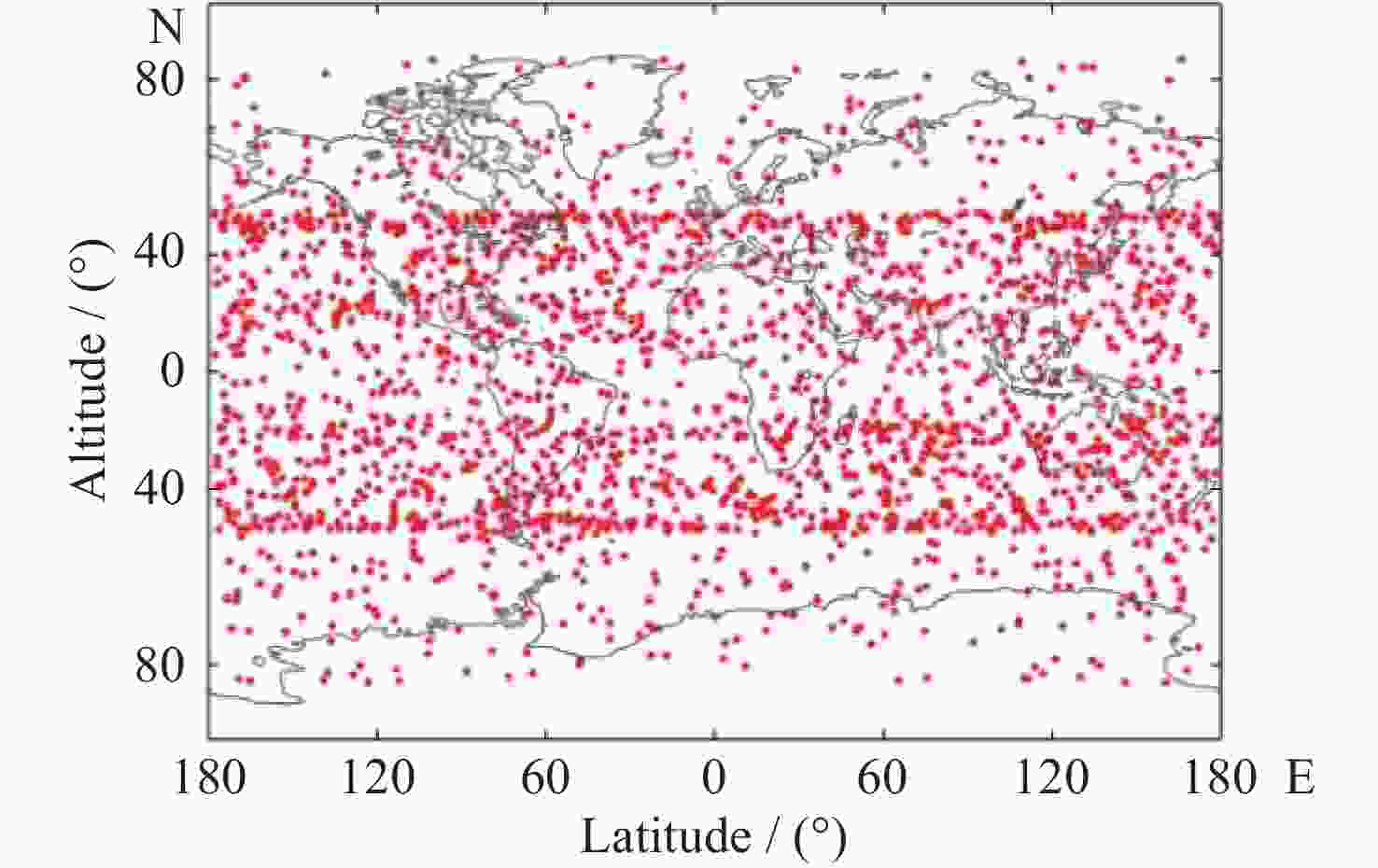
Table 2. Distribution of FY3D/GNOS and TIMED/SABER matching data
分类 匹配数目 纬度 低纬 839 中纬 1194 高纬 302 季节 春季 470 夏季 688 秋季 643 冬季 534 年份 2019年 737 2020年 779 2021年 819 总共 2335 -
[1] LIAO M, ZHANG P, YANG G L, et al. Preliminary validation of the refractivity from the new radio occultation sounder GNOS/FY-3C[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2016, 9(2): 781-792 doi: 10.5194/amt-9-781-2016 [2] WANG D W, TIAN Y S, SUN Y Q, et al. Preliminary in-orbit evaluation of GNOS on FY3D satellite[C]//Proceedings of 2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS). Valencia, Spain: IEEE, 2018 [3] 徐晓华, 朱洲宗, 罗佳. 利用IGRA2探空数据和COSMIC掩星资料对FY-3C掩星中性大气产品进行质量分析[J]. 武汉大学学报·信息科学版, 2020, 45(3): 384-393XU Xiaohua, ZHU Zhouzong, LUO Jia. Quality analysis of the neutral atmospheric products from FY‐3C radio occultation based on IGRA2 Radiosonde data and COSMIC radio occulation products[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2020, 45(3): 384-393 [4] 郭佳宾, 金双根. 利用FY-3C卫星GNSS掩星数据分析中国区域对流层顶参数变化[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2021, 41(1): 21-26GUO Jiabin, JIN Shuanggen. Variations of tropopause parameters over China from FY-3C GNSS radio occultation observations[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2021, 41(1): 21-26 [5] BI Y M, YANG Z D, ZHANG P, et al. An introduction to China FY3 radio occultation mission and its measurement simulation[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2012, 49(7): 1191-1197 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2012.01.014 [6] 廖蜜. 风云GNOS大气掩星资料处理方法与误差分析研究[D]. 北京: 中国气象科学研究院, 2020LIAO Mi. Study on the Retrieval and Error Analysis of Radio Occultation Data on FY Series[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences, 2020 [7] DU Q F, SUN Y Q, BAI W H, et al. The on-orbit performance of FY-3D GNOS[C]//Proceedings of 2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Yokohama, Japan: IEEE, 2019: 7669-7671 [8] BORMANN N, DUNCAN D, ENGLISH S, et al. Growing operational use of FY-3 data in the ECMWF system[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2021, 38(8): 1285-1298 doi: 10.1007/s00376-020-0207-3 [9] REMSBERG E E, MARSHALL B T, GARCIA-COMAS M, et al. Assessment of the quality of the Version 1.07 temperature-versus-pressure profiles of the middle atmosphere from TIMED/SABER[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2008, 113(D17): D17101 [10] GARCÍA-COMAS M, LÓPEZ-PUERTAS M, MARSHALL B T, et al. Errors in Sounding of the Atmosphere using Broadband Emission Radiometry (SABER) kinetic temperature caused by non-local-thermodynamic-equilibrium model parameters[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2008, 113(D24): D24106 [11] MERTENS C J, MLYNCZAK M G, LÓPEZ-PUERTAS M, et al. Retrieval of mesospheric and lower thermospheric kinetic temperature from measurements of CO2 15 μm Earth limb emission under non-LTE conditions[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2001, 28(7): 1391-1394 doi: 10.1029/2000GL012189 [12] 宫晓艳, 胡雄, 吴小成, 等. COSMIC大气掩星与SABER/TIMED探测温度数据比较[J]. 地球物理学报, 2013, 56(7): 2152-2162GONG Xiaoyan, HU Xiong, WU Xiaocheng, et al. Comparison of temperature measurements between COSMIC atmospheric radio occultation and SABER/TIMED[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2013, 56(7): 2152-2162 [13] 徐寄遥, 纪巧, 袁韡, 等. TIMED卫星探测的全球大气温度分布及其与经验模式的比较[J]. 空间科学学报, 2006, 26 (3): 177-182XU Jiyao, JI Qiao, YUAN Wei, et al. Comparison between the TIMED observed global temperature distribution and the NRLMSISE-00 empirical atmospheric model[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2006, 26 (3): 177-182 [14] MLYNCZAK M G, DANIELS T, HUNT L A, et al. Radiometric stability of the SABER instrument[J]. Earth and Space Science, 2020, 2(7): e2019EA001011 [15] MLYNCZAK M G, MARSHALL B T, GARCIA R R, et al. Algorithm stability and the long‐term geospace data record from TIMED/SABER[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2023, 50(5): e2022GL102398 doi: 10.1029/2022GL102398 [16] BAI W H, SUN Y Q, DU Q F, et al. An introduction to the FY3 GNOS instrument and mountain-top tests[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2014, 7(6): 1817-1823 doi: 10.5194/amt-7-1817-2014 [17] KUO Y H, SCHREINER W S, WANG J, et al. Comparison of GPS radio occultation soundings with radiosondes[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2005, 32(5): L05817 [18] 徐晓华, 罗佳. COSMIC掩星折射指数廓线的统计验证[J]. 武汉大学学报·信息科学版, 2009, 34(2): 214-217XU Xiaohua, LUO Jia. Statistical validation of COSMIC radio occultation refractivity profiles[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2009, 34(2): 214-217 [19] 徐晓华, 汪海洪. 不同季节GPS掩星廓线精度的比较研究[J]. 武汉大学学报·信息科学版, 2010, 35(6): 639-643XU Xiaohua, WANG Haihong. Comparison of precision of GPS Radio occultation profiles in different seasons[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2010, 35(6): 639-643 -
-





 刘红珊 女, 1999年5月出生于云南省昆明市, 硕士研究生. 硕士就读于中国科学院大学国家空间科学中心, 专业为空间物理学, 主要研究方向为中高层大气物理与化学. E-mail:
刘红珊 女, 1999年5月出生于云南省昆明市, 硕士研究生. 硕士就读于中国科学院大学国家空间科学中心, 专业为空间物理学, 主要研究方向为中高层大气物理与化学. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: