基于XGBoost的空间高温材料实验炉控制系统建模
doi: 10.11728/cjss2023.04.2022-0061 cstr: 32142.14.cjss2023.04.2022-0061
Modeling of Temperature Control System of Space Experiment High-temperature Furnace Based on XGBoost
-
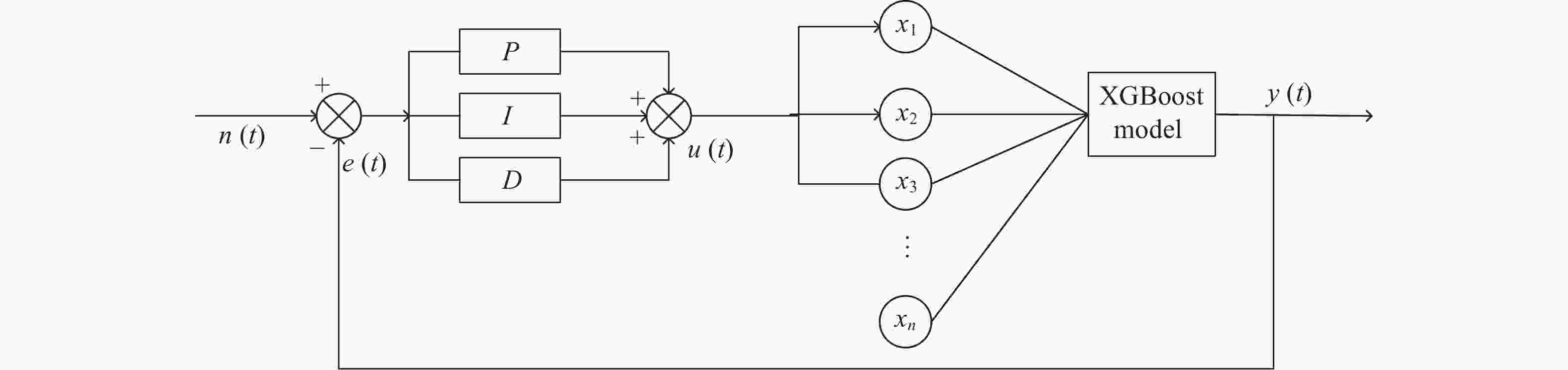
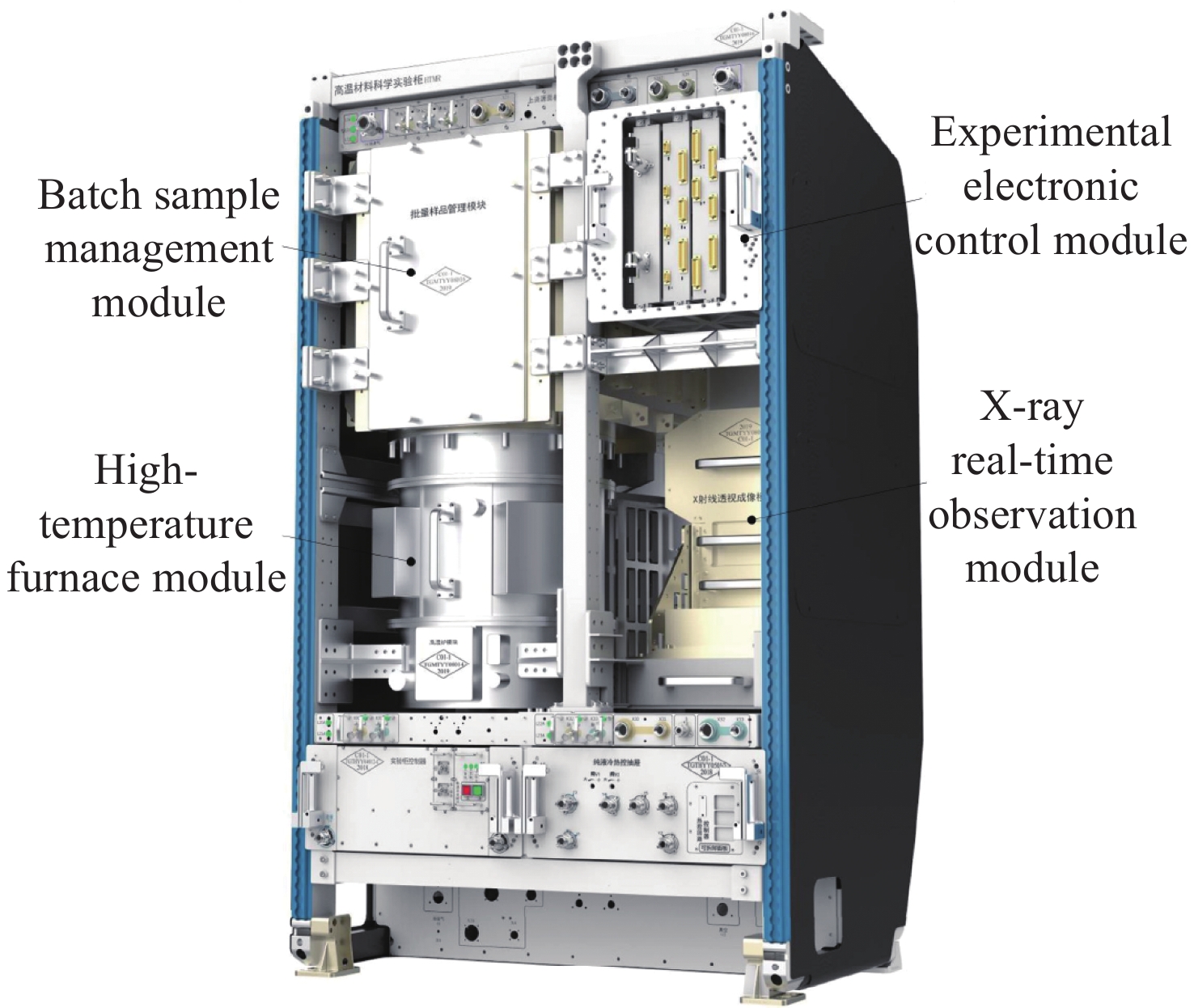
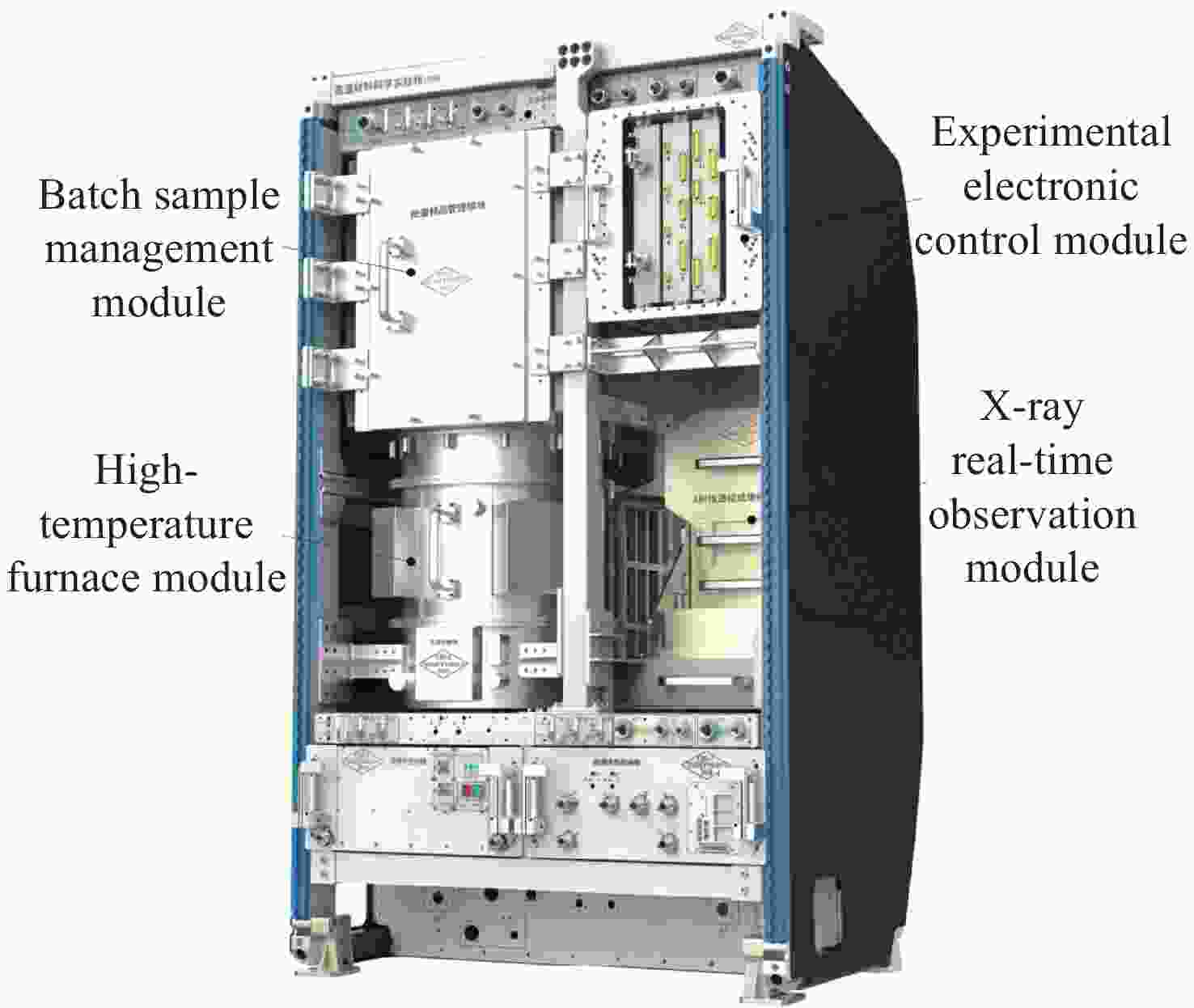
摘要: 为确保高温材料科学实验柜科学实验系统能够成功地进行空间材料科学实验,在空间进行高温材料科学实验的时候要求其温度稳定在±0.25℃范围内。面对如此之高的温度稳定度要求,提出一个新的解决方案:在实验输入和输出数据的基础上,确定一个与高温炉控制系统内部等价的模型,为获得满足实验要求的控制参数提供依据。本文将高温炉控制系统内部看作黑箱模型,基于XGBoost方法分别对四类样品实验的高温炉内部温区2和温区3进行建模,模型精确度全部可达到99.98%以上。与传统建模方式传递函数相对比,在传统方法表现最好的情况下,模型精度仍提高了3.8%,为获得控制参数以确保空间实验温度实现高稳定度提供了重要支持。Abstract: With the development of China’s space industry, the construction of China’s space station has been completed in 2022. In the future, China will carry out a series of space material science experiments in space. The high-temperature furnace in the high-temperature material science experimental rack, as the main equipment of the space material science experiment, requires the high-temperature furnace’s temperature to be stable within ± 0.25℃ when conducting the high temperature material science experiment in space. In the face of such high temperature stability requirements, in order to ensure that the scientific experimental system of the high-temperature material science rack can successfully conduct the space material science experiment, it is necessary to first establish the mathematical model of the high-temperature furnace control system. Because the object of high-temperature furnace is a kind of nonlinear and time-delay complex control object, it is difficult to model based on mechanism. To solve this problem, this paper proposes a new solution: based on the experimental input and output data, an intelligent modeling method is adopted to determine an internal equivalent model of the high-temperature furnace control system, which provides a basis for obtaining control parameters that meet the experimental requirements. In this paper, the control system of high-temperature furnace is regarded as a black box model, and four representative sample experimental data are selected. Based on XGBoost method, the mathematical models of temperature zone 2 and temperature zone 3 control system of high-temperature furnace are established respectively. The accuracy of the models can all reach more than 99.98%. Compared with the traditional modeling method, the transfer function is used as the basic model for parameter estimation, and the modeling effect varies according to different samples. In addition, under the best performance of traditional methods, the accuracy of the model based on XGBoost is still improved by 3.8%. The experimental results show that the modeling effect of high-temperature furnace control system based on XGBoost method is good, and the model provides important support for obtaining control parameters to ensure high stability of space experimental temperature.
-
Key words:
- XGBoost /
- Transfer function /
- System identification /
- High-temperature furnace
-
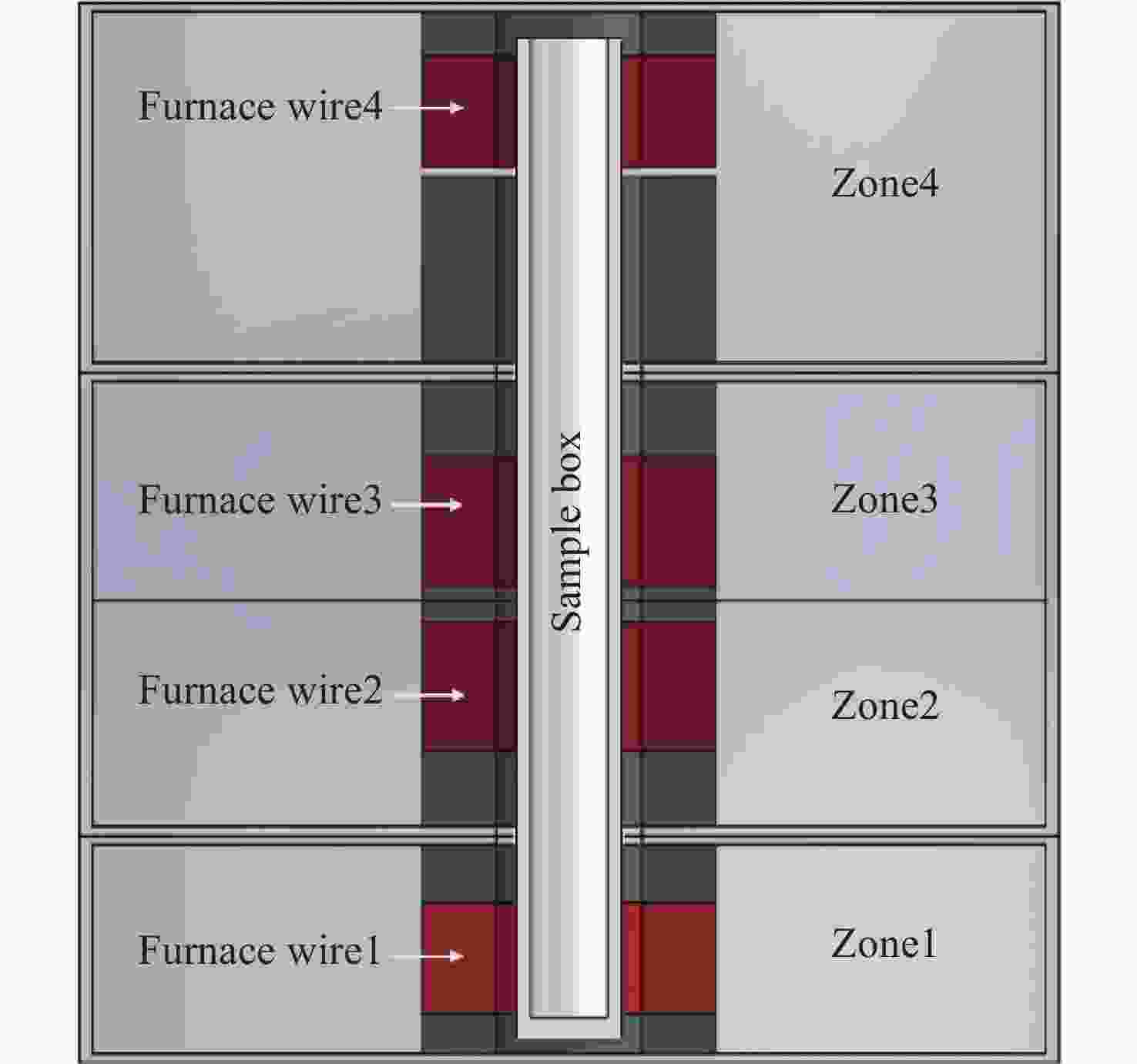
表 1 数据滤波后实验数据基本信息
Table 1. Basic information of experimental data after data filtering
实验名称 实验时长/h 数据条数 数据维度 温区2工况/℃ 温区3工况/℃ 非金属样品1号实验 30.25 108900 462 750~800 860~900 非金属样品2号实验 15.57 56040 462 600~800 600~750 金属样品1号实验 14.05 50580 462 900 900 金属样品2号实验 16.95 61020 462 1050~900 1050~900 表 2 部分输入特征
Table 2. A portion of input feature vector
序号 特征名称 相关系数 序号 特征名称 相关系数 1 目标温度 0.9971 6 炉丝电源温度 0.9298 2 计算上限值 0.9942 7 高温炉冷端 0.9050 3 输出占空比 0.9537 8 炉丝霍尔电流 0.8995 4 加热电压 0.9479 9 主控板28 V温度 0.8791 5 100 V霍尔电流 0.9449 10 高温炉壳温 0.8575 表 3 网格搜索参数优化
Table 3. Optimization of grid search parameters
参数名 寻优范围 取值 迭代次数 [50, 65, 75, 80, 100,
150, 200, 350]150 学习率 [0.01, 0.03, 0.05, 0.08, 0.1, 0.2, 0.25, 0.3] 0.2 树的最大深度 [1, 3, 5, 8] 5 表 4 传递函数参数估计结果
Table 4. Estimation results of transfer function parameters
传递函数 温区2 温区3 $ {R}^{2} $ $ {E}_{\mathrm{m}\mathrm{s}\mathrm{e}} $ $ {R}^{2} $ $ {E}_{\mathrm{m}\mathrm{s}\mathrm{e}} $ 非金属样品1号 0.1105 5.45 $ \times {10}^{4} $ 0.5386 4.00 $ \times {10}^{4} $ 非金属样品2号 - 3.28 $ \times {10}^{4} $ 0.9613 952.5176 金属样品1号 0.4114 3.56 $ \times {10}^{3} $ 0.4659 3.15 $ \times {10}^{3} $ 金属样品2号 0.4369 2.94 $ \times {10}^{3} $ 0.4982 2.51 $ \times {10}^{3} $ 表 5 XGBoost建模结果
Table 5. XGBoost modeling results
XGBoost 温区2 温区3 $ {R}^{2} $ $ {E}_{\mathrm{m}\mathrm{s}\mathrm{e}} $ $ {R}^{2} $ $ {E}_{\mathrm{m}\mathrm{s}\mathrm{e}} $ 非金属样品1号 0.999999 0.064715 0.999999 0.096201 非金属样品2号 0.999999 0.077839 0.999999 0.077566 金属样品1号 0.999998 1.56 $ \times {10}^{-1} $ 0.999998 1.57 $ \times {10}^{-1} $ 金属样品2号 0.999998 2.48 $ \times {10}^{-1} $ 0.999998 2.33 $ \times {10}^{-1} $ 表 6 XGBoost模型较传统模型的性能比较
Table 6. XGBoost model performance improvemencompared with traditional models
实验名称 $ {d}_{{R}^{2}} $ $ {d}_{{E}_{\mathrm{m}\mathrm{s}\mathrm{e}}} $ 非金属样品1号 温区2 0.889 5.4500 $ \times {10}^{4} $ 温区3 0.461 4.0000 $ \times {10}^{4} $ 非金属样品2号 温区2 - 3.2799 $ \times {10}^{4} $ 温区3 0.039 9.5244 $ \times {10}^{2} $ 金属样品1号 温区2 0.588 3.5598 $ \times {10}^{3} $ 温区3 0.534 3.1500 $ \times {10}^{3} $ 金属样品2号 温区2 0.563 2.9398 $ \times {10}^{3} $ 温区3 0.502 2.5098 $ \times {10}^{3} $ -
[1] 阮莹, 胡亮, 闫娜, 等. 空间材料科学研究进展与未来趋势[J]. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2020, 50(6): 603-649RUAN Ying, HU Liang, XIE Wenjun, et al. Recent advances and future perspectives of space materials science[J]. Scientia Sinica Technologica, 2020, 50(6): 603-649 [2] 王其红, 史国栋, 薛国新, 张奕. 基于BP神经网络的化工过程建模研究[J]. 江苏石油化工学院学报, 2000(02): 45-47Wang Qihong, Shi Guodong, Xue Guoxin, et al. A Study on the Modeling of Chemical Processes with BP Neural Networks[J]. Journal of Changzhou University(Natural Science Edition), 2000(02): 45-47 [3] 李昱, 袁磊. 线性系统的系统辨识综述[J]. 探测与控制学报, 2021, 43(3): 22-29LI Yu, YUAN Lei. Overview on system identification for linear systems[J]. Journal of Detection & Control, 2021, 43(3): 22-29 [4] 于强, 吕旭涛, 石春, 等. 空间晶体生长炉温度系统建模[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2008, 20(13): 3596-3599 doi: 10.16182/j.cnki.joss.2008.13.020YU Qiang, LV Xutao, SHI Chun, et al. Modeling of temperature system in space crystal growth furnace[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2008, 20(13): 3596-3599 doi: 10.16182/j.cnki.joss.2008.13.020 [5] 王刚. 三温区空间晶体生长炉温度系统机理建模与控制[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2009WANG Gang. Mechanism Modeling and Control of the Temperature System of Three Zone Furnace for Space Crystal Growth[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2009 [6] 梁兴壮, 黄志远, 艾凤明, 等. 板翅式换热器传递函数动态模型及参数确定方法[J/OL]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 1-14[2022-10-09]. https://doi.org/10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2022.0202LIANG Xingzhuang, HUANG Zhiyuan, AI Fengming, et al. Dynamic model by transfer function and parameter determination method of plate fin heat exchanger[J/OL]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 1-14[2022-10-09]. https://doi.org/10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2022.0202 [7] 鲁杨, 邓晓亭. 基于非线性因素的电子节气门系统状态空间模型的分析[J]. 汽车实用技术, 2022, 47(13): 63-69 doi: 10.16638/j.cnki.1671-7988.2022.013.015LU Yang, DENG Xiaoting. Analysis of state space model of electronic throttle system based on nonlinear factors[J]. Automobile Applied Technology, 2022, 47(13): 63-69 doi: 10.16638/j.cnki.1671-7988.2022.013.015 [8] CHEN T Q, GUESTRIN C. XGBoost: a scalable tree boosting system[C]//Proceedings of the 22 nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. San Francisco: ACM, 2016: 785-794 [9] 段美玲, 潘巨龙. 基于Lasso-LGB的老人跌倒检测算法研究[J]. 中国计量大学学报, 2021, 32(1): 67-73,117 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-2835.2021.01.010DUAN Meiling, PAN Julong. Research on elderly fall detection algorithms based on Lasso-LGB[J]. Journal of China University of Metrology, 2021, 32(1): 67-73,117 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-2835.2021.01.010 [10] 郭银景, 宋先奇, 杨蕾, 等. 基于梯度提升回归树的井下定位算法[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2019, 19(8): 138-144 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.08.021GUO Yinjing, SONG Xianqi, YANG Lei, et al. A coal mine underground positioning algorithm based on gradient boost regression tree[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2019, 19(8): 138-144 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.08.021 [11] 中国载人航天工程办公室. 中国空间站科学实验资源手册[EB/OL]. (2019-04-22)[2022-09-05]. http://www.cmse.gov.cn/gfgg/201904/P020200225328481496691.pdfChina Manned Space. China Space Station Science Experiment Resource Manual [EB/OL]. (2019-04-22)[2022-09-05]. http://www.cmse.gov.cn/gfgg/201904/P020200225328481496691.pdf [12] 戴春媛. 面向空间站高温柜匹配试验的遥操作客户端系统[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院国家空间科学中心), 2021. DOI: 10.27562/d.cnki.gkyyz.2021.000063DAI Chunyuan. Telecontrol Client System for Matching Test of High Temperature Cabinet Client of Space Station[D]. Beijing: National Space Science Center, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2021. DOI: 10.27562/d.cnki.gkyyz.2021.000063 [13] 陶洋, 祝小钧, 杨柳. 基于皮尔逊相关系数和信息熵的多传感器数据融合[J]. 小型微型计算机系统, 2023, 44(5): 1075-1080 doi: 10.20009/j.cnki.21-1106/TP.2021-0698TAO Yang, ZHU Xiaojun, YANG Liu. Multi-sensor data fusion based on Pearson coefficient and information entropy[J]. Journal of Chinese Computer Systems, 2023, 44(5): 1075-1080 doi: 10.20009/j.cnki.21-1106/TP.2021-0698 [14] 肖宇, 赵建有, 叱干都, 等. 基于XGBoost的短时出租车速度预测模型[J]. 交通信息与安全, 2022, 40(3): 163-170 doi: 10.3963/j.jssn.1674-4861.2022.03.017XIAO Yu, ZHAO Jianyou, CHIGAN Du, et al. A short-term prediction model for taxi speed based on XGBoost[J]. Journal of Transport Information and Safety, 2022, 40(3): 163-170 doi: 10.3963/j.jssn.1674-4861.2022.03.017 [15] 谢宇. 回归分析[M]. 北京: 社会科学文献出版社, 2010: 59-61XIE Yu. Regression Analysis[M]. Beijing: Social Sciences Academic Press (China), 2010: 59-61 -
-





 下载:
下载: