A Two-layer Hybrid Scheduling Approach for Electromagnetic Spectrum Monitoring Satellite Mission Planning
-
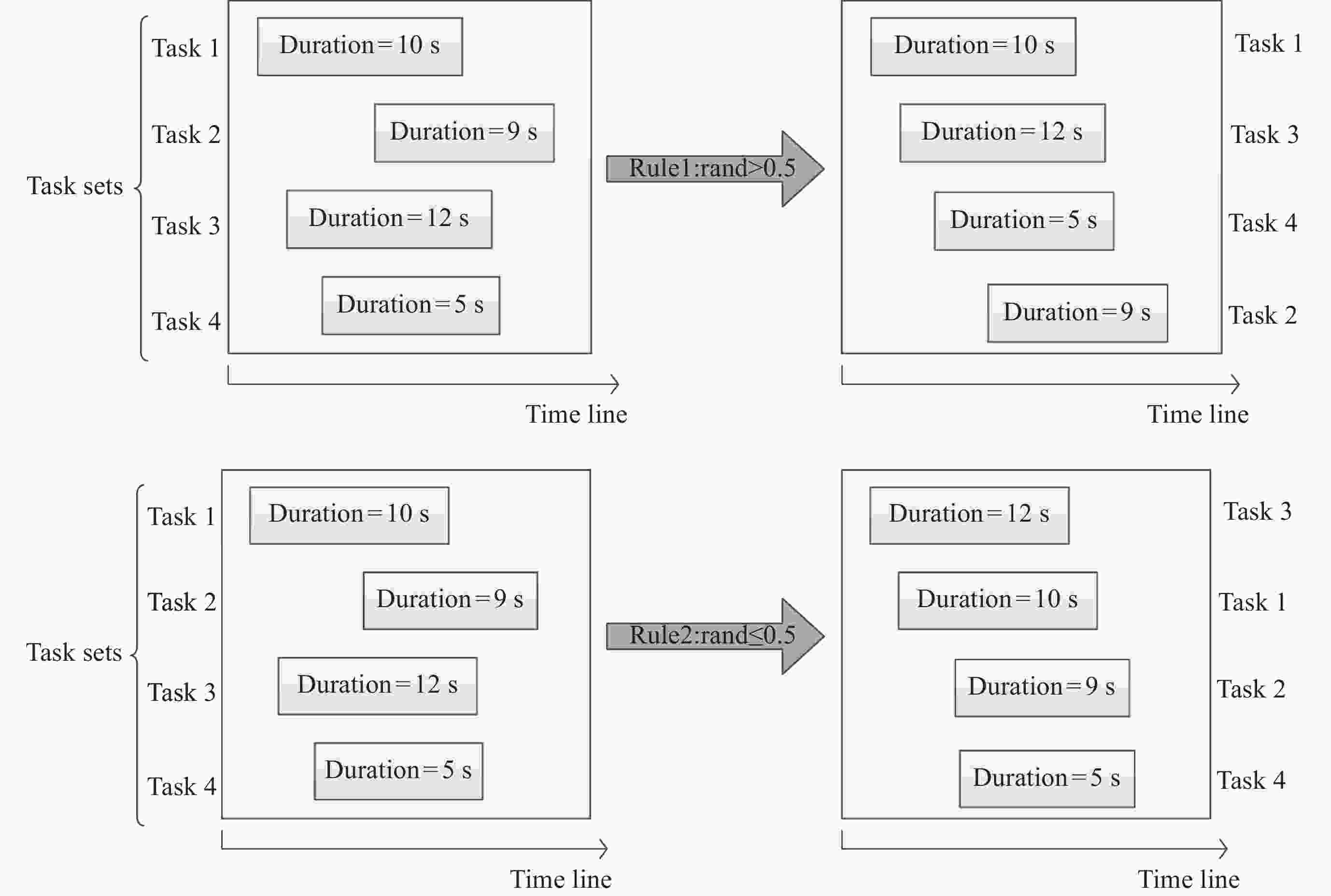
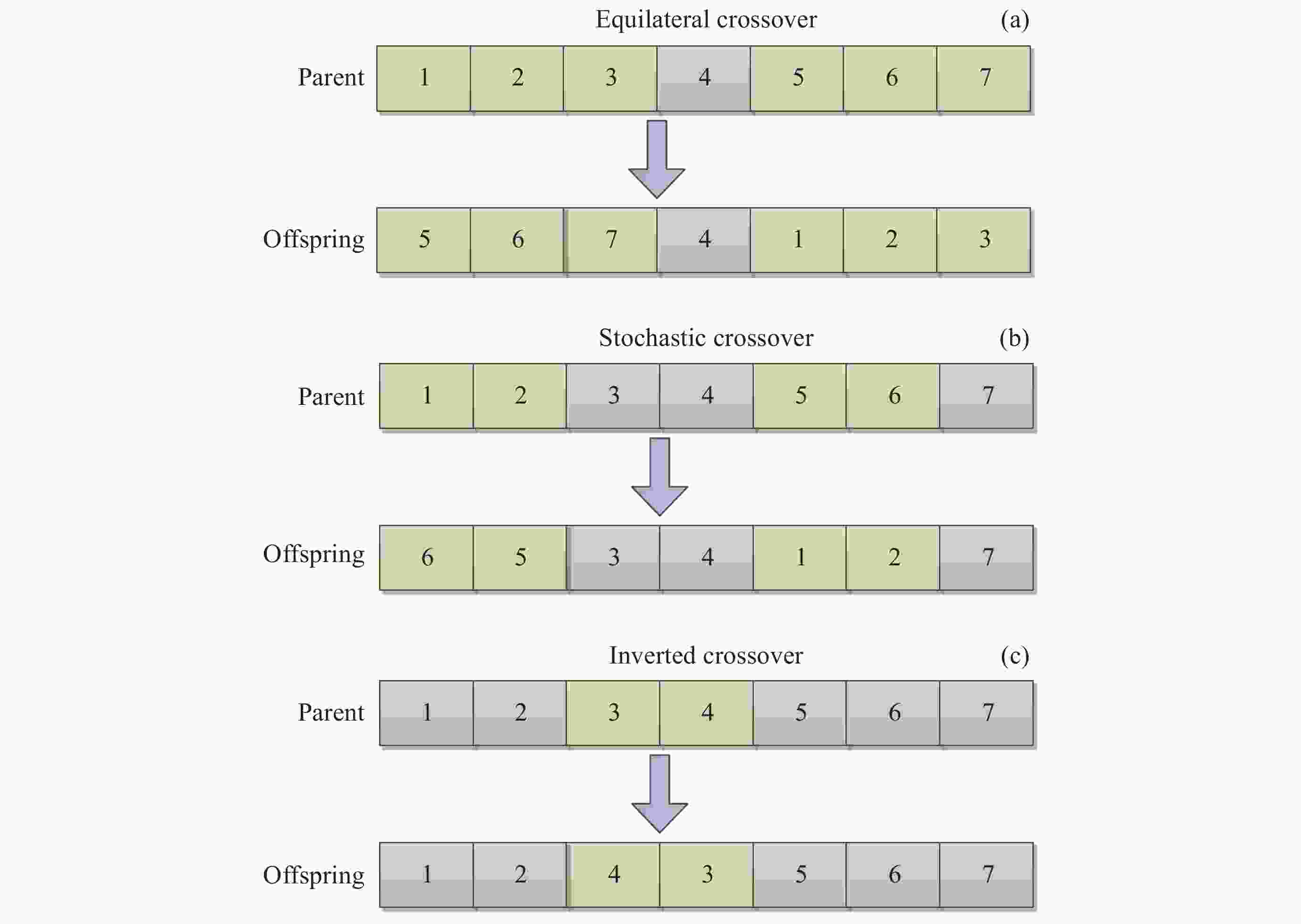
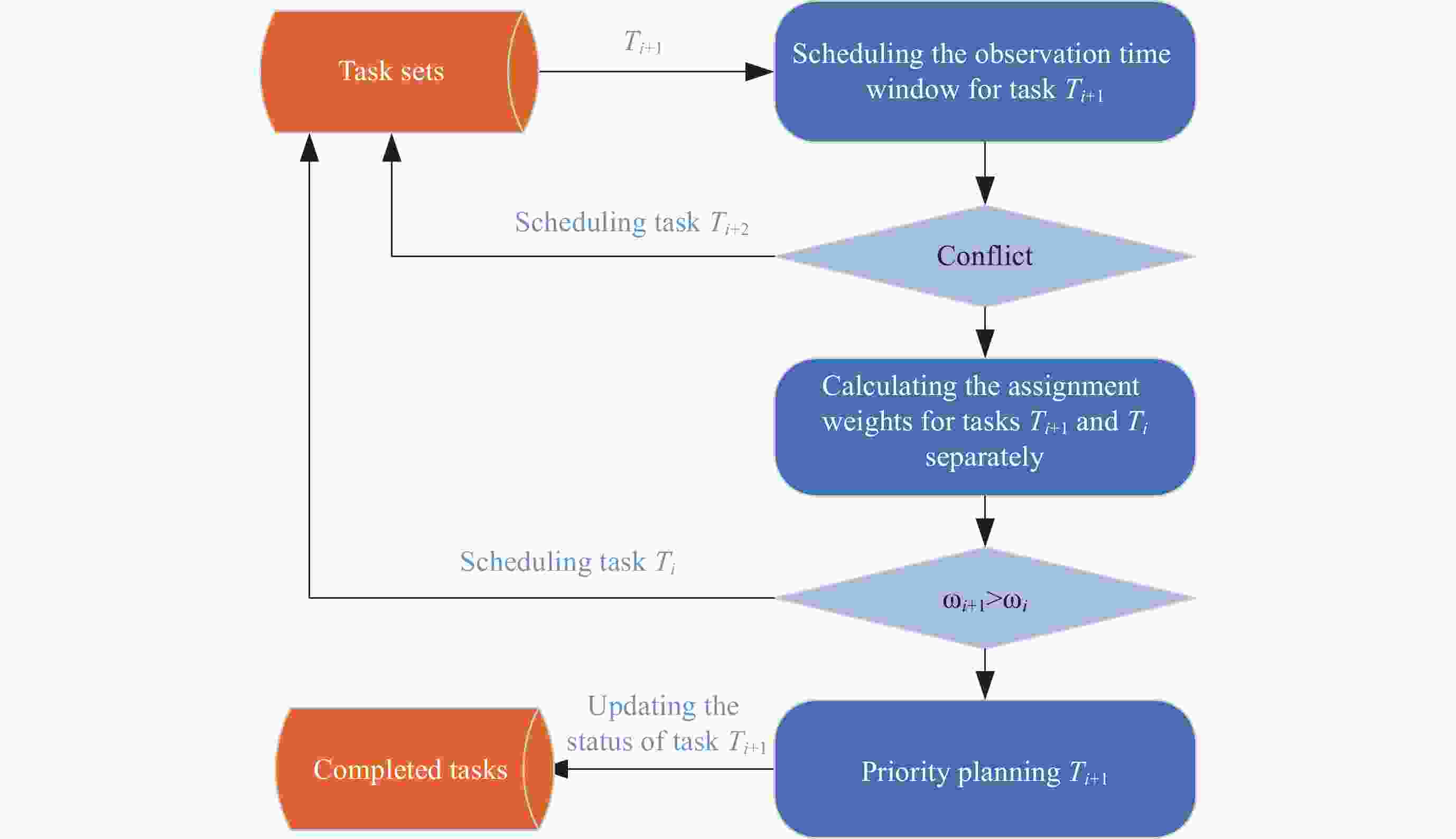
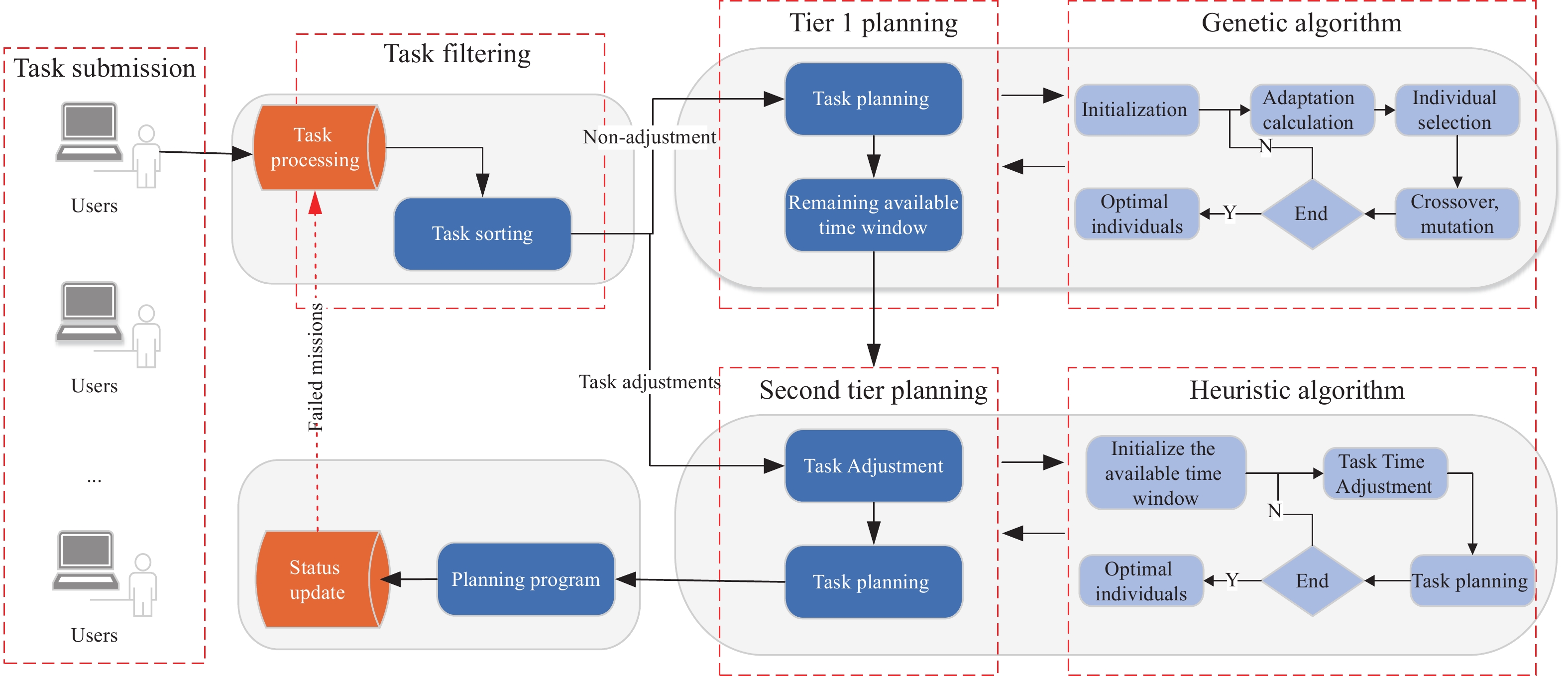
摘要: 近年来, 卫星呈规模化发展且迅速壮大, 对地探测需求随之增长, 面向电磁频谱监测卫星(Electromagnetic Spectrum Monitoring Satellite, ESMS)任务的精细化管控要求越来越高. 卫星任务规划时不考虑动态调整将导致大量时间资源浪费, 因此对任务进行动态调整并分配合适的卫星资源是有效执行监测任务的重要保证. 本文首先构建考虑任务动态调整的任务规划模型, 然后面向任务可调整性设计一种双层混合规划方法(Two-layer Hybrid Scheduling Approach, TH-SA). 该方法第一层采用遗传算法处理不可动态调整的任务序列, 第二层基于启发式规则对可动态调整的任务进行规划. 基于规则的初始化策略和多样化的交叉模式可保证遗传算法的探索和开发效率, 而启发式算法(Heuristic Algorithm, HA)则通过任务调整和资源分配实现可动态调整任务的优化调度. 通过对任务分类处理, 在保证不可动态调整任务完成率的同时, 提升算法对可动态调整任务的规划效率. 仿真实验验证了算法在不同规模任务规划中能保持较高的收益, 有效提升电磁频谱监测卫星资源的应用效益.Abstract: In recent years, there has been a significant and rapid expansion in the satellite field, with a corresponding increase in the demand for Earth observation. This led to a growing need for sophisticated management of Electromagnetic Spectrum Monitoring Satellite (ESMS) missions. Neglecting to incorporate dynamic adjustments in satellite mission planning will lead to a considerable loss of time and resources. Dynamic adjustments to missions and allocation of appropriate satellite resources are crucial for the effective execution of monitoring tasks. This paper begins by developing a mission planning model that incorporates dynamic adjustments. Subsequently, we introduce a Two-Layer Hybrid Scheduling Approach (TH-SA) designed for task flexibilty. The approach uses a genetic algorithm in the first layer to deal with non-dynamically adjustable task sequences. The second layer relies on heuristic rules to plan dynamically adjustable tasks. A rule-based initialization strategy and diverse crossover patterns enhance the exploration and exploitation efficiency of the genetic algorithm, while the heuristic algorithm optimizes the scheduling of dynamically adjustable tasks through task reconfiguration and resource allocation. By categorizing and processing tasks, the algorithm enhances the efficiency of planning for dynamically adjustable tasks and ensures the completion rate of those that are not dynamically adjustable. Finally, simulation experiments confirm that the algorithm maintains high performance in task planning of varying scales, demonstrating its effectiveness in improving the performance of Electromagnetic Spectrum Monitoring Satellite task planning.
-
表 1 卫星轨道参数
Table 1. Satellite orbital parameters
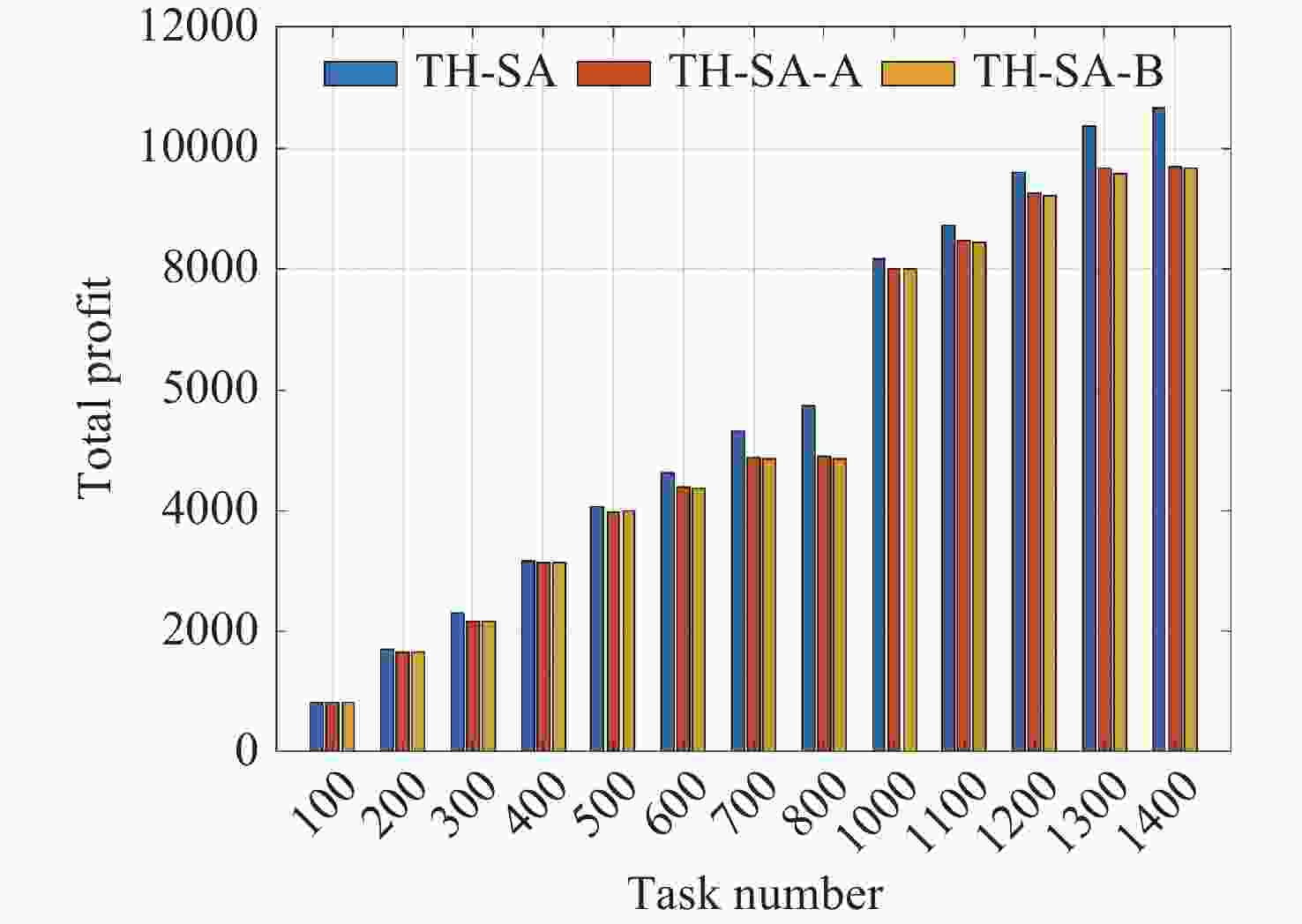
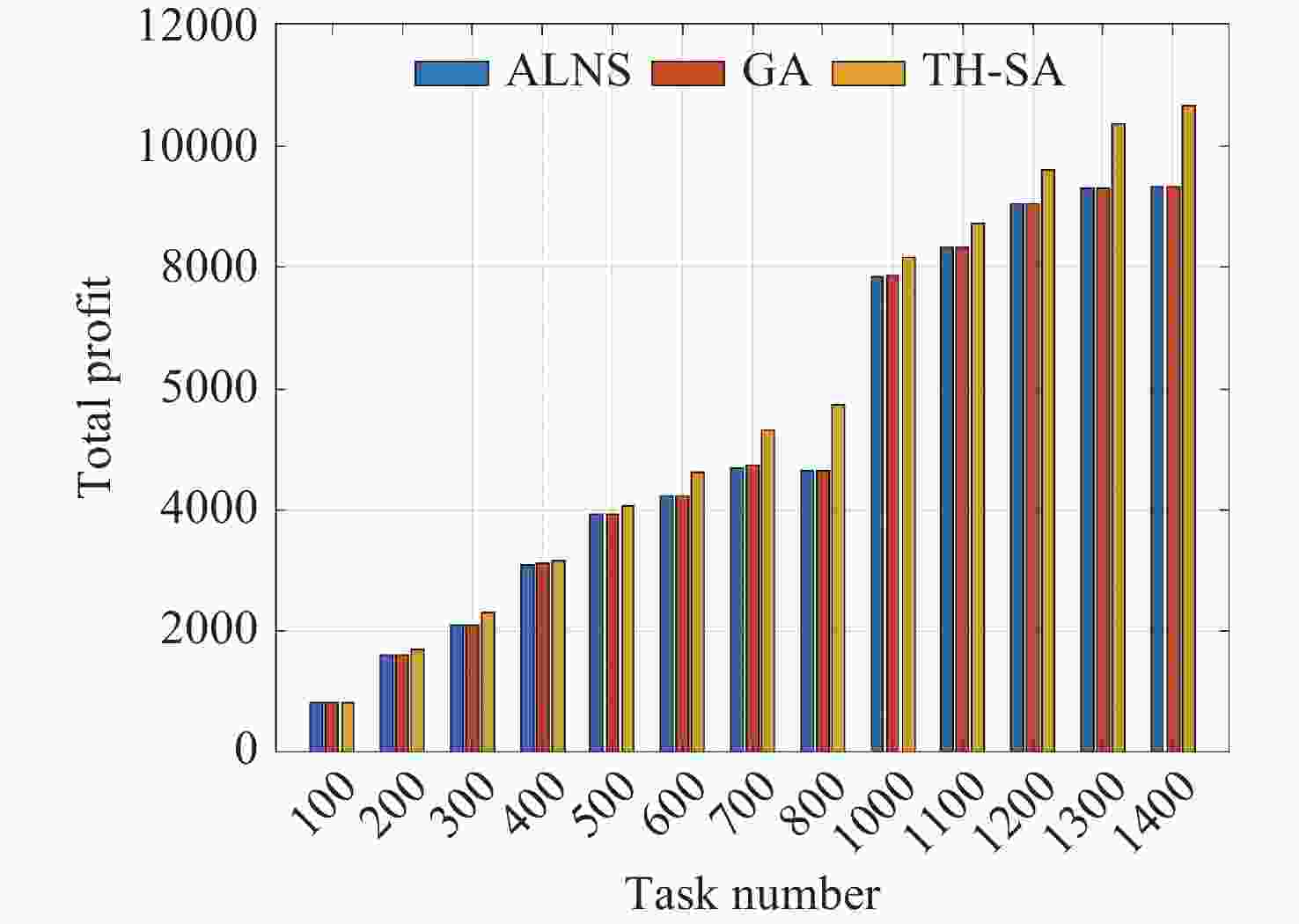
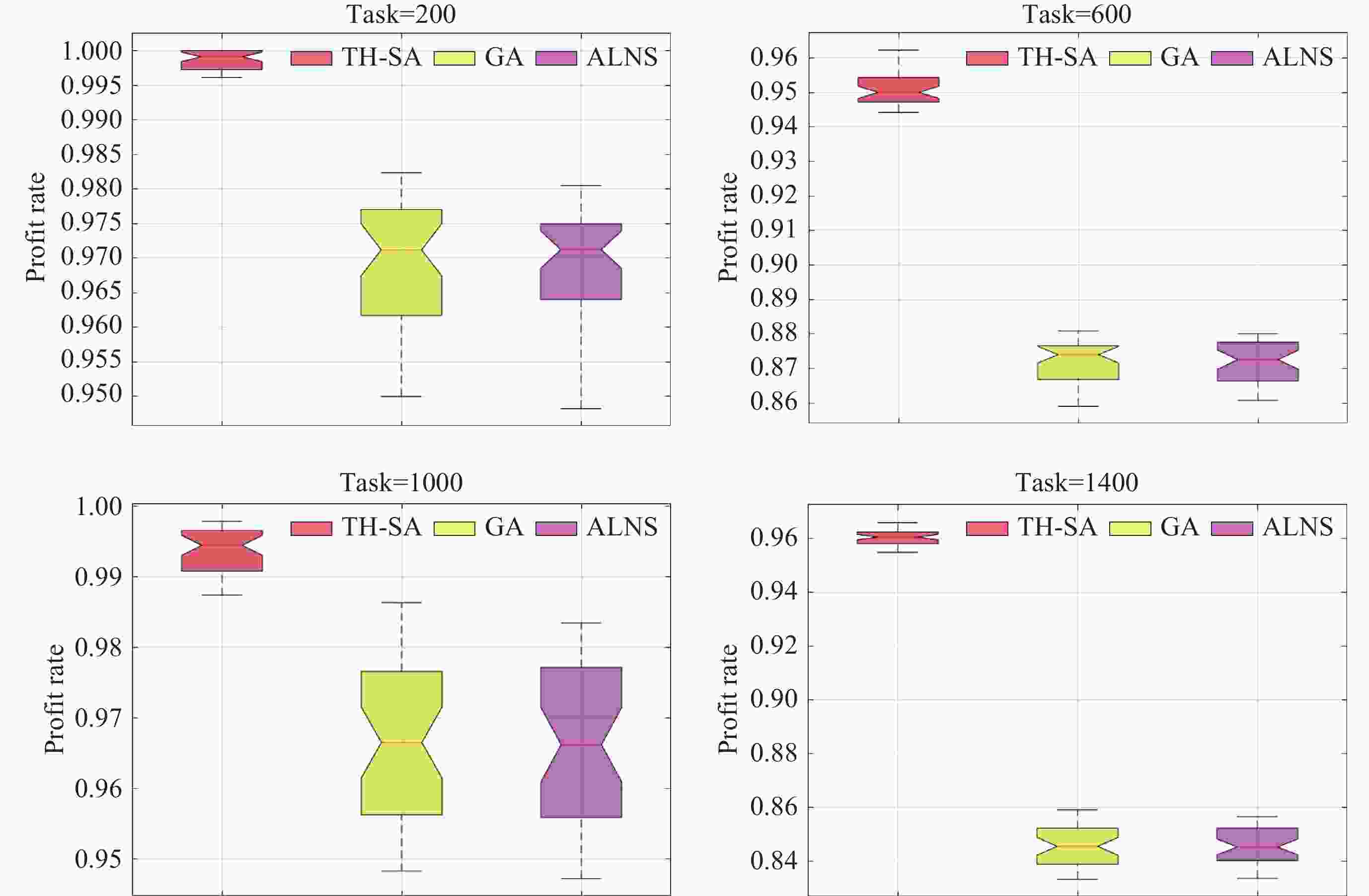
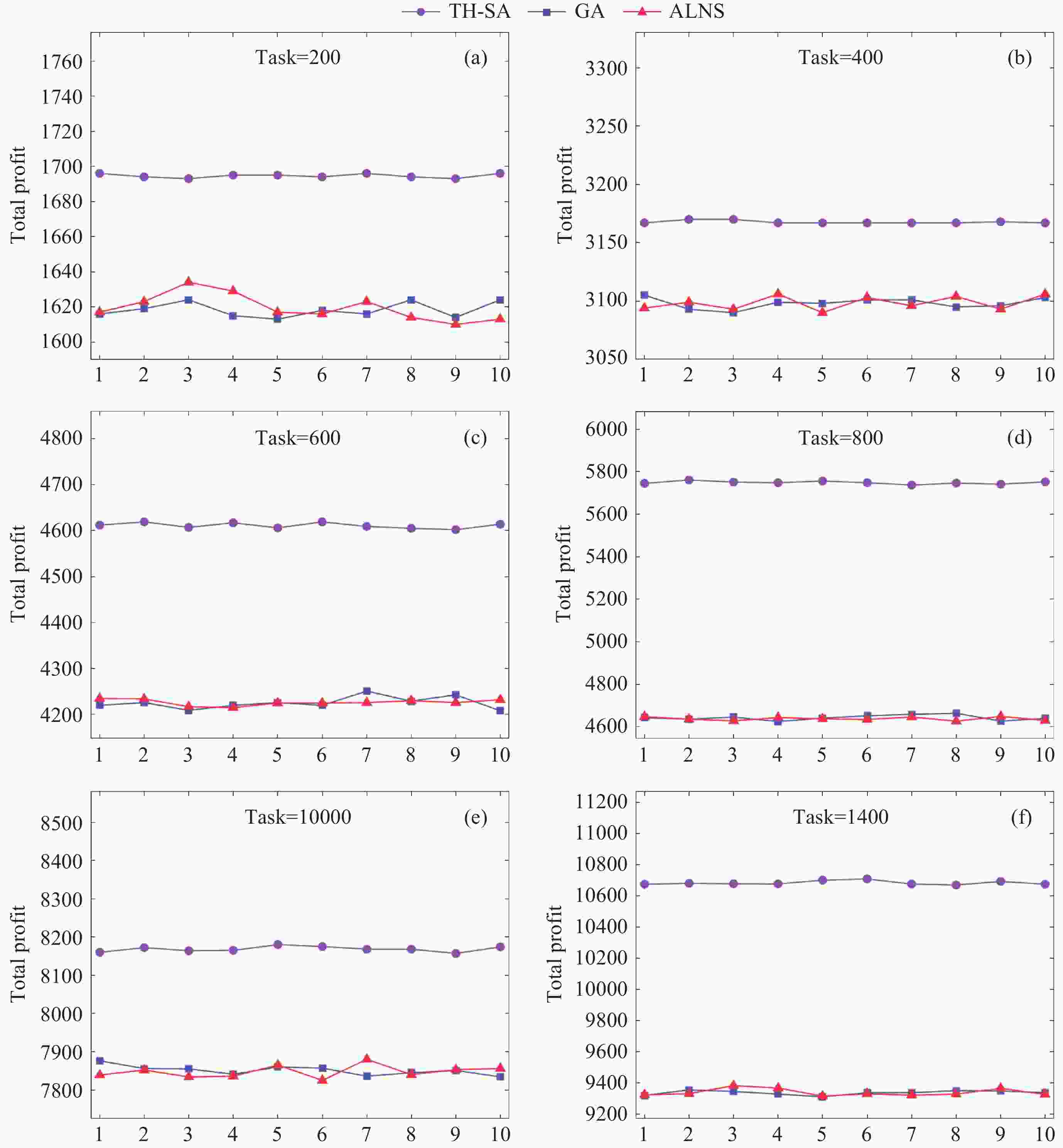
参数名称 数值 a/km 1150 e 0.00016 i 100.082 Ω/(º) 0 ω/(º) 21.25 М/(º) 149.94 表 2 GA, ALNS, HA, TH-SA算法不同规模任务集的实验结果对比
Table 2. Comparison of GA, ALNS, HA and TH-SA algorithms for different task scale
任务集 TH-SA GA ALNS HA fmax fmean Std.Dev fmax fmean Std.Dev fmax fmean Std.Dev 100 829 829.0 0 823 820.1 1.552 823 818.9 2.591 790 200 1693 1687.8 2.8537 1617 1605.9 5.789 1611 1602.9 5.162 1513 300 2307 2295.9 5.3133 2095 2073.7 11.63 2088 2069 9.915 1869 400 3167 3161.4 2.6193 3105 3082.7 8.391 3094 3080.3 8.651 2906 500 4071 4056.6 5.7151 3917 3891.9 13.213 3914 3892.9 11.596 3651 600 4621 4589.7 10.626 4235 4199.8 20.551 4217 4182.9 13.673 3758 700 5289 5273.7 9.795 4703 4649.3 21.93 4687 4644.4 24.408 4133 800 5765 5717.9 17.969 4702 4585.8 30.647 4659 4583 26.989 3815 1000 8169 8146.9 9.2912 7876 7806.1 25.16 7839 7804.2 20.745 7431 1100 8717 8697.3 9.3548 8318 8282.8 18.655 8323 8277.8 23.564 7970 1200 9589 9566.7 9.7921 9021 8978.7 22.778 8997 8973.4 15.776 8468 1300 10357 10322.0 16.92 9318 9256.3 30.679 9334 9254.5 29.066 8439 1400 10687 10640.0 21.715 9365 9253.6 39.265 9322 9252.6 37.973 8456 表 3 不同任务规模下算法运行时间(单位: s)
Table 3. Mean CPU service time for different task scales (Unit: s)
任务集 TH-SA GA ALNS 100 0.1786 0.1715 0.2314 200 0.2907 0.3447 0.4039 300 0.4648 0.4979 0.5386 400 0.7495 0.7929 0.8682 500 0.8572 1.0234 1.0881 600 1.0799 1.3051 1.3983 700 1.2866 1.614 1.7194 800 1.5199 1.8827 1.9788 1000 2.0191 2.8366 2.9503 1100 2.2655 3.2001 3.2477 1200 2.5913 3.5522 3.6606 1300 2.8031 3.8833 3.9863 1400 3.1638 4.6034 4.9579 -
[1] 邱涤珊, 王慧林, 祝江汉, 等. 面向区域普查的电子侦察卫星任务调度[J]. 小型微型计算机系统, 2011, 32(2): 379-384QIU Dishan, WANG Huilin, ZHU Jianghan, et al. Area census-oriented electronic reconnaissance satellites scheduling technique[J]. Journal of Chinese Computer Systems, 2011, 32(2): 379-384 [2] 李耀东, 张静, 江建军. 多区域多维覆盖联合优化卫星任务规划[J]. 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报, 2019, 17(1): 40-45 doi: 10.11805/TKYDA201901.0040LI Yaodong, ZHANG Jing, JIANG Jianjun. Mission scheduling of electronic reconnaissance satellites based on multi-area[J]. Journal of Terahertz Science and Electronic Information Technology, 2019, 17(1): 40-45 doi: 10.11805/TKYDA201901.0040 [3] 杜永浩, 邢立宁, 姚锋, 等. 航天器任务调度模型、算法与通用求解技术综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(12): 2715-2741DU Yonghao, XING Lining, YAO Feng, et al. Survey on models, algorithms and general techniques for spacecraft mission scheduling[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(12): 2715-2741 [4] 李长春, 祝江汉. 面向移动目标连续侦察的电子侦察卫星任务规划方法研究[J]. 装备指挥技术学院学报, 2011, 22(1): 67-72LI Changchun, ZHU Jianghan. Research on the method of electronic reconnaissance satellites mission planning for continuous reconnaissance of moving target[J]. Journal of the Academy of Equipment Command :Times New Roman;">& Technology, 2011, 22(1): 67-72 [5] SONG Y J, WEI L N, YANG Q, et al. RL-GA: a reinforcement learning-based genetic algorithm for electromagnetic detection satellite scheduling problem[J]. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2023, 77: 101236 doi: 10.1016/j.swevo.2023.101236 [6] TSENG L Y, CHEN S C. Two-phase genetic local search algorithm for the multimode resource-constrained project scheduling problem[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2009, 13(4): 848-857 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2008.2011991 [7] 刘士新, 宋健海, 唐加福. 蚁群最优化——模型、算法及应用综述[J]. 系统工程学报, 2004, 19(5): 496-502 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5781.2004.05.010LIU Shixin, SONG Jianhai, TANG Jiafu. Ant colony optimization review: modelling, algorithms and applications[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering, 2004, 19(5): 496-502 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5781.2004.05.010 [8] JIANG X M, SONG Y J, XING L N. Dual-population artificial bee colony algorithm for joint observation satellite mission planning problem[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 28911-28921. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3157286 [9] CHEN H K, TIAN Y, PEDRYCZ W, et al. Hyperplane assisted evolutionary algorithm for many-objective optimization problems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(7): 3367-3380 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2019.2899225 [10] 李夏苗, 陈新江, 伍国华, 等. 考虑断点续传的中继卫星调度模型及启发式算法[J]. 航空学报, 2019, 40(11): 269-284LI Xiamiao, CHEN Xinjiang, WU Guohua, el al. Scheduling model and heuristic algorithm for tracking and data relay satellite considering breakpoint transmission[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2019, 40(11): 269-284 [11] CHEN X J, LI X M, WANG X W, et al. Task scheduling method for data relay satellite network considering breakpoint transmission[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(1): 844-857 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3046304 [12] HE Y M, WU G H, CHEN Y W, et al. A two-stage framework and reinforcement learning-based optimization algorithms for complex scheduling problems[OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2103.05847, 2021 [13] 李阳阳, 罗俊仁, 张万鹏, 等. 多星协同观测遗传-演进双层任务规划算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2024, 46(6): 2044-2053LI Yangyang, LUO Junren, ZHANG Wanpeng, et al. Genetic-evolutionary bi-level mission planning algorithm for multi-satellite cooperative observation[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(6): 2044-2053 [14] 刘润滋, 马天赐, 吴伟华, 等. 基于分层强化学习的中继卫星网络任务动态调度方法[J]. 通信学报, 2023, 44(7): 207-217 doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2023130LIU Runzi, MA Tianci, WU Weihua, et al. Dynamic task scheduling method for relay satellite networks based on hierarchical reinforcement learning[J]. Journal on Communications, 2023, 44(7): 207-217 doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2023130 [15] WANG Y, LIU D S, LIU J T. A bilevel programming model for multi-satellite cooperative observation mission planning[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12: 145439-145449. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3465633 [16] MICHALEWICZ Z, SCHOENAUER M. Evolutionary algorithms for constrained parameter optimization problems[J]. Evolutionary Computation, 1996, 4(1): 1-32 doi: 10.1162/evco.1996.4.1.1 [17] CÁMARA M, ORTEGA J, DE TORO F. A single front genetic algorithm for parallel multi-objective optimization in dynamic environments[J]. Neurocomputing, 2009, 72(16/17/18): 3570-3579 [18] MUKHOPADHYAY A, MAULIK U, BANDYOPADHYAY S. Multiobjective genetic algorithm-based fuzzy clustering of categorical attributes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2009, 13(5): 991-1005 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2009.2012163 [19] BARBULESCU L, WATSON J P, WHITLEY L D, et al. Scheduling space-ground communications for the air force satellite control network[J]. Journal of Scheduling, 2004, 7(1): 7-34 doi: 10.1023/B:JOSH.0000013053.32600.3c [20] KIM K, JEONG I J. Flow shop scheduling with no-wait flexible lot streaming using an adaptive genetic algorithm[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2009, 44(11/12): 1181-1190 -
-




 周晓光 男, 1981年出生于云南省昭通市, 博士, 现为西南电子电信技术研究所高级工程师, 主要研究方向为信号处理、卫星载荷应用管理、卫星地面系统设计.E-mail:
周晓光 男, 1981年出生于云南省昭通市, 博士, 现为西南电子电信技术研究所高级工程师, 主要研究方向为信号处理、卫星载荷应用管理、卫星地面系统设计.E-mail:  孙正波 男, 1975年出生于山东省青岛市, 博士, 现为西南电子电信技术研究所正高级工程师、重点实验室主任、博士生导师, 主要研究方向为卫星系统设计应用、信号处理与定位技术.E-mail:
孙正波 男, 1975年出生于山东省青岛市, 博士, 现为西南电子电信技术研究所正高级工程师、重点实验室主任、博士生导师, 主要研究方向为卫星系统设计应用、信号处理与定位技术.E-mail: 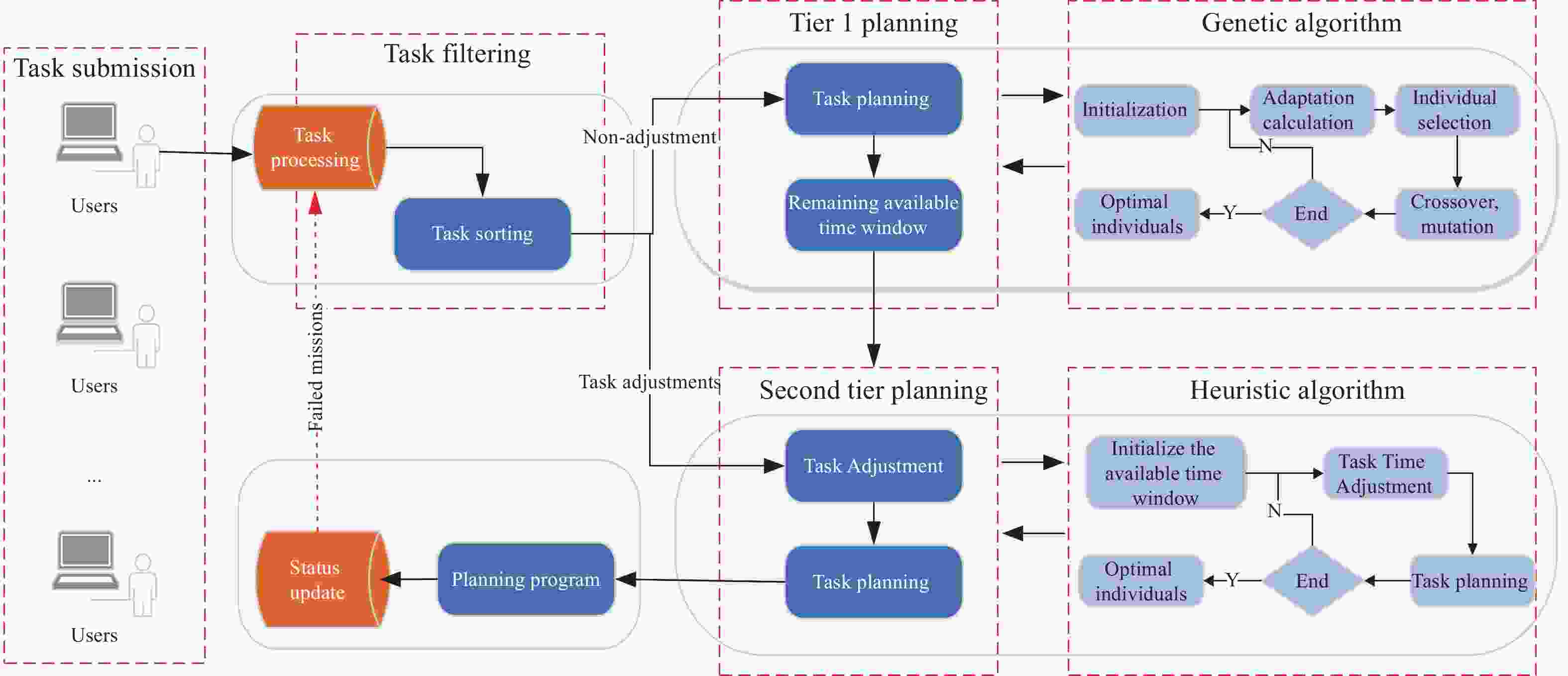
 下载:
下载: