Long-time Simulation of Stiff Chemical Kinetics Using Conservation-constrained Physics-informed Neural Network
-
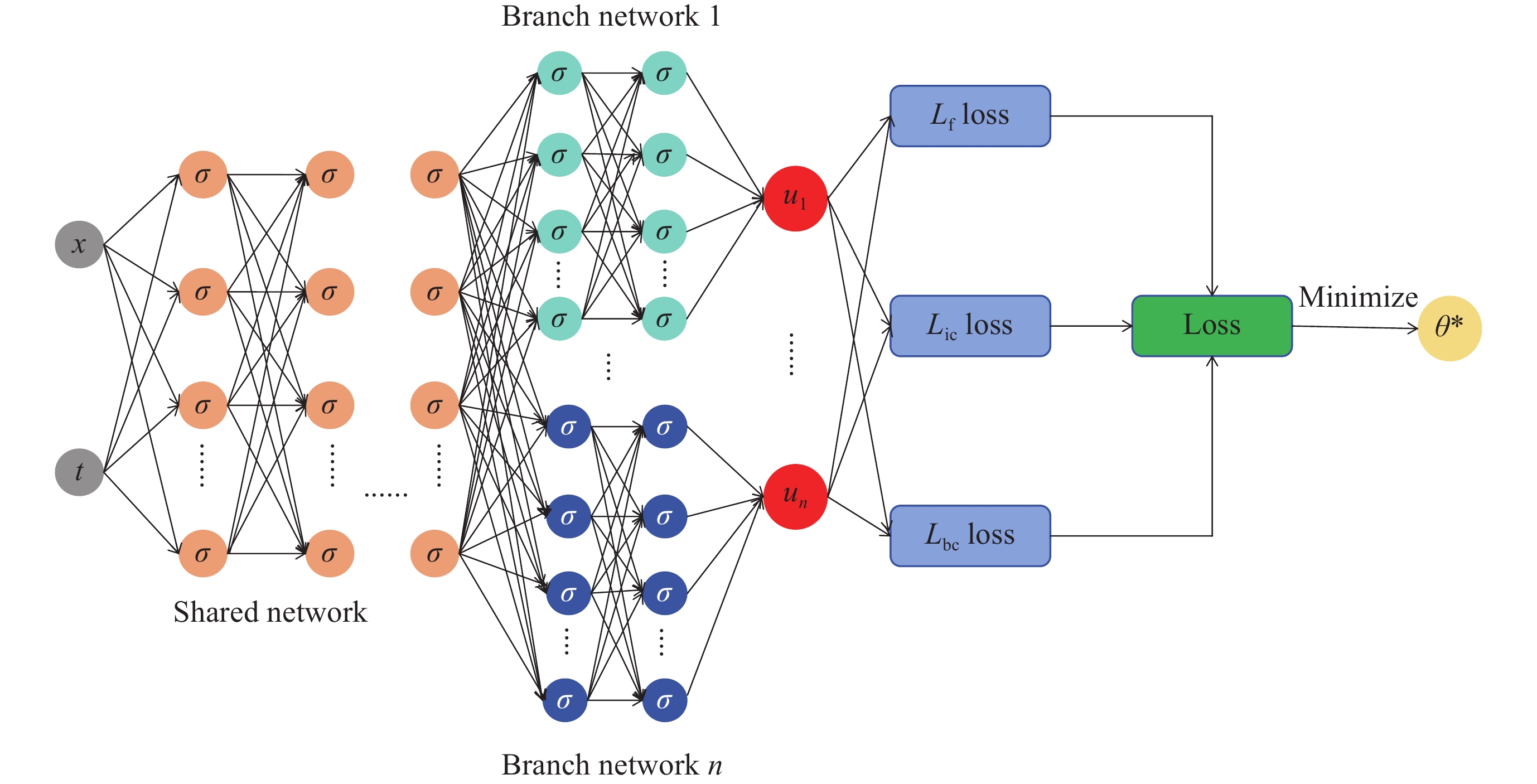
摘要: 刚性化学动力学方程在空间科学、大气科学等领域具有重要意义. 近年来, 物理信息神经网络(Physics-Informed Neural Network, PINN)作为一种融合物理定律与深度学习的框架, 被广泛应用于求解各种偏微分方程. 然而, 在求解刚性化学动力学方程时, PINN将出现优化失败, 难以有效求解. 为解决该问题, 本文提出一种新的守恒约束PINN方法. 该方法利用共享–分支网络有效处理耦合问题, 通过引入物质守恒约束显著提升刚性化学动力学方程的求解性能. 同时, 分段采样策略进一步增强长时模拟的精度和稳定性. 实验结果表明, 该方法能够在多时间尺度的复杂系统中实现长时稳定模拟, 为解决空间科学中的问题(例如无碰撞等离子体波动和星际物质化学反应)提供了一种新的方法.Abstract: Long-term simulation of Partial Differential Equations (PDEs) holds significant applications across various fields, including space physics and atmospheric science. Conventional numerical techniques, such as the finite difference, finite element, and finite volume methods have been extensively employed to solve PDEs across various disciplines. However, these methods often struggle with dimensional curse and complex geometry. In recent years, Physics-Informed Neural Network (PINN), which integrates physical laws within deep learning frameworks, has emerged as a powerful alternative for solving PDEs. Since PINN and its variants are mesh-free, they can avoid dimensional curse to a certain degree. Nonetheless, deep learning related approaches frequently encounter optimization challenges, particularly when applied to multi-time scale issues such as stiff chemical kinetics equations, which involve multiple reactions with different rates, leading to both fast and slow dynamics coexisting. To address these issues, this study introduces a novel Conservation-Constrained Physics-Informed Neural Network (CC-PINN) approach. This method combines shared-branch networks with a segmented sampling strategy. First, the shared-branch networks can effectively deal with coupling equations and reduce the difficulties during the optimization of neural networks. On the other hand, the conservation constraint is embedded into the loss function, ensuring the conservation of physical laws and the accuracy of the simulation results, which significantly improves the performance of PINN. At the same time, according to the dynamics of chemical kinetics in different time intervals, the segmented sampling strategy is adopted, which further improves the accuracy and stability of long-term simulation. In addition, the influence of different expressions of conservation constraints has also been discussed. Experimental results clearly show that, by combining the shared-branch networks and segmented sampling strategy, the new proposed CC-PINN can accurately integrate the stiff chemical kinetics equations in a long-time scale. In summary, this research contributes a new tool for solving problems, such as collisionless plasma fluctuations and interstellar matter chemical reaction, in space science.
-
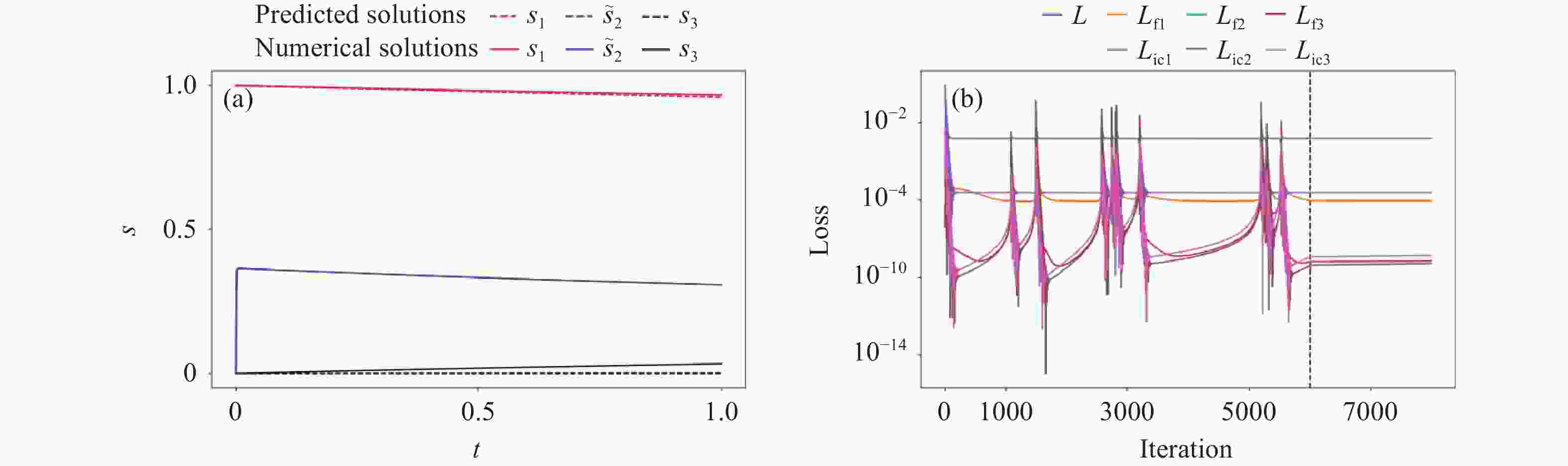
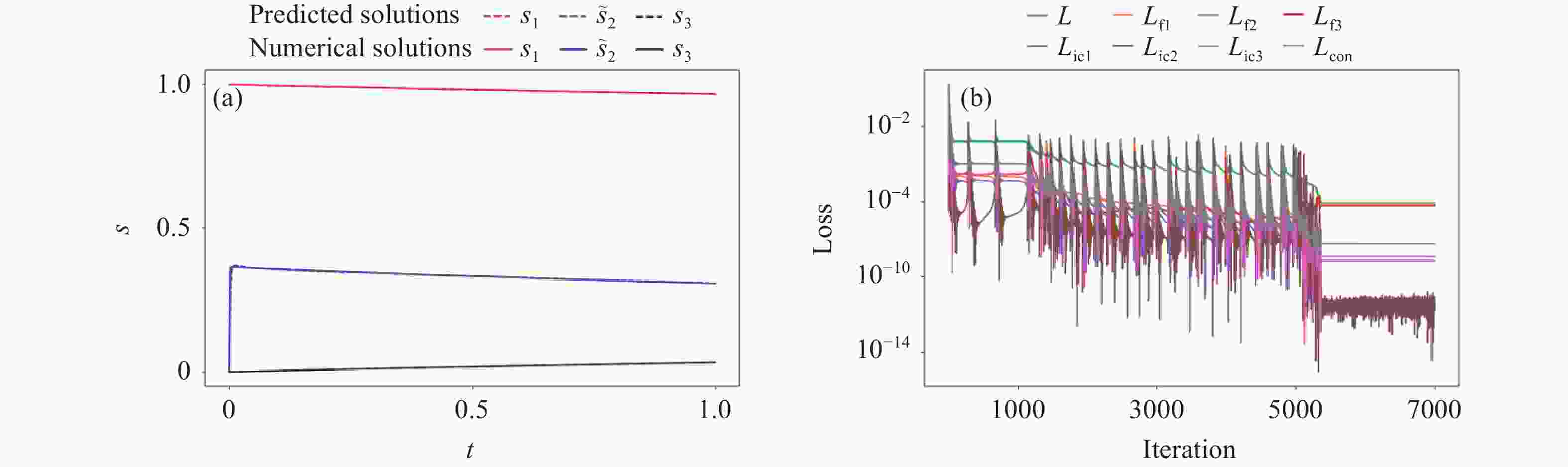
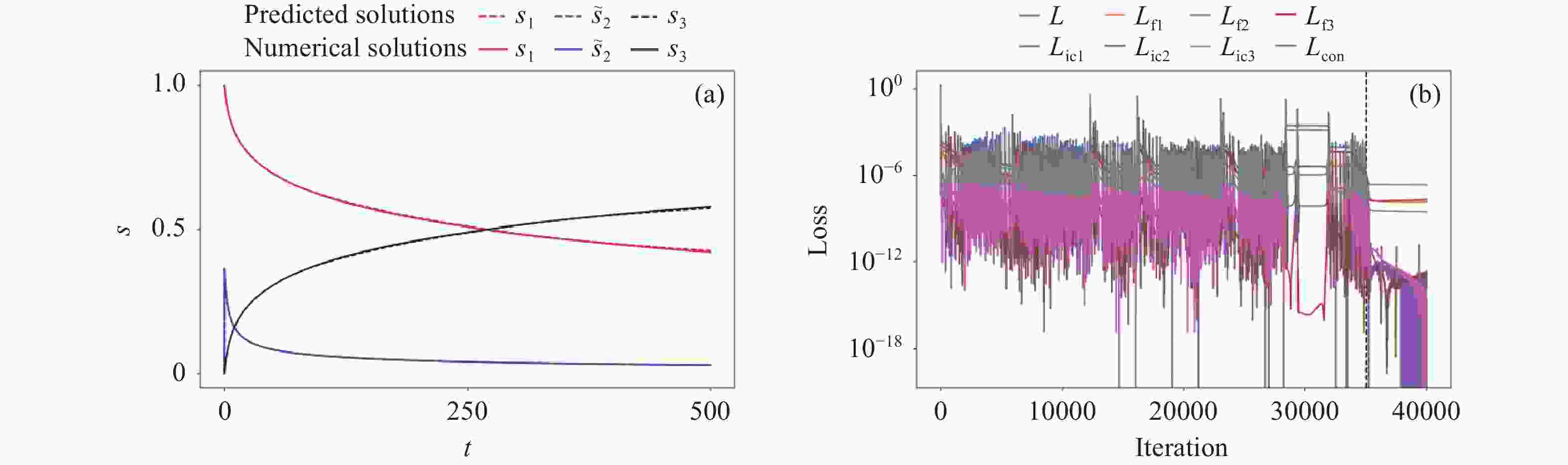
图 7 守恒约束PINN在随机采样策略下的预测结果(a)(c)和损失函数(b)(d). (a) (b)采样点数为1000, (c) (d)采样点数为20000
Figure 7. Predicted results (a)(c) and loss functions (b)(d) with conservation constraint of PINN under random sampling strategy. The number of sampling points in panels (a) and (b) is 1000, while in panels (c) and (d) is 20000
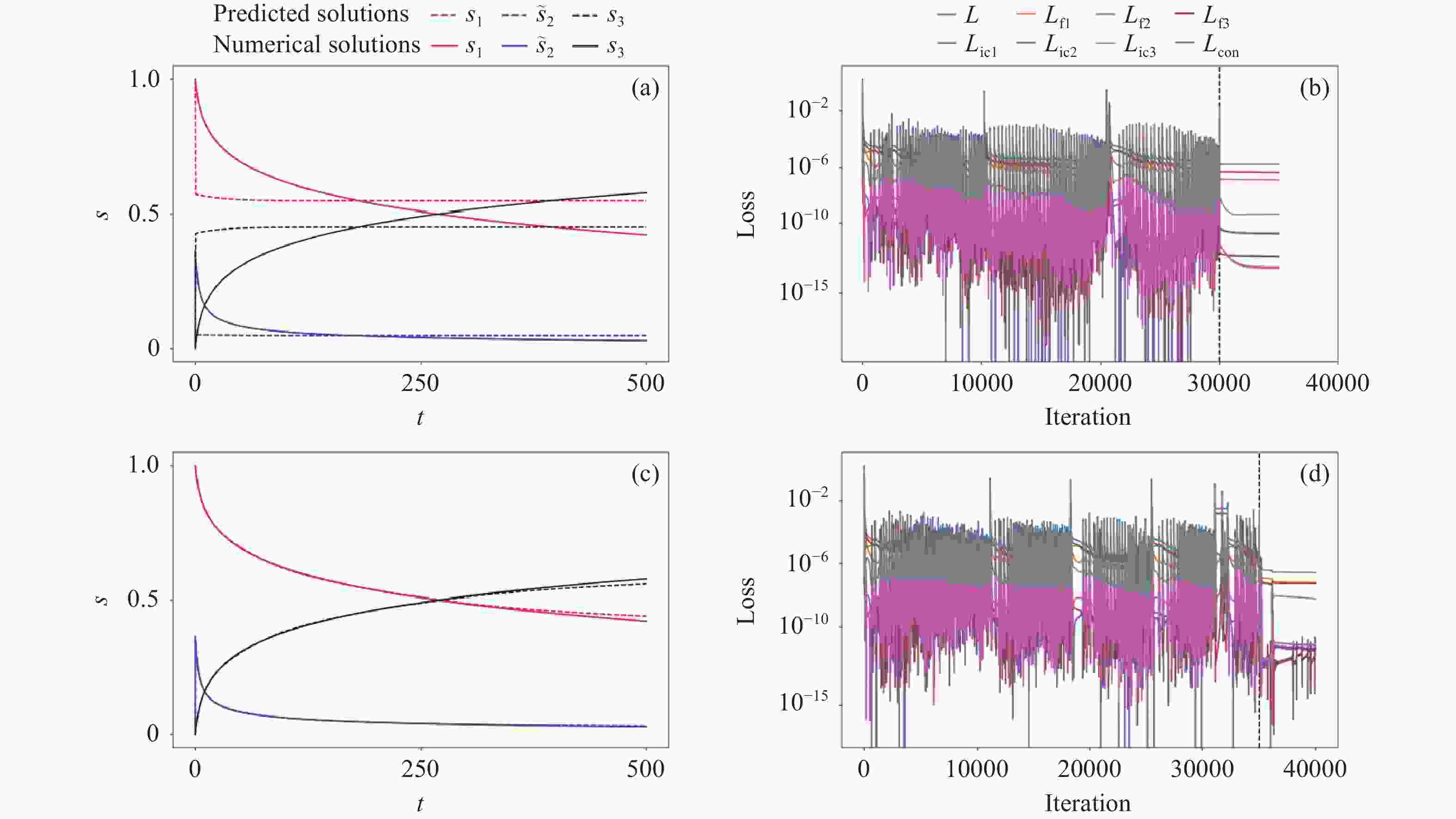
表 1 随机采样策略和分段采样策略的相对误差
Table 1. Relative error of the random sampling strategy and the segmented sampling strategy
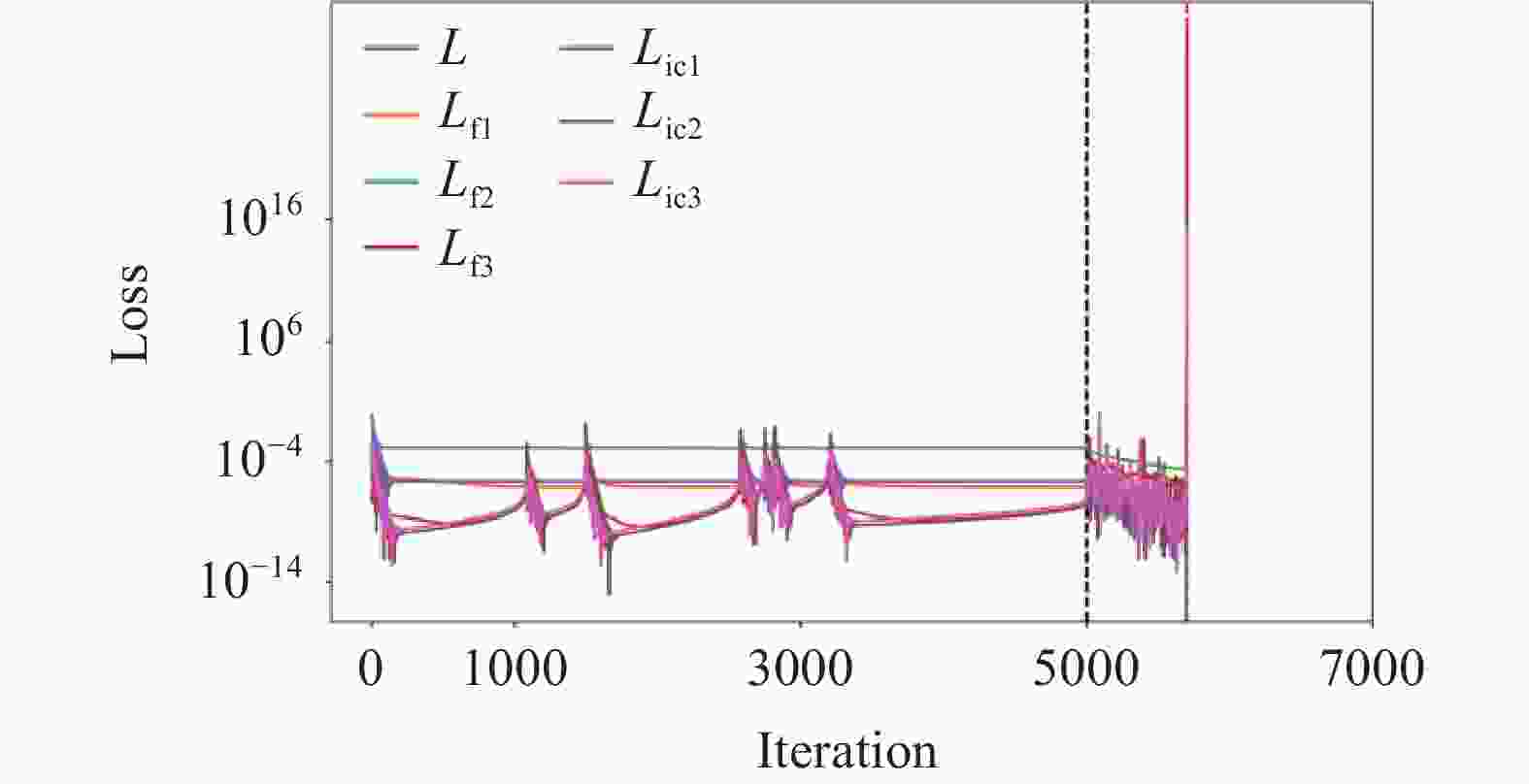
采样策略 采样点数量 Adam L-BFGS $ {s}_{1} $相对误差/(%) $ {s}_{2} $相对误差/(%) $ {s}_{3} $相对误差/(%) 随机采样 20000, t ∈[0, 500] 35000 5000 1.22 99.99 1.42 分段采样 12000, t ∈ [0, 50];
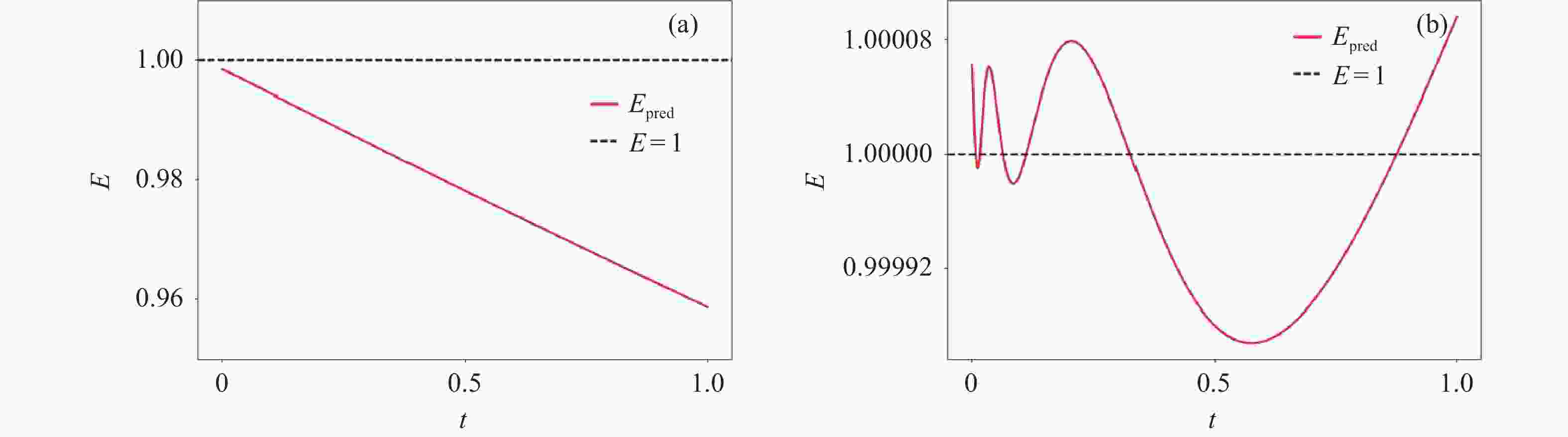
8000, t ∈ [50, 500]35000 5000 0.40 10.72 0.47 表 2 三种不同形式物质守恒约束对应的预测结果
Table 2. Predicted results for three different forms of material conservation constraint
守恒形式 Adam L-BFGS 时间/min $ {s}_{1} $相对误差/(%) $ {s}_{2} $相对误差/(%) $ {s}_{3} $相对误差/(%) $ E = 1 $ 35000 5000 13.58 0.40 10.72 0.46 $ {E^2} = 1 $ 35000 5000 12.26 85.38 99.99 99.71 $ \sqrt E = 1 $ 35000 5000 13.59 0.52 99.99 0.64 -
[1] DROZDOV A Y, SHPRITS Y Y, USANOVA M E, et al. EMIC wave parameterization in the long-term VERB code simulation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2017, 122(8): 8488-8501 doi: 10.1002/2017JA024389 [2] QIAN Y, LEUNG L R. A long-term regional simulation and observations of the hydroclimate in China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2007, 112(D14): D14104 [3] DE FLORIO M, SCHIASSI E, FURFARO R. Physics-informed neural networks and functional interpolation for stiff chemical kinetics[J]. Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science, 2022, 32(6): 063107 doi: 10.1063/5.0086649 [4] HUANG Y L, SEINFELD J H. A neural network-assisted Euler integrator for stiff kinetics in atmospheric chemistry[J]. Environmental Science :Times New Roman;">& Technology, 2022, 56(7): 4676-4685 [5] WU Z Y, LI M J, HE C, et al. Physics-informed learning of chemical reactor systems using decoupling-coupling training framework[J]. AIChE Journal, 2024, 70(7): e18436 doi: 10.1002/aic.18436 [6] CHEN W B, WANG X M, YAN Y, et al. A second order BDF numerical scheme with variable steps for the Cahn--Hilliard equation[J]. SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis, 2019, 57(1): 495-525 [7] 陈丽容, 刘德贵. 求解刚性常微分方程的并行Rosenbrock方法[J]. 计算数学, 1998, 20(3): 251-260 doi: 10.12286/jssx.1998.3.251CHEN Lirong, LIU Degui. Parallel rosenbrock methods for stiff ordinary differential equations[J]. Mathematica Numerica Sinica, 1998, 20(3): 251-260 doi: 10.12286/jssx.1998.3.251 [8] RAISSI M, PERDIKARIS P, KARNIADAKIS G E. Physics-informed neural networks: a deep learning framework for solving forward and inverse problems involving nonlinear partial differential equations[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2019, 378: 686-707 doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2018.10.045 [9] LU L, MENG X H, MAO Z P, et al. DeepXDE: a deep learning library for solving differential equations[J]. SIAM Review, 2021, 63(1): 208-228 doi: 10.1137/19M1274067 [10] LIU G R, GU Y T. An Introduction to Meshfree Methods and Their Programming[M]. Dordrecht: Springer, 2005 [11] ZHONG L L, WU B Y, WANG Y F. Low-temperature plasma simulation based on physics-informed neural networks: frameworks and preliminary applications[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2022, 34(8): 087116 doi: 10.1063/5.0106506 [12] BATY H, VIGON V. Modelling solar coronal magnetic fields with physics-informed neural networks[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2024, 527(2): 2575-2584 [13] MA J Y, FU H Y, HUBA J D, et al. A novel ionospheric inversion model: PINN-SAMI3 (physics informed neural network based on SAMI3)[J]. Space Weather, 2024, 22(4): e2023SW003823 doi: 10.1029/2023SW003823 [14] DAHLBÜDDING D, MOLAVERDIKHANI K, ERCOLANO B, et al. Approximating Rayleigh scattering in exoplanetary atmospheres using physics-informed neural networks[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2024, 533(3): 3475-3483 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stae1872 [15] LIVERMORE P W, WU L Y, CHEN L W, et al. Reconstructions of Jupiter’s magnetic field using physics-informed neural networks[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2024, 533(4): 4058-4067 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stae1928 [16] WANG S F, TENG Y J, PERDIKARIS P. Understanding and mitigating gradient flow pathologies in physics-informed neural networks[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 2021, 43(5): A3055-A3081 doi: 10.1137/20M1318043 [17] JI W Q, QIU W L, SHI Z Y, et al. Stiff-PINN: physics-informed neural network for stiff chemical kinetics[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2021, 125(36): 8098-8106 doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.1c05102 [18] WENG Y T, ZHOU D Z. Multiscale physics-informed neural networks for stiff chemical kinetics[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2022, 126(45): 8534-8543 doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.2c06513 [19] WANG S F, PERDIKARIS P. Long-time integration of parametric evolution equations with physics-informed deeponets[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 475: 111855 doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2022.111855 [20] 韦昌, 樊昱晨, 周永清, 等. 基于龙格库塔法的多输出物理信息神经网络模型[J]. 力学学报, 2023, 55(10): 2405-2416 doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-23-299WEI Chang, FAN Yuchen, ZHOU Yongqing, et al. Multi-output physics-informed neural networks model based on the Runge-Kutta method[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2023, 55(10): 2405-2416 doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-23-299 [21] HUANG Q M, MA J X, XU Z. Mass-preserving Spatio-temporal adaptive PINN for Cahn-Hilliard equations with strong nonlinearity and singularity[OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2404.18054, 2024 [22] 宋家豪, 曹文博, 张伟伟. FD-PINN: 频域物理信息神经网络[J]. 力学学报, 2023, 55(5): 1195-1205 doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-23-169SONG Jiahao, CAO Wenbo, ZHANG Weiwei. FD-PINN: frequency domain physics-informed neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2023, 55(5): 1195-1205 doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-23-169 [23] CHEN Z, LIU Y, SUN H. Physics-informed learning of governing equations from scarce data[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 6136 doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26434-1 [24] SIVAMOHAN S, SRIDHAR S S, KRISHNAVENI S. An effective recurrent neural network (RNN) based intrusion detection via bi-directional long short-term memory[C] //Proceedings of 2021 International Conference on Intelligent Technologies (CONIT). Hubli: IEEE, 2021: 1-5 [25] WU K L, XIU D. Data-driven deep learning of partial differential equations in modal space[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2020, 408: 109307 doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2020.109307 [26] BRANDSTETTER J, WORRALL D E, WELLING M. Message passing neural PDE solvers[C]//Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Learning Representations. ICLR, 2022 [27] JAGTAP A D, KHARAZMI E, KARNIADAKIS G E. Conservative physics-informed neural networks on discrete domains for conservation laws: applications to forward and inverse problems[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 365: 113028 doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2020.113028 [28] LIN S N, CHEN Y. A two-stage physics-informed neural network method based on conserved quantities and applications in localized wave solutions[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 457: 111053 doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2022.111053 [29] 李道伦, 沈路航, 查文舒, 等. 基于神经算子与类物理信息神经网络智能求解新进展[J]. 力学学报, 2024, 56(4): 875-889 doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-23-407LI Daolun, SHEN Luhang, ZHA Wenshu, et al. New progress in intelligent solution of neural operators and physics-informed-based methods[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2024, 56(4): 875-889 doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-23-407 [30] MENG X H, LI Z, ZHANG D K, et al. PPINN: parareal physics-informed neural network for time-dependent PDEs[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 370: 113250 doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2020.113250 [31] ISHIGURO S, USAMI S, HORIUCHI R, et al. Multi-scale simulation for plasma science[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2010, 257(1): 012026 [32] AKINSOLA V O, OKE E O, AMAO F A, et al. Numerical solutions of robertson chemical kinetic equation using a modified semi implicit extrapolation method and Runge-Kutta method of order four[J]. Adeleke University Journal of Science, 2023, 2(1): 22-33 [33] GUO J W, YAO Y Z, WANG H, et al. Pre-training strategy for solving evolution equations based on physics-informed neural networks[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 489: 112258 doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2023.112258 [34] 潘小果, 王凯, 邓维鑫. 基于NTK理论和改进时间因果的物理信息神经网络加速收敛算法[J]. 力学学报, 2024, 56(7): 1943-1958 doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-24-087PAN Xiaoguo, WANG Kai, DENG Weixin. Accelerating convergence algorithm for physics-informed neural networks based on NTK theory and modified causality[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2024, 56(7): 1943-1958 doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-24-087 [35] KINGMA D P, BA J. Adam: a method for stochastic optimization[OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1412.6980, 2014 [36] BYRD R H, LU P H, NOCEDAL J, et al. A limited memory algorithm for bound constrained optimization[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 1995, 16(5): 1190-1208 doi: 10.1137/0916069 -
-




 方涵敏 女, 1998年12月出生于安徽省合肥市, 现为安徽工业大学计算机科学与技术学院硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为AI for Science和智能科学计算. E-mail:
方涵敏 女, 1998年12月出生于安徽省合肥市, 现为安徽工业大学计算机科学与技术学院硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为AI for Science和智能科学计算. E-mail: 

 下载:
下载: