ICON/MIGHTI与TIMED/SABER探测温度数据的对比
doi: 10.11728/cjss2024.05.2023-0094 cstr: 32142.14.cjss2024.05.2023-0094
Comparative between Temperature Data Detected by ICON/MIGHTI and TIMED/SABER
-
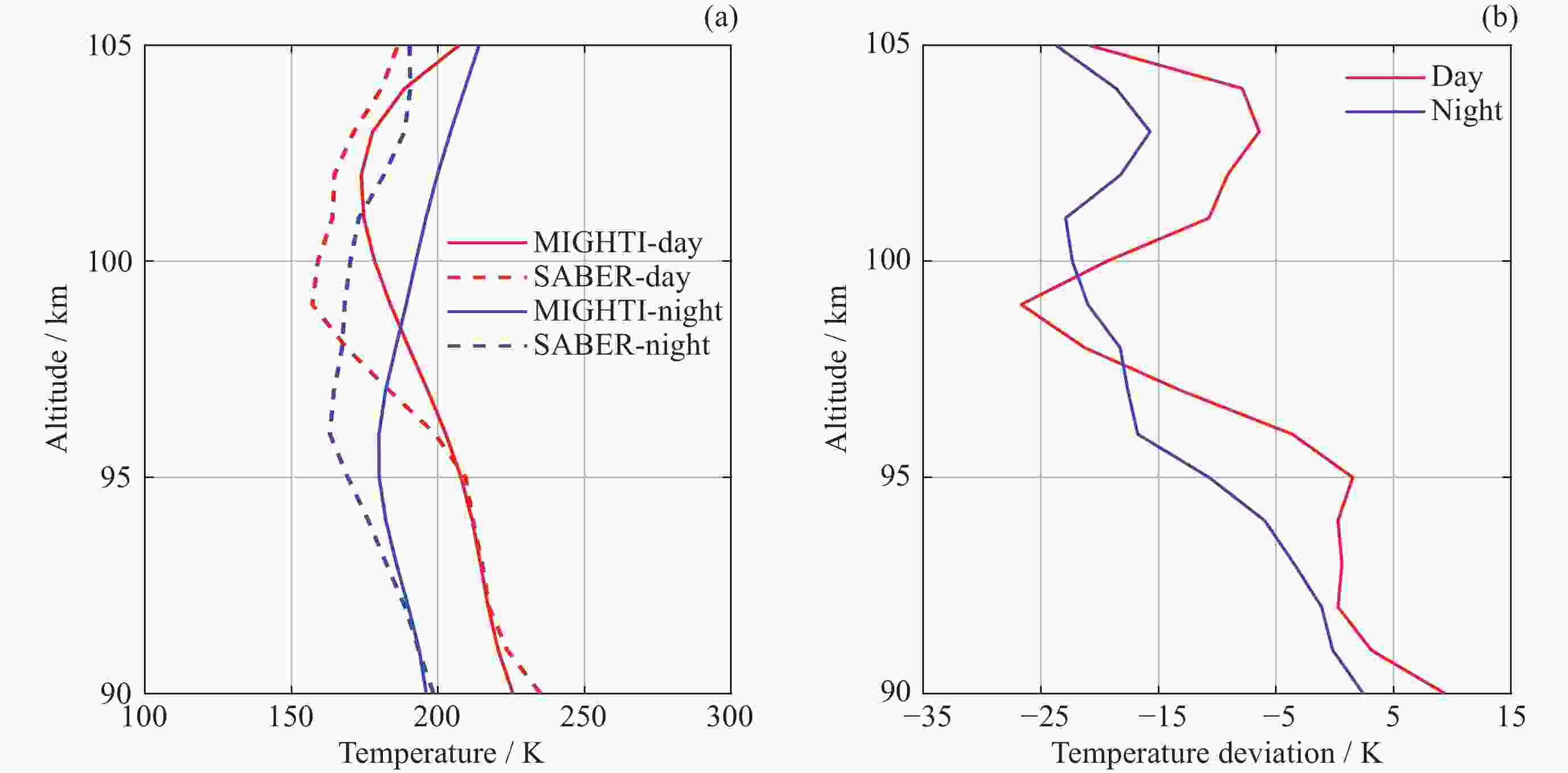
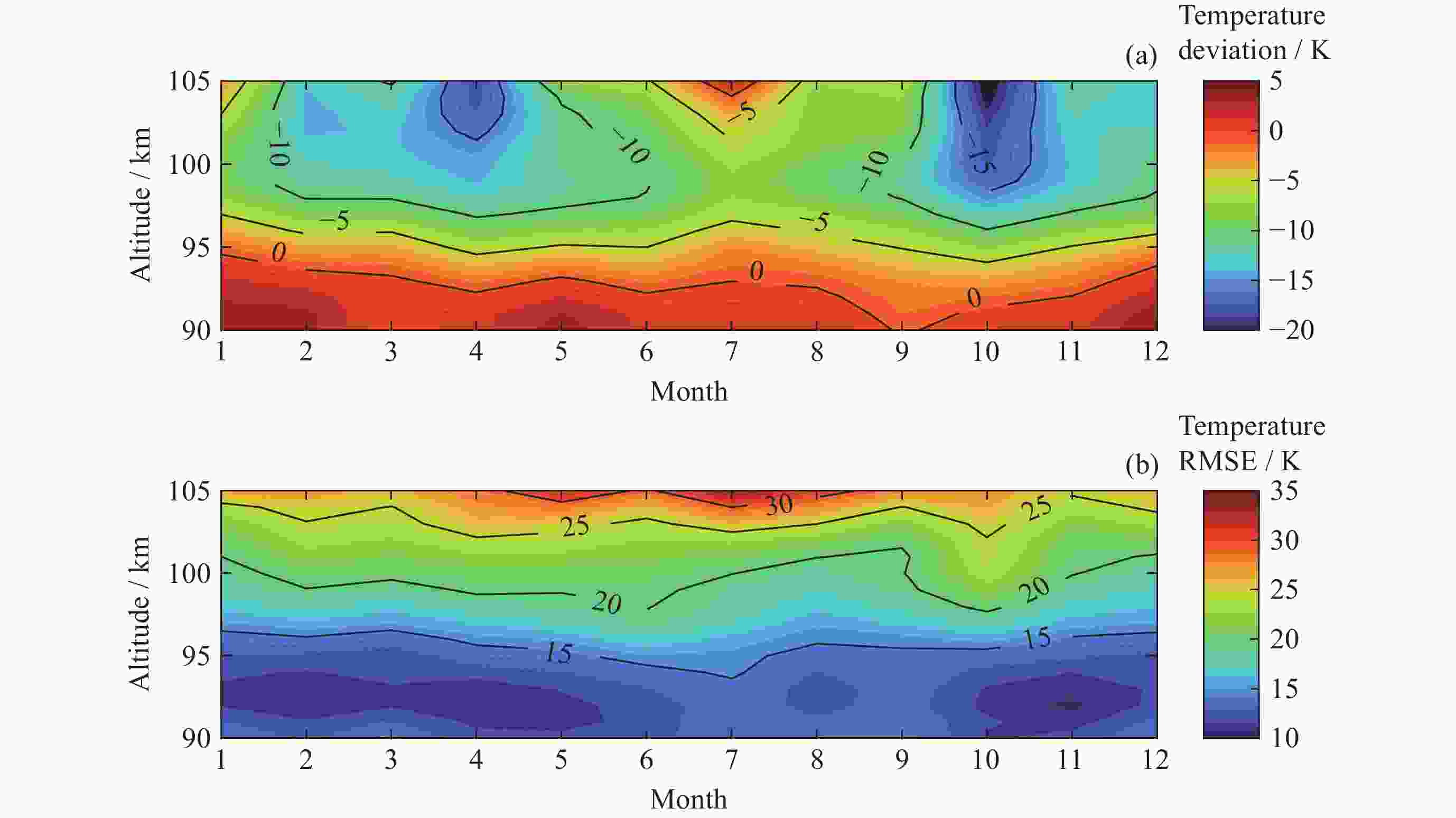
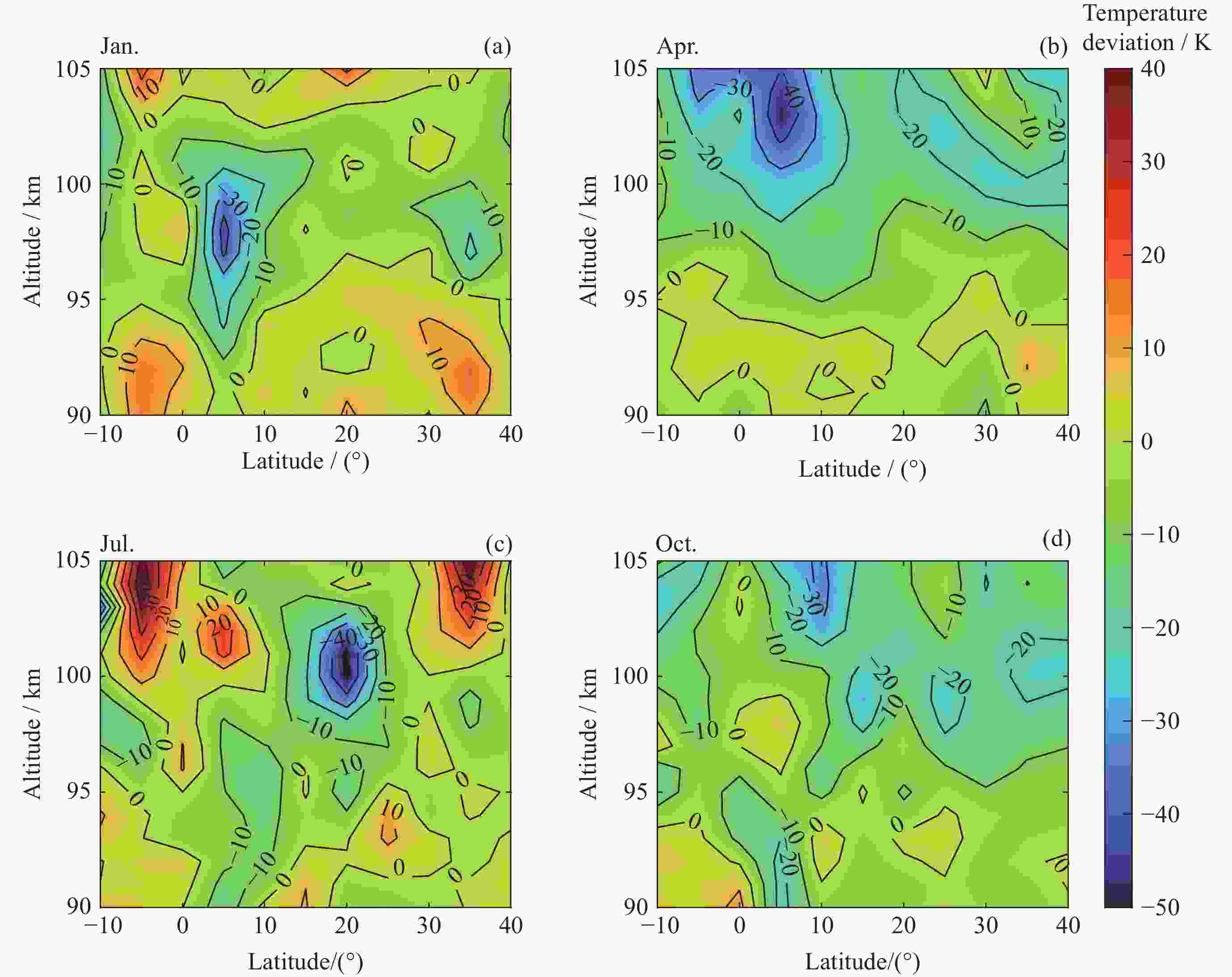
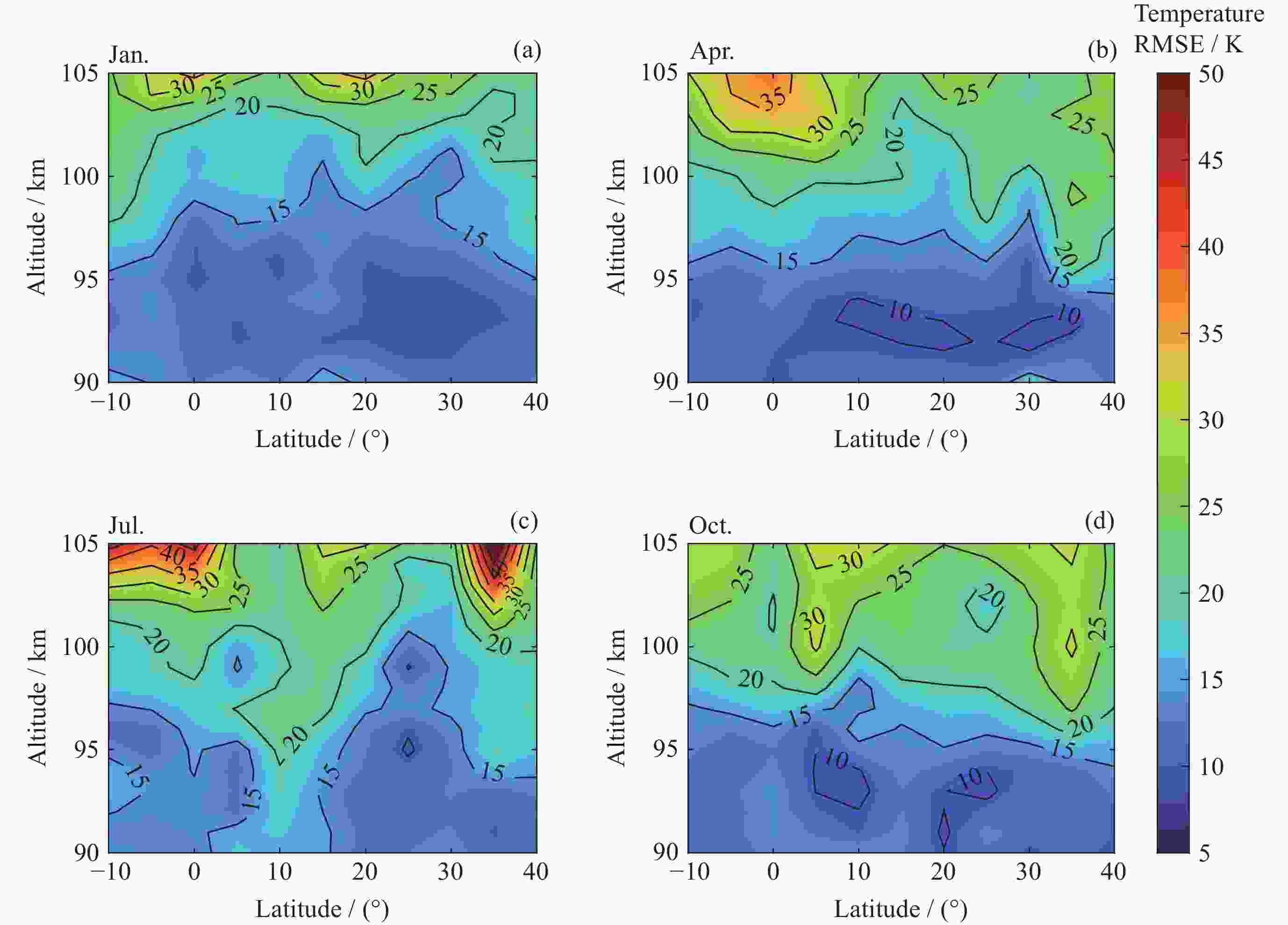
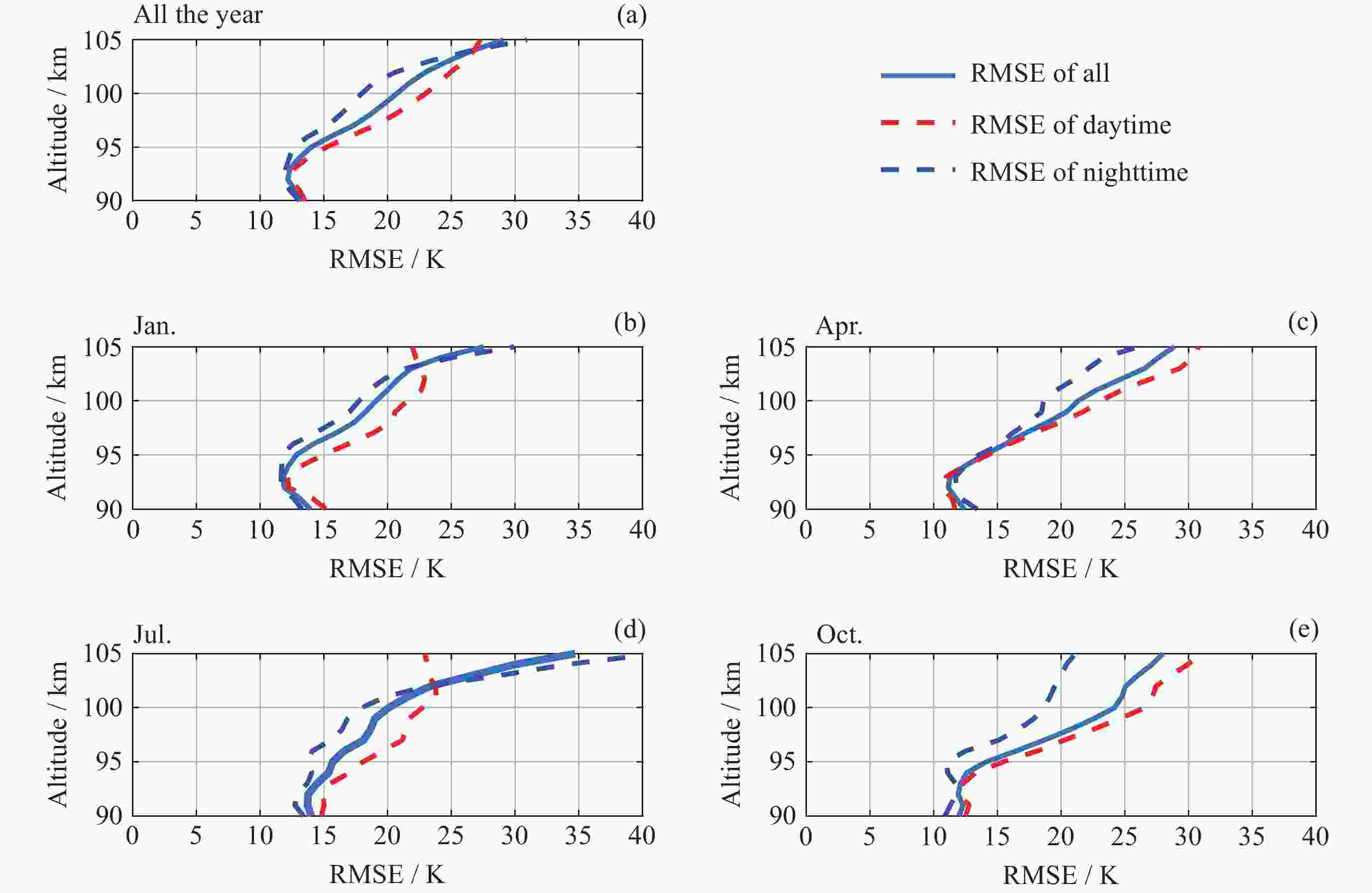
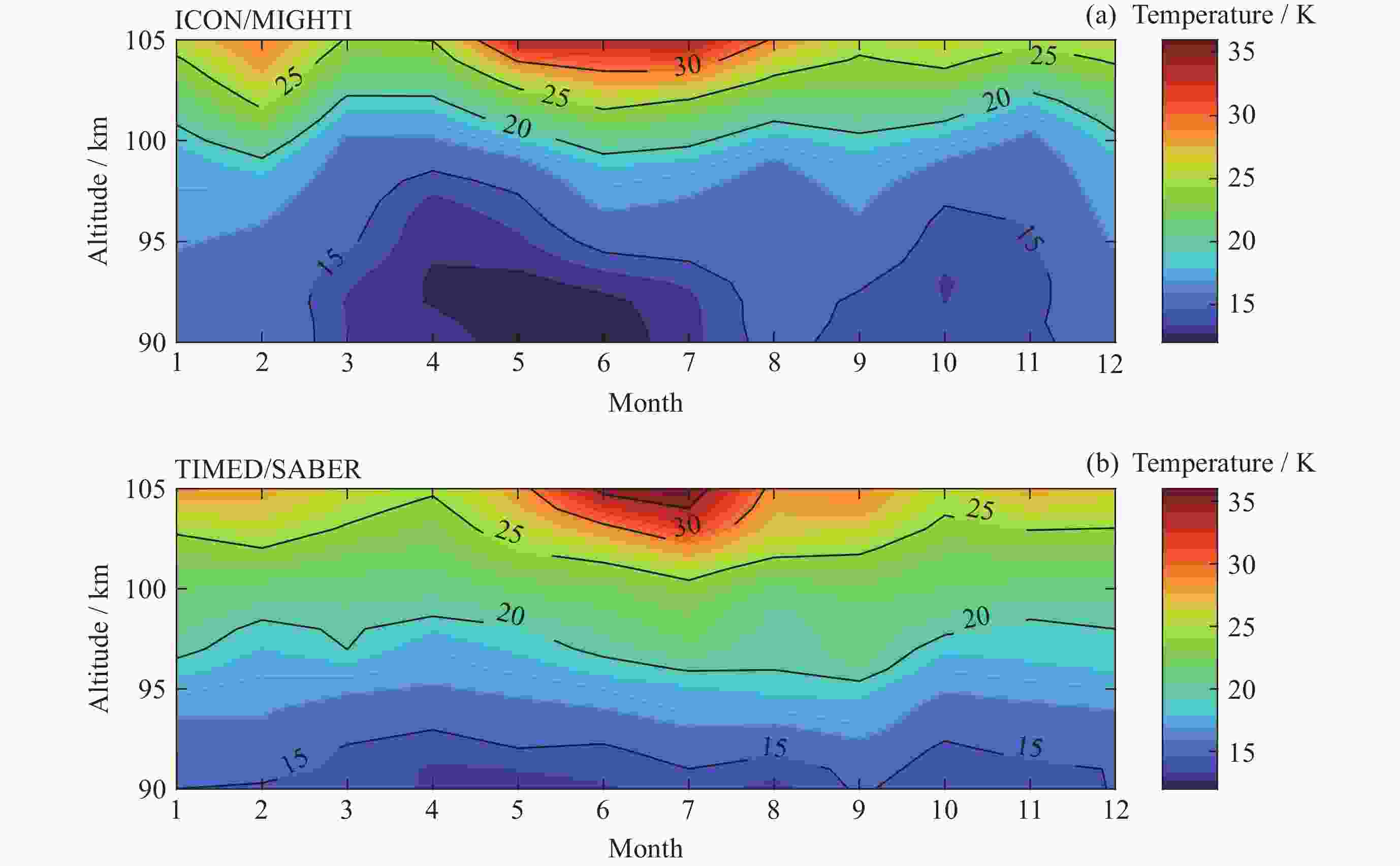
摘要: ICON卫星为临近空间环境特性研究、建模和预报提供了新数据. 通过对ICON/MIGHTI与TIMED/SABER在90~105 km高度探测温度数据的比较, 计算两者的年平均温度偏差和均方根误差, 同时分析月平均温度偏差在不同月份中随高度和纬度的分布情况, 为MIGHTI和SABER温度探测数据在临近空间大气建模和预报应用提供参考依据. 结果表明, MIGHTI和SABER的温度垂直廓线变化趋势基本吻合, 数值上有所差异. 在12°S-42°N范围内, MIGHTI探测温度与SABER相比, 在90~93 km时偏低, 偏差最大值约2.5 K, 在93~105 km偏高, 偏差的绝对值最大约10 K. 在不同季节, 白天的温度偏差通常高于夜晚. SABER和MIGHTI的月平均温度偏差随季节和纬度的变化显著, 夏季时的月平均温度偏差最大, 且温度的均方根误差最大.
-
关键词:
- 大气温度 /
- 临近空间 /
- 数据比较 /
- ICON/MIGHTI /
- TIMED/SABER
Abstract: The ICON satellite provides new data for environmental characterization, modeling, and forecasting in near space. In this paper, the ICON/MIGHTI and TIMED/SABER temperature datasets were compared and analyzed in the range of 90~105 km, and the mean temperature deviation and root-mean-square error of both were calculated. The distribution of monthly mean temperature deviation with altitude and latitude in different months was also analyzed, which is useful for applying the MIGHTI and SABER temperature data in the model and forecast. The results showed that the MIGHTI and SABER vertical profile detections agreed. In the range of 12°S-42°N, the MIGHTI probe temperature is lower than that of SABER in the range of 90~93 km, with a maximum deviation of about 2.5 K, and higher in the range of 93~105 km, with a maximum absolute value of the deviation of about 10 K. The deviation was usually higher during the day than at night. The mean temperature deviation varied significantly with season and latitude and had the largest mean deviation range and the largest root-mean-square temperature error in summer.-
Key words:
- Atmospheric temperature /
- Near space /
- Data comparison /
- ICON/MIGHTI /
- TIMED/SABER
-
图 2 MIGHTI与SABER探测温度个例比较结果及温度偏差. MIGHTI (4.46°N, 25.44°W, 16:06 LT), SABER (4.57°N, 26.13°W, 15:42 LT), MIGHTI (39.95°N, 167.13°E, 02:12 LT), SABER (39.74°N, 166.87°E, 02:48 LT)
Figure 2. Comparison of individual profiles of temperatures detected and temperature deviation by ICON/MIGHTI and TIMED/SABER. MIGHTI (4.46°N, 25.44°W, 16:06 LT), SABER (4.57°N, 26.13°W, 15:42 LT), MIGHTI (39.95°N, 167.13°E, 02:12 LT), SABER (39.74°N, 166.87°E, 02:48 LT)
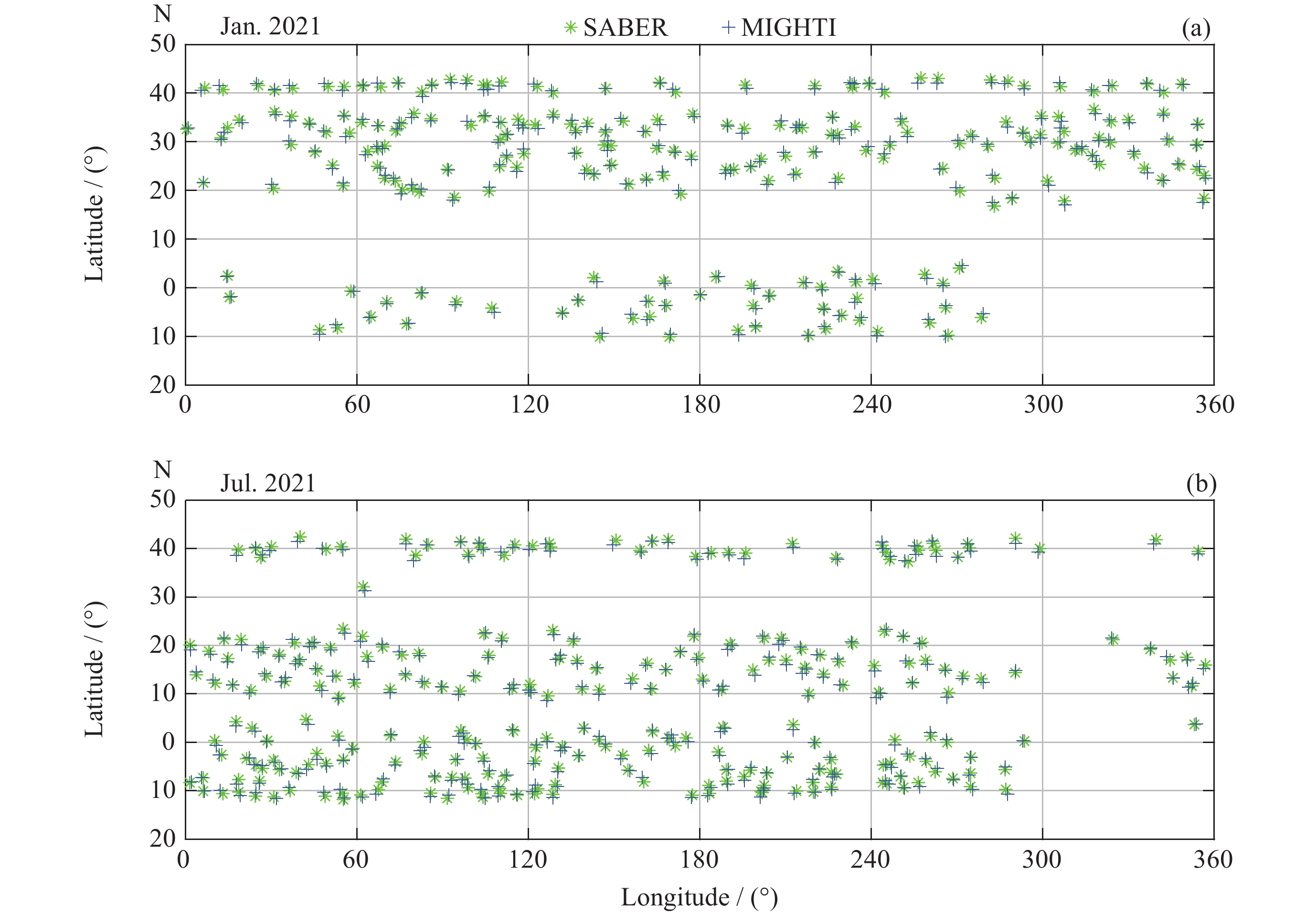
表 1 MIGHTI/ICON和TIMED/SABER温度探测数据匹配情况
Table 1. Numbers of matching data of ICON/MIGHTI and TIMED/SABER
纬度分布 1月 4月 7月 10月 10°S-0° 267 193 214 334 0°-10°N 93 182 41 223 10°N-20°N 64 176 223 166 20°N-30°N 140 231 80 136 30°N-40°N 195 367 231 330 总数 759 1149 789 1075 -
[1] 肖存英, 胡雄, 王博, 等. 临近空间大气扰动变化特性的定量研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016, 59(4): 1211-1221XIAO Cunying, HU Xiong, WANG Bo, et al. Quantitative study of atmospheric disturbance variation characteristics in the near space[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(4): 1211-1221 [2] SHE C Y, LIU A Z, YUAN T, et al. MLT science enabled by atmospheric lidars[M]//WANG W B, ZHANG Y L, PAXTON L J. Upper Atmosphere Dynamics and Energetics. Hoboken: Wiley-American Geophysical Union, 2021: 395-450 [3] 闫召爱, 胡雄, 郭文杰, 等. 临近空间多普勒激光雷达技术及其应用(特邀)[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2021, 50(3): 20210100 doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210100YAN Zhaoai, HU Xiong, GUO Wenjie, et al. Near space Doppler lidar techniques and applications (Invited)[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2021, 50(3): 20210100 doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210100 [4] SOX L, WICKWAR V B, YUAN T, et al. Simultaneous rayleigh‐scatter and sodium resonance lidar temperature comparisons in the mesosphere-lower thermosphere[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2018, 123(18): 10688-10706 [5] DABAS A, DENNEULIN M L, FLAMANT P, et al. Correcting winds measured with a Rayleigh Doppler lidar from pressure and temperature effects[J]. Tellus A: Dynamic Meteorology and Oceanography, 2008, 60(2): 206-215 doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0870.2007.00284.x [6] 王博, 胡雄, 肖存英, 等. 子午工程首次火箭探空数据准单色惯性重力波特性分析[J]. 空间科学学报, 2017, 37(5): 547-553 doi: 10.11728/cjss2017.05.547WANG Bo, HU Xiong, XIAO Cunying, et al. Characteristics of quasi-monochromatic inertia gravity waves revealed by first meteorological rocket data of the meridian space weather monitoring project[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2017, 37(5): 547-553 doi: 10.11728/cjss2017.05.547 [7] WRASSE C M, FECHINE J, TAKAHASHI H, et al. Temperature comparison between CHAMP radio occultation and TIMED/SABER measurements in the lower stratosphere[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2008, 41(9): 1423-1428 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2007.06.073 [8] 宫晓艳, 胡雄, 吴小成, 等. COSMIC大气掩星与SABER/TIMED探测温度数据比较[J]. 地球物理学报, 2013, 56(7): 2152-2162GONG Xiaoyan, HU Xiong, WU Xiaocheng, et al. Comparison of temperature measurements between COSMIC atmospheric radio occultation and SABER/TIMED[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2013, 56(7): 2152-2162 [9] SCHWARTZ M J, LAMBERT A, MANNEY G L, et al. Validation of the Aura Microwave Limb Sounder temperature and geopotential height measurements[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2008, 113(D15): D15S11 [10] 谢衍新, 肖存英, 胡雄, 等. TIMED/SABER与AURA/MLS临近空间探测温度数据比较[J]. 空间科学学报, 2018, 38(3): 361-367 doi: 10.11728/cjss2018.03.361XIE Yanxin, XIAO Cunying, HU Xiong, et al. Comparison between temperature data of TIMED/SABER and AURA/MLS[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2018, 38(3): 361-367 doi: 10.11728/cjss2018.03.361 [11] PARK J, EVANS J S, EASTES R W, et al. Exospheric temperature measured by NASA‐GOLD under low solar activity: comparison with other data sets[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2022, 127(3): e2021JA030041 doi: 10.1029/2021JA030041 [12] 胡向瑞, 李发泉, 王后茂, 等. MIGHTI/ICON卫星的中高层大气温度反演与验证[J]. 光学学报, 2023, 43(12): 1201006 doi: 10.3788/AOS221914HU Xiangrui, LI Faquan, WANG Houmao, et al. Retrieval and verification of mid-upper atmospheric temperature from MIGHTI/ICON satellite[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2023, 43(12): 1201006 doi: 10.3788/AOS221914 [13] STEVENS M H, ENGLERT C R, HARLANDER J M, et al. Temperatures in the upper mesosphere and lower thermosphere from O2 atmospheric band emission observed by ICON/MIGHTI[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2022, 218(8): 67 doi: 10.1007/s11214-022-00935-x [14] ENGLERT C R, HARLANDER J M, MARR K D, et al. Michelson interferometer for global high-resolution thermospheric imaging (MIGHTI) on-orbit wind observations: data analysis and instrument performance[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2023, 219(3): 27 doi: 10.1007/s11214-023-00971-1 [15] HARDING B J, CHAU J L, HE M S, et al. Validation of ICON-MIGHTI thermospheric wind observations: 2. Green-line comparisons to specular meteor radars[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(3): e2020JA028947 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028947 [16] IMMEL T J, ENGLAND S L, MENDE S B, et al. The ionospheric connection explorer mission: mission goals and design[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2018, 214(1): 13 doi: 10.1007/s11214-017-0449-2 [17] ENGLERT C R, HARLANDER J M, BROWN C M, et al. Michelson interferometer for global high-resolution thermospheric imaging (MIGHTI): instrument design and calibration[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2017, 212(1/2): 553-584 [18] STEVENS M H, ENGLERT C R, HARLANDER J M, et al. Retrieval of lower thermospheric temperatures from O2 a band emission: the MIGHTI experiment on ICON[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2018, 214(1): 4 doi: 10.1007/s11214-017-0434-9 [19] REZAC L, KUTEPOV A, RUSSELL J M, et al. Simultaneous retrieval of T(p) and CO2 VMR from two-channel non-LTE limb radiances and application to daytime SABER/TIMED measurements[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2015, 130-131: 23-42 doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2015.05.004 [20] BIZUNEH C L, JAYA PRAKASH RAJU U, NIGUSSIE M, et al. Long-term temperature and ozone response to natural drivers in the mesospheric region using 16 years (2005–2020) of TIMED/SABER observation data at 5°–15°N[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2022, 70(7): 2095-2111 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2022.06.051 [21] ZHAO X R, SHENG Z, SHI H Q, et al. Long-term trends and solar responses of the mesopause temperatures observed by SABER during the 2002–2019 period[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2020, 125(11): e2020JD032418 doi: 10.1029/2020JD032418 [22] FAN Z Q, ZHOU Y F, GU C L, et al. Temperature fusion of TIMED/SABER data and COSMIC data in stratosphere[J]. Radio Science, 2023, 58(2): e2022RS007560 doi: 10.1029/2022RS007560 [23] EMMERT J T, DROB D P, PICONE J M, et al. NRLMSIS 2.0: a whole‐atmosphere empirical model of temperature and neutral species densities[J]. Earth and Space Science, 2021, 8(3): e2020EA001321 doi: 10.1029/2020EA001321 [24] DAS U. Spatial variability in long-term temperature trends in the middle atmosphere from SABER/TIMED observations[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2021, 68(7): 2890-2903 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2021.05.014 [25] LÓPEZ-GONZÁLEZ M J, GARCÍA-COMAS M, RODRÍGUEZ E, et al. Ground-based mesospheric temperatures at mid-latitude derived from O2 and OH airglow SATI data: comparison with SABER measurements[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2007, 69(17/18): 2379-2390 [26] REZAC L, JIAN Y, YUE J, et al. Validation of the global distribution of CO2 volume mixing ratio in the mesosphere and lower thermosphere from SABER[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2015, 120(23): 12067-12081 [27] DAWKINS E C M, FEOFILOV A, REZAC L, et al. Validation of SABER v2.0 operational temperature data with ground‐based lidars in the mesosphere‐lower thermosphere region (75–105 km)[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2018, 123(17): 9916-9934 doi: 10.1029/2018JD028742 [28] 程旋, 肖存英, 胡雄, 等. 基于TIMED/SABER卫星温度数据对大气经验模型的评估[J]. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学, 2018, 48 (10): 104701CHENG Xuan, XIAO Cunying, HU Xiong, et al. Evaluation of atmospheric empirical model based on TIMED/SABER satellite temperature data[J]. Scientia Sinica Physica, Mechanica & Astronomica, 2018, 48 (10): 104701 [29] YUAN T, STEVENS M H, ENGLERT C R, et al. Temperature tides across the mid-latitude summer turbopause measured by a sodium lidar and MIGHTI/ICON[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2021, 126(16): e2021JD035321 doi: 10.1029/2021JD035321 [30] GARCIA R R, LÓPEZ-PUERTAS M, FUNKE B, et al. On the distribution of CO2 and CO in the mesosphere and lower thermosphere[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2014, 119(9): 5700-5718 doi: 10.1002/2013JD021208 [31] FOMICHEV V I, BLANCHET J P, TURNER D S. Matrix parameterization of the 15 μm CO2 band cooling in the middle and upper atmosphere for variable CO2 concentration[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 1998, 103(D10): 11505-11528 doi: 10.1029/98JD00799 [32] OFFERMANN D, GUSEV O, DONNER M, et al. Relative intensities of middle atmosphere waves[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2009, 114(D6): D06110 -
-




 牟宵 女, 1997年2月出生于四川省成都市, 现为中国科学院国家空间科学中心学生, 主要研究方向为临近空间飞行环境等. E-mail:
牟宵 女, 1997年2月出生于四川省成都市, 现为中国科学院国家空间科学中心学生, 主要研究方向为临近空间飞行环境等. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: