2000-2021年青藏高原地区地表净辐射的时空变化
doi: 10.11728/cjss2023.06.2023-0080 cstr: 32142.14.cjss2023.06.2023-0080
Spatio-temporal Changes in Surface Net Radiation in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau from 2000 to 2021
-
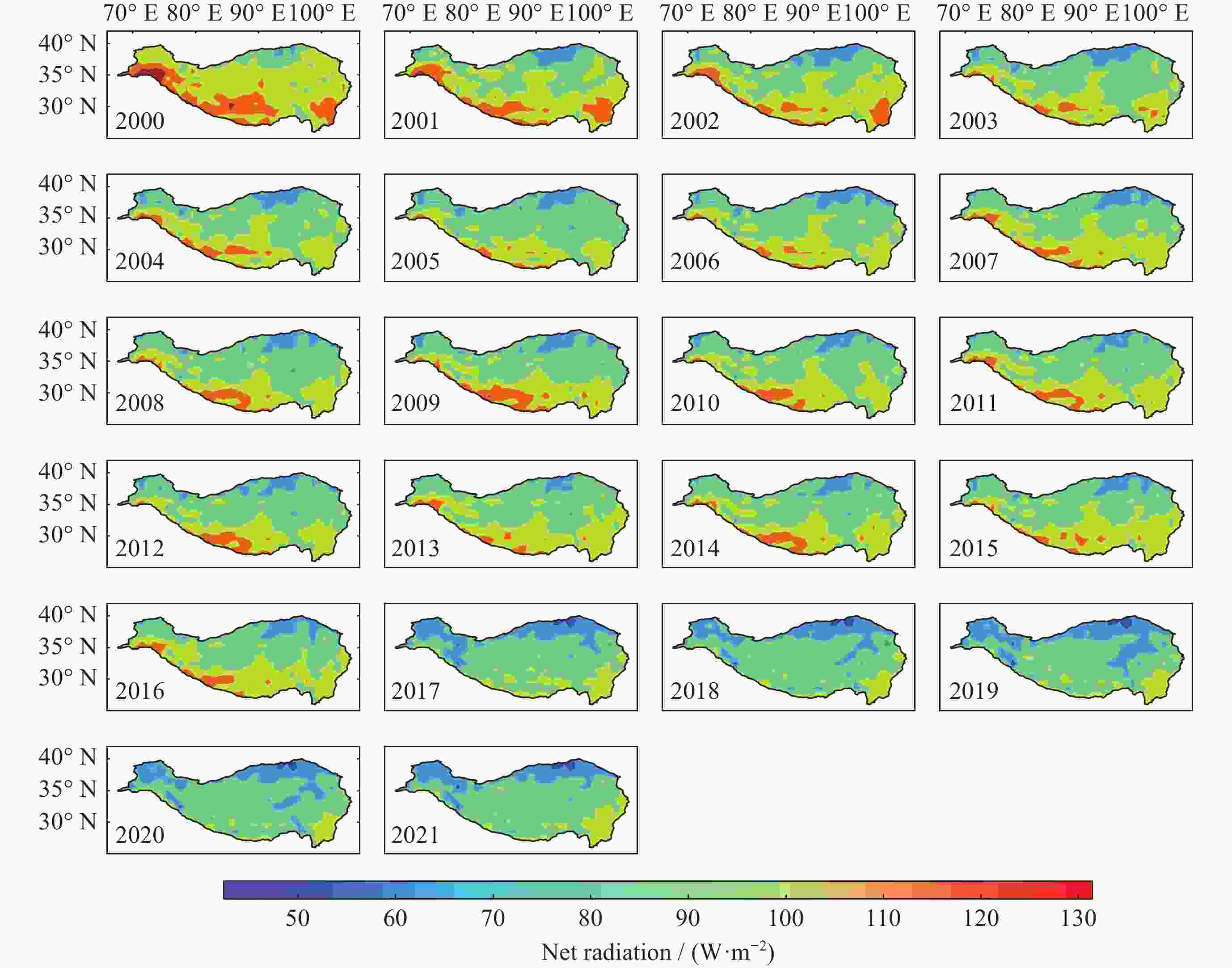
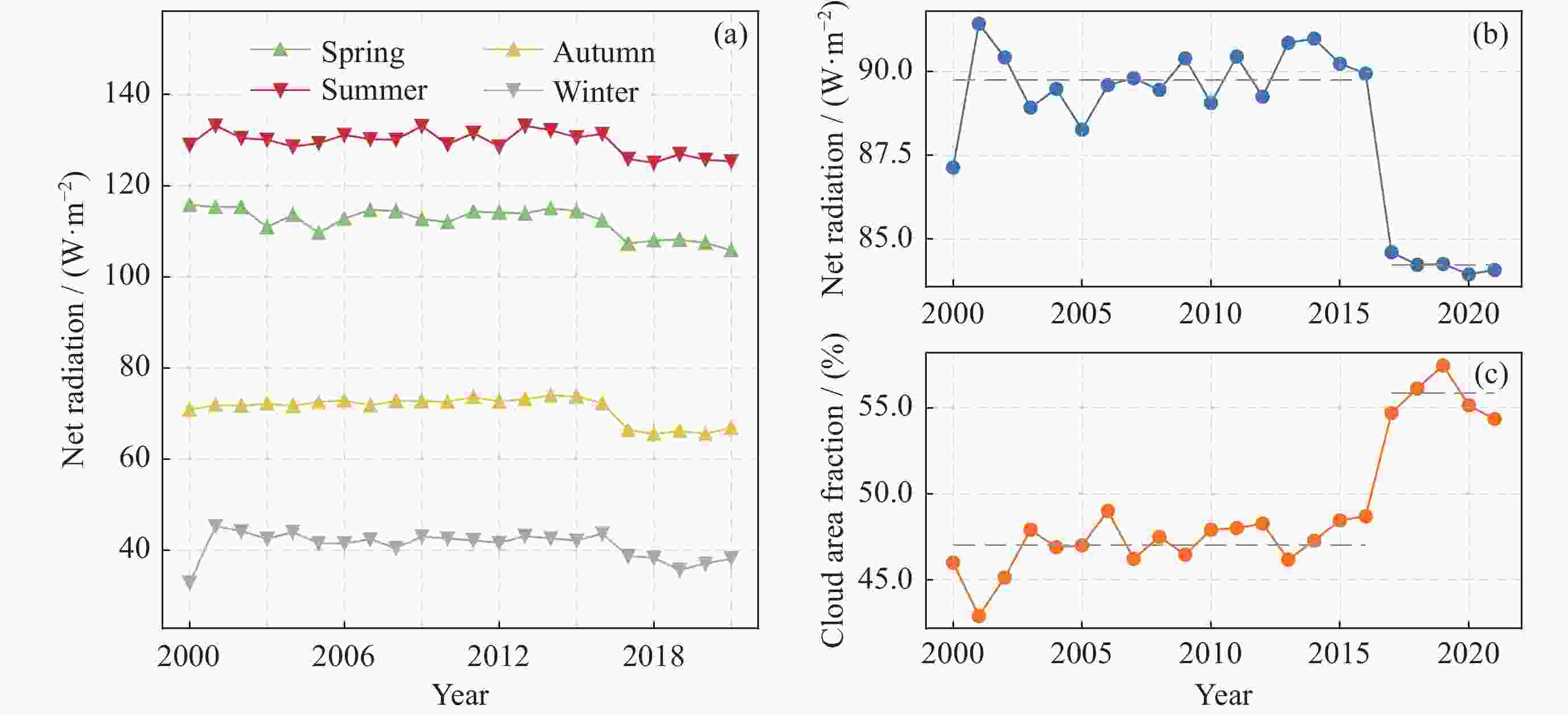
摘要: 基于CERES卫星提供的2000年3月至2022年2月SYN1 deg–Level 3辐射数据,结合Theil-Sen Median趋势分析、Mann-Kendall检验以及EOF分析等方法,分析了22年间青藏高原地表净辐射的时空变化规律。研究发现,在空间分布特征上,青藏高原地表净辐射总体呈现南高北低的分布特征,地表净辐射变化趋势具有高度一致性,但在青藏高原南部地表净辐射变化量级远高于青藏高原北部;在时间演化特征上,地表净辐射呈现准正弦振动,年周期变化明显,特别是2016-2017年出现突变,下降约5.52 W·m–2,同期云覆盖度年平均值提高约18.75%。
-
关键词:
- 青藏高原 /
- 地表净辐射 /
- 时空变化 /
- EOF分析 /
- Theil-Sen Median趋势 /
- Mann-Kendall检验
Abstract: Based on the SYN1 deg-Level 3 radiation product from the CERES satellite spanning from March 2000 to February 2022, The Theil-Sen Median trend analysis, Mann-Kendall test, and EOF analysis were combined to investigate the spatiotemporal patterns of surface net radiation on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau over the past 22 years. The study found that in terms of spatial distribution characteristics, the surface net radiation in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau exhibits a general pattern of higher values in the southern region and lower values in the northern region. The variation trend of surface net radiation shows a high degree of consistency, but the fluctuation amplitude of it in the southern region of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau is much higher than that in the northern region of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Regarding to the temporal evolution, the surface net radiation displayed quasi-sinusoidal oscillations with a noticeable annual periodicity. Notably, there was a sudden decrease of approximately 5.52 W·m–2 in the period from 2016 to 2017. Concurrently, there was an increase of about 18.75% in the cloud area fraction during the same period. -
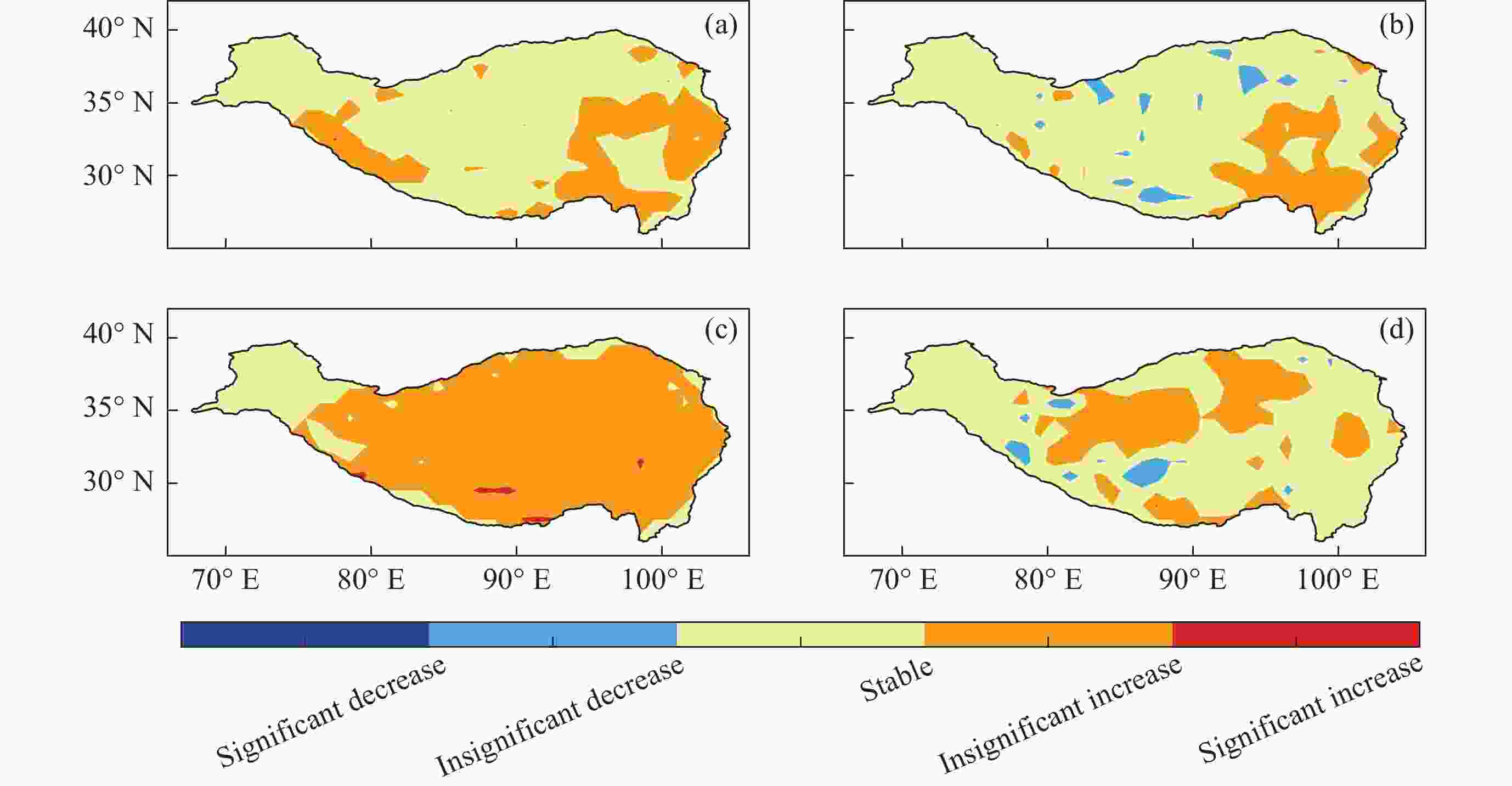
图 5 2000-2021年青藏高原地区地表辐射各分量地表上行短波辐射(a)、地表下行短波辐射(b)、 地表上行长波辐射(c)和地表下行长波辐射(d)变化分布
Figure 5. Distribution of changes in surface radiation components in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau region from 2000 to 2021, including surface upward shortwave radiation (a), surface downward shortwave radiation (b), surface upward longwave radiation (c), and surface downward longwave radiation (d)
图 7 2000-2021年青藏高原地区地表净辐射第1模态(a)特征向量分布及对应月时间分布(b) ,第2模态(c)特征向量分布及对应月时间分布(d)
Figure 7. Distribution of the first mode (a) and corresponding monthly time distribution (b) of surface net radiation, distribution of the second mode (c) and corresponding monthly time distribution (d) in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau region from 2000 to 2021
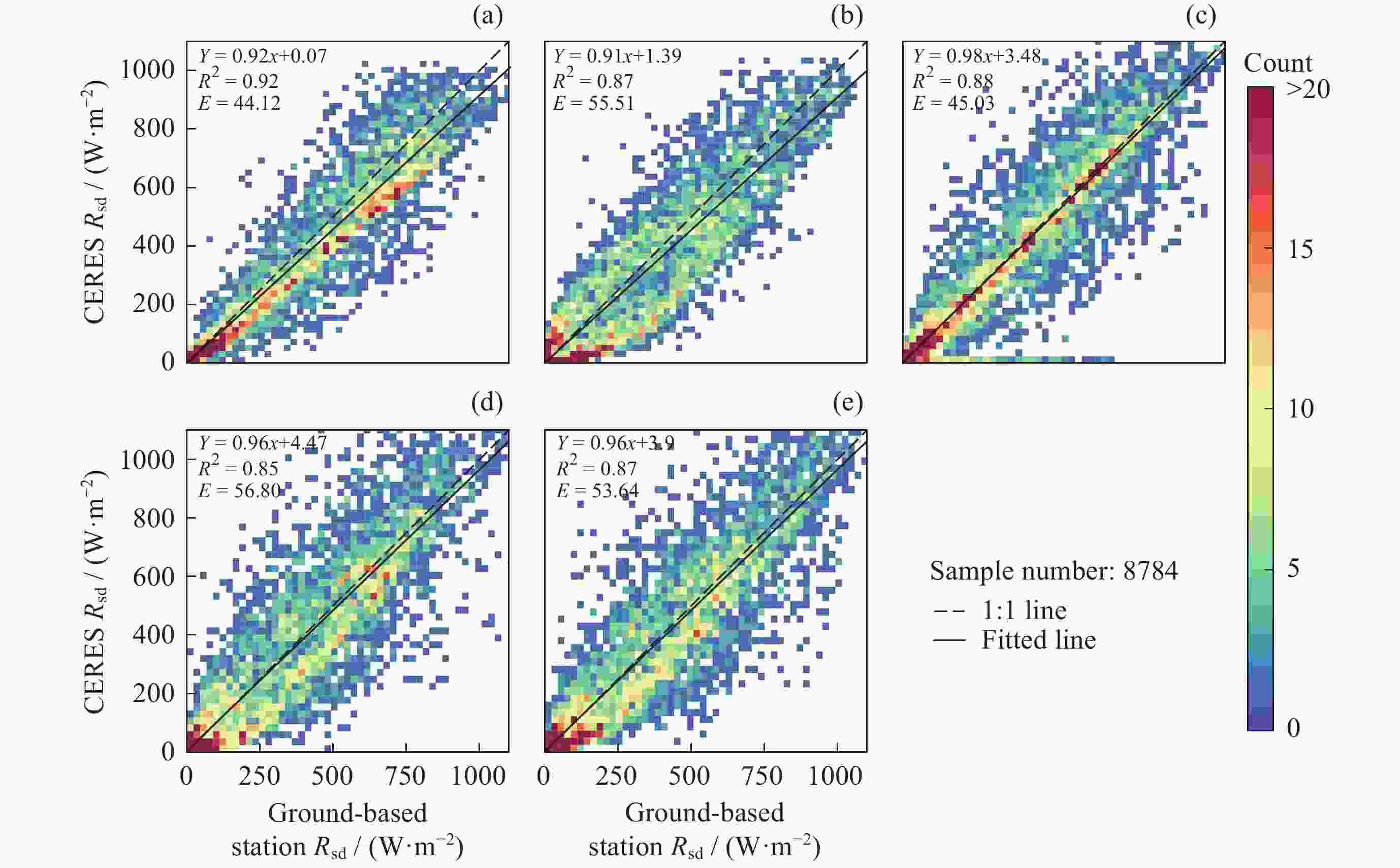
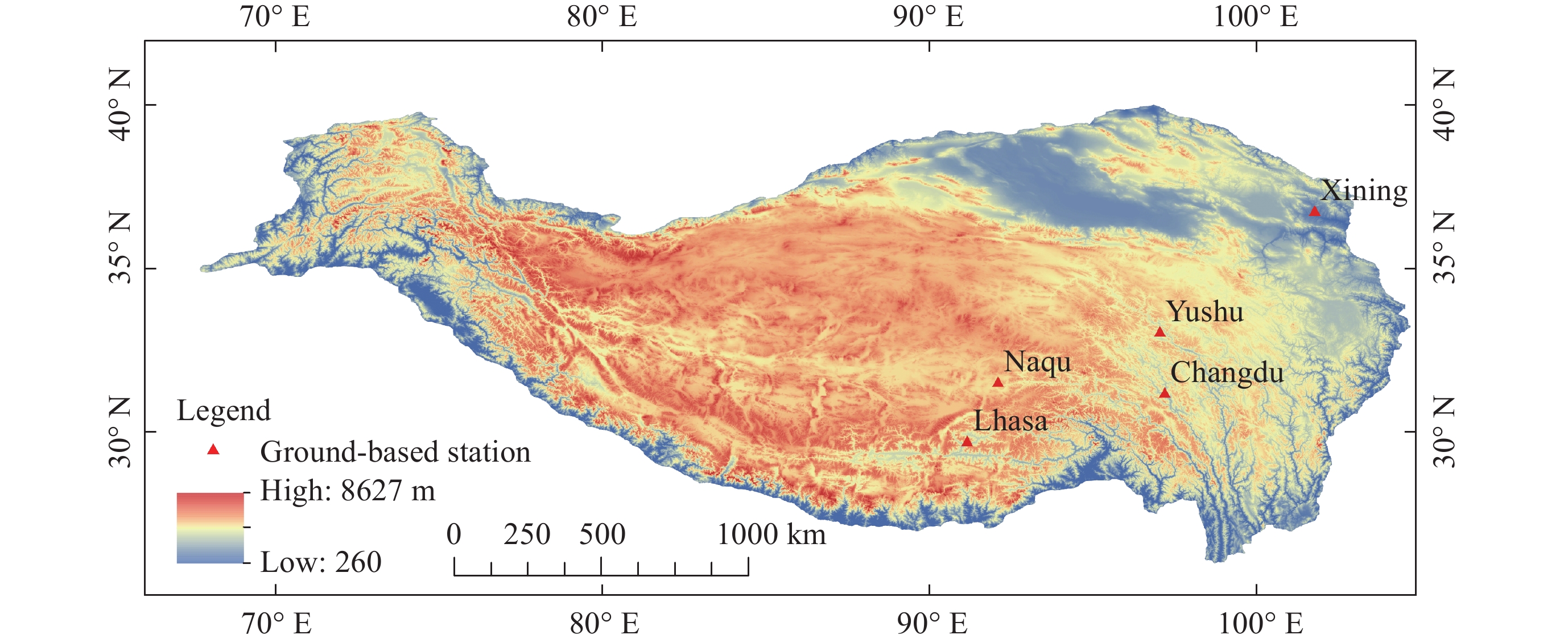
表 1 青藏高原地区拉萨、西宁、那曲、昌都和玉树5个地基站点参数
Table 1. Parameters of five ground stations in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau region, including Lhasa, Xining, Naqu, Changdu and Yushu
地基站点名称 经度(E)/(°) 纬度(N) /(°) 海拔/m 拉萨(55591) 91.13 29.67 3648 西宁(58866) 101.75 36.72 2295 那曲(55299) 92.07 31.48 4507 昌都(56137) 97.17 31.15 3306 玉树(56029) 97.02 33.02 3681 表 2 地表净辐射变化特征划分标准
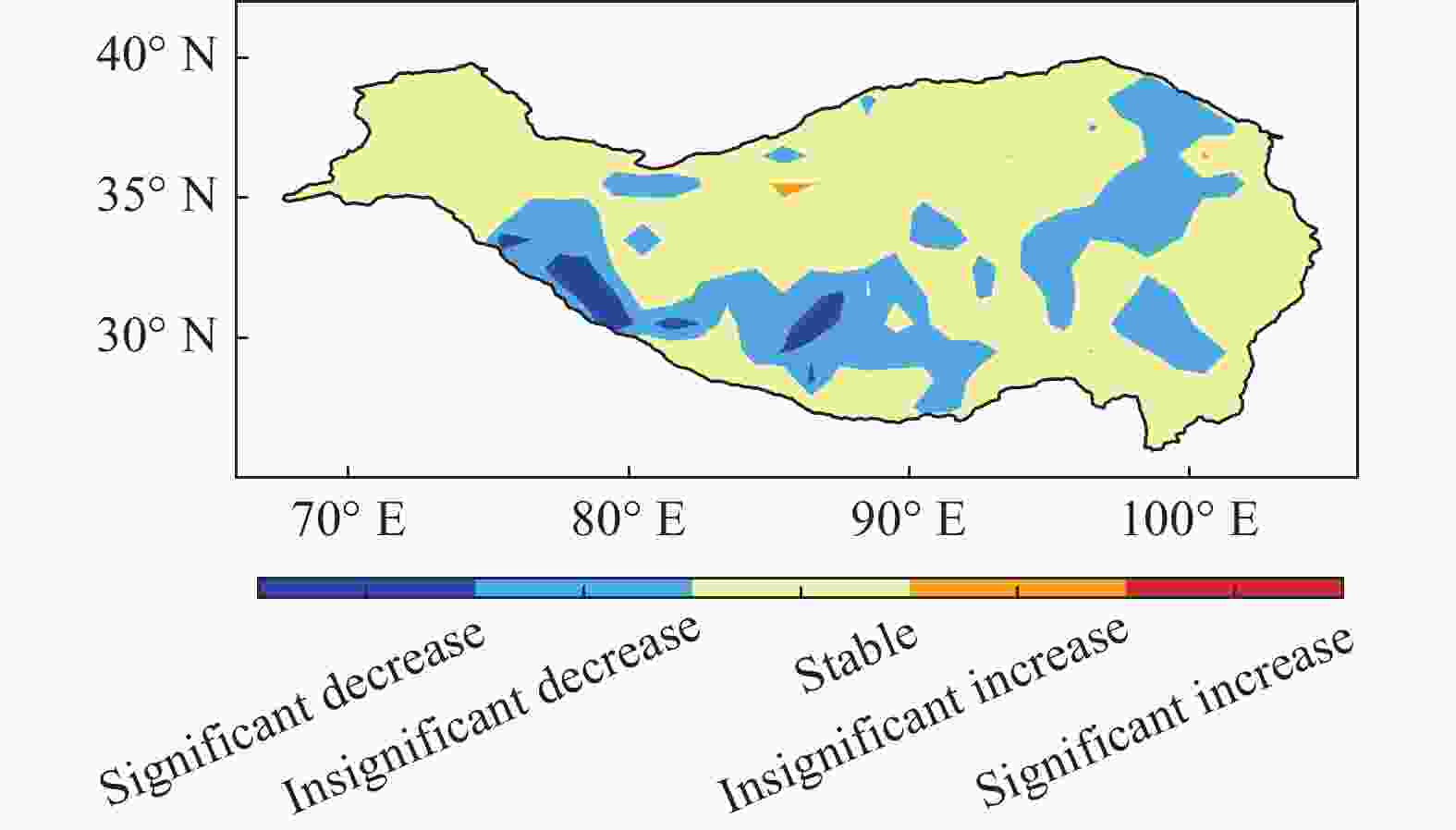
Table 2. Criteria for classifying changes in surface net radiation
趋势(S) 显著水平(Z值) 趋势特征 $ S > 0 $ $ \left|Z\right|\ge 2.58 $ 显著增加 $ 1.96 < \left|Z\right| < 2.58 $ 不显著增加 $ \left|Z\right|\le 1.96 $ 稳定不变 $ S=0 $ $ \left|Z\right| $ 稳定不变 $ S < 0 $ $ \left|Z\right|\le 1.96 $ 稳定不变 $ 1.96 < \left|Z\right| < 2.58 $ 不显著减少 $ \left|Z\right|\ge 2.58 $ 显著减少 表 3 青藏高原地区地表净辐射时空场EOF分解前5个模态特征值与方差贡献率
Table 3. Characteristic values and variances contribution rate of the first five EOF modes for the spatial-temporal pattern of surface net radiation in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau region
特征向量 特征根 方差贡献率/(%) 累积方差贡献率/(%) 特征根误差下限 特征根误差上限 1 591207.56 75.55 75.55 539749.55 642665.58 2 59337.21 7.58 83.13 54172.57 64501.85 3 34403.61 4.40 87.53 31409.16 37398.06 4 14341.27 1.83 89.36 13093.02 15589.52 5 11292.01 1.44 90.80 10309.16 12274.85 -
[1] 高扬子, 何洪林, 张黎, 等. 近50年中国地表净辐射的时空变化特征分析[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2013, 15(1): 1-10 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1047.2013.00001GAO Yangzi, HE Honglin, ZHANG Li, et al. Spatio-temporal variation characteristics of surface net radiation in China over the past 50 years[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 2013, 15(1): 1-10 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1047.2013.00001 [2] LETU H, NAKAJIMA T Y, WANG T X, et al. A new benchmark for surface radiation products over the East Asia-Pacific region retrieved from the Himawari-8/AHI next-generation geostationary satellite[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2022, 103(3): E873-E888 doi: 10.1175/BAMS-D-20-0148.1 [3] LIANG S L, WANG D D, HE T, et al. Remote sensing of earth's energy budget: synthesis and review[J]. International Journal of Digital Earth, 2019, 12(7): 737-780 doi: 10.1080/17538947.2019.1597189 [4] TANG W B, XUE D J, LONG Z Y, et al. Near-real-time estimation of 1-km all-weather land surface temperature by integrating satellite passive microwave and thermal infrared observations[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 7001305 [5] LIANG H, JIANG B, LIANG S L, et al. A global long-term ocean surface daily/0.05° net radiation product from 1983–2020[J]. Scientific Data, 2022, 9(1): 337 doi: 10.1038/s41597-022-01419-x [6] 谷星月, 马耀明, 马伟强, 等. 青藏高原地表辐射通量的气候特征分析[J]. 高原气象, 2018, 37(6): 1458-1469GU Xingyue, MA Yaoming, MA Weiqiang, et al. Climatic characteristics of surface radiation flux over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2018, 37(6): 1458-1469 [7] CHEN L, YAN G J, WANG T X, et al. Estimation of surface shortwave radiation components under all sky conditions: modeling and sensitivity analysis[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2012, 123: 457-469 doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2012.04.006 [8] KANG S C, XU Y W, YOU Q L, et al. Review of climate and cryospheric change in the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2010, 5(1): 015101 doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/5/1/015101 [9] 张明礼, 王斌, 王得楷, 等. 降雨对青藏高原多年冻土区地表辐射的影响——以北麓河地区为例[J]. 冰川冻土, 2021, 43(4): 1092-1101ZHANG Mingli, WANG Bin, WANG Dekai, et al. The effects of rainfall on the surface radiation of permafrost regions in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: a case study in Beiluhe area[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2021, 43(4): 1092-1101 [10] 蔡鸿泽, 王开存. 基于最新观测和大气再分析估计全球能量平衡[J]. 科学通报, 2022, 67(35): 4263-4280 doi: 10.1360/TB-2022-0089CAI Hongze, WANG Kaicun. Updating global energy balance based on the latest observations and reanalyses[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2022, 67(35): 4263-4280 doi: 10.1360/TB-2022-0089 [11] LIN C G, WU H P, OU T H, et al. A new perspective on solar dimming over the Tibetan Plateau[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2019, 39(1): 302-316 doi: 10.1002/joc.5807 [12] WILD M, GILGEN H, ROESCH A, et al. From dimming to brightening: decadal changes in solar radiation at Earth's surface[J]. Science, 2005, 308(5723): 847-850 doi: 10.1126/science.1103215 [13] 张艳武, 冯起, 黄静, 等. 黑河下游绿洲地表辐射平衡及小气候特征分析[J]. 冰川冻土, 2012, 28(2): 191-198ZHANG Yanwu, FENG Qi, HUANG Jing, et al. Ground energy balance and microclimate characteristics in the oasis of lower reaches of Heihe River[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2012, 28(2): 191-198 [14] 次仁尼玛, 单增罗布, 宣越健, 等. 青藏高原羊八井地区地表辐射的季节变化特征[J]. 高原气象, 2013, 32(5): 1253-1260CIREN Nima, DANZENG Luobu, XUAN Yuejian, et al. Characteristic of seasonal variation of surface radiation balance at Yangbajing in Qinghai-Xizang Plateau[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2013, 32(5): 1253-1260 [15] 李平, 王鸽, 王顺久. 阿里地区狮泉河近30年总辐射和净辐射的变化特征[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 2022, 42(4): 110-114LI Ping, WANG Ge, WANG Shunjiu. Variation characteristics of total radiation and net radiation in Ali area in recent 30 years[J]. Plateau and Mountain Meteorology Research, 2022, 42(4): 110-114 [16] 赵文娜, 次仁尼玛, 王一楠, 等. 西藏羊八井地区地表辐射的时间变化特征研究[J]. 高原科学研究, 2022, 6(4): 42-49ZHAO Wenna, TSERING-NYIMA, WANG Yinan, et al. Study on the temporal variation of surface radiation at Yangbajing on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Plateau Science Research, 2022, 6(4): 42-49 [17] 马茜蓉, 游庆龙, 蔡淼, 等. 基于CERES卫星资料分析中国近15 a云量变化[J]. 干旱气象, 2018, 36(6): 911-920MA Qianrong, YOU Qinglong, CAI Miao, et al. The cloud variation over China in recent 15 years based on CERES satellite data[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(6): 911-920 [18] ZHANG X T, LIANG S L, ZHOU G Q, et al. Generating Global Land Surface Satellite incident shortwave radiation and photosynthetically active radiation products from multiple satellite data[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2014, 152: 318-332 doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2014.07.003 [19] 苏红军, 许仲林. 2000—2015年新疆植被指数的时空动态分析[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2022, 61(10): 48-55,63 doi: 10.14088/j.cnki.issn0439-8114.2022.10.008SU Hongjun, XU Zhonglin. Temporal and spatial dynamics analysis of vegetation index in Xinjiang from 2000 to 2015[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 61(10): 48-55,63 doi: 10.14088/j.cnki.issn0439-8114.2022.10.008 [20] 周蕊, 高钰婷, 石丽荣, 等. 近22年民勤地区植被变化的时空特征及其驱动因素[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2023, 51(2): 68-74ZHOU Rui, GAO Yuting, SHI Lirong, et al. Temporal and spatial characteristics of vegetation change and its driving factors in Minqin region in recent 22 years[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 51(2): 68-74 [21] BAMBANG I, SARAVANAN S, REDDY N M, et al. An investigation of the changing patterns of rainfall in the Indravathi subbasin utilizing the Mann-Kendall and Sen’s slope methods[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2023, 1173(1): 012036 doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/1173/1/012036 [22] GAO H, JIN J X. Analysis of water yield changes from 1981 to 2018 using an improved Mann-Kendall test[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(9): 2009 doi: 10.3390/rs14092009 [23] MERINO A, SÁNCHEZ J L, GARCÍA-ORTEGA S, et al. Hailfalls in southwest Europe: EOF analysis for identifying synoptic pattern and their trends[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2019, 215: 42-56 doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2018.08.006 [24] TIAN X M, TANG C L, WU X, et al. The global spatial-temporal distribution and EOF analysis of AOD based on MODIS data during 2003–2021[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2023, 302: 119722 doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2023.119722 [25] SUN M D, KIM G, LEI K, et al. Evaluation of technology for the analysis and forecasting of precipitation using cyclostationary EOF and regression method[J]. Atmosphere, 2022, 13(3): 500 doi: 10.3390/atmos13030500 [26] 翁笃鸣. 青藏高原地表净辐射若干重要特征研究[J]. 南京气象学院学报, 1991, 14(2): 151-159WENG Duming. Some major features of surface net radiation in the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau[J]. Journal of Nanjing Institute of Meteorology, 1991, 14(2): 151-159 [27] 马越界, 黄建平, 刘玉芝. 利用星载云雷达资料分析夏季青藏高原的云辐射强迫[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 47(5): 48-54 doi: 10.13885/j.issn.0455-2059.2011.05.015MA Yuejie, HUANG Jianping, LIU Yuzhi. Impact of clouds on radiative fluxes in summer over the Tibetan Plateau from Cloudsat data[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences), 2011, 47(5): 48-54 doi: 10.13885/j.issn.0455-2059.2011.05.015 -
-






 下载:
下载: