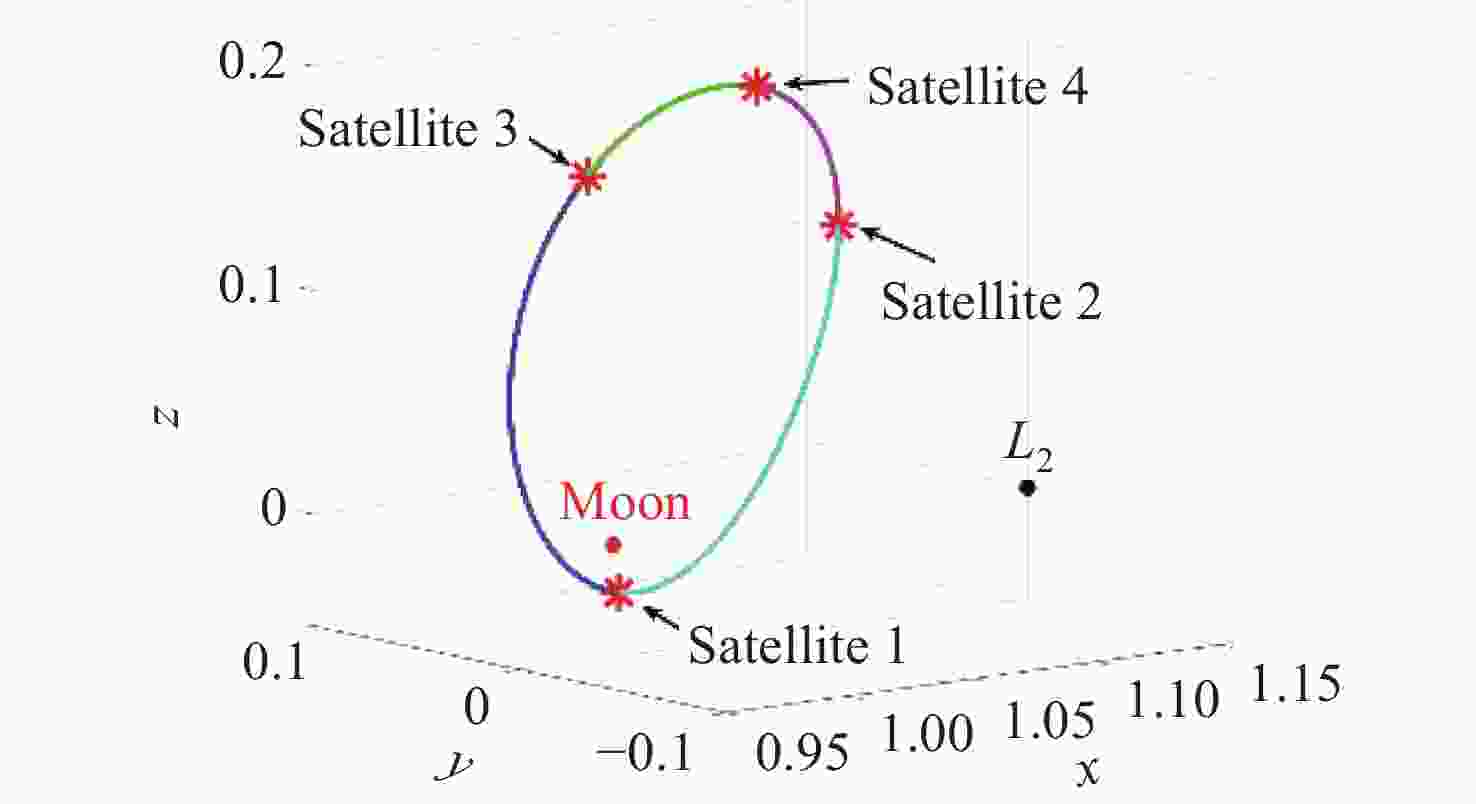
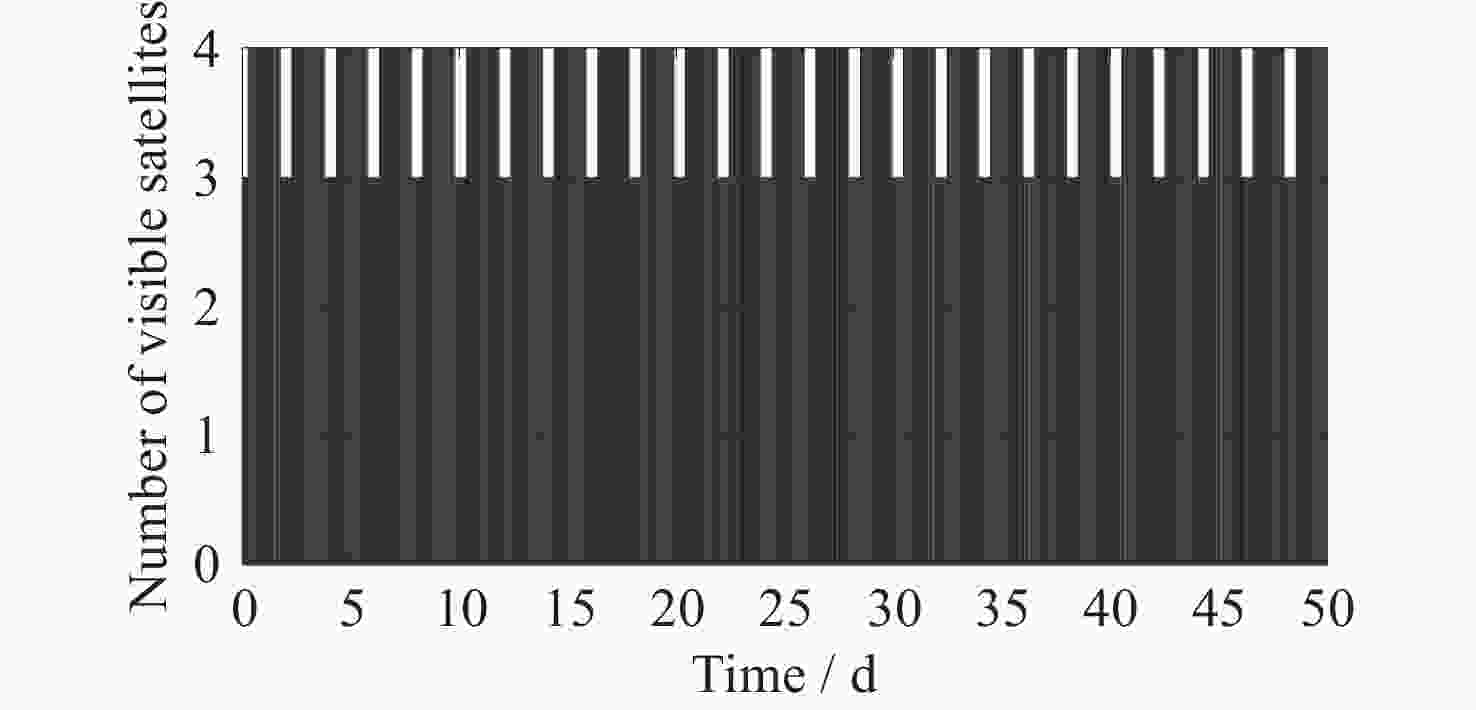
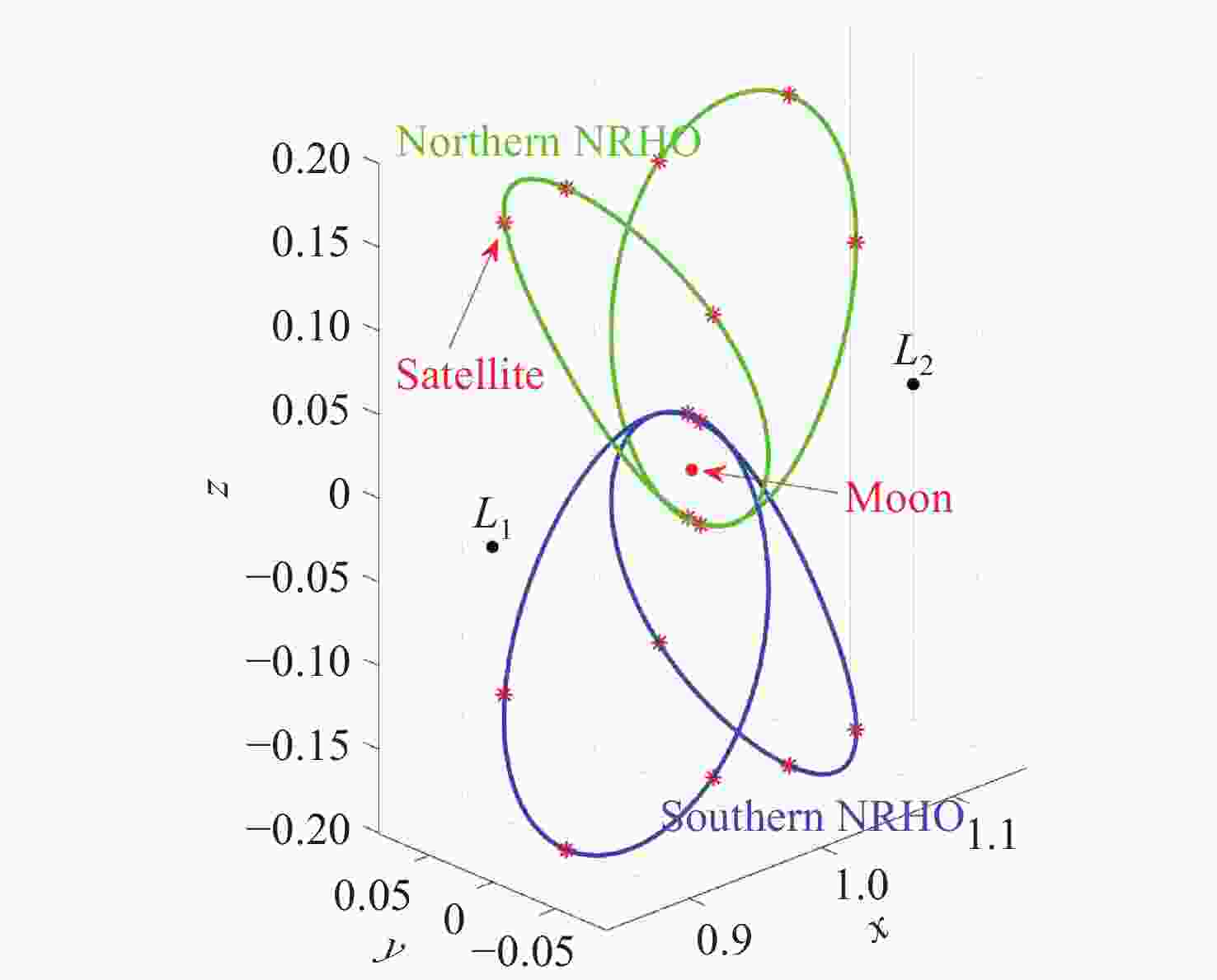
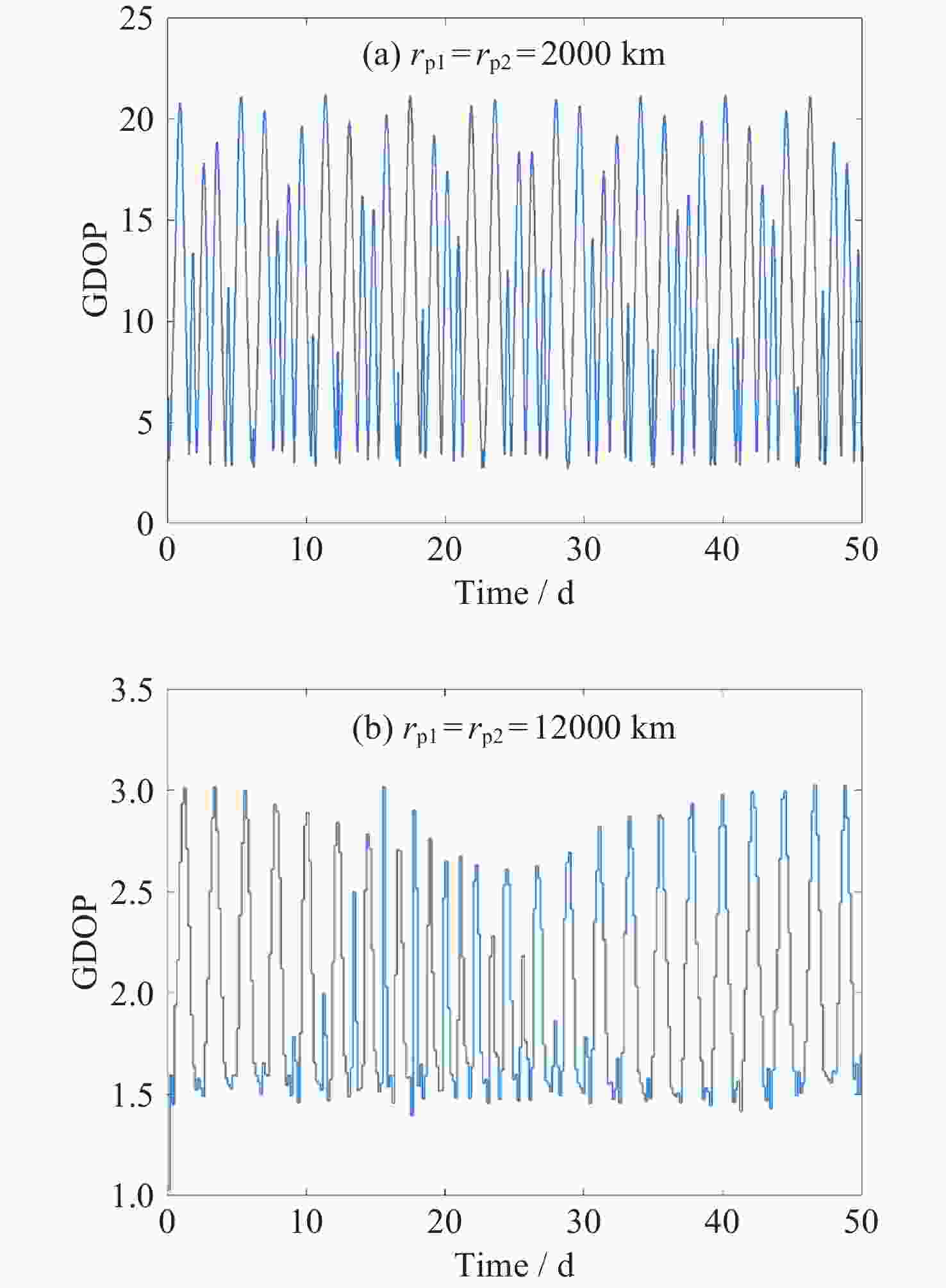
Research on NRHO-Based Lunar Global Positioning System
-
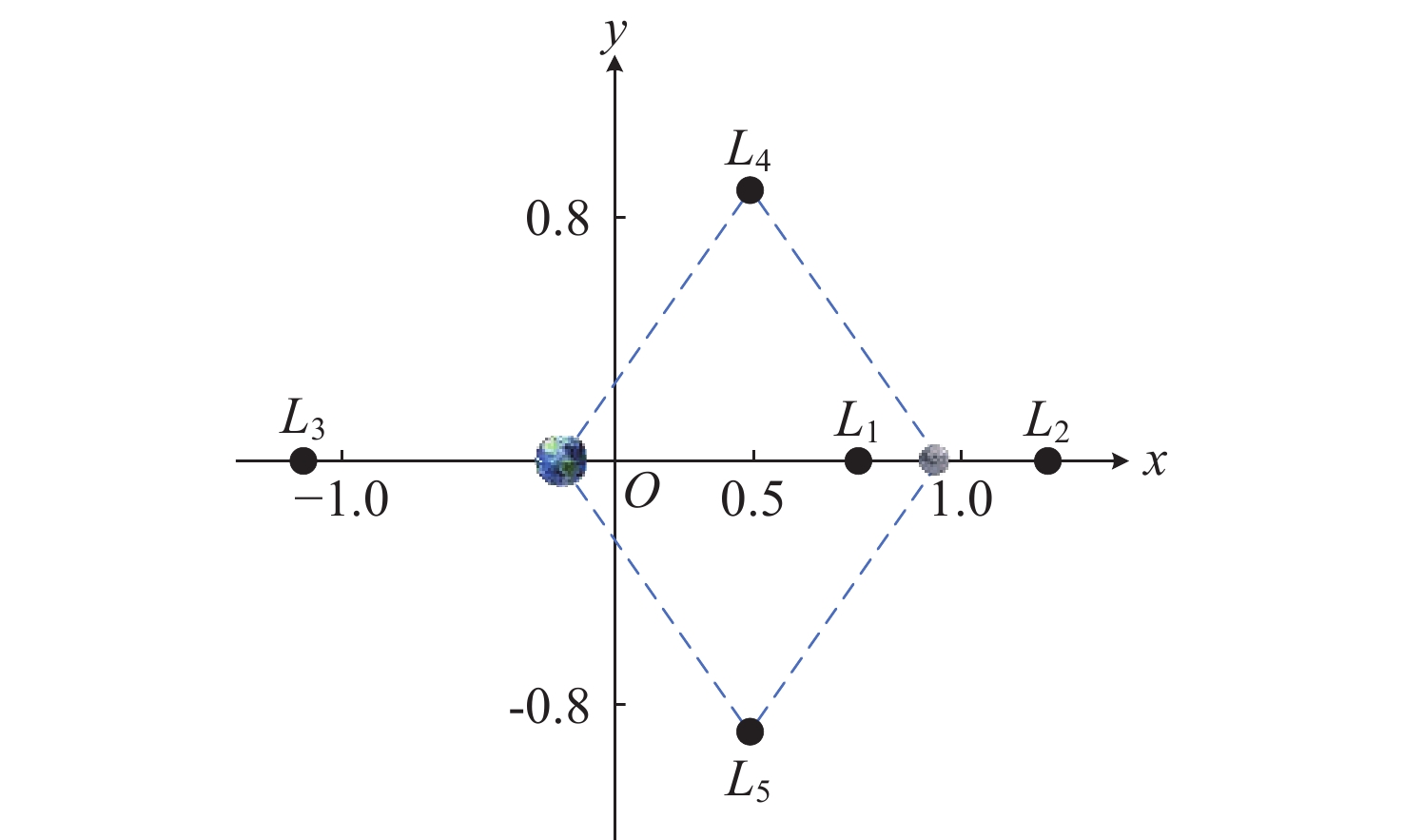
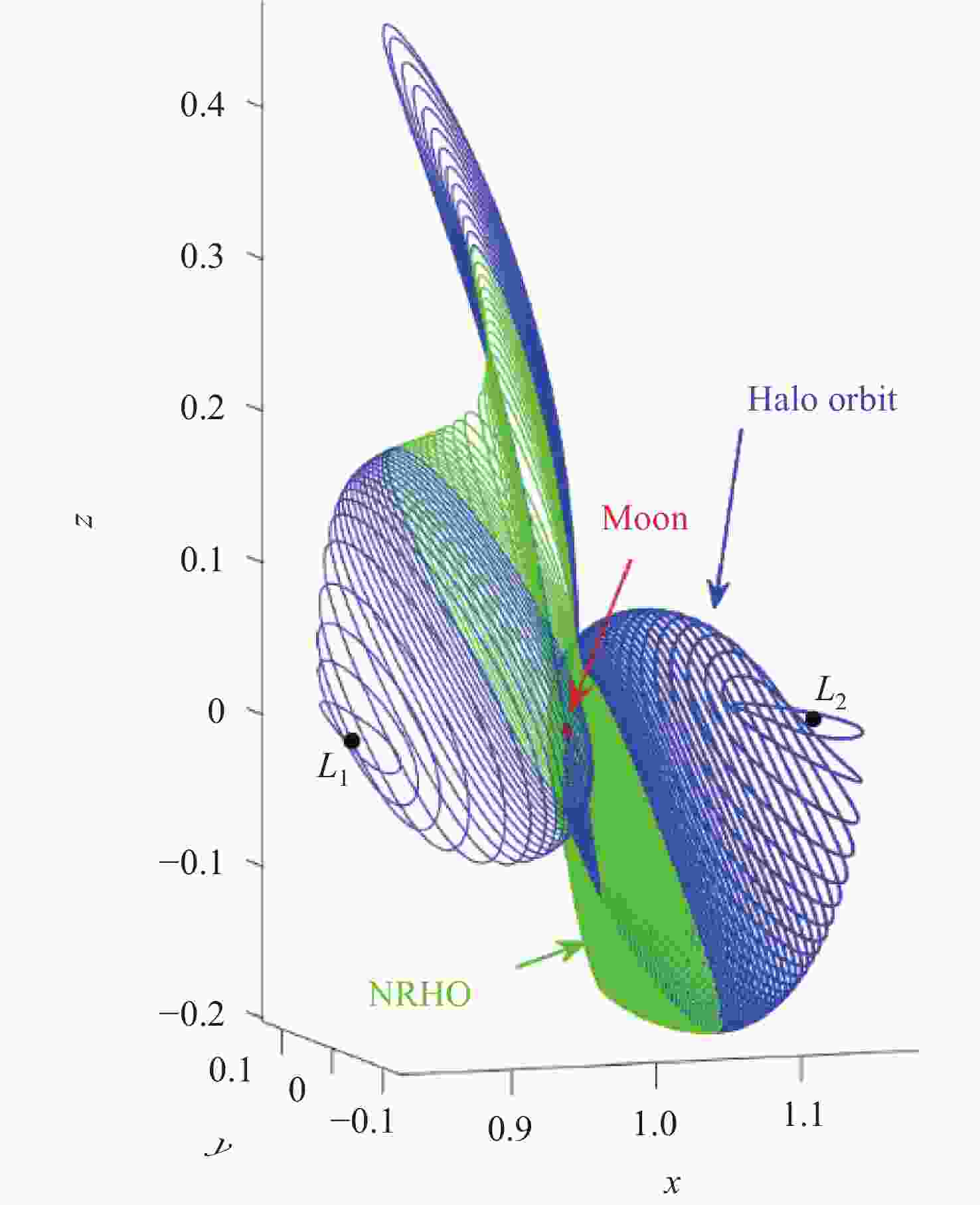
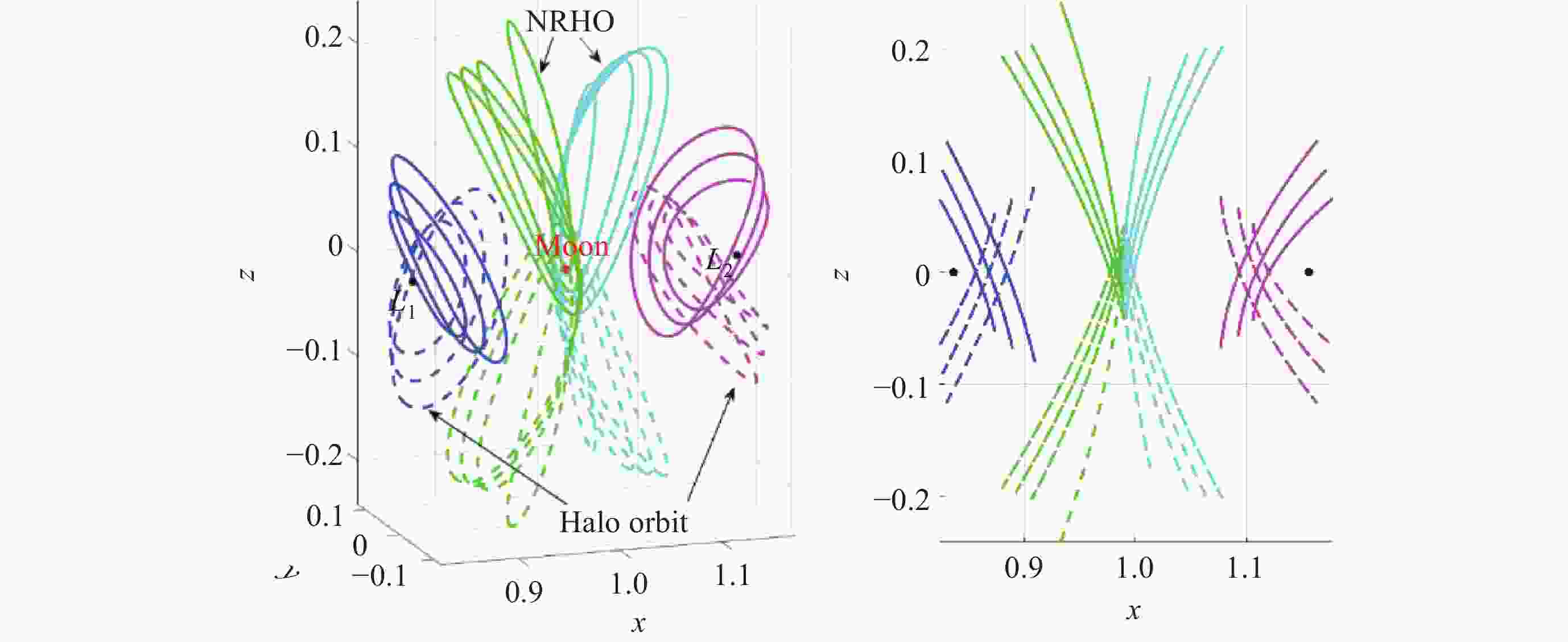
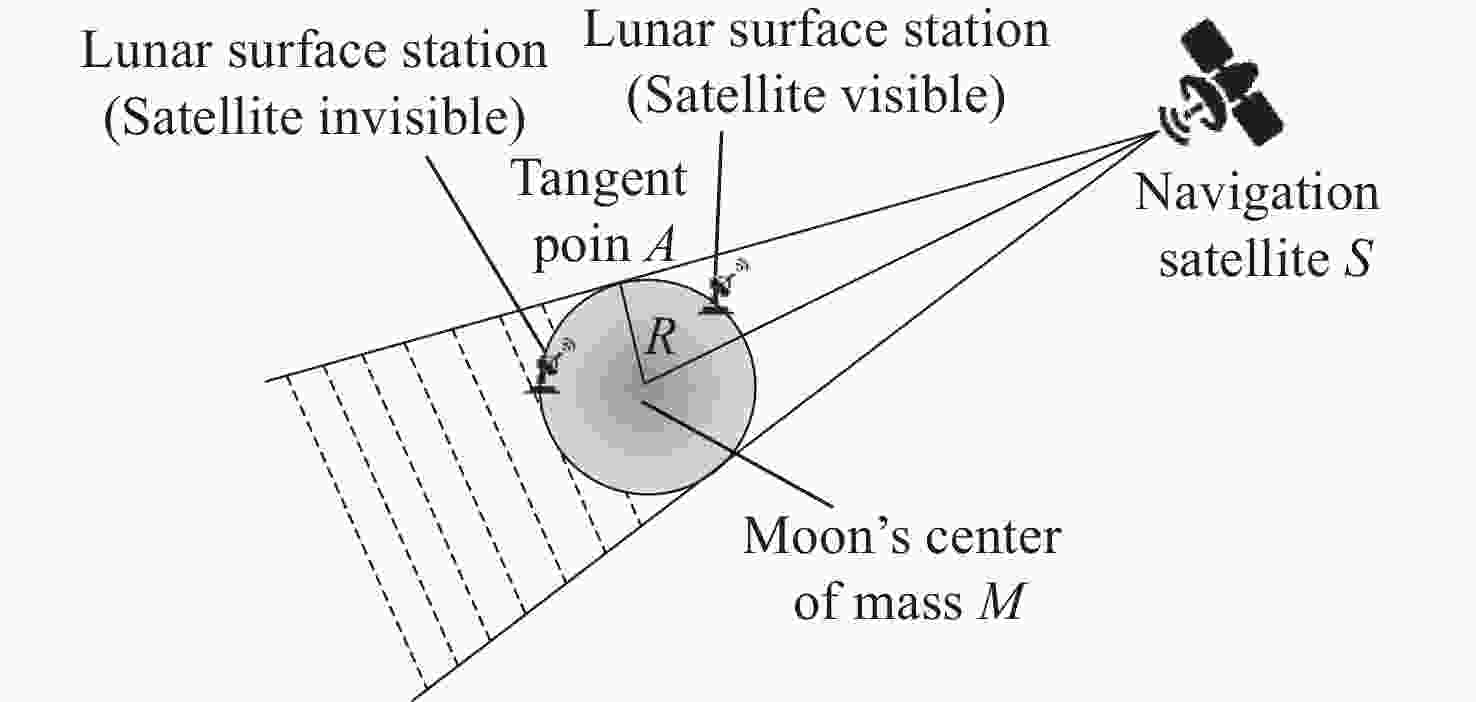
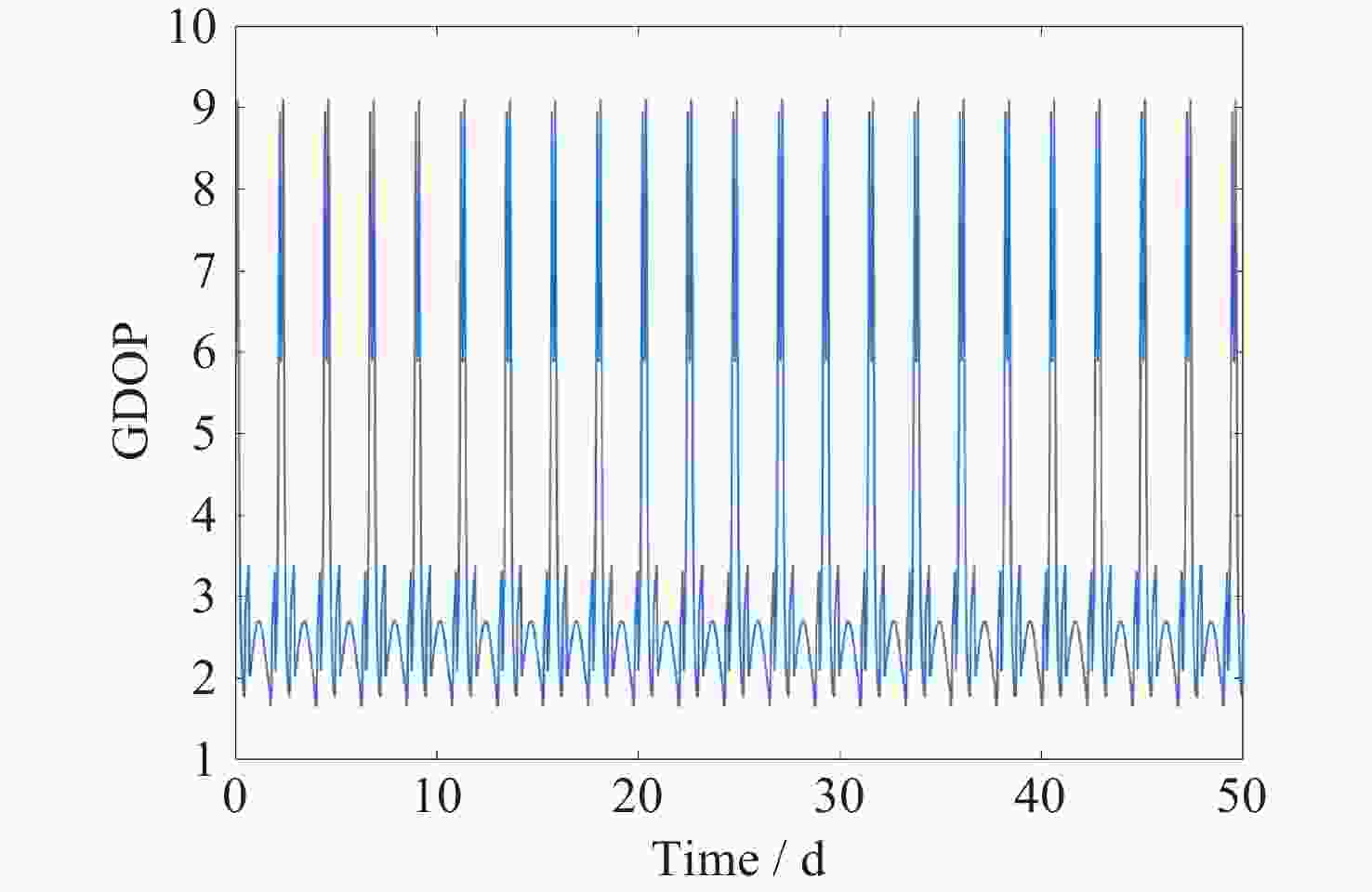
摘要: 针对未来月球探测与开发等任务对月球全球定位服务的需求, 利用近直线晕轨道(NRHO)特殊的轨道空间几何特性, 提出了以地月系NRHO作为参考轨道的月球全球定位系统(LGPS). 首先, 考虑轨道分布、卫星数目、轨道尺寸等星座构型参数, 设计了多个星座构型方案; 然后, 从可见星数目、月球全球覆盖特性以及几何精度因子(GDOP)等方面, 分析了不同构型参数对LGPS星座导航性能的影响. 仿真结果表明, 与Halo轨道相比, 基于NRHO的LGPS在月球高纬度区域, 尤其是对月球极区, 具有更优的持续覆盖能力和定位精度, GDOP可达3以内. 本文研究可对未来的月球开发任务提供导航定位方面的技术参考.Abstract: In order to meet the increasing requirement of lunar global positioning services for future lunar exploration and exploitation missions, the Lunar Global Positioning System (LGPS) using the Near Rectilinear Halo Orbit (NRHO) as a reference orbit is proposed. First, multiple constellation configuration schemes are designed, considering configuration parameters such as orbit distribution, satellite number, orbit size, etc. Then, the impact of different constellation configuration parameters on the navigation performance of the LGPS constellation is analyzed, including the number of visible satellites, the lunar global coverage characteristics and the Geometric Dilution of Precision (GDOP, $ {\sigma }_{\mathrm{G}\mathrm{D}\mathrm{O}\mathrm{P}} $). Simulation results show that, compared with the Halo orbit case, the NRHO-based LGPS is superior in the continuous coverage and positioning accuracy ($ {\sigma }_{\mathrm{G}\mathrm{D}\mathrm{O}\mathrm{P}} $ < 3) within the lunar high latitude region, especially in the lunar polar region. This study can provide technical reference on the navigation and positioning service for future lunar exploitation missions.
-
表 1 月面代表位置
Table 1. Representative locations for the lunar surface
所选位置 经纬度 赤道 +25°, 0° 中纬度 –55°, +45° 高纬度(南极区域) +35°, –80° 高经度高纬度(北极区域) +85°, +85° 表 2 L2单一北族NRHO 4星可见性和$ {{\bar {\boldsymbol{\sigma}} }_{\bf{G}\bf{D}\bf{O}\bf{P}}} $
Table 2. Visibility and ${{ \bar {\boldsymbol{\sigma}} }_{\bf{G}\bf{D}\bf{O}\bf{P}}} $ of L2 single northern NRHO with 4 satellites
rp / km 经度/(º) 纬度/(º) 最小卫星数 最大卫星数 $ {{\bar \sigma }_{\mathrm{G}\mathrm{D}\mathrm{O}\mathrm{P}}} $ $ {\delta }_{\text{CTP}} $/(%) 2000 25 0 3 4 170.6065 5.58 2000 –55 45 3 4 2230.7161 88.75 2000 35 –80 0 1 - 0 2000 85 85 3 4 1467.1571 94.33 8000 25 0 3 4 49.7617 10.92 8000 –55 45 3 4 2982.7853 60.58 8000 35 –80 0 1 - 0 8000 85 85 3 4 401.7979 75.50 12000 25 0 3 4 31.8642 9.58 12000 –55 45 3 4 297.0158 45.75 12000 35 –80 0 1 - 0 12000 85 85 3 4 330.2189 60.08 16000 25 0 3 4 23.3501 11.25 16000 –55 45 3 4 44.2958 30.42 16000 35 –80 0 1 - 0 16000 85 85 3 4 323.9554 47.08 表 3 双轨8星两种方案的可见性和$ {{\bar {\boldsymbol{\sigma}} }_{\bf{G}\bf{D}\bf{O}\bf{P}}} $
Table 3. Visibility and $ {{\bar {\boldsymbol{\sigma}} }_{\bf{G}\bf{D}\bf{O}\bf{P}}} $ of two schemes for 8-satellite-2-orbit
rp / km 经纬度/(º) L2 南北族NRHO L1, L2 北族NRHO 最小/最大卫星数 $ {{\bar \sigma }_{\mathrm{G}\mathrm{D}\mathrm{O}\mathrm{P}}} $ $ {\delta }_{\text{CTP}} $/(%) 最小/最大卫星数 $ {{\bar \sigma }_{\mathrm{G}\mathrm{D}\mathrm{O}\mathrm{P}}} $ $ {\delta }_{\text{CTP}} $/(%) 2000 25, 0 6/8 15.7933 100 3/5 28.8518 35.25 2000 –55, 45 3/5 1978.9484 88.75 6/8 11.8093 100 2000 35, –80 3/4 1396.0754 95.67 0/2 - 0 2000 85, 85 3/4 1385.3785 95.67 6/8 11.1710 100 8000 25, 0 6/8 6.9092 100 3/5 8.2863 56.83 8000 –55, 45 3/5 1795.0248 68.75 6/8 3.1919 100 8000 35, –80 3/4 359.5158 94.00 0/2 - 0 8000 85, 85 3/4 308.5043 94.00 6/8 3.0121 100 12000 25, 0 6/8 5.2746 100 3/5 5.6048 65.92 12000 –55, 45 3/5 8.2629 61.58 6/8 2.4515 100 12000 35, –80 3/5 223.0813 91.33 0/2 - 0 12000 85, 85 3/4 205.5970 92.67 6/8 2.2291 100 16000 25, 0 6/8 4.5476 100 3/5 4.1621 68.50 16000 –55, 45 3/5 10.7901 82.92 5/7 2.1632 100 16000 35, –80 3/5 162.3518 91.67 0/2 - 0 16000 85, 85 3/5 162.1141 90.00 6/8 1.9270 100 表 4 L1和L2 NRHO南北族轨道16星可见性和$ {{\bar {\boldsymbol{\sigma}} }_{\bf{G}\bf{D}\bf{O}\bf{P}}} $
Table 4. Visibility and $ {{\bar {\boldsymbol{\sigma}} }_{\bf{G}\bf{D}\bf{O}\bf{P}}} $ for L1 and L2 southern and northern NRHO with 16 satellites
rp1 和 rp2 /km 经度/(º) 纬度/(º) 最小卫星数 最大卫星数 $ {{\bar \sigma }_{\mathrm{G}\mathrm{D}\mathrm{O}\mathrm{P}}} $ $ {\delta }_{\text{CTP}} $/(%) 2000 25 0 6 10 11.8770 100 2000 –55 45 6 9 11.7464 100 2000 35 –80 6 8 11.1813 100 2000 85 85 6 8 11.1531 100 8000 25 0 6 10 4.3464 100 8000 –55 45 6 9 2.5860 100 8000 35 –80 6 8 2.8616 100 8000 85 85 6 8 2.8570 100 12000 25 0 6 10 2.9649 100 12000 –55 45 6 10 1.9135 100 12000 35 –80 6 9 2.0141 100 12000 85 85 6 9 2.0059 100 16000 25 0 6 10 2.5497 100 16000 –55 45 6 9 1.5447 100 16000 35 –80 6 9 1.6469 100 16000 85 85 6 9 1.6422 100 -
[1] 叶培建, 于登云, 孙泽洲, 等. 中国月球探测器的成就与展望[J]. 深空探测学报, 2016, 3(4): 323-333YE Peijian, YU Dengyun, SUN Zezhou, et al. Achievements and prospect of Chinese lunar probes[J]. Journal of Deep Space Exploration, 2016, 3(4): 323-333 [2] 裴照宇, 刘继忠, 王倩, 等. 月球探测进展与国际月球科研站[J]. 科学通报, 2020, 65(24): 2577-2586 doi: 10.1360/TB-2020-0582PEI Zhaoyu, LIU Jizhong, WANG Qian, et al. Overview of lunar exploration and International Lunar Research Station[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2020, 65(24): 2577-2586 doi: 10.1360/TB-2020-0582 [3] FARQUHAR R W. The Utilization of Halo Orbits in Advanced Lunar Operations[M]. Washington: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, 1971 [4] GREBOW D J, OZIMEK M T, HOWELL K C, et al. Multibody orbit architectures for lunar south pole coverage[J]. Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 2008, 45(2): 344-358 doi: 10.2514/1.28738 [5] SCHONFELDT M, GRENIER A, DELÉPAUT A, et al. A system study about a lunar navigation satellite transmitter system[C]//2020 European Navigation Conference (ENC). Dresden, Germany: IEEE, 2020: 1-10 [6] CARRETERO G S. Study of a lunar satellite navigation system[C]//Proceeding of 63rd International Astronautical Congress. Naples: International Astronautical Federation, 2012 [7] PERGOLA P, ALESSI E M. Libration point orbit characterization in the earth-moon system[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2012, 426(2): 1212-1222 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21585.x [8] ZHANG L, XU B. A universe light house—candidate architectures of the libration point satellite navigation system[J]. The Journal of Navigation, 2014, 67(5): 737-752 doi: 10.1017/S0373463314000137 [9] ROMAGNOLI D, CIRCI C. Lissajous trajectories for lunar global positioning and communication systems[J]. Celestial Mechanics and Dynamical Astronomy, 2010, 107(4): 409-425 doi: 10.1007/s10569-010-9279-1 [10] CIRCI C, ROMAGNOLI D, FUMENTI F. Halo orbit dynamics and properties for a lunar global positioning system design[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2014, 442(4): 3511-3527 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stu1085 [11] GAO Z Y, HOU X Y. Coverage analysis of lunar communication/navigation constellations based on halo orbits and distant retrograde orbits[J]. The Journal of Navigation, 2020, 73(4): 932-952 doi: 10.1017/S0373463320000065 [12] GAO Z Y, HOU X Y. Comparison of autonomous orbit determination for satellite pairs in lunar halo and distant retrograde orbits[J]. NAVIGATION: Journal of the Institute of Navigation, 2022, 69(2): navi. 522 [13] WANG K, LI K Z, LV S K, et al. Multi-orbit lunar GNSS constellation design with distant retrograde orbit and Halo orbit combination[J]. Scientific Reports, 2023, 13(1): 10158 doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-37348-x [14] GARDNER T, CHEETHAM B, CLARKSON M. CAPSTONE: Mission updates and ongoing efforts at the moon[C]//ASCEND 2023. Las Vegas, Nevada: American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2023 [15] DAVIS D, BHATT S, HOWELL K, et al. Orbit maintenance and navigation of human spacecraft at cislunar near rectilinear halo orbits[C]//AAS/AIAA Space Flight Mechanics Meeting. San Antonio: AIAA, 2017 [16] ZIMOVAN E M. Characteristics and design strategies for near rectilinear halo orbits within the earth-moon system[D]. West Lafayette, Indiana: Purdue University, 2017 [17] ZIMOVAN E M, HOWELL K C, DAVIS D C. Near rectilinear halo orbits and their application in cis-lunar space[C]//3rd IAA Conference on Dynamics and Controls of Space Systems. Moscow: IAA, 2017 [18] ZIMOVAN-SPREEN E M, HOWELL K C, DAVIS D C. Near rectilinear halo orbits and nearby higher-period dynamical structures: orbital stability and resonance properties[J]. Celestial Mechanics and Dynamical Astronomy, 2020, 132(5): 28 doi: 10.1007/s10569-020-09968-2 [19] 关梅倩. 地月空间综合PNT星座设计及导航定位性能分析[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2022GUAN Meiqian. Integrated-PNT Constellation Design and Navigation Performance Analysis in Cislunar Space[D]. Ji’nan: Shandong University, 2022 [20] GÓMEZ G, KOON W S, LO M W, et al. Connecting orbits and invariant manifolds in the spatial restricted three-body problem[J]. Nonlinearity, 2004, 17(5): 1571-1606 doi: 10.1088/0951-7715/17/5/002 [21] CHEN H R, MA J. Phasing trajectories to deploy a constellation in a halo orbit[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2017, 40(10): 2662-2667 doi: 10.2514/1.G002518 -
-





 晋守聪 男, 1999年3月出生于山东省济南市, 现为北京邮电大学智能工程与自动化学院在读硕士, 主要研究方向为平动点轨道设计、地月空间导航星座等. E-mail:
晋守聪 男, 1999年3月出生于山东省济南市, 现为北京邮电大学智能工程与自动化学院在读硕士, 主要研究方向为平动点轨道设计、地月空间导航星座等. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: