改进YOLOv5的闪电哨声波轻量化自动检测模型
doi: 10.11728/cjss2024.03.2023-0067 cstr: 32142.14.cjss2024.03.2023-0067
Lightweight Automatic Detection Model for Lightning Whistle Waves Based on Improved YOLOv5
-
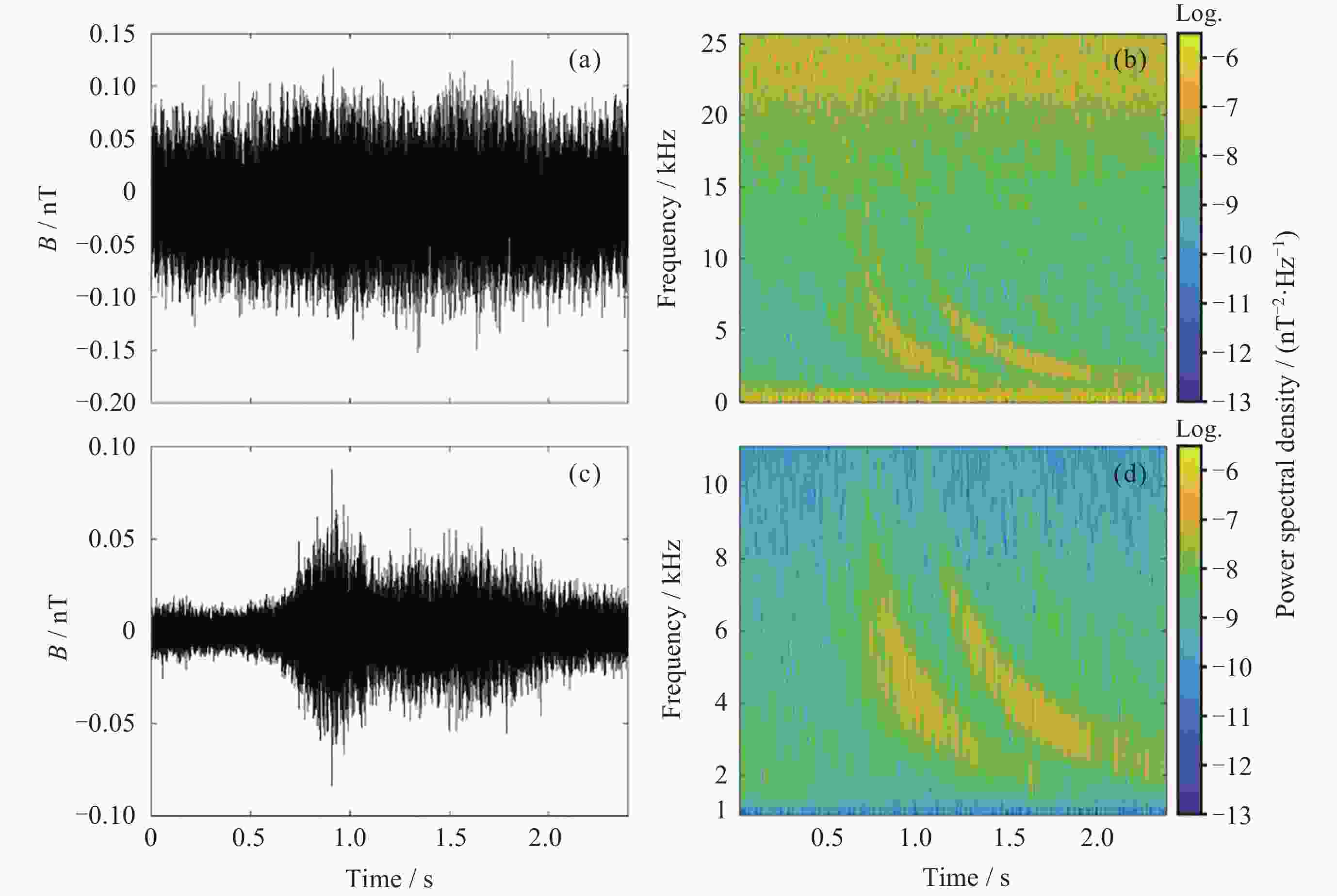
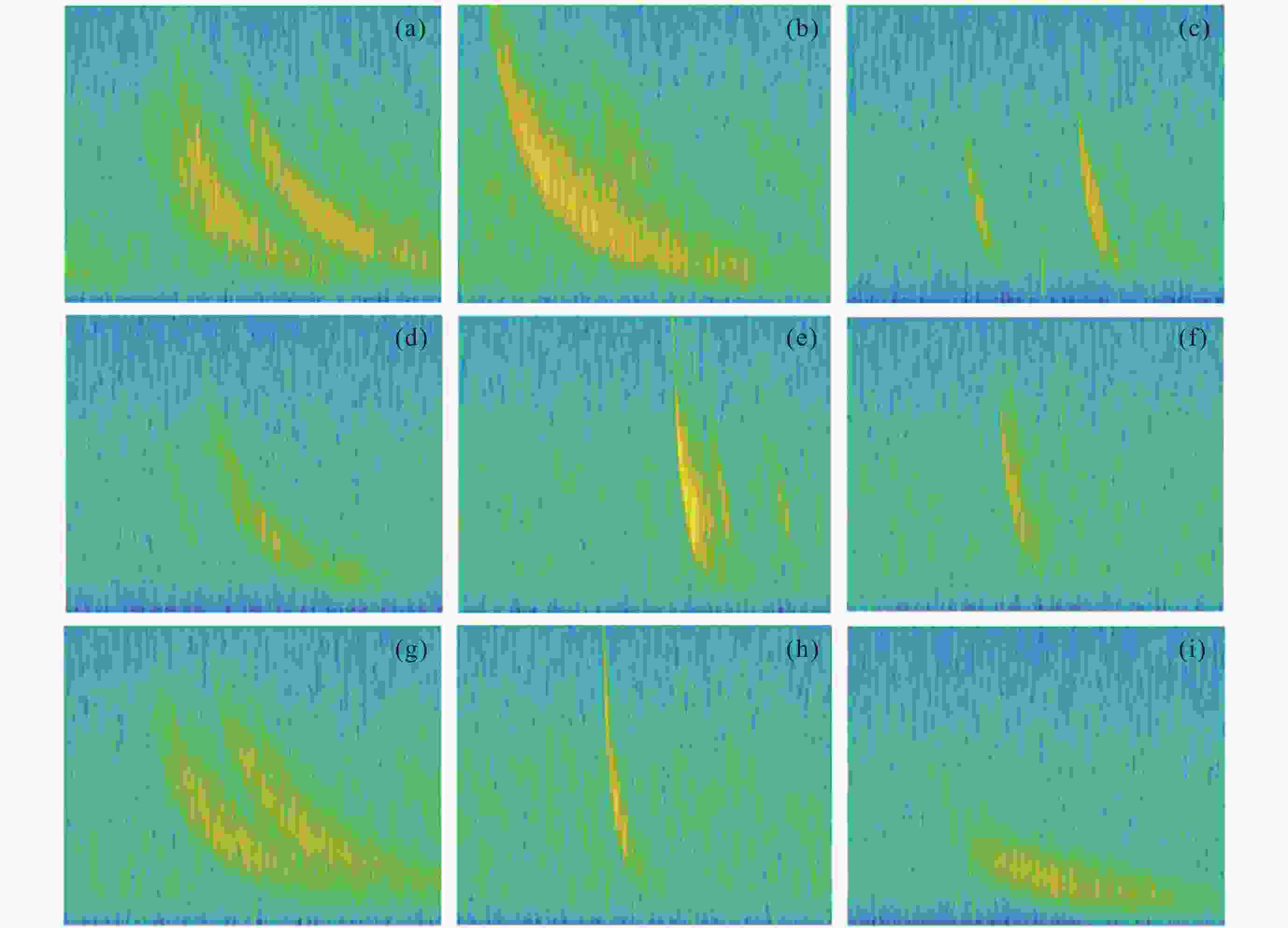
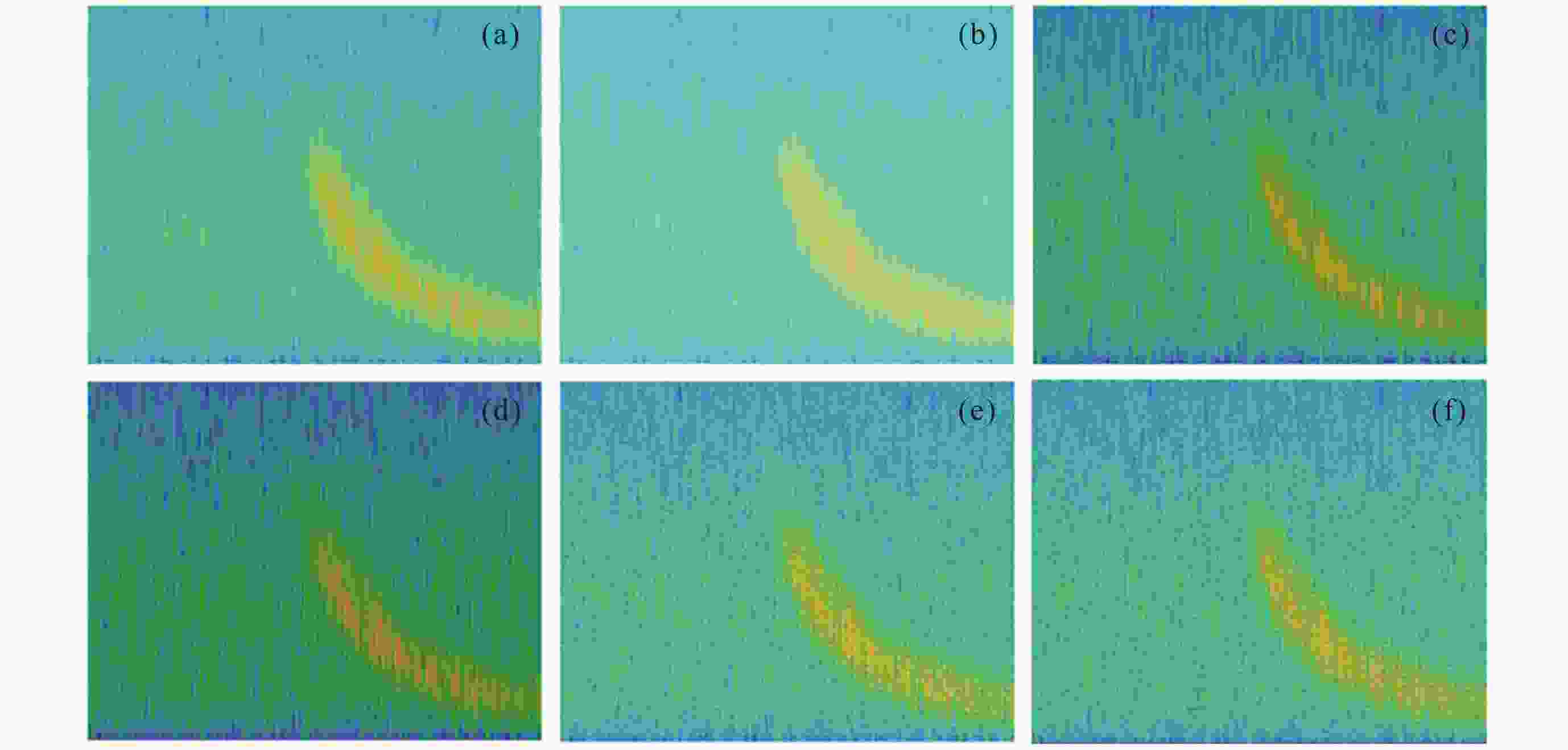
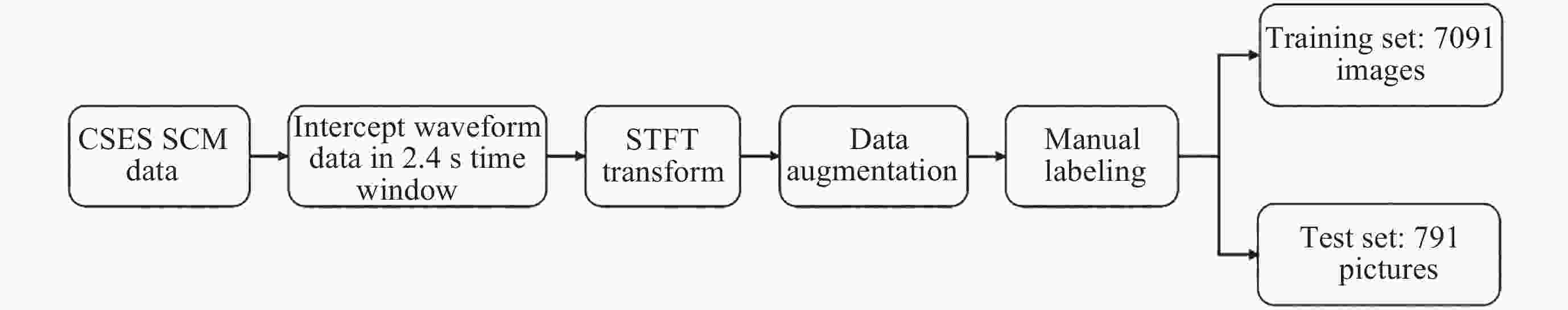
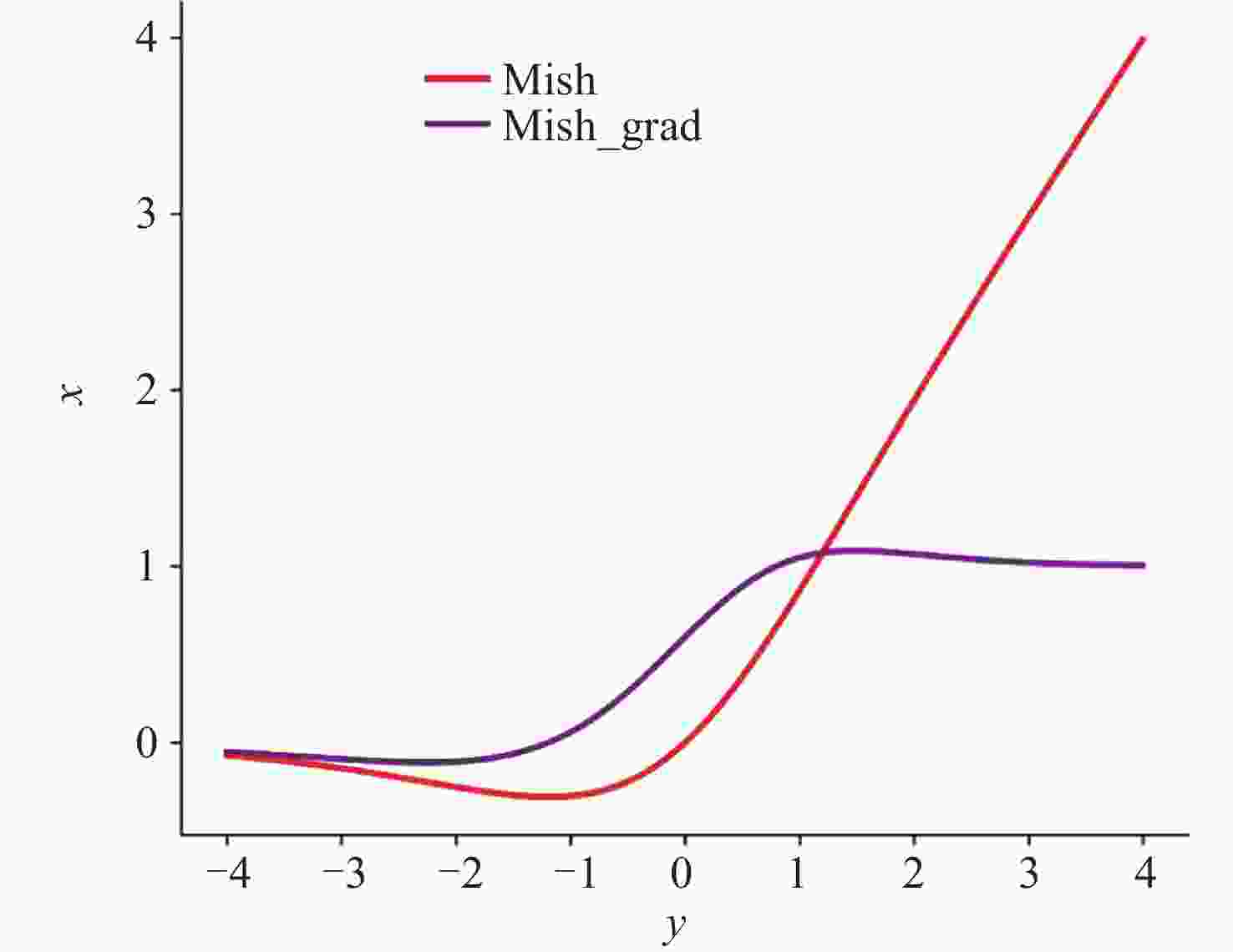
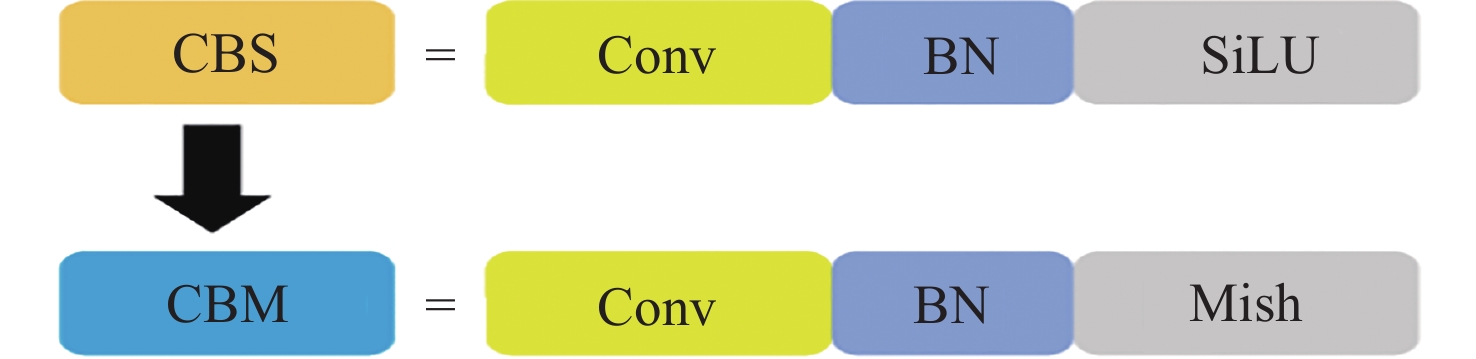
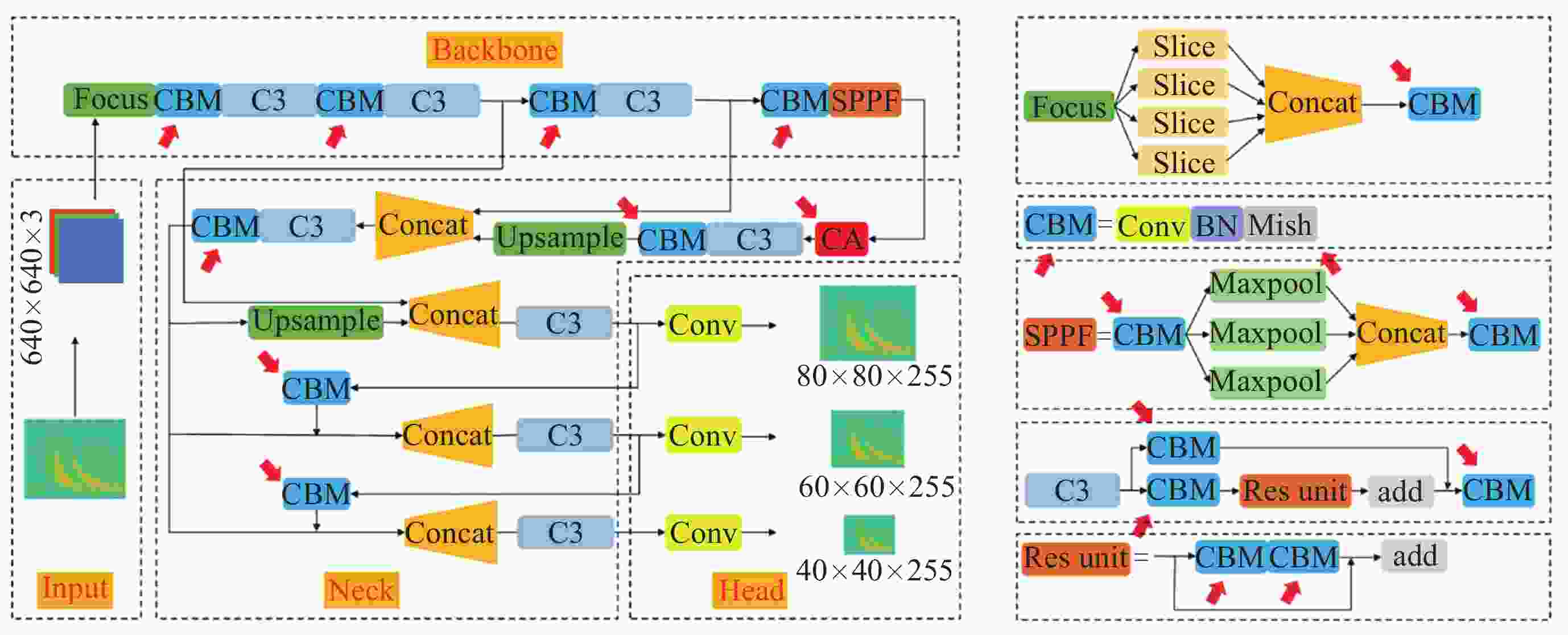
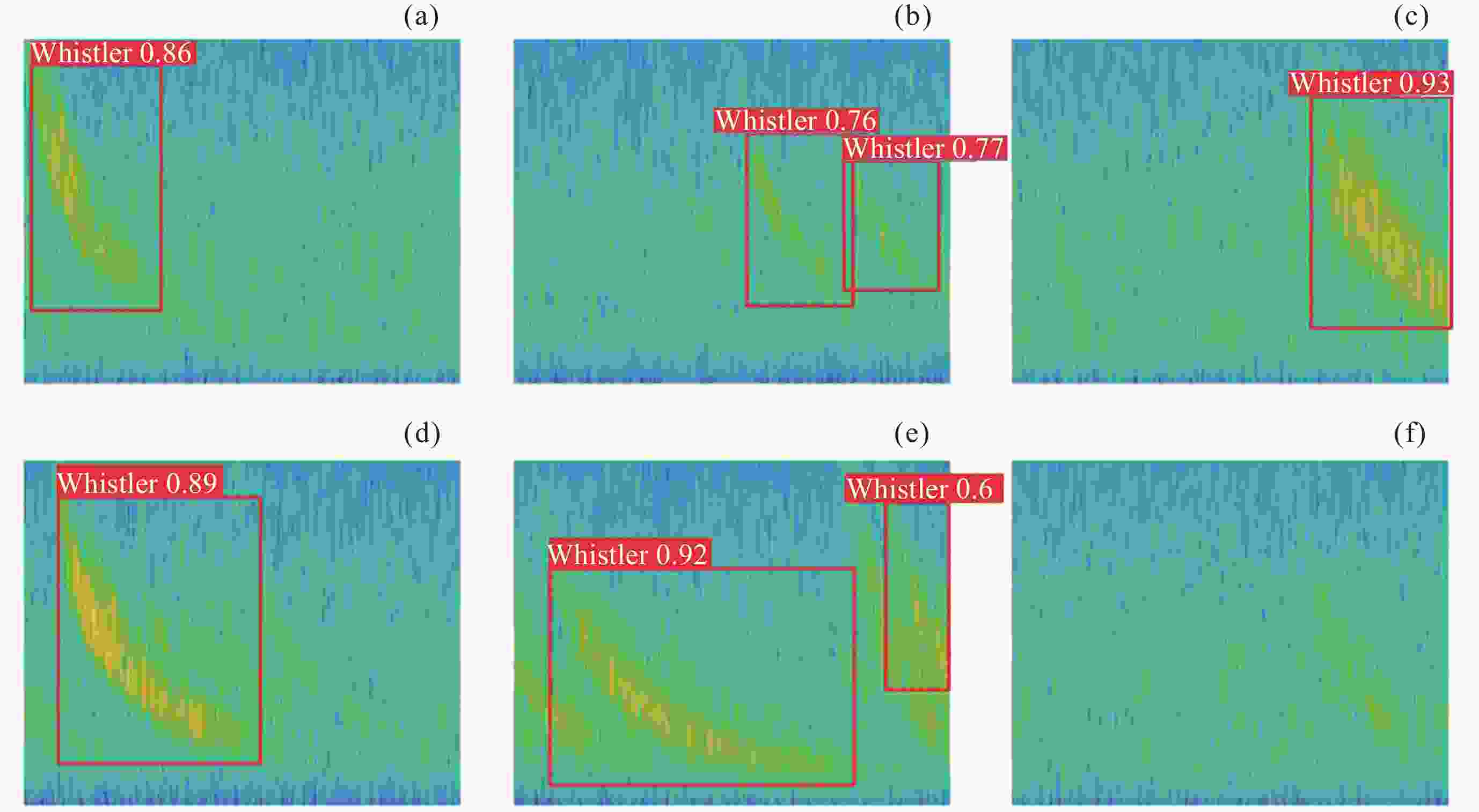
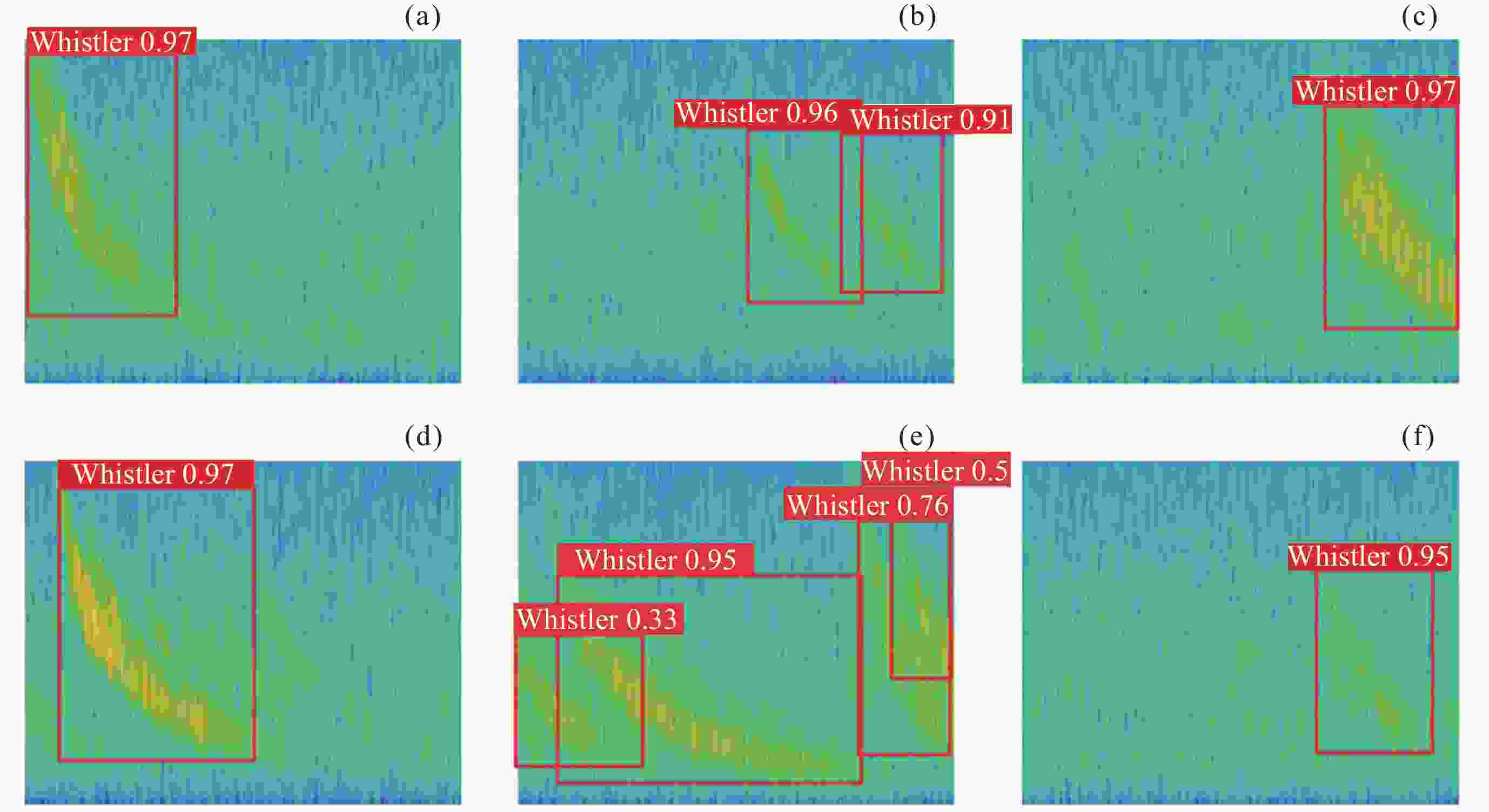
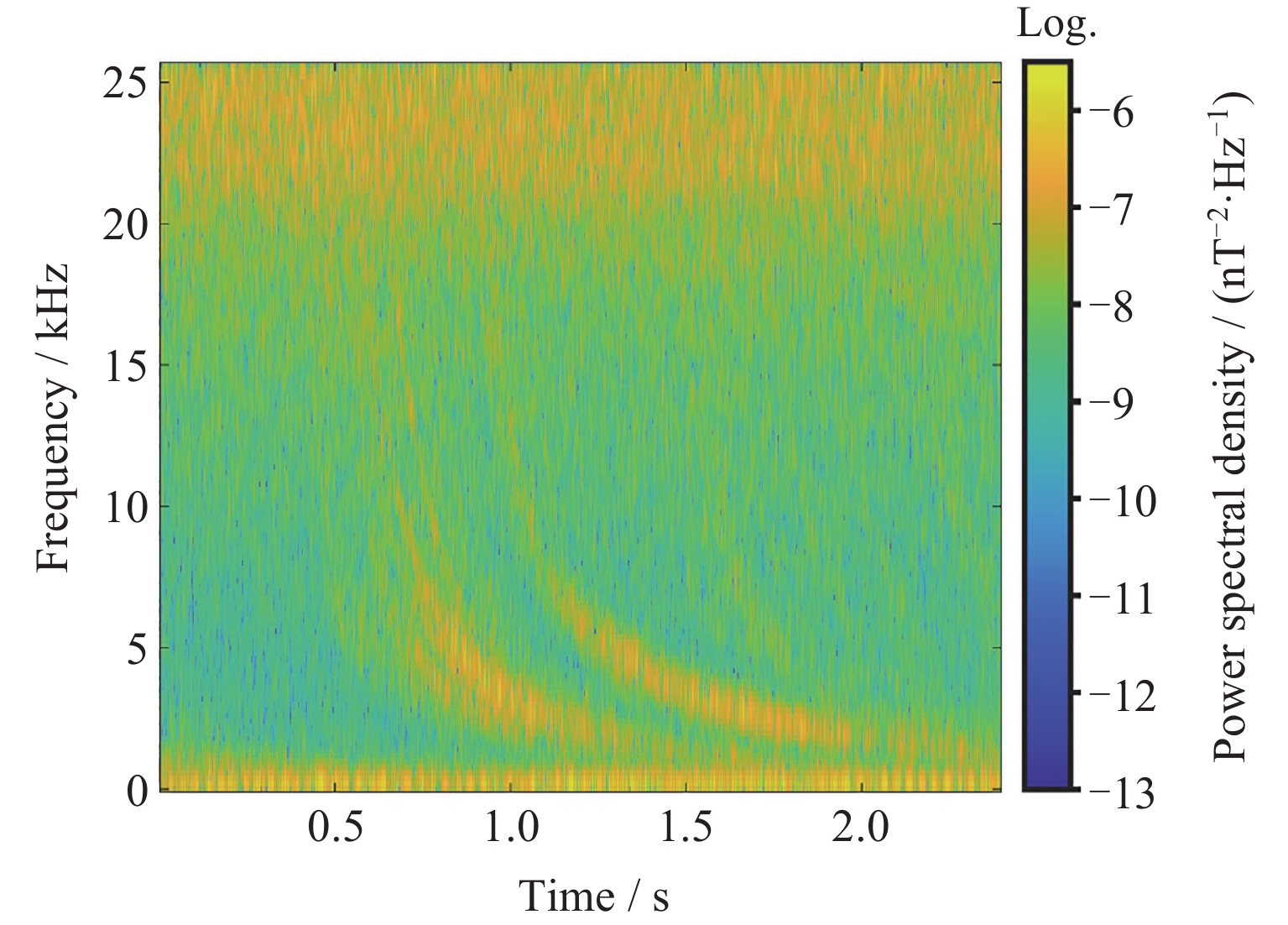
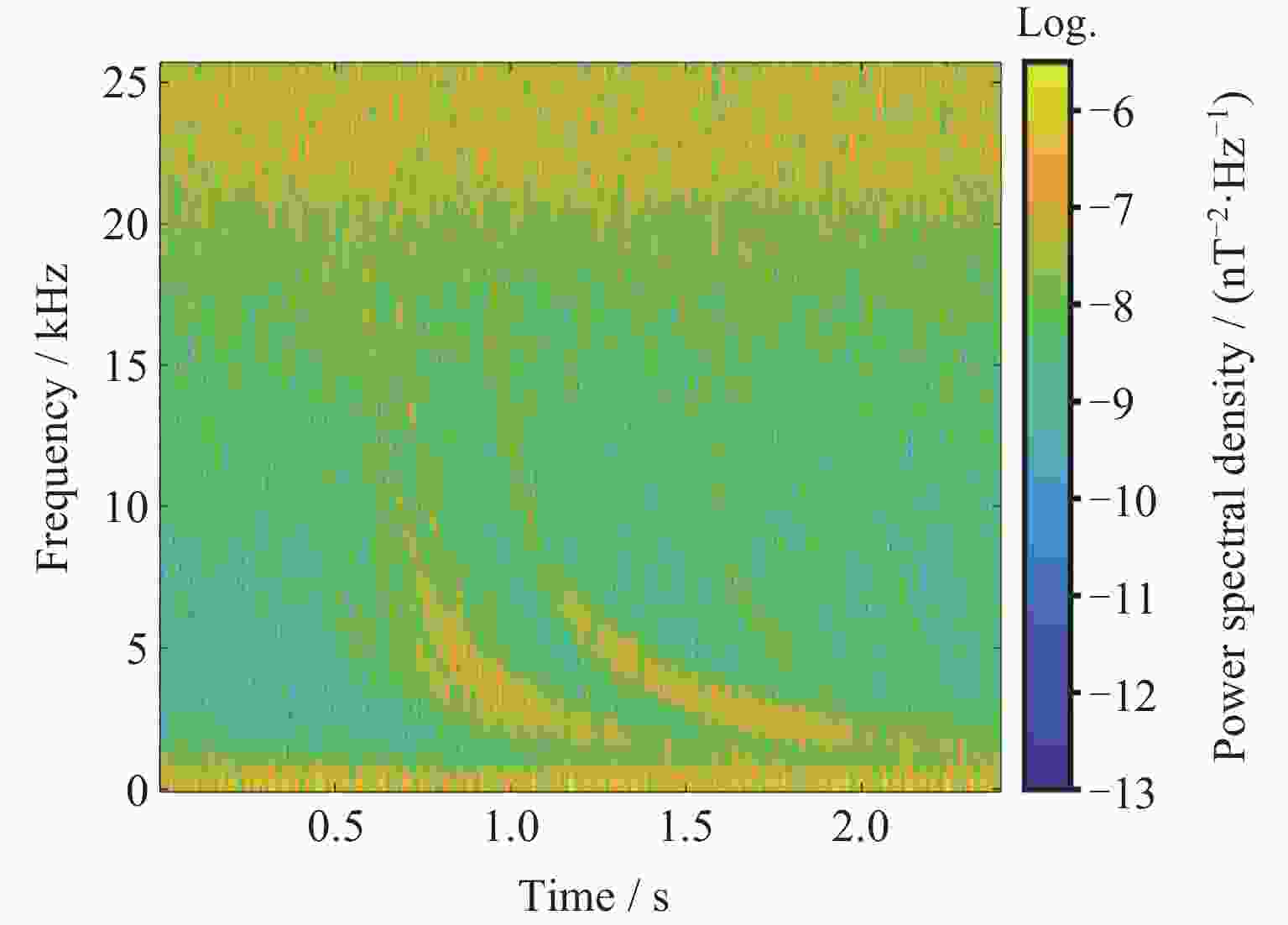
摘要: 提出一种改进YOLOv5(You-Only-Look-Once version 5)检测模型YOLOv5-Upgraded. 为了更快定位真实边框, 该模型将损失函数CIoU (Complete IoU)替换为SIoU(Scylla IoU); 同时为了避免网络训练过程中梯度消失、梯度爆炸以及神经元坏死等现象, 将激活函数SiLU(Sigmoid-weighted Linear Unit)替换为具有更好梯度流的Mish; 在主干网络中插入注意力 (Coordinate Attention, CA)机制, 帮助模型更精准地识别闪电哨声波, 大大降低了漏检率. 基于张衡一号感应磁力仪(Search Coil Magnetometer, SCM)数据, 以2.4 s时间窗口截取数据, 经带通滤波、短时傅里叶变换得到1126张时频图数据集, 再经图像增强操作扩充至7882张, 其中7091张作为训练集, 791张作为测试集. 实验结果表明, 基于改进YOLOv5的模型平均精度均值为99.09%, 召回率为96.20%, 与YOLOv5s相比, 分别提升了2.75%和5.07%, 与基于时频图的YOLOv3模型相比, 平均精度均值和召回率则分别提高了5.89%和9.62%. 基于智能语音的LSTM (Long Short Term Memory Networks)闪电哨声波识别模型大小为82.89 MB, YOLOv5-Upgraded仅为13.78 MB, 约节省83.38%的内存资源. 研究表明改进后的轻量化模型大大降低了闪电哨声波的漏检现象, 在测试集中取得了较好结果, 并且其轻量化特征易于部署到卫星设备, 极大地提高了星载识别的可能性.Abstract: This project proposes an improved YOLOv5 detection algorithm YOLOv5 Upgraded. To address this issue, the study proposes an improved YOLOv5 detection algorithm called YOLOv5-Upgraded.The model takes into account the vector angle between the predicted edge and the real edge, The model replaces the loss function CIoU (Complete IoU) with SIoU (Scylla IoU); at the same time, in order to avoid phenomena such as gradient disappearance, gradient explosion, and neuron necrosis during network training, the activation function SiLU (Sigmoid-weighted Linear Unit) is replaced with Mish with better gradient flow; The CA attention mechanism is inserted into the backbone network to help the model identify the Lightning whistler waves more accurately and greatly reduce the missed detection rate. The study is based on the VLF-band data of CSES Satellite SCM with 2.4 seconds time window to intercept data, and 1126 time-frequency map data sets are obtained by band-pass filtering and short-time Fourier transform, and then expanded to 7882 images by image enhancement operations, of which 7091 are used as training set and 791 are used as test set. Experimentally, the average mean accuracy (mAP) of the improved YOLOv5-based model is 99.09% and the Recall is 96.20%, which are improved by 2.75% and 5.07% compared with the plain YOLOv5s, and 5.89% and 9.62% compared with the time-frequency map-based YOLOv3 model. The size of LSTM based on the speech processing technology lightning whistler waves recognition model is 82.89MB, while the YOLOv5-Upgraded model is only 13.78 MB, saving about 83.38% of memory resources. It is shown that the model greatly reduces the leakage problem of Lightning whistler waves, achieves better results in test set, and its lightweight features are easy to deploy to satellite devices, which greatly improves the possibility of satellite recognition.
-
Key words:
- CSES /
- Lightning whistler waves /
- YOLOv5 /
- Lightweight /
- Automatic detection
-
表 1 数据集划分详情
Table 1. Dataset division details
数据集 训练集 测试集 合计 原始数据 1013 113 1126 图像亮化 2026 226 2252 图像暗化 2026 226 2252 增加高斯噪声 1013 113 1126 增加椒盐噪声 1013 113 1126 合计 7091 791 7882 表 2 模型训练的超参数设置
Table 2. Hyperparameter setting of model training
参数名 参数值 Weight decay (权重衰减) 0.0001 Momentum (动量) 0.900 Batch size (批量大小) 16 Training epoch (训练轮次) 150 Learning rate (学习率) 0.001 表 3 符号定义
Table 3. Symbol defination
预测类别 描述 TP 正确预测, 被模型预测为正类的正样本 FN 错误预测, 被模型预测为负类的正样本 FP 错误预测, 被模型预测为正类的负样本 TN 正确预测, 被模型预测为负类的负样本 表 4 五种目标检测网络性能比较
Table 4. Performance comparison of five object detection networks
模型 平均精度 召回率/(%) Size/(MB) FPS YOLOv3
YOLOv5s93.20
96.3486.58
91.07117.77
13.7780
105YOLOv5m 96.69 93.21 40.08 103 YOLOv5 l
YOLOv5-Upgraded95.38
99.0989.15
96.2088.36
13.787
112表 5 消融实验结果
Table 5. Ablation experimental results
模型 Mish SIoU CA 平均精度(0.5)/(%) 召回率
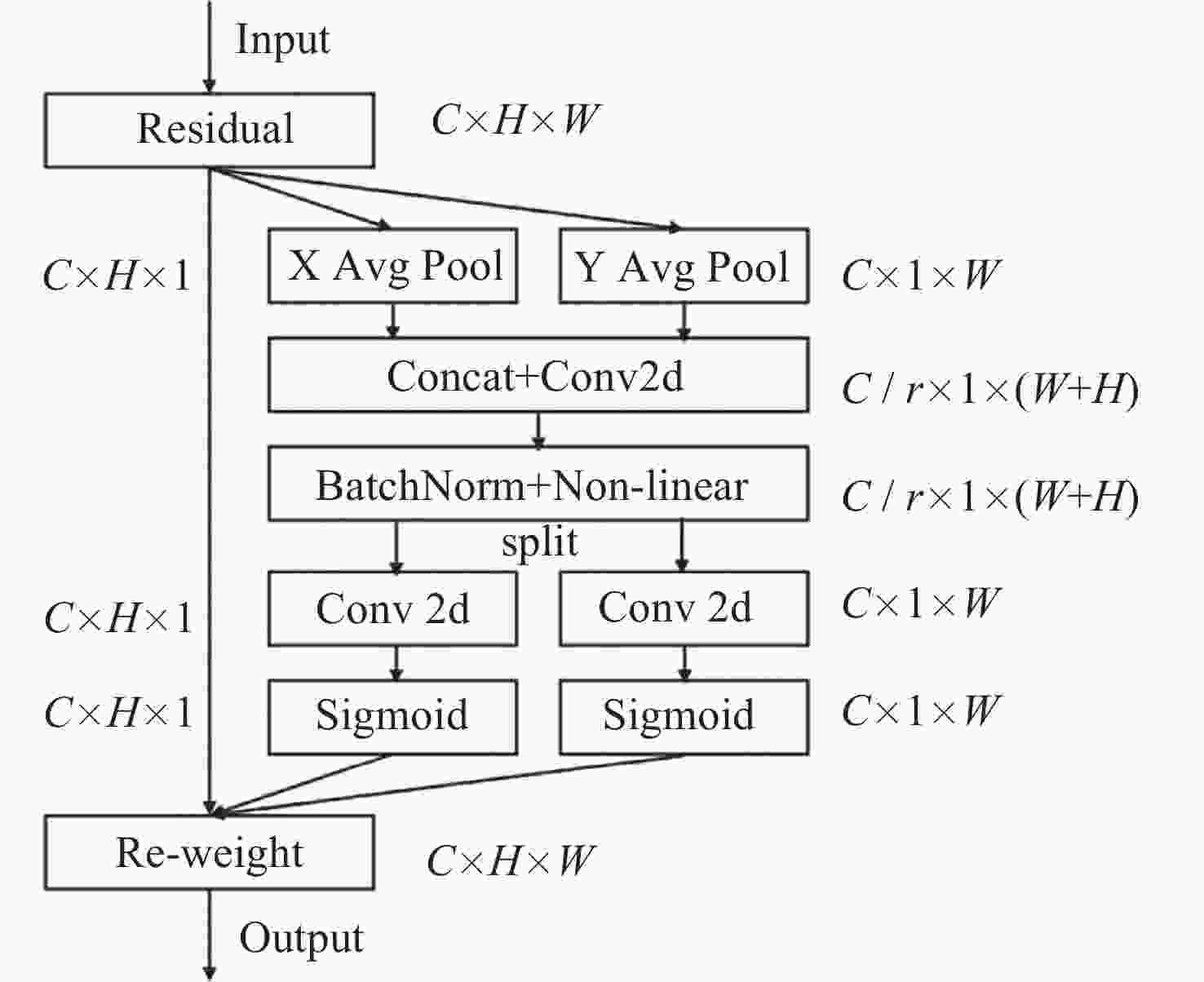
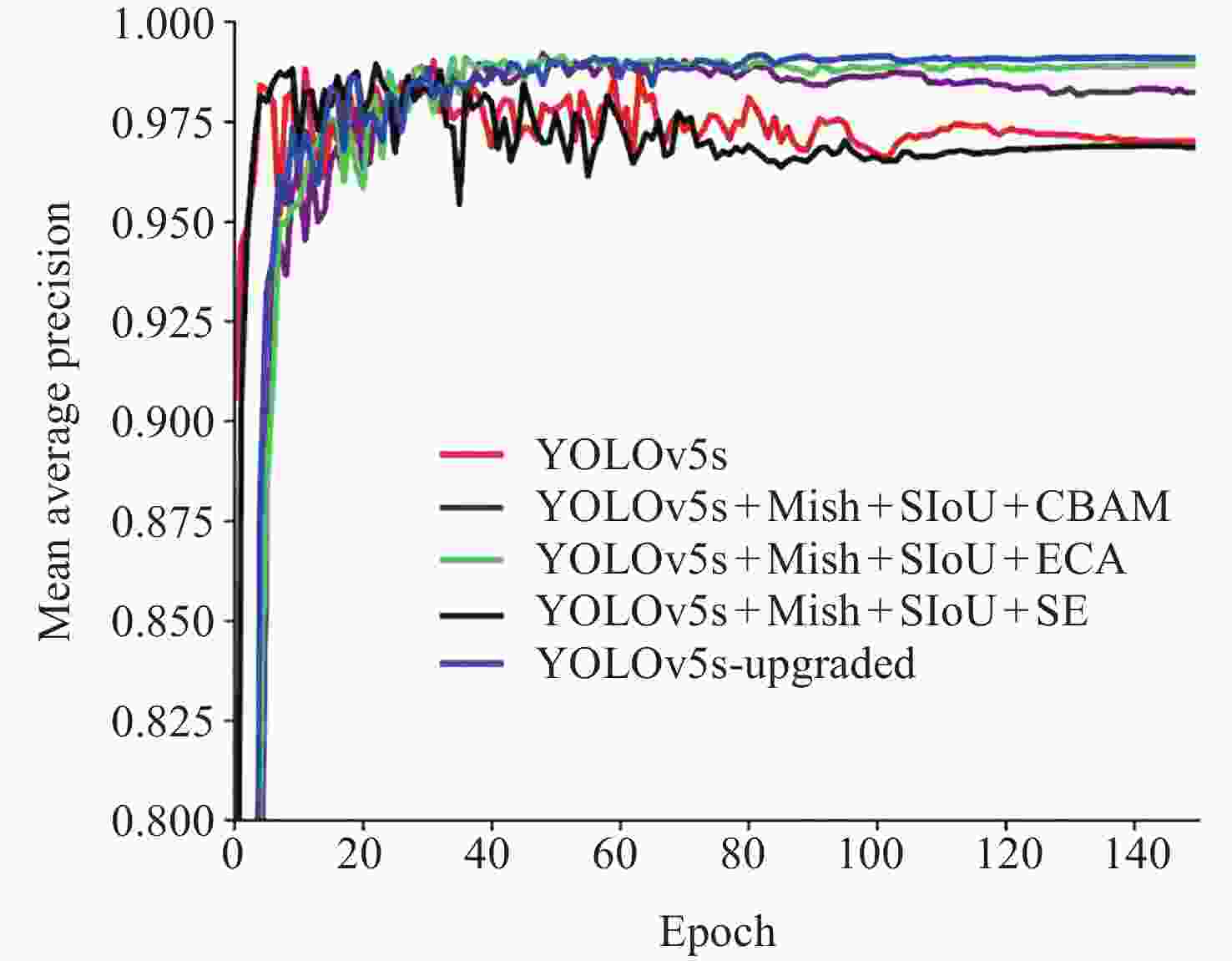
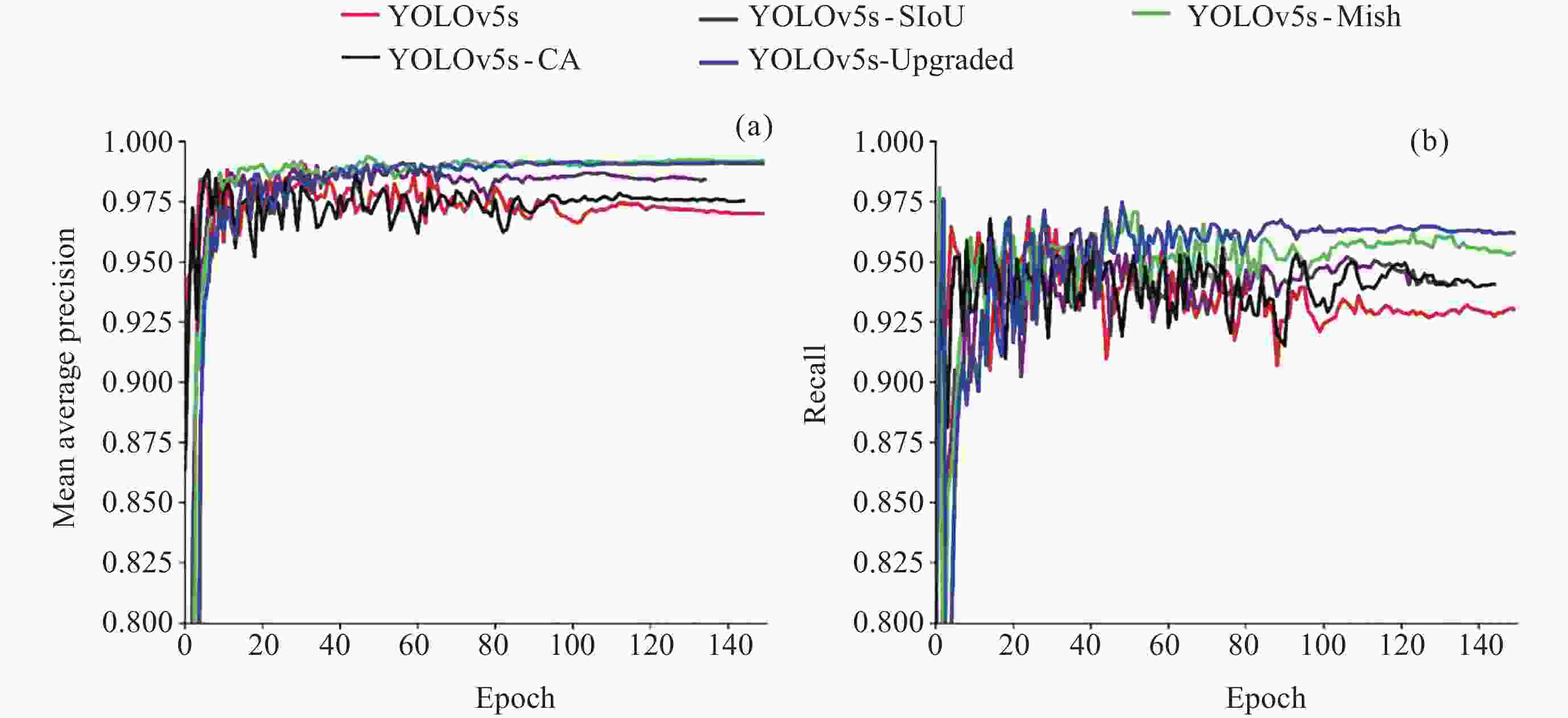
/(%)YOLOv5s × × × 96.34 90.83 YOLOv5s-Mish √ × × 99.20 93.37 YOLOv5s-SIoU × √ × 98.41 94.06 YOLOv5s-CA × × √ 97.53 94.70 YOLOv5-Upgraded √ √ √ 99.09 96.20 -
[1] SANTOLÍK O, PARROT M, INAN U S, et al. Propagation of unducted whistlers from their source lightning: A case study[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2009, 114(A3): A03212 [2] 袁静, 王桥, 张学民, 等. 基于电磁卫星的闪电哨声波智能检测算法的研究进展[J]. 地球物理学报, 2021, 64(5): 1471-1495YUAN Jing, WANG Qiao, ZHANG Xuemin, et al. Advances in the automatic detection algorithms for lightning whistlers recorded by electromagnetic satellite data[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2021, 64(5): 1471-1495 [3] BAYUPATI I P A, KASAHARA Y, GOTO Y. Study of dispersion of lightning whistlers observed by akebono satellite in the Earth’s plasmasphere[J]. IEICE Transactions on Communications, 2012, E95.B(11): 3472-3479 doi: 10.1587/transcom.E95.B.3472 [4] PARROT M, BENOIST D, BERTHELIER J J, et al. The magnetic field experiment IMSC and its data processing onboard DEMETER: Scientific objectives, description and first results[J]. Planetary and Space Science, 2006, 54(5): 441-455 doi: 10.1016/j.pss.2005.10.015 [5] 泽仁志玛, 刘大鹏, 孙晓英, 等. 张衡一号电磁卫星在轨情况及主要的科学成果[J]. 地球与行星物理论评(中英文), 2023, 54(4): 455-465ZEREN Zhima, LIU Dapeng, SUN Xiaoying, et al. Current status and scientific progress of the Zhangheng-1 satellite mission[J]. Reviews of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, 2023, 54(4): 455-465 [6] CAO J B, ZENG L, ZHAN F, et al. The electromagnetic wave experiment for CSES mission: Search coil magnetometer[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2018, 61(5): 653-658 doi: 10.1007/s11431-018-9241-7 [7] HUANG J P, LEI J G, LI S X, et al. The Electric Field Detector (EFD) onboard the ZH-1 satellite and first observational results[J]. Earth and Planetary Physics, 2018, 2(6): 469-478 doi: 10.26464/epp2018045 [8] ZEREN Z M, HUANG J P, SHEN X H, et al. Simultaneous observations of ELF/VLF rising‐tone quasiperiodic waves and energetic electron precipitations in the high‐latitude upper ionosphere[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(5): e2019JA027574 doi: 10.1029/2019JA027574 [9] HU Y P, ZEREN Z M, FU H S, et al. A large‐scale magnetospheric line radiation event in the upper ionosphere recorded by the China‐Seismo‐Electromagnetic satellite[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2023, 128(2): e2022JA030743 doi: 10.1029/2022JA030743 [10] WANG Y L, ZEREN Z M, WANG X, et al. Statistical characteristics of the local proton cyclotron band emissions observed by the CSES[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2022, 127(11): e2022JA030860 doi: 10.1029/2022JA030860 [11] FISER J, CHUM J, DIENDORFER G, et al. Whistler intensities above thunderstorms[J]. Annales Geophysicae, 2010, 28(1): 37-46 doi: 10.5194/angeo-28-37-2010 [12] Oike Y, Kasahara Y, Goto Y. Spatial distribution and temporal variations of occurrence frequency of lightning whistlers observed by VLF/WBA onboard Akebono[J]. Radio Science: 12 [13] ALI AHMAD U, KASAHARA Y, MATSUDA S, et al. Automatic detection of lightning whistlers observed by the plasma wave experiment onboard the arase satellite using the OpenCV library[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(15): 1785 doi: 10.3390/rs11151785 [14] KONAN O J E Y, MISHRA A K, LOTZ S. Machine learning techniques to detect and characterise whistler radio waves[OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2002.01244, 2020 [15] 袁静, 王桥, 杨德贺, 等. 张衡一号感应磁力仪数据闪电哨声波自动识别[J]. 地球物理学报, 2021, 64(11): 3905-3924 doi: 10.6038/cjg2021O0164YUAN Jing, WANG Qiao, YANG Dehe, et al. Automatic recognition algorithm of lightning whistlers observed by the Search Coil Magnetometer onboard the Zhangheng-1 Satellite[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2021, 64(11): 3905-3924 doi: 10.6038/cjg2021O0164 [16] 袁静, 王子杰, 泽仁志玛, 等. 基于智能语音技术的闪电哨声波自动识别[J]. 地球物理学报, 2022, 65(3): 882-897 doi: 10.6038/cjg2022P0365YUAN Jing, WANG Zijie, ZEREN Zhima, et al. Automatic recognition algorithm of the lightning whistler waves by using speech processing technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2022, 65(3): 882-897 doi: 10.6038/cjg2022P0365 [17] 泽仁志玛, 申旭辉, 曹晋滨, 等. 强震前ELF/VLF磁场的扰动特征统计研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2012, 55(11): 3699-3708 doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.11.017ZEREN Zhima, SHEN Xuhui, CAO Jinbin, et al. Statistical analysis of ELF/VLF magnetic field disturbances before major earthquakes[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2012, 55(11): 3699-3708 doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.11.017 [18] 胡云鹏, 泽仁志玛, 黄建平, 等. 张衡一号卫星记录的空间电磁波传播特征分析方法及算法实现[J]. 地球物理学报, 2020, 63(5): 1751-1765 doi: 10.6038/cjg2020N0405HU Yunpeng, ZEREN Zhima, HUANG Jianping, et al. Algorithms and implementation of wave vector analysis tool for the electromagnetic waves recorded by the CSES satellite[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2020, 63(5): 1751-1765 doi: 10.6038/cjg2020N0405 [19] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: unified, real-time object detection[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas: IEEE, 2016 [20] MISRA D. Mish: A Self Regularized Non-Monotonic Activation Function[M/OL]. arXiv, 2020 [21] GEVORGYAN Z. SIoU loss: More powerful learning for bounding box regression[OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2205.12740, 2022 [22] HU J, SHEN L, SUN G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]//2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City: IEEE, 2018 [23] HOU Q B, ZHOU D Q, FENG J S. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design[C]//2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, TN, USA: IEEE, 2021: 13708-13717 -
-





 路超 男, 2000年2月出生, 现在中国科学院大学攻读硕士学位, 专业为计算机技术. E-mail:
路超 男, 2000年2月出生, 现在中国科学院大学攻读硕士学位, 专业为计算机技术. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: