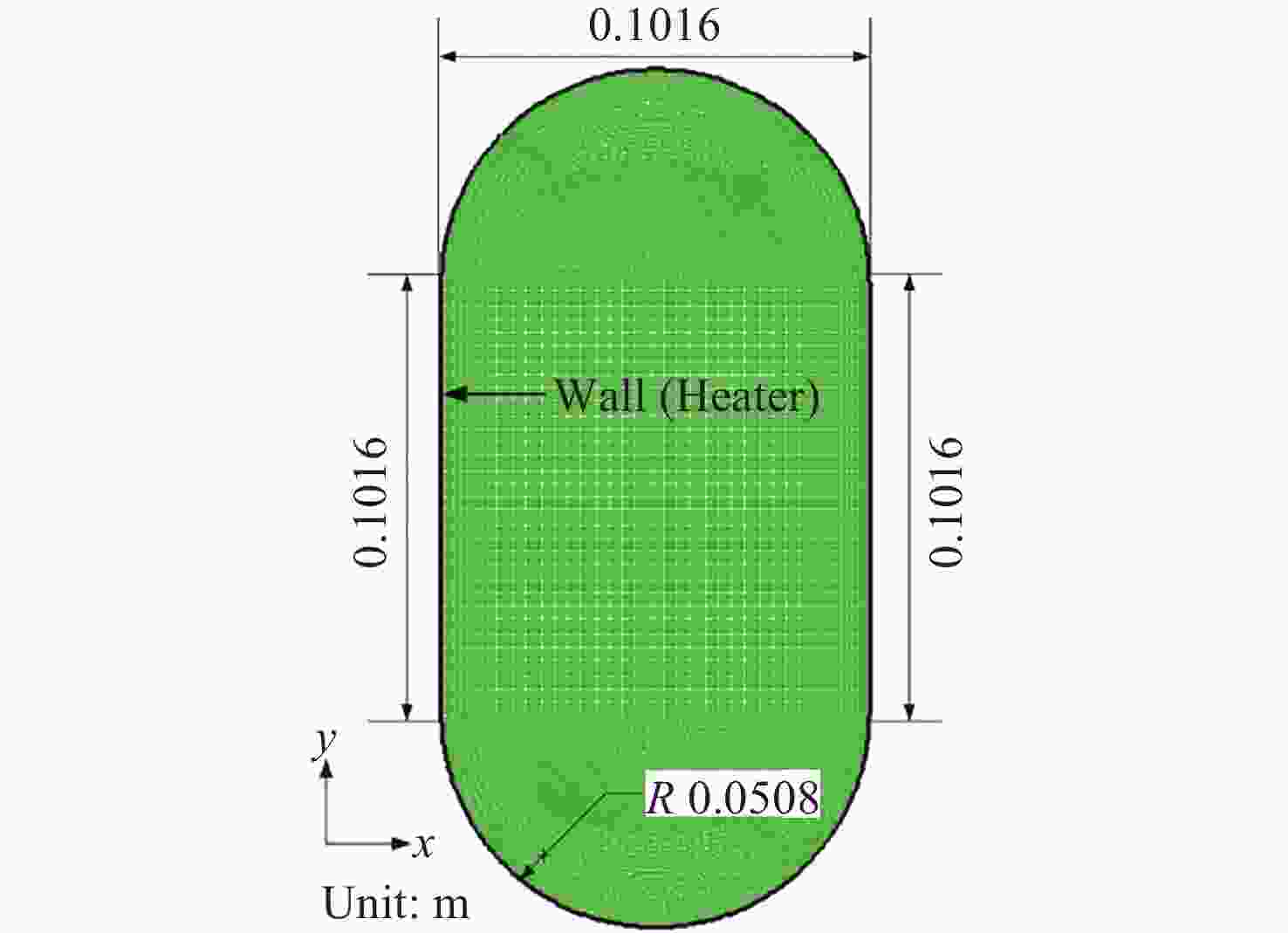
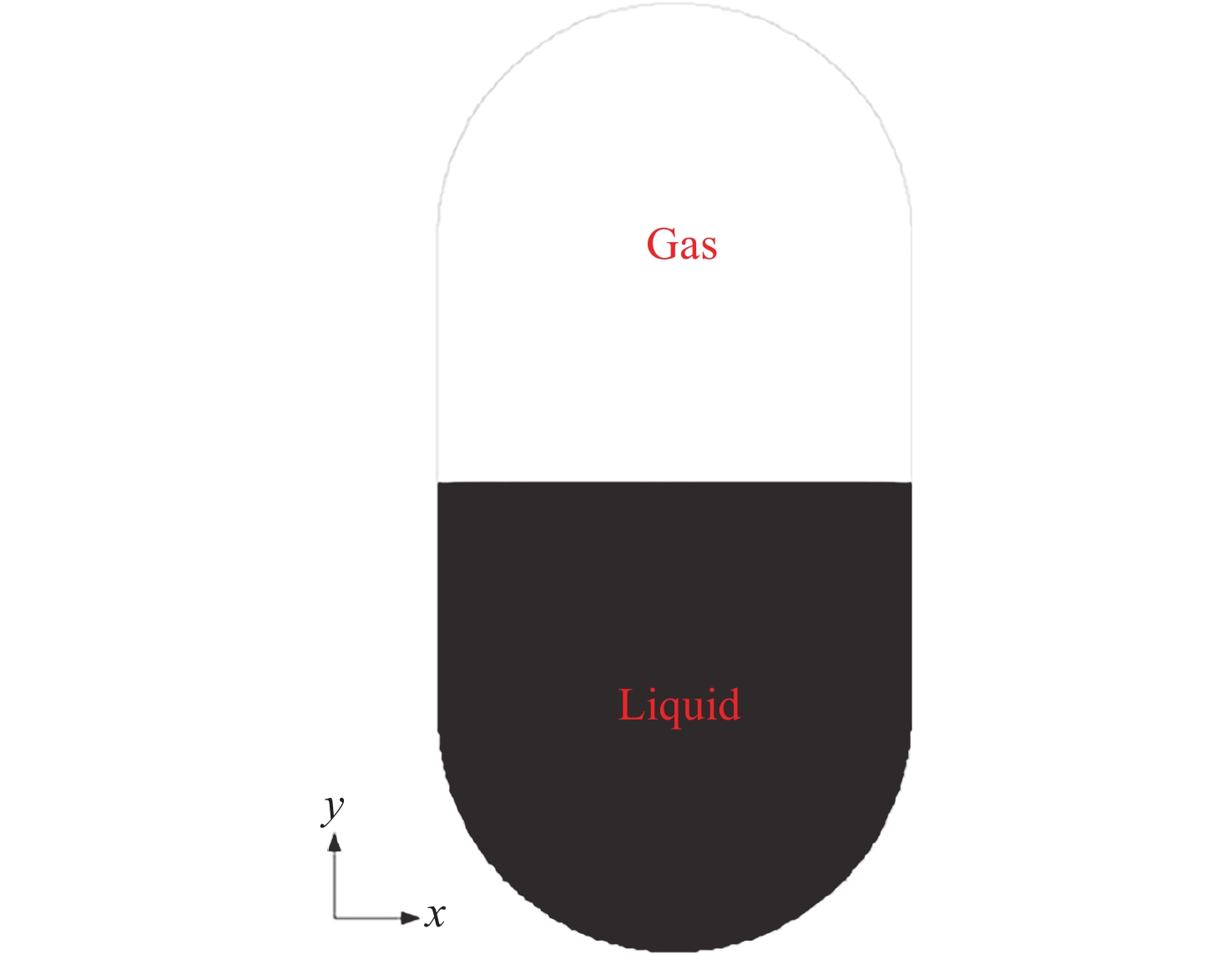
Research on Interfacial Flow and Thermal Stratification of Cryogenic Liquid Nitrogen in Variable Gravity
-
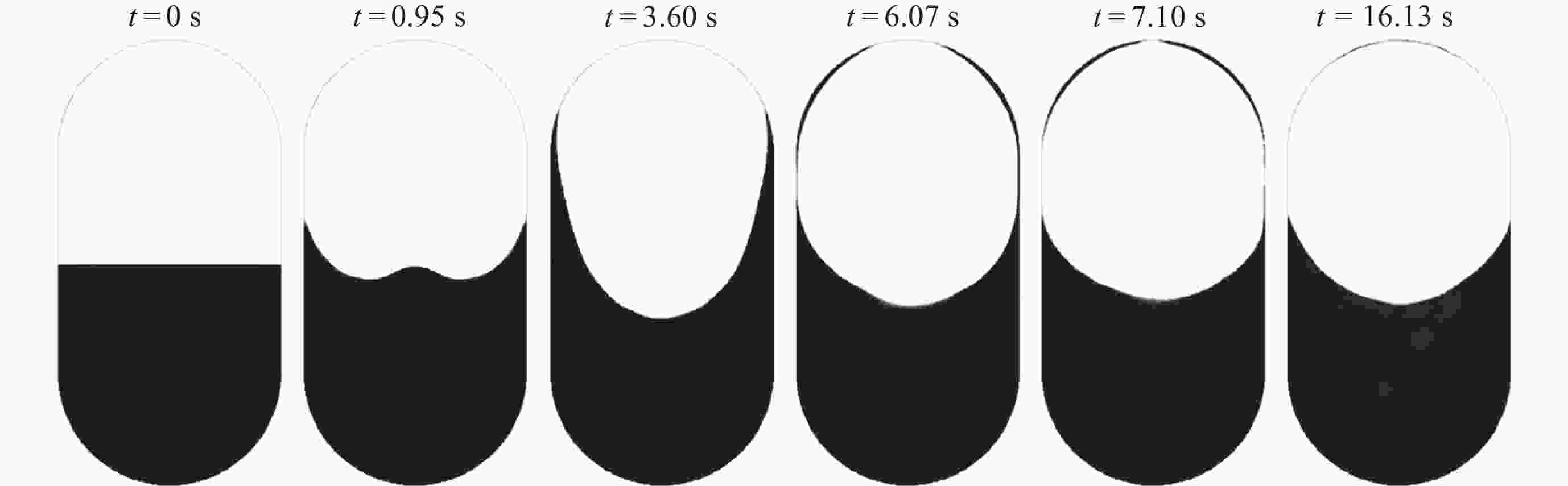
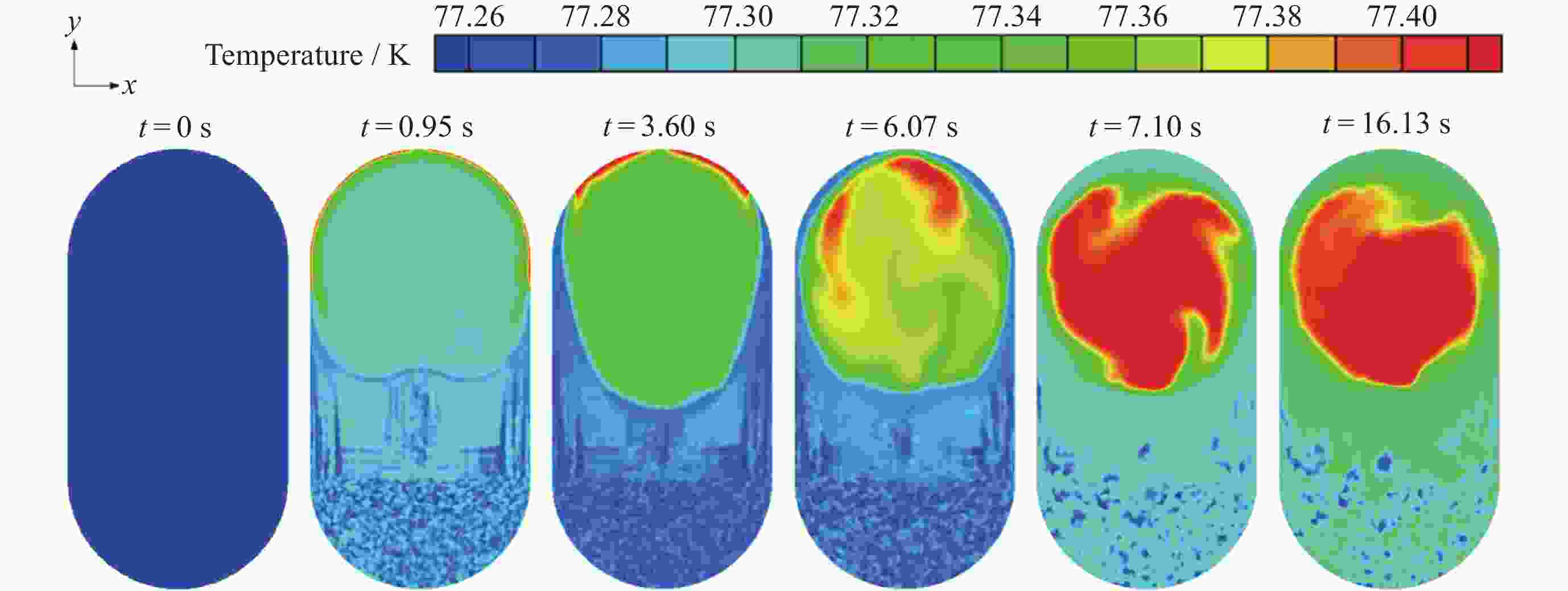
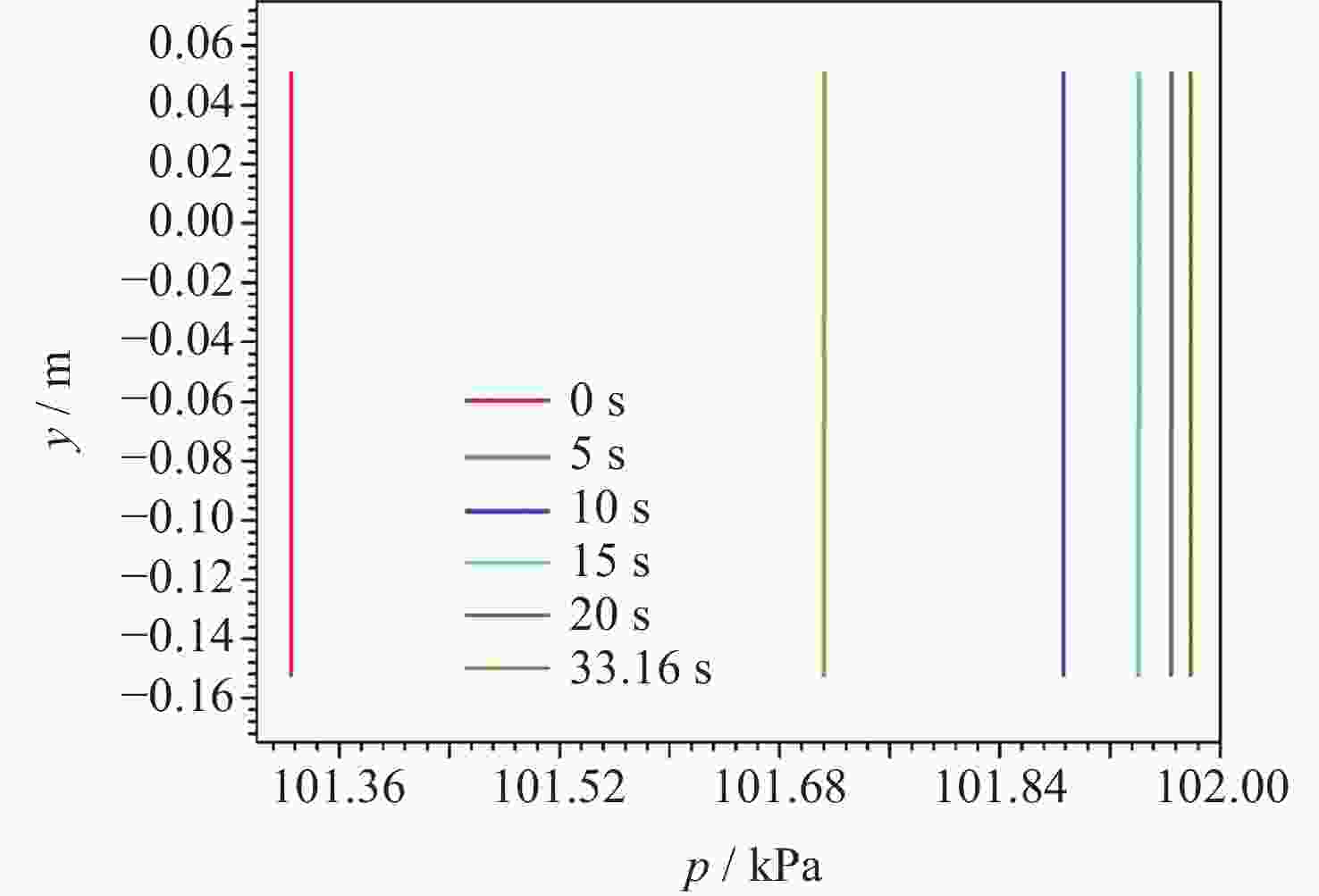
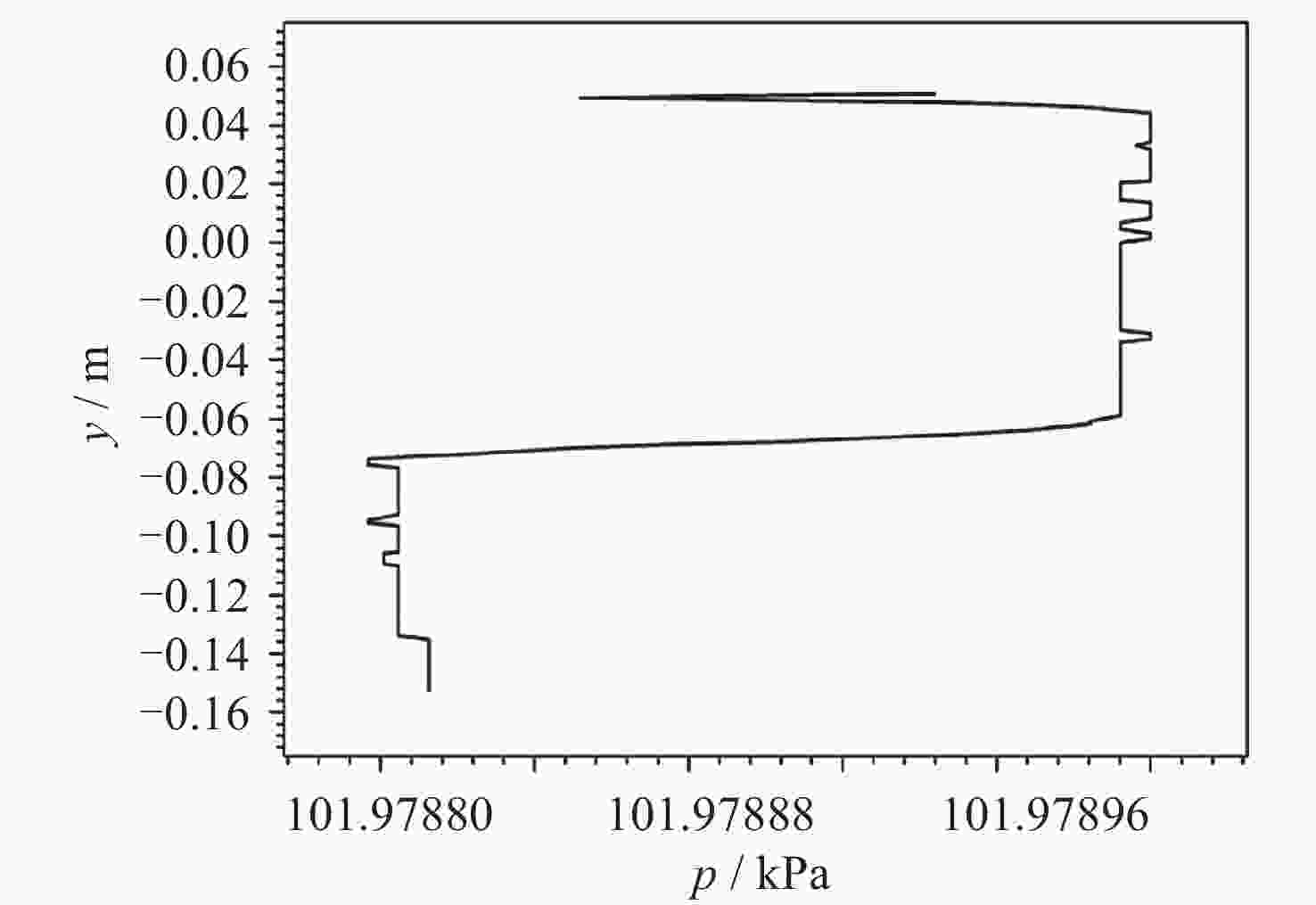
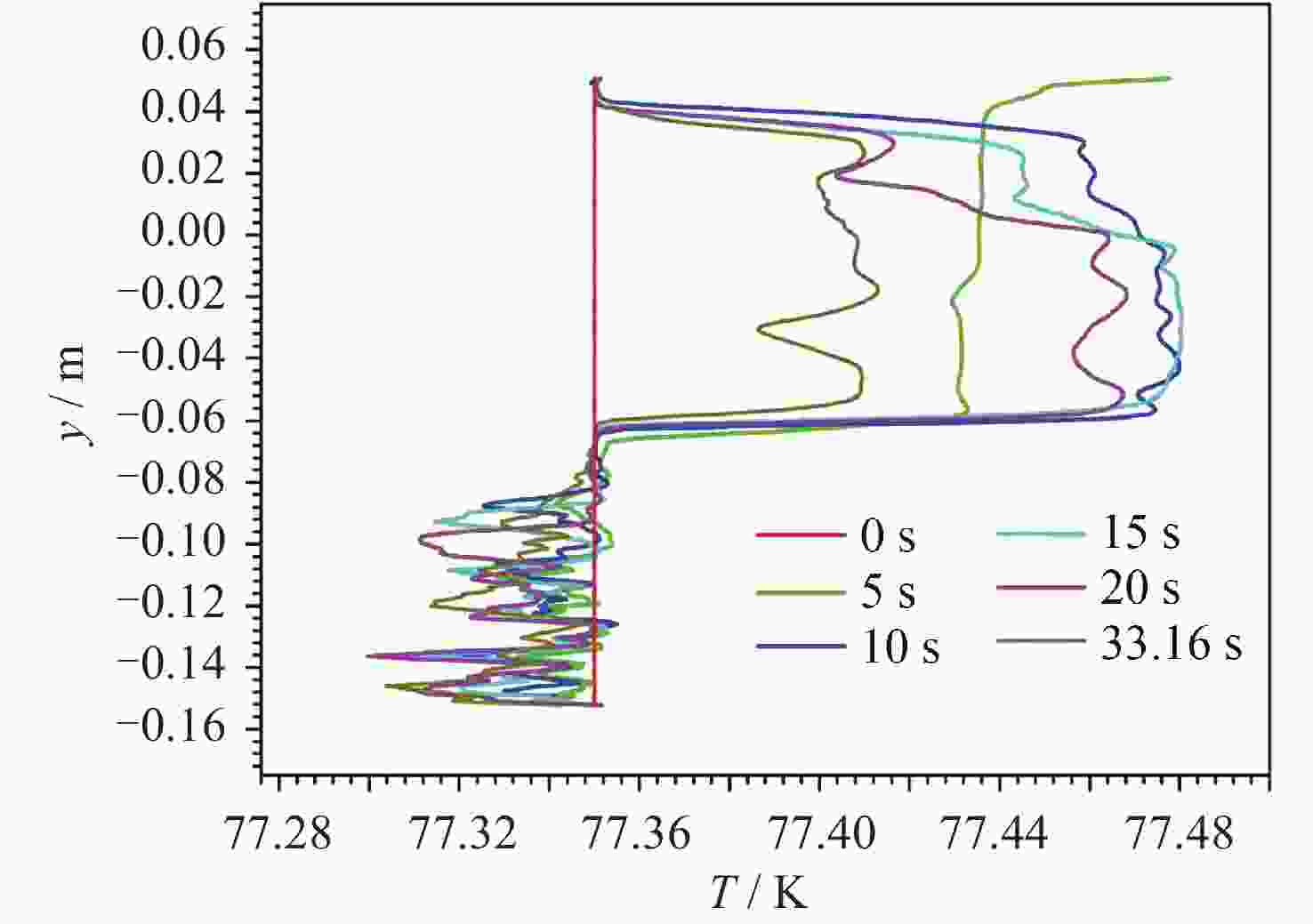
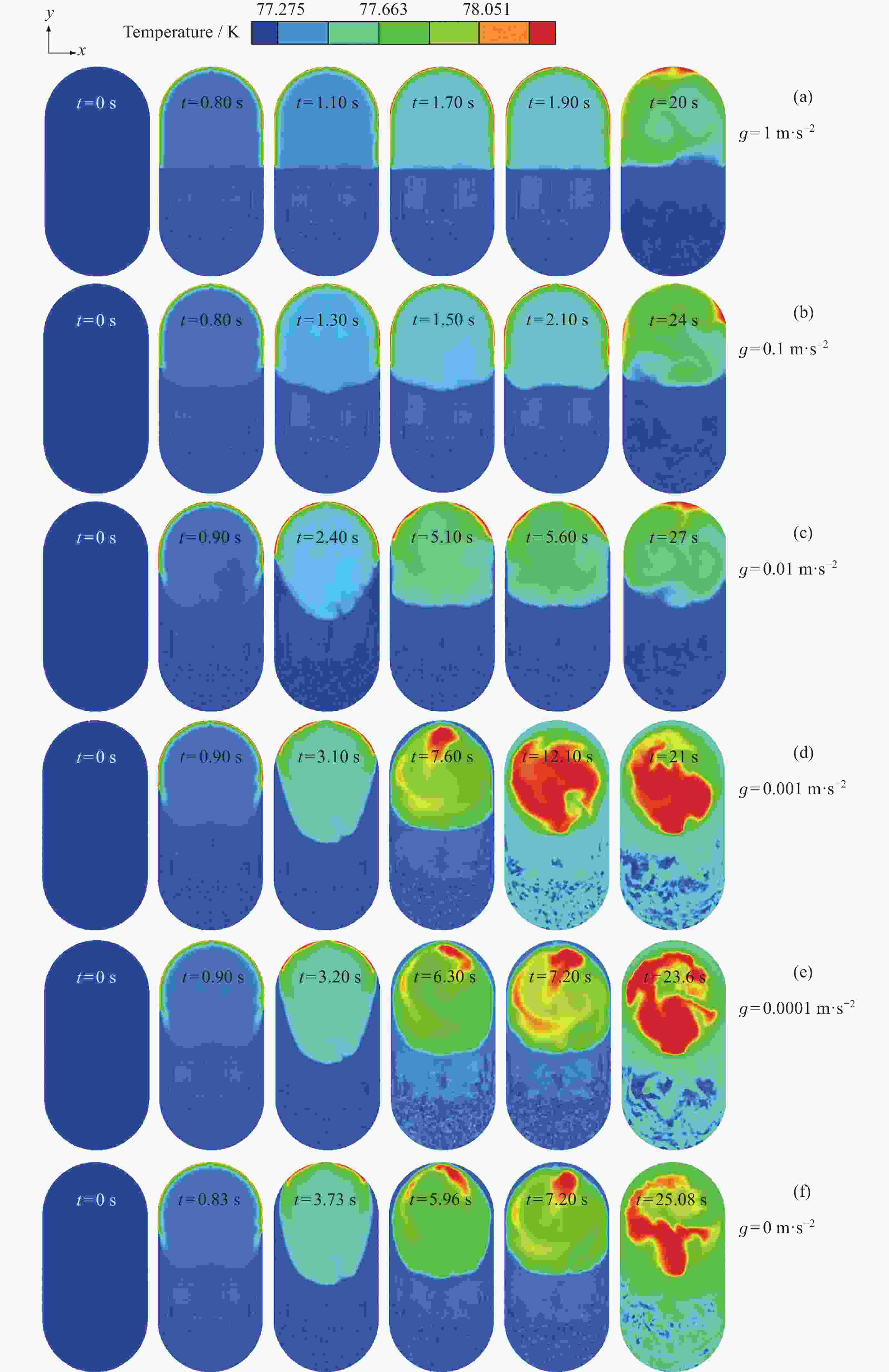
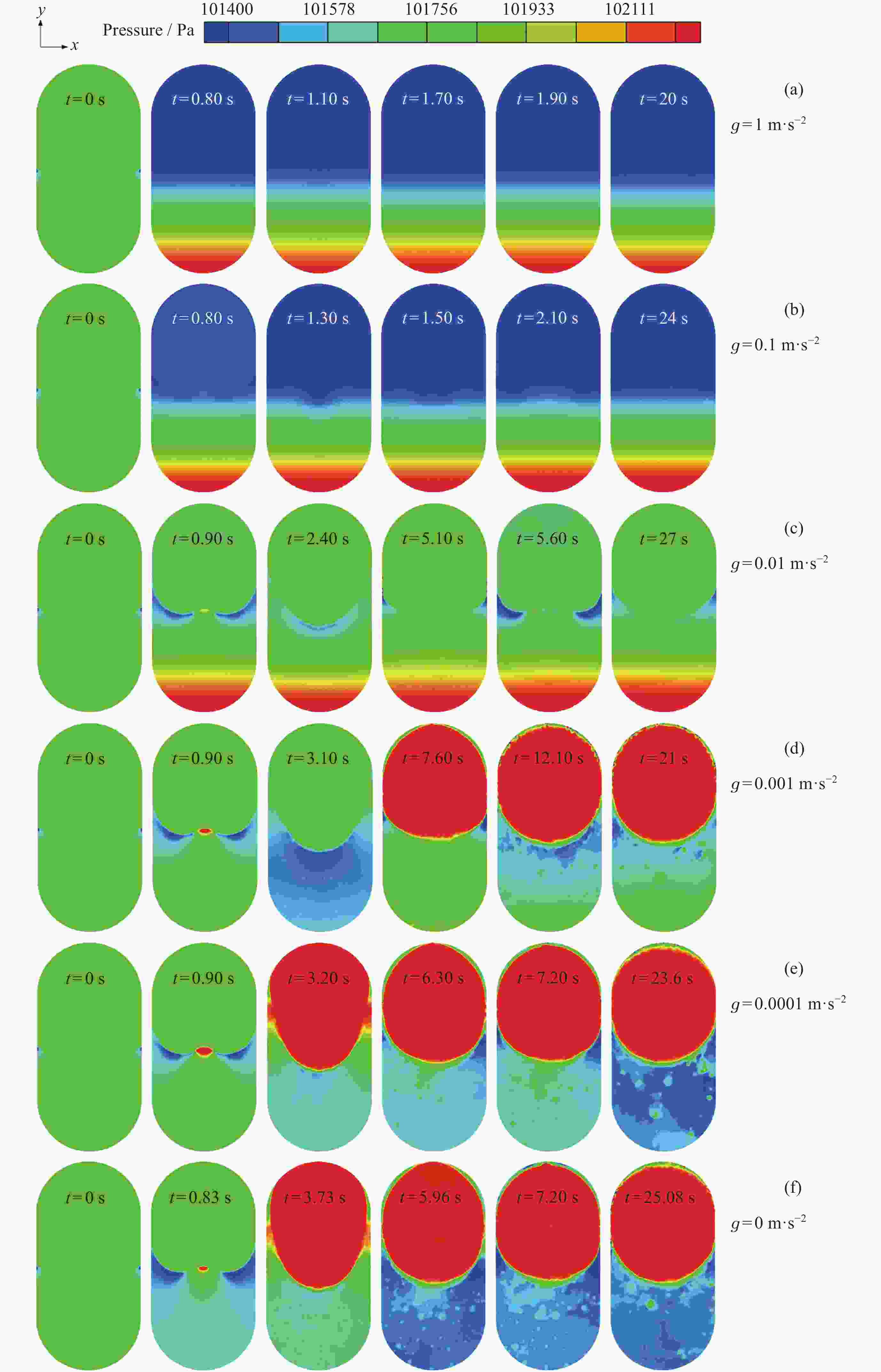
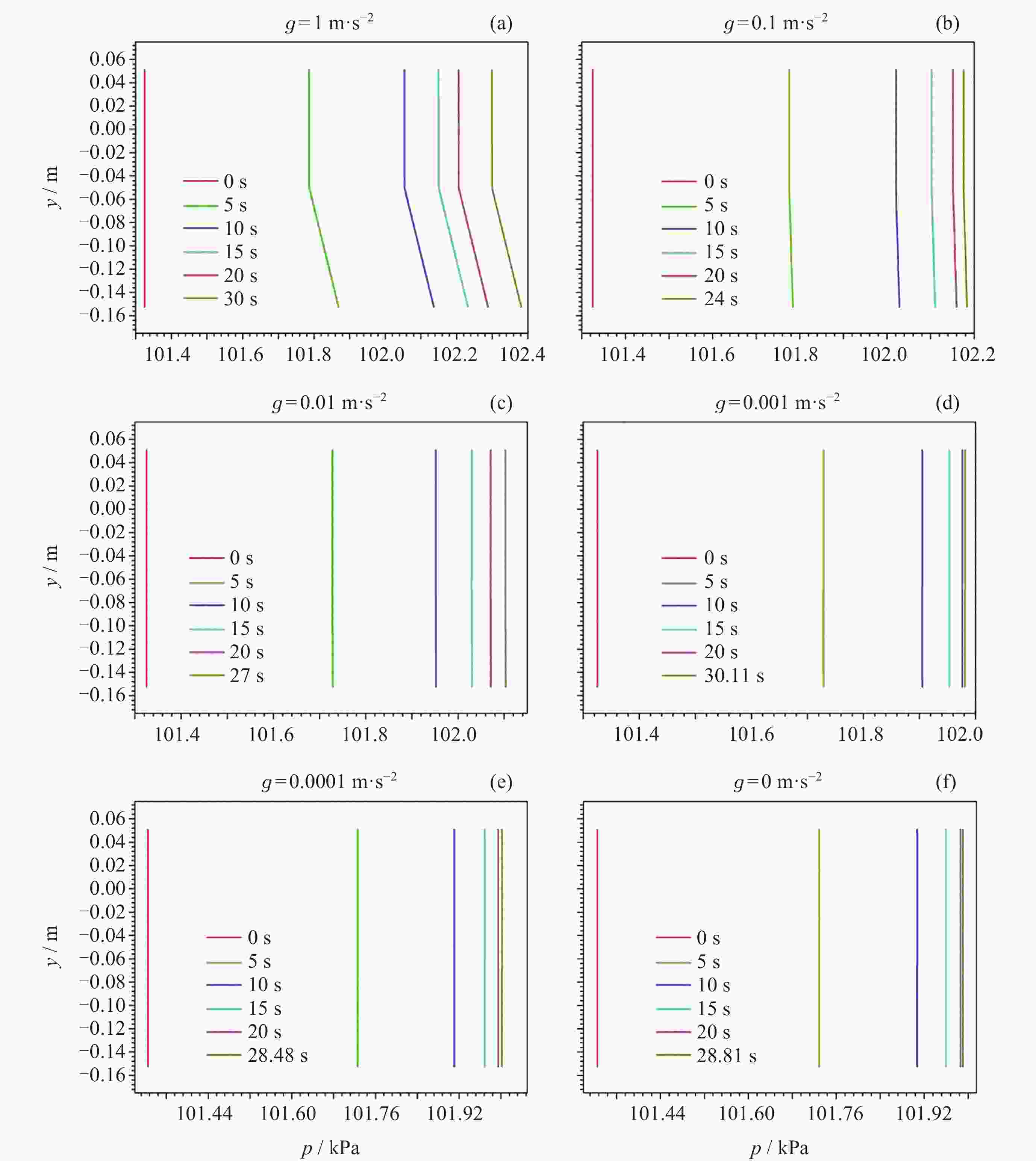
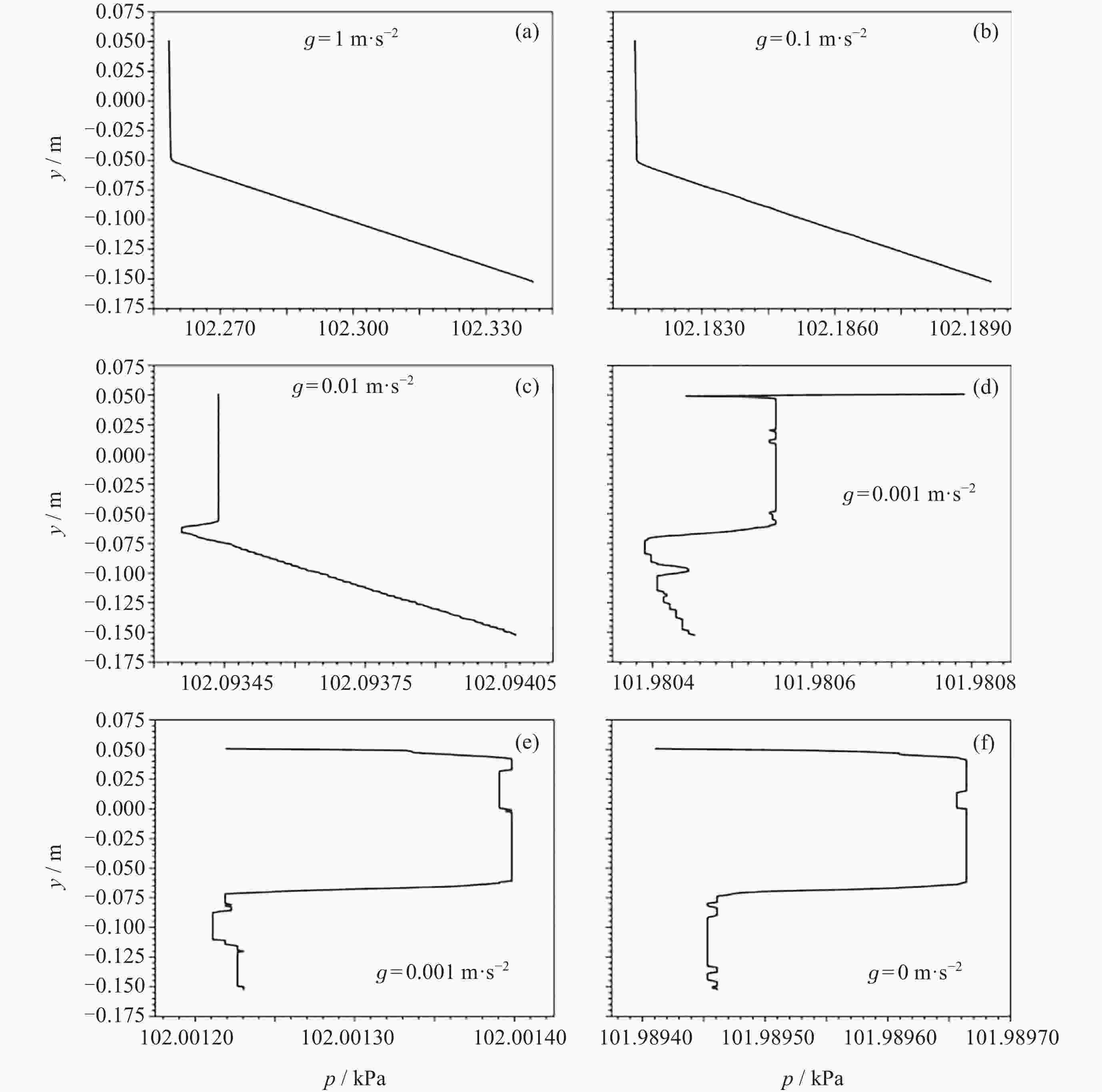
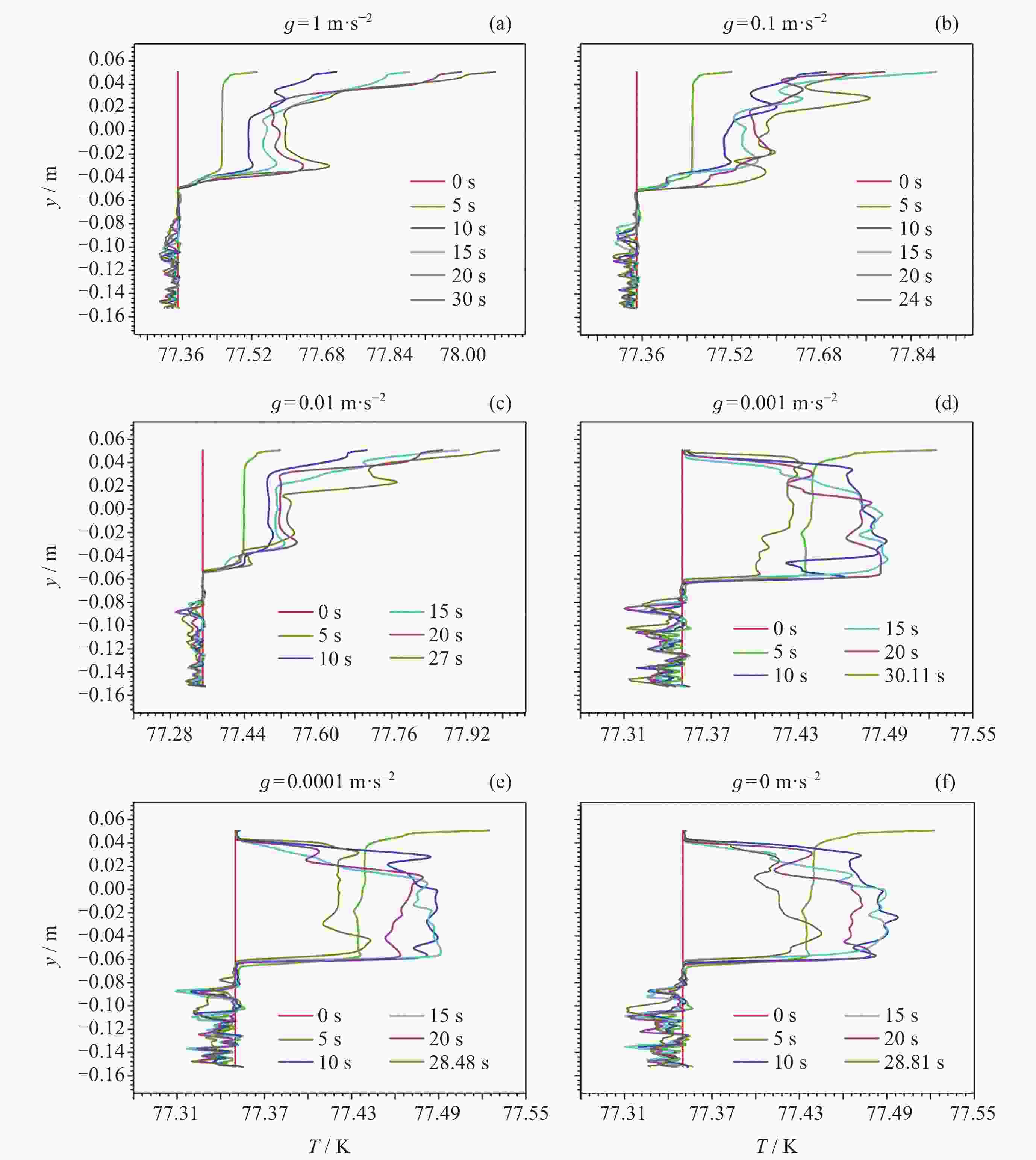
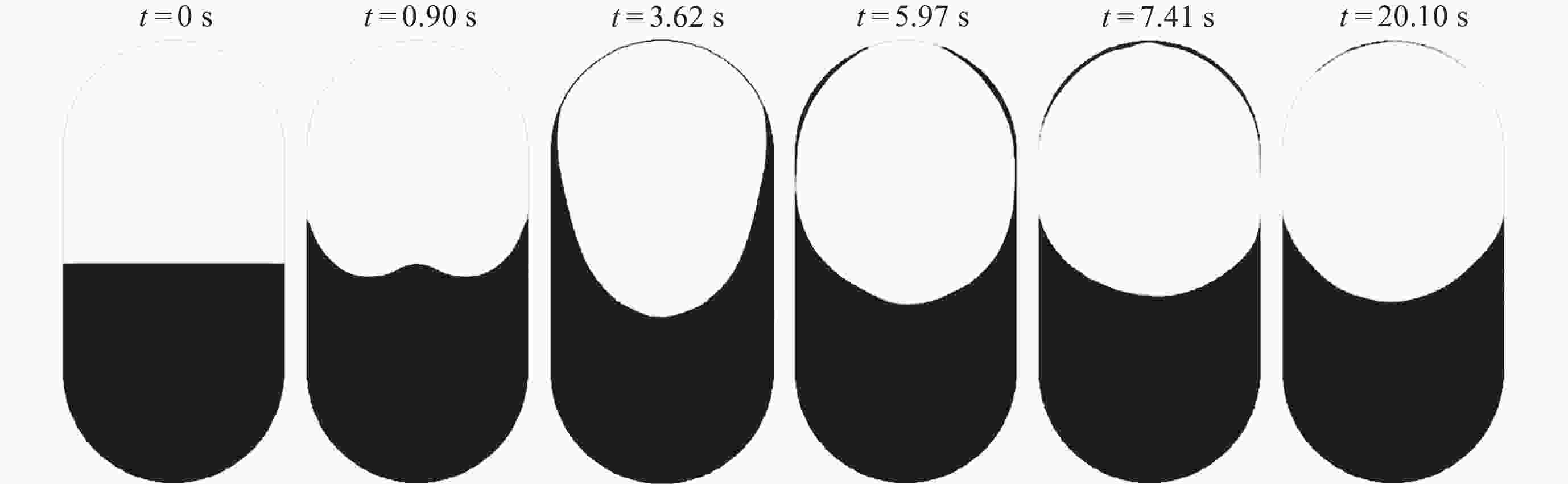
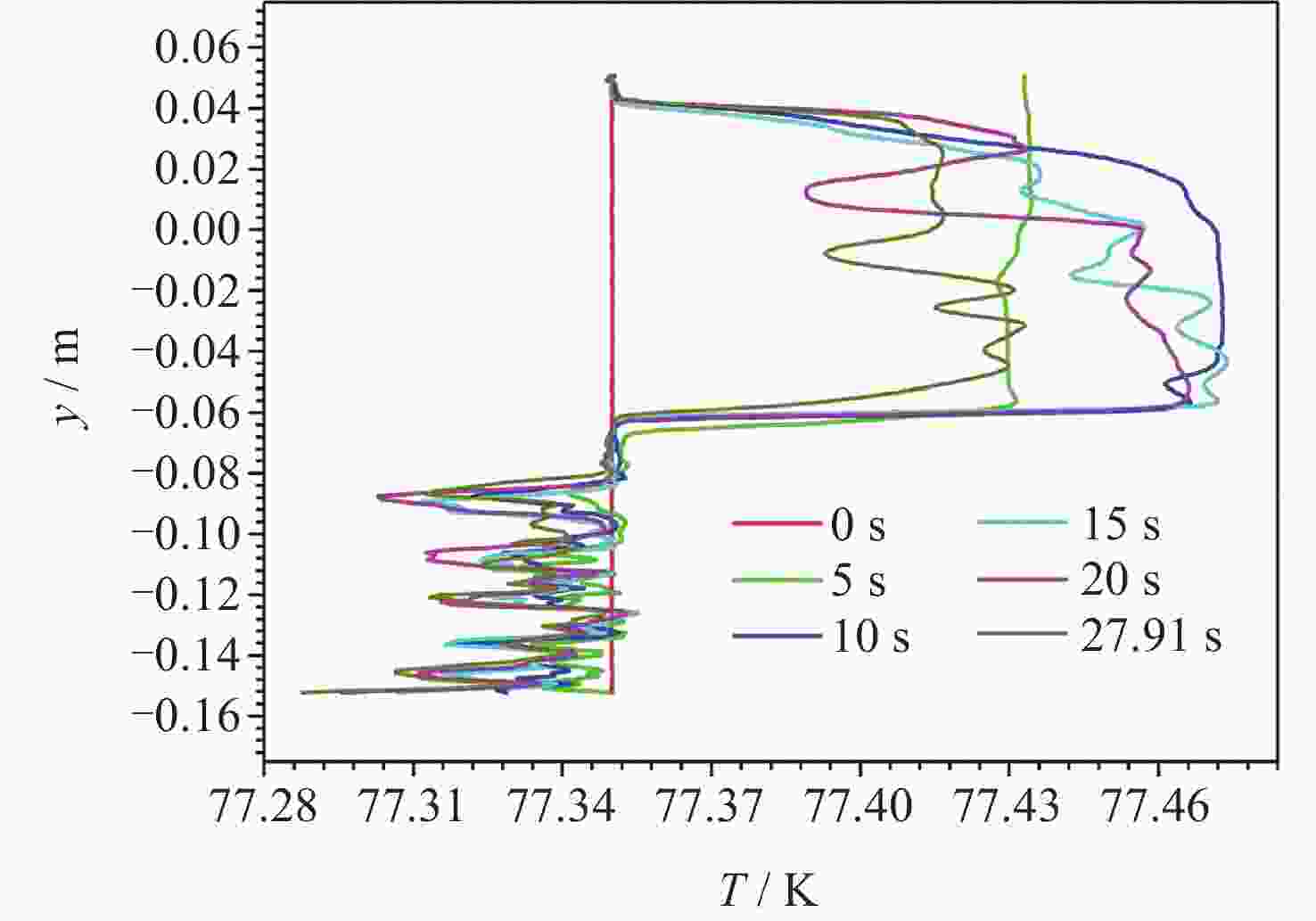
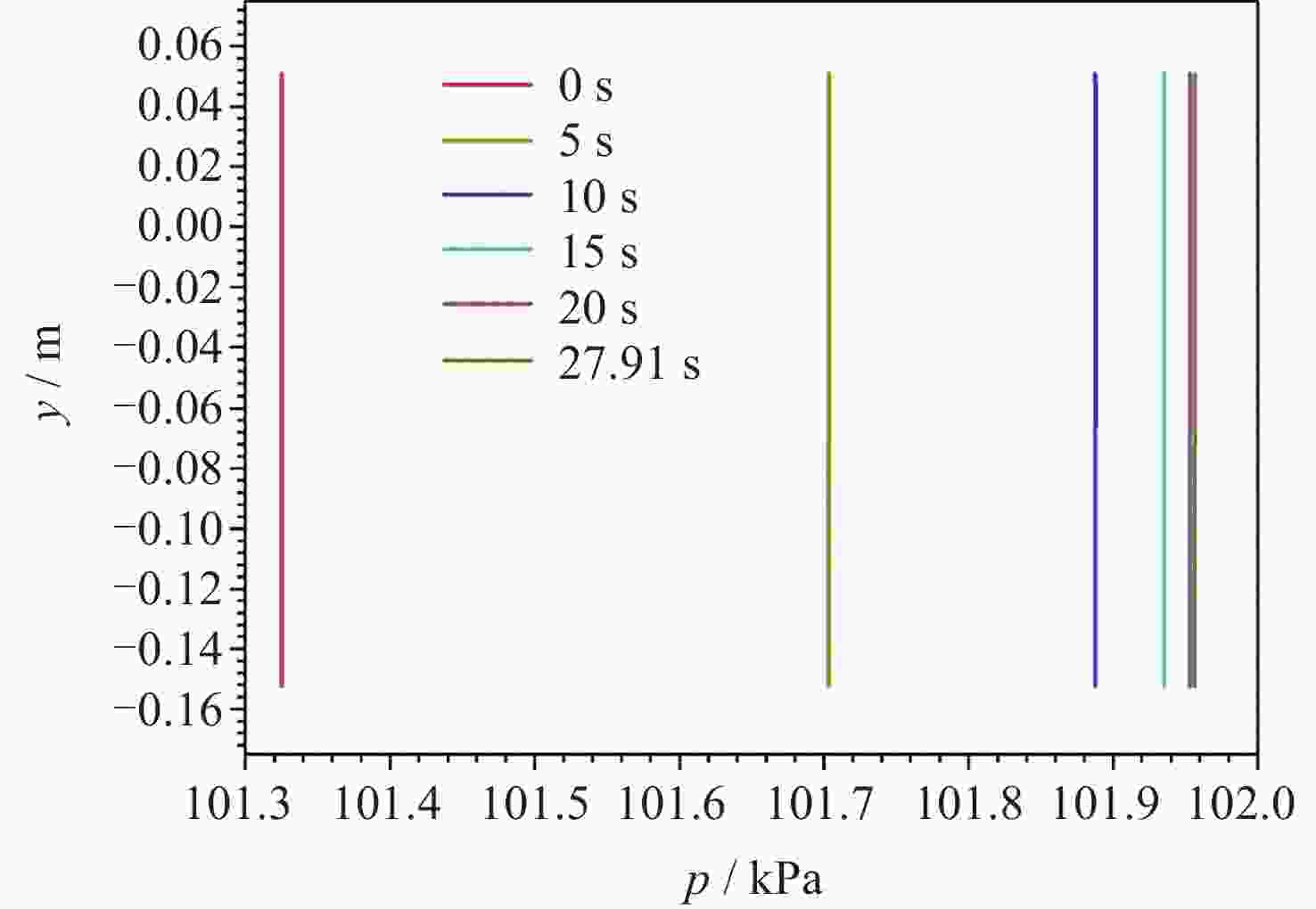
摘要: 为了研究残余重力加速度g对液氮贮箱自加压期间贮箱内流体的流动、相分布、温度分布以及压强分布的影响, 针对液氮贮箱, 采用流体体积(Volume-of-Fluid, VOF)方法数值模拟了不同g条件下液氮贮箱的自加压过程. 研究结果表明: 在大g情况下, 贮箱内压强沿g的方向逐渐增大, 贮箱内气枕的温度随贮箱壁面的持续漏热而不断升高, 且靠近壁面区域气体的温度最高, 靠近液体区域气体的温度最低; 随着g的减小, 贮箱内的液体更容易沿贮箱壁面爬升, 贮箱内流体温度差异性逐渐减小; 在小g情况下, 贮箱内流体流动稳定后会将气枕包裹于贮箱中部, 形成球形气泡, 贮箱内流体温度的差异性随时间先逐渐增大然后逐渐减小. 在零重力环境下, 贮箱壁面漏热(qw = 0.5 W·m–2)存在与否对贮箱内流体运动和相分布的影响均不显著, 并且在起始一段时间间隔$\Delta t_{\mathrm{f}} $ (0 ≤ $\Delta t_{\mathrm{f}} $ ≤ 40 s)内, 除贮箱壁面附近之外, qw存在与否对贮箱内流体温度分布的影响也不显著.Abstract: In order to study the effects of residual gravitational acceleration g on the flow, phase distribution, temperature distribution, and pressure distribution of liquid nitrogen tank during self-pressurization, the self-pressurization process of liquid nitrogen tank under different g was numerically simulated by the Volume-of-Fluid (VOF) method. The results show that under the condition of large g, the fluid pressure in the tank increases gradually along the direction of residual gravity, and the temperature of the ullage in the tank increases with the continuous heat leakage of the tank wall, and the gas temperature near the wall is the highest, and the gas temperature near the liquid is the lowest, while the temperature in the liquid bulk zone of the tank changes little with time. With the decrease of g, the liquid in the tank is more likely to climb along the wall of the tank with better infiltration, and the temperature difference of the fluid in the tank is gradually reduced. In the case of small g, after the fluid flow in the tank is stable, the ullage will be wrapped in the middle of the tank, forming a spherical bubble. The difference of the fluid temperature in the tank gradually increases and then decreases with time. In zero gravity environment, the presence or absence of heat leakage (qw = 0.5 W⋅m–2) on the tank wall has no significant influence on the fluid movement and phase distribution in the tank, and within the initial time interval $\Delta t_{\mathrm{f}} $ (0 ≤ $\Delta t_{\mathrm{f}} $ ≤ 40 s), the influence of the presence or absence of qw on the temperature distribution of the fluid in the tank also is not significant except near the wall of the tank. Numerical simulation results are expected to provide references to further study the on-orbit pressure control technique of cryogenic liquid tanks and space cryogenic fluid management.
-
表 1 液氮在1 atm下的饱和物性参数
Table 1. Saturated physical property parameters of liquid nitrogen under 1 atm
Working fluid Density
/(kg⋅m–3)Saturation temperature
/KThermal conductivity
/(W⋅m–1⋅K–1)Specific heat at constant pressure
/(kJ⋅kg–1⋅K–1)Latent heat of vaporization
/(kJ⋅kg–1)Dynamic viscosity
(×10–5)/(Pa⋅s)Surface
tension
(×10–3)/(N⋅m–1)Contact angle
/(°)Liquid nitrogen 806.08 77.35 0.1462 2.042 199.2 16.065 8.87 7 N2 1.138 77.35 0.0242 1.041 - 1.663 - - 表 2 NASA常温流体PnP贮箱自增压仿真的初边值条件
Table 2. Initial boundary conditions for the self-pressurization simulation of NASA’s normal-temperature fluid PnP tank
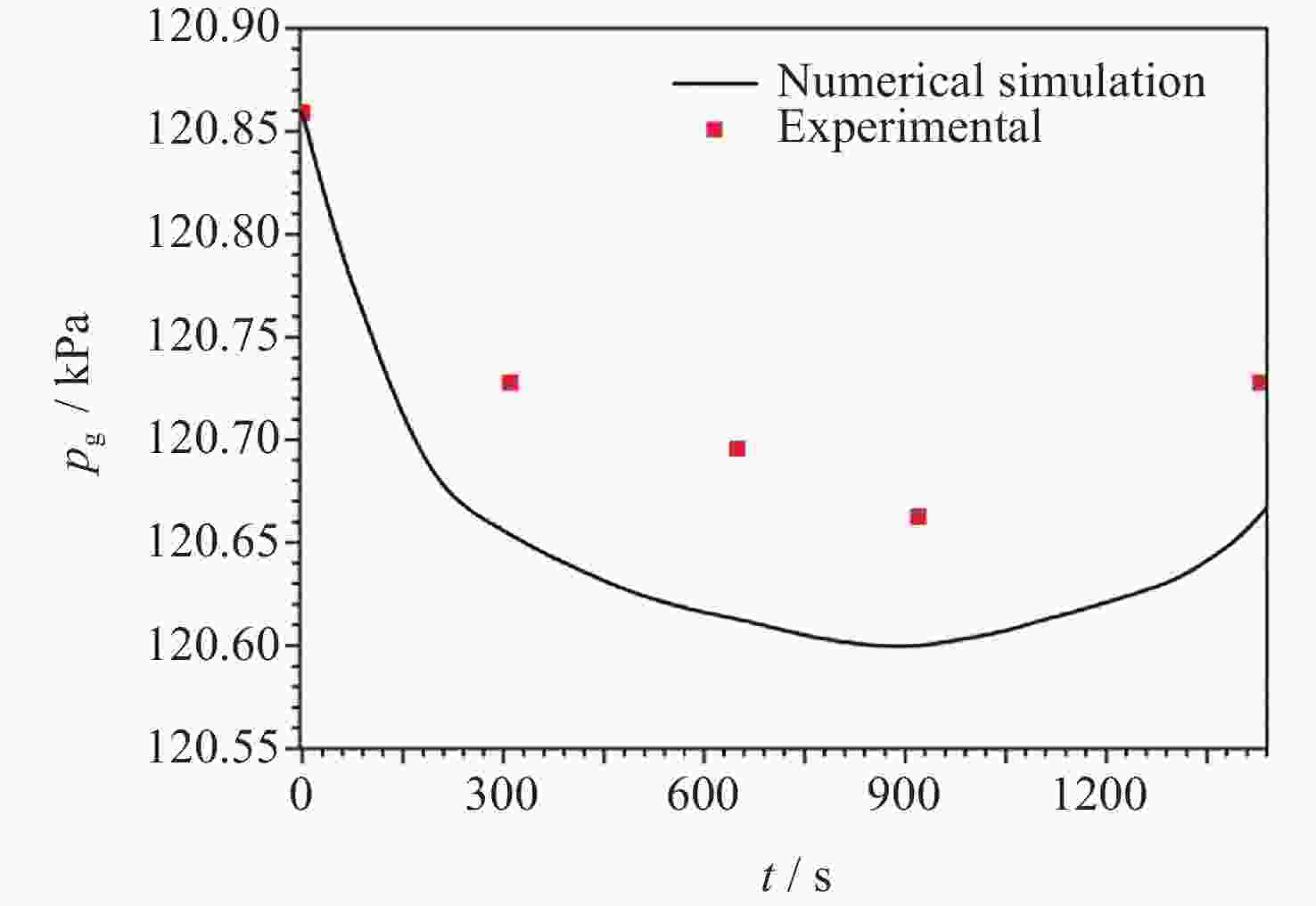
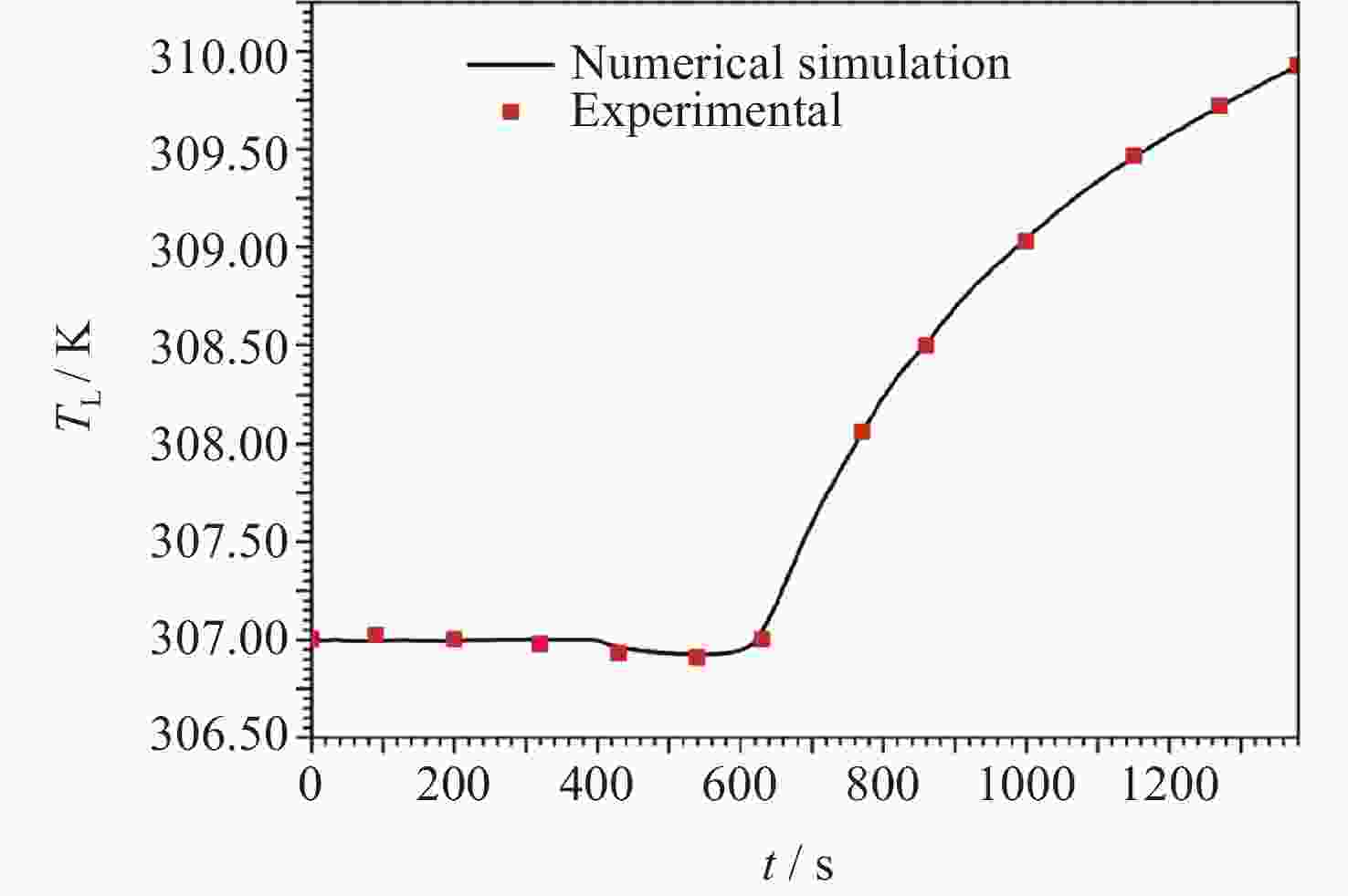
Variable Physical significance Experimental value p0 / Pa Initial pressure of normal-temperature fluid PnP 120859 Tg,0 / K Initial temperature of the ullage 307 Tl,0 / K Initial temperature of normal-temperature fluid PnP 307 f0 /(%) Initial volume filling ratio of normal-temperature fluid PnP 80.82 g0 /(m⋅s–2) Residual gravitational acceleration 5×10–6 qh /(W⋅m–2) Average heat leakage density of tank wall in the heating zone 0.5 qw /(W⋅m–2) Average heat leakage density of tank wall out of the heating zone 0 表 3 不同g条件下低温流体液氮贮箱自加压仿真的边值条件
Table 3. Boundary conditions for the self-pressurization simulation of cryogenic fluid tank for liquid nitrogen under different g conditions
Operating condition C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 g/(m·s–2) 1 0.1 0.01 0.001 0.0001 0 qw/(W·m–2) 1 1 1 1 1 1 -
[1] 王磊, 厉彦忠, 张少华, 等. 低温推进剂空间管理技术研究进展与展望[J]. 宇航学报, 2020, 41(7): 978-988WANG Lei, LI Yanzhong, ZHANG Shaohua, et al. Research progress and outlooks of cryogenic propellant space management technologies[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2020, 41(7): 978-988 [2] 王磊, 贾洲侠, 瞿淼, 等. 低温流体管理技术重力依赖性分析与微重力试验方案[J]. 制冷学报, 2021, 42(4): 1-11WANG Lei, JIA Zhouxia, QU Miao, et al. Gravity-dependence analysis of cryogenic fluid management techniques in space and experimental scheme suggestions[J]. Journal of Refrigeration, 2021, 42(4): 1-11 [3] SZABO S V JR, GROESBECK W A, BAND K W, et al. Atlas-Centaur Flight AC-4 Coast-Phase Propellant and Vehicle Behavior[R/P]. NASA TM X-1189, 1965 [4] LACOVIC R F, YEB F C, SZABO S V JR, et al. Management of Cryogenic Propellants in A Full Scale Orbiting Space Vehicle[R]. Washington: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, 1968 [5] AYDELOTT J C. Effect of gravity on self-pressurization of spherical liquid-hydrogen tankage[R]. Washington: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, 1967 [6] BENTZ M D, MESEROLE J S, KNOLL R H. Jet mixing in low gravity: results of the Tank pressure control space experiment[C]//Proceedings of the 28th Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit, 1992 [7] 周振君, 雷刚, 王天祥. 低温液氮贮箱增压性能及热分层研究[J]. 低温与超导, 2017, 45(1): 6-10,37ZHOU Z J, LEI G, WANG T X. Investigation on pressurization performance and thermal stratification in cryogenic nitrogen tank[J]. Cryogenics & Superconductivity, 2017, 45(1): 6-10,37 [8] KRENN A, STEWART M, MITCHELL D, et al. Flight servicing of robotic refueling mission 3[C]//Space Cryogenics Workshop. Washington: NASA, 2019 [9] 李佳超. 氢氧推进剂贮箱的工作过程与在轨热管理技术研究[D]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学, 2019LI Jiachao. Research on the Operation Process and On-orbit Thermal Management Technology of Hydrogen-oxygen Propellant Tanks[D]. Beijing: Beihang University, 2019 [10] CHATO D, KASSEMI M. The zero boil-off tank experiment contributions to the development of cryogenic fluid management[C]//Space Cryogenics Workshop. Washington: NASA, 2015 [11] CHATO D, KASSEMI M. The zero boil-off tank (ZBOT) experiment role in development of cryogenic fluid storage and transfer technologies[C]//Proceedings of the 28th Annual Meeting of the American Society for Gravitational and Space Research. New Orleans: NASA, 2012 [12] KASSEMI M, HYLTON S, KARTUZOVA O. Zero-boil-off tank (ZBOT) experiment – ground-based validation of self-pressurization & pressure control two-phase CFD model[C]//Proceedings of the 33rd Annual Meeting American Society for Gravitational and Space Research. Seattle: NASA, 2017 [13] KARTUZOVA O, KASSEMI M. CFD jet mixing model validation against zero-boil-off tank (ZBOT) microgravity experiment[C]//Proceedings of the AIAA/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion and Energy Forum and Exposition 2019. Indianapolis: AIAA, 2019 [14] KASSEMI M, HYLTON S, KARTUZOVA O. 1G and microgravity tank self-pressurization: experiments and CFD model validations across Ra and Bo regimes[J]. International Journal of Microgravity Science and Application, 2020, 37(1): 370103 [15] SAKOWSKI B, HAUSER D M, KASSEMI M. SINDA/FLUINT and thermal desktop multi-node settled and unsettled propellant tank modeling of zero boil off test[C]//Proceedings of the 55th AIAA/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference. Indianapolis: AIAA, 2019 [16] GRAYSON G D, LOPEZ A, CHANDLER F, et al. Cryogenic tank modeling for the Saturn AS-203 experiment[C]//Proceedings of the 42nd AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference & Exhibit. Sacramento: AIAA, 2006 [17] BARSI S, KASSEMI M. Numerical simulations of the zero boil-off tank experiment[C]//Proceedings of the 46th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit. Reno: AIAA, 2008 [18] AHUJA V, HOSANGADI A, MATTICK S, et al. Computational analyses of pressurization in cryogenic tanks[C]//Proceedings of the 44th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference & Exhibit. Hartford: AIAA, 2008 [19] MATTICK S J, LEE C P, HOSANGADI A, et al. Progress in modeling pressurization in propellant tanks[C]//Proceedings of the 46th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference & Exhibit. Nashville: AIAA, 2010 [20] 李章国. 空间流体界面现象与在轨流体管理数值模拟与实验研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院研究生院, 2010LI Zhangguo. Numerical Simulation and Experimental Investigation of Fluid Interface Behavior and Fluid Management in Space[D]. Beijing: Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2010 [21] 陈亮, 梁国柱, 邓新宇, 等. 贮箱内低温推进剂汽化过程的CFD数值仿真[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2013, 39(2): 264-268CHEN Liang, LIANG Guozhu, DENG Xinyu, et al. CFD numerical simulation of cryogenic propellant vaporization in tank[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2013, 39(2): 264-268 [22] FU J, SUNDEN B, CHEN X Q, et al. Influence of phase change on self-pressurization in cryogenic tanks under microgravity[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2015, 87: 225-233 doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.05.020 [23] YANG H Q, WEST J. CFD extraction of heat transfer coefficient in cryogenic propellant tanks[C]//Proceedings of the 51st AIAA/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference. Orlando: AIAA, 2015 [24] 刘展, 孙培杰, 李鹏, 等. 微重力下低温液氧贮箱热分层研究[J]. 低温工程, 2016(1): 25-31,53LIU Zhan, SUN Peijie, LI Peng, et al. Research on thermal stratification of cryogenic liquid oxygen tank in microgra-vity[J]. Cryogenics, 2016(1): 25-31,53 [25] AGRAWAL G, JOSEPH J, AGARWAL D, et al. Mathematical modelling of thermal stratification in a cryogenic propellant tank[J]. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2017, 171(1): 012045 [26] LUDWIG C, DREYER M E, HOPFINGER E J. Pressure variations in a cryogenic liquid storage tank subjected to periodic excitations[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2013, 66: 223-234 doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2013.06.072 [27] BRACKBILL J U, KOTHE D B, ZEMACH C. A continuum method for modeling surface tension[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1992, 100(2): 335-354 doi: 10.1016/0021-9991(92)90240-Y [28] LEE W H. A pressure iteration scheme for two-phase flow modeling [M]. Los Alamos: Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory, 1980: 407-431 -
-





 章敏 男, 1987年5月出生于安徽省枞阳县, 现为中国科学院力学研究所博士后, 主要研究方向为空间低温流体管理、液态金属气雾化制备金属粉末过程研究等. E-mail:
章敏 男, 1987年5月出生于安徽省枞阳县, 现为中国科学院力学研究所博士后, 主要研究方向为空间低温流体管理、液态金属气雾化制备金属粉末过程研究等. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: