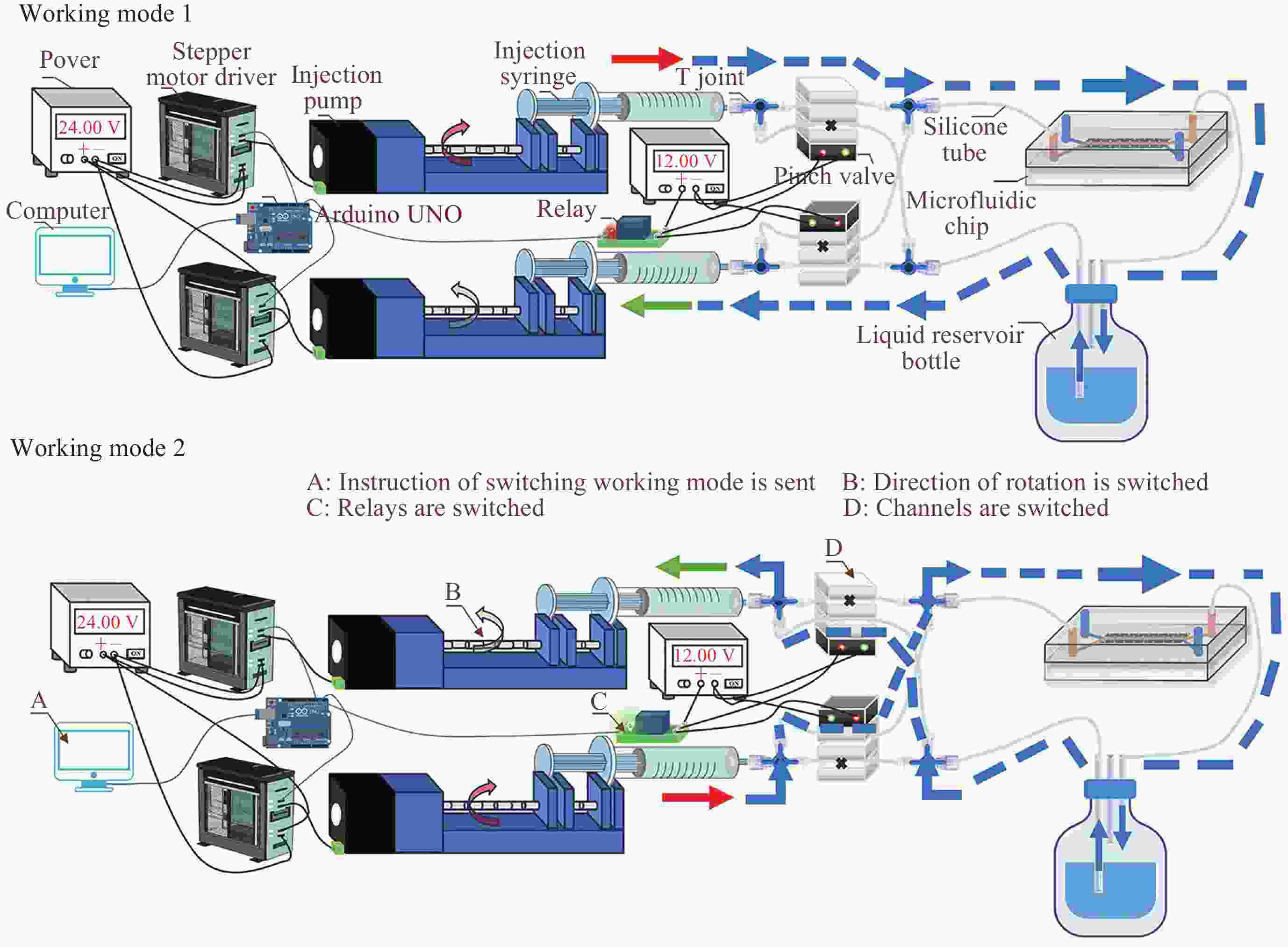
Construction and Validation of Blood Vessel-bone Matrix Interactive Microfluidic Chip Experimental System
-
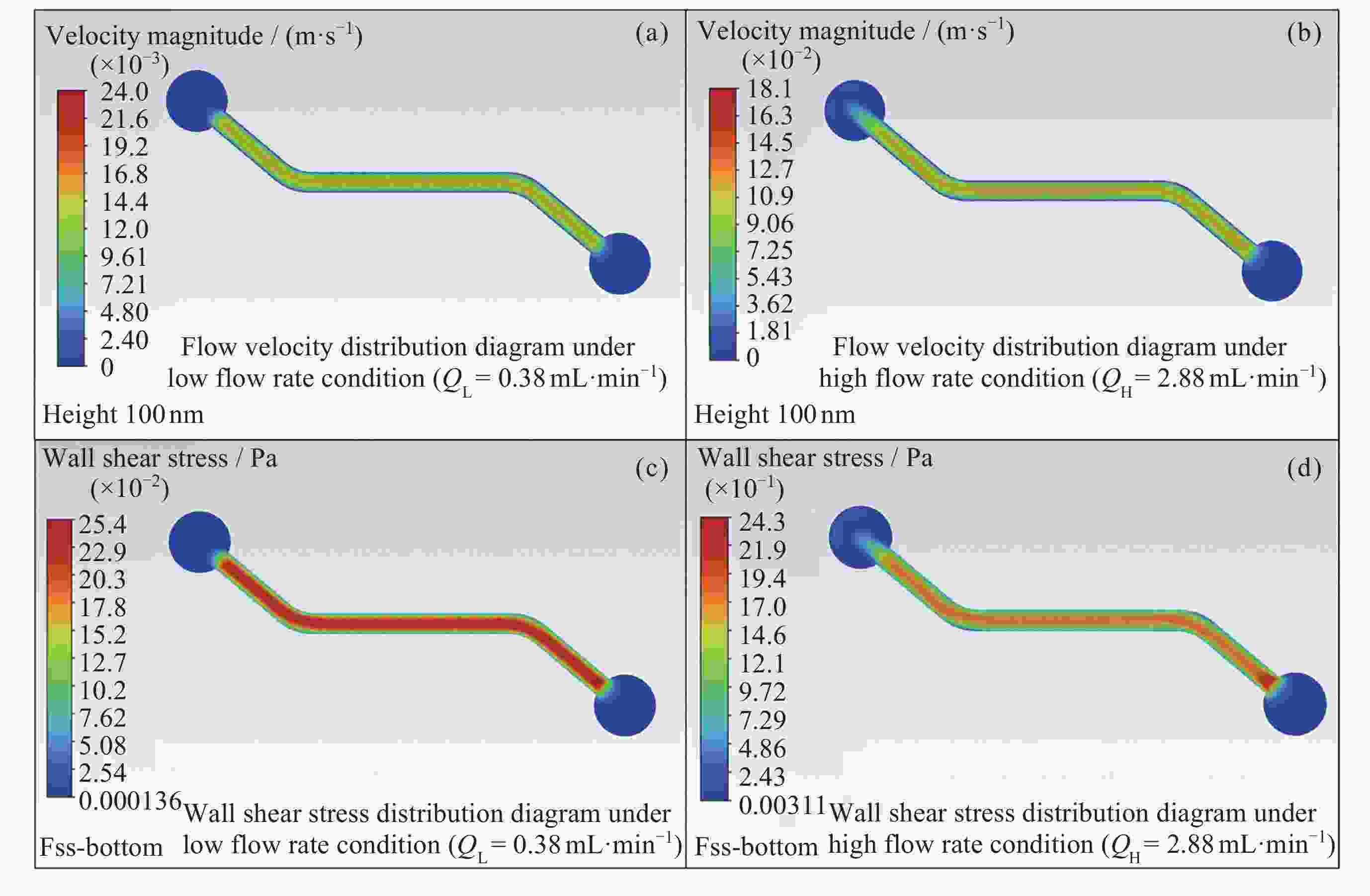
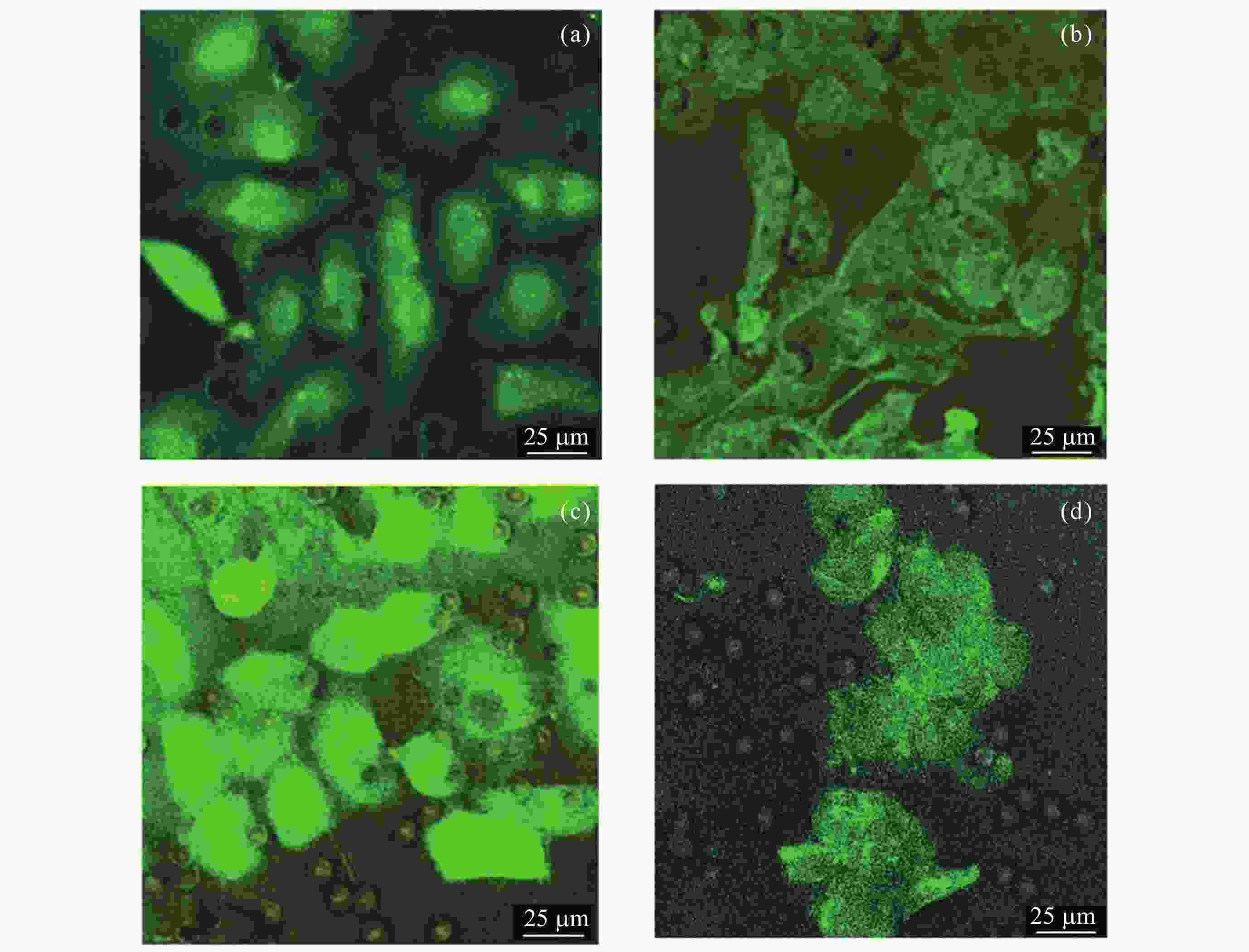
摘要: 晚期糖基化终末产物(AGEs)是葡萄糖与骨胶原发生非酶糖基化交联的产物, 与失重性骨丢失的发生机制相关, 而其在骨基质中积聚的机制尚不明确. 微重力下流速较慢的L型骨微血管数量增加, 可能与AGEs在骨中的积聚有关. 为研究流速对血管内葡萄糖分子向骨基质的输运及AGEs生成的影响, 开发了体外模拟血管-骨交互界面的双层通道微流控芯片实验体系, 自研可长时连续定向供液的双注射泵系统搭载于芯片, 通过实验验证体系的生物相容性、稳定性及组织间交互性. 结果显示, 芯片内通道主要反应区液体应力分布均匀, 为层流流动; 加载2.88 mL·min–1和0.38 mL·min–1的高糖培养基72 h后, 芯片中内皮细胞可正常生长; 低流量比高流量的葡萄糖分子经微孔膜向下层胶原通道扩散的速率更高, 胶原中生成的AGEs更多. 本文构建的实验体系具有良好的生物相容性、长时运行稳定性及组织间交互性, 可为后续开展骨基质AGEs积聚的生物物理学机制奠定技术基础, 具备应用于空间生命科学研究的潜力.Abstract: Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs) in bone matrix are the products of non-enzymatic glycation of glucose and collagen, which are closely related to the mechanism of weightless bone loss. However, how AGEs accumulate in bone matrix remains unclear. The type L microvessels with slower blood flow velocity were increased under microgravity, which may be related to the accumulation of AGEs in bone. To study the effects of flow velocity on the transport of intravascular glucose molecules into bone matrix and the formation of AGEs in bone matrix, a bilayer channel microfluidic chip experimental system was constructed to simulate the blood vessel-bone matrix interface in vitro. A self-developed double-injection-pump continuous directional liquid supply system was applied to the chip, and the biocompatibility, stability and interorganizational interactivity of the system were verified by experiments. The results show that the fluid stress distribution in the main region of the channel in fabricated chip is uniform, and the flow is laminar. The endothelial cells in microfluidic chips could grow normally after loading high sugar medium of 2.88 mL·min–1 and 0.38 mL·min–1 for 72 h, respectively. The diffusion rate of glucose molecules from to the lower collagen channel through the microporous membrane was higher under low flow rate loading than under high flow rate loading, and more AGEs generated in collagen. The experimental system constructed in this paper has excellent biocompatibility, long-term operational stability and interorganizational interactivity, which lays a technical foundation for further in-depth research on biophysical mechanisms related to AGEs accumulation in bone matrix, and has the potential to be applied to space life science research.
-
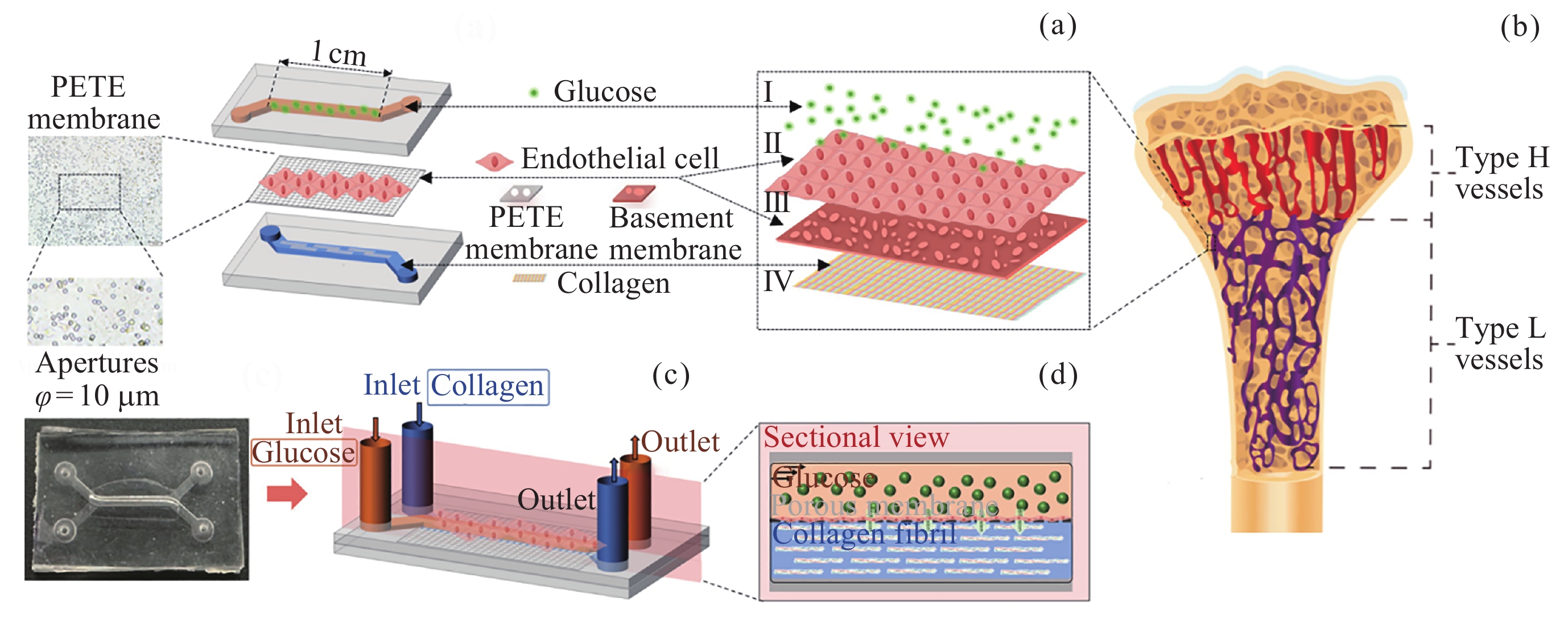
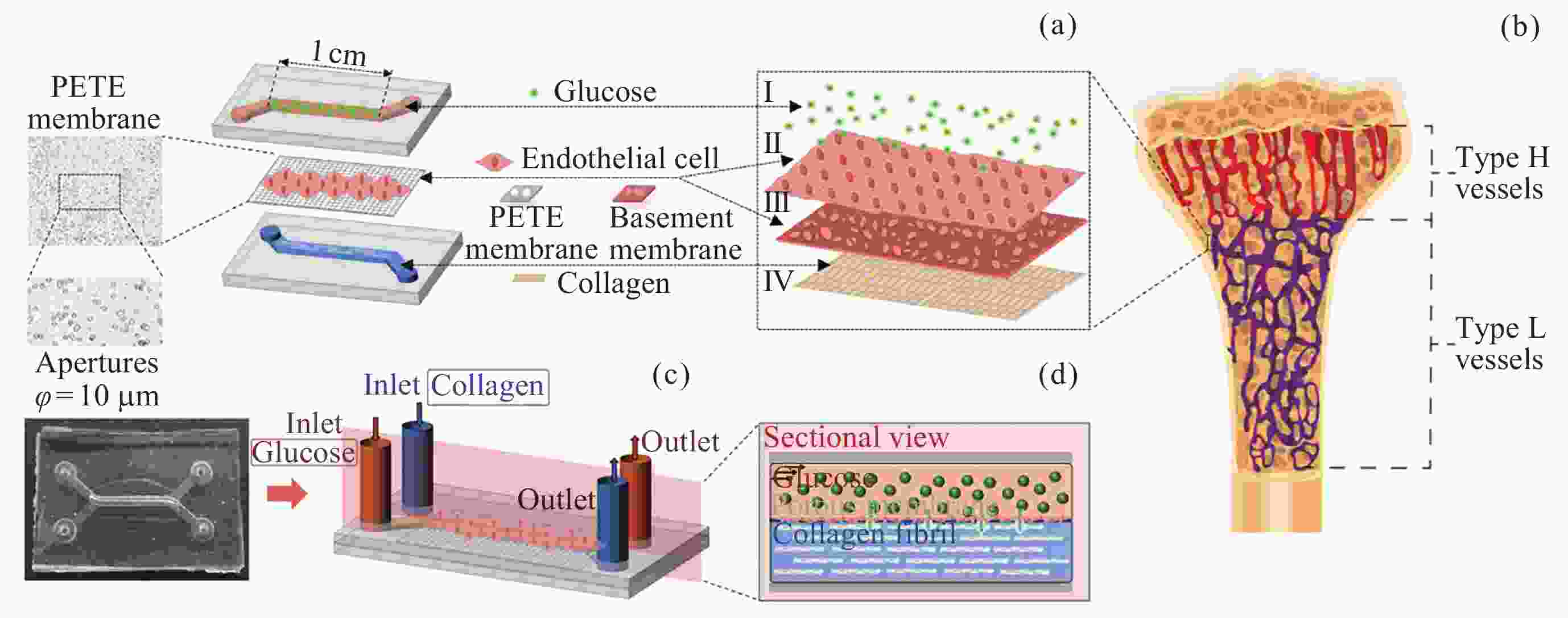
图 1 血管–骨基质交互微流控芯片设计. (a)微流控芯片三维结构, (b)微流控芯片模拟的血管–骨基质交互界面, (c)微流控芯片实物, (d)微流控芯片内交互界面剖面
Figure 1. Design of blood vessel-bone matrix interactive microfluidic chip. (a) 3D structural diagram of microfluidic chip, (b) the blood vessel-bone matrix interactive interface simulated by microfluidic chip, (c) the picture of microfluidic chip, (d) the sectional view of interactive interface inside microfluidic chip
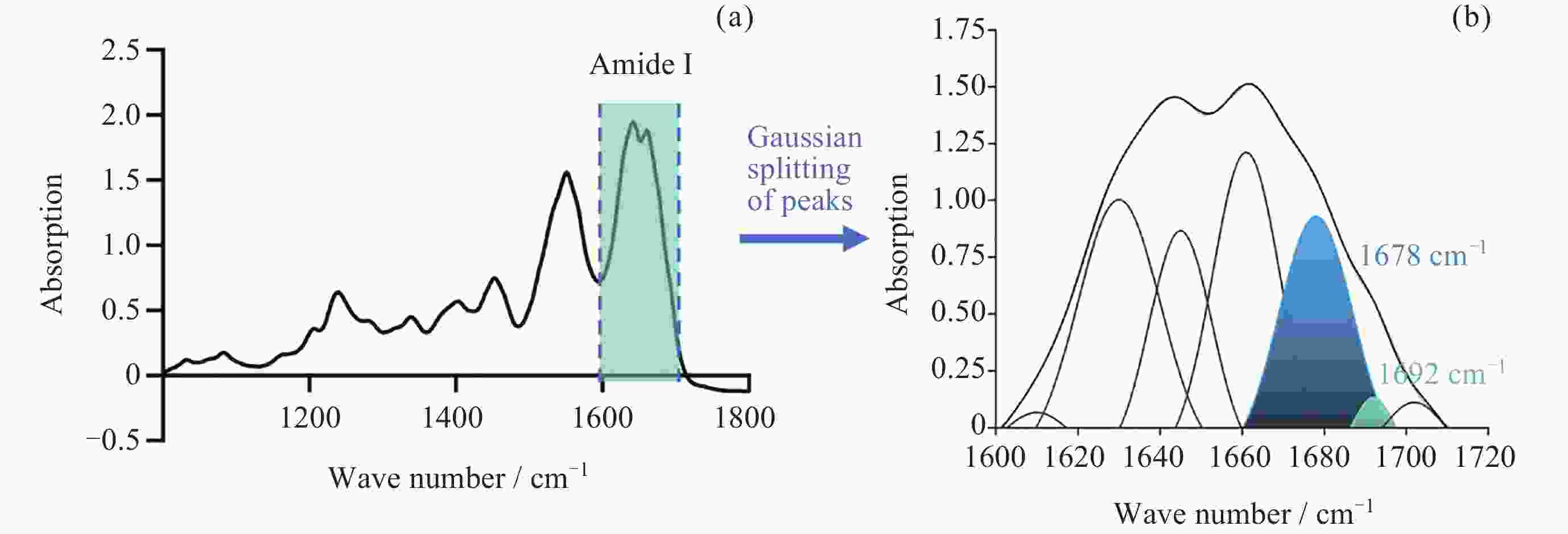
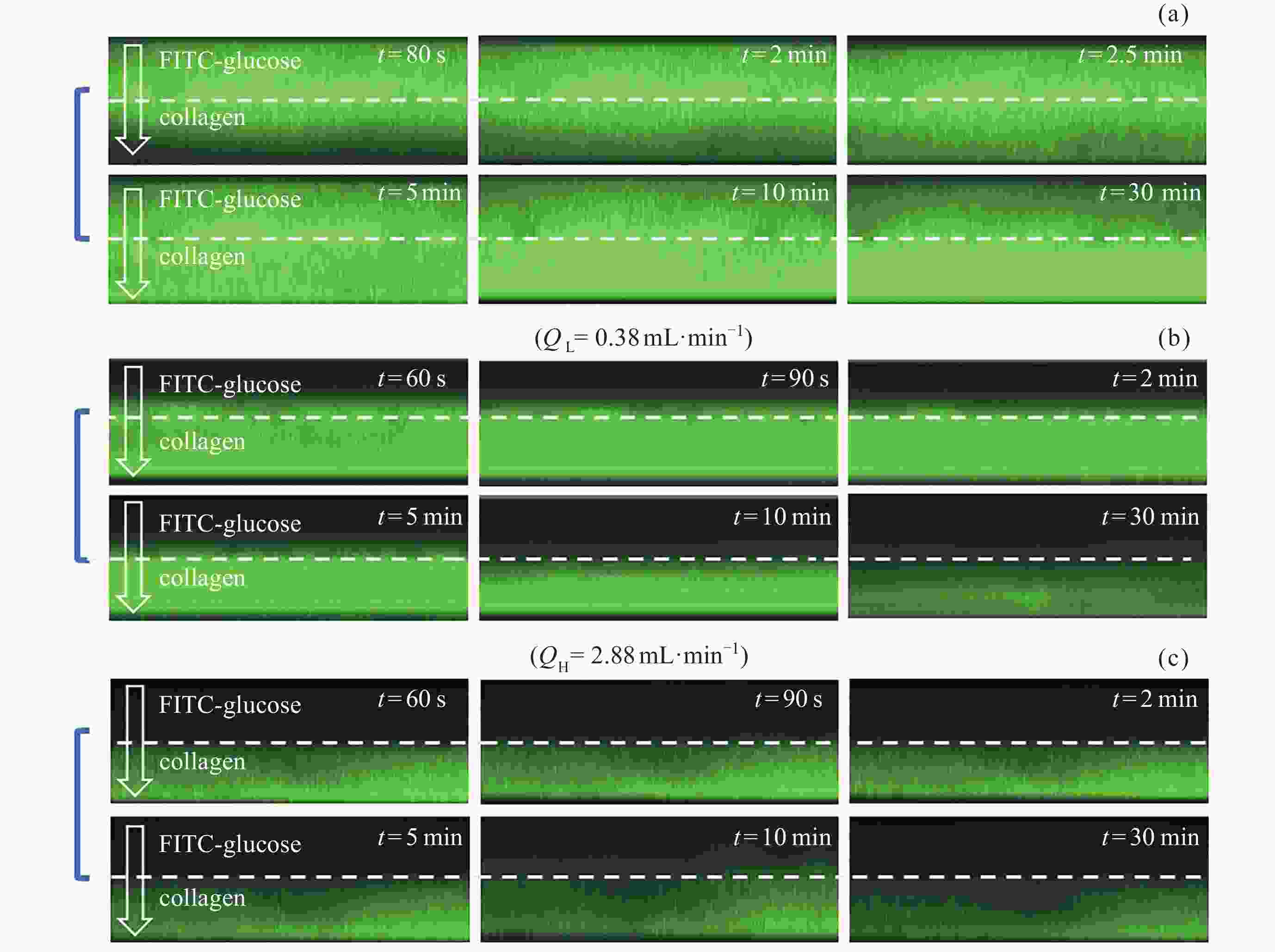
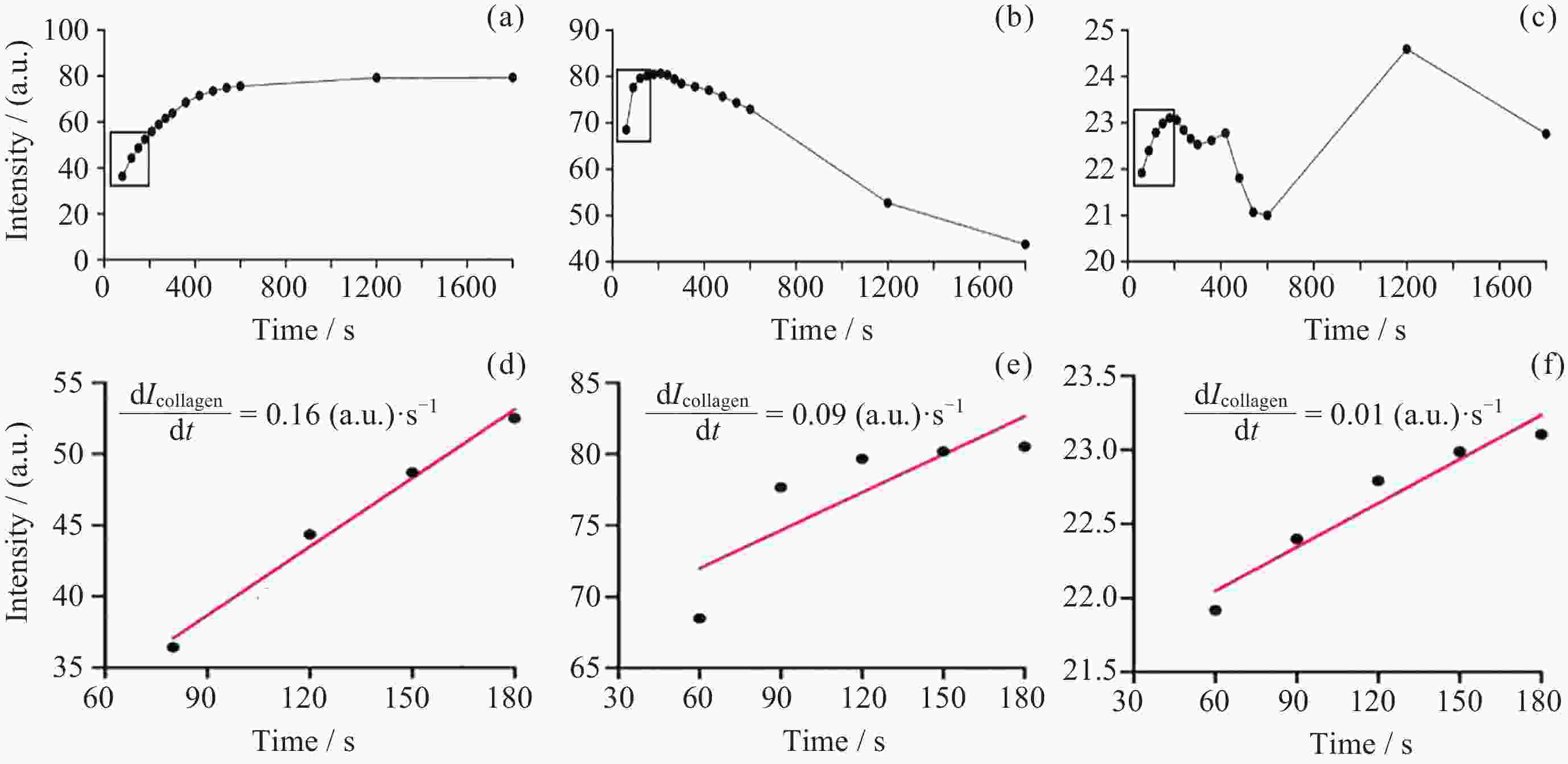
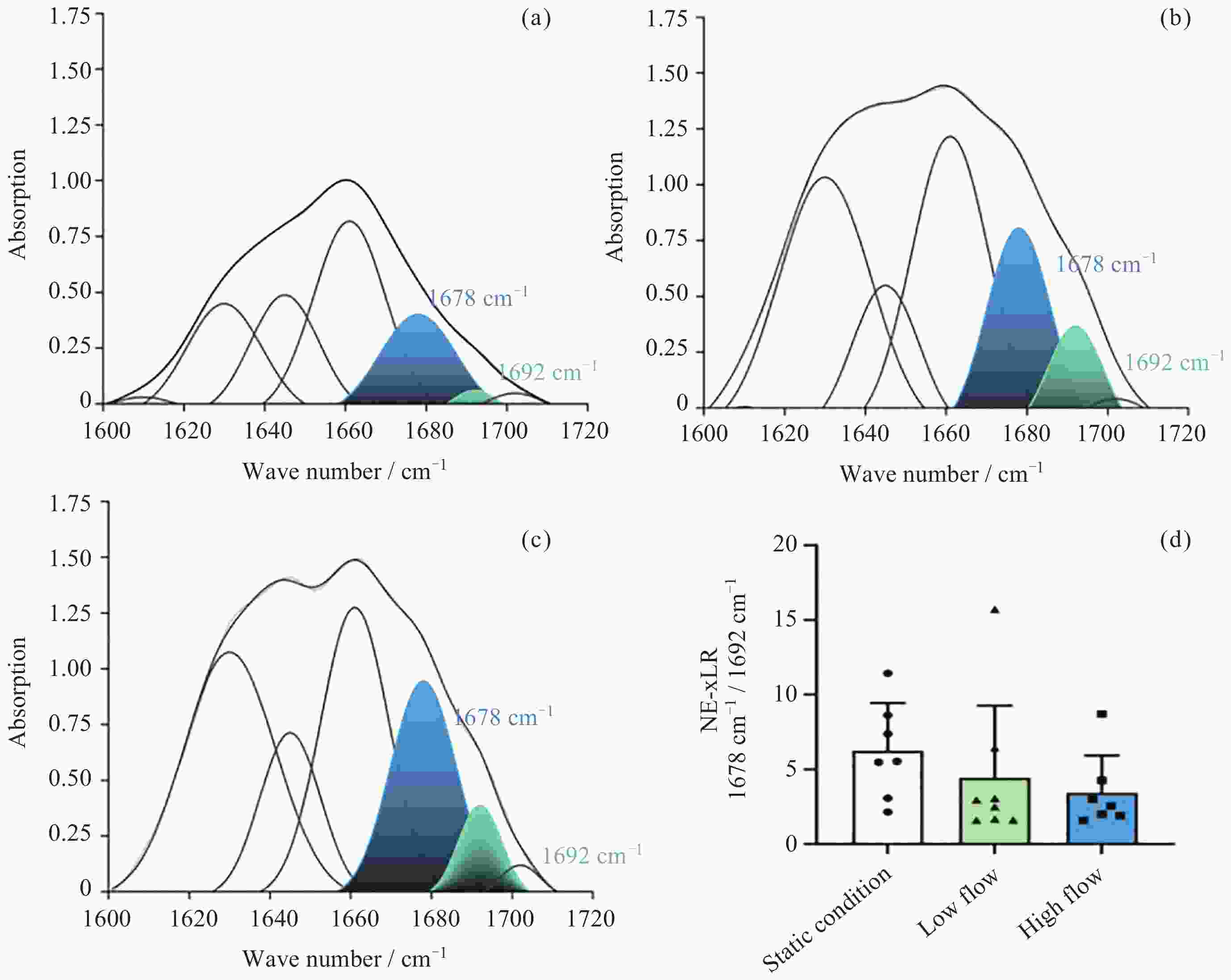
图 9 双注射泵连续定向供液系统对微流控芯片进行动态培养3天, 通过FTIR检测静置(a)、低流速(b)和高流速(c)情况下胶原中AGEs含量定量分析统计结果 (d)
Figure 9. Microfluidic chip was dynamically cultured for 3 days using a dual-syringe pump continuous directional infusion system. AGEs content in collagen was quantitatively analyzed via FTIR under static (a), low-flow (b), and high-flow (b) conditions, with statistical results shown in (d)
-
[1] BUCKEY J C, THAMER S, LAN M M. Bone loss and kidney stone risk in weightlessness[J]. Current Opinion in Nephrology and Hypertension, 2023, 32(2): 172-176 doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000863 [2] BARAN R, WEHLAND M, SCHULZ H, et al. Microgravity-related changes in bone density and treatment options: a systematic review[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(15): 8650 doi: 10.3390/ijms23158650 [3] GARNERO P. The role of collagen organization on the properties of bone[J]. Calcified Tissue International, 2015, 97(3): 229-240 doi: 10.1007/s00223-015-9996-2 [4] BALASUBRAMANIAN P, PRABHAKARAN M P, SIREESHA M, et al. Collagen in human tissues: structure, function, and biomedical implications from a tissue engineering perspective[M]//ABE A, KAUSCH H H, MÖLLER M, et al. Polymer Composites – Polyolefin Fractionation – Polymeric Peptidomimetics – Collagens. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2012: 173-206 [5] LIU C J, YANG X, MAO Y, et al. The alteration of advanced glycation end products and its potential role on bone loss under microgravity[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2023, 206: 114-122 doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2023.02.019 [6] LIU C J, YANG X, WANG S H, et al. Preventing disused bone loss through inhibition of advanced glycation end products[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(5): 4953 doi: 10.3390/ijms24054953 [7] PENG Y, WU S, LI Y S, et al. Type H blood vessels in bone modeling and remodeling[J]. Theranostics, 2020, 10(1): 426-436 doi: 10.7150/thno.34126 [8] WANG S H, YANG X, DING D, et al. The changes of bone vessels and their role in bone loss in tail-suspended rats[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2021, 189: 368-378 doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2021.08.031 [9] LIANG S, LING S K, DU R K, et al. The coupling of reduced type H vessels with unloading-induced bone loss and the protection role of Panax quinquefolium saponin in the male mice[J]. Bone, 2021, 143: 115712 doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2020.115712 [10] ECKLY A, SCANDOLA C, OPRESCU A, et al. Megakaryocytes use in vivo podosome-like structures working collectively to penetrate the endothelial barrier of bone marrow sinusoids[J]. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 2020, 18(11): 2987-3001 doi: 10.1111/jth.15024 [11] RAMASAMY S K, KUSUMBE A P, SCHILLER M, et al. Blood flow controls bone vascular function and osteogenesis[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7(1): 13601 doi: 10.1038/ncomms13601 [12] LEUNG C M, DE HAAN P, RONALDSON-BOUCHARD K, et al. A guide to the organ-on-a-chip[J]. Nature Reviews Methods Primers, 2022, 2(1): 33 doi: 10.1038/s43586-022-00118-6 [13] 王文甲, 彭钊, 吕雪飞, 等. 微流控芯片细胞灌流培养技术及其应用研究进展[J]. 载人航天, 2021, 27(5): 646-654 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5825.2021.05.016WANG Wenjia, PENG Zhao, LV Feixue, et al. Research progress of microfluidic chip cell perfusion culture technology and its application[J]. Manned Spaceflight, 2021, 27(5): 646-654 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5825.2021.05.016 [14] LIN L, CHUNG C K. PDMS microfabrication and design for microfluidics and sustainable energy application: review[J]. Micromachines, 2021, 12(11): 1350 doi: 10.3390/mi12111350 [15] MOORE S K, KLEIS S J. Characterization of a novel miniature cell culture device[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2008, 62(10/11): 632-638 [16] MA T, SUN S X, LI B Q, et al. Piezoelectric peristaltic micropump integrated on a microfluidic chip[J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2019, 292: 90-96 doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2019.04.005 [17] 殷小进. 医用注射、输液泵质量安全控制体系及质控结果的分析及探讨[J]. 中国设备工程, 2024(5): 85-87 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0711.2024.05.037YIN Xiaojin. Analysis and discussion on quality safety control system and quality control results of medical injection and infusion pumps[J]. China Plant Engineering, 2024(5): 85-87 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0711.2024.05.037 [18] CHOI B, CHOI J W, JIN H, et al. Condensed ECM-based nanofilms on highly permeable PET membranes for robust cell-to-cell communications with improved optical clarity[J]. Biofabrication, 2021, 13(4): 045020 doi: 10.1088/1758-5090/ac23ad [19] BIXEL M G, KUSUMBE A P, RAMASAMY S K, et al. Flow dynamics and HSPC homing in bone marrow microvessels[J]. Cell Reports, 2017, 18(7): 1804-1816 doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.01.042 [20] POLACHECK W J, KUTYS M L, YANG J L, et al. A non-canonical Notch complex regulates adherens junctions and vascular barrier function[J]. Nature, 2017, 552(7684): 258-262 doi: 10.1038/nature24998 [21] SROGA G E, STEPHEN S J, WANG B W, et al. Techniques for advanced glycation end product measurements for diabetic bone disease: pitfalls and future directions[J]. Current Opinion in Endocrinology :Times New Roman;">& Diabetes and Obesity, 2022, 29(4): 333-342 [22] MUKWAYA A, JENSEN L, LAGALI N. Relapse of pathological angiogenesis: functional role of the basement membrane and potential treatment strategies[J]. Experimental :Times New Roman;">& Molecular Medicine, 2021, 53(2): 189-201 [23] NAZARI S S, DOYLE A D, YAMADA K M. Mechanisms of basement membrane micro-perforation during cancer cell invasion into a 3D collagen gel[J]. Gels, 2022, 8(9): 567 doi: 10.3390/gels8090567 [24] PICOLLET-D’HAHAN N, ZUCHOWSKA A, LEMEUNIER I, et al. Multiorgan-on-a-chip: a systemic approach to model and decipher inter-organ communication[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2021, 39(8): 788-810 doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2020.11.014 [25] MANCINELLI E, ZUSHI N, TAKUMA M, et al. Porous polymeric nanofilms for recreating the basement membrane in an endothelial barrier-on-chip[J]. ACS Applied Materials :Times New Roman;">& Interfaces, 2024, 16(10): 13006-13017 [26] MIRELES M, GABORSKI T R. Fabrication techniques enabling ultrathin nanostructured membranes for separations[J]. Electrophoresis, 2017, 38(19): 2374-2388 doi: 10.1002/elps.201700114 [27] HUNTER W L, ARSENAULT A L. Vascular invasion of the epithyseal growth plate: analysis of metaphyseal capillary ultrastructure and growth dynamics[J]. The Anatomical Record, 1990, 227(2): 223-231 doi: 10.1002/ar.1092270211 [28] SU H R, LI K X, LIU X, et al. Microfluidic chips for the endothelial biomechanics and mechanobiology of the vascular system[J]. Biocell, 2021, 45(4): 797-811 doi: 10.32604/biocell.2021.014900 [29] HAMPEL U, GARREIS F, BURGEMEISTER F, et al. Effect of intermittent shear stress on corneal epithelial cells using an in vitro flow culture model[J]. The Ocular Surface, 2018, 16(3): 341-351 doi: 10.1016/j.jtos.2018.04.005 [30] GENG B C, CHEN X, CHI J Y, et al. Platelet membrane-coated alterbrassicene A nanoparticle inhibits calcification of the aortic valve by suppressing phosphorylation P65 NF-κB[J]. Theranostics, 2023, 13(11): 3781-3793 doi: 10.7150/thno.85323 [31] QUINTARD C, TUBBS E, JONSSON G, et al. A microfluidic platform integrating functional vascularized organoids-on-chip[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15(1): 1452 doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45710-4 [32] ZHAO Y M, LV X F, LI X Q, et al. Microfluidic actuated and controlled systems and application for lab-on-chip in space life science[J]. Space: Science & Technology, 2023, 3: 0008 [33] YU Z H, CHEN Y Q, LI J J, et al. A tempo-spatial controllable microfluidic shear-stress generator for in-vitro mimicking of the thrombus[J]. Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 2024, 22(1): 187 doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02334-6 [34] JAIN P, RAUER S B, MÖLLER M, et al. Mimicking the natural basement membrane for advanced tissue engineering[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2022, 23(8): 3081-3103 doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.2c00402 [35] 李慧, 李秀娟, 古力热巴·夏依买旦, 等. EA. HY926人脐静脉内皮细胞株与原代细胞生物特性的比较研究[J]. 新疆医科大学学报, 2014, 37(1): 36-39 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5551.2014.01.010LI Hui, LI Xiujuan, GULIREBA Xiayimaidan, et al. Comparative study of biological characteristics between primary human umbilical vein endothelial cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cell line[J]. Journal of Xinjiang Medical University, 2014, 37(1): 36-39 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5551.2014.01.010 [36] SUI C, ZILBERBERG J, LEE W. Microfluidic device engineered to study the trafficking of multiple myeloma cancer cells through the sinusoidal niche of bone marrow[J]. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12(1): 1439 doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-05520-4 [37] JILKOVA Z M, LISOWSKA J, MANET S, et al. CCM proteins control endothelial β1 integrin dependent response to shear stress[J]. Biology Open, 2014, 3(12): 1228-1235 doi: 10.1242/bio.201410132 [38] TONOVA K, LAZAROVA M, DENCHEVA-ZARKOVA M, et al. Separation of glucose, other reducing sugars and phenolics from natural extract by nanofiltration: effect of pressure and cross-flow velocity[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2020, 162: 107-116 doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2020.07.030 [39] LU W Z, DUAN Y H, LI K, et al. Glucose uptake and distribution across the human skeleton using state-of-the-art total-body PET/CT[J]. Bone Research, 2023, 11(1): 36 doi: 10.1038/s41413-023-00268-7 [40] SONI P, ANUPOM T, LESANPEZESHKI L, et al. Microfluidics-integrated spaceflight hardware for measuring muscle strength of Caenorhabditis elegans on the International Space Station[J]. npj Microgravity, 2022, 8(1): 50 doi: 10.1038/s41526-022-00241-4 [41] MAIR D B, TSUI J H, HIGASHI T, et al. Spaceflight-induced contractile and mitochondrial dysfunction in an automated heart-on-a-chip platform[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2024, 121(40): e2404644121 [42] LIDBERG K A, JONES-ISAAC K, YANG J, et al. Modeling cellular responses to serum and vitamin D in microgravity using a human kidney microphysiological system[J]. npj Microgravity, 2024, 10(1): 75 doi: 10.1038/s41526-024-00415-2 [43] LOW L A, GIULIANOTTI M A. Tissue chips in space: modeling human diseases in microgravity[J]. Pharmaceutical Research, 2020, 37(1): 8 doi: 10.1007/s11095-019-2742-0 -
-





 刘丛锦 女, 1997年9月出生于河北省衡水市, 现为北京航空航天大学生物与医学工程学院博士研究生, 主要研究方向为失重性骨质疏松的发生机制研究. E-mail:
刘丛锦 女, 1997年9月出生于河北省衡水市, 现为北京航空航天大学生物与医学工程学院博士研究生, 主要研究方向为失重性骨质疏松的发生机制研究. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: