X-ray Transmission Characteristics Based on Numerical Model of Upper Atmosphere
-
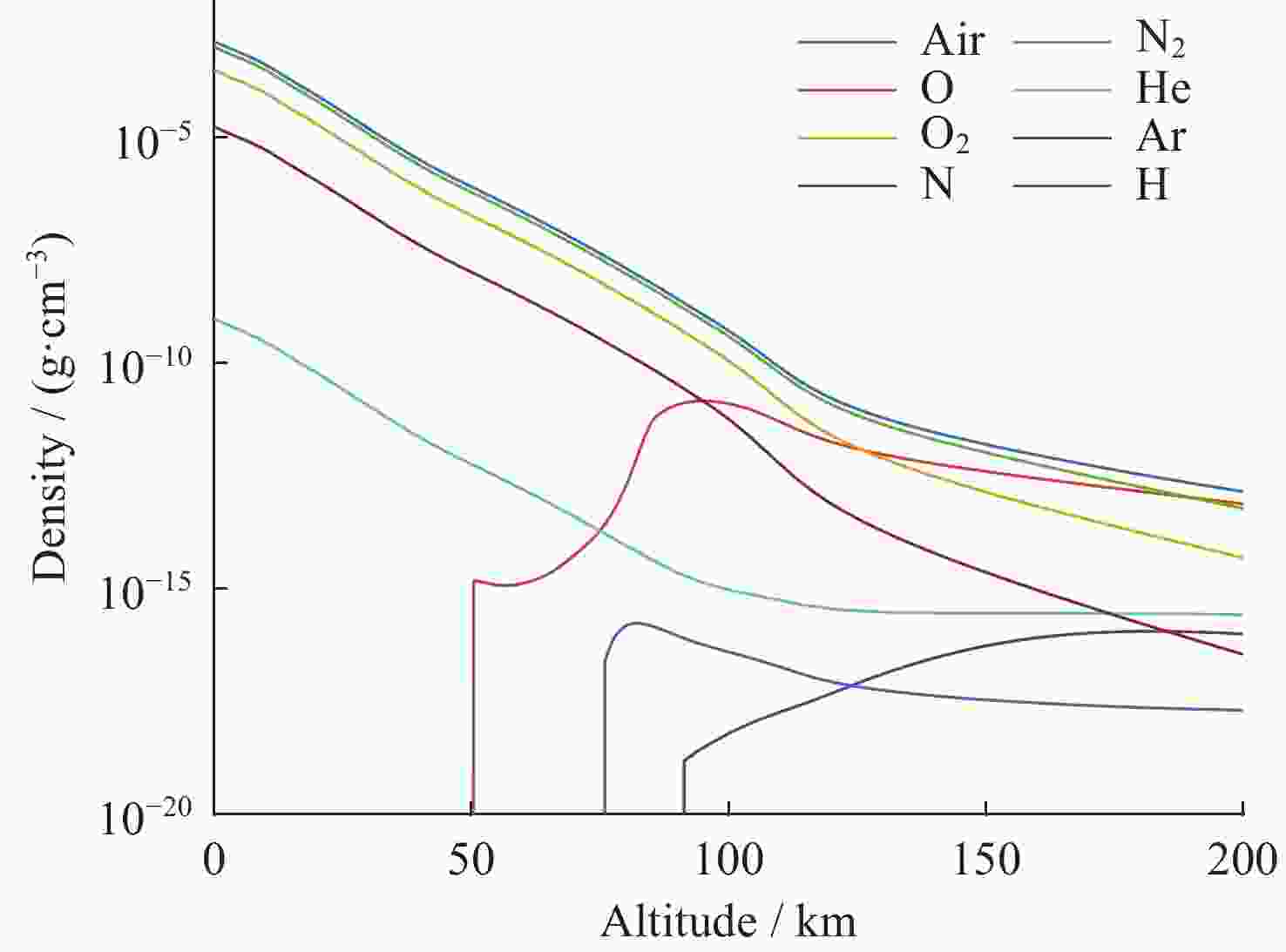
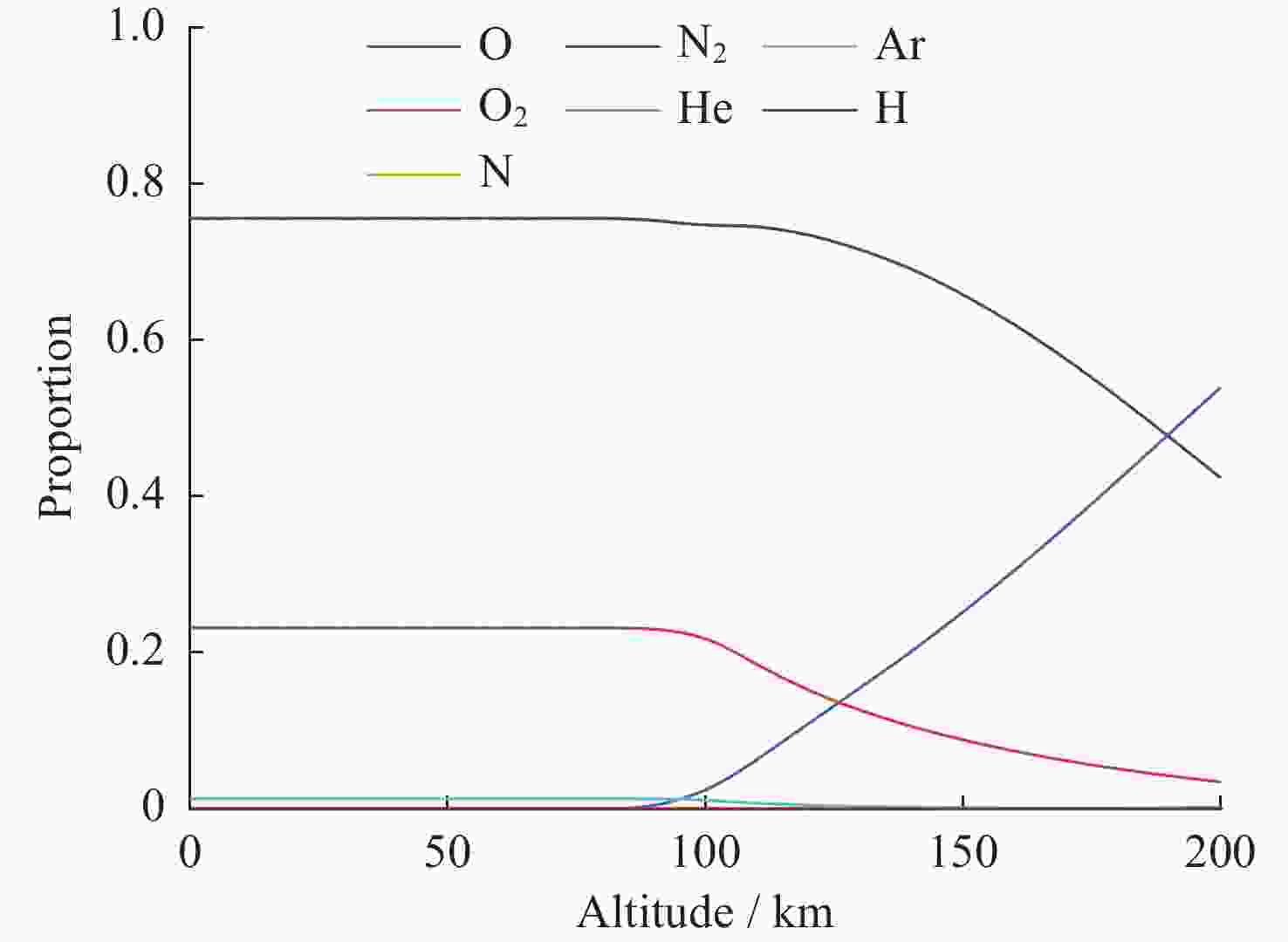
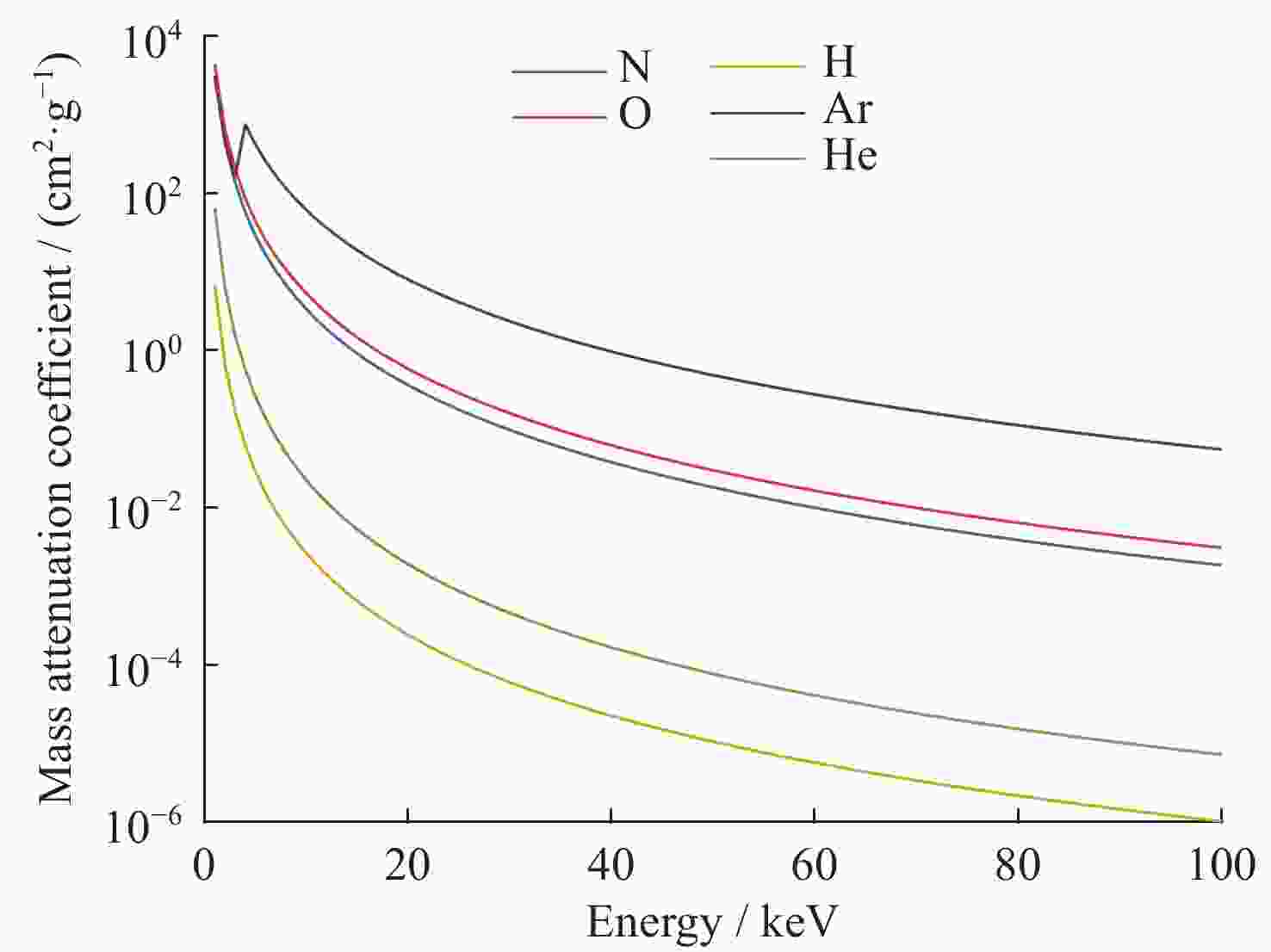
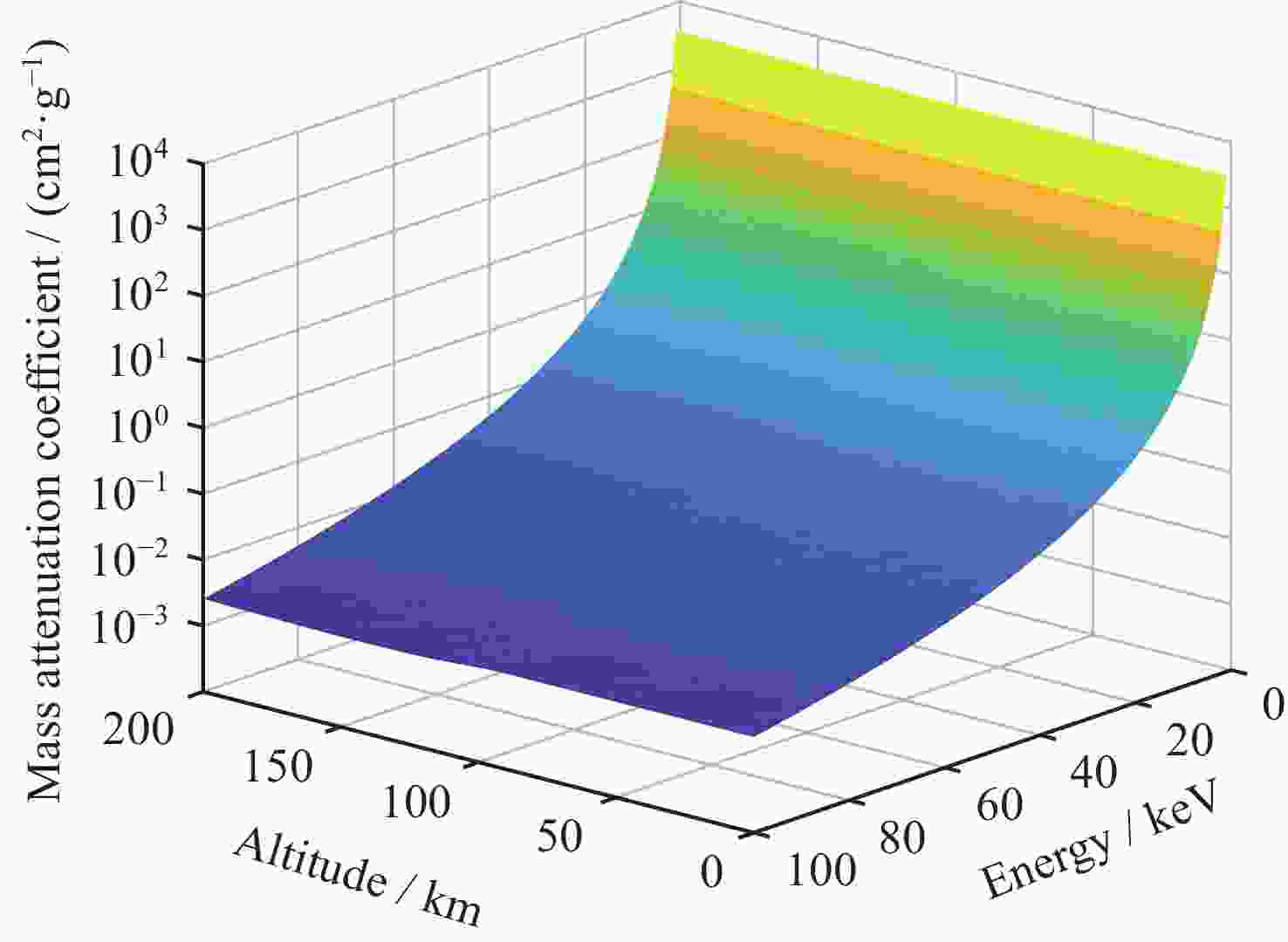
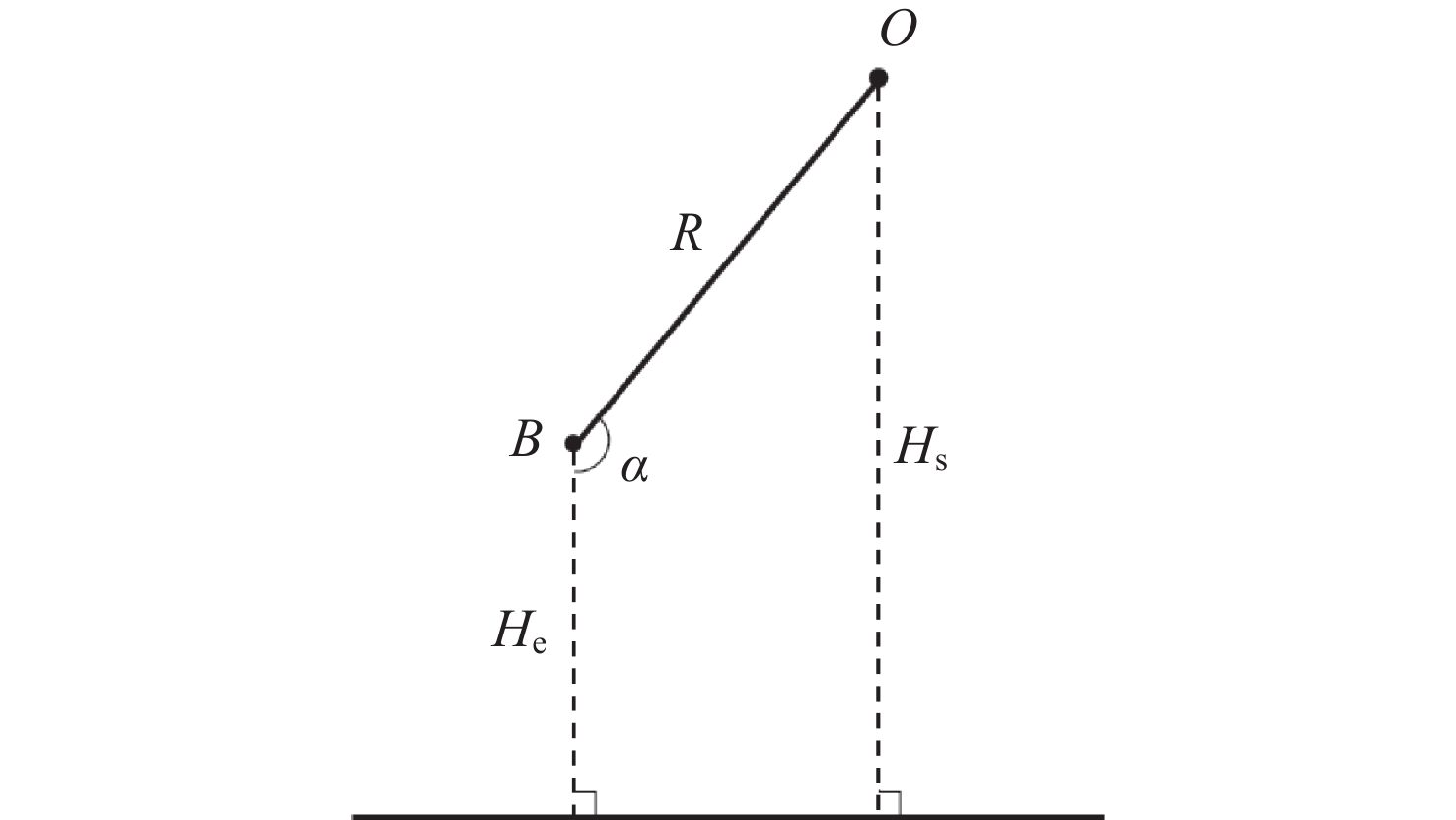
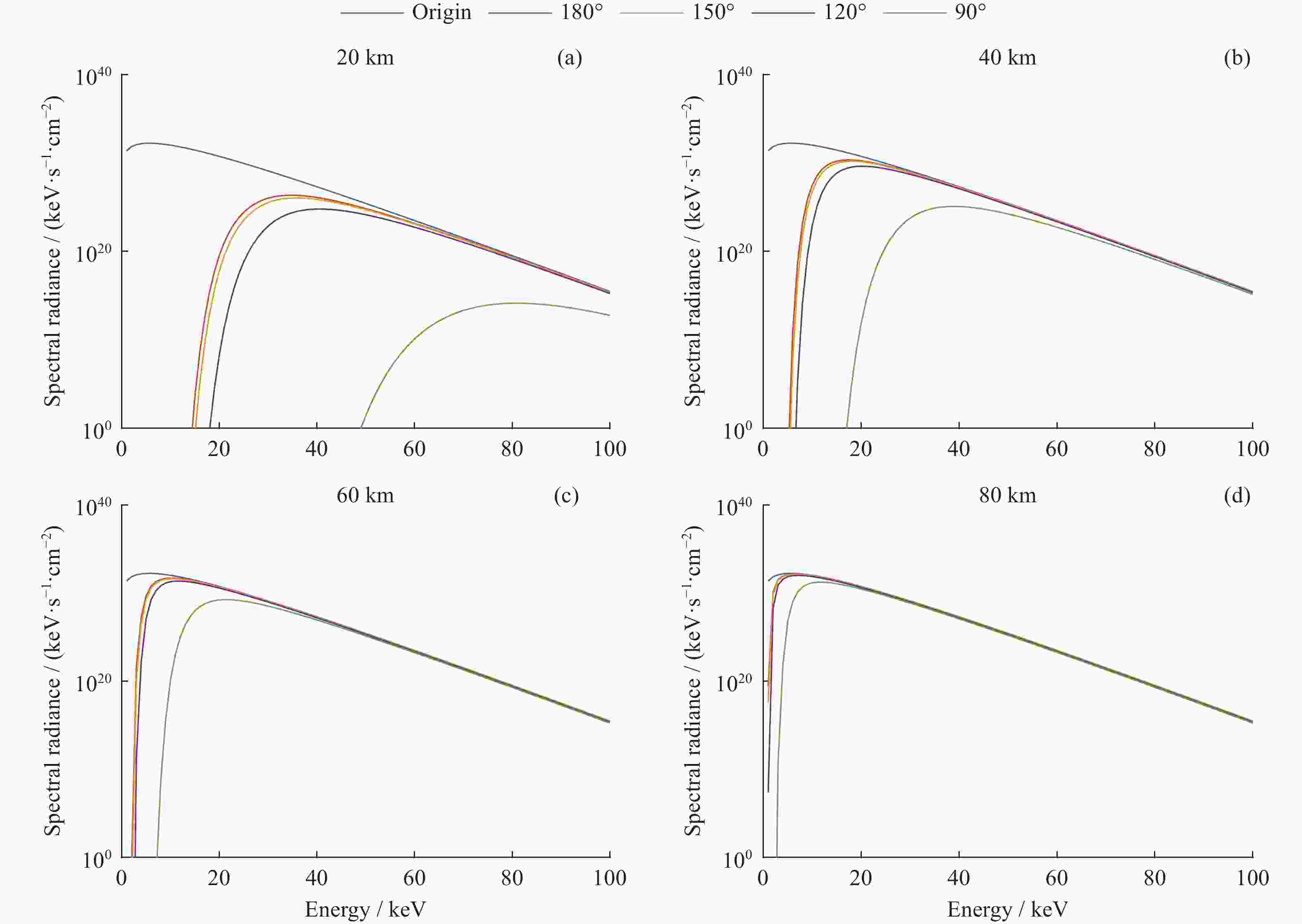
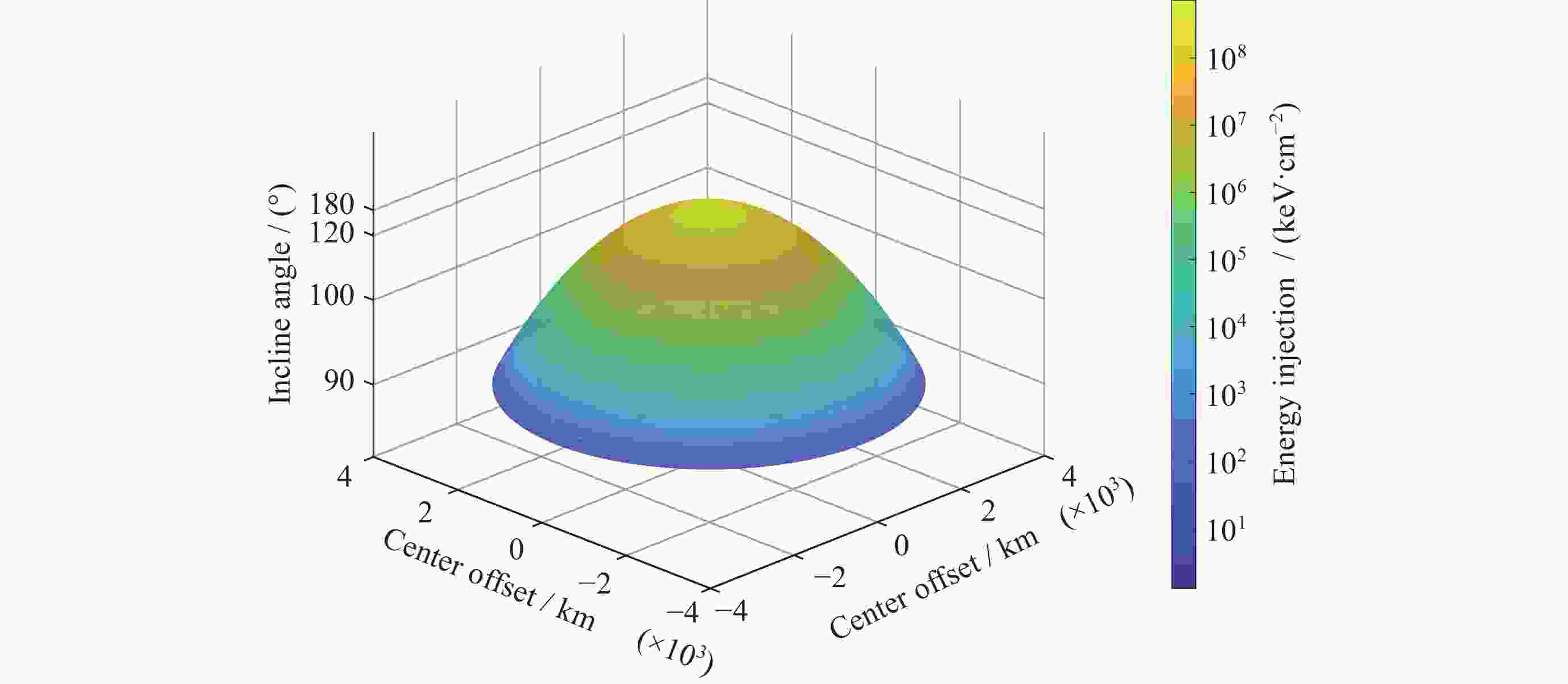
摘要: 核爆炸的大部分能量是以X射线形式释放的,研究X射线辐射特性对于天基核爆事件监测,当量反演都具有一定参考价值。根据核爆炸X射线能谱特性,构建了黑体辐射模型;根据NRLMSIS大气模型成分数据和高度密度数据,构建大气分层数值模型,并结合NIST数据库,构建分层大气质量吸收系数模型,提高了大气模型与大气质量吸收系数模型准确度。使用数值模拟程序对X射线在大气中的传输特性进行研究,模拟在临近空间高度核爆炸产生的X射线经过大气吸收后的能谱特性以及不同海拔高度点位的能注量。结果表明,在检测点高度恒定的情况下,斜径角变小会增大X射线传输路径,X射线经过的大气吸收路径越长,能谱峰值越往高能处偏移。在相同高度下,爆炸点的正上方处能注量最大,其他位置随着斜径角减小能注量呈指数级衰减。Abstract: Most of the energy of a nuclear explosion is released in the form of X-ray. It is important to understand the characteristics of the X-ray radiation for the monitoring of space-based nuclear explosion events and the calculation of explosion yield. In this paper, the blackbody radiation model is constructed based on the X-ray energy spectrum characteristics of nuclear explosion, and a stratified atmospheric numerical model is constructed based on the NRLMSIS atmospheric model composition data and height density data. The stratified atmospheric mass absorption coefficient model is combined with the NIST database to improve the accuracy of the atmospheric model and the atmospheric mass absorption coefficient model. The transmission characteristics of X-ray in the atmosphere are studied using the code, and the energy spectral characteristics of X-ray generated by nuclear explosions at near-space altitude were simulated, after atmospheric absorption and assuming the energy injection at different altitude points. The results show that the height of the detection point is constant, the smaller the slant angle the larger the ray transmission path, i.e., the longer the atmospheric absorption path that the ray passes through, and thus the more the peak of the energy spectrum will shift to the higher energy. At the same height, the energy fluence is the largest directly above the explosion point, and the energy fluence at other positions decays exponentially as the angle decreases.
-
Key words:
- Atmospheric numerical model /
- X-ray /
- Atmospheric absorption /
- Energy spectrum /
- Energy injection
-
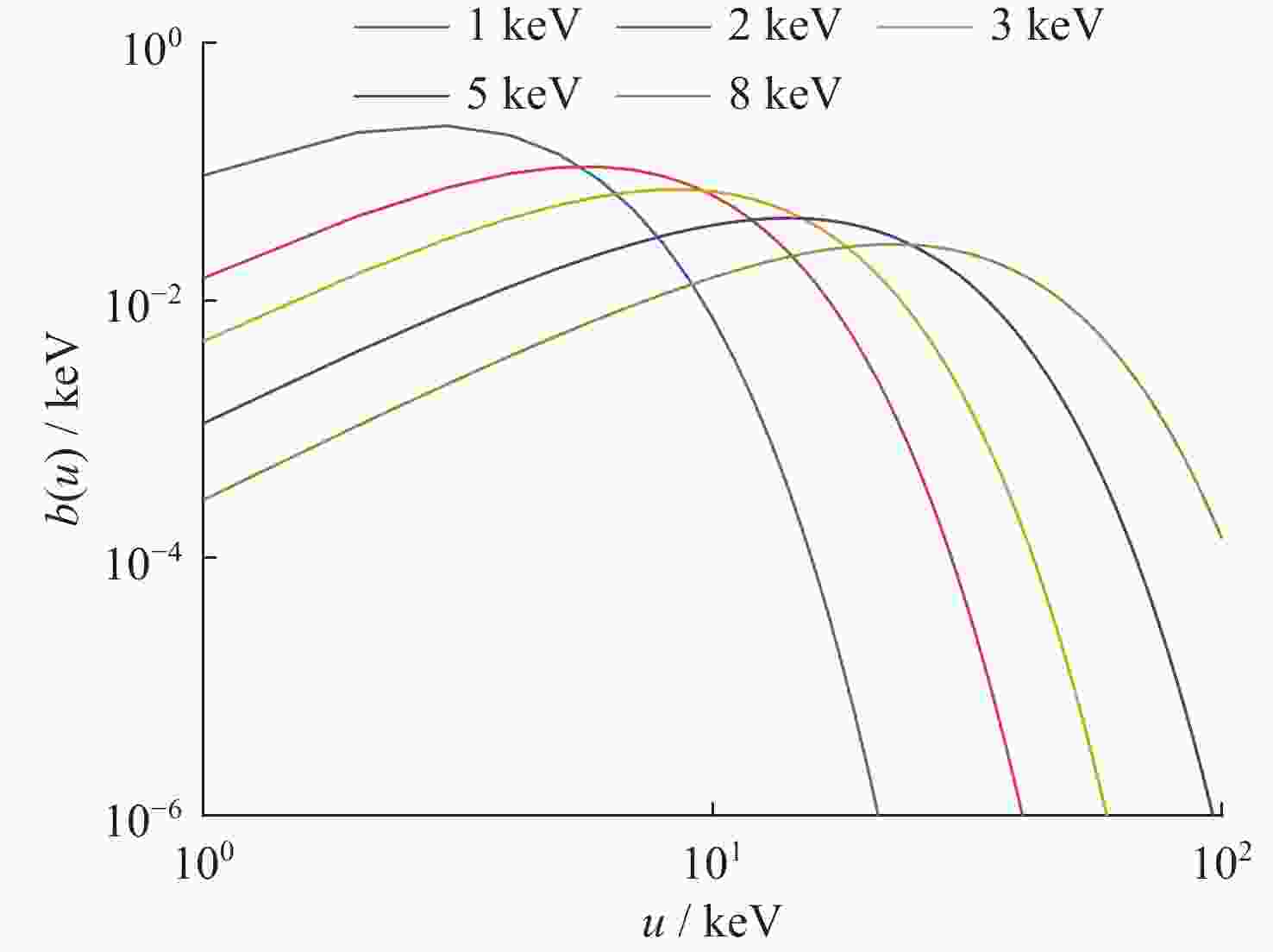
表 1 爆炸当量与等效黑体温度对照
Table 1. Explosion equivalent versus equivalent black body temperature
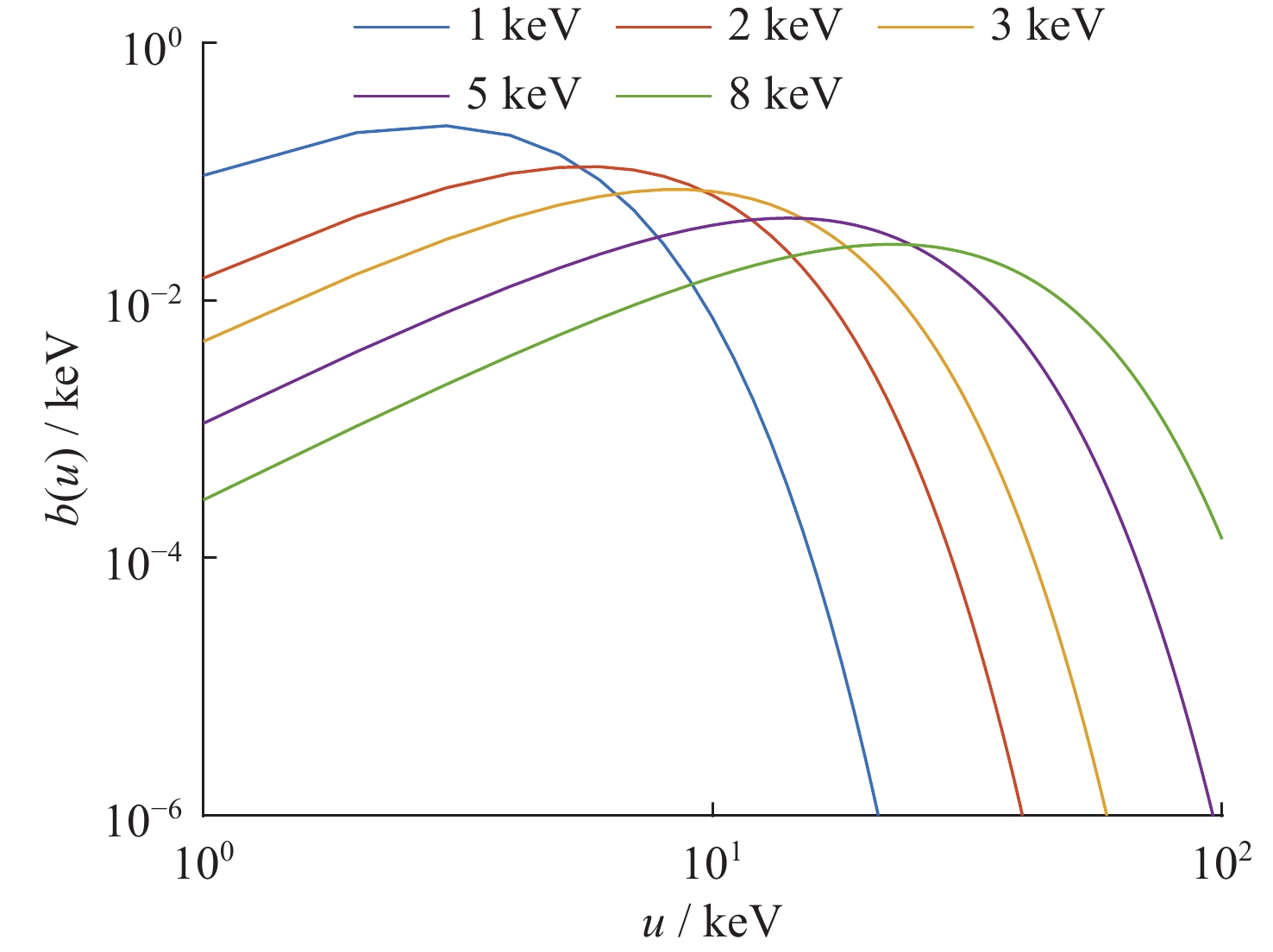
当量 / kt 1 10 100 1000 等效黑体温度 / keV 1 2 5 8 表 2 未经大气吸收后的能注量数值 (单位 keV·cm–2)
Table 2. Energy fluence value without atmospheric absorption (Unit keV·cm–2)
高度 / km 斜径角 / (o) 90 120 150 180 600 1.89×1011 1.37×1012 3.42×1012 4.44×1012 1000 1.08×1011 5.25×1011 1.20×1012 1.53×1012 10000 6.36×109 9.70 ×109 1.31×1010 1.45 ×1010 20000 2.21×109 2.83 ×109 3.39 ×109 3.62 ×109 表 3 经过大气吸收后的能注量数值 (单位 keV·cm–2)
Table 3. Energy fluence value after atmospheric absorption (Unit keV·cm–2)
高度 / km 斜径角 / (o) 90 120 150 180 600 2.22 7.88×107 1.08×109 2.09×109 1000 1.27 3.02×107 3.77×108 7.22×108 10000 0.07 5.57×105 4.11×106 6.84×106 20000 0.03 1.63×105 1.07×106 1.70×106 -
[1] ZHANG Dawei. Theoretical and Laboratorial Studies of Radiative Characteristics of Soft X-Rays from High-Altitude Nuclear Explosions[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanicsand Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2006 [2] 欧阳建明, 马燕云, 邵福球, 等. 高空核爆炸X射线电离的时空分布数值模拟[J]. 物理学报, 2012, 61(24): 242801 doi: 10.7498/aps.61.242801OUYANG Jianming, MA Yanyun, SHAO Fuqiu, et al. Numerical simulation of temporal and spatial distribution of X-ray ionization with high-altitude nuclear explosion[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2012, 61(24): 242801 doi: 10.7498/aps.61.242801 [3] AGENCY U S D A. The Effects of Nuclear Weapons[M]. Washington: U. S. Atomic Energy Commission, 1962 [4] HOERLIN H. Artificial Aurora and Upper Atmospheric Shock Produced by Teak[R]. Los Alamos: Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory, 1961 [5] HOERLIN H. United States High-altitude Test Experiences. A Review Emphasizing the Impact on the Environment[R]. Los Alamos: Los Alamos National Lab, 1976 [6] QIAO Dengjiang. Introduction to Nuclear Explosion Physics[M]. Beijing: Atomic Energy Press, 1988 [7] XU Heng. Research on the Energy Deposition of X-Rays and Characteristic of Thermal Radiation in the High Altitude Nuclear Detonation[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2020 [8] RYBICKI G B, LIGHTMAN A P. Radiative Processes in Astrophysics[M]. Hoboken: Wiley, 2008 [9] TAYLOR B N. The International System of Units (SI)[M]. Washington: US Department of Commerce, Technology Administration, National Institute of Standards and Technology, 2002 [10] PEDROTTI F L, PEDROTTI L M, PEDROTTI L S. Introduction to Optics[M]. 3rd ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2017 [11] State Bureau of Technical Supervision. GB/T 3102.6-1993 Quantities and Units—Light and Related Electromagnetic Radiations[S]. Beijing: State Bureau of Technical Supervision, 1993 [12] WANG Jianguo, NIU Shengli, ZHANG Dianhui, et al. Manual of Parameters for High-Altitude Nuclear Explosion Effects[M]. Beijing: Atomic Energy Press, 2010 [13] 高芬, 安莹, 董威. 基于MATLAB的黑体辐射量计算[J]. 光学与光电技术, 2005, 3(5): 30-32 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3392.2005.05.009GAO Fen, AN Ying, DONG Wei. Calculation of the blackbody radiation quantity based on MATLAB[J]. Optics & Optoelectronic Technology, 2005, 3(5): 30-32 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3392.2005.05.009 [14] SINGH H B. Composition, Chemistry, and Climate of the Atmosphere[M]. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold, 1995 [15] National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration of China, National Aeronautics and Space Administration and United States Air Force Department. U. S. Standard Atmosphere, 1976[M]. REN Xian, QIAN Zhimin, trans. Beijing: Science Press, 1982 [16] ZHAO Jiuzhang. Physics of the Upper Atmosphere: Volume I[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1965 [17] JIA Yue, NASA. NRLMSIS atmosphere model[EB/OL]. (2020-09)[2023-01-14]. https://ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/models/NRLMSIS~v2.0 [18] HUBBELL J H, SELTZER S M. X-Ray Mass Attenuation Coefficients[EB/OL]. (2004-07)[2023-01-14]. https://www.nist.gov/pml/x-ray-mass-attenuation-coefficients [19] ATTIX F H. Energy-absorption coefficients for γ-rays in compounds or mixtures[J]. Physics in Medicine & Biology, 1984, 29(7): 869-871 [20] CHANTLER C T, OLSEN K, DRAGOSET R A, et al. X-Ray Form Factor, Attenuation, and Scattering Tables[EB/OL]. (2005-01)[2023-01-14]. https://www.nist.gov/pml/x-ray-form-factor-attenuation-and-scattering-tables [21] 欧阳建明, 马燕云, 邵福球, 等. 高空核爆炸下大气的X射线电离及演化过程数值模拟[J]. 物理学报, 2012, 61(8): 135-140OUYANG Jianming, MA Yanyun, SHAO Fuqiu, et al. Numerical simulation of X-ray ionization and atmospheric temporal evolutions with high-altitude nuclear explosions[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2012, 61(8): 135-140 [22] 曹鼎汉. 斯特藩-玻尔兹曼辐射定律及其应用[J]. 红外技术, 1994(3): 46-48CAO Dinghan. Stefan-Boltzmann radiation law and applications[J]. Infrared Technology, 1994(3): 46-48 [23] MOHR P J, TAYLOR B N. CODATA recommended values of the fundamental physical constants: 1998[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2000, 72(2): 351-495 doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.72.351 -
-





 下载:
下载: