Error Prediction Method of Geomagnetic Model Based on Extreme Learning Machine
-
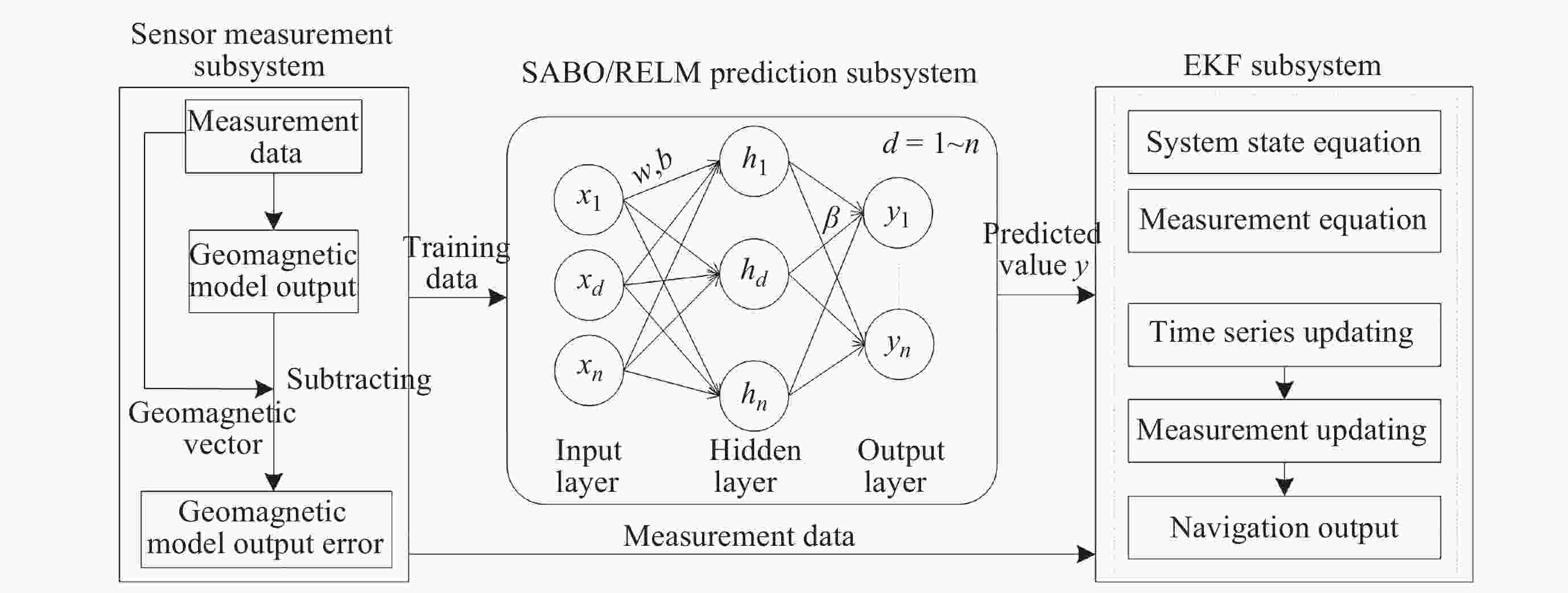
摘要: 高精度地磁场模型是近地卫星自主导航的重要基础, 但地磁模型因观测误差、球谐系数截断误差及更新缓慢等原因制约了导航精度的提高. 为了解决这个问题, 基于正则化极限学习机提出一种地磁模型误差预测方法, 采用减法均值器对正则化系数C进行最优估计, 减少了参数调试中的主观性和随机性, 提高了学习的效率和预测的精度, 另外该方法可以有效提高地磁观测序列中存在异常值时误差估计精度; 与滤波算法进行融合, 提出一种模型误差补偿的地磁导航方法, 并利用在轨卫星真实的地磁测量数据进行了仿真验证. 结果表明, 所提出方法的预测精度优于常用的几种神经网络预测方法, 导航精度达到了1.26 km, 表明所提出的误差预测模型可以有效地改善地磁导航性能.Abstract: The high-precision geomagnetic field model is an important foundation for autonomous navigation of near earth satellites, but the improvement of navigation accuracy is constrained by observation errors, spherical harmonic truncation errors, and slow updates of the geomagnetic model. To solve this problem, this paper proposes a geomagnetic model error prediction method based on regularized extreme learning machine. The optimal estimation of the regularization coefficient C is achieved by using a subtraction mean algorithm, which reduces subjectivity and randomness in parameter tuning, improves learning efficiency and prediction accuracy. In addition, this method can effectively improve the error estimation accuracy when outliers exist in geomagnetic observation sequences. Then, a geomagnetic navigation method with model error compensation was proposed by integrating it with filtering algorithms, and simulation verification was conducted using real geomagnetic measurement data from in orbit satellites. The results show that the prediction accuracy of the method proposed in this paper is superior to several commonly used neural network prediction methods, and the navigation accuracy reaches 1.26 km, indicating that the proposed error prediction model can effectively improve the performance of geomagnetic navigation.
-
表 1 2020年和2024年地磁模型误差对比
Table 1. Comparison of geomagnetic field errors in 2020 and 2024
日期 Bx By Bz Perror 均值/nT 标准差 均值/nT 标准差 均值/nT 标准差 误差/km 2020年1月 68.72 46.90 –0.83 24.01 –5.29 39.81 7.16 2024年1月 82.91 58.17 –2.28 51.56 –6.30 45.52 10.47 表 2 地磁模型实际误差与修正后的地磁模型误差对比
Table 2. Statistical comparison of actual model error and prediction error
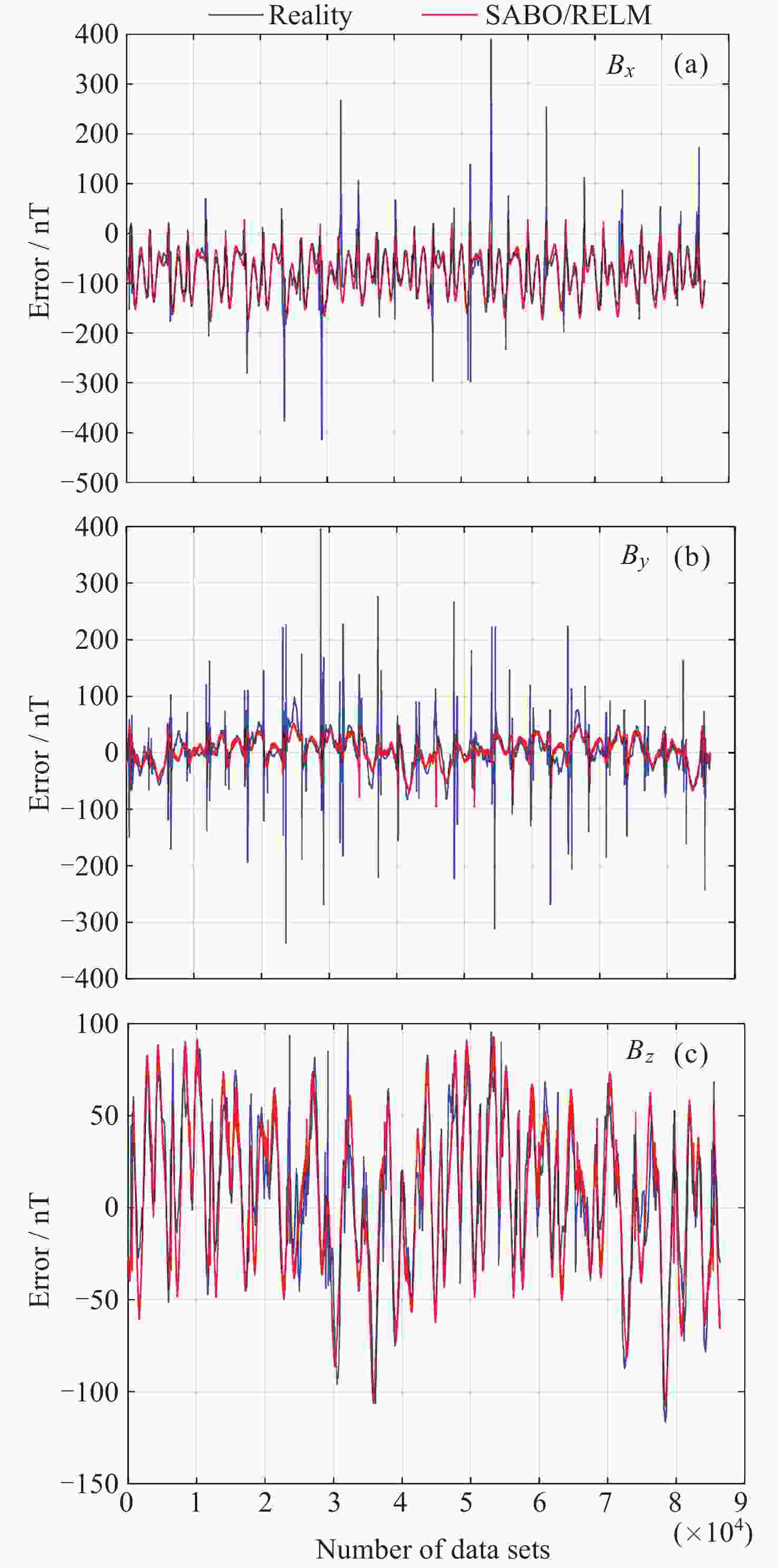
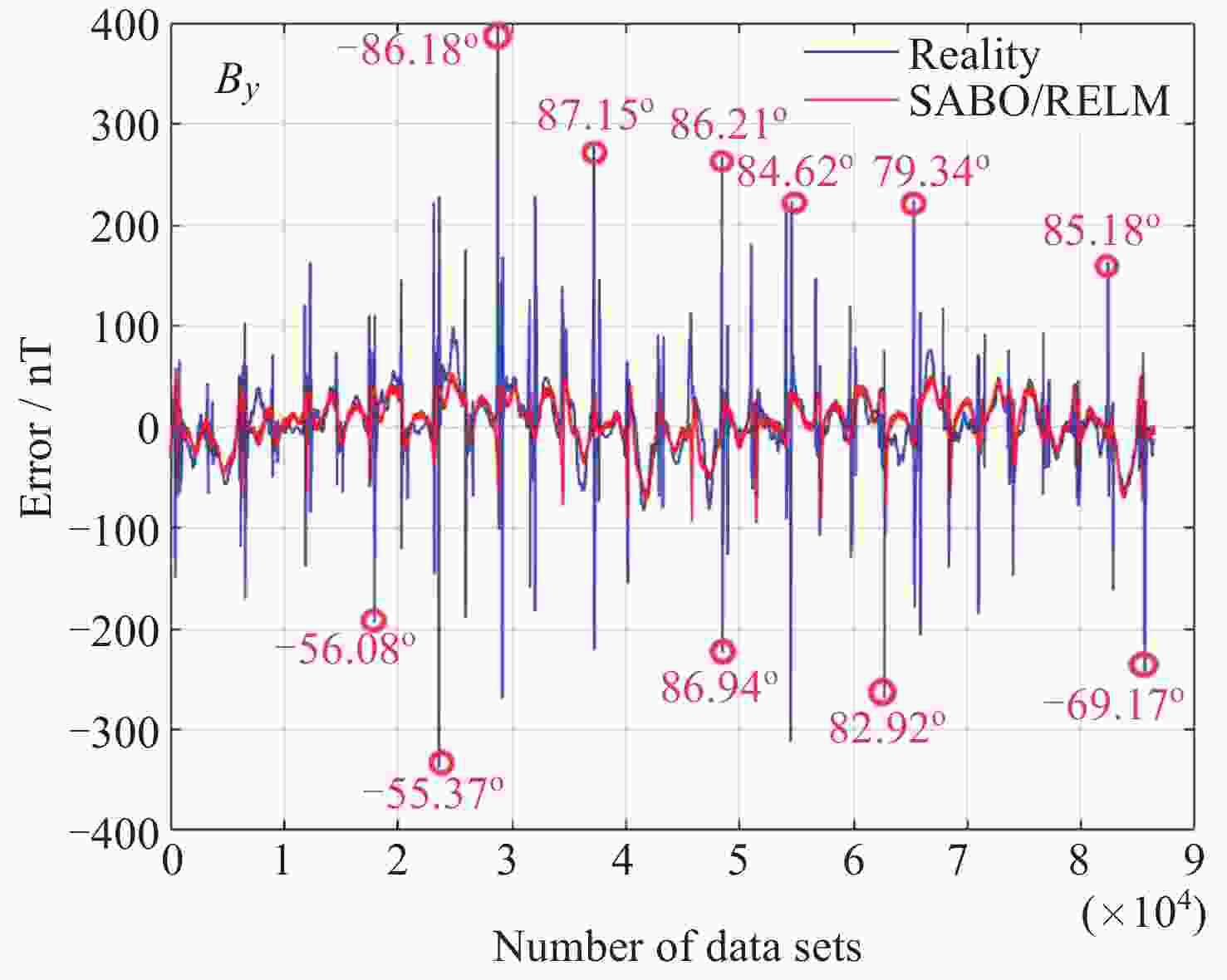
地磁矢量 地磁模型实际误差 修正后模型误差 优化比例 均值/nT 标准差 均值/nT 标准差 均值/(%) 标准差/(%) Bx –77.61 46.90 –2.40 28.11 96.91 40.06 By 2.64 35.56 1.03 28.56 60.98 19.69 Bz 7.49 39.06 –1.01 17.56 86.52 55.04 表 3 神经网络预测结果的误差统计
Table 3. Error statistics of neural network prediction results
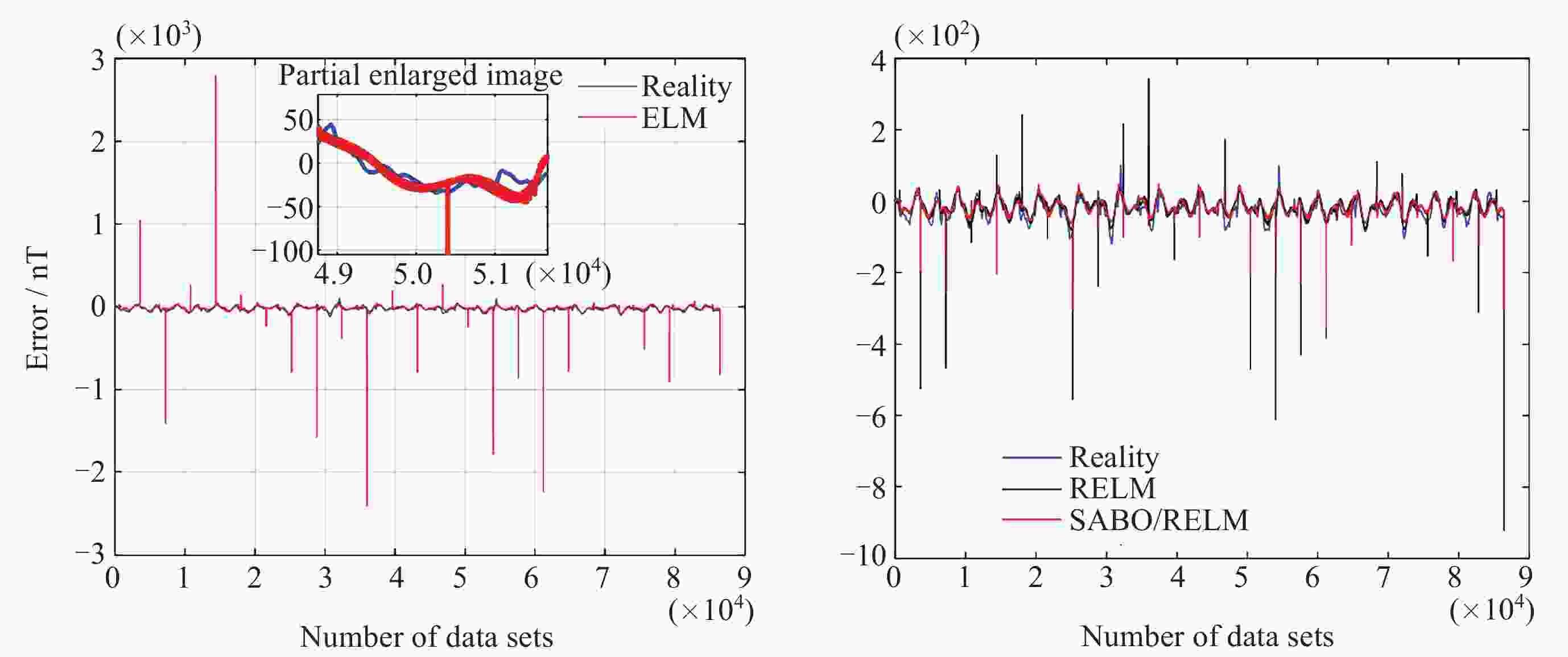
方法 Bx By Bz 均值/nT 标准差 均值/nT 标准差 均值/nT 标准差 ELM (不含异常值) –80.01 40.91 3.68 23.34 6.48 40.45 ELM (含异常值) –80.28 52.26 4.19 53.42 6.40 57.04 RELM (含异常值) –79.61 37.94 3.56 18.77 6.78 36.82 SABO/RELM (含异常值) –79.70 40.59 3.67 21.83 6.75 39.31 表 4 地磁导航方法的误差统计
Table 4. Comparison of error statistics of multiple filter navigation
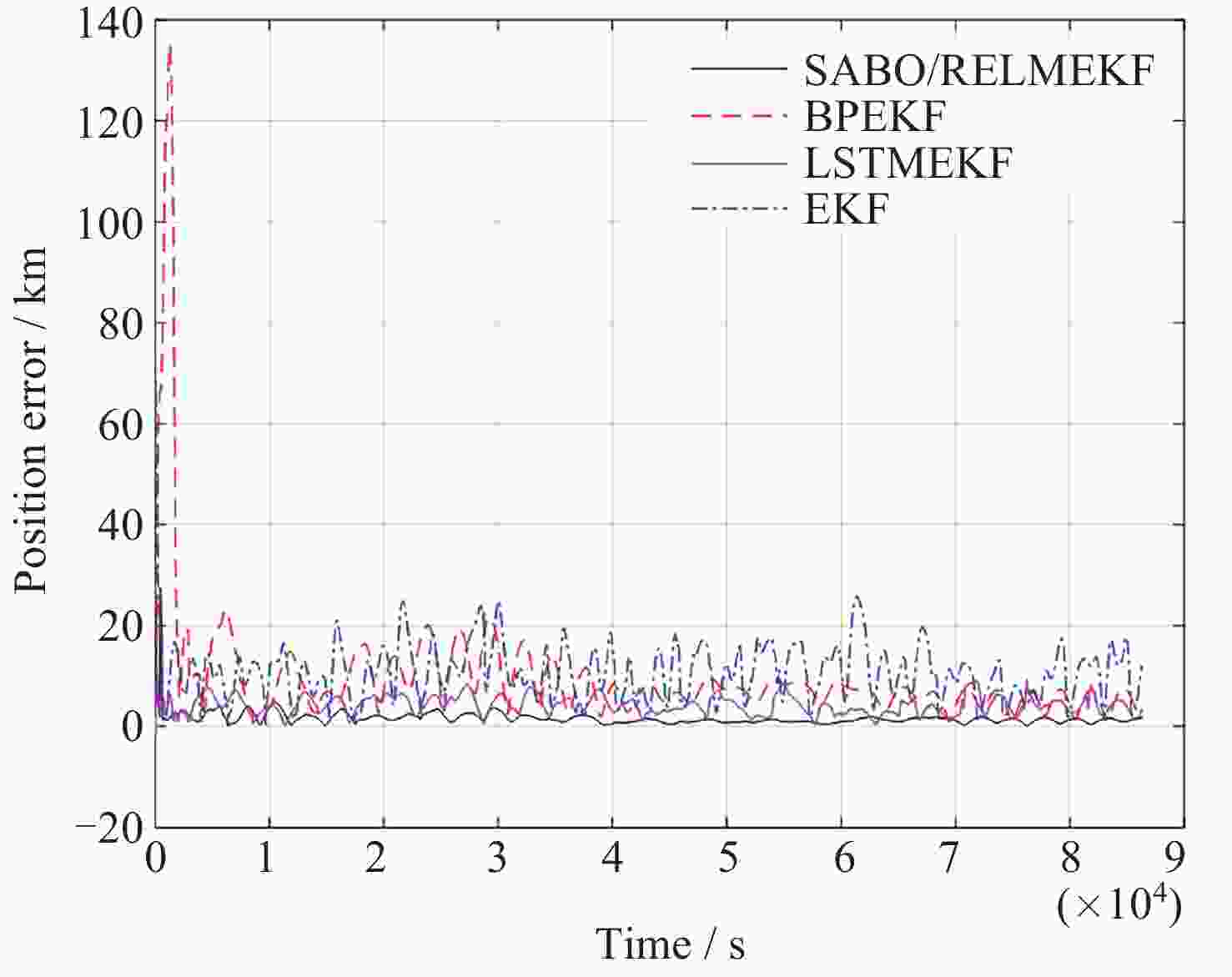
导航方法 位置误差/km 速度误差/(m·s–1) SABO/RELM 1.26 1.39 BP 5.17 5.70 LSTM 3.75 4.08 EKF 11.54 12.21 -
[1] CHEN G F, YU F, ZONG H, et al. Geomagnetic orbit determination using fuzzy regulating unscented Kalman filter[J]. Transactions of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 38(4): 695-703 [2] KIANI M, POURTAKDOUST S H. Adaptive square-root cubature – quadrature Kalman particle filter via KLD-sampling for orbit determination[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2015, 46: 159-167 doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2015.07.008 [3] LI X, SONG B Q, WANG Y J, et al. Calibration and alignment of tri-axial magnetometers for attitude determination[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(18): 7399-7406 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2859832 [4] XIANG Fengzhuo, LI Guangyun, WANG Li, et al. Three-axis magnetometer online self-calibration method based on recursive least square[J]. Transducer and Microsystems Technologies, 2019, 38(2): 30-33 [5] BAI W Q, ZHANG X H, ZHANG S L, et al. Long-distance geomagnetic navigation in GNSS-denied environments with deep reinforcement learning[OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2410.15837, 2024 [6] CHEN Z, LIU K J, ZHANG Q, et al. Geomagnetic vector pattern recognition navigation method based on probabilistic neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5909608 [7] WINTOFT P, WIK M. Exploring three recurrent neural network architectures for geomagnetic predictions[J]. Frontiers in Astronomy and Space Sciences, 2021, 8: 664483 doi: 10.3389/fspas.2021.664483 [8] HE Xinran, ZHONG Qiuzhen, CUI Yanmei, et al. Solar flare short-term forecast model based on long and short-term memory neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2022, 42(5): 862-872 (何欣燃, 钟秋珍, 崔延美, 等. 基于长短期记忆神经网络的太阳耀斑短期预报[J]. 空间科学学报, 2022, 42(5): 862-872 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.05.210315028HE Xinran, ZHONG Qiuzhen, CUI Yanmei, et al. Solar flare short-term forecast model based on long and short-term memory neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2022, 42(5): 862-872 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.05.210315028 [9] SICILIANO F, CONSOLINI G, TOZZI R, et al. Forecasting SYM‐H index: a comparison between long short‐term memory and convolutional neural networks[J]. Space Weather, 2020, 19(2): e2020SW002589 [10] TASISTRO-HART A, GRAYVER A, KUVSHINOV A. Probabilistic geomagnetic storm forecasting via deep learning[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(1): e2020JA028228 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028228 [11] YANG Mao, ZHANG Shutian, WANG Bo. Short-term wind power forecasting method based on a causal regularized extreme learning machine[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52(11): 127-136 [12] WANG H, XU L W, TAO Y, et al. OP performance prediction for complex mobile multiuser networks based on extreme learning machine[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 14557-14564 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2966690 [13] TROJOVSKY P, MOHAMMAD D. Subtraction-average-based optimizer: a new swarm-inspired metaheuristic algorithm for solving optimization problems[J]. Biomimetics, 2023, 8(2): 149 doi: 10.3390/biomimetics8020149 [14] ALKEN P, THÉBAULT E, BEGGAN C D, et al. International geomagnetic reference field: the thirteenth generation[J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 2021, 73: 49 doi: 10.1186/s40623-020-01288-x [15] ZHANG Tao, ZHANG Wenbo, GAO Dong, et al. A geomagnetic navigation method based on neural network prediction model error[J]. Aerospace Control, 2024, 42(1): 37-42 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3242.2024.01.006 [16] WINCH D E, IVERS D J, TURNER J P R, et al. Geomagnetism and Schmidt quasi-normalization[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2005, 160(2): 487-504 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2004.02472.x [17] GAO Dong, ZHU Minghui, HAN Peng. A geomagnetic/inertial depth fusion navigation method[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2022, 30(4): 437-444 [18] JIAO M, WANG D Q, YANG Y, et al. More intelligent and robust estimation of battery state-of-charge with an improved regularized extreme learning machine[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 104: 104407 doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2021.104407 [19] LU Zhaoxing, LÜ Zhifeng, LI Ting, et al. Forecasting of the variable geomagnetic field based on BP neural network[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2021, 41(3): 229-233 -
-




 郭红阳 男, 2001年3月出生于河南省洛阳市, 2022年于辽宁工程技术大学获得学士学位. 目前于河南工业大学机电工程学院就读硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为自主导航、人工智能. E-mail:
郭红阳 男, 2001年3月出生于河南省洛阳市, 2022年于辽宁工程技术大学获得学士学位. 目前于河南工业大学机电工程学院就读硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为自主导航、人工智能. E-mail: 

 下载:
下载: