基于雷诺数的大气阻力模型在飞行器再入预报中的应用
doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.02.210222020 cstr: 32142.14.cjss2022.02.210222020
Application of Atmospheric Drag Model Based on Reynolds Number in Reentry Prediction of Rocket Bodies
-
摘要: 随着对空间技术服务需求的增加和空间碎片主动移除技术的实现,未来空间碎片将以数量多、质量大、难分解等特点频繁再入大气层,给地面人员和财产安全造成更多威胁。因此,亟需对火箭体等大型航天器的大气再入进行预警,然而因缺乏合适的大气阻力系数模型难以实现高精度的大气再入预报。为此,在简化航天器模型的基础上引入基于雷诺数的大气动力模型,通过RK6(7)对运动微分方程数值积分得到预报结果,并与高精度数值轨道传播器HPOP以及半解析轨道传播器WHU-SST的预报结果进行对比。实验表明:在运动微分方程中引入基于雷诺数的大气动力模型提前30天对火箭体进行大气再入预报,精度显著提升,某些目标的预报误差从96%下降至7.8%;仅使用TLE数据,将新模型用于地面风险评估能够使真实陨落位置位于预报的统计陨落位置中。Abstract: With the increasing demand for space technology services and the realization of active space debris removal technology, space debris will frequently re-enter the atmosphere in the future with the characteristics of large quantity, high quality and difficult decomposition, causing more threats to the safety of people and property. Therefore, there is an urgent need for early warning of atmospheric reentry of large spacecraft such as rocket body. However, due to the lack of appropriate atmospheric drag coefficient model, it is difficult to achieve high-precision atmospheric reentry prediction. Therefore, an atmospheric dynamic model based on Reynolds number is introduced for simplified spacecraft model, and the prediction results are obtained by numerical integration of the differential equation of motion through RK6(7), which are compared with the prediction results of high-precision numerical orbital propagator HPOP and semi analytical orbital propagator WHU-SST. The experimental results show that using the differential equation of motion with the atmospheric dynamic model based on Reynolds number to predict the reentry of the rocket body 30 days in advance, the accuracy of prediction is significantly improved, and the prediction error of an object is reduced from 96% to 7.8%; Using the new model for ground risk assessment with TLE data only, the real decayed location can be located in the predicted statistical decayed location.
-
Key words:
- Reentry prediction /
- Atmospheric drag coefficient /
- Rocket bodies /
- Reynolds number
-
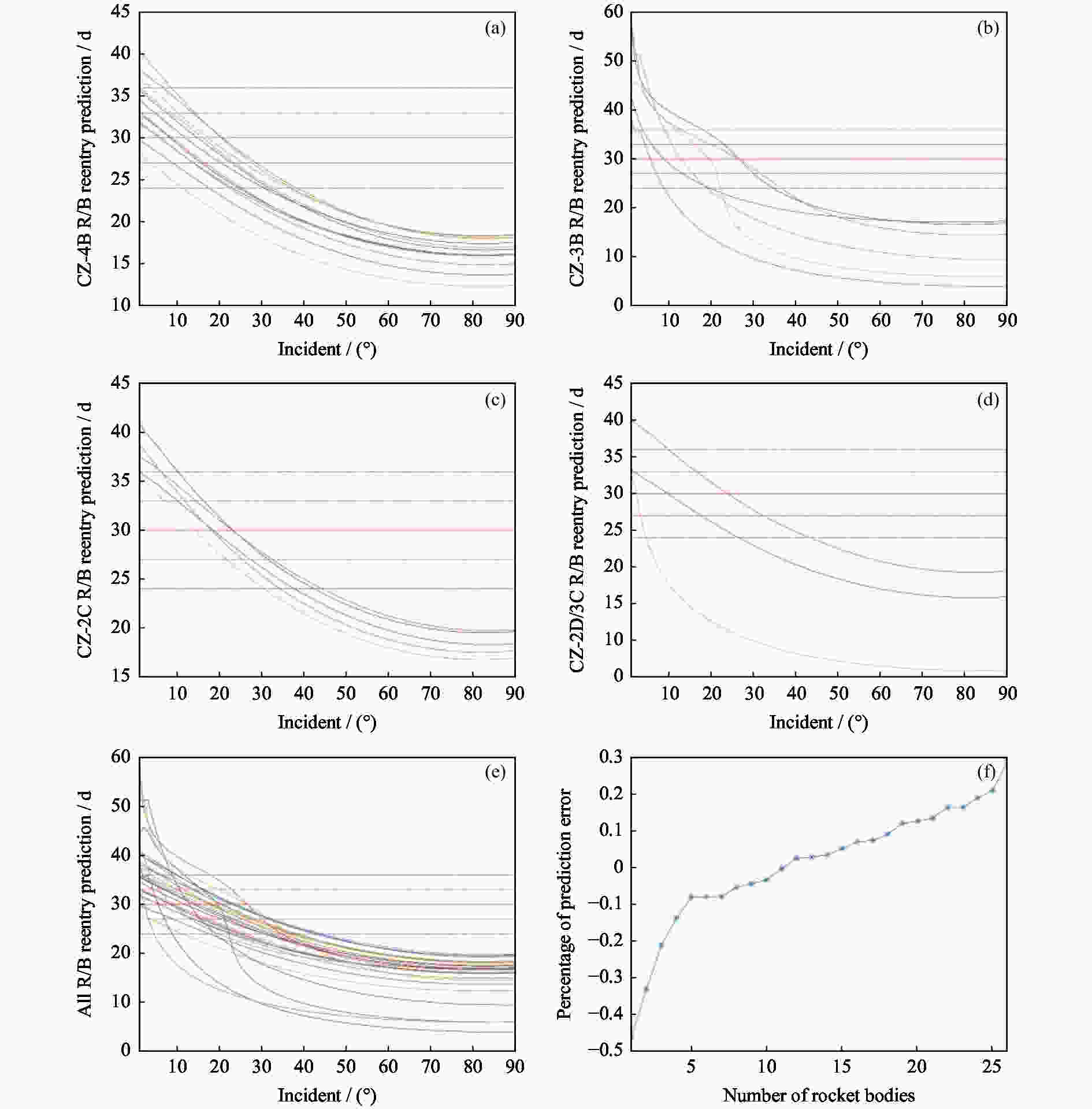
图 3 入射角对火箭体再入预报的影响和入射角为12°时火箭体的预报误差百分比(红色实横线是预测误差为0的基线,即第30天结果,红色点线为预报误差±10%的范围线,品红点线为预报误差±20%的范围线)
Figure 3. Influence of the incident angle on the reentry prediction of the rocket body and the prediction error percentage of the rocket body when the incident angle is 12° (Red solid line is baseline with 0 prediction error, the red dotted line deviates ±10% from the baseline, and the magenta dotted line deviates ±20%)
表 1 5种长征系列火箭体的二级火箭尺寸和质量
Table 1. Size and mass of two-stage rockets of five kinds of Long March series rocket carriers
目标类型 起飞
质量/t结构
质量/t推进剂质量/t 长度/m 直径/m 等效球体直径/m CZ-2C R/B 38.2 3.2 35 8.387 3.35 5.2071 CZ-2D R/B 40.644 3.122 34.736 9.007 3.35 5.3324 CZ-3B R/B - - 49.4 9.943 3.35 5.5110 CZ-3C R/B 48.644 3.222 43.736 9.943 3.35 5.5110 CZ-4B R/B - - 52.7 10.9 3.35 5.6825 表 2 8个火箭体轨道信息和预报误差
Table 2. Orbit information and prediction errors of 8 rocket bodies
NORAD_ID 目标类型 倾角/
(°)远地点/
km近地点/
km偏心率 再入时间 HPOP预报
误差WHU-SST
预报误差新模型预报
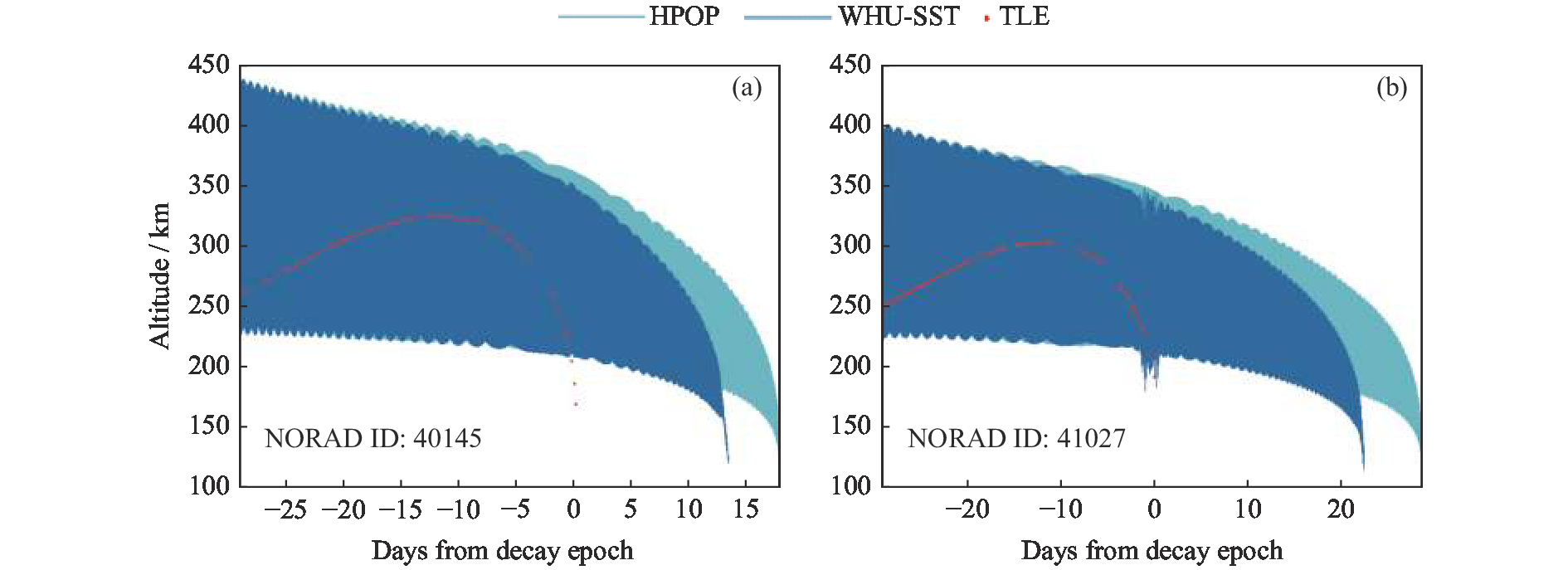
误差34840 CZ-2C R/B 97.49 148 133 0.002326 2014-12-14 0.1838 0.1103 0.0464 37942 CZ-2C R/B 97.06 128 115 0.001491 2014-03-19 0.4401 0.3047 0.1075 38253 CZ-3B R/B 54.71 257 119 0.112676 2017-08-18 Fail 0.8361 –0.1591 40120 CZ-4B R/B 98.12 153 137 0.002277 2017-05-27 –0.7333 Fail 0.0397 40138 CZ-2D R/B 97.95 155 133 0.014247 2015-06-14 0.3437 0.1375 0.1610 40145 CZ-4B R/B 97.47 164 132 0.016632 2014-10-23 0.552 0.4127 0.0068 40550 CZ-3C R/B 54.54 390 86 0.389825 2016-03-23 0.3484 0.2091 - 41027 CZ-4B R/B 97.35 155 127 0.014069 2015-12-26 0.9655 0.7586 0.0781 注 Fail表示预报误差超过100%。 -
[1] PARDINI C, ANSELMO L. Uncontrolled re-entries of spacecraft and rocket bodies: a statistical overview over the last decade[J]. Journal of Space Safety Engineering, 2019, 6(1): 30-47 doi: 10.1016/j.jsse.2019.02.001 [2] XU K, PANG B J, PENG K K. Research on the arithmetic for space debris long-term orbit propagation in LEO[C]//Proceedings of the 5 th European Conference on Space Debris. Darmstadt: ESA, 2009: 672 [3] CHOI S J. Results of automated conjunction analysis tool using in-house generated KOMPSAT-2 ephemeris[C]//Proceedings of SpaceOps 2010 Conference. Huntsville: AAAI, 2010 [4] REFAAT A, BADAWY A, ASHRY M, et al. High accuracy spacecraft orbit propagator validation[C]//Proceedings of the 18 th International Conference on Applied Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering. Cairo: Military Technical College, 2018: 1-9 [5] LI Bin. Researches on Key Technologies of Fast and Accurate Orbit Determination and Prediction of Space Debris[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2017 [6] MOE M M, WALLACE S D, MOE K. Refinements in determining satellite drag coefficients: method for resolving density discrepancies[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 1993, 16(5): 991 doi: 10.2514/3.21118 [7] PARDINI C, ANSELMO L, MOE K, et al. Drag and energy accommodation coefficients during sunspot maximum[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2010, 45(5): 638-650 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2009.08.034 [8] MEHTA P M, LINARES R, WALKER A C. Photometric data from nonresolved objects for improved drag and reentry prediction[J]. Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 2018, 55(4): 959-970 doi: 10.2514/1.A33825 [9] SCHAAF S A, CHAMBRE P L. Flow of Rarefied Gases[M]. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2017 [10] CAO Z, TAFTI D K. Investigation of drag, lift and torque for fluid flow past a low aspect ratio (1∶4) cylinder[J]. Computers & Fluids, 2018, 177: 123-135 [11] PARDINI C, ANSELMO L. Assessing the risk and the uncertainty affecting the uncontrolled re-entry of manmade space objects[J]. Journal of Space Safety Engineering, 2018, 5(1): 46-62 doi: 10.1016/j.jsse.2018.01.003 -
-





 下载:
下载: