基于最优估计法的瑞利激光雷达反演大气温度研究
doi: 10.11728/cjss2023.04.2022-0035 cstr: 32142.14.cjss2023.04.2022-0035
Research on Atmospheric Temperature Retrieval Based on Rayleigh Lidar Using Optimal Estimation Method
-
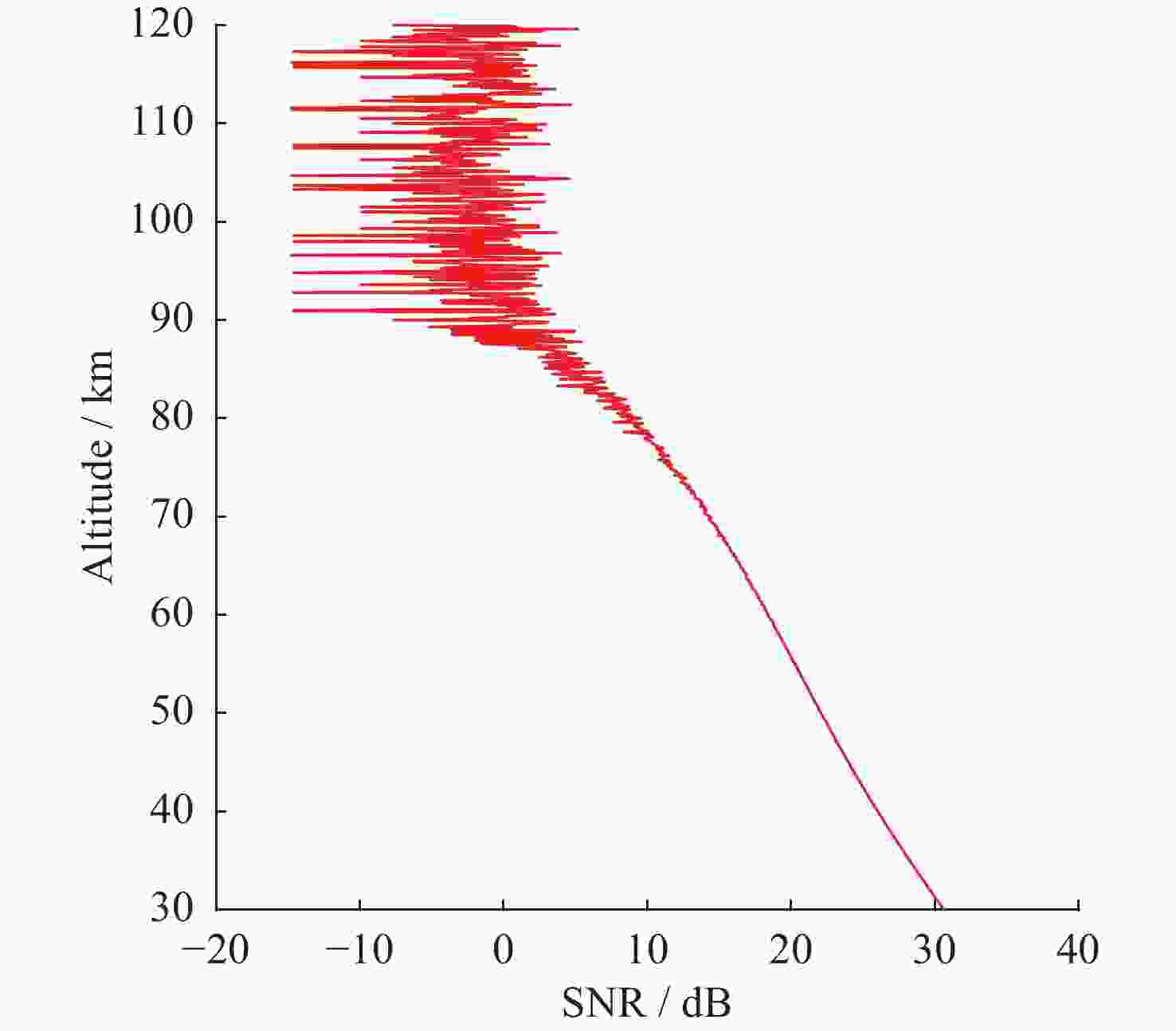
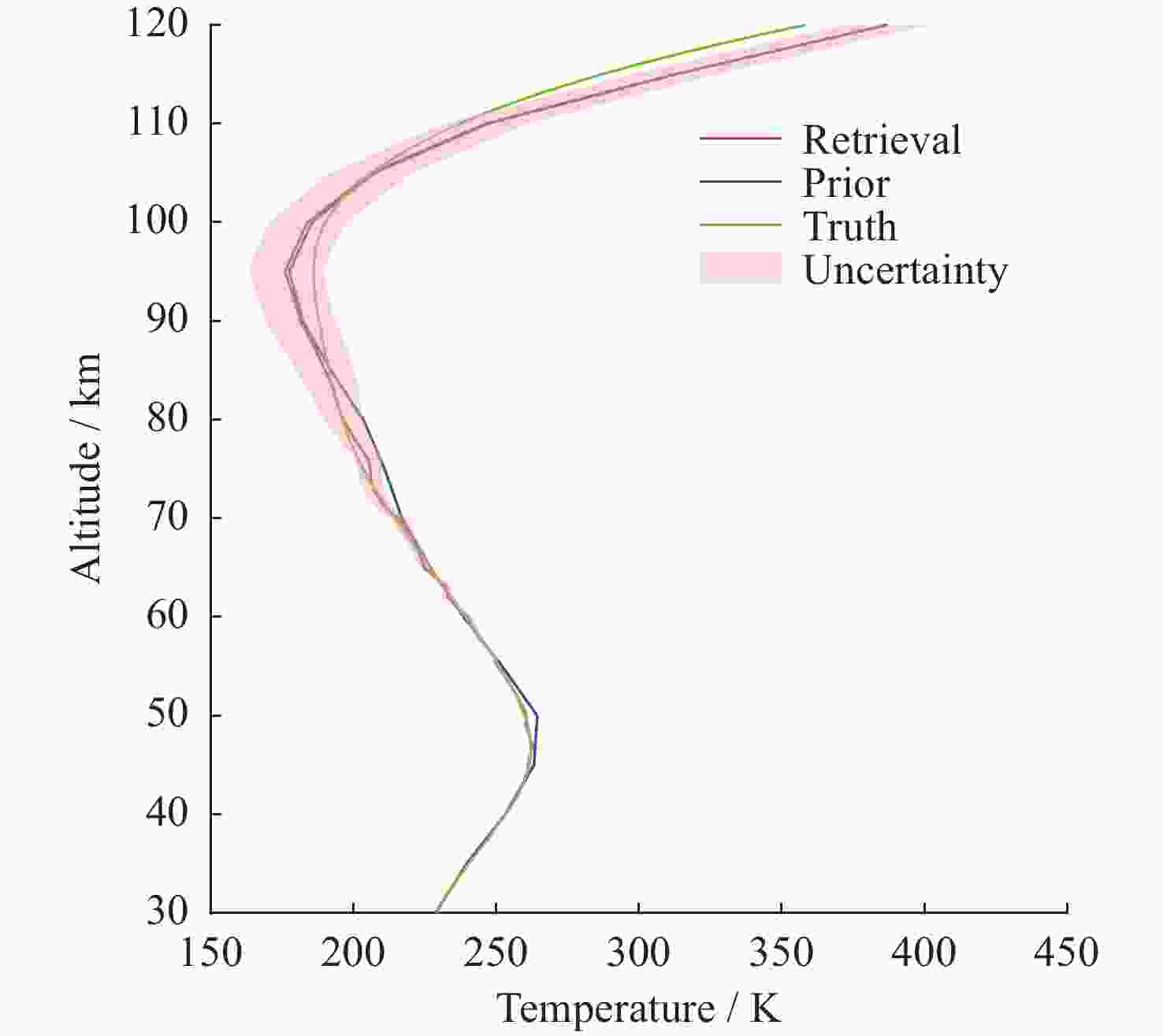
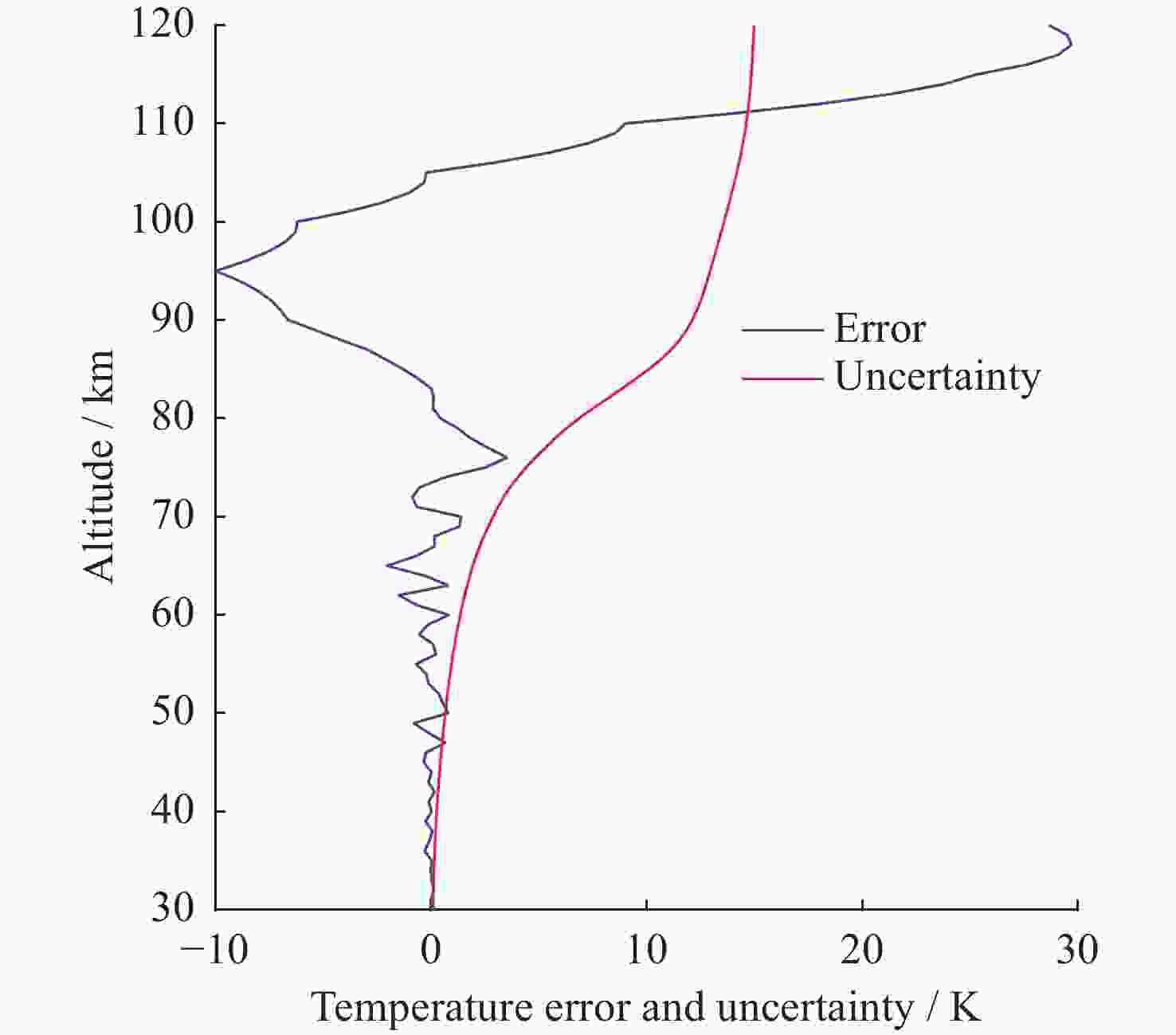
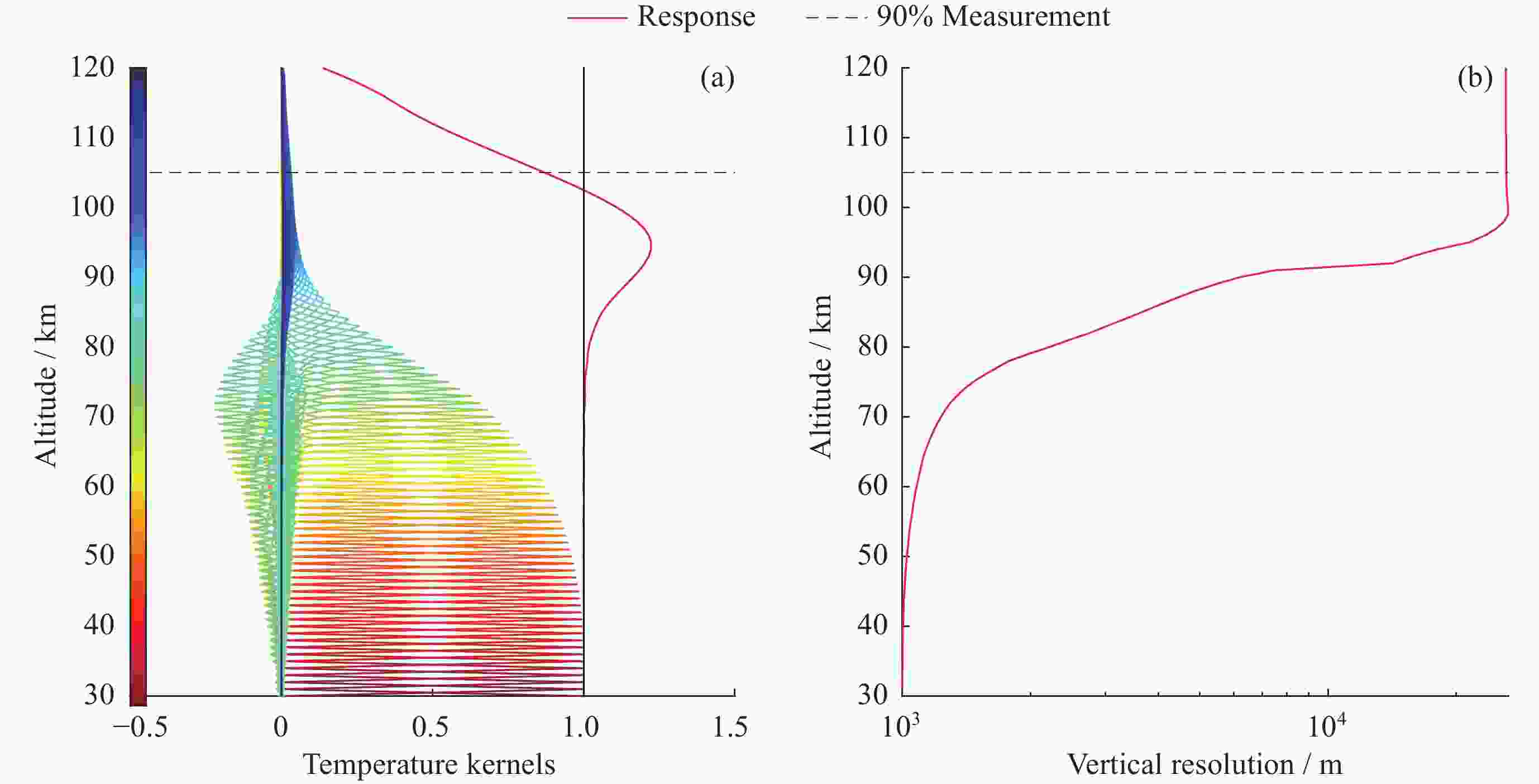
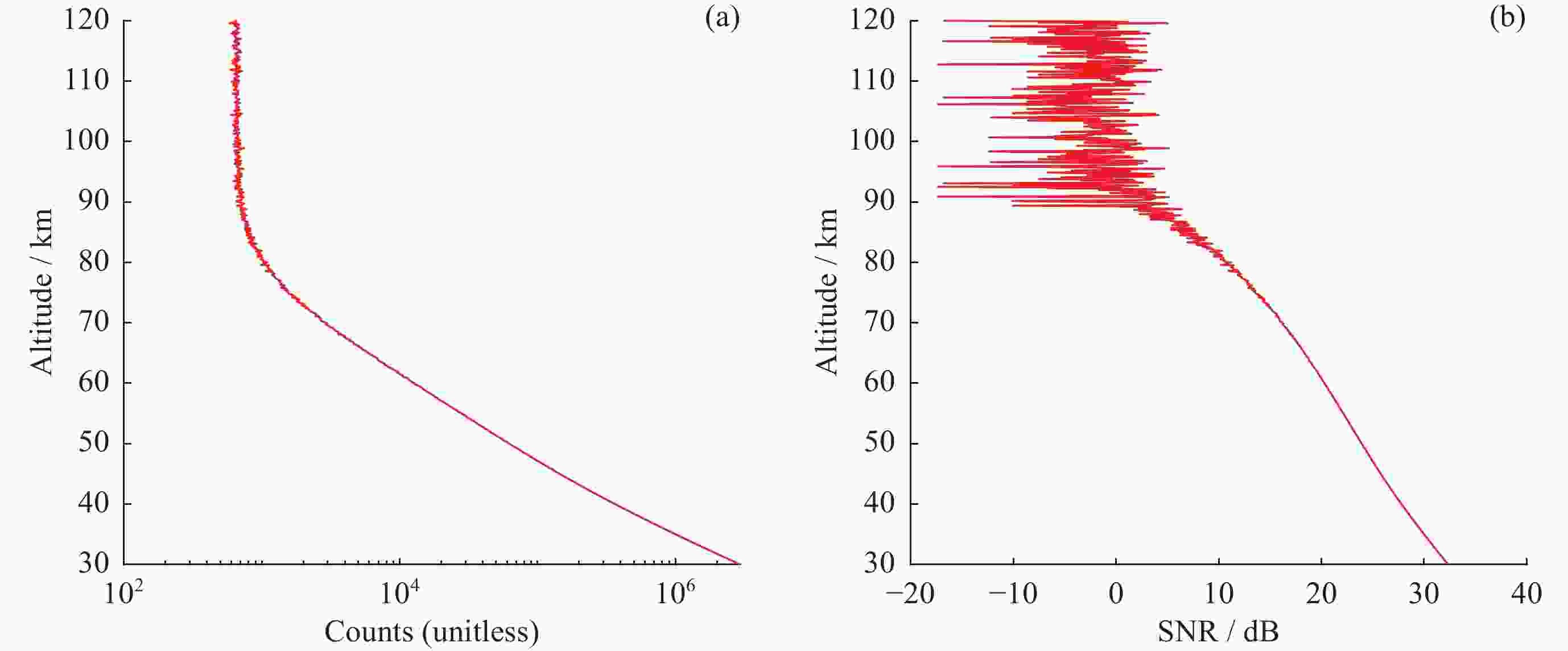
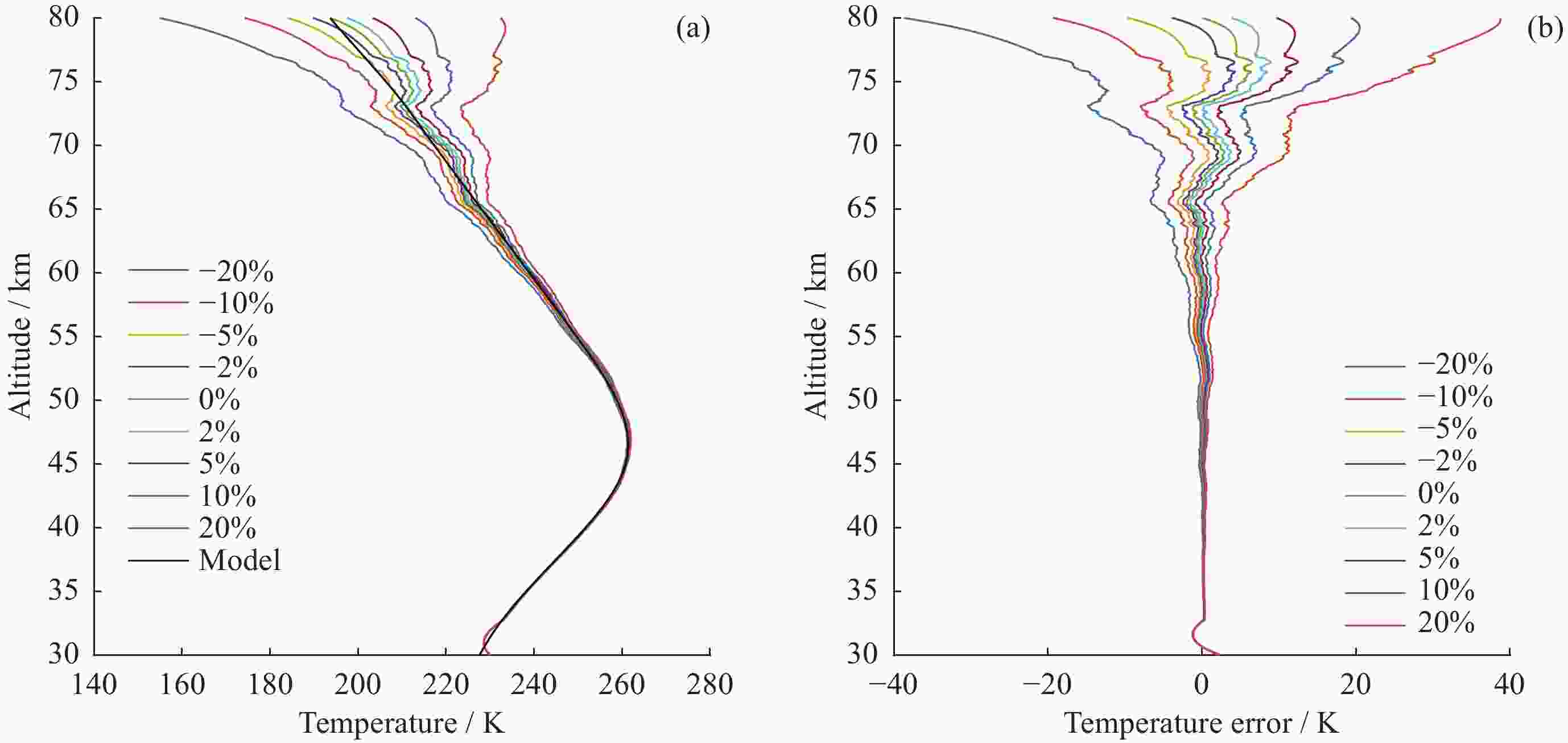
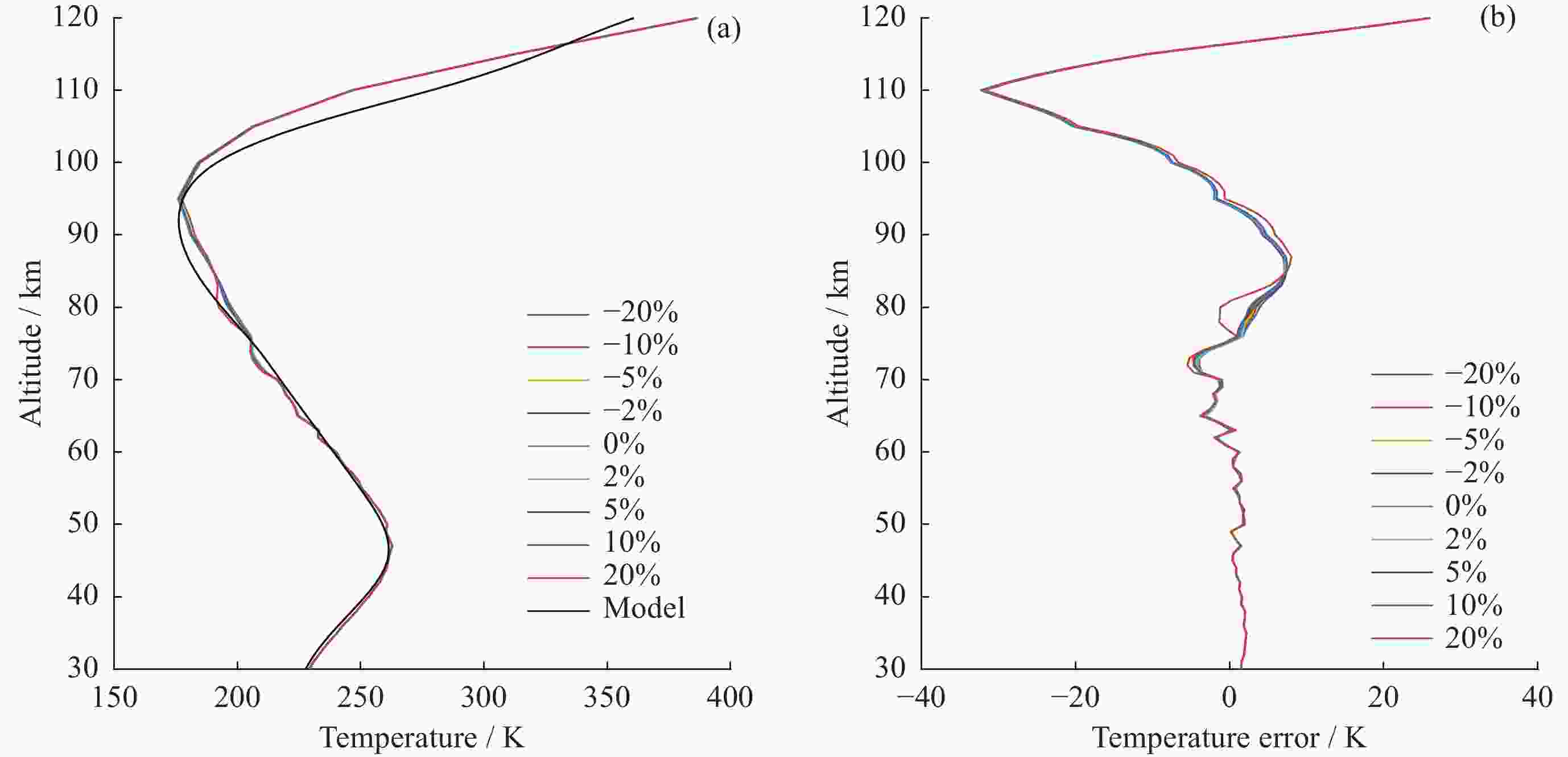
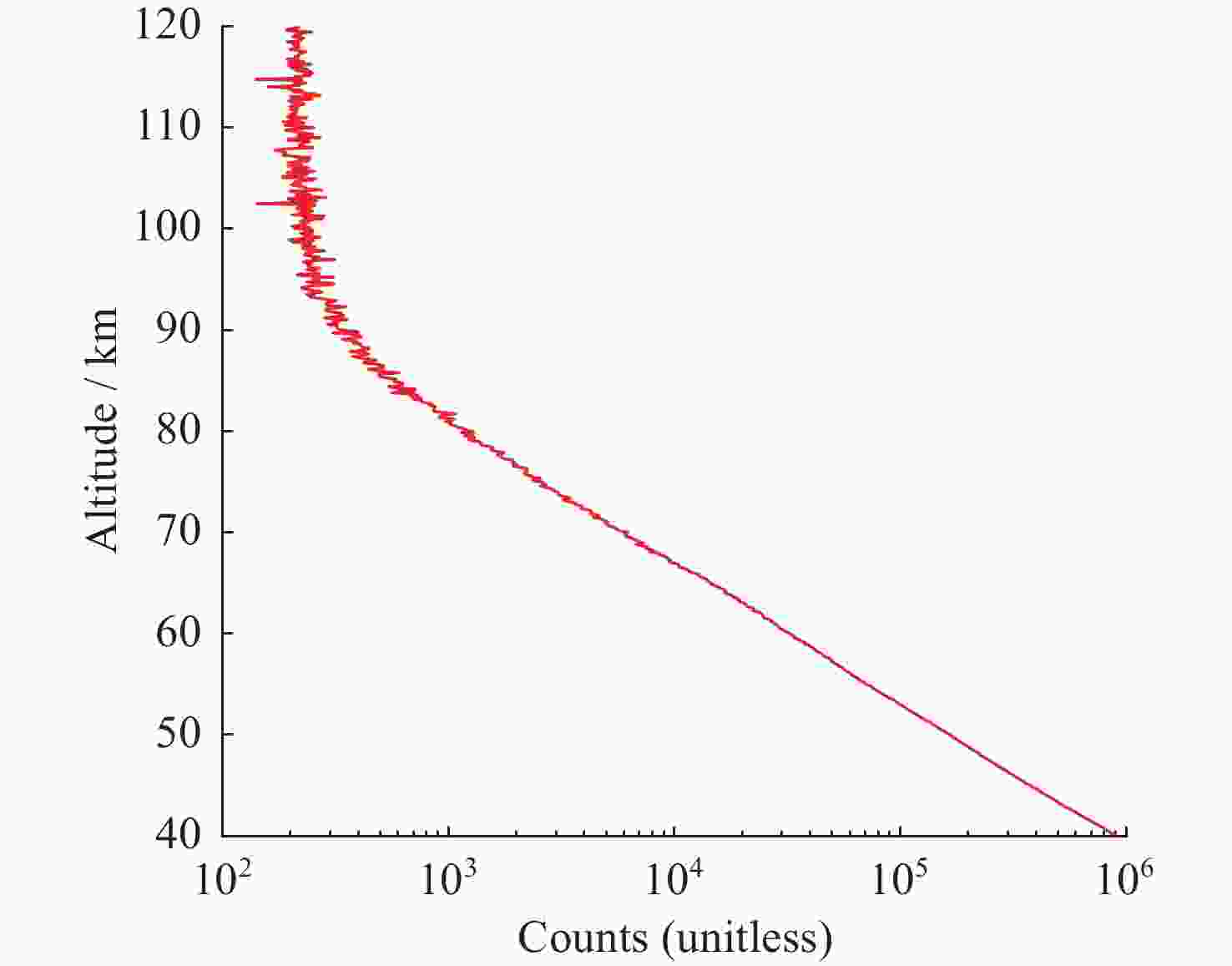
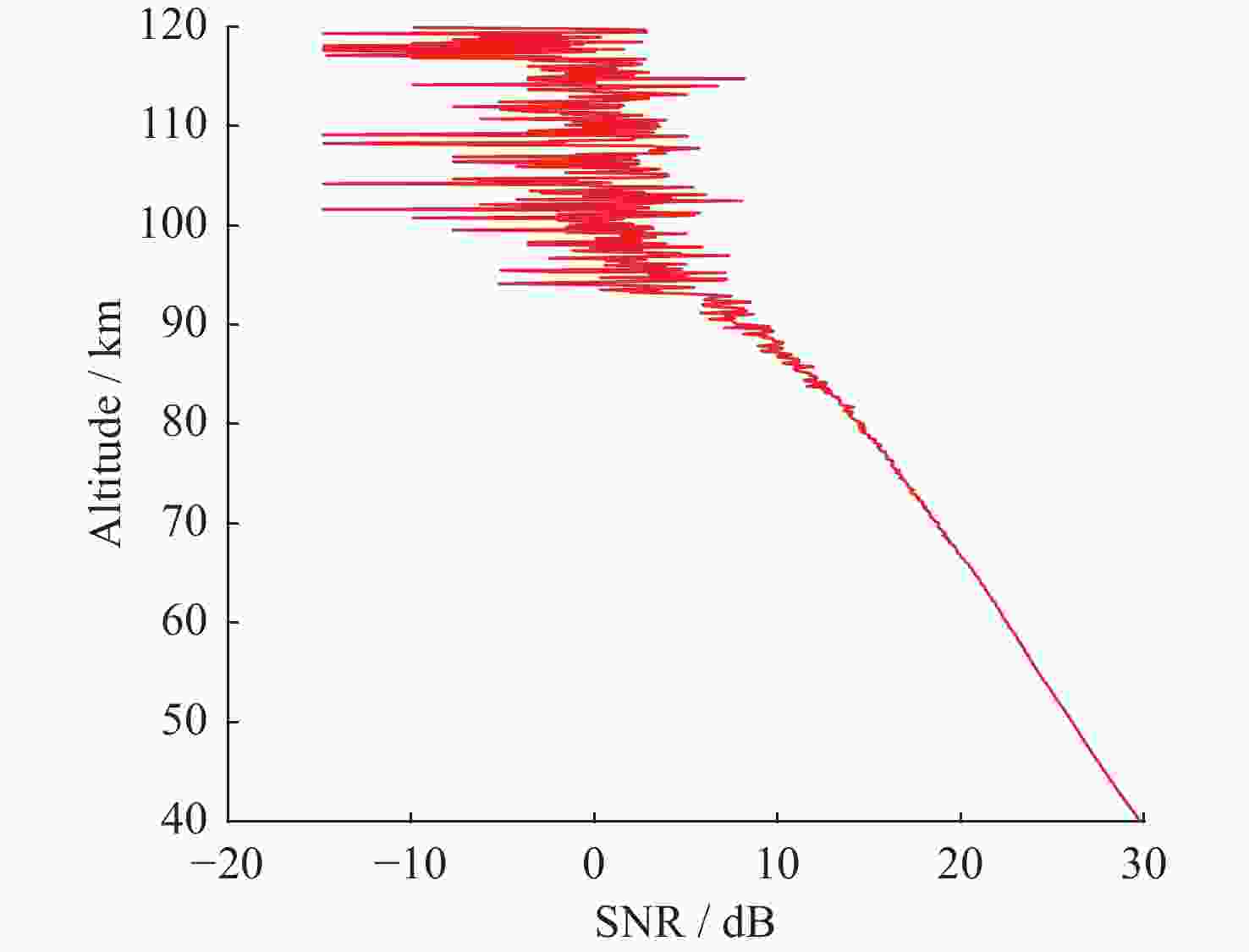
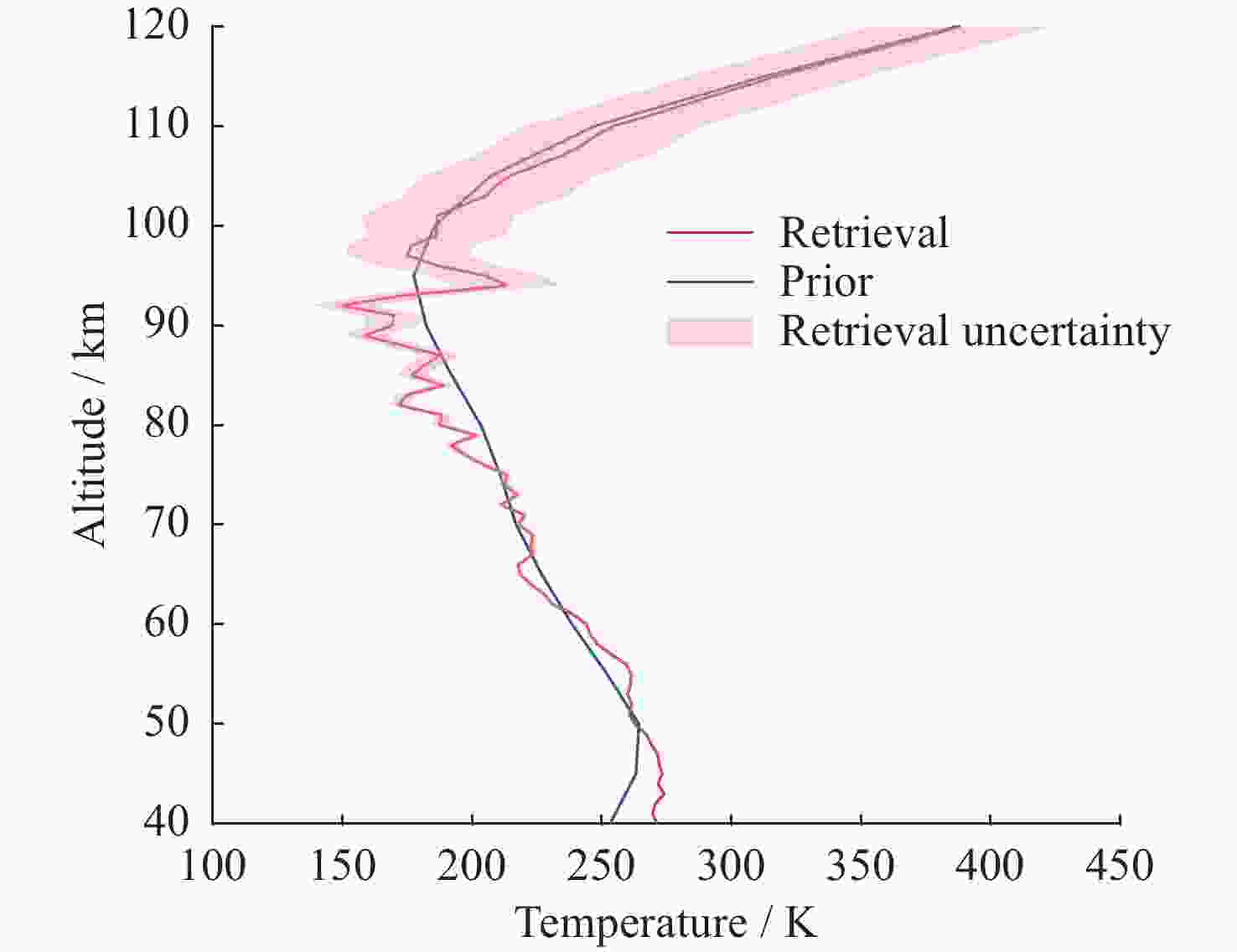
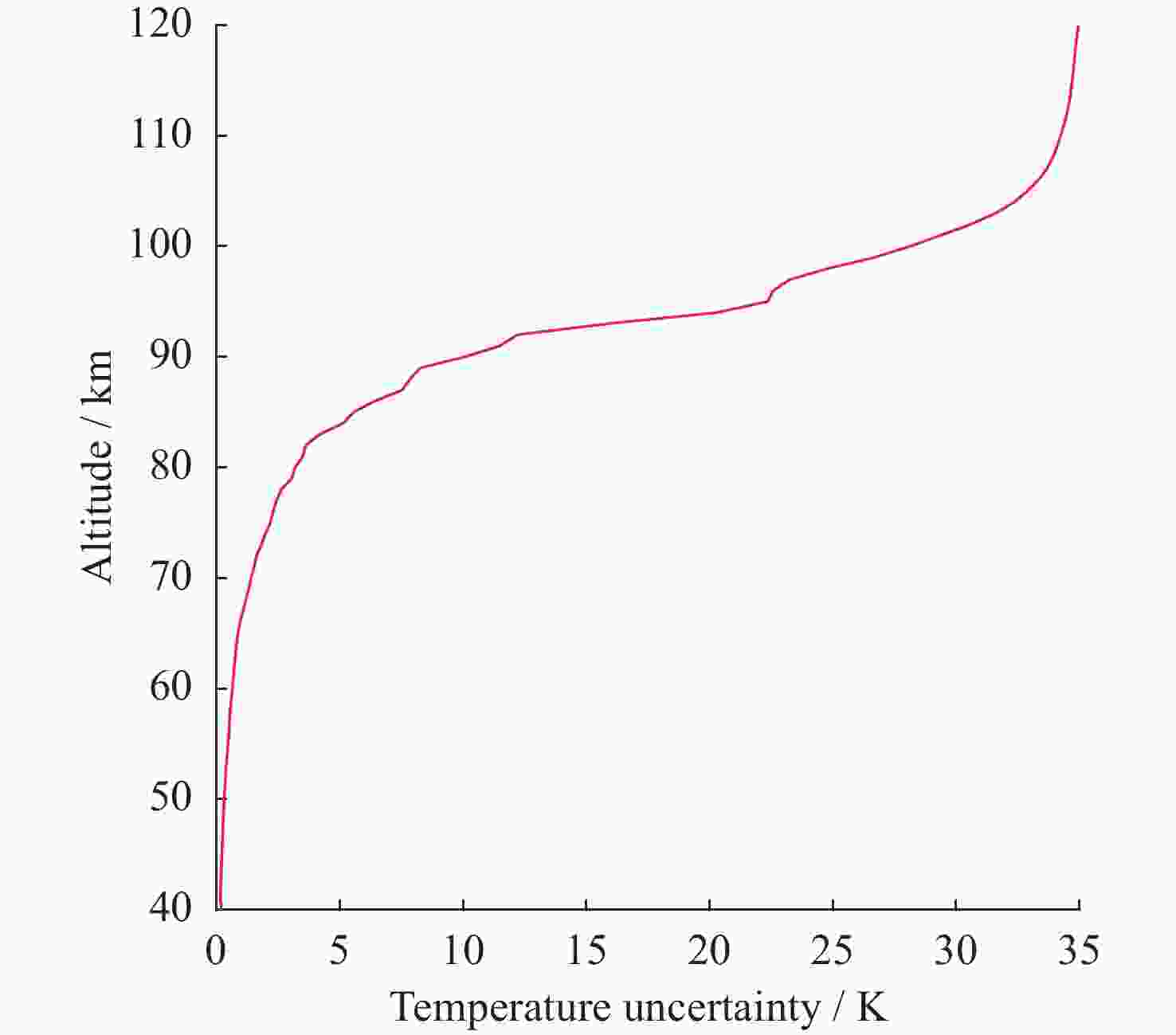
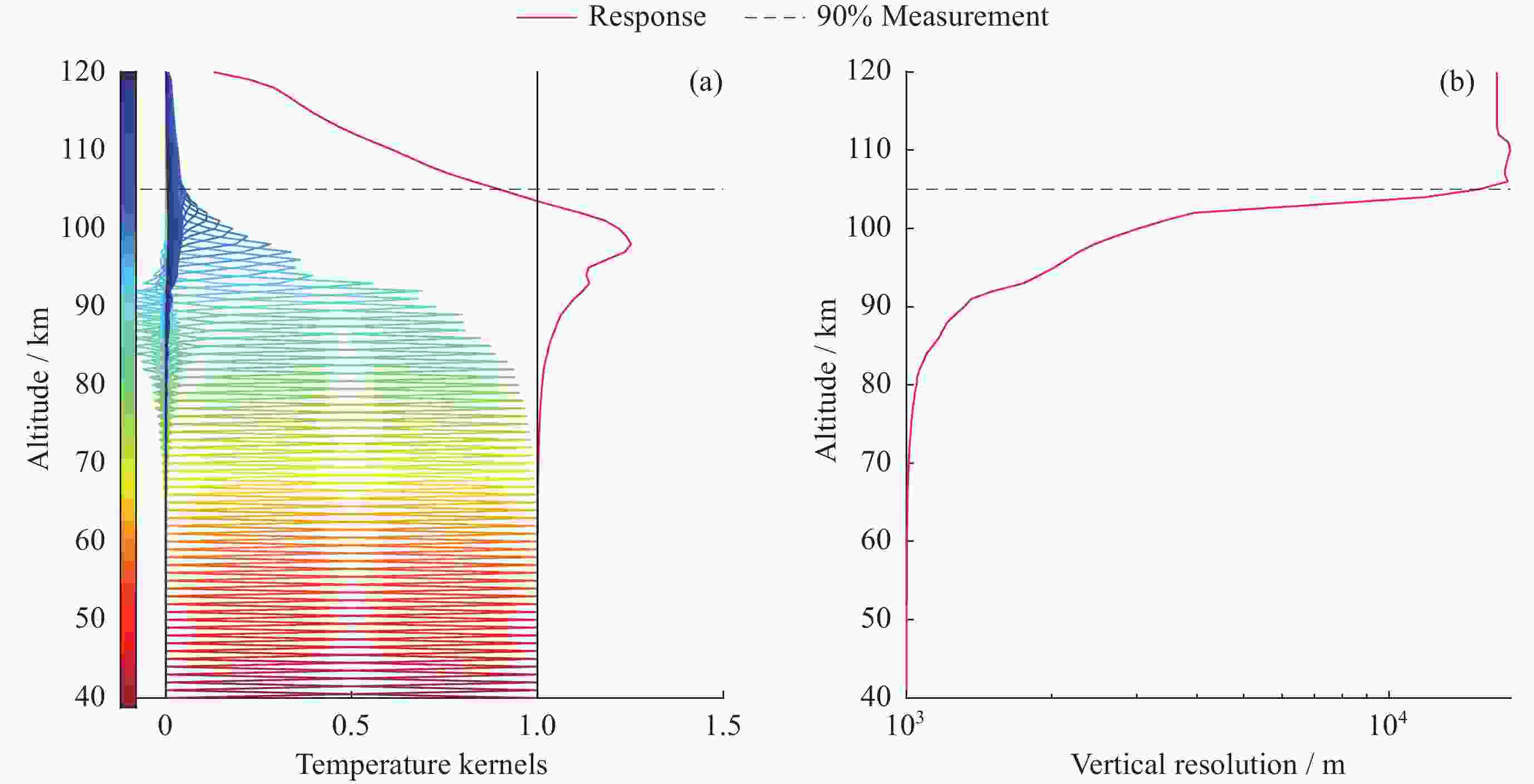
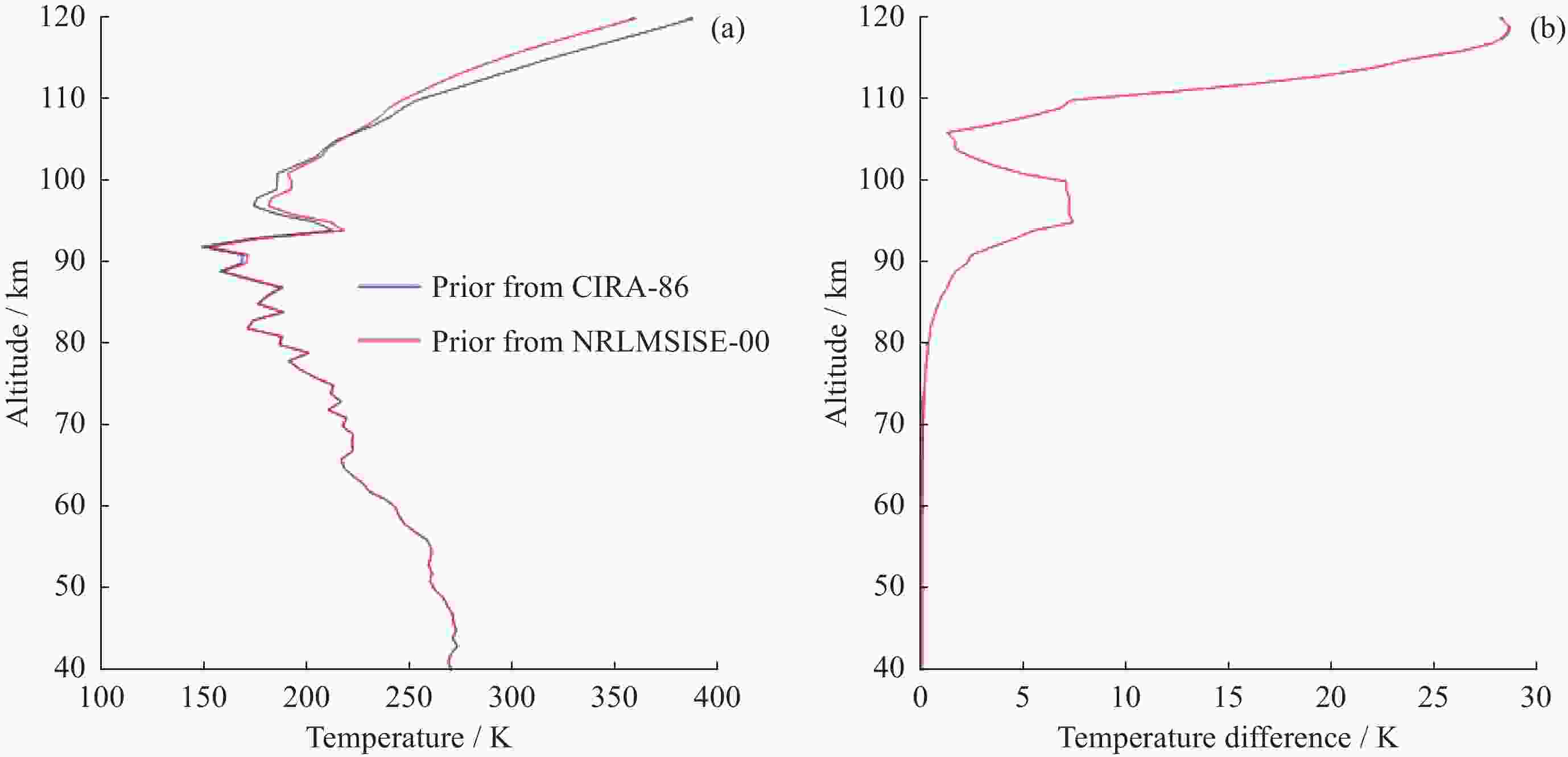
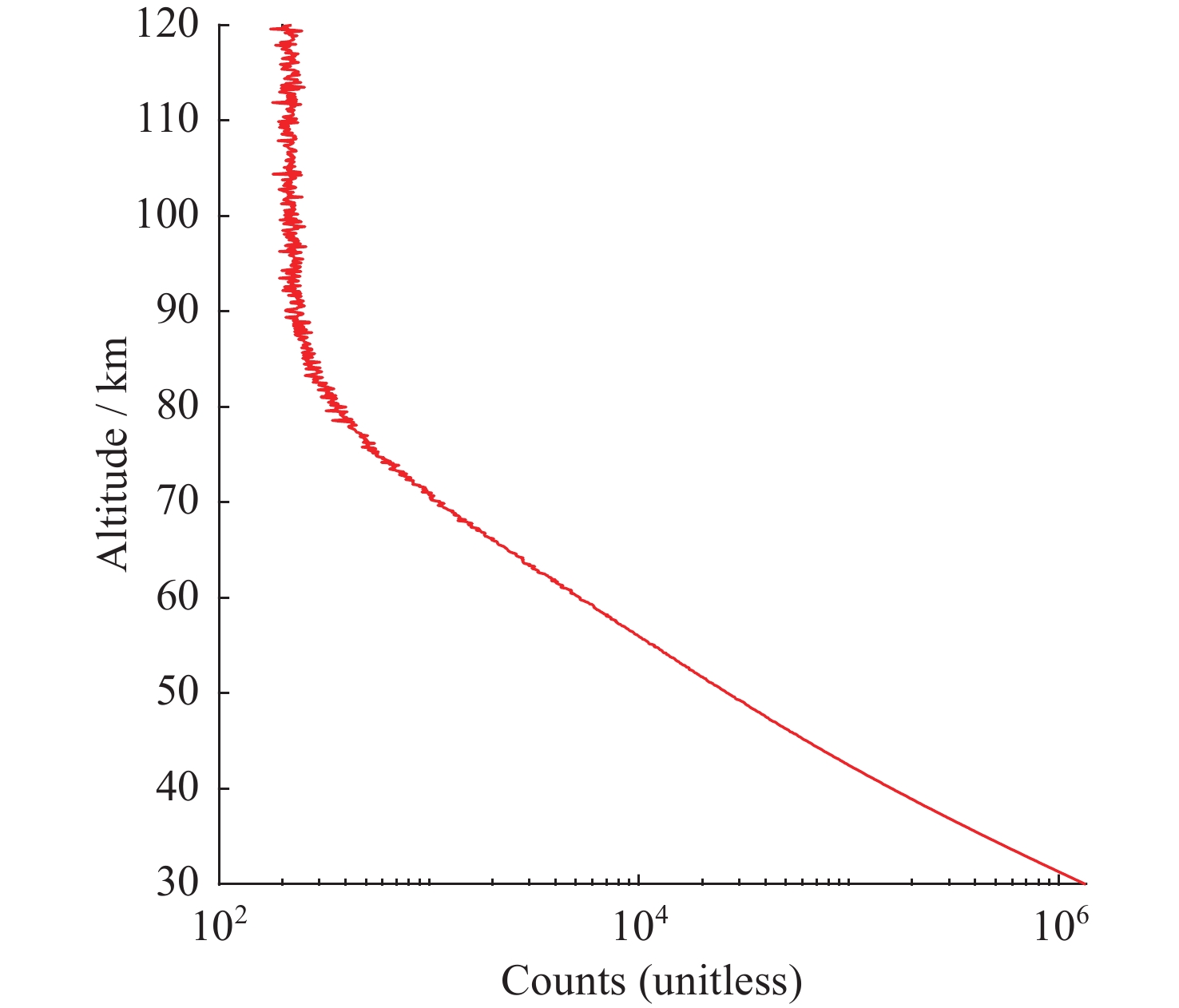
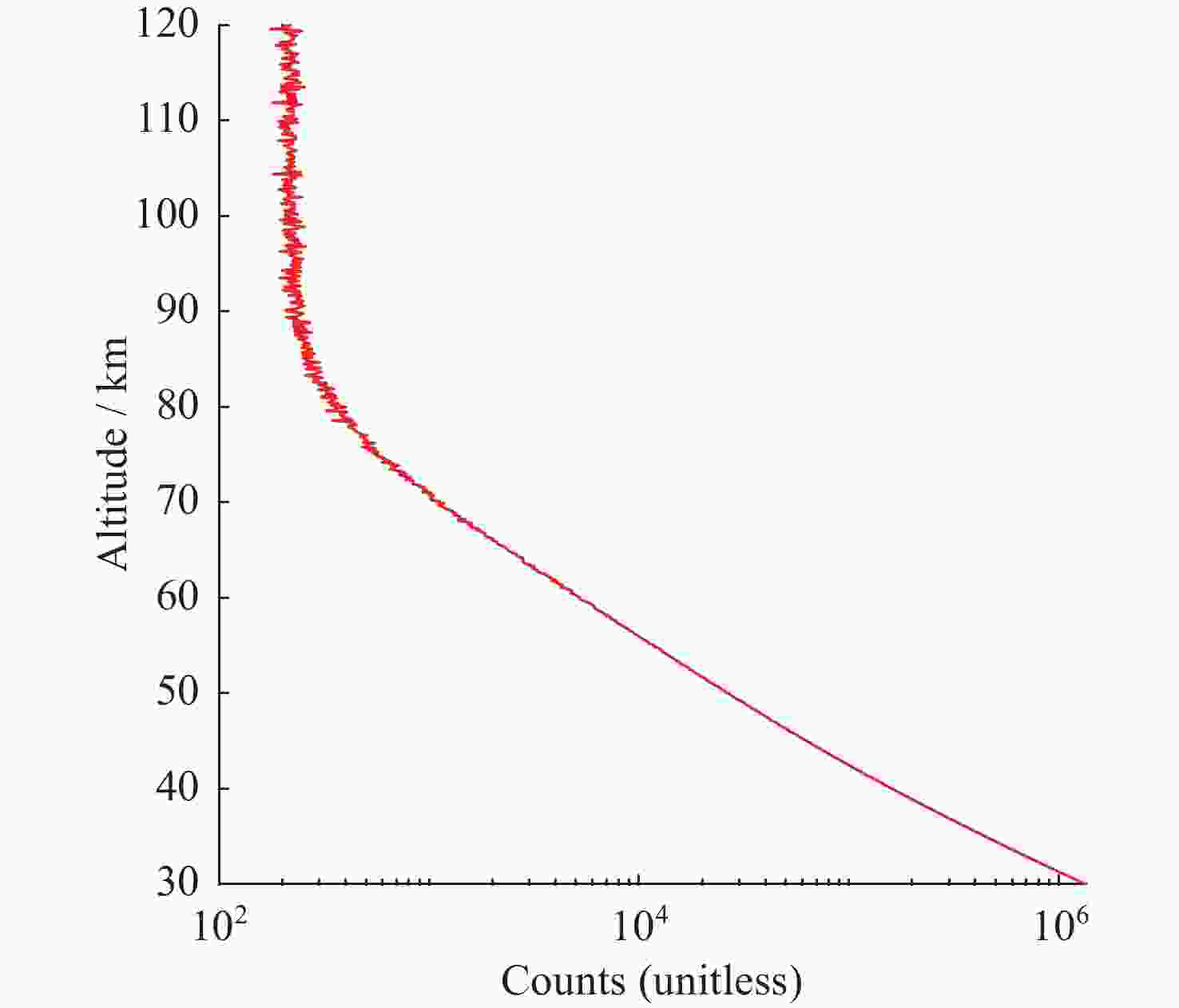
摘要: 基于瑞利激光雷达的回波光子信号对中层大气进行探测,结合最优估计法,对大气温度进行反演。本文基于瑞利散射激光雷达方程建立正向模型,选择大气模型的温度廓线作为先验状态信息,构建用于最优化处理的成本函数,利用Levenberg-Marquardt最优化算法对成本函数执行最优化处理,得到大气温度的反演结果,对反演结果的不确定度分析的同时利用平均核矩阵对反演结果中真实信息的贡献进行评估。利用瑞利激光雷达方程产生的模拟回波信号进行了大气温度的反演处理与分析,对中国科学院国家空间中心提供的瑞利激光雷达实测数据进行大气温度的最优估计反演。结果表明,90 km以下的反演不确定度在10 K以内,且相较于CH方法,最优估计法具有反演有效范围高的优势;在回波光子信噪比较高的区域,反演不确定度较小,且真实信息对反演结果的贡献占主导地位。Abstract: The middle atmosphere is detected based on the echo photon signal of Rayleigh lidar, combined with the optimal estimation method, the atmospheric temperature is retrieved. In this paper, the forward model is established based on the Rayleigh scattering lidar equation, the temperature profile of the atmospheric model is selected as the prior state information, and the cost function for optimization is constructed, and the cost function is optimized using the Levenberg-Marquardt optimization algorithm, get the inversion results of atmospheric temperature, and use the average kernel matrix to evaluate the contribution of the real information in the inversion results while analyzing the uncertainty of the inversion results. Using the simulated echo signal generated by the Rayleigh lidar equation, the inversion processing and analysis of the atmospheric temperature is carried out, and the optimal estimation inversion of the atmospheric temperature is carried out on the Rayleigh lidar measured data provided by the National Space Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. The results show that the inversion uncertainty below 90 km is within 10 K, and compared with the CH method, the optimal estimation method has the advantage of a higher inversion effective range; the inversion uncertainty is small, and the contribution of real information to the inversion results is dominant.
-
Key words:
- Middle atmosphere /
- Rayleigh lidar /
- Optimal estimation method /
- Average kernel matrix
-
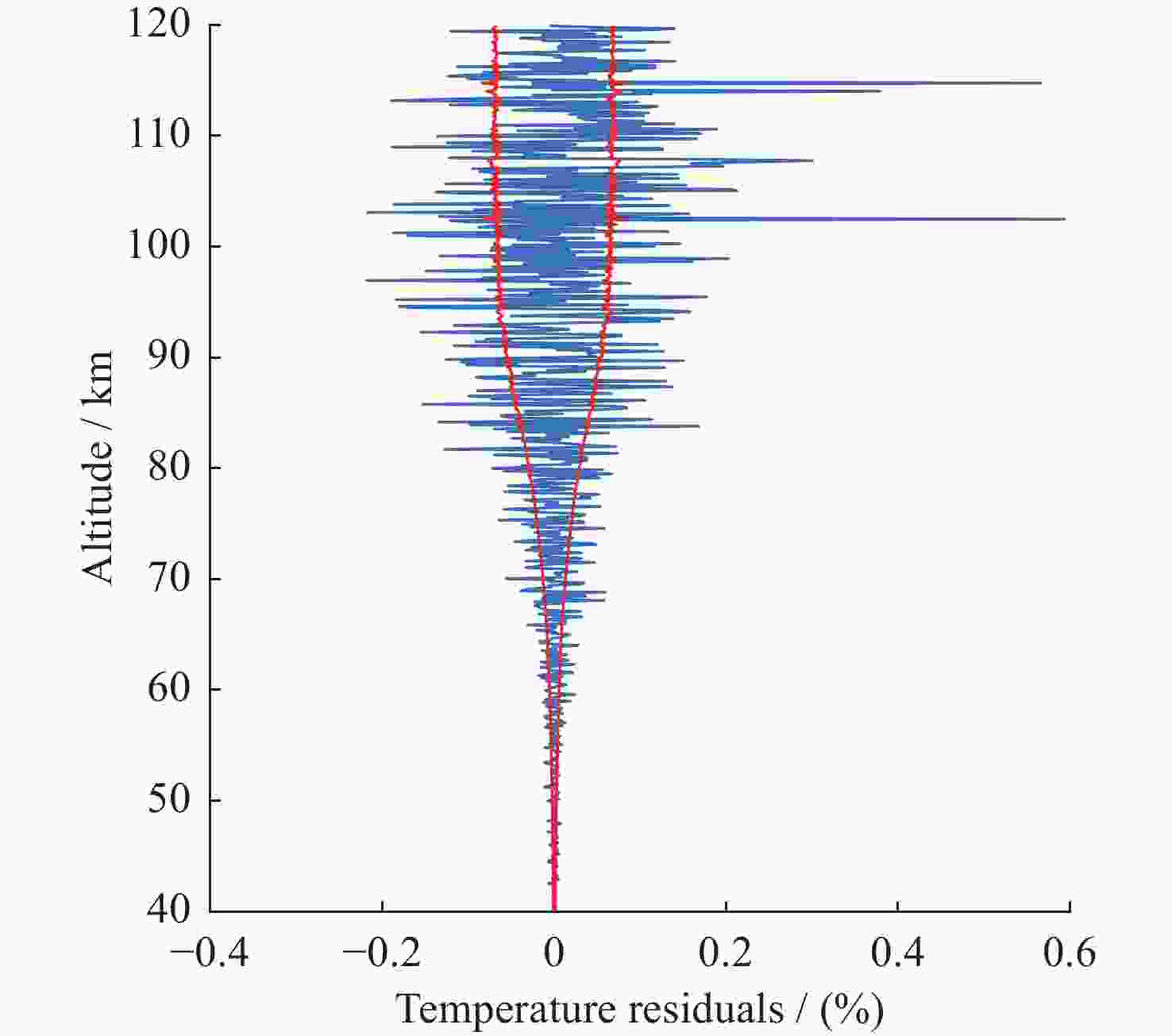
图 13 正向模型与测量值的残差(蓝色曲线是反演状态的正向模型测量值与实际测量值的百分比偏差,红色曲线是测量不确定度占测量值得百分比重)
Figure 13. Residual error between the forward model and the measured value (The blue curve is the percentage deviation between the forward model measured value of the inversion state and the actual measured value, and the red curve is the percentage weight of the measurement uncertainty in the measured value)
表 1 模拟激光雷达系统参数
Table 1. Simulation lidar system parameters
系统参数 参数选值 脉冲能量/ mJ 40 重复频率/ Hz 50 激光波长/ nm 532 望远镜口径/ mm 350 系统效率(unitless) 0.191 表 2 实测数据的瑞利散射激光雷达系统参数
Table 2. National space center rayleigh lidar system parameters
系统参数 参数选值 脉冲能量/mJ 500 脉冲宽度/ns 8 重复频率/Hz 30 激光波长/nm 532 望远镜口径/mm 1000 系统效率(unitless) 0.02 -
[1] HAUCHECORNE A, CHANIN M L. Density and temperature profiles obtained by lidar between 35 and 70 km[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1980, 7(8): 565-568 doi: 10.1029/GL007i008p00565 [2] 刘星, 杨国韬, 王继红, 等. 瑞利激光雷达反演中层大气温度算法[J]. 空间科学学报, 2019, 39(2): 186-190 doi: 10.11728/cjss2019.02.186LIU Xing, YANG Guotao, WANG Jihong, et al. Retrieval algorithm of middle atmospheric temperature using rayleigh lidar[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2019, 39(2): 186-190 doi: 10.11728/cjss2019.02.186 [3] RODGERS C D. Inverse Methods for Atmospheric Sounding: Theory and Practice[M]. Singapore: World Scientific, 2000 [4] MAAHN M, TURNER D D, LÖHNERT U, et al. Optimal estimation retrievals and their uncertainties: what every atmospheric scientist should know[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2020, 101(9): E1512-E1523 doi: 10.1175/BAMS-D-19-0027.1 [5] POVEY A C, GRAINGER R G, PETERS D M, et al. Retrieval of aerosol backscatter, extinction, and lidar ratio from Raman lidar with optimal estimation[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2014, 7(3): 757-776 doi: 10.5194/amt-7-757-2014 [6] SICA R J, HAEFELE A. Retrieval of temperature from a multiple-channel Rayleigh-scatter lidar using an optimal estimation method[J]. Applied Optics, 2015, 54(8): 1872-1889 doi: 10.1364/AO.54.001872 [7] SICA R J, HAEFELE A. Retrieval of water vapor mixing ratio from a multiple channel Raman-scatter lidar using an optimal estimation method[J]. Applied Optics, 2016, 55(4): 763-777 doi: 10.1364/AO.55.000763 [8] WEITKAMP C. Lidar: Range-Resolved Optical Remote Sensing of the Atmosphere[M]. New York: Springer, 2005 [9] LEVENBERG K. A method for the solution of certain non-linear problems in least squares[J]. Quarterly of Applied Mathematics, 1944, 2(2): 164-168 doi: 10.1090/qam/10666 [10] MARQUARDT D W. An algorithm for least-squares estimation of nonlinear parameters[J]. Journal of the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 1963, 11(2): 431-441 doi: 10.1137/0111030 [11] SICA R J, HAEFELE A, JALALI A, et al. How to apply the optimal estimation method to your lidar measurements for improved retrievals of temperature and composition[J]. EPJ Web of Conferences, 2018, 176: 01025 doi: 10.1051/epjconf/201817601025 [12] ARGALL P S. Upper altitude limit for Rayleigh lidar[J]. Annales Geophysicae, 2007, 25(1): 19-25 doi: 10.5194/angeo-25-19-2007 [13] PICONE J M, HEDIN A E, DROB D P, et al. NRLMSISE-00 empirical model of the atmosphere: statistical comparisons and scientific issues[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2002, 107(A12): 1468 [14] National Geophysical Data Center. U. S. standard atmosphere (1976)[J]. Planetary and Space Science, 1992, 40(4): 553-554 [15] CHANDRA S, FLEMING E L, SCHOEBERL M R, et al. Monthly mean global climatology of temperature, wind, geopotential height and pressure for 0-120 km[J]. Advances in Space Research, 1990, 10(6): 3-12 doi: 10.1016/0273-1177(90)90230-W [16] ERIKSSON P, JIMÉNEZ C, BUEHLER S A. Qpack, a general tool for instrument simulation and retrieval work[J]. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer, 2005, 91(1): 47-64 doi: 10.1016/j.jqsrt.2004.05.050 [17] BUEHLER S A, MENDROK J, ERIKSSON P, et al. ARTS, the Atmospheric Radiative Transfer Simulator - version 2.2, the planetary toolbox edition[J]. Geoscientific Model Development, 2018, 11(4): 1537-1556 doi: 10.5194/gmd-11-1537-2018 [18] BERENS P. CircStat: A MATLAB toolbox for circular statistics[J]. Journal of Statistical Software, 2009, 31(10): 1-21 -
-





 下载:
下载: