基于改进CNN-BiLSTM模型和地磁监测数据的多时间长度GIC预测
doi: 10.11728/cjss2024.03.2023-0084 cstr: 32142.14.cjss2024.03.2023-0084
Multiscale GIC Prediction Based on Improved CNN-BiLSTM Model and Geomagnetic Monitoring Data
-
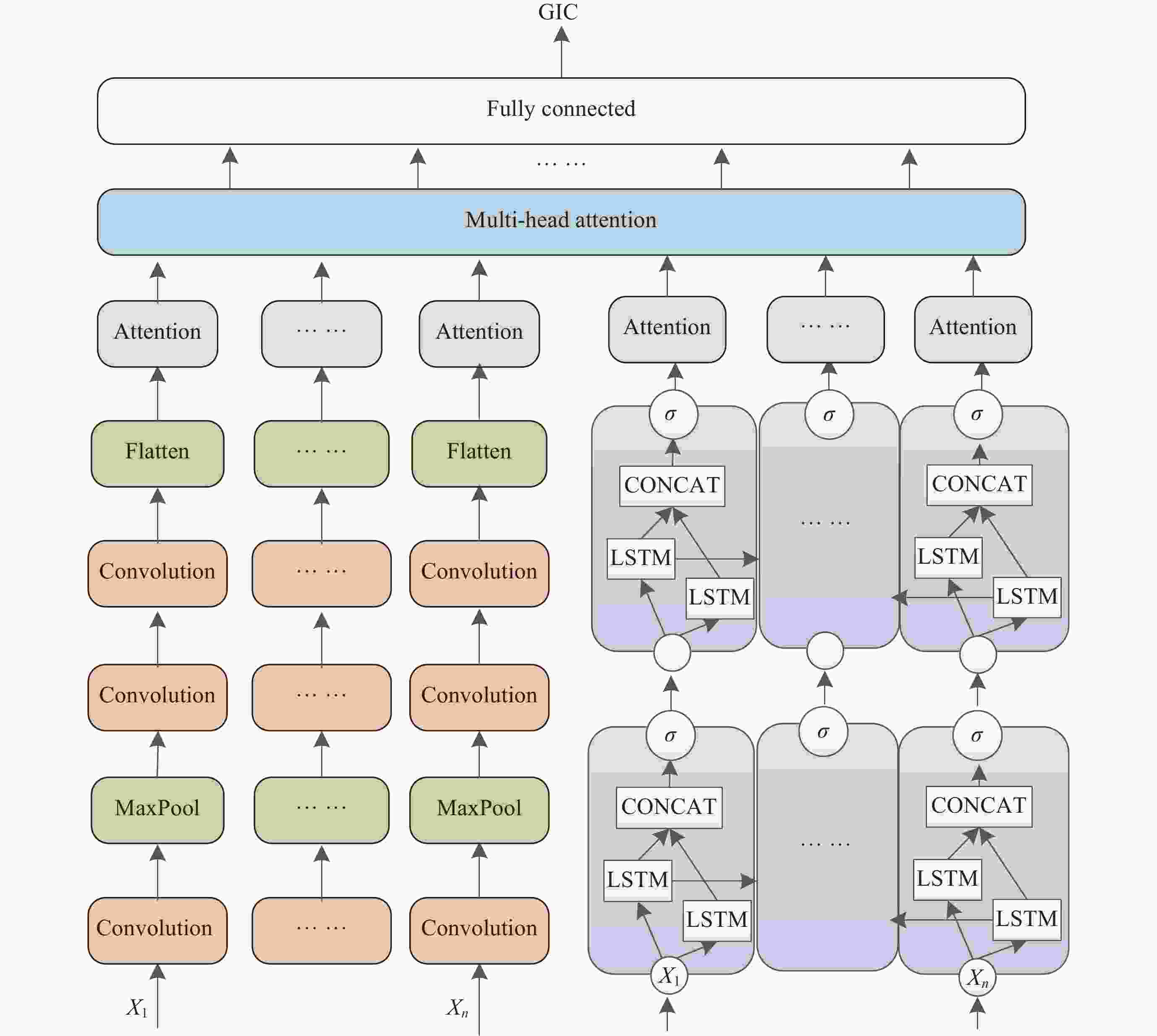
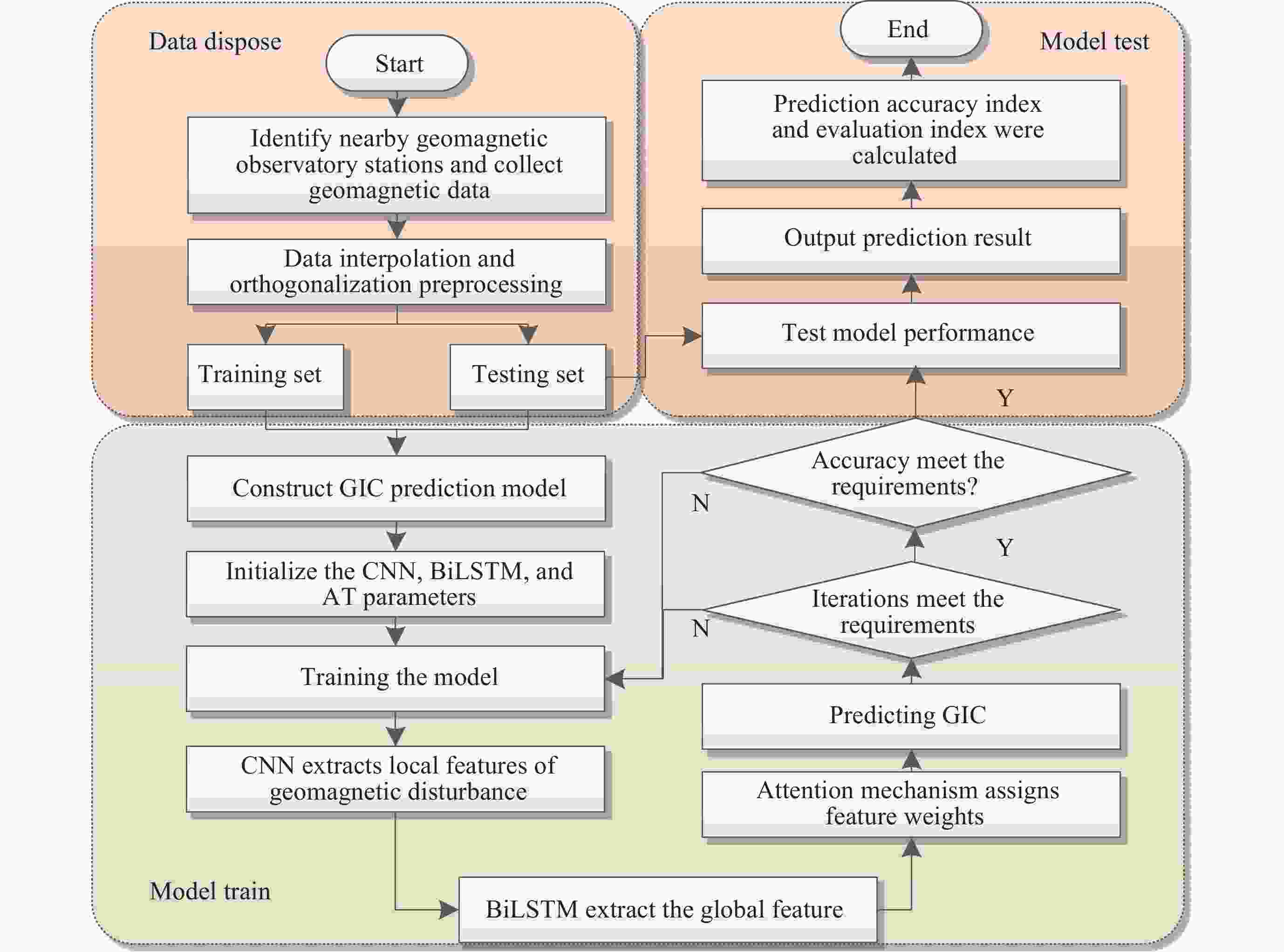
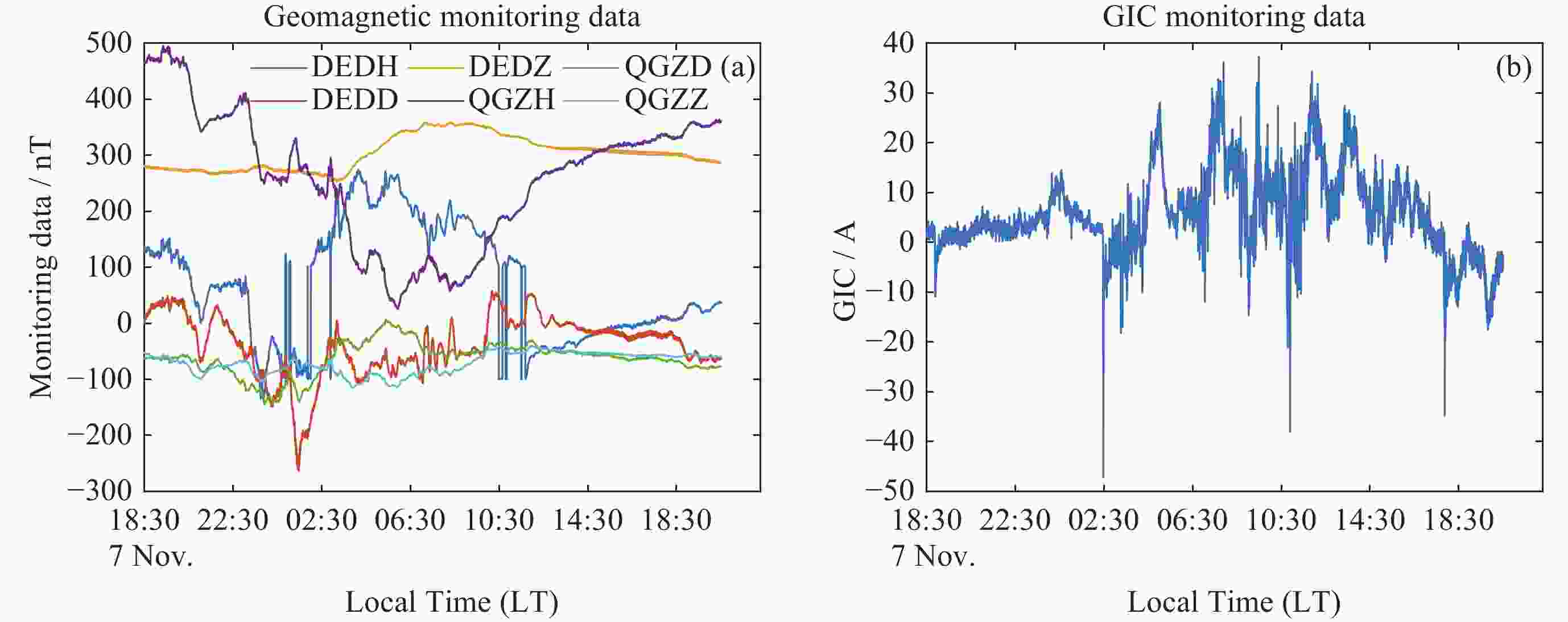
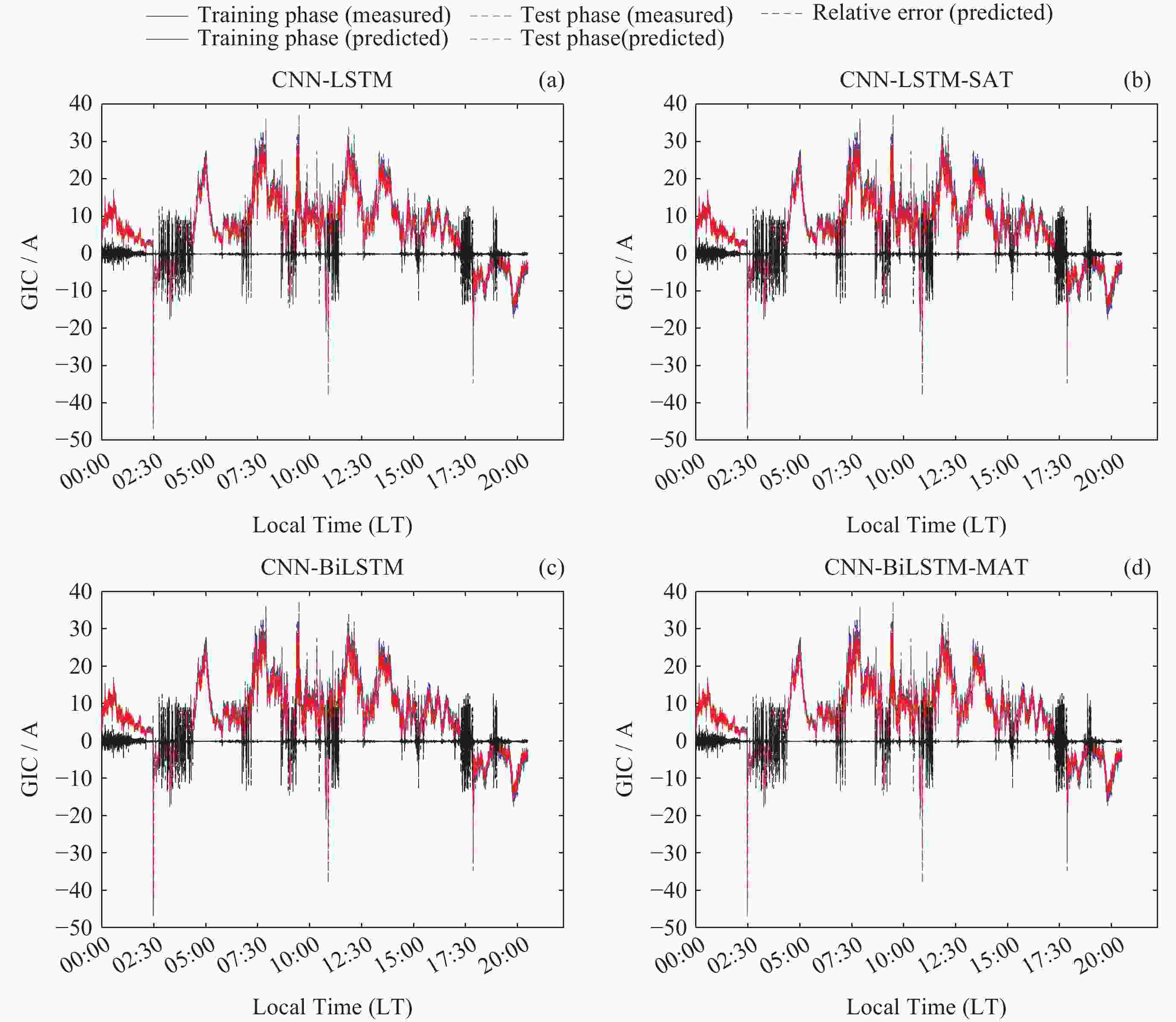
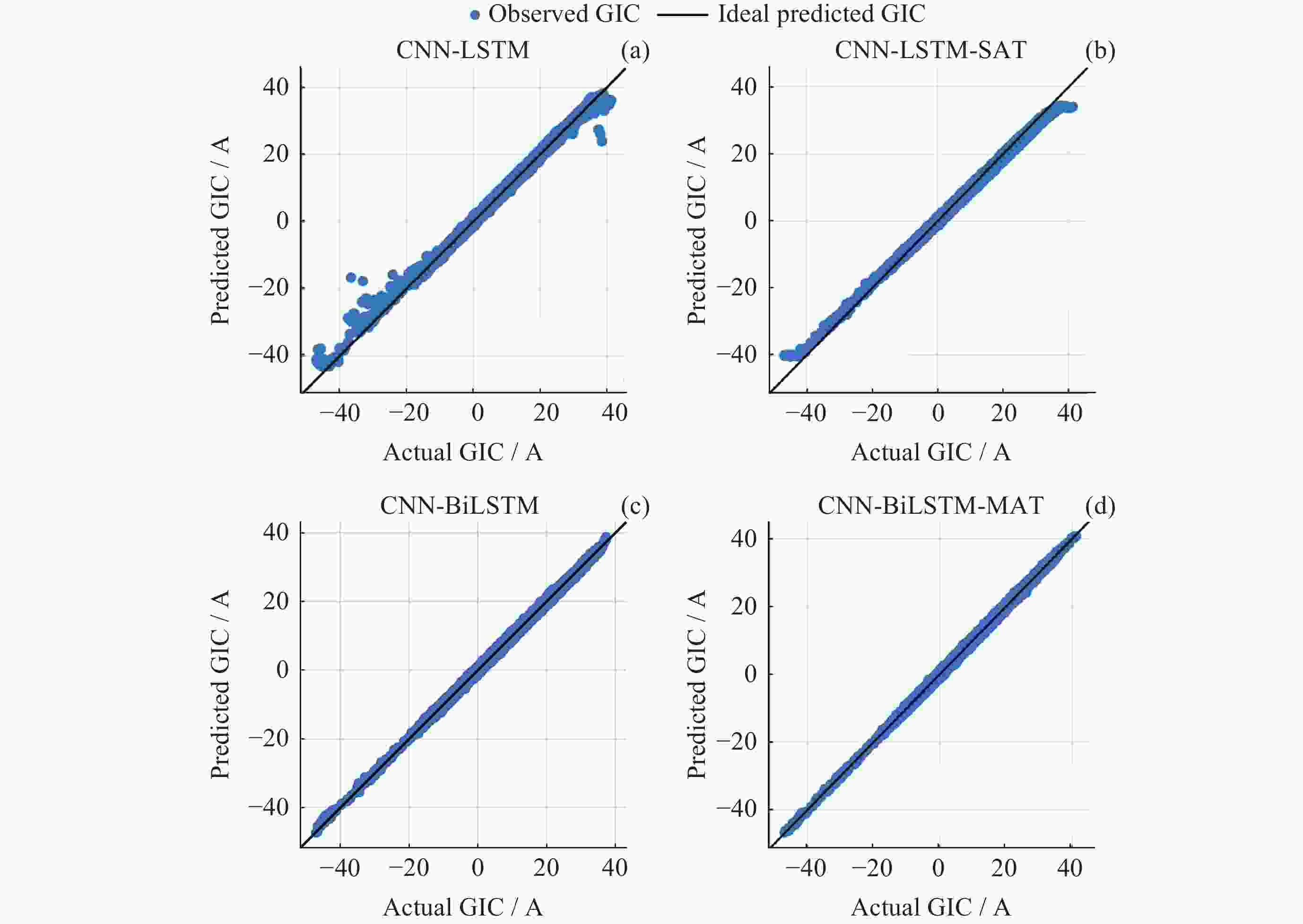
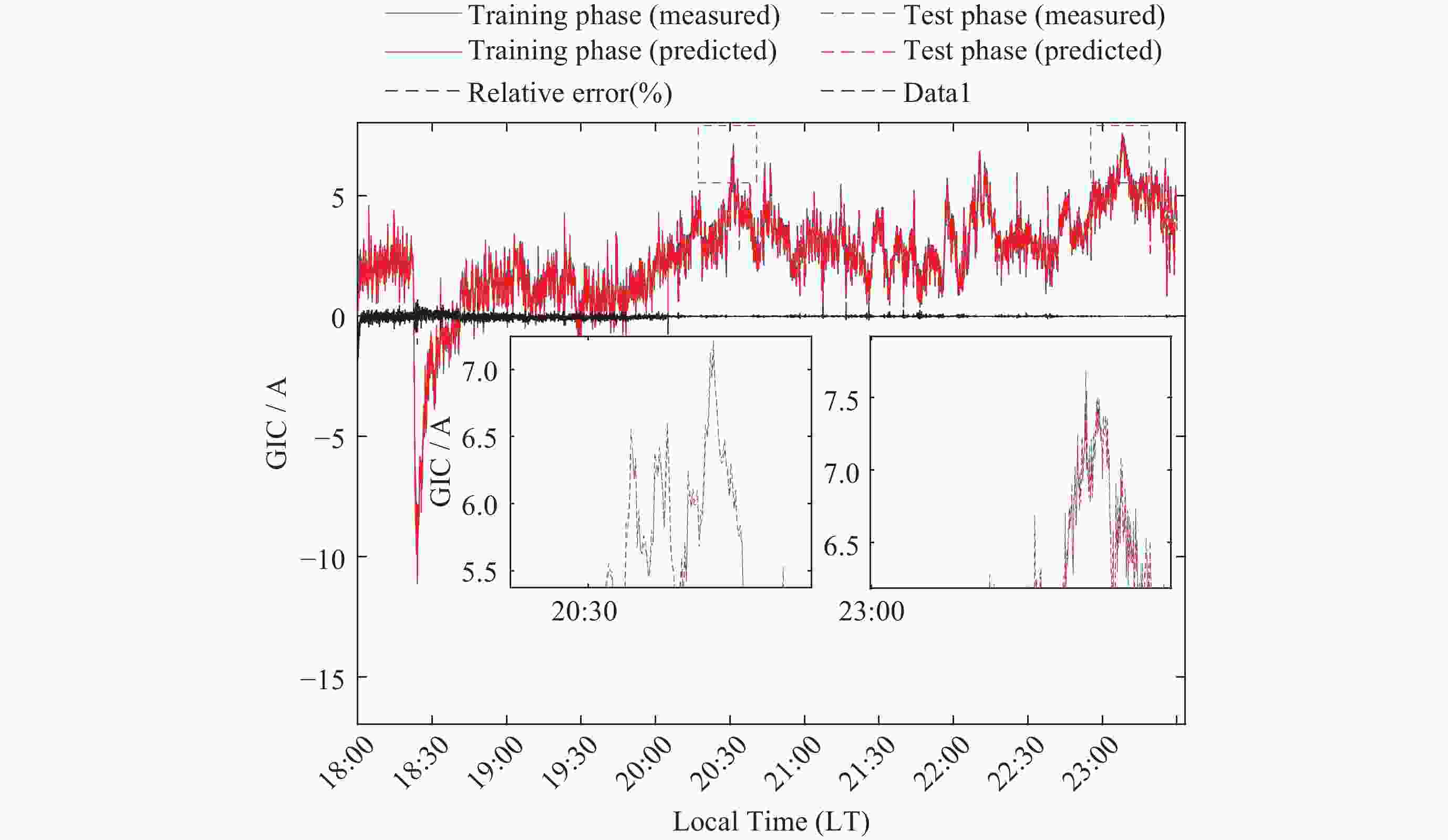
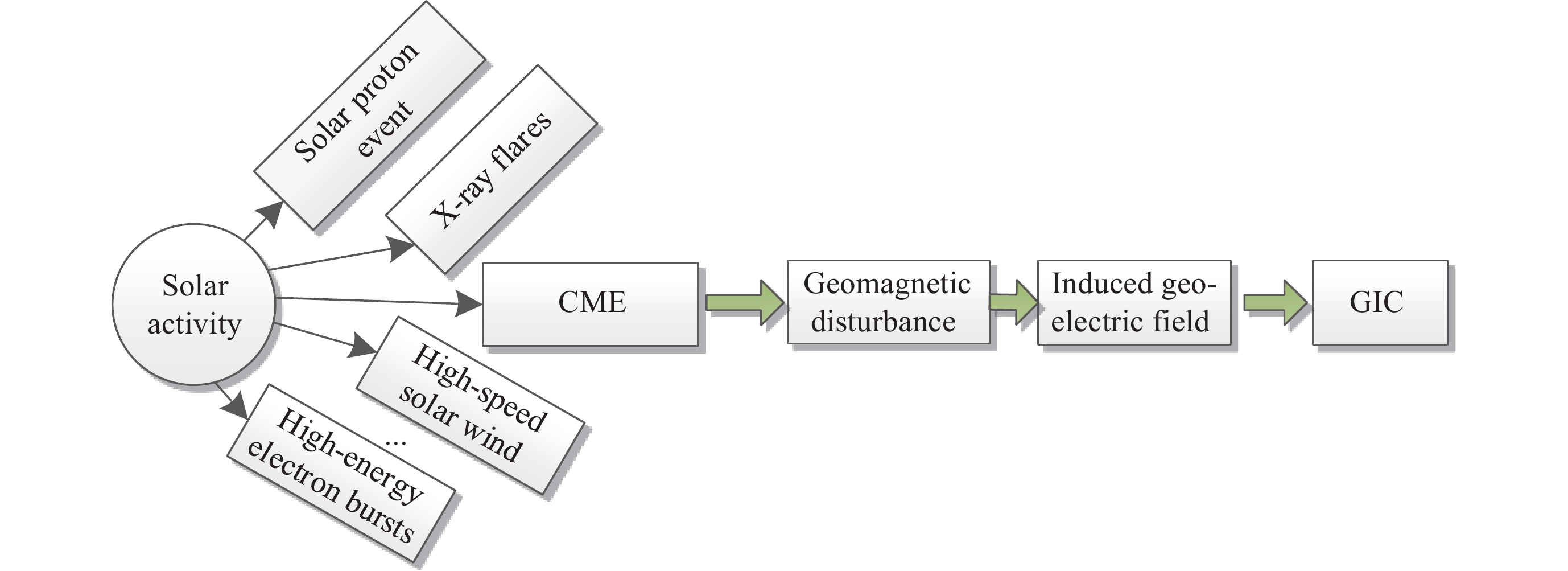
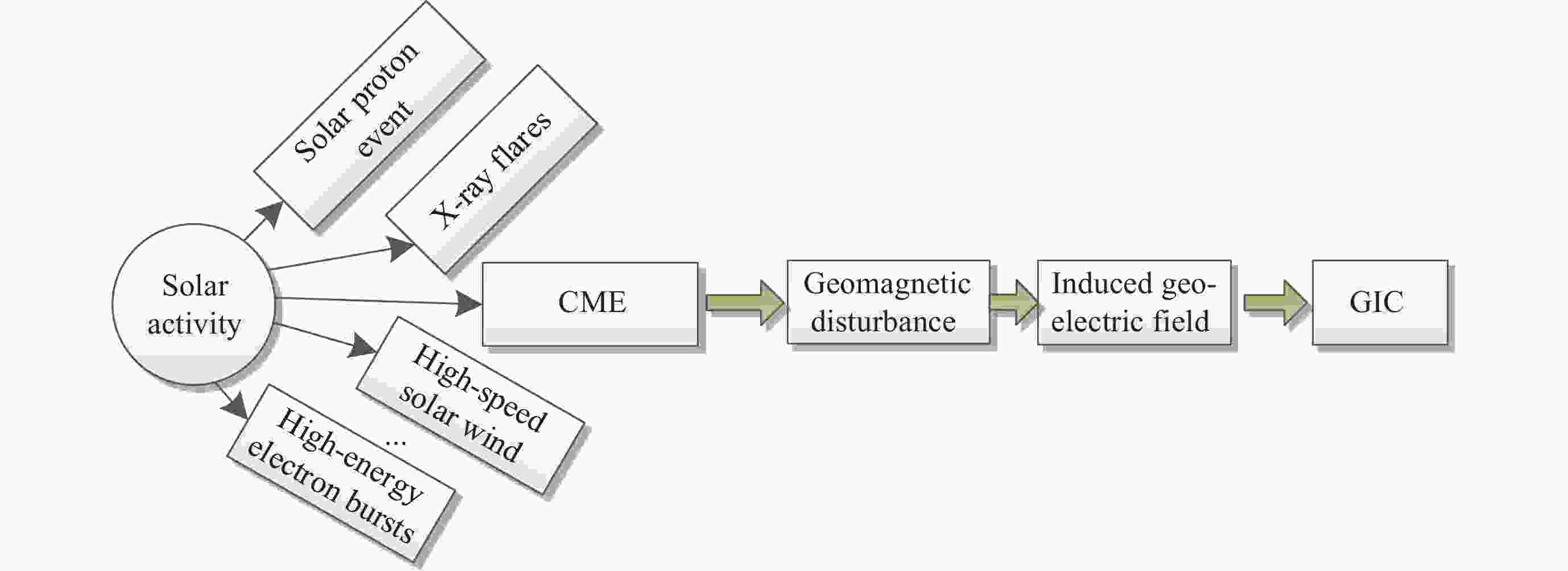
摘要: 太阳风暴在电力系统网络中驱动产生的GIC会影响电力设备和系统的安全运行, 严重时还会引发大面积停电事件. 预测电网GIC水平能够为电力系统保护措施提供重要参考, 然而对这方面的研究仍显不足. 为了解决该问题, 将卷积神经网络(CNN)与双向长短时记忆(BiLSTM)以及注意力机制相结合, 利用空间天气的相关监测信息, 提出了大规模电网GIC多时间长度的预测方法. 本文在分析太阳风暴驱动产生电网地磁感应电流(Geomagnetically Induced Current, GIC)基础上, 构建了GIC预测模型; 提出了基于多头注意力机制的CNN-BiLSTM改进模型, 对GIC进行预测, 并给出了预测流程. 采用CNN捕获地磁扰动局部信息, 根据BiLSTM综合地磁暴扰动信息的全局特征, 综合利用多头注意力机制评估对GIC关键作用的地磁信息片段, 实现电网GIC的预测. 利用2004年11月8日00:00 LT-20:00 LT巨型磁暴期间DED地磁台站和QGZH地磁台监测数据, 应用所提方法对岭澳500 kV变电站GIC进行回归预测. 经过训练后, GIC预测相对误差均在12%以内, 精度高于其他模型的预测结果.Abstract: The GIC generated by solar storms driving in power system networks can affect the safe operation of power equipment and systems, and even lead to major power outages. Predicting the level of GIC in power grids can provide an important reference for power system protection measures, but research in this area continues to be insufficient. In order to solve this problem, a multi-scale GIC prediction method for large-scale power grids is proposed by combining Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Bidirectional Long and Short Term Memory (BiLSTM), and attention mechanisms, using relevant monitoring information of spatial weather. Firstly, based on the analysis of the mechanism of GIC generated by solar storms, a GIC prediction model is constructed; Secondly, a dual-channel GIC prediction architecture based on CNN-BiLSTM is proposed: first, local geomagnetic disturbance information is captured using CNN, then the global characteristics of geomagnetic storm disturbance information are synthesized using BiLSTM, and finally, the geomagnetic information fragments that play a key role in GIC are comprehensively evaluated using the multi-head attention mechanism, achieving the prediction of the power grid GIC. Using monitoring data of the DED geomagnetic station and the QGZH geomagnetic station during the giant magnetic storm from 00:00 LT-20:00 LT on 8 November 2004, the proposed method was applied to regression prediction of the GIC of the 500 kV Ling’Ao substation. After 220 rounds of training, the relative error of GIC prediction is within 12%, the accuracy is higher than the prediction results of other models.
-
Key words:
- Solar storm /
- GIC prediction /
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) /
- Geomagnetic data
-
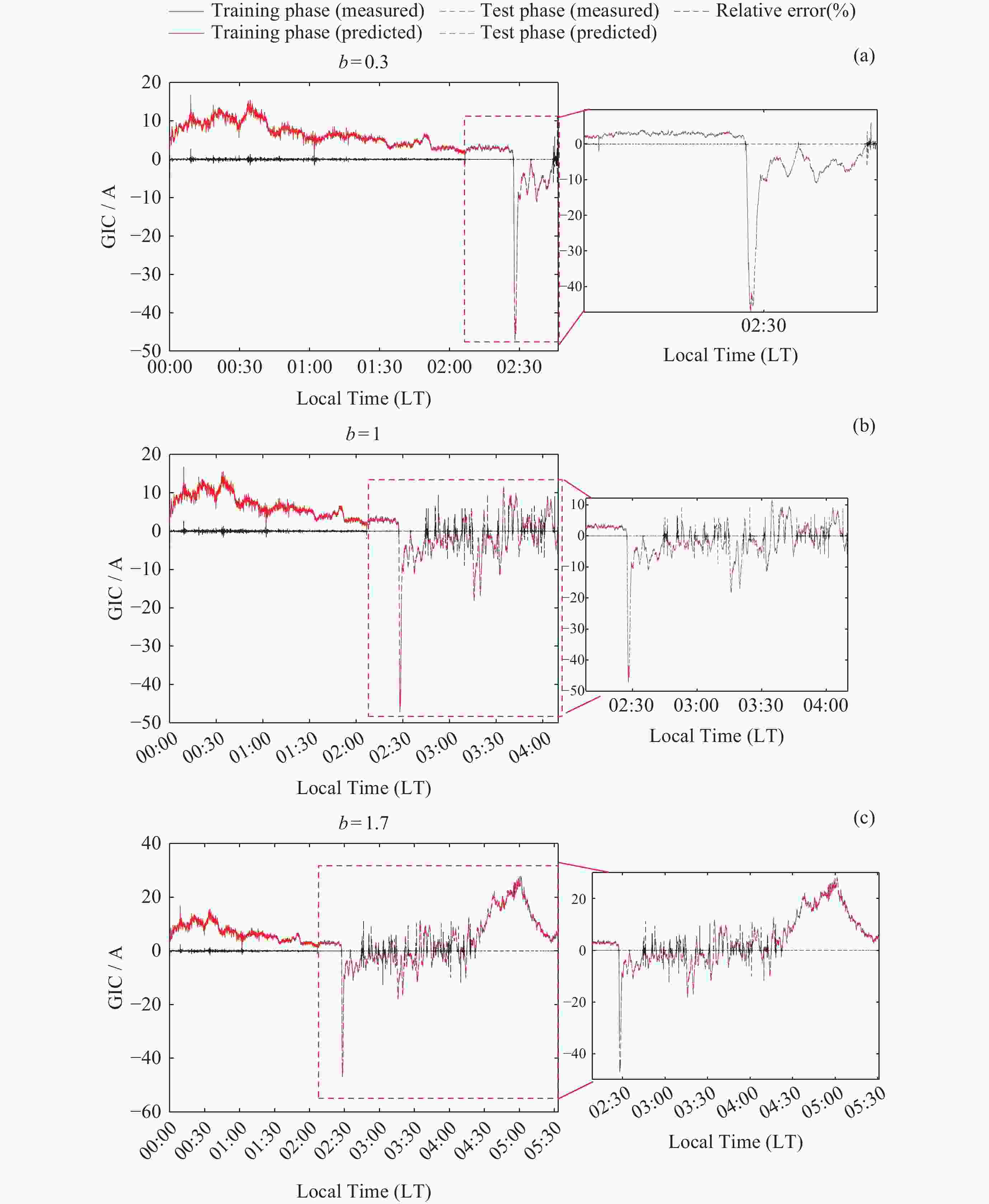
表 1 不同测试集长度时模型评价指标
Table 1. Model evaluation indicators for different test set lengths
训练集长度 测试精度 训练精度 CP PPTS(γ) MAE RMSE MAE RMSE b=0.3 0.02563 0.1223 0.0269 0.2101 0.9689 3.63% b=1 0.0201 0.1025 0.0209 0.1767 0.9926 8.08% b=1.7 0.0212 0.1114 0.0254 0.1960 0.9765 9.22% 表 2 4种模型GIC预测评价指标
Table 2. GIC prediction evaluation indicators for four models
样本集(LT) 模型 Relative error/(%) RMSE MAE PCC $ {\text{PPTS}}\left( 5 \right) $/(%) 00:00-03:00 CNN-BiLSTM-MAT 11.21 0.2314 0.0210 0.976 7.22 CNN-BiLSTM 13.33 0.4871 0.0226 0.944 14.24 CNN-LSTM-SAT 13.37 0.4614 0.0243 0.909 15.33 CNN-LSTM 14.71 0.6385 0.0579 0.897 20.35 03:01-06:00 CNN-BiLSTM-MAT 11.10 0.2042 0.0198 0.987 7.80 CNN-BiLSTM 13.22 - 0.0432 - 15.22 CNN-LSTM-SAT 13.98 0.4348 0.0342 0.931 16.21 CNN-LSTM 15.09 0.9590 0.0654 0.823 23.24 06:01-09:00 CNN-BiLSTM-MAT 10.07 0.2333 0.0208 0.993 8.11 CNN-BiLSTM 13.08 0.3211 0.0299 0.945 15.33 CNN-LSTM-SAT 14.13 0.4476 0.0566 0.912 14.56 CNN-LSTM 14.34 0.9271 0.0579 0.899 21.22 09:01-12:00 CNN-BiLSTM-MAT 9.98 0.2242 0.0187 0.997 7.06 CNN-BiLSTM 13.97 0.2499 0.0286 0.922 14.67 CNN-LSTM-SAT 13.87 0.4681 0.0276 0.899 15.17 CNN-LSTM 14.87 0.9433 0.0688 0.881 19.23 12:01-15:00 CNN-BiLSTM-MAT 10.79 0.2111 0.0211 0.987 7.89 CNN-BiLSTM 13.09 0.2876 0.0321 0.901 16.44 CNN-LSTM-SAT 13.98 0.4473 0.0453 0.892 16.13 CNN-LSTM 14.91 0.9445 0.07651 0.879 21.08 15:01-18:00 CNN-BiLSTM-MAT 10.99 0.1923 0.0209 0.988 8.06 CNN-BiLSTM 13.13 0.2980 0.0298 0.911 14.55 CNN-LSTM-SAT 13.01 0.4091 0.4033 0.923 14.35 CNN-LSTM 14.65 0.9374 0.0654 0.899 21.19 18:01-20:30 CNN-BiLSTM-MAT 11.13 0.2121 0.0214 0.981 7.98 CNN-BiLSTM 12.99 0.3342 0.0329 0.908 15.18 CNN-LSTM-SAT 13.54 0.4445 0.0332 0.911 14.23 CNN-LSTM 14.54 0.9189 0.0561 0.891 21.33 注 黑体数字为最优指标. -
[1] WINTOFT P, WIK M. Exploring three recurrent neural network architectures for geomagnetic predictions[J]. Frontiers in Astronomy and Space Sciences, 2021, 8: 664483 doi: 10.3389/fspas.2021.664483 [2] ZHANG J J, WANG C, TANG B B. Modeling geomagnetically induced electric field and currents by combining a global MHD model with a local one-dimensional method[J]. Space Weather, 2012, 10(5): S05005 doi: 10.1029/2012sw000772 [3] 王开让, 刘连光, 魏恺, 等. 基于行星际太阳风信息和三维磁流体力学模型预测电网GIC的计算方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2015, 35(24): 6341-6350WANG Kairang, LIU Lianguang, WEI Kai, et al. A GIC forecasting algorithm for power grid based on interplanetary solar wind information and three dimensional magnetohydrodynamics model[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2015, 35(24): 6341-6350 [4] KEESEE A M, PINTO V, COUGHLAN M, et al. Comparison of deep learning techniques to model connections between solar wind and ground magnetic perturbations[J]. Frontiers in Astronomy and Space Sciences, 2020, 7: 550874 doi: 10.3389/FSPAS.2020.550874 [5] ROSENQVIST L, HALL J O. Regional 3-D modeling and verification of geomagnetically induced currents in Sweden[J]. Space Weather, 2019, 17(1): 27-36 doi: 10.1029/2018SW002084 [6] PULKKINEN A, HESSE M, KUZNETSOVA M, et al. First-principles modeling of geomagnetically induced electromagnetic fields and currents from upstream solar wind to the surface of the Earth[J]. Annales Geophysicae, 2007, 25(4): 881-893 doi: 10.5194/angeo-25-881-2007 [7] WINTOFT P, WIK M, VILJANEN A. Solar wind driven empirical forecast models of the time derivative of the ground magnetic field[J]. Journal of Space Weather & Space Climate, 2015, 5: A7 doi: 10.1051/swsc/2015008 [8] PULKKINEN A, HESSE M, HABIB S, et al. Solar shield: forecasting and mitigating space weather effects on high-voltage power transmission systems[J]. Natural Hazards, 2010, 53(2): 333-345 doi: 10.1007/s11069-009-9432-x [9] BHASKAR A, VICHARE G. Forecasting of SYMH and ASYH indices for geomagnetic storms of solar cycle 24 including St. Patrick’s Day, 2015 storm using NARX neural network[J]. Journal of Space Weather and Space Climate, 2019, 9: A12 doi: 10.1051/swsc/2019007 [10] BAILEY R L, LEONHARDT R, MÖSTL C, et al. Forecasting GICs and geoelectric fields from solar wind data using LSTMs: application in Austria[J]. Space Weather, 2022, 20(3): e2021SW002907 doi: 10.1029/2021SW002907 [11] 欧阳福莲, 王俊, 周杭霞. 基于改进迁移学习和多时间长度CNN-BiLSTM-Attention的短期电力负荷预测方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2023, 51(2): 132-140 doi: 10.19783/j.cnki.pspc.220422OUYANG Fulian, WANG Jun, ZHOU Hangxia. Short-term power load forecasting method based on improved hierarchical transfer learning and multi-scale CNN-BiLSTM-Attention[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2023, 51(2): 132-140 doi: 10.19783/j.cnki.pspc.220422 [12] AGGA A, ABBOU A, LABBADI M, et al. CNN-LSTM: An efficient hybrid deep learning architecture for predicting short-term photovoltaic power production[J]. Electric Power Systems Research, 2022, 208: 107908 doi: 10.1016/j.jpgr.2022.107908 [13] REN L, DONG J B, WANG X K, et al. A data-driven Auto-CNN-LSTM prediction model for lithium-ion battery remaining useful life[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(5): 3478-3487 doi: 10.1109/TII.2020.3008223 [14] LI X X, KANG Y F, LI F. Forecasting with time series imaging[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2020, 160: 113680 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113680 [15] ZHANG Y D, CHEN X. Motif difference field: A simple and effective image representation of time series for classification[OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2001.07582, 2020. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2001.07582 [16] 孙庆凯, 王小君, 张义志, 等. 基于LSTM和多任务学习的综合能源系统多元负荷预测[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45(5): 63-70SUN Qingkai, WANG Xiaojun, ZHANG Yizhi, et al. Multiple load prediction of integrated energy system based on long short-term memory and multi-task learning[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45(5): 63-70 [17] 刘泽, 张闯, 齐磊, 等. 基于CNN-BiLSTM的锂电池剩余使用寿命概率密度预测[J]. 电源技术, 2023, 47(1): 57-61 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-087X.2023.01.013LIU Ze, ZHANG Chuang, QI Lei et al. Prediction of probability density of remaining useful life of lithium ion battery based on CNN-BiLSTM[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Source, 2023, 47(1): 57-61 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-087X.2023.01.013 [18] 刘春明. 中低纬电网地磁感应电流及其评估方法研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学(北京), 2009LIU Chunming. Med-Low Latitude Power Grid Geomagnetically Induced Currents and its Assessing Method[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University (Beijing), 2009 [19] 李小明, 王颖, 刘春明. 基于ARIMA的电网地磁感应电流预测研究[J]. 计算机与数字工程, 2012, 40(9): 3-136 doi: CNKI:SUN:JSSG.0.2012-09-047LI X M, WANG Y, LIU C M. Short-time Forecasting of GIC in Power Grid Based on ARIMA Model[J]. Computer & Digital Engineering, 2012, 40(9): 3-136 doi: CNKI:SUN:JSSG.0.2012-09-047 -
-





 蓝东亮 男, 1991年8月生于江西省宜春市, 现为中国大唐集团科学技术研究总院有限公司华东电力试验研究院工程师. 主要研究方向为电力系统安全防护、高电压试验技术、绝缘子检测和外绝缘故障辨识等. E-mail:
蓝东亮 男, 1991年8月生于江西省宜春市, 现为中国大唐集团科学技术研究总院有限公司华东电力试验研究院工程师. 主要研究方向为电力系统安全防护、高电压试验技术、绝缘子检测和外绝缘故障辨识等. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: