Simulation of Rotating System Microwave Scatterometer Performance and Observation of Tropical Cyclone
-
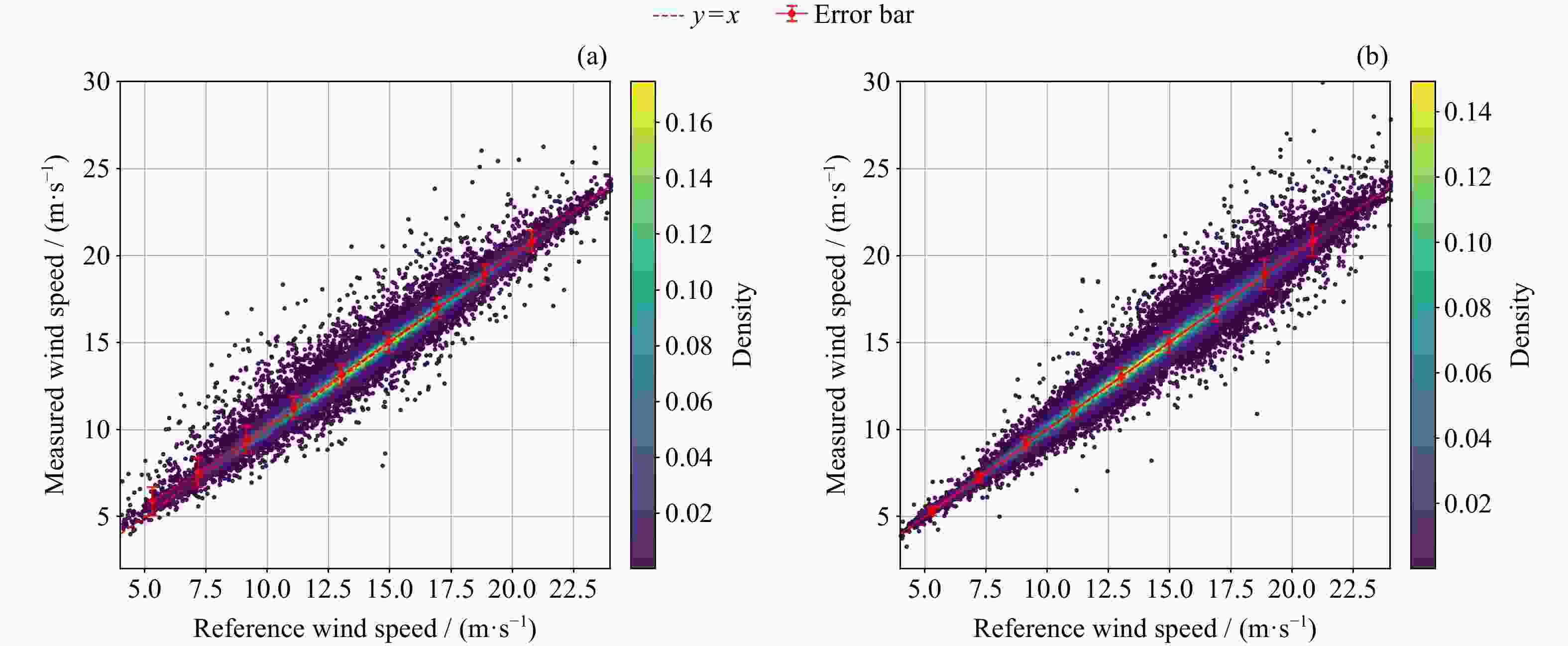
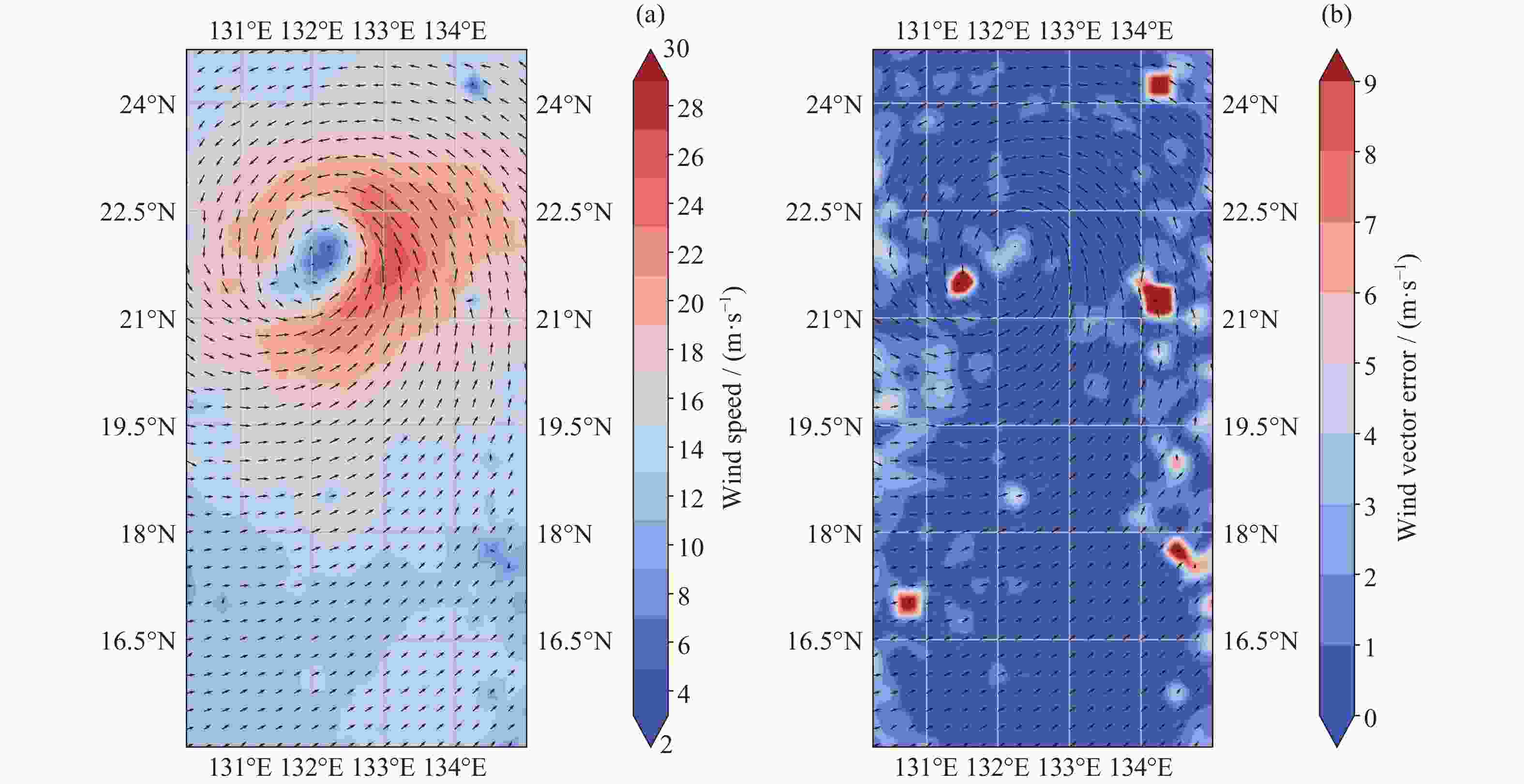
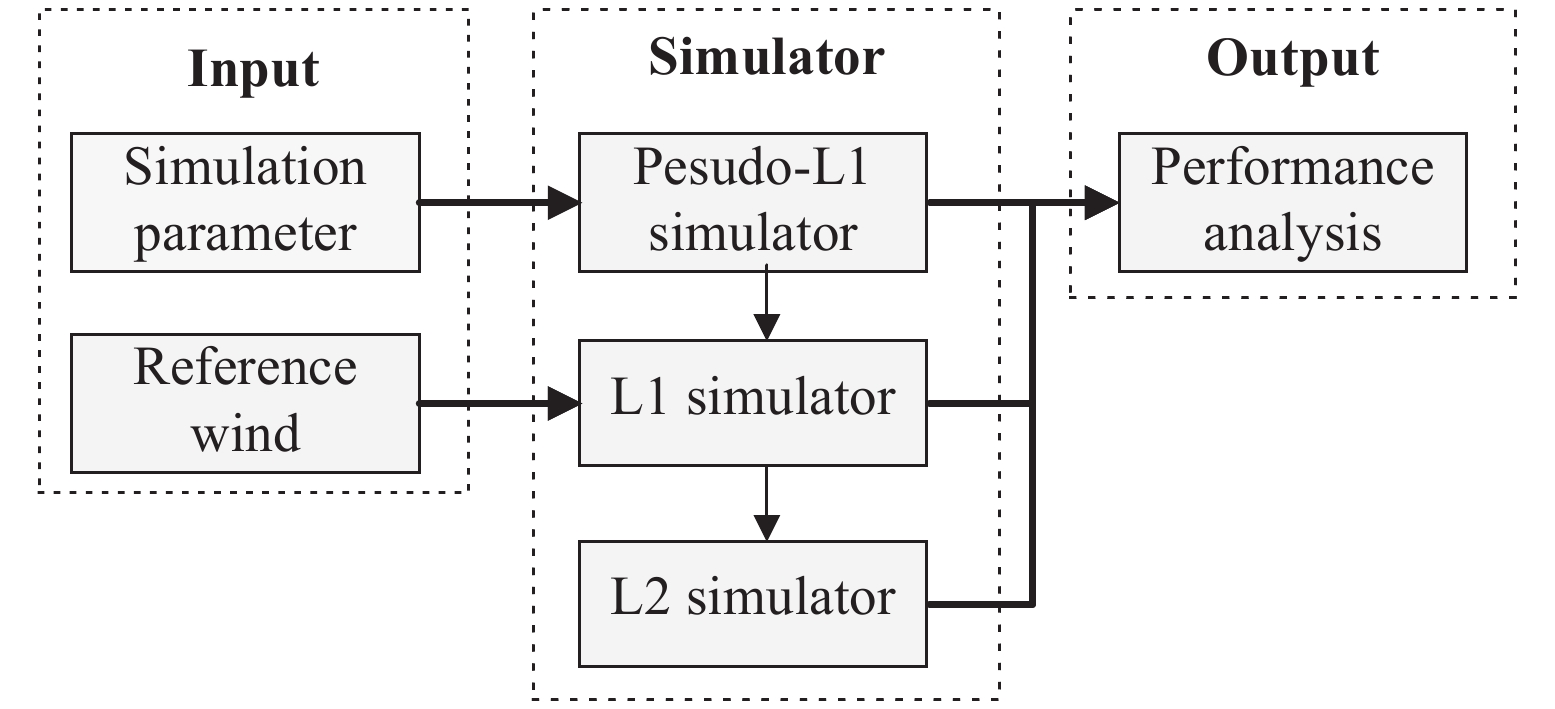
摘要: 高风速风场, 特别是热带气旋风场的散射计观测长期备受关注. 本研究针对我国业务化运行的两种散射计——旋转扇形波束体制散射计和旋转笔形波束体制散射计, 通过系统仿真方法分析其在不同风速条件下的后向散射系数测量精度和风场反演性能, 并评估其对热带气旋的观测能力. 参考现有在轨运行散射计参数得到的实验结果表明, 旋转扇形波束体制散射计各观测视数能够取得更多独立观测样本数, 在20 m·s–1以上高风速风场的后向散射系数测量和风场反演仿真中性能表现更佳. 而旋转笔形波束体制散射计各观测视数拥有更大的归一化信噪比, 在低于20 m·s–1的低风速和中等风速风场观测仿真中性能表现更佳. 研究揭示了两种散射计体制在不同风速区间的性能特点, 对高风速风场反演及热带气旋观测有重要参考意义, 同时, 结论也为后续不同体制散射计设计和信号处理算法改进研究奠定了基础.Abstract: The observation of high speed wind fields, especially tropical cyclone wind fields, has long been an important research subject in scatterometer remote sensing. In this study, we analyzed the backscattering coefficient measurement accuracies and wind retrieval performances of the two scatterometer systems that have been operational in China: the rotating fan-beam system and the rotating pencil-beam system by simulation methods. Simulations at varying wind speed wind fields and tropical cyclone wind fields observations are conducted for both systems. Simulation results obtained with reference to the parameters of existing operational scatterometers show that the rotating fan-beam system demonstrates superior sampling capacity compared to the rotating pencil-beam system, with the vast majority of its observation views gaining a greater number of independent observation samples than 1000, whereas the rotating pencil-beam system has mainly 100~400 independent observation samples for each observation view only. This sampling advantage enables the rotating fan-beam system to achieve better performance in backscattering coefficient measurement and wind field retrieval in the simulations for wind fields with high wind speeds above 20 m·s–1. At the same time, the normalized SNR of each observation view is higher for the rotating pencil-beam system, which is about 300~600 per observation view, compared to 6~14 for the rotating fan-beam system. This SNR superiority enables the rotating pencil-beam system to maintain a more precise observation for wind fields with low and medium wind speeds below 20 m·s–1 in the simulation. This study reveals the performance characteristics of backscattering coefficient measurement and wind field retrieval of different scatterometer systems under various wind speed conditions, which is of reference significance for high speed wind fields retrieval and tropical cyclone wind fields observation. Meanwhile, the conclusions of this study also lay a foundation for subsequent research on the improvement of scatterometer wind field observation accuracy and optimization of signal processing algorithms for different scatterometer systems.
-
表 1 散射计系统参数
Table 1. Scatterometer system parameters
参数 旋转扇形波束体制 旋转笔形波束体制 脉冲载频/GHz 13.256 13.256 脉冲时宽/ms 1.3 1.5 脉冲重复频率/Hz 150 185 接收带宽/MHz 0.5 1.0 发射功率/W 120 120 天线峰值增益/dB 32 39 天线转速/(r·min–1) 3.4 16.7 系统损耗/dB 1.0 1.0 噪声系数/dB 6.0 5.0 VV极化波束
观测俯仰角/(º)25~44 41 HH极化波束
观测俯仰角/(º)25~44 35 轨道高度/km 520 970 表 2 独立观测样本数和归一化信噪比统计特性
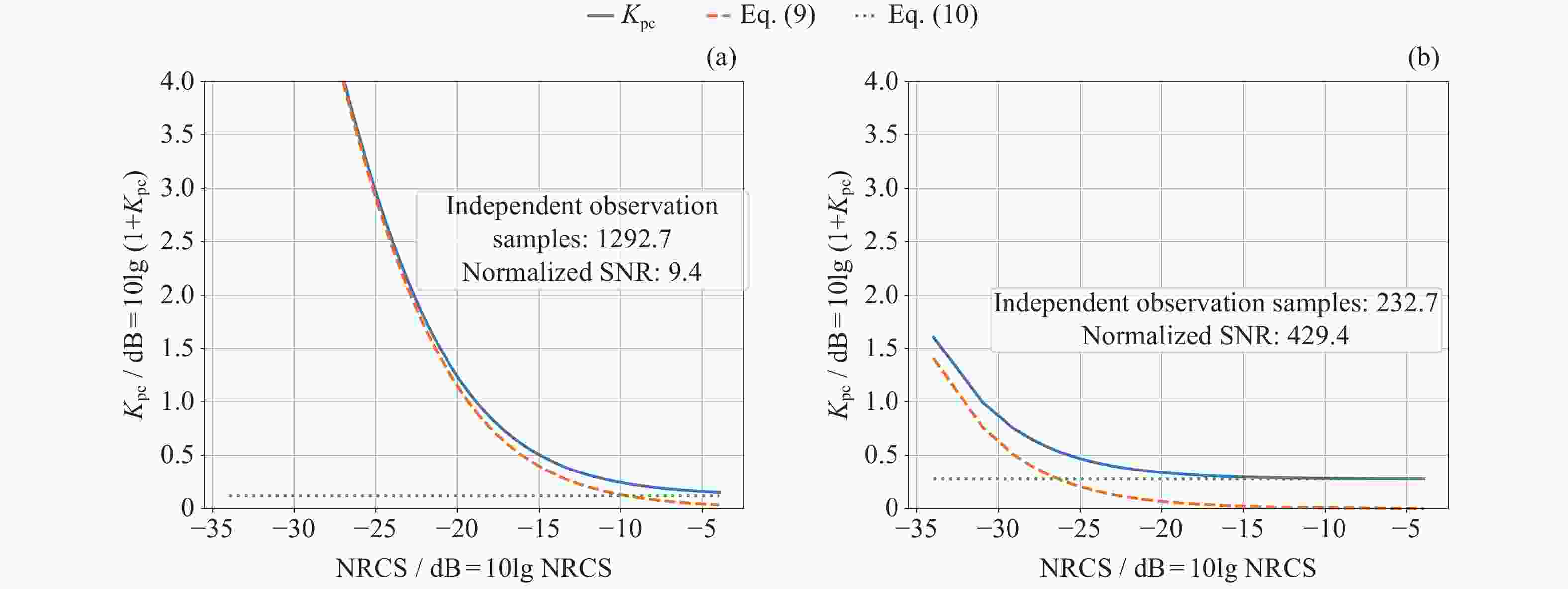
Table 2. Independent observation samples ($ {N}_{{\mathrm{sample}}} $) and normalized SNR ($ R_{\mathbf{S}\mathbf{N}\mathbf{R}'} $) statistics
散射计体制 $ {\mathit{N}}_{\mathbf{s}\mathbf{a}\mathbf{m}\mathbf{p}\mathbf{l}\mathbf{e}} $均值 $ {\mathit{N}}_{\mathbf{s}\mathbf{a}\mathbf{m}\mathbf{p}\mathbf{l}\mathbf{e}} $标准差 $ R_{\mathbf{S}\mathbf{N}\mathbf{R}'} $均值 $ R_{\mathbf{S}\mathbf{N}\mathbf{R}'} $标准差 旋转扇形波束体制 1292.7 401.2 9.4 2.9 旋转笔形波束体制 232.7 110.6 429.4 121.1 表 3 不同散射计体制下第K风场解被选为最优解的占比统计
Table 3. Percentage distribution of the K-th ranked wind solution selected as optimal under different scatterometer systems
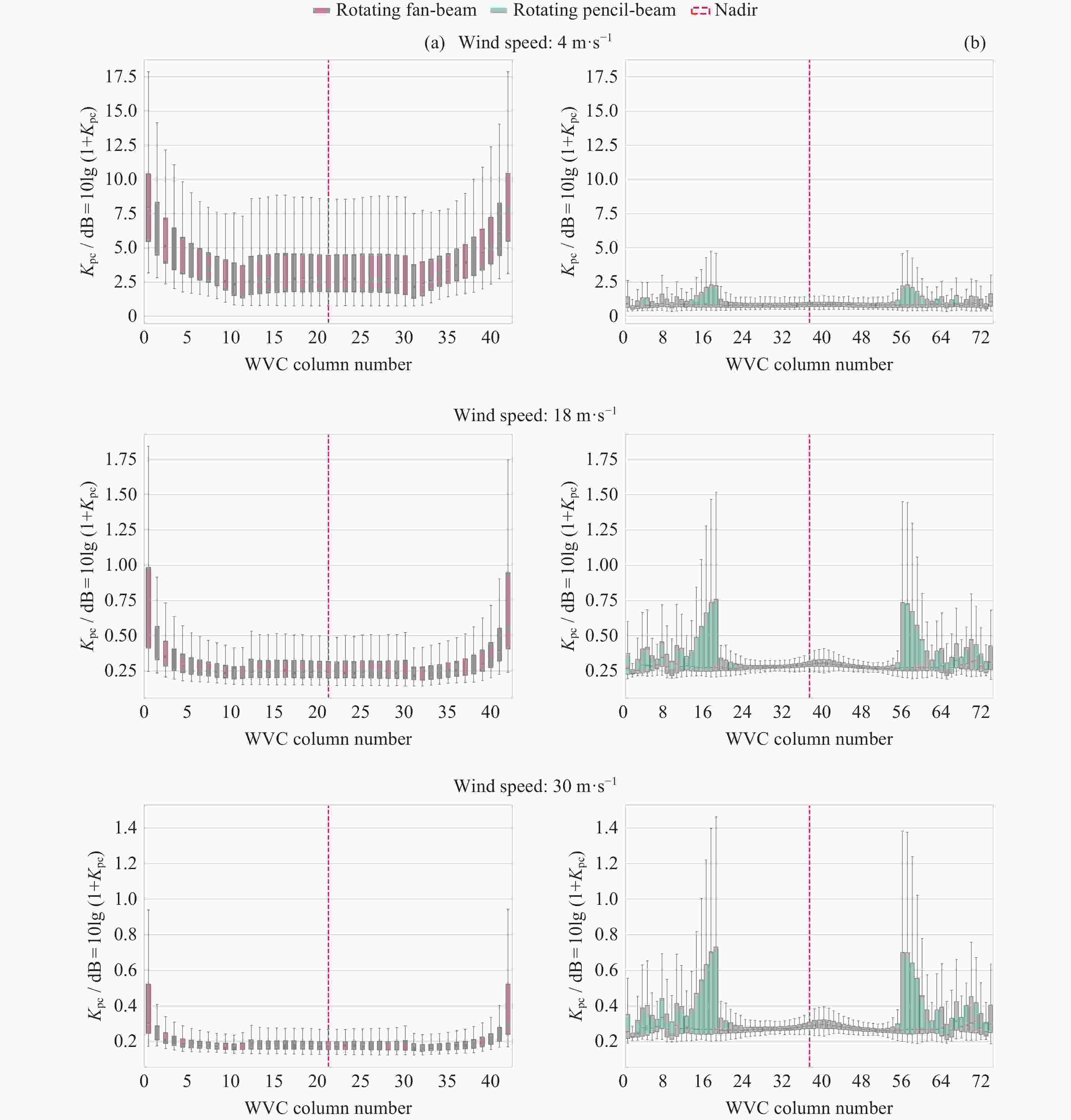
散射计体制 K 4 m·s–1 18 m·s–1 30 m·s–1 旋转扇形波束体制 1 47.8 89.9 92.3 2 31.2 9.2 6.3 3 16.4 0.6 0.9 4 4.4 0.1 0.3 旋转笔形波束体制 1 60.5 62.5 52.0 2 25.9 28.3 31.0 3 10.1 6.2 11.3 4 3.4 2.9 5.5 注 最优解为最接近真实风场的解. -
[1] HAUSER D, ABDALLA S, ARDHUIN F, et al. Satellite remote sensing of surface winds, waves, and currents: where are we now?[J]. Surveys in Geophysics, 2023, 44(5): 1357-1446 doi: 10.1007/s10712-023-09771-2 [2] BOURASSA M A, MEISSNER T, CEROVECKI I, et al. Remotely sensed winds and wind stresses for marine forecasting and ocean modeling[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2019, 6: 443 doi: 10.3389/fmars.2019.00443 [3] 郎姝燕, 孙从容, 鲁云飞, 等. 中法海洋卫星微波散射计近海岸产品在台风遥感监测中的应用[J]. 海洋气象学报, 2022, 42(2): 74-80LANG Shuyan, SUN Congrong, LU Yunfei, et al. Application of Chinese-French oceanography satellite scatterometer coastal product in typhoon remote sensing monitoring[J]. Journal of Marine Meteorology, 2022, 42(2): 74-80 [4] IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change[M]. Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA: Cambridge University Press, 2021 [5] SPENCER M W, WU C, LONG D G. Tradeoffs in the design of a spaceborne scanning pencil beam scatterometer: application to SeaWinds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1997, 35(1): 115-126 doi: 10.1109/36.551940 [6] ANDERSON C, BONEKAMP H, DUFF C, et al. Analysis of ASCAT ocean backscatter measurement noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(7): 2449-2457 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2190739 [7] LIN W M, DONG X L, PORTABELLA M, et al. A Perspective on the Performance of the CFOSAT rotating Fan-beam scatterometer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(2): 627-639 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2858852 [8] SHANG J, WANG Z X, DOU F L, et al. Preliminary performance of the WindRAD scatterometer onboard the FY-3E meteorological satellite[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5100813 [9] 宋忠国, 董晓龙, 林文明, 等. 星载全极化微波散射计系统仿真与性能分析[J]. 电子学报, 2013, 41(12): 2382-2390 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2013.12.010SONG Zhongguo, DONG Xiaolong, LIN Wenming, et al. Spaceborne polarimetric microwave scatterometer system simulation and performance analysis[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2013, 41(12): 2382-2390 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2013.12.010 [10] 杨晟, 邹巨洪, 林明森. 星载全极化微波散射计仿真与海面风场反演研究[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2018, 37(2): 179-184 doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2018.02.004YANG Sheng, ZOU Juhong, LIN Mingsen. Spaceborne fully polarized microwave scatterometer simulation and ocean surface wind retrieval[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2018, 37(2): 179-184 doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2018.02.004 [11] BAO Q L, DONG X L, ZHU D, et al. The feasibility of ocean surface current measurement using pencil-beam rotating scatterometer[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(7): 3441-3451 doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2414451 [12] POLVERARI F, PORTABELLA M, LIN W M, et al. On high and extreme wind calibration using ASCAT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 4202210 [13] XU X G, STOFFELEN A, NI W C, et al. Extreme winds from Ku-band and C-band wind scatterometers[C]//IGARSS 2023-2023 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Pasadena: IEEE, 2023: 4064-4067 [14] C3S. ERA5 hourly data on single levels from 1940 to present[DS/OL]. Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) Climate Data Store (CDS). 2018[2024–11-10]. https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/doi/10.24381/cds.adbb2d47 [15] ZHANG Y, LIN M S, XIE X T, et al. The improvement of HY-2 Satellite’s microwave scatterometer instrument and NRCS calculation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5112109 [16] 于淼淼, 朱迪, 董晓龙, 等. 中法海洋卫星微波散射计后向散射测量误差分析[J]. 海洋气象学报, 2024, 44(4): 46-53YU Miaomiao, ZHU Di, DONG Xiaolong, et al. Analysis of backscattering measurement error of CSCAT[J]. Journal of Marine Meteorology, 2024, 44(4): 46-53 [17] 林文明. 星载扇形波束扫描微波散射计系统研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院研究生院, 2011LIN Wenming. Study on Spaceborne Rotating, Range-Gated, Fanbeam Scatterometer System[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2011 [18] 林明森, 邹巨洪, 解学通, 等. HY-2A微波散射计风场反演算法[J]. 中国工程科学, 2013, 15(7): 68-74 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2013.07.010LIN Mingsen, ZOU Juhong, XIE Xuetong, et al. HY-2A microwave scatterometer wind retrieval algorithm[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2013, 15(7): 68-74 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2013.07.010 [19] 董楹, 林文明. CFOSAT散射计海面后向散射系数误差及影响[J]. 空间科学学报, 2024, 44(2): 326-334 doi: 10.11728/cjss2024.02.2023-0144DONG Ying, LIN Wenming. analysis of sea surface backscatter coefficient errors and its effects for the CFOSAT scatterometer[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2024, 44(2): 326-334 doi: 10.11728/cjss2024.02.2023-0144 [20] LIN C C, STOFFELEN A, DE KLOE J, et al. Wind retrieval capability of rotating range-gated fanbeam spaceborne scatterometer[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 4881, Sensors, Systems, and Next-Generation Satellites VI. Crete, Greece: SPIE, 2003: 268 [21] 郎姝燕. 星载微波散射计系统仿真、性能评估与优化[D]. 中国科学院研究生院, 2008LANG Shuyan. Simulation and Optimization of Spaceborne Microwave Scatterometer[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2008 [22] 董晓龙, 朱迪, 林文明, 等. 中法海洋卫星微波散射计在轨性能验证[J]. 空间科学学报, 2020, 40(3): 425-431 doi: 10.11728/cjss2020.03.425DONG Xiaolong, ZHU Di, LIN Wenming, et al. Orbit performances validation for CFOSAT scatterometer[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2020, 40(3): 425-431 doi: 10.11728/cjss2020.03.425 [23] ZHANG Y, MU B, LIN M S, et al. An evaluation of the Chinese HY-2B Satellite’s microwave scatterometer instrument[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(6): 4513-4521 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3008405 -
-




 董字名 男, 2002年生于河北省廊坊市, 现为中国科学院国家空间科学中心硕士研究生. 主要研究方向为星载微波散射计系统仿真. E-mail:
董字名 男, 2002年生于河北省廊坊市, 现为中国科学院国家空间科学中心硕士研究生. 主要研究方向为星载微波散射计系统仿真. E-mail: 

 下载:
下载: