Development Status and Prospects of Near Space Observatories
-
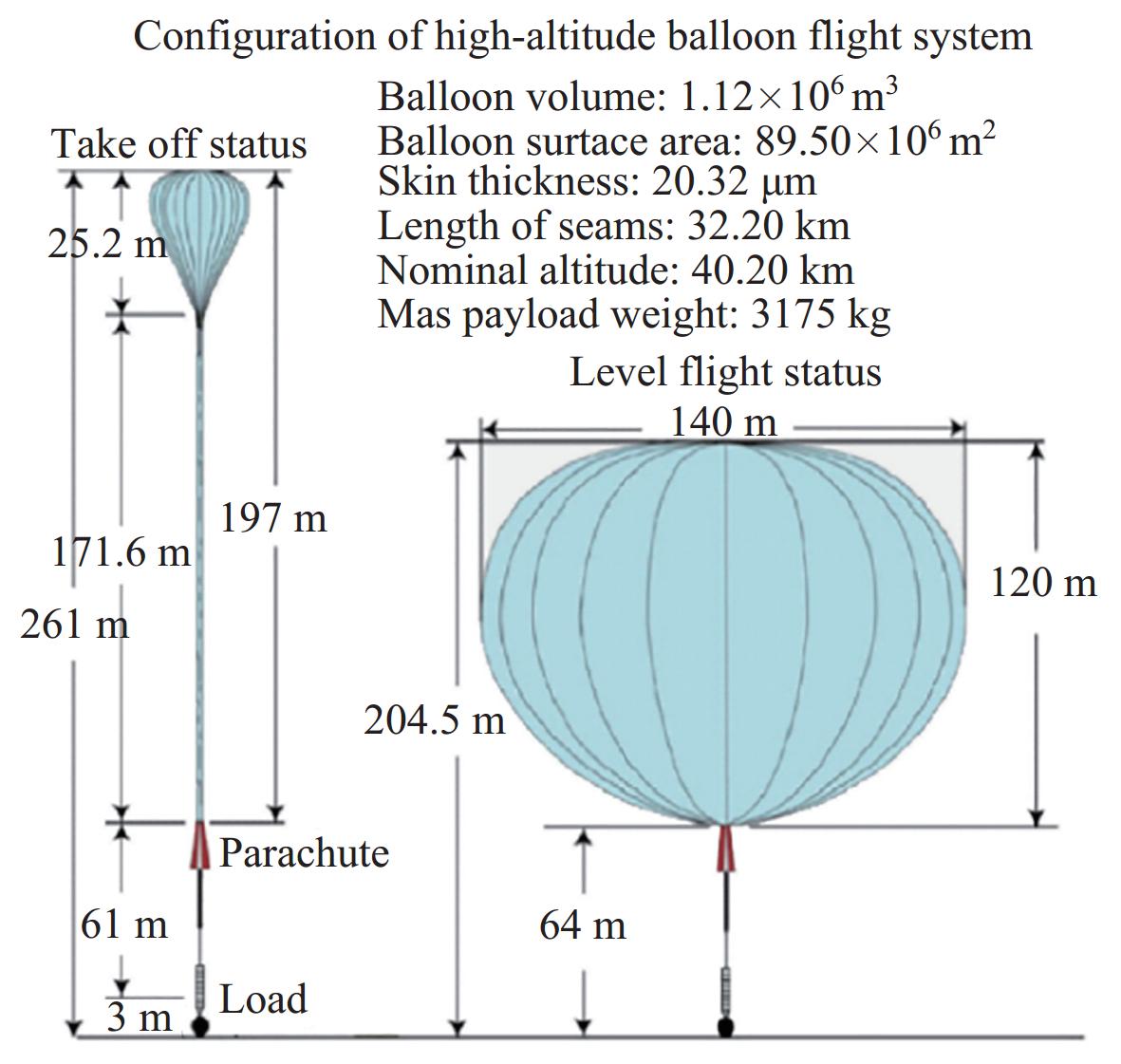
摘要: 临近空间天文台是一种特殊的天文台, 其选址于临近空间, 主要依托于高空科学气球浮空器平台. 中美等国家在20世纪大力推动高空科学气球技术发展, 形成了完整和成熟的科学气球系统, 进而促进了临近空间天文台的发展. 目前基于高空科学气球的临近空间天文台发展已经进入实用阶段, 在具体技术的研究上, 已从基础性应用技术向多用途、多功能的平台结构, 高可靠性、高稳定性和高精度控制等方面发展. 制约临近空间天文台发展的关键技术正在不断取得进展: 长航时飞行技术通过超压气球的实现得到突破, 高精度稳定指向技术由通过WASP系统的实现得到突破. 基于高空科学气球的临近空间天文台能够作为空间科学天文观测先进仪器的前期验证平台, 有效提升天基天文台任务的成功率.Abstract: Unlike ground-based observatories and space-based observatories, the Near Space Balloon Observatory is a unique type of observatory located in near space, mainly relying on high-altitude scientific balloon platforms. Throughout the last century, countries such as China and the United States have invested significant effort in promoting the development of high-altitude scientific balloon technology, resulting in the establishment of a comprehensive and advanced scientific balloon system, facilitating a wide range of balloon-borne scientific activities, which have facilitated the maturity of near-space observatories. It has the advantages and potential of low distribution and usage costs, short preparation cycles, large payload capacity, recyclability for multiple uses, and more flight opportunities. The development of near space observatories, utilizing high-altitude scientific balloons, has now entered the practical stage. In terms of specific technical research, the focus has shifted from basic application technology to the development of multi-purpose, multifunctional platform structures with high reliability, stability, and precision control. With the ongoing advancements in two key technologies, namely long endurance flight and high-precision pointing, the potential of near-space balloon observatories is being increasingly explored. As early validation platforms for advanced instruments and innovative ideas in space science and astronomy observations, it can effectively enhance the success rate of space-based observatory observation tasks and accelerate the development lifecycle of space-based observatories. As a platform for nurturing space science talents, it can also cultivate more leading experts and strengthen the research team. This article takes the opening of China’s fifth Antarctic Station, the Qinling Station, as an opportunity to suggest timely conducting high-altitude scientific balloon flight tests at the Qinling Station in Antarctica, further promoting the astronomical observation of Antarctica by China’s near space observatory, and contributing greater strength.
-
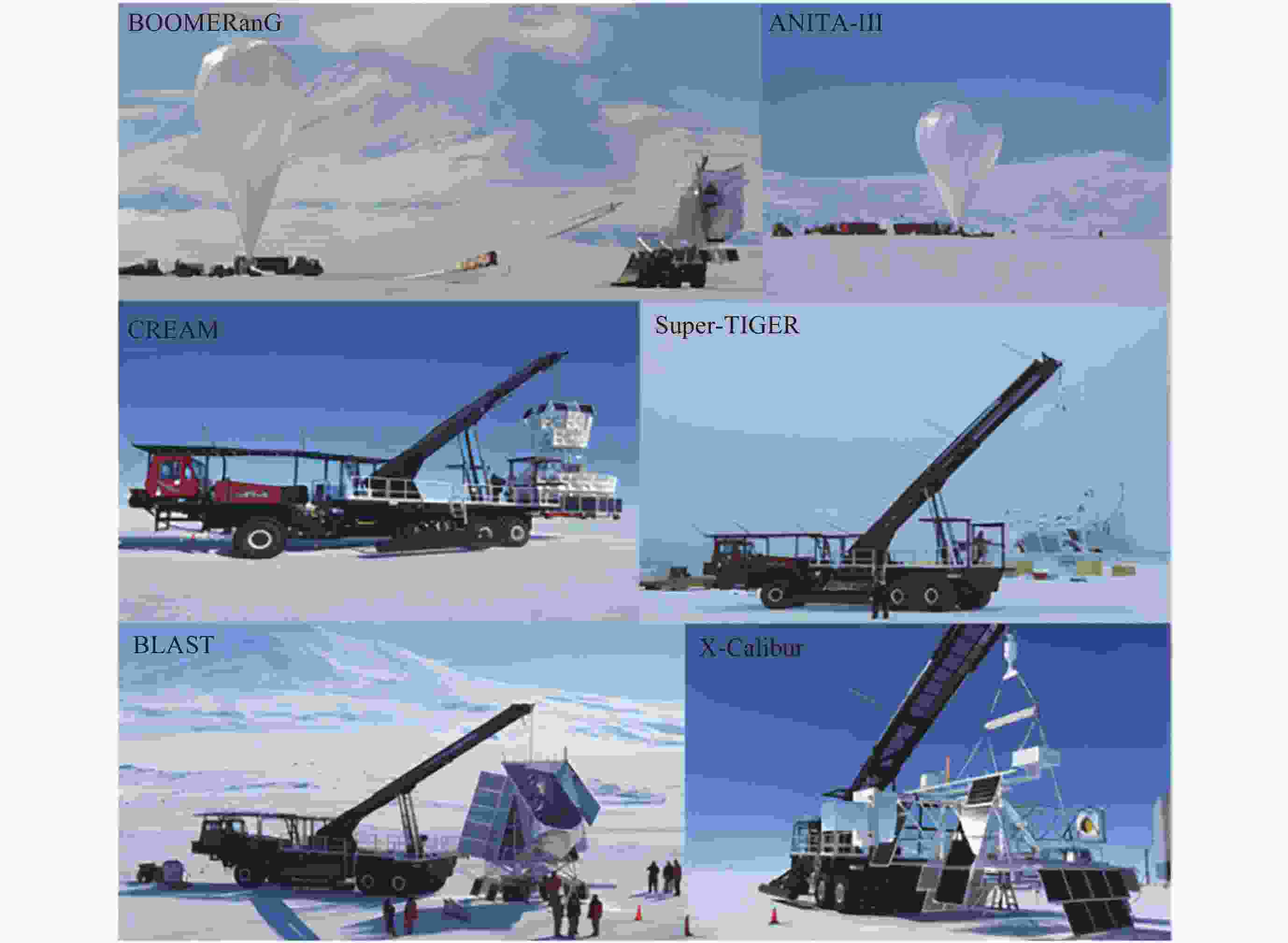
表 1 南极气球天文计划 (非粒子天体物理)
Table 1. Antarctic balloon astronomy program (non particle astrophysics)
课题 主要计划和关注领域 大爆炸宇宙学 ARCADE宇宙/天体物理和扩散辐射绝对辐射计: 全新厘米波精密差分辐射计
EREX E/B模实验
NCT 核康普顿望远镜
BLAST球载大孔径亚毫米波望远镜
SPIDER宇宙再电离时代偏振仪
BETTII 红外干涉双望远镜
CoFE-T 背景前景探测
HALO 高空透镜观测台(暗能量)
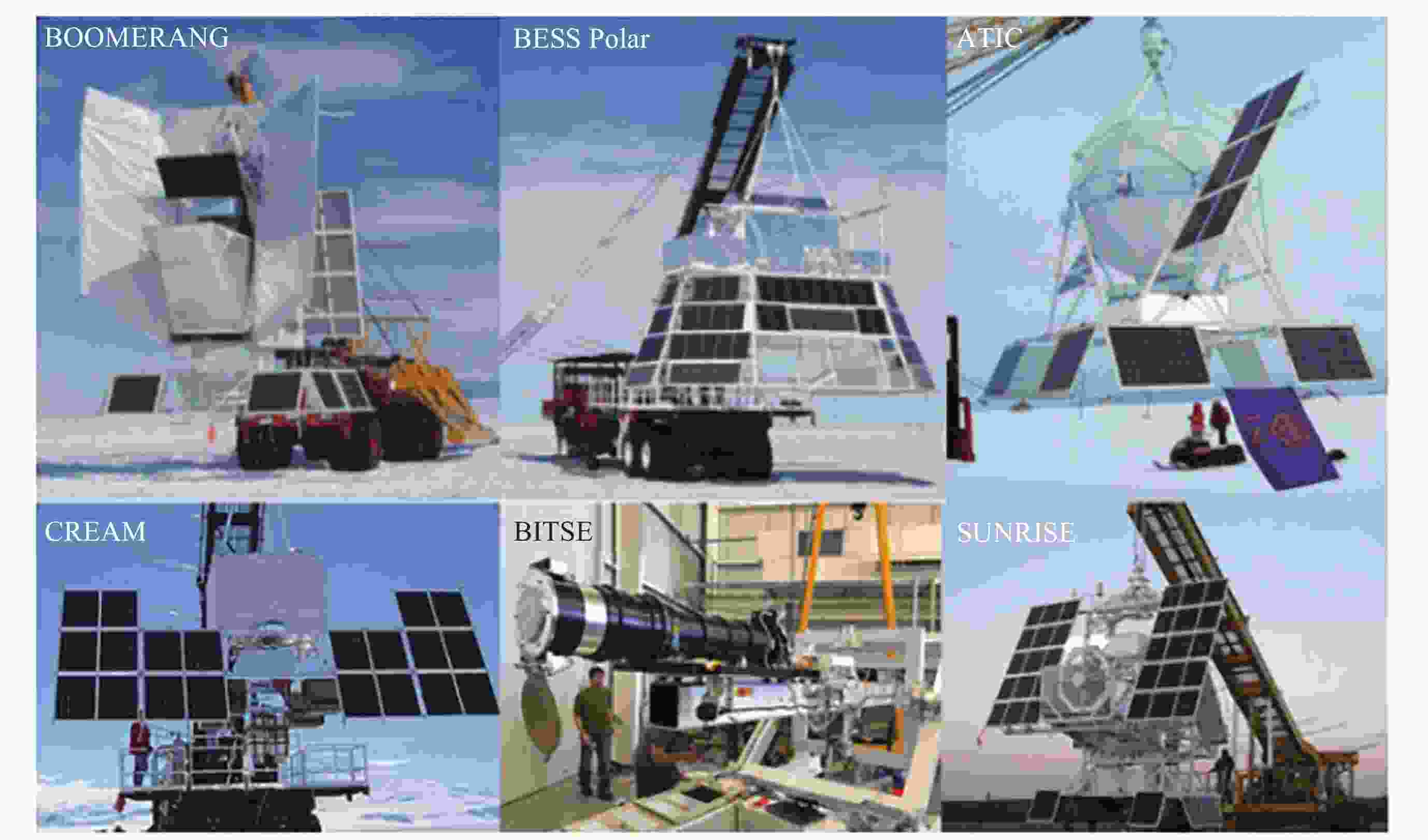
BOOMERanG 毫米波段气候观天计划X射线和 γ 射线源 DoGONE 多普勒敏感核γ探测
GRAPR γ 射线偏振仪实验
X-Calibur 硬X射线偏振飞行任务系外行星和宇宙生物学 BEST 球载系外行星光谱望远镜
ICarbS行星离子碳谱仪
Planet Scope 行星望远镜
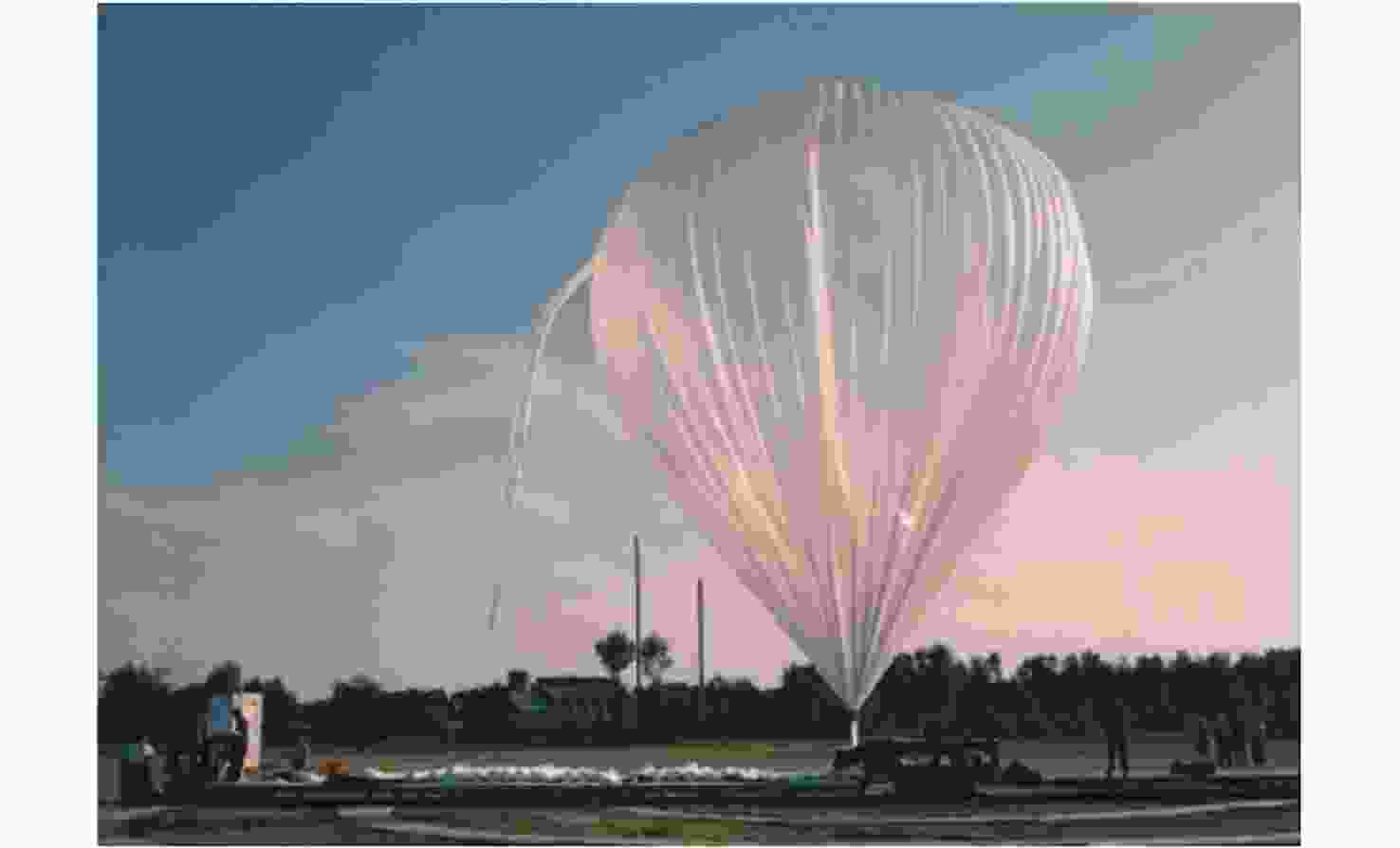
Zidiac 系外星尘盘探测
STO平流层太赫兹天文台表 2 南极气球天文计划 (粒子天体物理)
Table 2. Antarctic balloon astronomy program (particle astrophysics)
课题 主要计划和关注领域 宇宙线起源和加速 ATIC宇宙先进薄型离子量能器
CREAM 宇宙线能量和质量探测器: 穿越辐射探测器和钨闪烁光纤测能量
CREST 宇宙线电子同步辐射望远镜: 测高能电子地磁场同步γ辐射
Super-TIGER 超级超铁银河元素记录仪: 闪烁/硅阵列粒子谱仪中微子天文 ANITA 南极暂现脉冲天线 暗物质和反物质 BESS Polar 气球超导磁谱仪实验: 测量宇宙线中的低能反质子
ATIC 先进薄型离子量能器
GAPS 通用总反物质谱仪: 寻找反氘核和中微子湮灭通道表 3 从气球飞行的仪器中衍生的航天器仪器部分案例
Table 3. Partial examples of spacecraft instruments derived from balloon flying instruments
序号 航天器仪器 衍生于气球项目 1 康普顿 γ 射线天文台的仪器 美国NASA气球飞行仪器设备 2 宇宙微波背景探测器COBE卫星/威尔金森观测卫星WMAP 宇宙微波背景辐射探测BOOMERANG 3 鲁万–拉马蒂高能太阳光谱成像仪RHESSI探测器 由气球携带的开发仪器改进 4 高级宇宙定位探测器ACE的宇宙射线同位素光谱仪 首次演示在气球飞行中进行 5 地球观测系统EOS: Aura卫星仪器 可以追溯到气球飞行仪器设备 6 火星挥发物和气候勘测器MVACS 可以追溯到气球飞行仪器设备 7 火星极地着陆器上的热和进化气体分析仪TEGA 可以追溯到气球飞行仪器设备 8 国际空间站项目: 阿尔法磁谱仪AMS 气球实验: 超导磁谱仪实验BESS Polar 9 中国暗物质探测卫星DAMPE 气球实验: 先进薄型离子量能器ATIC 10 国际空间站项目ISS-CREAM 气球宇宙线能量和质量探测器CREAM 11 国际空间站项目: 日冕诊断实验CODEX 日冕温度和电子速度气球研究BITSE 12 中国硬X射线调制望远镜卫星: 慧眼HXMT 中国高空科学气球HIPI-1~4 13 欧洲航天局的太阳轨道飞行器 日出SUNRISE气球飞行任务的IMaX仪器 14 国际空间站项目JEM-EUSO EUSO-Balloon 任务 -
[1] 王海名. 美国国家科学院发布天文学和天体物理学十年调查报告[J]. 空间科学学报, 2022, 42(1): 5-8WANG Haiming. The National Academy of Sciences releases its Decadal Survey of Astronomy and Astrophysics[J]. Journal of Space Science, 2022, 42(1): 5-8 [2] 冉凡辉. 基于RTS2的天文选址望远镜远程控制系统研究与设计[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2015RAN Fanhui. Research and Design of Remote Control System for Astronomical Site Selection Telescope Based on RTS2[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2015 [3] 刘浩成. 基于多源遥感的冷湖区域天文台选址地理环境适宜度研究[D]. 西宁: 青海大学, 2023LIU Haocheng. Study on Geographical Environment Suitability of Observatory Site Selection Based on Multi-source Remote Sensing at Lenghu Region[D]. Xining: Qinghai University, 2023 [4] COSTA J, BOCK A, EMMART C, et al. Interactive visualization of atmospheric effects for celestial bodies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2021, 27(2): 785-795 doi: 10.1109/TVCG.2020.3030333 [5] RODIMOVA O B. Carbon dioxide and water vapor continuum absorption in the infrared spectral region[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Optics, 2018, 31(6): 564-569 doi: 10.1134/S1024856018060143 [6] ZHANG L H, XIONG R, CHEN J, et al. Optical image compression and encryption transmission-based ondeep learning and ghost imaging[J]. Applied Physics B, 2020, 126(1): 18 doi: 10.1007/s00340-019-7362-1 [7] BAUER S E, IM U, MEZUMAN K, et al. Desert dust, industrialization, and agricultural fires: Health impacts of outdoor air pollution in Africa[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2019, 124(7): 4104-4120 doi: 10.1029/2018JD029336 [8] 顾逸东. 关于空间科学发展的一些思考[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2022, 37(8): 1031-1049GU Yidong. Thoughts on space science development[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2022, 37(8): 1031-1049 [9] 白青江, 范全林, 时蓬, 等. 关于新一代旗舰型科学卫星WFIRST发展的分析[J]. 科技导报, 2021, 39(11): 38-45BAI Qingjiang, FAN Quanlin, SHI Peng, et al. On the development of NASA’s next generation flagship scientific mission WFIRST[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2021, 39(11): 38-45 [10] 吴季, 王赤, 范全林. 中国科学院空间科学战略性先导科技专项实施11年回顾与展望[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2022, 37(8): 1019-1030WU Ji, WANG Chi, FAN Quanlin. Review on 11 years of implementation of Strategic Priority Program (SPP) on space science and its prospect[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2022, 37(8): 1019-1030 [11] CHANG J, AMBROSI G, AN Q, et al. The DArk matter particle explorer mission[J]. Astroparticle Physics, 2017, 95: 6-24 doi: 10.1016/j.astropartphys.2017.08.005 [12] ZHANG S N, LI T P, LU F J, et al. Overview to the hard X-ray modulation telescope (Insight-HXMT) satellite[J]. Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 2020, 63 (4): 249502 [13] 李新乔, 文向阳, 安正华, 等. GECAM卫星有效载荷介绍[J]. 中国科学(物理学 力学 天文学), 2020, 50 (12): 80-96LI Xinqiao, WEN Xiangyang, AN Zhenghua, et al. The GECAM and its payload[J]. Scientia Sinica Physica, Mechanica & Astronomica, 2020, 50 (12): 80-96 [14] GAN W Q, FENG L, SU Y. A Chinese solar observatory in space[J]. Nature Astronomy, 2022, 6(1): 165 doi: 10.1038/s41550-021-01593-9 [15] Yuan W, Zhang C, Feng H, et al. Einstein probe — a small mission to monitor and explore the dynami X-ray universe[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science & Technology, 2015, 23(4): 383-6 [16] 黄宛宁, 张晓军, 李智斌, 等. 临近空间科学技术的发展现状及应用前景[J]. 科技导报, 2019, 37(21): 46-62HUANG Wanning, ZHANG Xiaojun, LI Zhibin, et al. Development status and application prospect of near space science and technology[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2019, 37(21): 46-62 [17] SMITH-PIERCE M C, CHAROENBOONVIVAT Y C, SHUKLA D, et al. High altitude aerodynamic reflectors to counter climate change[C]//2018 Applied Aerodynamics Conference. Atlanta: American Institute of Aeronautics, 2018 [18] 李智斌, 黄宛宁, 张钊, 等. 2020年临近空间科技热点回眸[J]. 科技导报, 2021, 39(1): 54-68LI Zhibin, HUANG Wanning, ZHANG Zhao, et al. Summary of the hot spots of near space science and technology in 2020[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2021, 39(1): 54-68 [19] 顾逸东. 气球科学观测100年[J]. 现代物理知识, 2020, 32(2): 3-12GU Yidong. 100 years of balloon science observation[J]. Modern Physics Knowledge, 2020, 32(2): 3-12 [20] 黄宛宁, 李智斌, 张钊, 等. 2019年临近空间科学技术热点回眸[J]. 科技导报, 2020, 38(1): 38-46HUANG Wanning, LI Zhibin, ZHANG Zhao, et al. Summary of hot spots of near space vehicles in 2019[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2020, 38(1): 38-46 [21] 李智斌, 黄宛宁, 张钊. 2018年临近空间科学热点回眸[J]. 科技导报, 2019, 37(1): 44-51LI Zhibin, HUANG Wanning, ZHANG Zhao. Summary of the hot spots of near space vehicles in 2018[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2019, 37(1): 44-51 [22] MCCARTHY D J. Operating characteristics of the stratoscope II balloon-borne telescope[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1969, AES-5(2): 323-329 doi: 10.1109/TAES.1969.309922 [23] SMITH JR I S. Advancements in NASA balloon research and development[J]. Advances in Space Research, 1996, 17(9): 37-44 doi: 10.1016/0273-1177(95)00674-4 [24] 陈旭. 长时高空气球的研制发展[J]. 航天器工程, 2007, 16(4): 83-88CHEN Xu. Development of long duration high altitude balloon[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2007, 16(4): 83-88 [25] 祝榕辰, 王生, 姜鲁华. 长航时超压气球技术的发展现状[C]//2014年中国浮空器大会. 哈尔滨: 中国航空学会, 2014ZHU Rongchen, WANG Sheng, JIANG Luhua. Development status of long endurance superpressure balloon technology[C]//Chinese Aeronautical Society. Harbin: Chinese Aeronautical Society, 2014 [26] ORR G D. The long duration balloon vehicle (LDBV) flight system development[C]//34th Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit. Reno: AIAA, 2012 [27] BINNS W R, BOSE R G, BRAUN D L, et al. The SUPERTIGER instrument: measurement of elemental abundances of ultra-heavy galactic cosmic rays[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2014, 788(1): 18 doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/788/1/18 [28] RAINWATER E L, SMITH M S. Ultra high altitude balloons for medium-to-large payloads[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2004, 33(10): 1648-1652 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2003.07.037 [29] LECINSKI A, CARD G, KNÖLKER M, et al. The design and performance of the gondola pointing system for the sunrise II balloon-borne stratospheric solar observatory[J]. Journal of Astronomical Instrumentation, 2017, 6(2): 1740007 doi: 10.1142/S2251171717400074 [30] 刘艳霄, 宋腾飞, 张涛, 等. 欧洲球载太阳望远镜SUNRISE及相关研究成果简介[J]. 天文研究与技术, 2021, 18(3): 314-336LIU Yanxiao, SONG Tengfei, ZHANG Tao, et al. Overview of balloon-borne solar telescope-SUNRISE[J]. Astronomical Research & Technology, 2021, 18(3): 314-336 [31] SHOJI Y, TAGUCHI M, NAKANO T, et al. FUJIN-2: balloon borne telescope for optical observation of planets[J]. Transactions of the Japan Society for Aeronautical and Space Sciences, Aerospace Technology Japan, 2016, 14(ists30): Pk_95-Pk_102 doi: 10.2322/tastj.14.Pk_95 [32] 顾逸东. 从高空气球到载人航天[J]. 现代物理知识, 2023, 35(S1): 192-199GU Yidong. From high-altitude balloons to manned spaceflight[J]. Modern Physics Knowledge, 2023, 35(S1): 192-199 [33] 李惕碚, 顾逸东. 我国的高空科学气球与高能天文观测[J]. 自然杂志, 1984(3): 163-169, 240LI Tibei, GU Yidong. China’s high altitude scientific balloon and high energy astronomical observation[J]. Nature Journal, 1984(3): 163-169, 240 [34] 卢方军. 从球载实验到慧眼卫星[J]. 现代物理知识, 2021, 33(2): 4-11LU Fangjun. From ball-borne experiments to HXMT[J]. Modern Physics Knowledge, 2021, 33(2): 4-11 [35] CHANG J, ADAMS J H, AHN H S, et al. An excess of cosmic ray electrons at energies of 300-800 GeV[J]. Nature, 2008, 456(7220): 362-365 doi: 10.1038/nature07477 [36] 叶祥明. 大型球载望远镜高精度姿态控制及指向技术研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院北京天文台, 1999YE Xiangming. Study on High-accuracy Attitude Control and Pointing Technology of A Large Balloon-borne Solar Telescope[D]. Beijing: National Astronomical Observatories, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 1999 [37] 林隽, 宋腾飞, 孙明哲, 等. 50 mm白光球载日冕仪: I. 基本结构与地面观测实验[J]. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学, 2023, 53 (5): 154-180LIN Jun, SONG Tengfei, SUN Mingzhe, et al. A 50-mm balloon-borne white-light coronagraph: Ⅰ. Basic structure and experiments on the ground[J]. Scientia Sinica (Physica, Mechanica & Astronomica), 2023, 53 (5): 154-180 [38] 李一健. 基于多敏感器组合的球载吊舱姿态控制技术研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2023LI Yijian. Research on attitude control Technology of Balloon borne Pod Based on Multi-sensor Fusion[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2023 [39] 王馨悦, 杜丹, 闫召爱, 等. 临近空间飞行平台青藏高原大气NO x原位观测实验[J]. 科学通报, 2022, 67(27): 3348-3356 doi: 10.1360/TB-2021-1279WANG Xinyue, DU Dan, YAN Zhao’ai, et al. In situ observation of atmospheric NO x over Qinghai-Tibet Plateau by scientific experiment system in near space program[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2022, 67(27): 3348-3356 doi: 10.1360/TB-2021-1279 [40] LI L, SU J F, CHEN T, et al. Measurement of atmospheric conductivity on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in China[J]. Meteorology and Atmospheric Physics, 2022, 134(2): 40 doi: 10.1007/s00703-022-00870-0 [41] 祝榕辰, 王生. 超压气球研究与发展现状[C]//第二十四届全国空间探测学术交流会论文摘要集. 西安: 中国空间科学学会, 2011ZHU Rongchen, WANG Sheng. Research and development status of superpressure balloons[C]//Summary of Papers at the 24th National Space Exploration Academic Exchange Conference. Xi’an: Chinese Society of Space Sciences, 2011 [42] 祝榕辰, 王生, 杨燕初, 等. 南瓜型超压气球球体设计与地面试验[C]//第四届高分辨率对地观测学术年会论文集. 北京: 高分辨率对地观测系统重大专项管理办公室 (中国科学院), 2017ZHU Rongchen, WANG Sheng, YANG Yanchu, et al. Design and ground experiments of pumpkin shaped superpressure balloon spheres[C]//Proceedings of the 4th Academic Annual Conference on High Resolution Earth Observation. Beijing: Office for Major Special Management of High Resolution Earth Observation Systems; Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017 [43] YAJIMA N. A new design and fabrication approach for pressurized balloon[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2000, 26(9): 1357-1360 doi: 10.1016/S0273-1177(00)00060-0 [44] GASKIN J A, SMITH I S, JONES W V. Introduction[J]. Journal of Astronomical Instrumentation, 2014, 3(2): 1403001 doi: 10.1142/S2251171714030019 [45] 祝榕辰. 超压气球实现临近空间首飞[J]. 现代物理知识, 2018, 30(1): 1ZHU Rongchen. Superpressure balloons achieve their first near space flight[J]. Modern Physics Knowledge, 2018, 30(1): 1 [46] CATHEY JR H M. Evolution of the NASA ultra long duration balloon[C]//AIAA Balloon Systems Conference. Williamsburg: AIAA, 2007 [47] CALLADINE C R. Stability of the “Endeavour” balloon[J]. Studies in Applied Mechanics, 1988, 19: 133-149 doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-70474-0.50011-2 [48] 卜亚楼, 蔡榕, 杨燕初, 等. 南瓜型超压气球展开稳定性研究[J]. 计算机仿真, 2023, 40(5): 56-63BU Yalou, CAI Rong, YANG Yanchu, et al. Study on stability of pumpkin shape super pressure balloon deployment[J]. Computer Simulation, 2023, 40(5): 56-63 [49] NAKASHINO K, SAITO Y, AKITA D, et al. Analytical study on the inflated shape of a superpressure balloon covered with a diamond-shaped net[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2023, 71(1): 705-719 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2022.08.074 [50] DEWEESE K D, WARD P R. Demonstration of a balloon borne arc-second pointer design[C]//36th COSPAR Scientific Assembly. Beijing: CNCOSPAR, 2006 [51] HANAGUD A, SIMPSON J, LANZI R, et al. A solar pointing system for the Long Duration Balloon missions[C]//International Balloon Technology Conference. San Francisco: AIAA, 2012 [52] STUCHLIK D W. The wallops arc second pointer-a balloon borne fine pointing system[C]//AIAA Balloon Systems Conference. Dallas: AIAA, 2015 [53] STUCHLIK D W, LANZI R. The NASA wallops arc-second pointer (WASP) system for precision pointing of scientific balloon instruments and telescopes[C]//AIAA Balloon Systems Conference. Denver: AIAA, 2017 [54] ABARR Q, AWAKI H, BARING M G, et al. XL-Calibur-a second-generation balloon-borne hard X-ray polarimetry mission[J]. Astroparticle Physics, 2021, 126 : 102529 [55] ABARR Q, BEHESHTIPOUR B, BEILICKE M, et al. Performance of the X-Calibur hard X-ray polarimetry mission during its 2018/19 long-duration balloon flight[J]. Astroparticle Physics, 2022, 143: 102749 doi: 10.1016/j.astropartphys.2022.102749 [56] GONG Q, GOPALSWAMY N, NEWMARK J. Innovative compact coronagraph approach for balloon-borne investigation of temperature and speed of electrons in the corona (BITSE)[C]//Proceedings of the SPIE 11116, Astronomical Optics: Design, Manufacture, and Test of Space and Ground Systems. San Diego: SPIE, 2019: 111160F [57] MENDILLO C B, HEWAWASAM K, MARTEL J, et al. The PICTURE-C exoplanetary imaging balloon mission: second flight results and the transition to a new mission, PICTURE-D[C]//Proceedings of the SPIE 12680, Techniques and Instrumentation for Detection of Exoplanets. San Diego: SPIE, 2023: 126800F [58] MENDILLO C B, HEWAWASAM K, HOWE G A, et al. Decoupling the image-plane and low-order wavefront sensors for the PICTURE-C coronagraph[C]//Proceedings of the SPIE 11117, Techniques and Instrumentation for Detection of Exoplanets. San Diego: SPIE, 2019: 111171R [59] YOUNG E. NASA’s GHAPS Project: A balloon-borne telescope for planetary science[C]//Egu General Assembly Conference. Vienna: EGU General Assembly, 2017 [60] VON EHRENFRIED M D. Stratospheric Balloons: Science and Commerce at the Edge of Space[M]. Cham: Springer, 2021 [61] GORHAM P W. Particle astrophysics in NASAʼs long duration balloon program[J]. Nuclear Physics B - Proceedings Supplements, 2013, 234/235/236/237/238/239/240/241/242/243/244: 231-238 -
-





 李一健 男, 1998年9月出生于江西省吉安市, 现为中国科学院空天信息创新研究院博士研究生, 飞行器设计与控制专业. E-mail:
李一健 男, 1998年9月出生于江西省吉安市, 现为中国科学院空天信息创新研究院博士研究生, 飞行器设计与控制专业. E-mail:  黄宛宁 男, 1980年5月出生于河南省南阳市, 现为中国科学院空天信息创新研究院高级工程师, 硕士生导师, 主要研究方向为临近空间浮空器科学探测, 多浮空器组网通信、空间信息网络等. E-mail:
黄宛宁 男, 1980年5月出生于河南省南阳市, 现为中国科学院空天信息创新研究院高级工程师, 硕士生导师, 主要研究方向为临近空间浮空器科学探测, 多浮空器组网通信、空间信息网络等. E-mail: 
 下载:
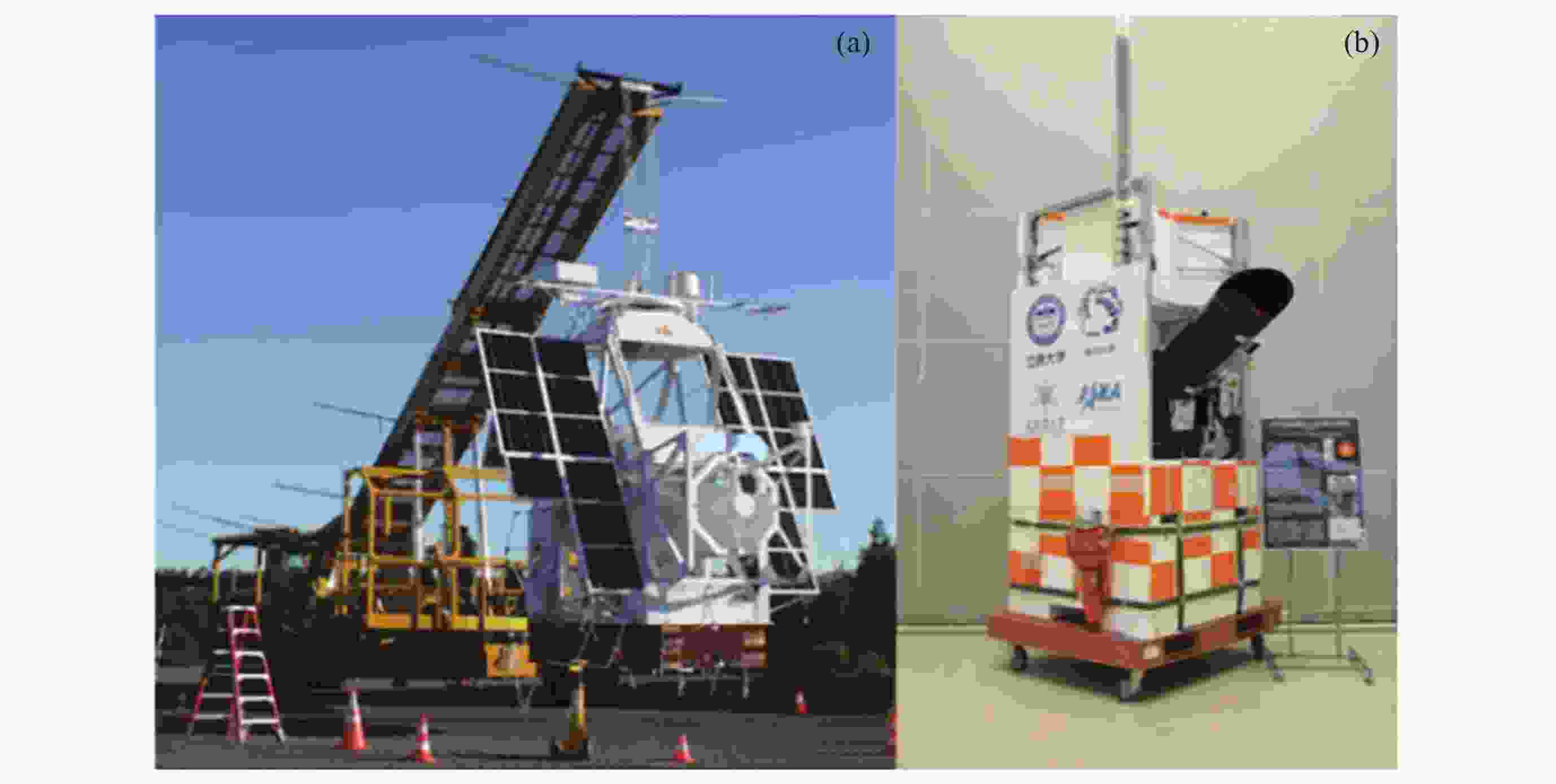
下载: