Using Deep Learning to Achieve Short Term Business Forecast of Dst Index
-
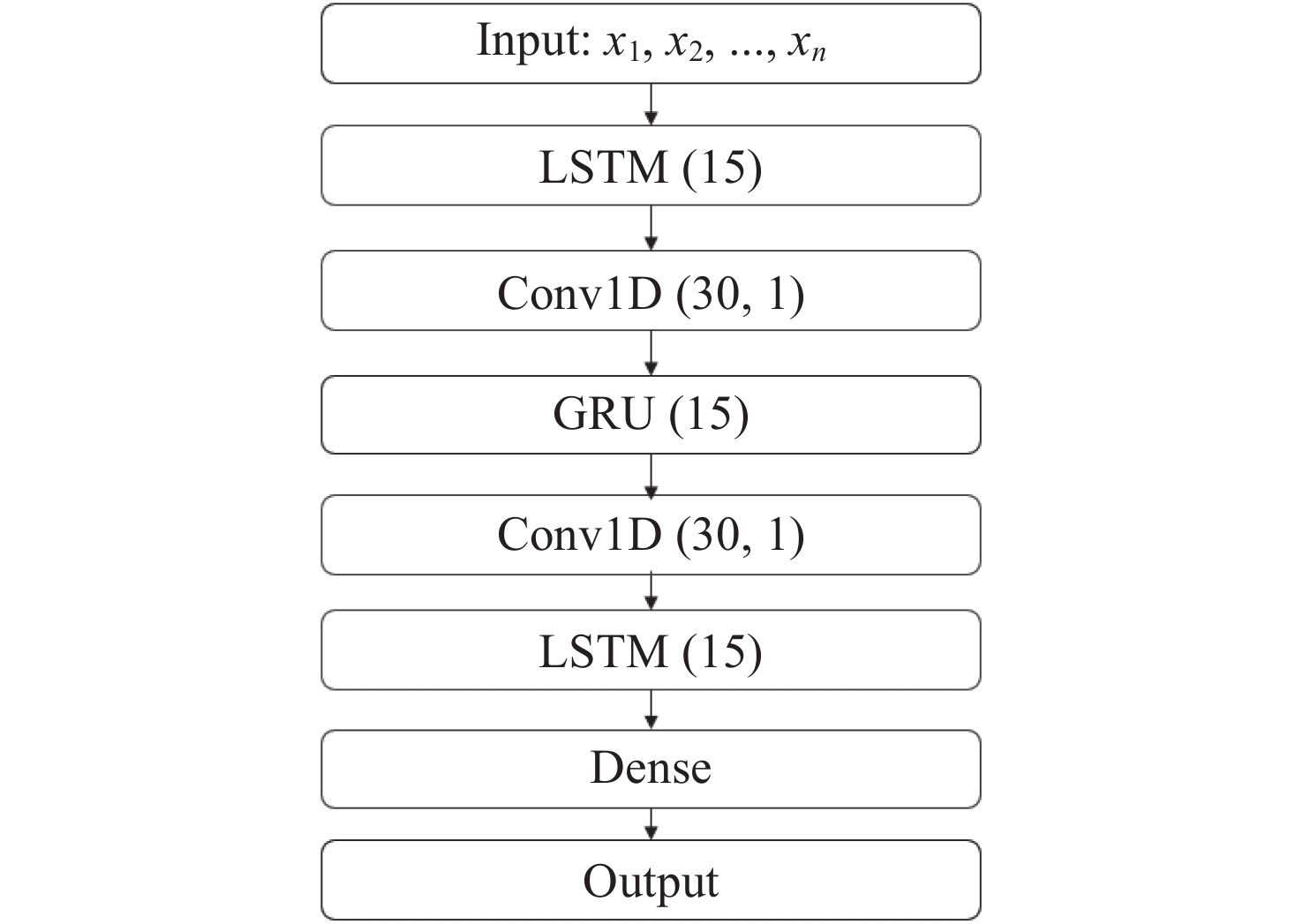
摘要: 由太阳活动引发的磁暴事件会导致地球磁场产生剧烈变化, 进而影响通信、导航、电力等工程应用系统的服务性能. 在空间物理领域通常利用Dst指数表征磁暴强度的变化, 本文提出一种基于卷积神经网络(CNN)、门控循环单元(GRU)和长短时记忆网络(LSTM)的磁暴预测模型(C-G-LSTM), 能够提前1~6 h预测Dst指数. 进一步利用美国航空航天局(National Aeronautics and Space Administration, NASA)提供的2010-2019年Dst指数评估混合深度学习预测模型的性能. 结果显示最大均方根误差不超过7.29 nT; 最大平均绝对误差不超过5.03 nT, 磁暴期间误差有所增大. 与已有研究结果相比, 本文所提出的模型具有较高精度, 且无须提供太阳风温度、太阳风动压以及行星际磁场分量等输入参数, 适用于业务预报.Abstract: Magnetic storm events triggered by solar activity can cause dramatic changes in the Earth’s magnetic field, significantly impacting the performance of systems such as communications, navigation, and power supply. These disturbances can interfere with radio signal propagation, reduce navigation accuracy, and disrupt power transmission networks. Therefore, accurately predicting magnetic storms is crucial for mitigating their effects. In space physics, the Dst index is commonly used to characterize the intensity of magnetic storms. It serves as a vital global indicator of geomagnetic activity. To enhance the prediction of magnetic storms and reduce their adverse effects, an efficient and accurate predictive model is essential. This paper proposes a magnetic storm prediction model based on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Gated Recurrent Units (GRU), and Long Short-Term Memory networks (LSTM), referred to as the C-G-LSTM model. This hybrid model leverages the strengths of CNN, GRU, and LSTM to predict the Dst index 1 to 6 h in advance, providing valuable lead time for responding to potential magnetic storm events. CNNs effectively extract spatial features from input data, while GRUs and LSTMs excel at handling time series data and capturing temporal dependencies. The performance of the C-G-LSTM model was evaluated using Dst index data provided by NASA, covering the period from 2010 to 2019. The results demonstrate that this model performs exceptionally well in predicting the Dst index. Specifically, the maximum Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) does not exceed 7.29 nT, and the Maximum Mean Absolute Error (MAE) does not exceed 5.03 nT. Although errors increase during intense magnetic activity, the model maintains high accuracy. A significant advantage of the C-G-LSTM model is that it does not require additional input parameters such as solar wind temperature, solar wind dynamic pressure, and interplanetary magnetic field components, which are often needed in other models. This makes the C-G-LSTM model more straightforward and practical for operational forecasting. Its high accuracy and efficiency in predicting magnetic storms can provide timely warnings, helping to mitigate potential impacts on communication, navigation, and power systems. In conclusion, the C-G-LSTM model represents a significant advancement in predicting magnetic storm events, offering a reliable and accurate method for forecasting the Dst index and enhancing our ability to manage the effects of solar activity on critical engineering systems.
-
表 1 混合神经网络模型与消融分析预测RMSE与MAE对比结果
Table 1. Comparison of the RMSE and MAE between the mixed neural network model and ablation analysis
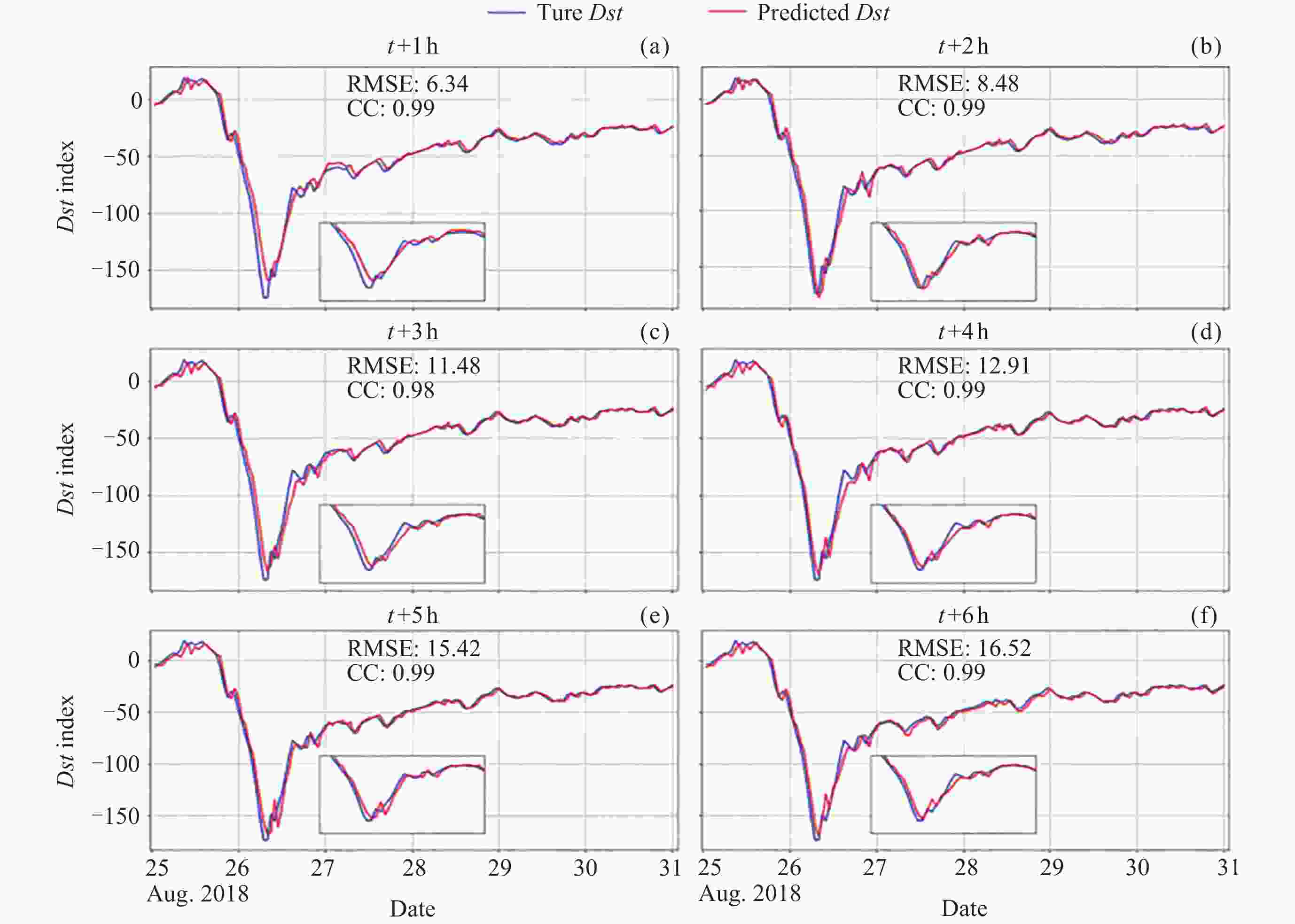
Model RMSE/MAE /nT 1 h 2 h 3 h 4 h 5 h 6 h C-G-LSTM 3.40/2.32 4.64/3.08 5.61/3.79 6.34/4.30 6.75/4.48 7.44/5.09 G-LSTM 5.74/4.15 6.17/4.24 6.96/4.76 7.60/5.41 8.25/6.00 7.90/5.31 C-LSTM 3.80/2.82 4.95/3.62 5.81/3.96 6.24/4.28 7.35/5.21 7.71/5.46 表 2 混合神经网络模型与Transformer模型均方根误差 (单位 nT) 对比结果
Table 2. Comparison of RMSE (unit: nT) between the mixed neural network model and Transformer model
Model Advance forecast time 1 h 2 h 3 h 4 h 5 h 6 h C-G-LSTM 3.34 4.55 5.50 6.21 6.61 7.29 Transformer 3.74 5.47 6.88 7.88 8.58 9.18 表 3 ANN模型与本文模型磁暴期间RMSE和MAE对比结果
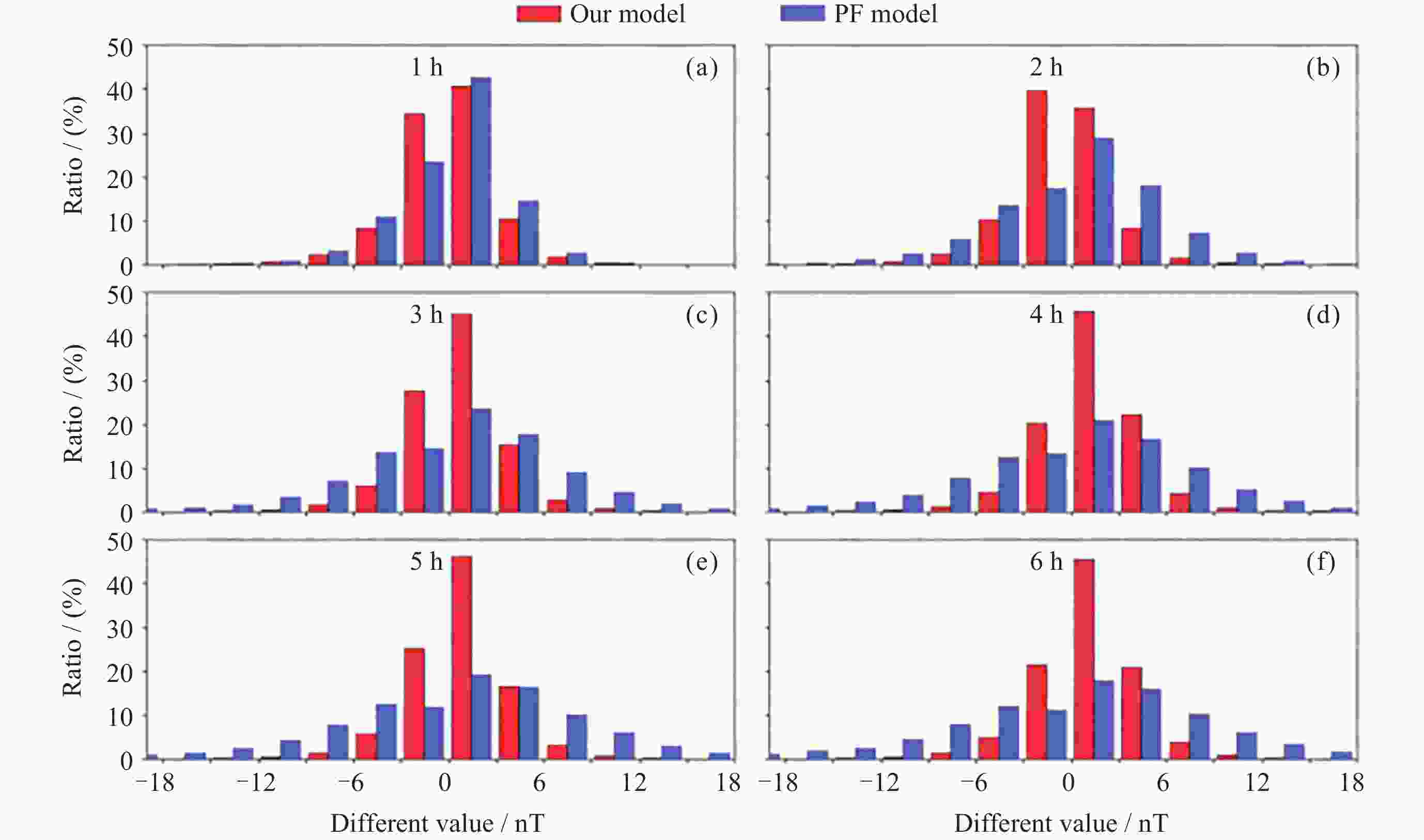
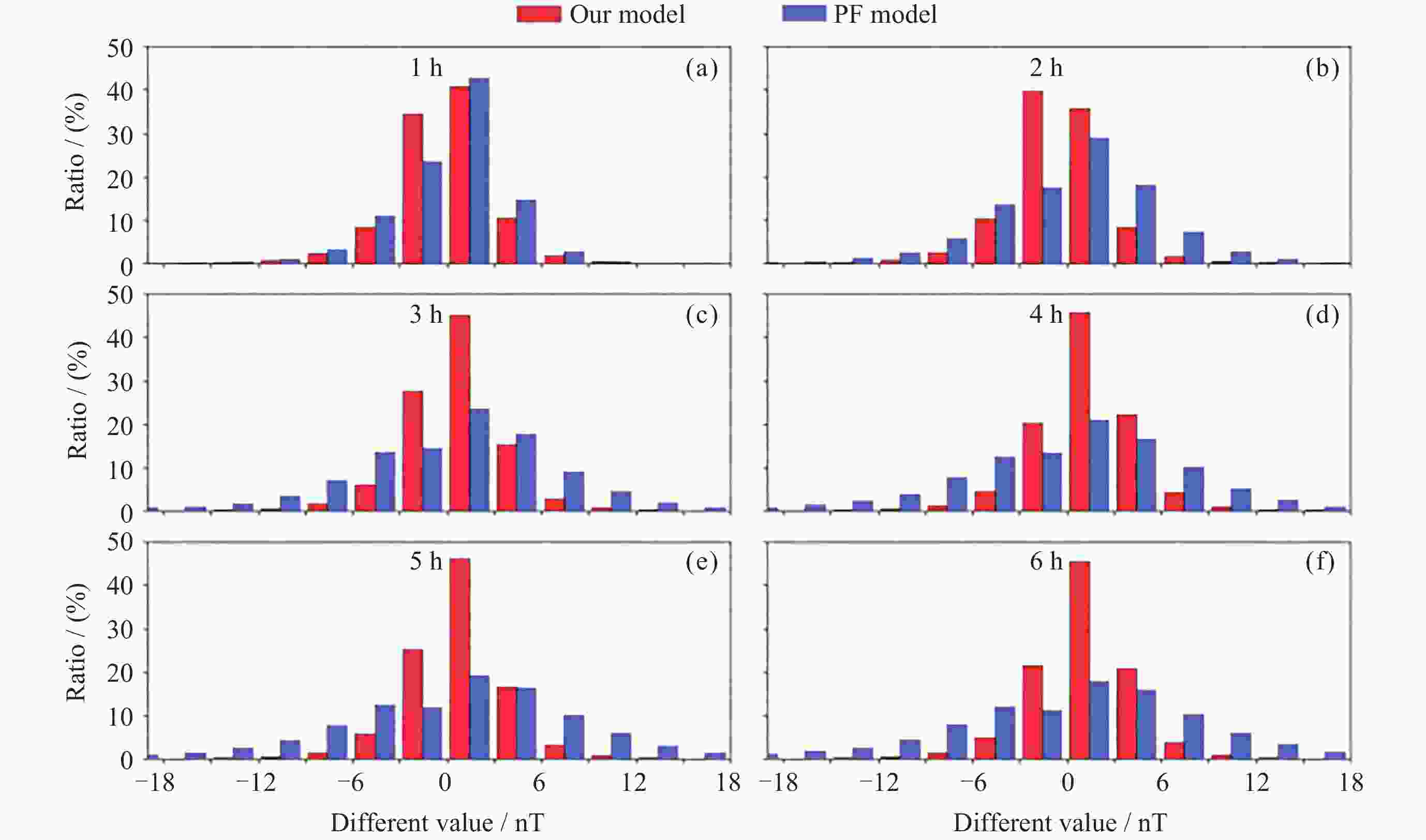
Table 3. Comparison of RMSE and MAE between ANN model and our model during magnetic storms
Storm time RMSE/MAE/nT
C-G-LSTM ModelRMSE/MAE/nT
ANN Model2 h 6 h 2 h 6 h 20-23 Jan. 2016 8.06/5.82 14.32/9.33 9.86/8.05 11.16/9.26 6-10 Mar. 2016 8.10/4.86 16.20/9.21 13.91/11.45 13.60/11.69 7-13 May 2016 7.16/4.31 10.94/6.73 7.53/5.40 8.78/6.09 22-26 Aug. 2016 6.34/4.05 10.40/6.68 8.01/6.94 7.78/6.53 12-17 Oct. 2016 7.03/4.68 13.01/8.50 12.79/8.31 10.61/7.19 表 4 混合神经网络模型与贝叶斯机器学习模型磁暴期间均方根误差 (单位 nT)对比结果
Table 4. Comparison of RMSE (unit: nT) between the mixed neural network model and Bayesian machine learning model
Model 18–19 February 2014 8–10 June
2015C-G-LSTM 4.23 10.86 Bayesian machine learning model 35.45 35.11 表 5 本文模型与持续预报模型在平静期与磁暴期显著性水平对比结果
Table 5. Comparison results of significance levels between our model and the persistence forecasting model during quiet periods and storm periods
Time P-value 1 h 2 h 3 h 4 h 5 h 6 h Quiet Period 1.15×10–17 6.02×10–12 2.00×10–54 6.92×10–141 8.31×10–50 2.37×10–82 Storm Period 5.98×10–7 5.66×10–15 2.07×10–8 5.86×10–14 2.33×10–4 1.95×10–31 -
[1] ZHU Yuncong. Research on the Correlation between Ionospheric TEC and Solar Activity Parameters[D]. Zibo: Shandong University of Technology, 2022. DOI: 10.27276/d.cnki.gsdgc.2022.000667 [2] BURTON R K, MCPHERRON R L, RUSSELL C T. An empirical relationship between interplanetary conditions and Dst[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1975, 80(31): 4204-4214 doi: 10.1029/ja080i031p04204 [3] TEMERIN M, LI X L. A new model for the prediction of Dst on the basis of the solar wind[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2002, 107 (A12): SMP 31-1-SMP 31-8. DOI: 10.1029/2001JA007532 [4] NURAENI F, RUHIMAT M, ARIS M A, et al. Development of 24 hours Dst index prediction from solar wind data and IMF B z using NARX[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2022, 2214(1): 012024 doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/2214/1/012024 [5] 李淑慧, 彭军还, 徐伟超, 等. 利用神经网络预报短期电离层TEC变化[J]. 测绘科学, 2013, 38(1): 8-9,12LI Shuhui, PENG JunHuan, XU Weichao, et al. Short-term ionospheric TEC change prediction by neural network[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2013, 38(1): 8-9,12 [6] LETHY A, EL-ERAKI M A, SAMY A, et al. Prediction of the Dst index and analysis of its dependence on solar wind parameters using neural network[J]. Space Weather, 2018, 16(9): 1277-1290 doi: 10.1029/2018SW001863 [7] XU W W, ZHU Y M, ZHU L, et al. A class of Bayesian machine learning model for forecasting Dst during intense geomagnetic storms[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2023, 72(9): 3882-3889 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2023.07.009 [8] 杨旭, 朱亚光, 杨升高, 等. LSTM神经网络在太阳F10.7射电流量中期预报中的应用[J]. 空间科学学报, 2020, 40(2): 176-185 doi: 10.11728/cjss2020.02.176YANG Xu, ZHU Yaguang, YANG Shenggao, et al. Application of LSTM neural network in F10.7 solar radio flux mid-term forecast[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2020, 40(2): 176-185 doi: 10.11728/cjss2020.02.176 [9] ZHANG J Y, FENG Y, ZHANG J X, et al. The short time prediction of the Dst index based on the long-short time memory and empirical mode decomposition–long-short time memory models[J]. Applied Sciences, 2023, 13(21): 11824 doi: 10.3390/app132111824 [10] GRUET M A, CHANDORKAR M, SICARD A, et al. Multiple-hour-ahead forecast of the Dst index using a combination of long short-term memory neural network and Gaussian process[J]. Space Weather, 2018, 16(11): 1882-1896 doi: 10.1029/2018SW001898 [11] LIU H J, LEI D X, YUAN J, et al. Ionospheric TEC prediction in China based on the multiple-attention LSTM model[J]. Atmosphere, 2022, 13(11): 1939 doi: 10.3390/atmos13111939 [12] ŞENTÜRK E, SAQIB M, ADIL M A. A Multi-Network based Hybrid LSTM model for ionospheric anomaly detection: A case study of the Mw 7.8 Nepal earthquake[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2022, 70(2): 440-455 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2022.04.057 [13] 杨旭, 崔瑞飞, 田超, 等. 基于线性样条和CNN-LSTM的北斗卫星缺失数据处理方法[J]. 空间科学学报, 2022, 42(1): 163-169 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.01.201116100YANG Xu, CUI Ruifei, TIAN Chao, et al. Linear spline and CNN-LSTM for missing values imputation of Beidou satellite radiation dose data[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2022, 42(1): 163-169 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.01.201116100 [14] ABDUALLAH Y, WANG J T L, BOSE P, et al. Forecasting the disturbance storm time index with Bayesian deep learning[C]//The International FLAIRS Conference Proceedings. Florida, USA, 2022, 35 [15] LI Leilei. Deep Learning Modeling Research on the Relationship between Solar Wind and Geomagnetic Storms and Earthquakes[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2022. DOI: 10.26991/d.cnki.gdllu.2022.001958 [16] BEJ A, BANERJEE A, CHATTERJEE T N, et al. One-hour ahead prediction of the Dst index based on the optimum state space reconstruction and pattern recognition[J]. The European Physical Journal Plus, 2022, 137(4): 479 doi: 10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-02687-7 [17] WANG Zhiyuan. Time Series Forecasting with Depth Probabilistic Models[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2023. DOI: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2023.000727 [18] TANG X G, FENG J H, ZHANG B Q, et al. Radio frequency fingerprint-based satellite TT&C ground station identification method[J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2023, 32(1): 1-12 doi: 10.15918/j.jbit1004-0579.2022.074 [19] GU J X, WANG Z H, KUEN J, et al. Recent advances in convolutional neural networks[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2018, 77: 354-377 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2017.10.013 [20] MA H Y, WU Y, LIU F, et al. Design of Super-X Test Facility monitoring and early warning system based on improved CNN-BiLSTM model[C]//2023 International Conference on Image Processing, Computer Vision and Machine Learning (ICICML). Chengdu, China: IEEE, 2023: 1015-1021. DOI: 10.1109/ICICML60161.2023.10424770 [21] SONG Y, SEBE N, WANG W. On the eigenvalues of global covariance pooling for fine-grained visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(3): 3554-3566 [22] DEY R, SALEM F M. Gate-variants of Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) neural networks[C]//2017 IEEE 60th International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS). Boston, MA, USA: IEEE, 2017: 1597-1600. DOI: 10.1109/MWSCAS.2017.8053243 [23] 唐丝语, 黄智. 基于因果卷积与LSTM网络的电离层总电子含量预报[J]. 空间科学学报, 2022, 42(3): 357-365 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.03.210401042TANG Siyu, HUANG Zhi. Prediction of ionospheric total electron content based on causal convolutional and LSTM network[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2022, 42(3): 357-365 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.03.210401042 -
-




 牛犇 男, 1999年8月出生于河南省漯河市, 现就读于江苏师范大学物理与电子工程学院电子信息专业, 主要研究方向为磁暴Dst指数的预测及异常检测. E-mail:
牛犇 男, 1999年8月出生于河南省漯河市, 现就读于江苏师范大学物理与电子工程学院电子信息专业, 主要研究方向为磁暴Dst指数的预测及异常检测. E-mail: 

 下载:
下载: