Beidou Satellite-based Augmentation System Performance Evaluation Analysis
-
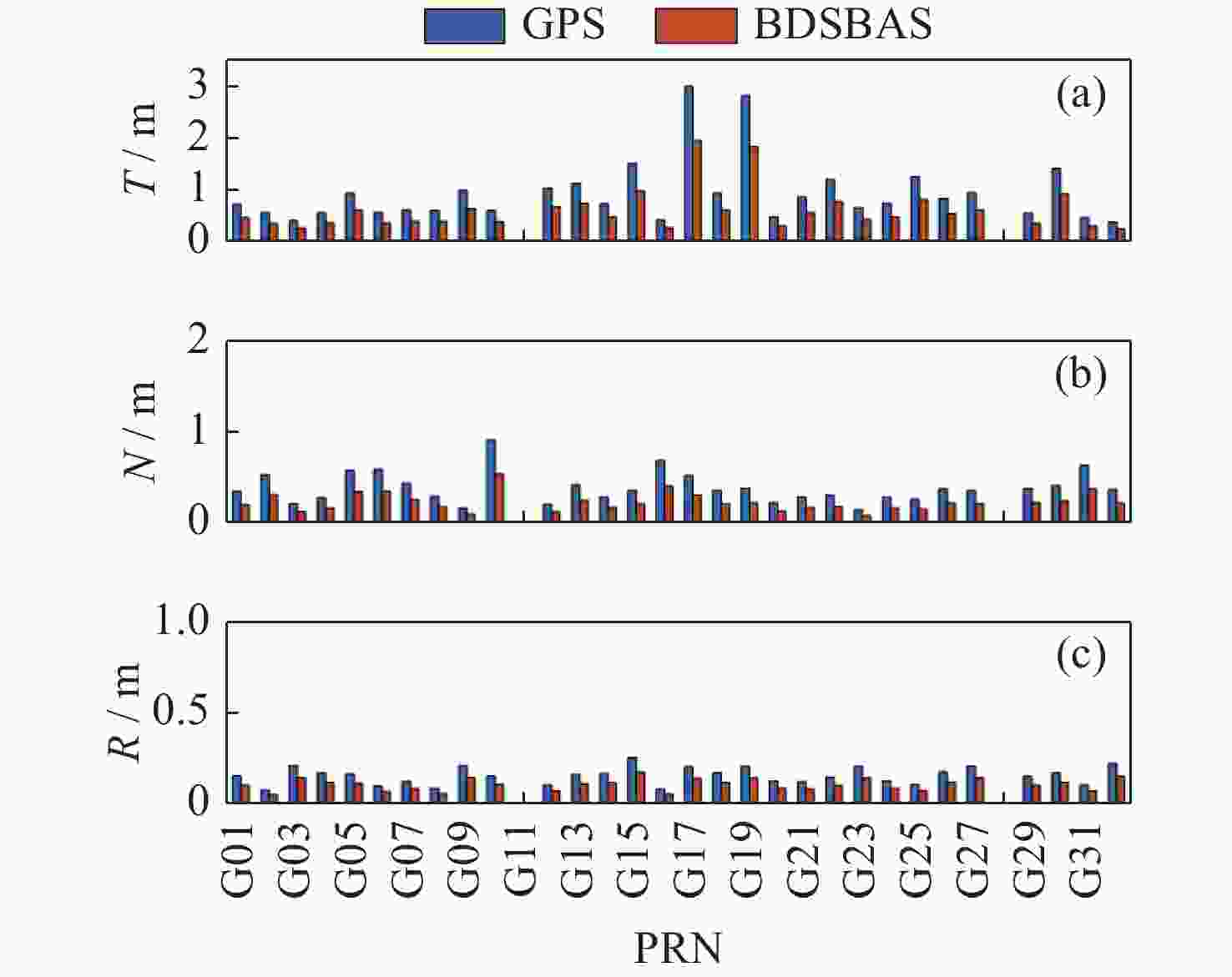
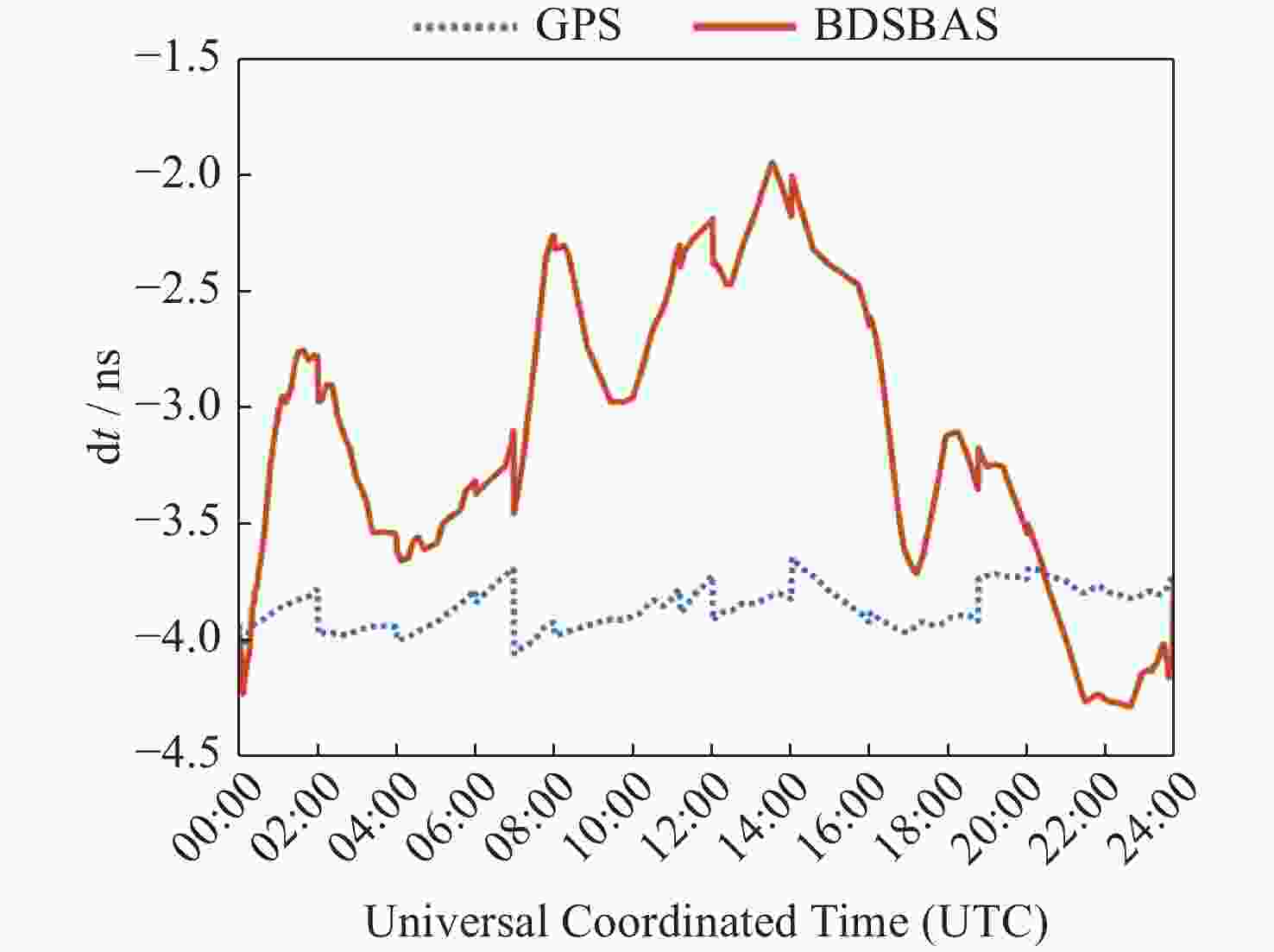
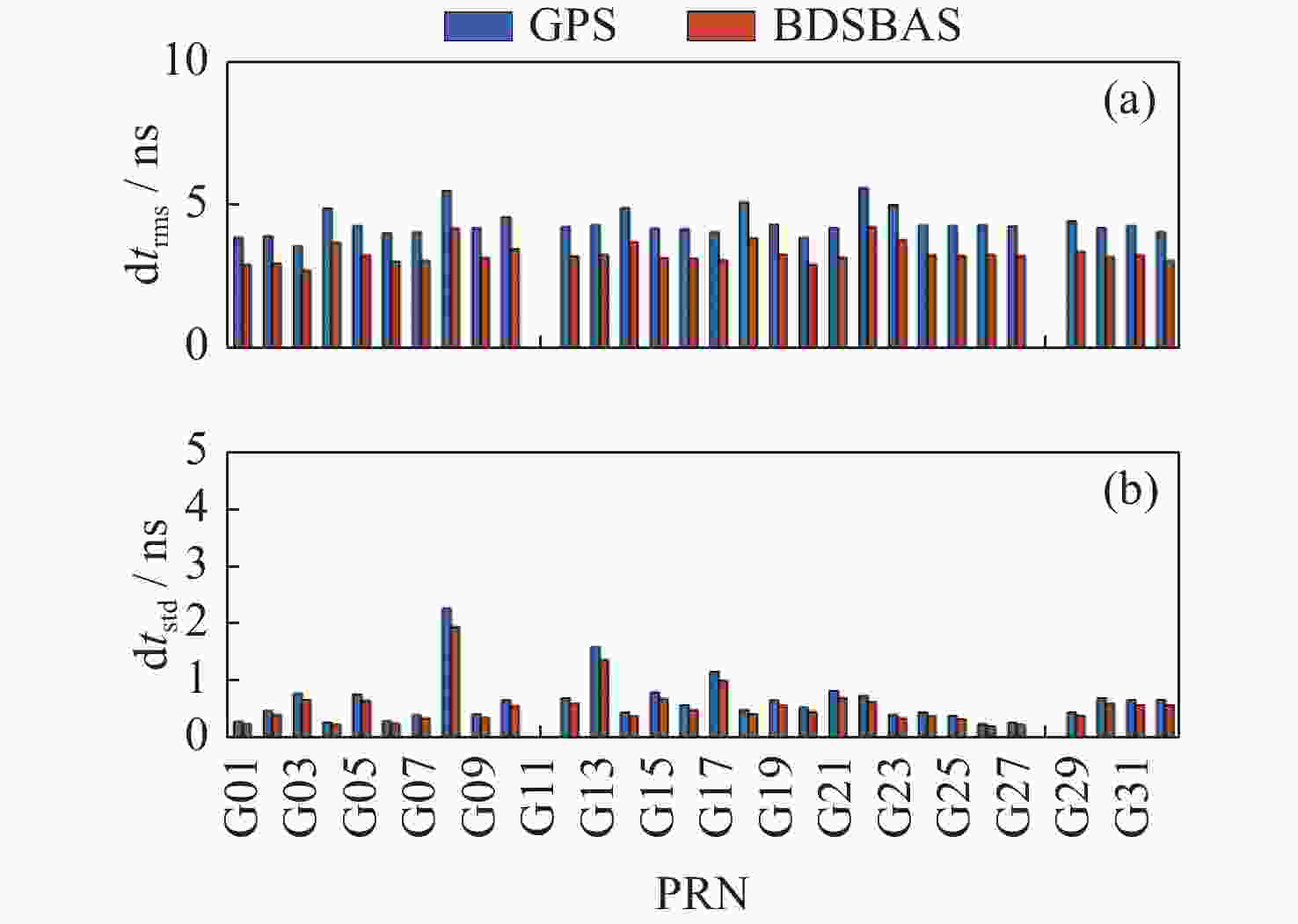
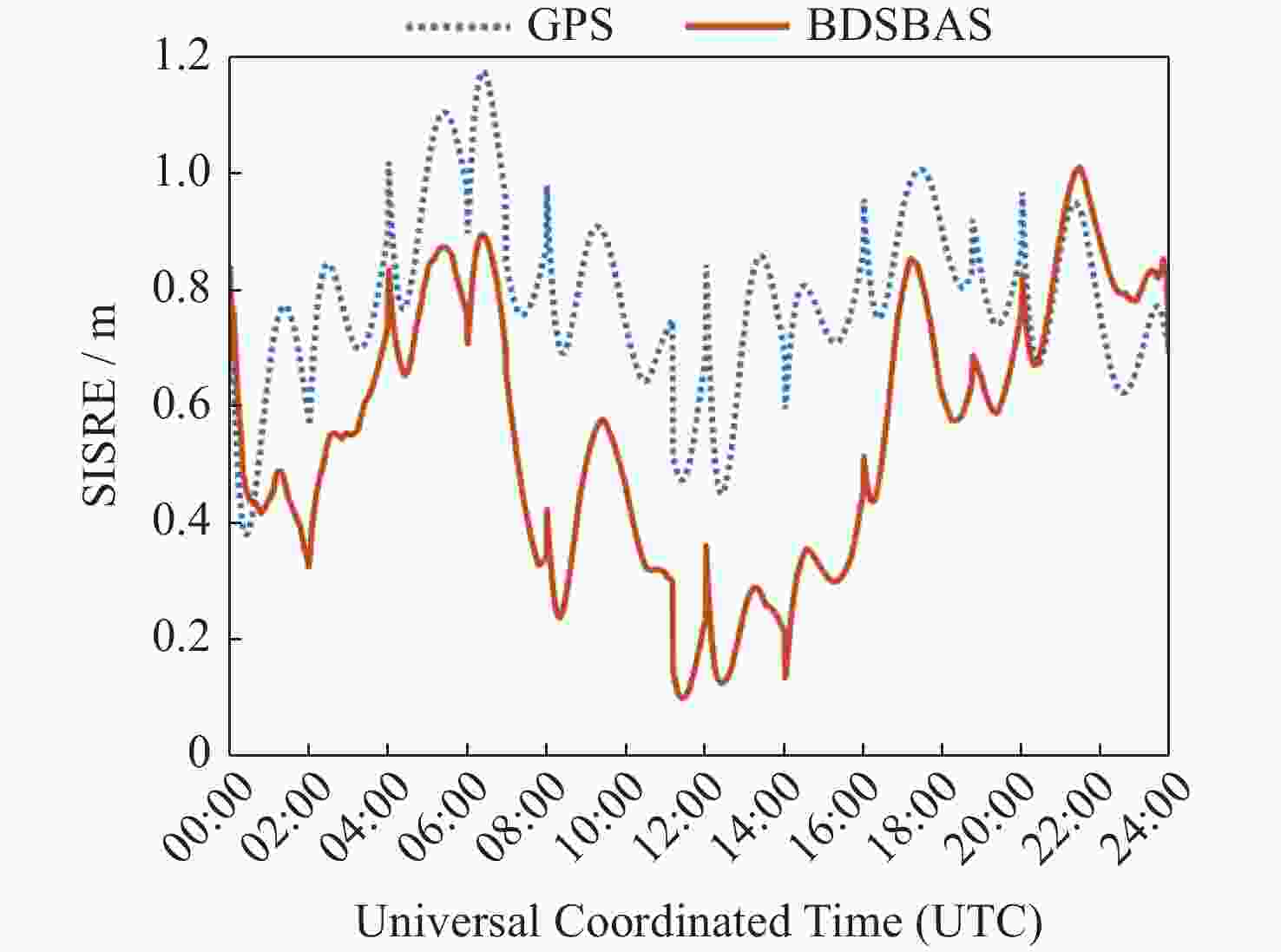
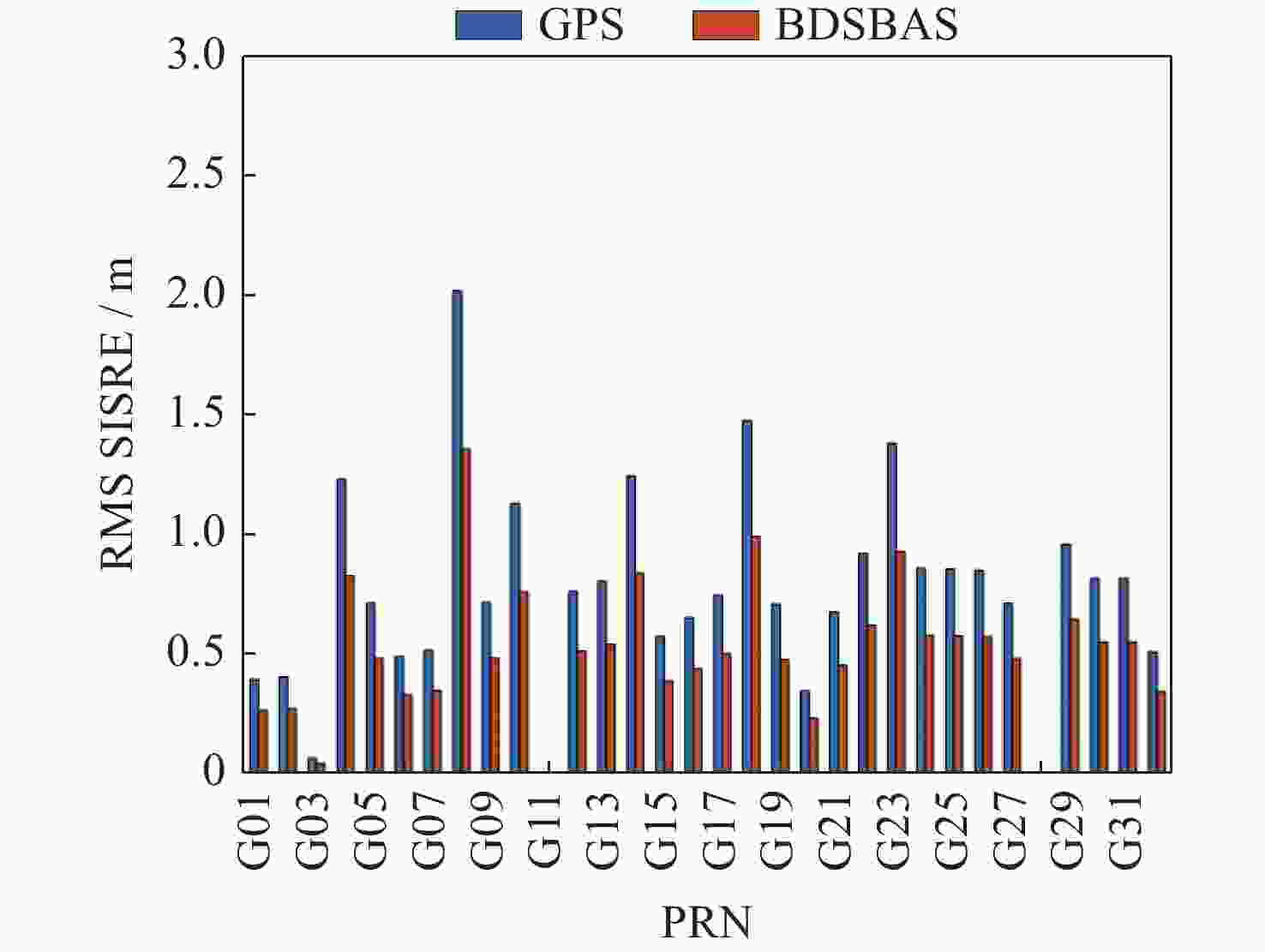
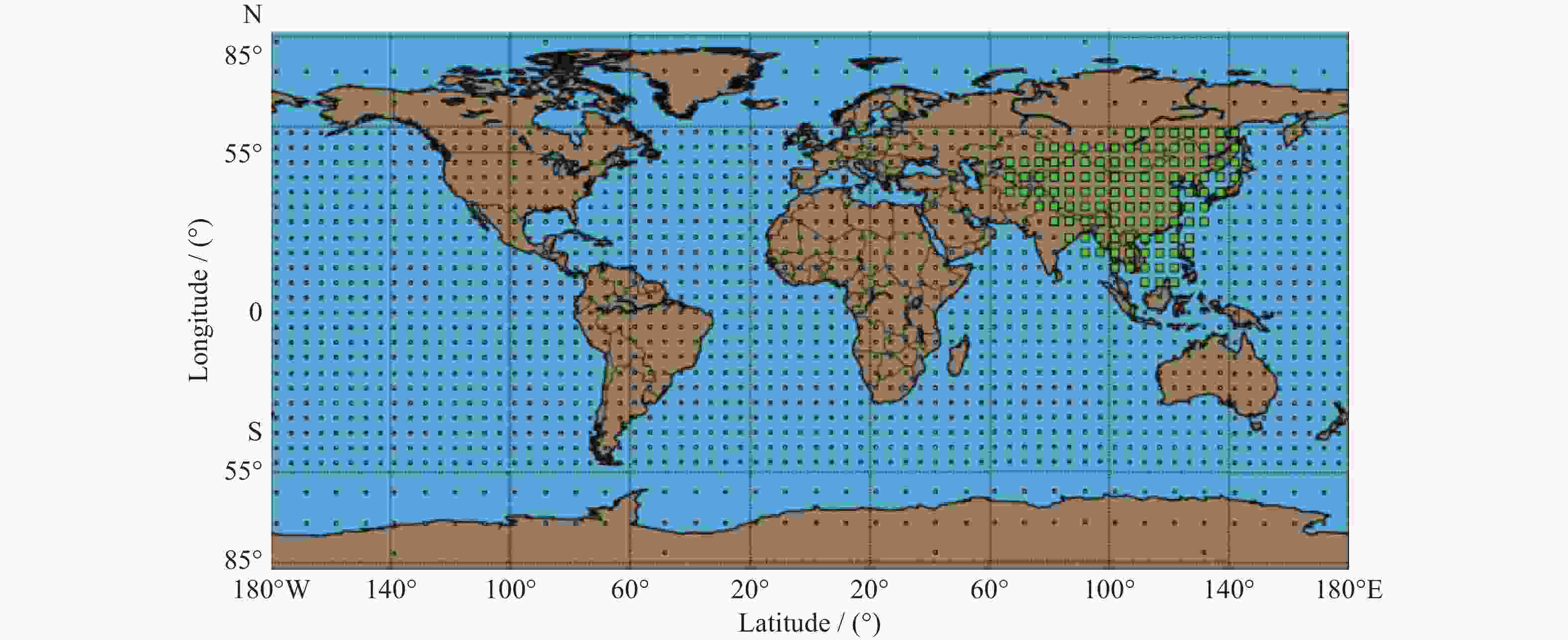
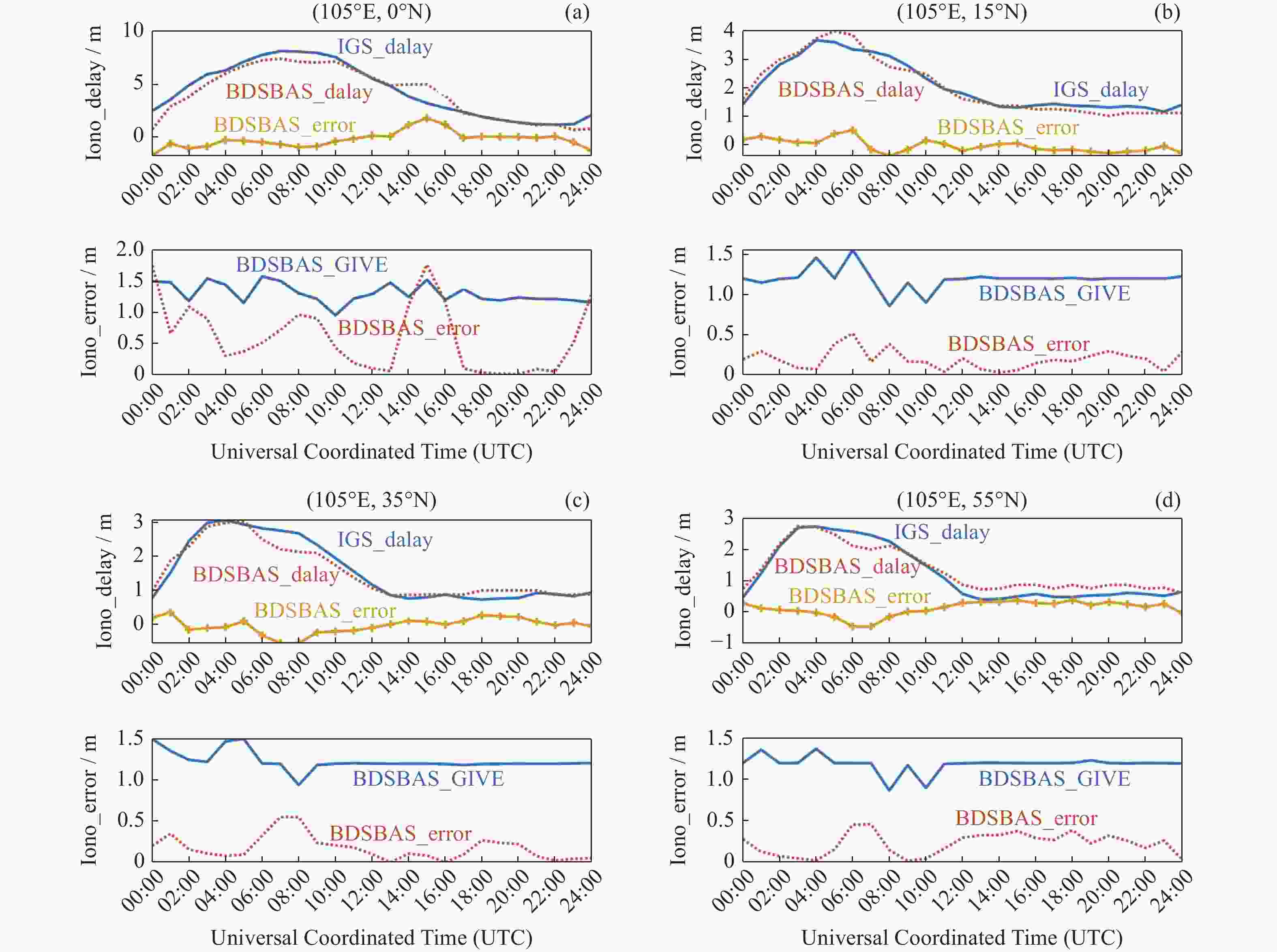
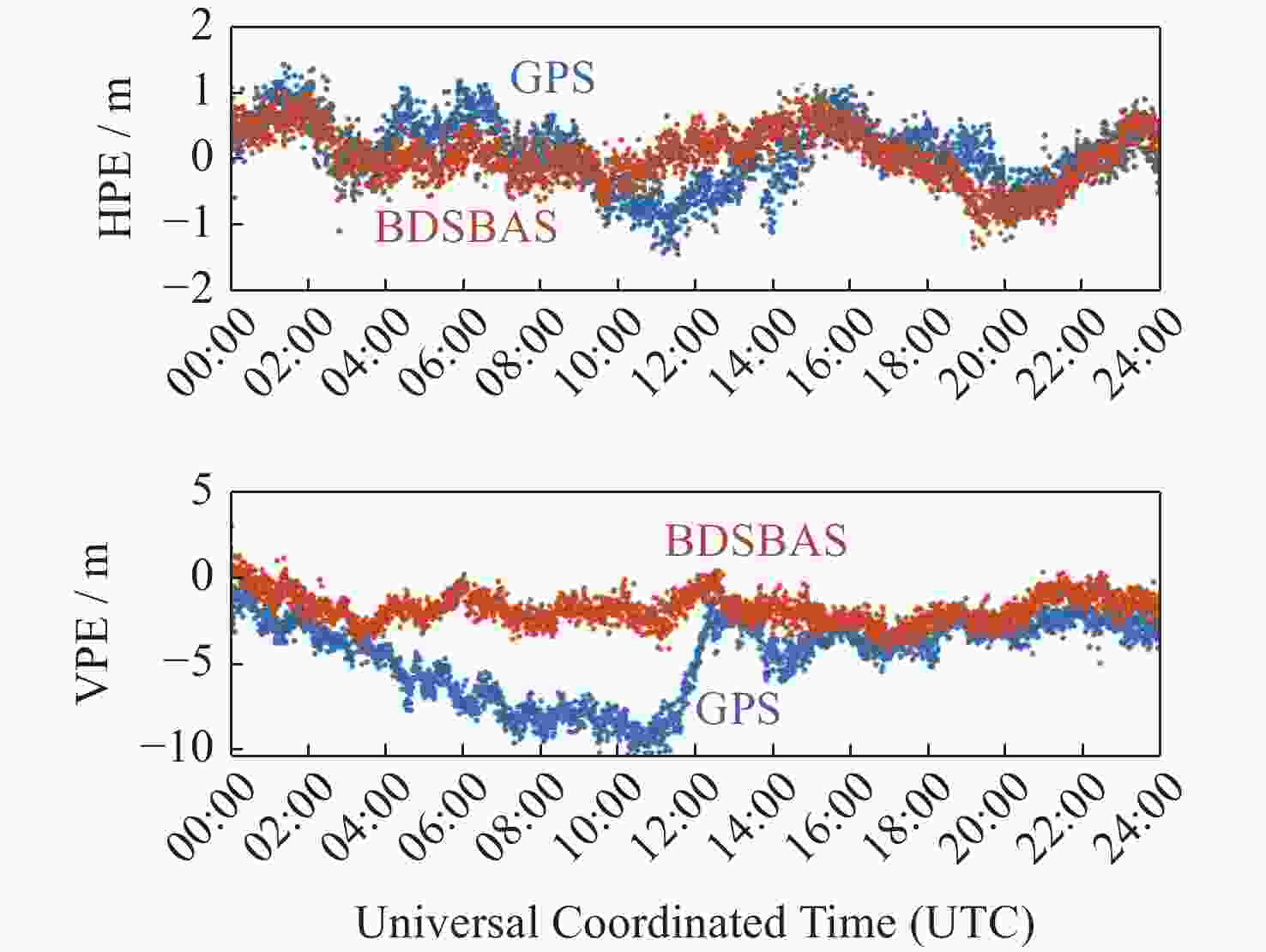
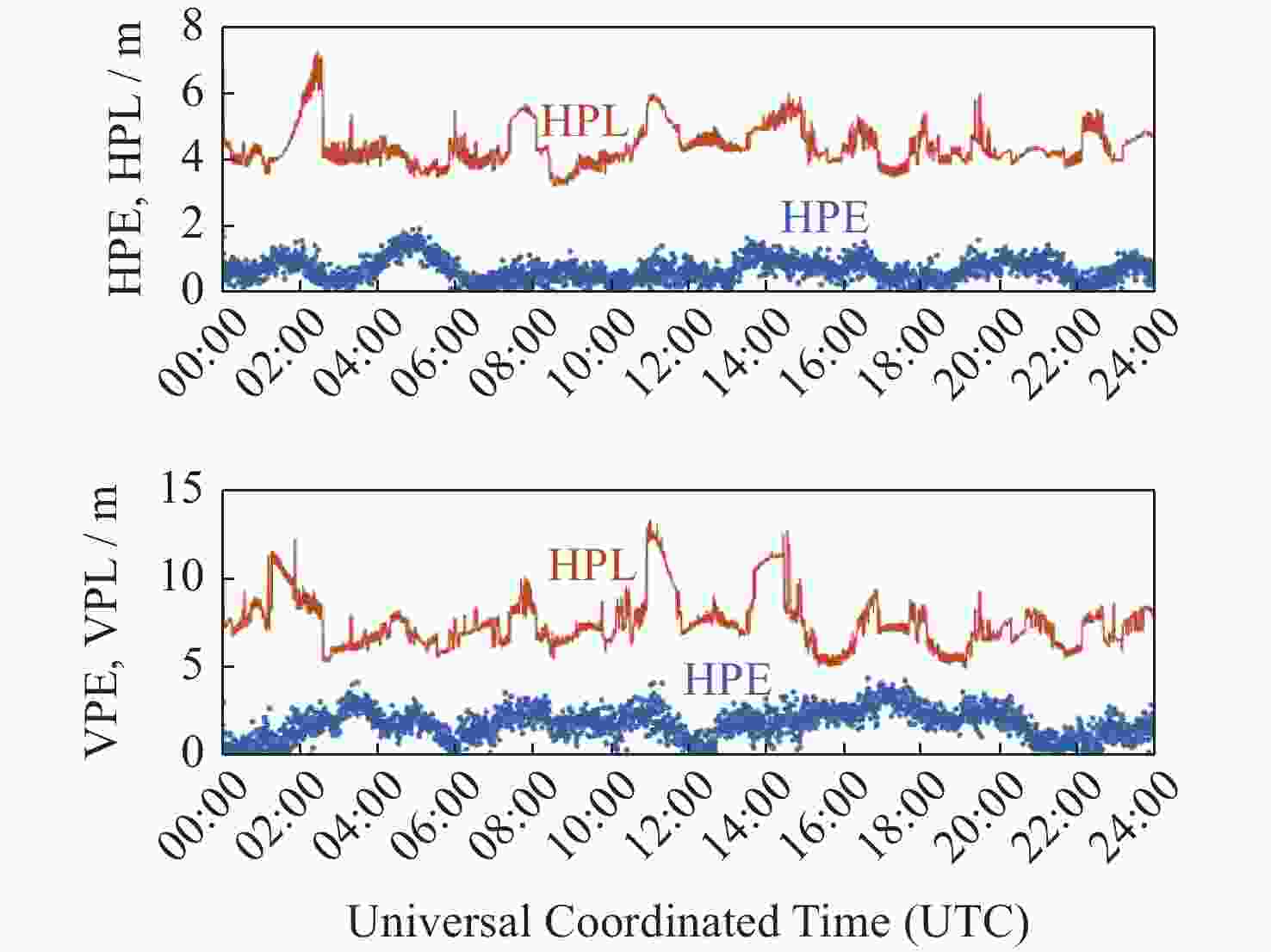
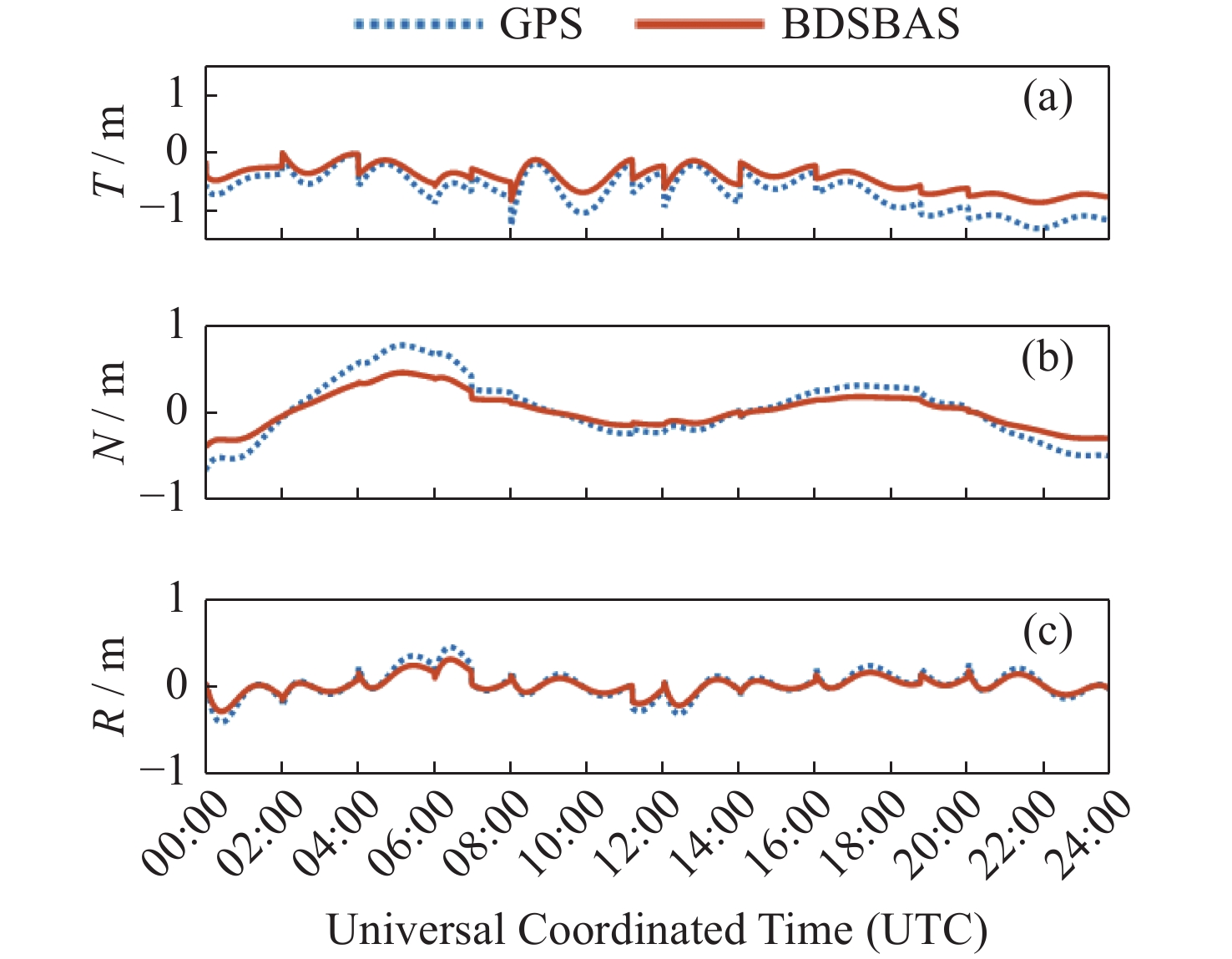
摘要: 以实际广播星历、精密星历和北斗星基增强系统(BDSBAS)增强报文为实验数据,通过计算BDSBAS轨道误差、卫星钟差、空间信号测距误差和BDSBAS格网电离层有效点、播发时间和电离层延迟误差6个指标,评估分析了BDSBAS空间信号的性能。结果显示:BDSBAS增强后的GPS卫星轨道误差在切向、法向、径向分别降低了34.57%,40.57%,30.90%;卫星钟差均方根降低了24.31%,卫星钟差标准差降低了16.8%;空间信号测距误差相比增强前降低了32.75%;BDSBAS格网电离层有效点覆盖了中国及周边地区;BDSBAS各点电离层延迟播发间隔均达到ICAO对精确差分定位的要求;电离层延迟在0°-5°N范围内误差在0.4 m以上,可信度均达到99.9%,在5°-55°N范围内误差小于0.4 m,可信度均为100%;BDSBAS水平定位误差提升超过25%,垂直定位误差提升超过50%,完好性均在99.9%以上。Abstract: In this paper, the performance of the BDSBAS space signal was evaluated and analyzed by calculating six indicators: BDSBAS orbit error, satellite clock difference, space signal ranging error and BDSBAS grid ionospheric effective point, broadcast time and ionospheric delay error, using actual broadcast ephemeris, precision ephemeris and augmentation messages of Beidou Satellite-Based Augmentation System (BDSBAS) as experimental data. Results showed that the orbital errors of GPS satellites after BDSBAS enhancement were reduced by 34.57%, 40.57% and 30.90% in tangential, normal and radial directions respectively; the root mean square of satellite clock deviation was reduced by 24.31%, and the standard deviation of satellite clock deviation was reduced by 16.8%; the spatial signal ranging error was reduced by 32.75% compared with that before enhancement; the effective ionospheric points of BDSBAS grid. The ionospheric delay broadcast interval of all BDSBAS points meets ICAO’s requirements for accurate differential positioning; the ionospheric delay error in the range of 0°-5°N is more than 0.4 m with a confidence level of 99.9%, and in the range of 5°-55°N, the error is less than 0.4 m with a confidence level of 100%; the horizontal positioning error of BDSBAS is improved by more than 25% improvement in horizontal positioning error and over 50% improvement in vertical positioning error, all with an integrity of 99.9% or more.
-
表 1 BDSBAS-B1 C频点播发电文类型
Table 1. BDSBAS-B1 C frequency broadcast message types
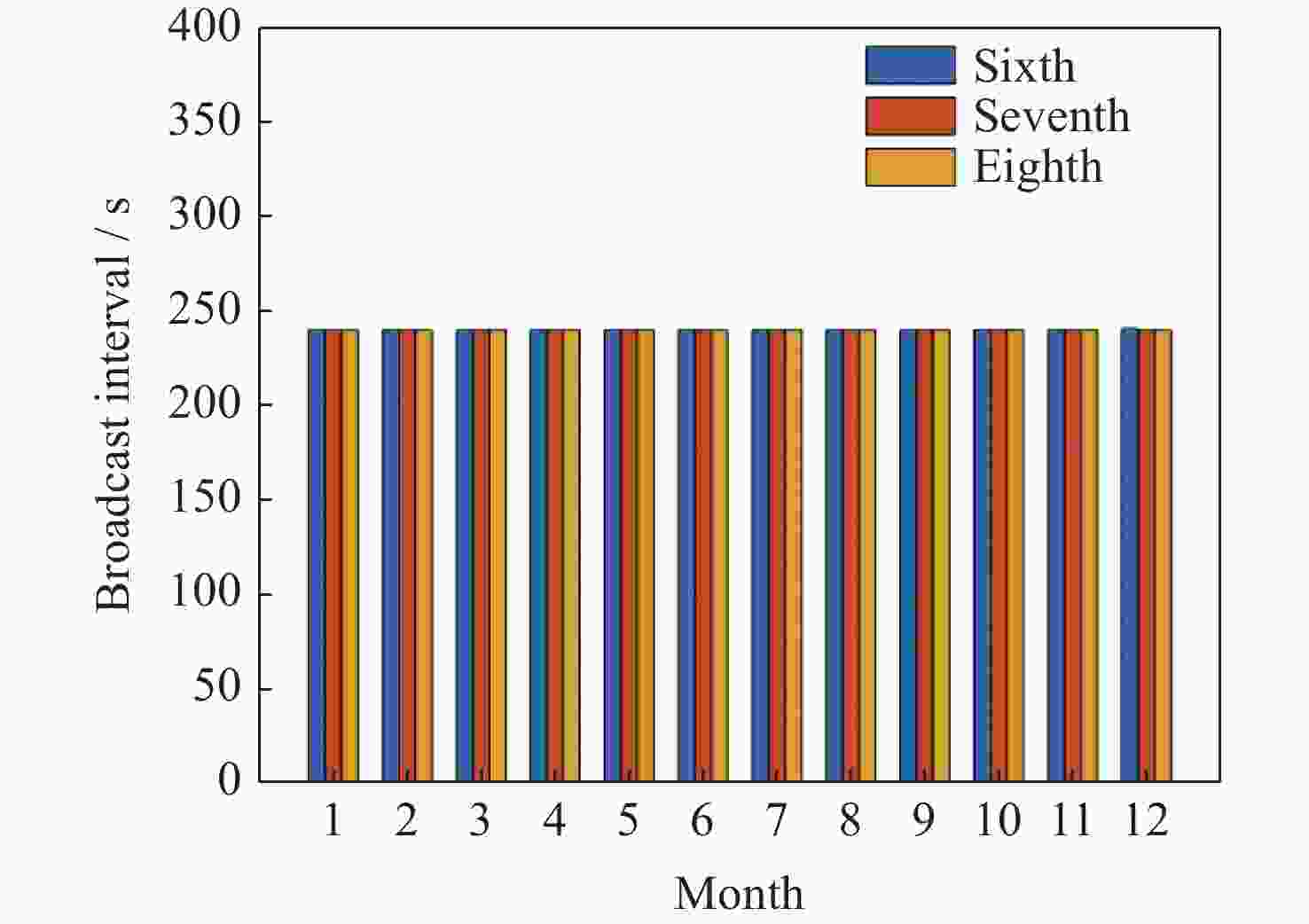
电文类型 电文内容 0 系统测试 1 PRN掩码 2~5 快变改正数 6 完好性信息 7 快变改正数降效因子 9 GEO卫星星历 10 降效参数 12 SNT与UTC偏差 17 GEO卫星星历 18 电离层格网掩码 24 快慢变混合改正数 25 慢变改正数 26 电离层延迟改正数 28 卫星时钟/星历协方差矩阵 62 内部测试信息 63 空白信息 表 2 数据广播间隔和所支持的功能
Table 2. Data broadcast interval and supported features
数据类型 最大广播间隔 基本差
分校正精确差分校正 电离层网格掩码 300 s - √ 电离层校正,GIVEI 300 s - √ 注 “√” 表示支持该功能必须广播的数据。 表 3 BDSBAS格网电离层延迟误差统计
Table 3. Statistics of BDSBAS grid ionospheric delay error
纬度 N /(°) Emax / m Erms / m C/(%) 0 1.72 0.81 95 5 0.75 0.42 100 10 0.52 0.34 100 15 0.47 0.26 100 20 0.50 0.22 100 25 0.46 0.23 100 30 0.55 0.25 100 35 0.53 0.24 100 40 0.54 0.23 100 45 0.50 0.26 100 50 0.51 0.23 100 55 0.46 0.26 100 表 4 BDSBAS定位精度
Table 4. BDSBAS positioning accuracy
Station Error/m GPS BDSBAS 误差减少/(%) BJFS HPE 0.63 0.46 26.9 VPE 4.86 2.24 53.9 JFNG HPE 0.68 0.45 33.8 VPE 3.86 1.98 48.7 HKSL HPE 0.87 0.54 37.9 VPE 5.12 2.33 54.5 TNML HPE 1.12 0.79 29.5 VPE 4.64 2.24 51.7 POL2 HPE 0.73 0.51 30.1 VPE 4.96 2.16 56.5 表 5 2021年BDSBAS定位完好性
Table 5. BDSBAS positioning integrity in 2021
台站 水平方向/(%) 垂直方向/(%) BJFS 100 100 JFNG 100 100 HKSL 100 100 TNML 99.9 99.9 POL2 100 99.9 -
[1] 蔡洪亮, 孟轶男, 耿长江, 等. 北斗三号全球导航卫星系统服务性能评估: 定位导航授时、星基增强、精密单点定位、短报文通信与国际搜救[J]. 测绘学报, 2021, 50(4): 427-435CAI Hongliang, MENG Yinan, GENG Changjiang, et al. BDS-3 performance assessment: PNT, SBAS, PPP, SMC and SAR[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2021, 50(4): 427-435 [2] CHEN J P, ZHANG Y Z, YU C, et al. Models and performance of SBAS and PPP of BDS[J]. Satellite Navigation, 2022, 3(1): 4 doi: 10.1186/s43020-022-00065-3 [3] 邵搏, 耿永超, 丁群, 等. 国际星基增强系统综述[J]. 现代导航, 2017, 8(3): 157-161 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7976.2017.03.001SHAO Bo, GENG Yongchao, DING Qun, et al. Summarize of international satellite based augmentation system[J]. Modern Navigation, 2017, 8(3): 157-161 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7976.2017.03.001 [4] ISBN 978-92-9258-504-4. International standards and recommended practices annex 10 vol. I. radio navigation aids[S]. Canada: ICAO, 2018 [5] NIE Z X, ZHOU P Y, LIU F, et al. Evaluation of orbit, clock and ionospheric corrections from five currently available SBAS L1 services: methodology and analysis[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(4): 411 doi: 10.3390/rs11040411 [6] ROVIRA-GARCIA A, JUAN J M, SANZ J, et al. Accuracy of ionospheric models used in GNSS and SBAS: methodology and analysis[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2016, 90(3): 229-240 doi: 10.1007/s00190-015-0868-3 [7] BAHRAMI M, FFOULKES-JONES G, ZHANG Q. Analysis of SBAS orbit and clock corrections for GPS and their applicability to today’s mass market multi-GNSS personal navigation[C]//29 th International Technical Meeting of The Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2016). Portland: ION, 2016 [8] 熊帅, 张键, 邵搏, 等. 北斗星基增强系统用户单频增强定位方法与精度评估[C]//第十二届中国卫星导航年会论文集——S03 导航信号与信号处理. 南昌: 中国卫星导航学术年会组委会, 2021: 46-64XIONG Shuai, ZHANG Jian, SHAO Bo, et al. Single-frequency augmented positioning method and accuracy evaluation for users of BeiDou satellite-based augmentation system[C]//Proceedings of the 12th Annual China Satellite Navigation Conference-S03 Navigation Signal and Signal Processing. Nanchang: China Satellite Navigation Conference, 2021: 46-64 [9] 张键, 邵搏, 熊帅, 等. 北斗星基增强系统单频服务区域可用性评估[J]. 导航定位与授时, 2021, 8(3): 137-145 doi: 10.19306/j.cnki.2095-8110.2021.03.018ZHANG Jian, SHAO Bo, XIONG Shuai, et al. Regional single frequency service availability evaluation of BDSBAS[J]. Navigation Positioning and Timing, 2021, 8(3): 137-145 doi: 10.19306/j.cnki.2095-8110.2021.03.018 [10] 金彪, 陈姗姗, 李祝莲, 等. SBAS GEO卫星URE精度及定位增强研究[J/OL]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2022: 1-11. [2022-03-22]. https://www.doc88.com/p-41873061468929.htmlJIN Biao, CHEN Shanshan, LI Zhulian, et al. SBAS GEO satellite user range error and position augmentation research[J/OL]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2022: 1-11. [2022-03-22]. https://www.doc88.com/p-41873061468929.html [11] FAA. Global positioning system Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS) performance standard[S]. Washington: FAA, 2008 [12] NSTB/WAAS T&E Team. Wide Area Augmentation System Performance Analysis Report[R]. Atlantic City International Airport: FAA William J. Hughes Technical Center, 2021 [13] KIM M, KIM J. A long-term analysis of the GPS broadcast orbit and clock error variations[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2015, 99: 654-658 doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2014.12.585 [14] U. S. Department of Defense. Global Positioning System Standard Positioning Service Performance Standard (4.0 th ed)[R]. Washington: U. S. Department of Defense, 2008: A17-A19 [15] CHEN J P, HU X G, TANG C P, et al. SIS accuracy and service performance of the BDS-3 basic system[J]. Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 2020, 63(6): 269511 [16] 刘路, 郭金运, 周茂盛, 等. GNSS广播星历轨道和钟差精度分析[J]. 武汉大学学报·信息科学版, 2022, 47(7): 1122-1132 doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20200166LIU Lu, GUO Jinyun, ZHOU Maosheng, et al. Accuracy analysis of GNSS broadcast ephemeris orbit and clock offset[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2022, 47(7): 1122-1132 doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20200166 [17] 严悦. WGS84与ITRF框架间的坐标转换分析[J]. 地理空间信息, 2021, 19(1): 74-77 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4623.2021.01.020YAN Yue. Analysis of the coordinate conversion between WGS84 and ITRF frame[J]. Geospatial Information, 2021, 19(1): 74-77 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4623.2021.01.020 [18] 张小红, 李盼, 李星星, 等. 天线相位中心改正模型对PPP参数估计的影响[J]. 武汉大学学报·信息科学版, 2011, 36(12): 1470-1473 doi: 10.13203/j.whugis2011.12.018ZHANG Xiaohong, LI Pan, LI Xingxing, et al. Influence of antenna phase center correction model on precise point positioning[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2011, 36(12): 1470-1473 doi: 10.13203/j.whugis2011.12.018 [19] 常志巧, 陈金平, 刘利, 等. WAAS电离层格网播发特性及其性能评估[J]. 天文学进展, 2021, 39(2): 265-275 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8349.2021.02.07CHANG Zhiqiao, CHEN Jinping, LIU Li, et al. Broadcast characteristics and performance evaluation of WAAS ionospheric grid[J]. Progress in Astronomy, 2021, 39(2): 265-275 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8349.2021.02.07 [20] YIN P, SHI S R, REN D D. SBAS ionospheric grid delay estimation based on ionospheric tomography: a case study on September 7-9, 2017[J]. GPS Solutions, 2022, 26(3): 86 doi: 10.1007/s10291-022-01259-7 [21] BILITZA D, MCKINNELL L A, REINISCH B, et al. The international reference ionosphere today and in the future[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2011, 85(12): 909-920 doi: 10.1007/s00190-010-0427-x [22] LIU A, WANG N B, LI Z S, et al. Validation of CAS’s final global ionospheric maps during different geomagnetic activities from 2015 to 2017[J]. Results in Physics, 2018, 10: 481-486 doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2018.06.057 [23] 中国卫星导航系统管理办公室. 北斗卫星导航系统空间信号接口控制文件星基增强服务信号BDSBAS-B1 C(1.0版)[EB/OL]. 2020. http://www.beidou.gov.cn/yw/xwzx/202008/t20200803_20930.htmlChina Satellite Navigation Office. BeiDou navigation satellite system signal in space interface control document: satellite-based augmentation system service signal BDSBAS-B1 C (version 1.0)[EB/OL]. 2020. http://www.beidou.gov.cn/yw/xwzx/202008/t20200803_20930.html [24] 黄观文. GNSS星载原子钟质量评价及精密钟差算法研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2012HUANG Guanwen. Research on Algorithms of Precise Clock Offset and Quality Evaluation of GNSS Satellite Clock[D]. Xi’an: Chang'an University, 2012 -
-





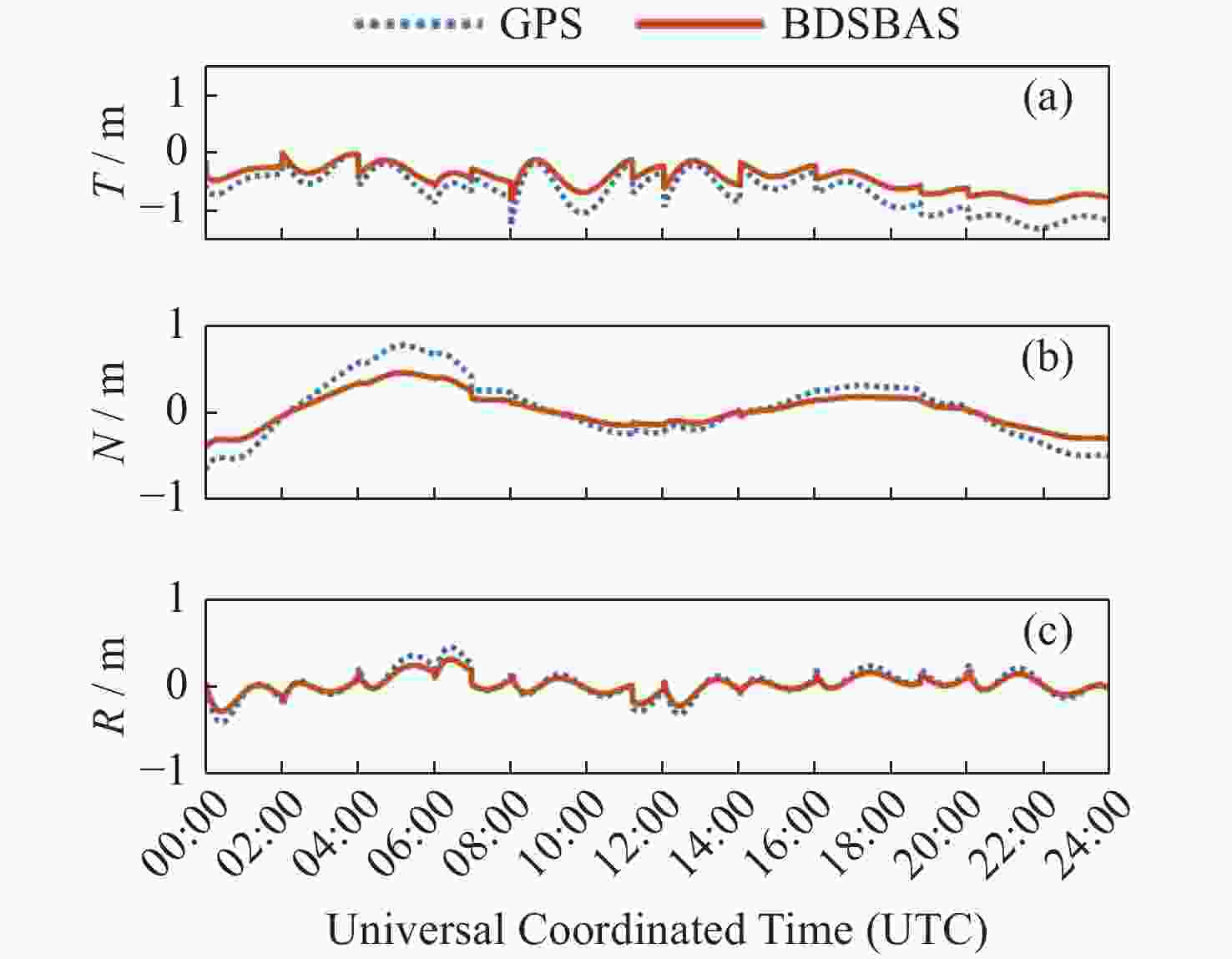
 下载:
下载: