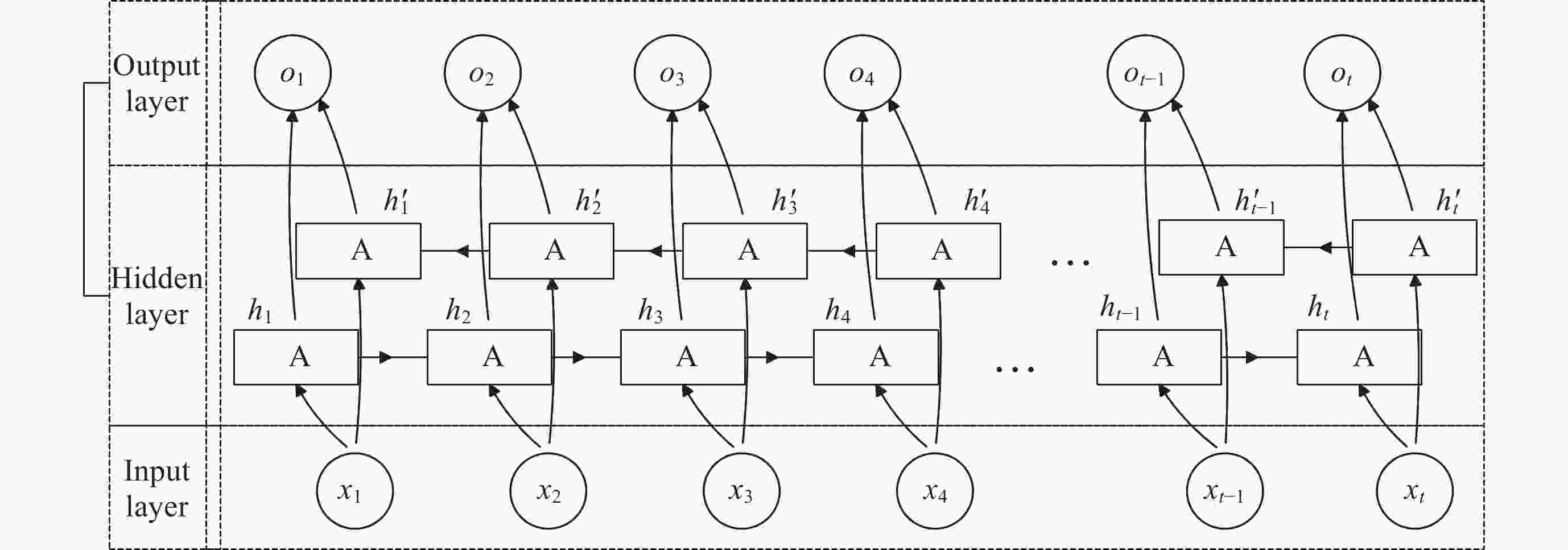
融合电离层参数相似特征的f0F2参数深度学习预测方法
doi: 10.11728/cjss2024.05.2023-0110 cstr: 32142.14.cjss2024.05.2023-0110
Deep Learning Prediction Method for f0F2 Parameters Based on the Ionospheric Parameter Similarity Features
-
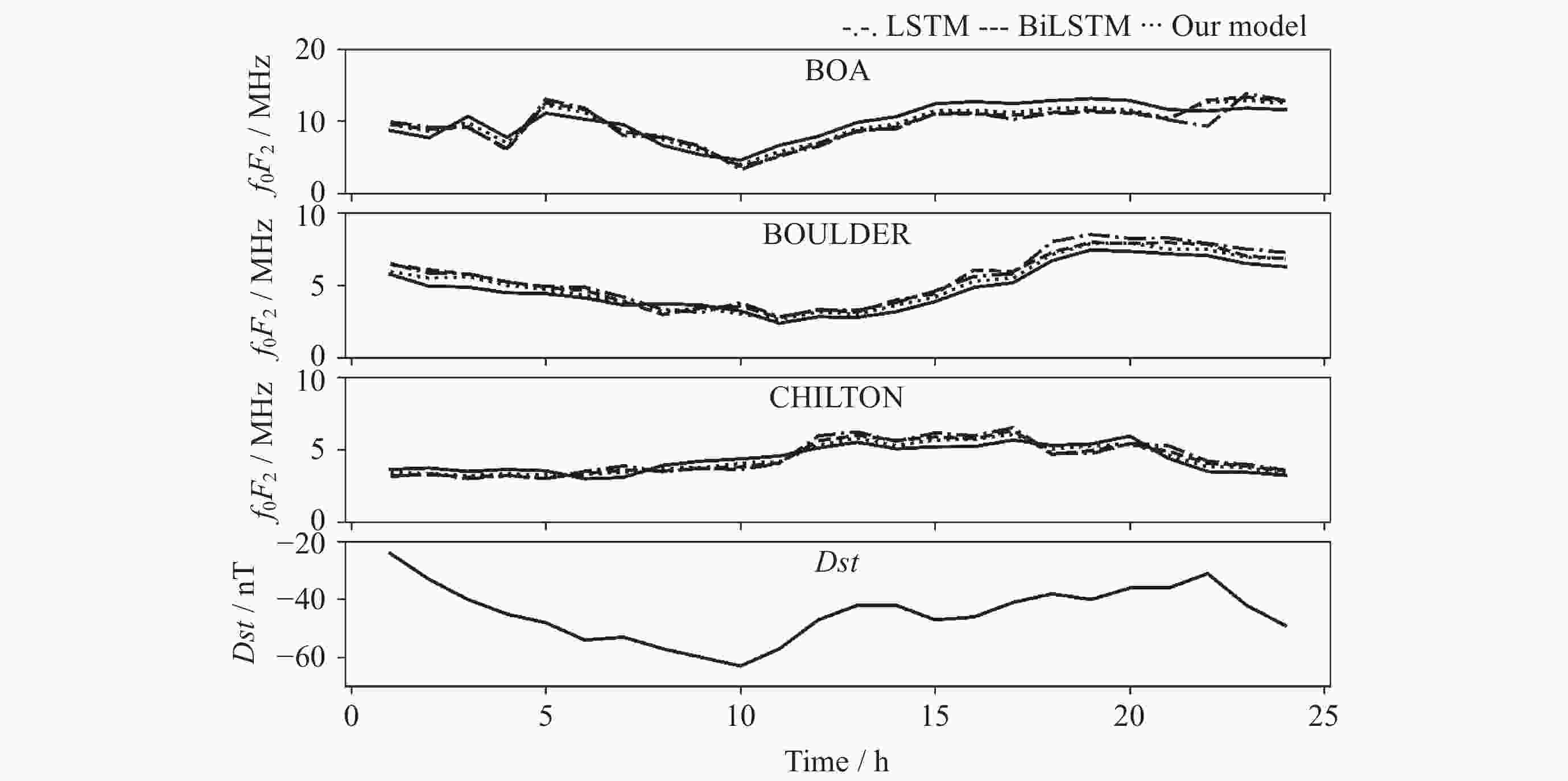
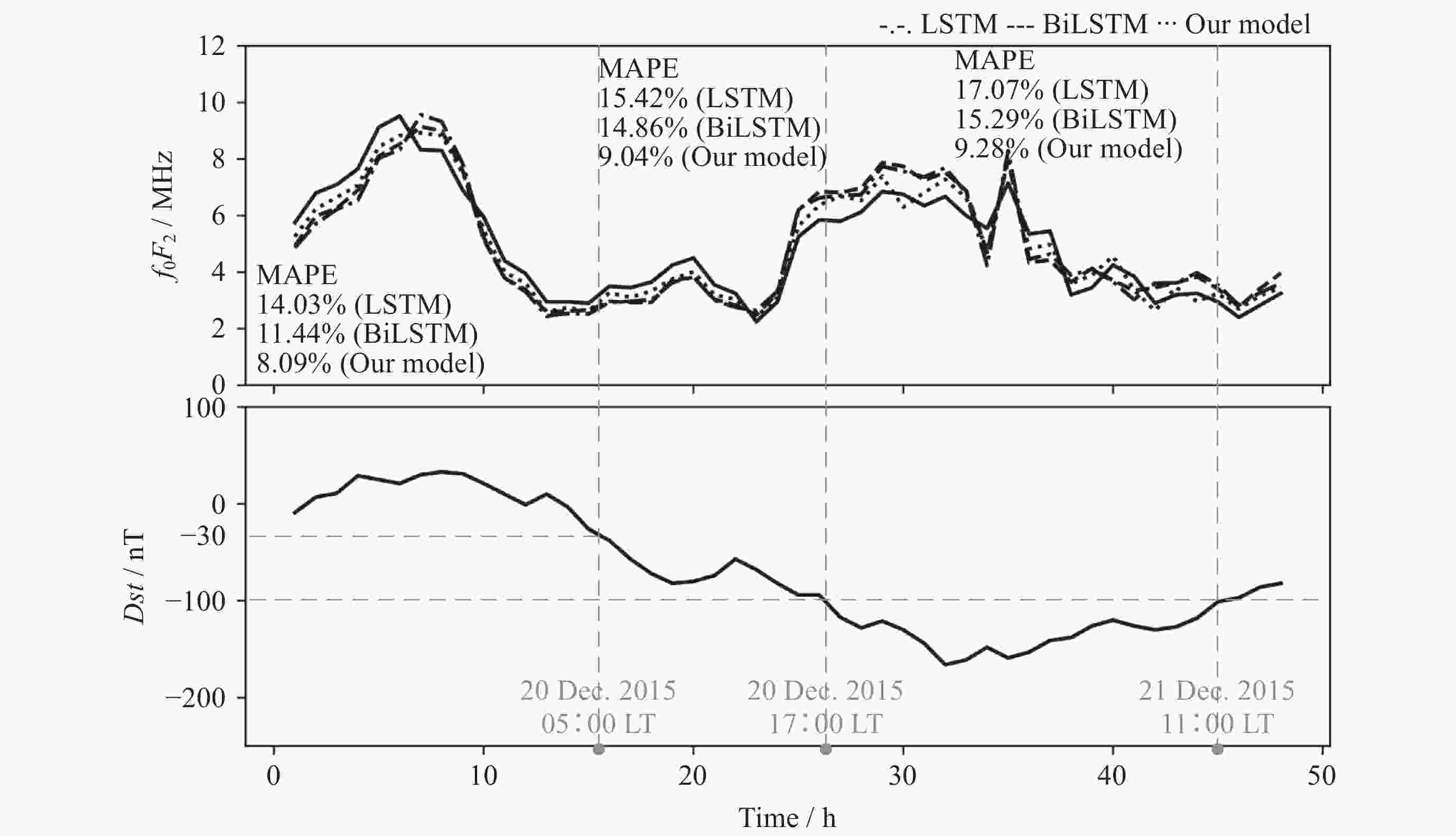
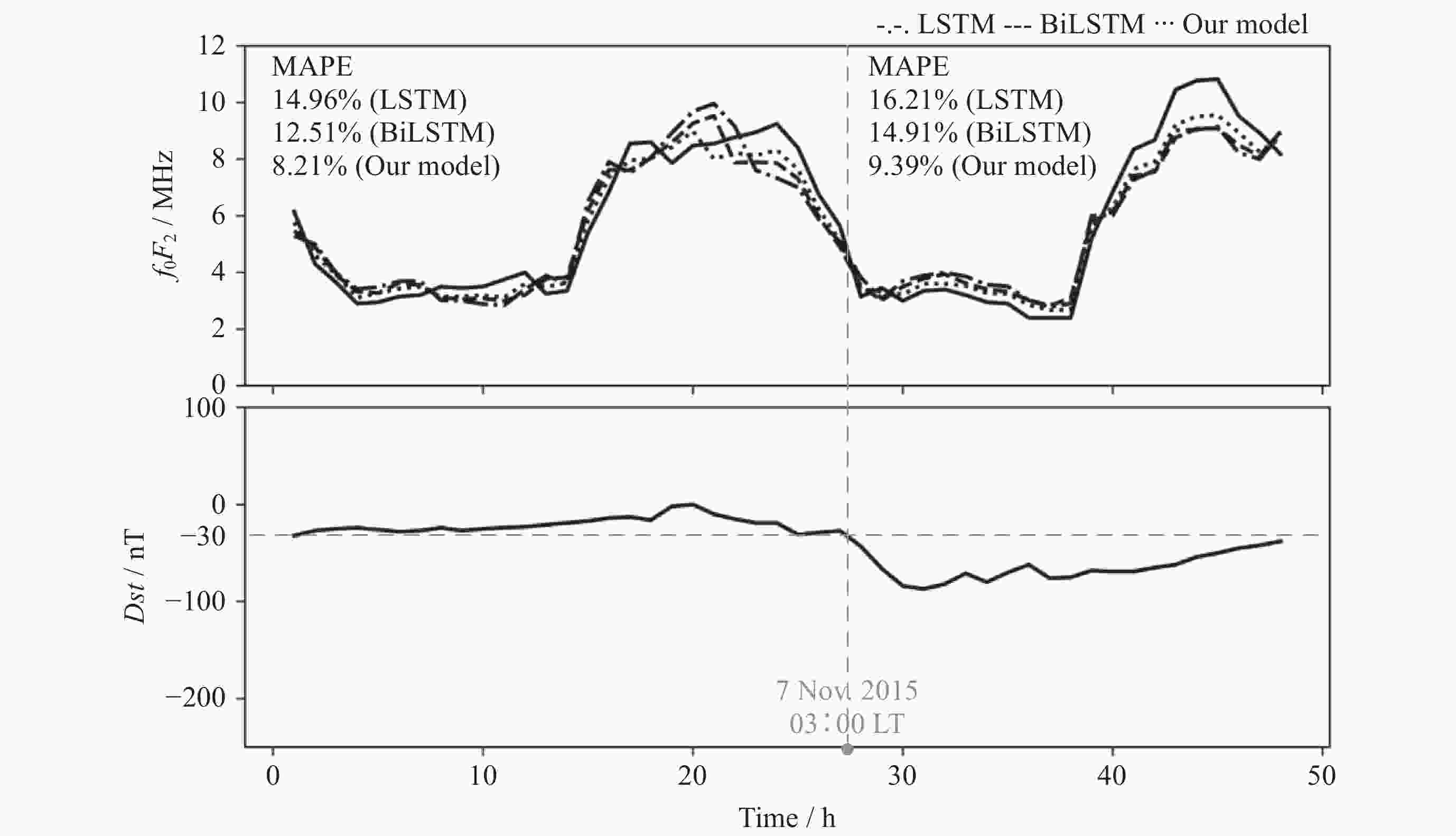
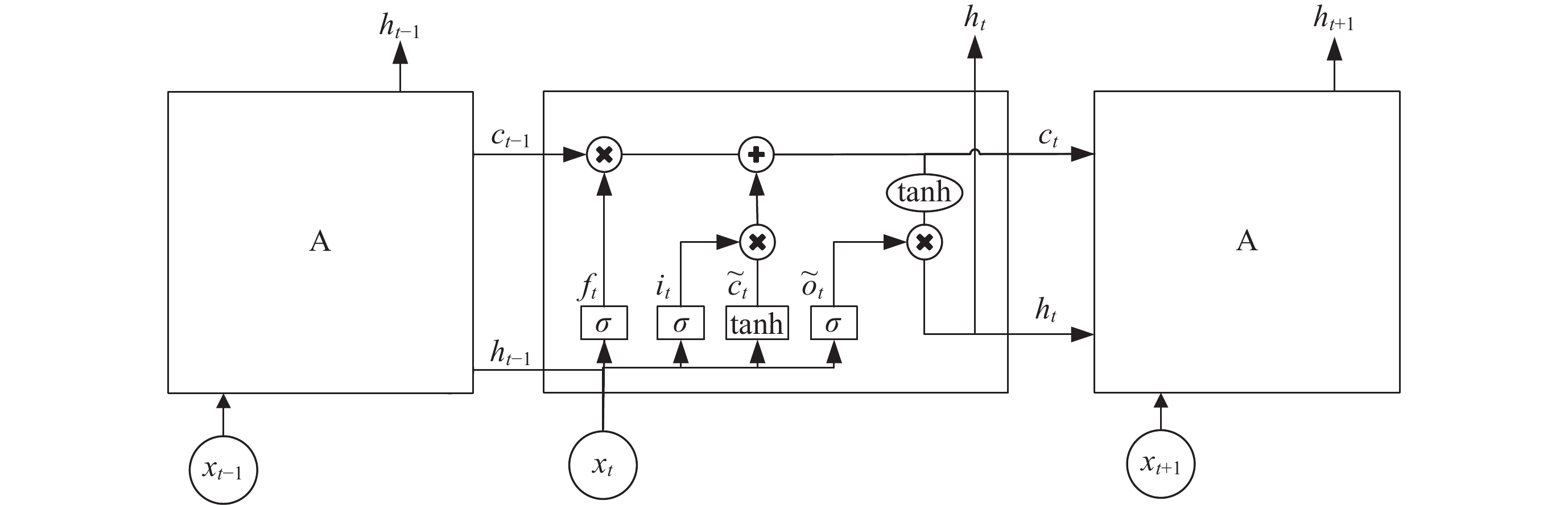
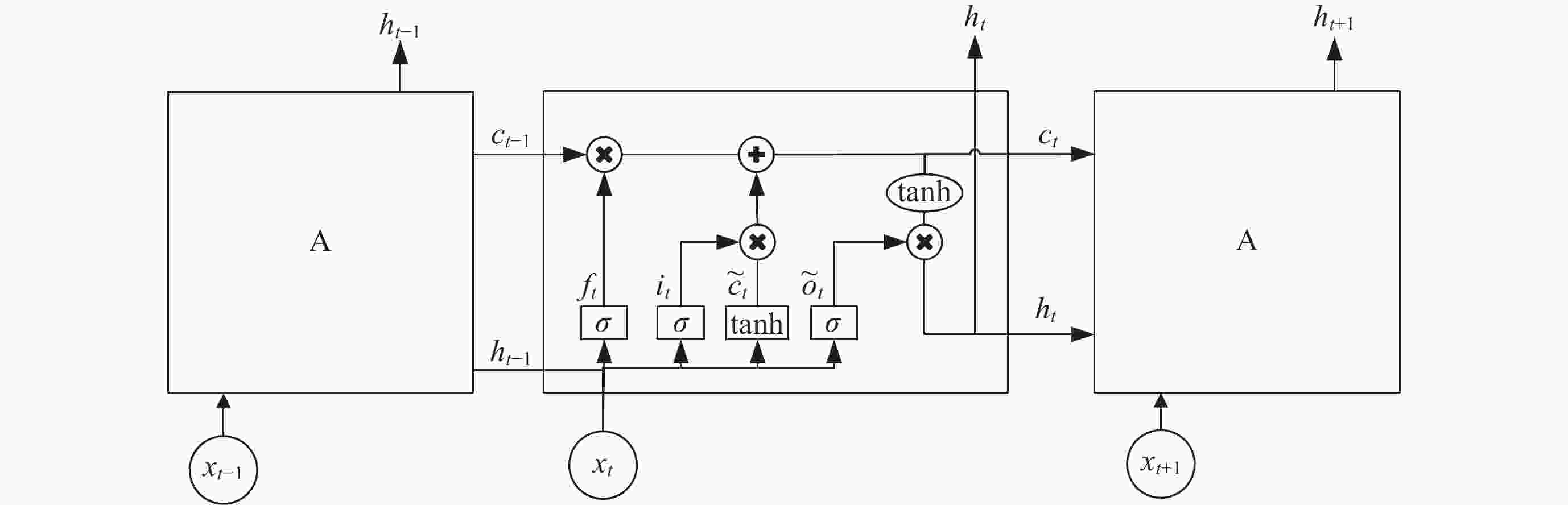
摘要: 电离层临界频率f0F2参数是重要的电离层参数之一, 开展f0F2参数预测具有重要的研究意义和应用价值. 提出了一种融合f0F2参数变化特性的深度学习预测方法, 采用双向长短时记忆神经网络(BiLSTM)和电离层参数相似特征相结合的模型实现电离层临界频率f0F2参数提前24 h预测. 结果表明, BiLSTM结合电离层参数相似特征模型预测f0F2参数的平均相对误差在8%~10%. 对不同纬度的探测站的f0F2参数预测结果表明, 随着纬度降低, 预测难度和误差都会增大, 预测精度降低. 对地磁暴期间的f0F2参数预测结果分析发现, 地磁暴期间的预测效果会受到一定程度的干扰, 预测误差增大. 在地磁暴期间, 相比长短时记忆神经网络 (LSTM)模型和BiLSTM模型, BiLSTM结合电离层参数相似特征模型对于f0F2参数的预测效果更优.
-
关键词:
- 电离层临界频率 /
- 深度学习 /
- 双向长短时记忆神经网络(BiLSTM) /
- 地磁暴
Abstract: The ionosphere is an important component of the solar terrestrial space environment, and the critical frequency f0F2 parameter is one of the most important and complex ionospheric parameters. The changes in f0F2 parameters will have a certain degree of impact on communication, navigation, radar and other technologies, so predicting f0F2 parameters has important research significance and application value. This article proposes a deep learning prediction method that integrates the characteristics of f0F2 parameter changes. A model combining bidirectional long short-term memory neural network BiLSTM network and ionospheric parameter similarity features is used to predict the ionospheric critical frequency f0F2 parameter 24 hours in advance. The results show that the average relative error of BiLSTM combined with ionospheric parameter similarity model in predicting f0F2 parameters is about 8%~10%. Compared with the Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) model, the average relative error has decreased by about 6% to 7%, while compared with the BiLSTM model, the average relative error has decreased by about 4% to 5%. The prediction results of the f0F2 parameter for different latitude detection stations show that as the latitude decreases, the difficulty of predicting the f0F2 parameter increases, the prediction errors of the three models increase, and the prediction accuracy decreases. The analysis of the prediction results of f0F2 parameters during geomagnetic storms shows that the predictive performance of the three models will be affected to varying degrees during the occurrence of geomagnetic storms, and the prediction error will increase. Compared to the calm period, the average relative error of the three models has increased by about 1% to 4%. During geomagnetic storms, compared with LSTM and BiLSTM models, BiLSTM combined with ionospheric parameter similarity feature models has better predictive performance for f0F2 parameters and better predictive performance. This method can also be applied to the prediction research of other ionospheric parameters such as Total Electron Content (TEC), hmF2, etc., and has a very broad application prospect. -
表 1 网络训练参数
Table 1. Network training parameters
Name Number Hidden size 128 Batch size 10 Learning rate 0.001 Epochs 200 表 2 电离层探测站信息
Table 2. Information of ionospheric detection stations
URSI Station Country Latitude (N)/(°) Longitude (W)/(°) BVJ03 BOA Brazil 2.8 60.7 BC840 BOULDER America 40.0 105.3 RL052 CHILTON Canada 51.5 100.6 表 3 三个模型的f0F2参数观测值和预测值之间的误差
Table 3. Errors between observed and predicted values of f0F2 parameters for three models
Station LSTM BiLSTM BiLSTM结合相似特征法 RMSE
/MHzMAE
/MHzMAPE
/(%)RMSE
/MHzMAE
/MHzMAPE
/(%)RMSE
/MHzMAE
/MHzMAPE
/(%)BOA 1.454 1.063 16.21 1.327 1.065 14.30 1.067 0.751 10.04 BOULDER 1.067 0.825 15.28 1.003 0.724 13.54 0.694 0.513 8.61 CHILTON 1.045 0.796 14.27 0.864 0.629 11.87 0.581 0.415 7.94 -
[1] BUONSANTO M J. Ionospheric storms — a review[J]. Space Science Reviews, 1999, 88(3): 563-601 doi: 10.1023/a:1005107532631 [2] BILITZA D, REINISCH B W. International reference ionosphere 2007: improvements and new parameters[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2008, 42(4): 599-609 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2007.07.048 [3] BILITZA D, ALTADILL D, REINISCH B, et al. The international reference ionosphere: model update 2016[C]//EGU General Assembly 2016. Vienna: EGU, 2016: EGU2016-9671 [4] COSPAR/URSI Working Group on IRI, BILITZA D. International reference ionosphere (1990)[J]. Planetary and Space Science, 1992, 40(4): 544 [5] STANISLAWSKA I, ZBYSZYNSKI Z. Forecasting of the ionospheric quiet and disturbed f0F2 values at a single location[J]. Radio Science, 2001, 36(5): 1065-1071 doi: 10.1029/1999RS002242 [6] CHAN A H Y, CANNON P S. Nonlinear forecasts of f0F2: variation of model predictive accuracy over time[J]. Annales Geophysicae, 2002, 20(7): 1031-1038 doi: 10.5194/angeo-20-1031-2002 [7] 张小红, 任晓东, 吴风波, 等. 自回归移动平均模型的电离层总电子含量短期预报[J]. 测绘学报, 2014, 43(2): 118-124ZHANG Xiaohong, REN Xiaodong, WU Fengbo, et al. Short-term TEC prediction of ionosphere based on ARIMA model[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2014, 43(2): 118-124 [8] 袁天娇, 陈艳红, 刘四清, 等. 基于深度学习递归神经网络的电离层总电子含量经验预报模型[J]. 空间科学学报, 2018, 38(1): 48-57 doi: 10.11728/cjss2018.01.048YUAN Tianjiao, CHEN Yanhong, LIU Siqing, et al. Prediction model for ionospheric total electron content based on deep learning recurrent neural networkormalsize[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2018, 38(1): 48-57 doi: 10.11728/cjss2018.01.048 [9] GERS F A, SCHMIDHUBER J, CUMMINS F. Learning to forget: continual prediction with LSTM[J]. Neural Computation, 2000, 12(10): 2451-2471 doi: 10.1162/089976600300015015 [10] MOON S, KIM Y H, KIM J H, et al. Forecasting the ionospheric F2 parameters over Jeju Station (33.43°N, 126.30°E) by using long short-term memory[J]. Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 2020, 77(12): 1265-1273 doi: 10.3938/JKPS.77.1265 [11] SRIVANI I, PRASAD G S V, RATNAM D V. A deep learning-based approach to forecast ionospheric delays for GPS signals[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(8): 1180-1184 doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2895112 [12] SIAMI-NAMINI S, TAVAKOLI N, NAMIN A S. The performance of LSTM and BiLSTM in forecasting time series[C]//Proceedings of 2019 IEEE International Conference on Big Data. Los Angeles: IEEE, 2019: 3285-3292 [13] HU A Q, ZHANG K F. Using bidirectional long short-term memory method for the height of F2 peak forecasting from ionosonde measurements in the Australian region[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(10): 1658 doi: 10.3390/rs10101658 [14] RAO T V, SRIDHAR M, RATNAM D V, et al. A bidirectional long short-term memory-based ionospheric f0F2 and hmF2 models for a single station in the low latitude region[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 8005405 doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.3045702 [15] 鞠平, 姜薇, 赵夏阳, 等. 96点短期负荷预测方法及其应用[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2001, 25(22): 32-36JU Ping, JIANG Wei, ZHAO Xiayang, et al. Ninety-six points short-term load forecasting-theory & applications[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2001, 25(22): 32-36 [16] 金海峰, 熊信艮, 吴耀武. 基于相似性原理的短期负荷预测方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2001, 25(23): 45-48 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1026.2001.23.011JIN Haifeng, XIONG Xingen, WU Yaowu. Short-term load forecasting based on analogous theory[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2001, 25(23): 45-48 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1026.2001.23.011 [17] 冯静, 柳文, 凡俊梅, 等. 一种电离层短期预报的新方法[J]. 装备环境工程, 2009, 6(3): 15-20 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9242.2009.03.004FENG Jing, LIU Wen, FAN Junmei, et al. A new method for short-term ionospheric forecast[J]. Equipment Environmental Engineering, 2009, 6(3): 15-20 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9242.2009.03.004 [18] 柳文, 焦培南, 冯静, 等. 电离层参数的相似日短期预测方法[J]. 电波科学学报, 2010, 25(2): 240-247 doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2010.02.003LIU Wen, JIAO Peinan, FENG Jing, et al. Method of similar days for ionospheric parameter short-term forecasting[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2010, 25(2): 240-247 doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2010.02.003 [19] REINISCH B W, GALKIN I A. Global Ionospheric Radio Observatory (GIRO)[J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 2011, 63(4): 377-381 doi: 10.5047/eps.2011.03.001 -
-





 郑丹丹 女, 1999年生, 福建人, 湘潭大学自动化与电子信息学院硕士研究生, 主要研究电离层参数预测方法. E-mail:
郑丹丹 女, 1999年生, 福建人, 湘潭大学自动化与电子信息学院硕士研究生, 主要研究电离层参数预测方法. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: