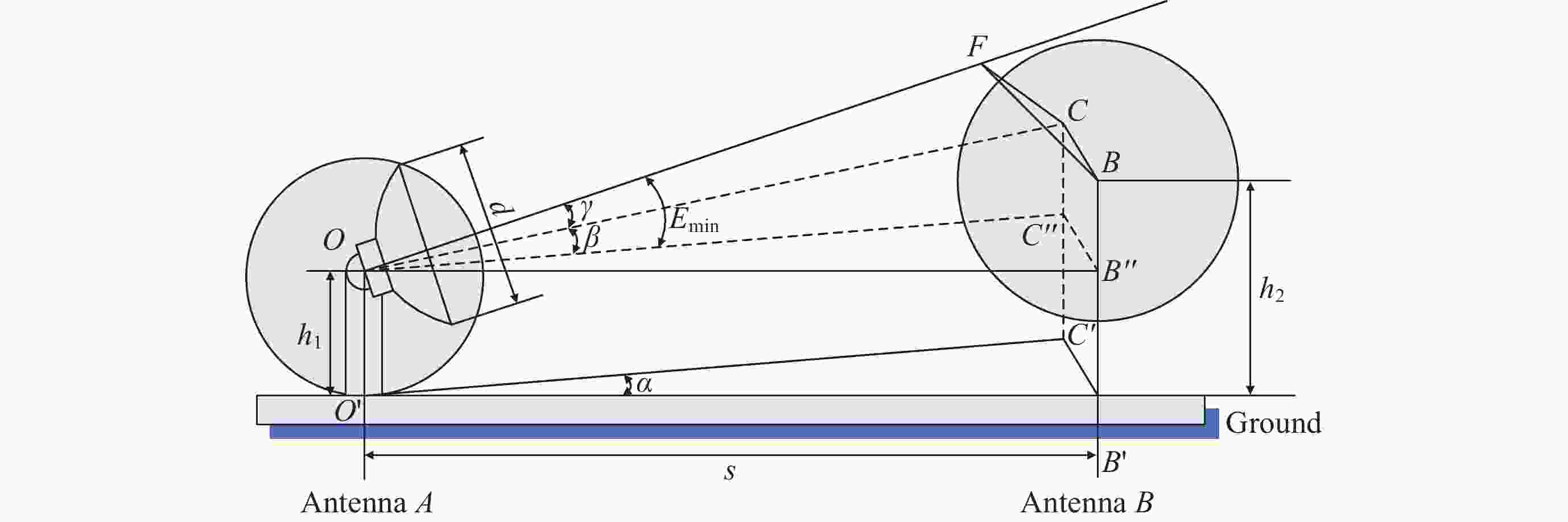
Remote Sensing Satellite Ground Station Antenna Occlusion Forecasting Model and its Application
-
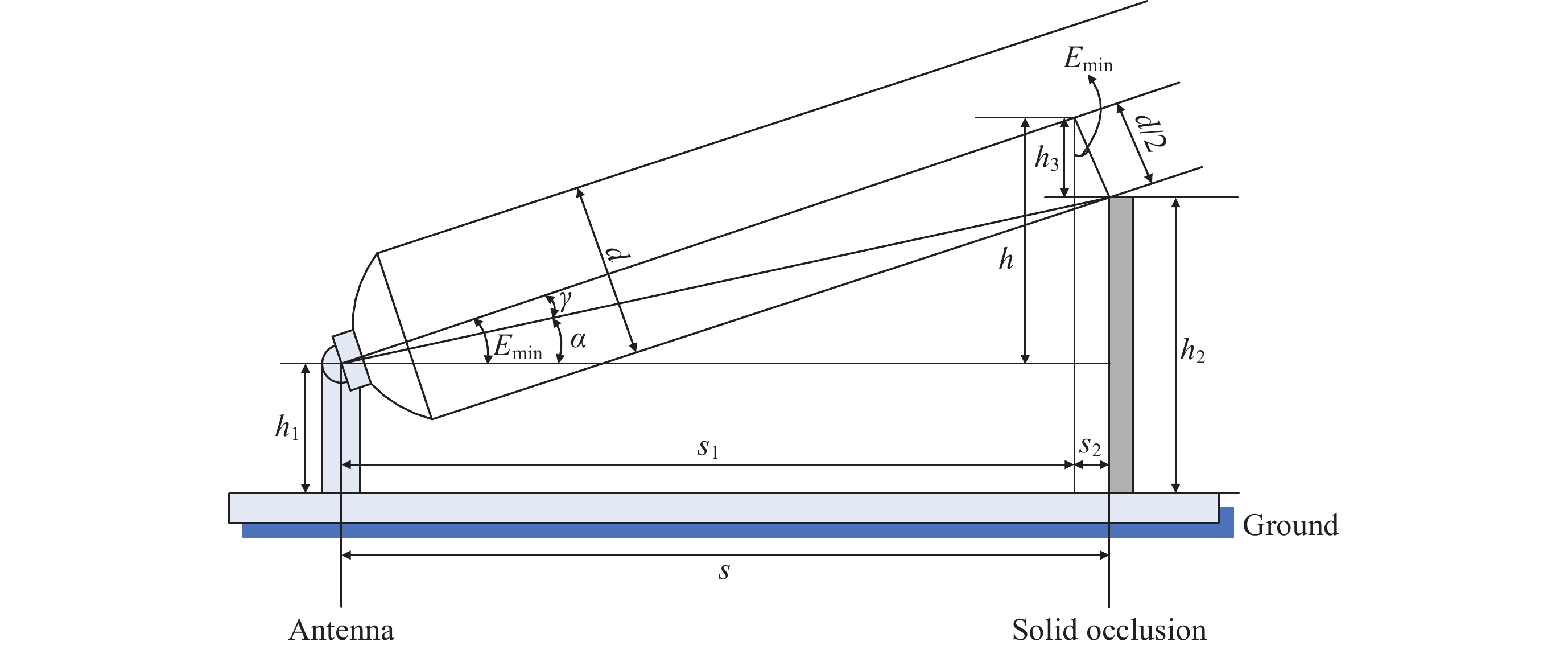
摘要: 基于遥感卫星地面站业务运行中所遇到的实际问题和运行经验, 为降低因地面站天线周边遮挡物对低轨道空间科学卫星、陆地观测卫星等极轨卫星的空间通信任务所产生的影响, 以提高航天器和地面的有效通信时长和通信质量为目标, 将地面站天线作为基准, 对周边环境的遮挡进行建模分析. 建立遮挡模型空间几何关系, 模型选择推导“天线无遮挡最小仰角”的求解思路, 通过模型分析和推导得到了遮挡物的实体遮挡模型公式和大型天线遮挡模型公式. 通过模型验证, 将模型计算结果同实际遮挡采样信息对比, 结果表明遮挡模型和遮挡实际情况基本吻合, 模型计算结果准确度可达到99.67%. 以天线遮挡预报模型为信息支持, 将天线遮挡预报封装成服务, 在任务规划阶段调用天线遮挡预报的计算服务和相应任务规划策略, 以实现天线遮挡预报模型在地面站运行管理资源调度中的工程应用. 经试运行和应用统计结果表明, 某地面站的运行管理资源调度优化率达到56.07%.Abstract: Based on the practical problems encountered in the operational operation of remote sensing satellite ground stations and operational experience, this paper aims to reduce the impact of obstructions around the antennas of ground stations on the space communication missions of polar orbit satellites such as low-orbit space science satellites and land observation satellites. With the goal of improving the effective communication duration and communication quality between the spacecraft and the ground, the ground station antenna is used as a benchmark for modeling and analyzing the obstructions in the surrounding environment. First establish the occlusion model spatial geometry relationship. The model is chosen to derive the solution for the “minimum elevation angle of the antenna without obstruction”. The solid occlusion model equations and large antenna Occlusion model equations are obtained through model analysis and derivation. Through the model validation, it shows that the model results and the actual situation of the occlusion basically match, and the accuracy of the model calculation results can reach 99.67%. Using the antenna occlusion forecast model as information support, the antenna occlusion forecast is encapsulated into a service, and the computation service of the antenna occlusion forecast and the corresponding mission planning strategy are invoked in the mission planning stage, so as to realize the engineering application of the antenna occlusion forecast model in the operation and management resource scheduling of a ground station. The results of trial operation and application statistics show that the optimization rate of operation management resource scheduling of a ground station has reached 56.07%.
-
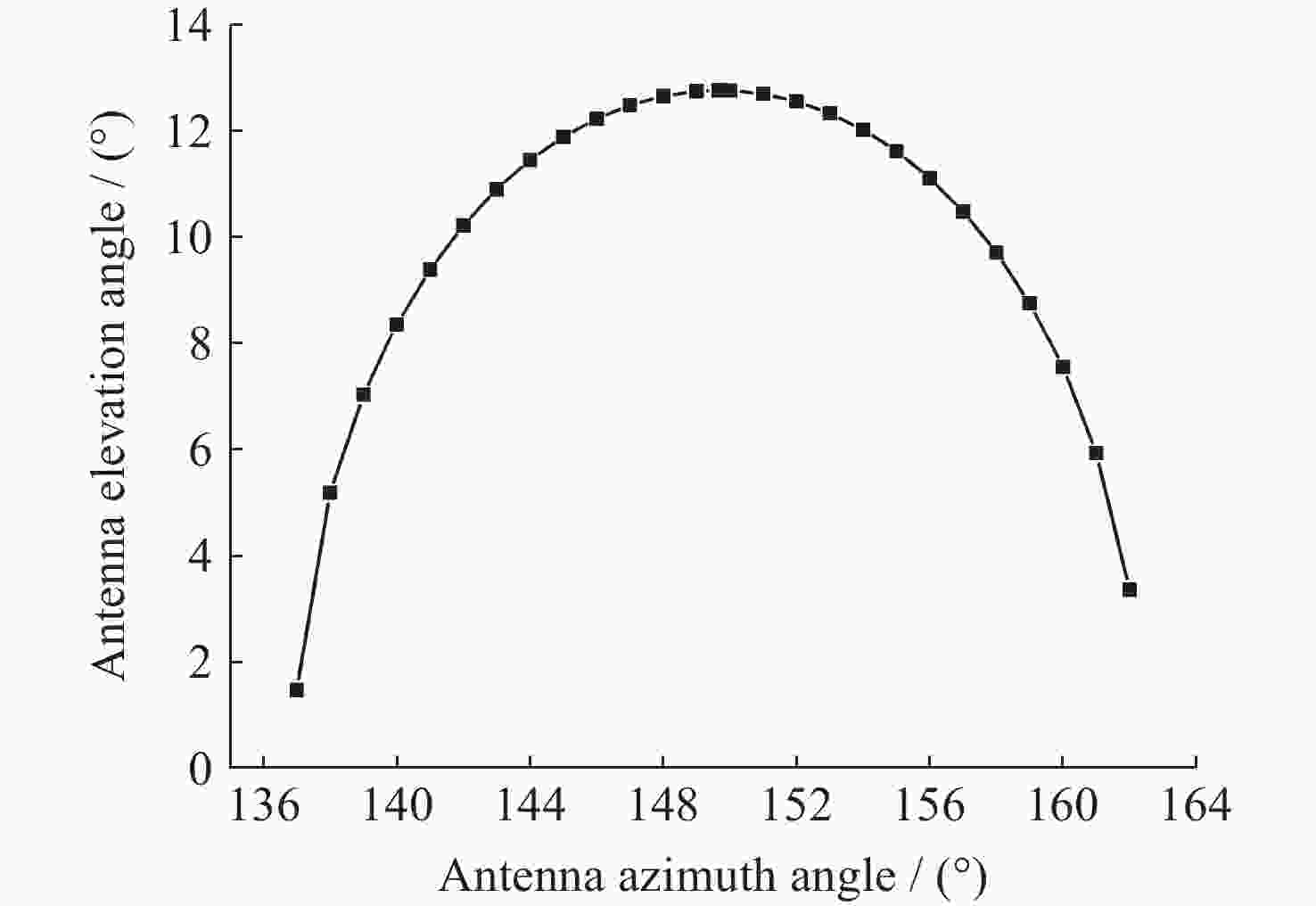
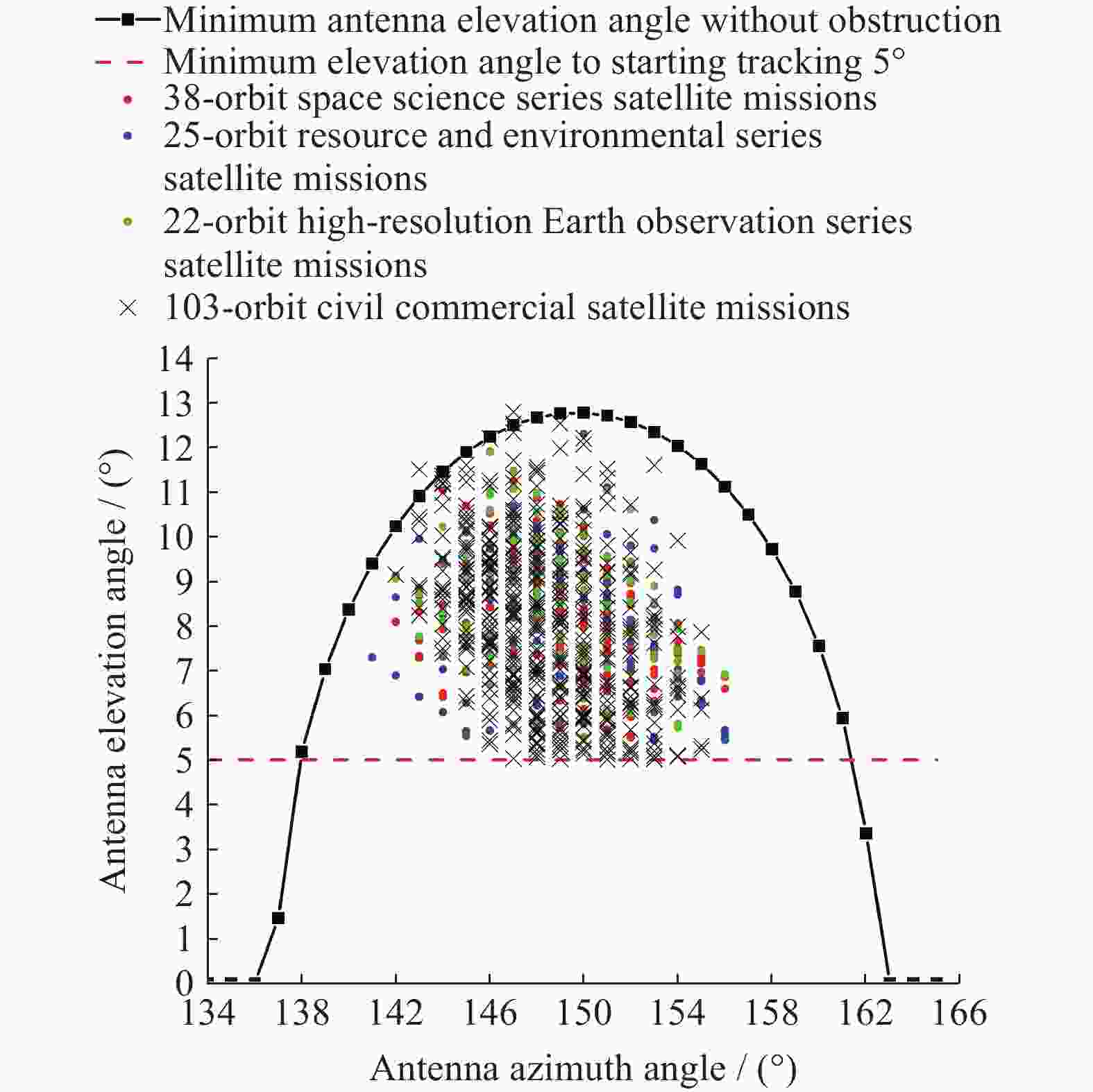
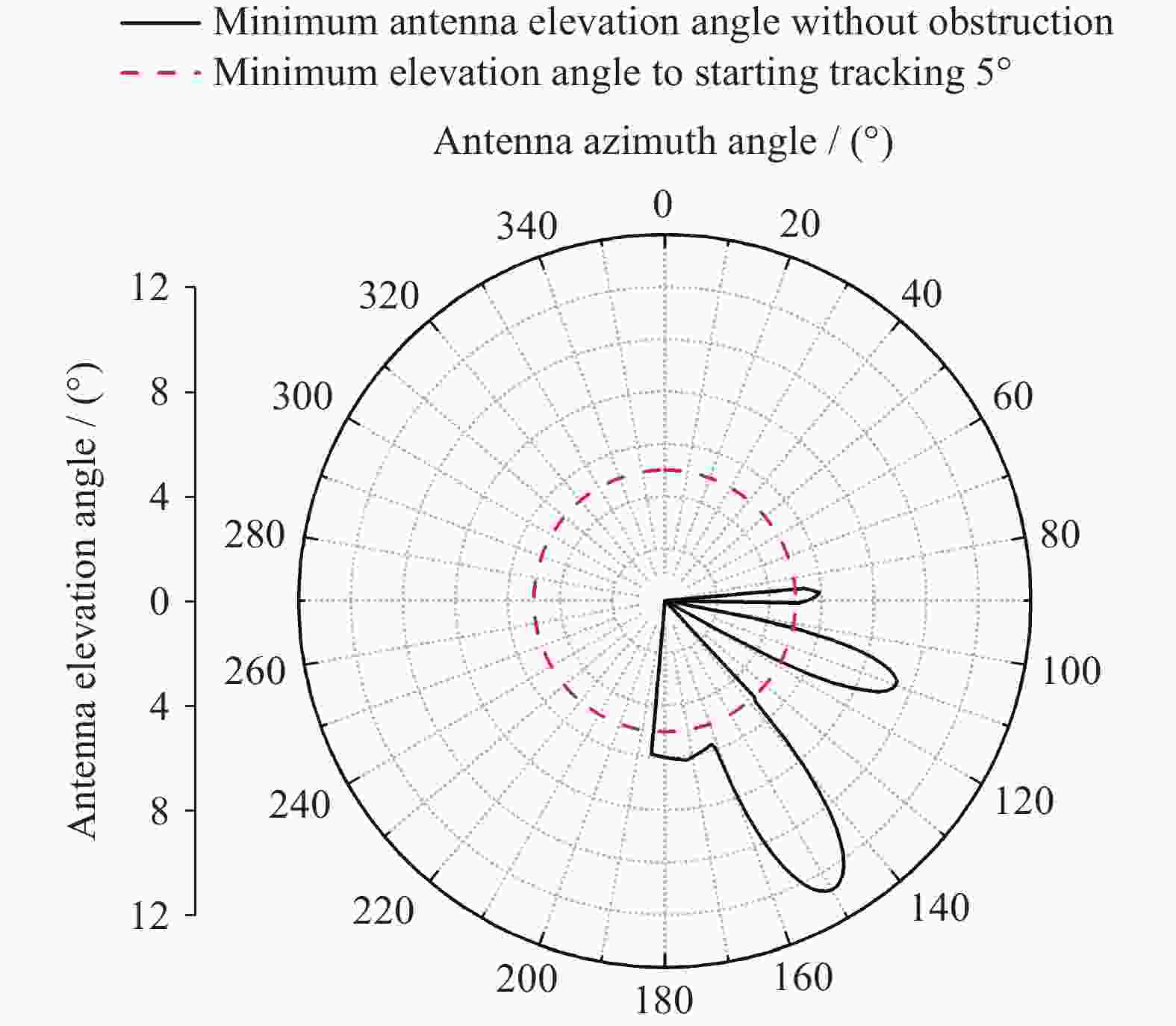
表 1 地面站天线A无遮挡最小仰角计算数据 (起始跟踪最小仰角为5º)
Table 1. Calculation data for the minimum elevation angles without obstruction of the ground station antenna A (Minimum elevation angle of 5º for initial tracking)
天线A方
位角度/(º)天线B
方位角/(º)夹角$ \alpha $
/(º)无遮挡最
小仰角$ {E}_{\mathrm{m}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}} $/(º)137 149.68 12.68 1.464 138 149.68 11.68 5.181 139 149.68 10.68 7.029 140 149.68 9.68 8.358 141 149.68 8.68 9.393 142 149.68 7.68 10.224 143 149.68 6.68 10.900 144 149.68 5.68 11.448 145 149.68 4.68 11.887 146 149.68 3.68 12.229 147 149.68 2.68 12.483 148 149.68 1.68 12.654 149 149.68 0.68 12.745 149.68 149.68 0 12.763 150 149.68 –0.32 12.759 151 149.68 –1.32 12.696 152 149.68 –2.32 12.554 153 149.68 –3.32 12.330 154 149.68 –4.32 12.021 155 149.68 –5.32 11.618 156 149.68 –6.32 11.111 157 149.68 –7.32 10.484 158 149.68 –8.32 9.713 159 149.68 –9.32 8.758 160 149.68 –10.32 7.550 161 149.68 –11.32 5.934 162 149.68 –12.32 3.359 表 2 某地面站S天线A周边地理环境参数
Table 2. Parameters of the geographic environment around the antenna of a ground station
试验
类型与天线A
距离/m俯仰轴绝对
海拔高度/m遮挡物相对
天线A的
方位角
/(º)天线A 0 47.165 0 天线B 72 47.165 137~161 天线C 97.3 47.165 102~117 山体 k 3432 330~396.45 85~91 建筑 z 230~270 64.8 137~185 表 3 某地面站天线遮挡预报试运行情况
Table 3. Trial operation of antenna occlusion forecasting at a ground station
采样
时间/d任务样本
总量/轨遮挡预报和
资源优化
任务量/轨运行管理
资源调度
优化率/ (%)23 2149 1205 56.07 -
[1] 安培浚, 王雪梅, 张志强, 等. 国外遥感卫星地面站分布及运行特点[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2008, 23(6): 697-704 doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2008.6.697AN Peijun, WANG Xuemei, ZHANG Zhiqiang, et al. Distribution of overseas satellites ground stations and their operational characteristics[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2008, 23(6): 697-704 doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2008.6.697 [2] 李安, 黄鹏, 石璐, 等. 中国遥感卫星地面站卫星地面系统的发展[J]. 遥感学报, 2021, 25(1): 251-266 doi: 10.11834/jrs.20210457LI An, HUANG Peng, SHI Lu, et al. Update of remote sensing satellite ground system of China remote sensing satellite ground station[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulle-tin, 2021, 25(1): 251-266 doi: 10.11834/jrs.20210457 [3] KRAUS J D, MARHEFKA R J. Antennas: For All Appli-cations[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2001 [4] 刘静怡, 田妙苗, 黄鹏, 等. 遥感卫星地面站资源调度的混合分解算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(理学版), 2020, 58(3): 611-619LIU Jingyi, TIAN Miaomiao, HUANG Peng, et al. Hybrid decomposition algorithm for remote sensing satellite ground station resource scheduling[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Science Edition), 2020, 58(3): 611-619 [5] 李瑞强, 杨金川, 张涛. 简便实用的抛物面天线方位角仰角定位方法[J]. 中国有线电视, 2006(2): 182-184 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7022.2006.02.021LI Ruiqiang, YANG Jinchuan, ZHANG Tao. Orientate directed angle and elevated angle method of parabolic antenna[J]. China Digital Cable TV, 2006(2): 182-184 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7022.2006.02.021 [6] 田世军, 朝鲁门. 广播电视卫星天线遮挡分析[J]. 数字传媒研究, 2018, 35(9): 43-45 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0751.2018.09.013TIAN Shijun, CHAO Lumen. Analysis of the possibility of radio and television satellite antennas being blocked[J]. Research on Digital Media, 2018, 35(9): 43-45 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0751.2018.09.013 [7] 张俊, 罗鹏. 关于卫星地球站天线场址选择的实例分析[J]. 广播电视信息, 2019(12): 72-74 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1997.2019.12.022ZHANG Jun, LUO Peng. Example analysis of satellite earth station antenna site selection[J]. Radio & Television Information, 2019(12): 72-74 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1997.2019.12.022 [8] 侯俊东. 501台现有天线场地增建两面12米口径C频段抛物面天线可行性分析[J]. 数字传媒研究, 2019, 36(12): 61-67 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0751.2019.12.019HOU Jundong. Feasibility analysis for the construction of two additional 12-metre C-band parabolic antennas at the existing antenna site at Radio 501[J]. Research on Digital Media, 2019, 36(12): 61-67 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0751.2019.12.019 [9] 王志波. 卫星通信天线遮挡分析[J]. 通信技术, 2020, 53(7): 1803-1805 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0802.2020.07.038WANG Zhibo. Analysis of satellite communication antenna occlusion[J]. Communications Technology, 2020, 53(7): 1803-1805 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0802.2020.07.038 [10] 王万玉, 周自宽. 遥感卫星地面站跟踪技术探讨[C]//中国空间科学学会空间探测专业委员会第十三次学术会议. 成都: 中国空间科学学会, 2000WANG Wanyu, ZHOU Zikuan. Exploration of remote sensing satellite ground station tracking technology[C]//The Thirteenth Academic Conference of the Space Exploration Committee of the Chinses Society of Space Science. Chengdu: Chinese Society of Space Research, 2000 -
-





 付伟龙 男, 1989年3月出生于河北省廊坊市, 现为中国科学院空天信息创新研究院工程师, 主要研究方向为卫星地面接收系统工程技术、电磁场与微波技术等. E-mail:
付伟龙 男, 1989年3月出生于河北省廊坊市, 现为中国科学院空天信息创新研究院工程师, 主要研究方向为卫星地面接收系统工程技术、电磁场与微波技术等. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: