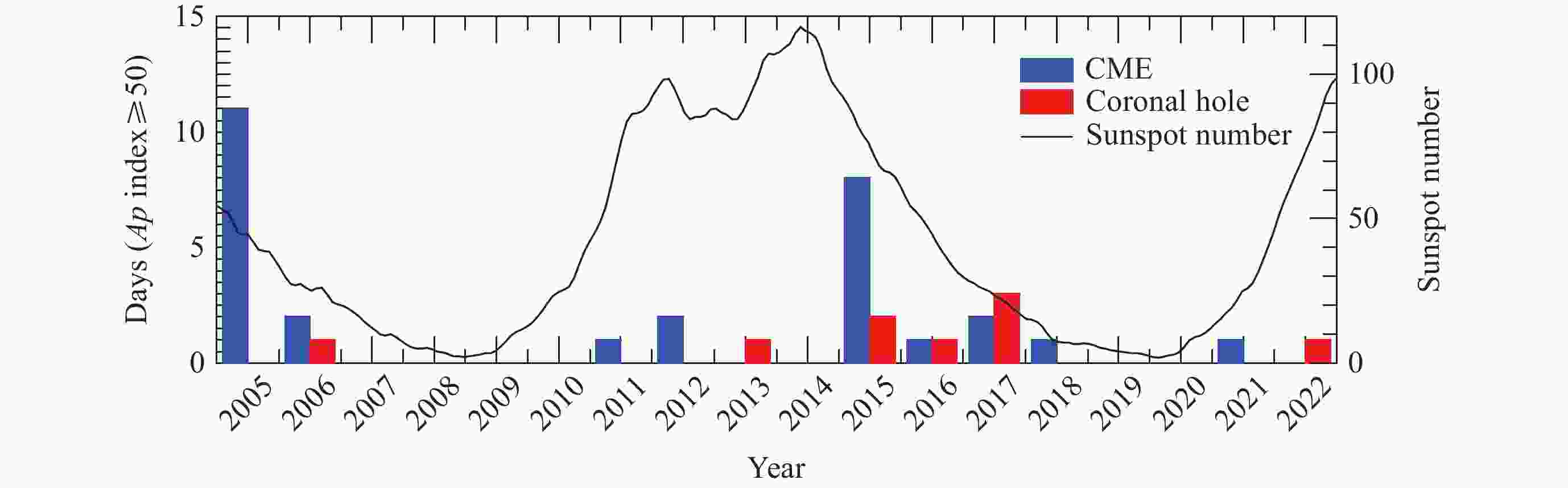
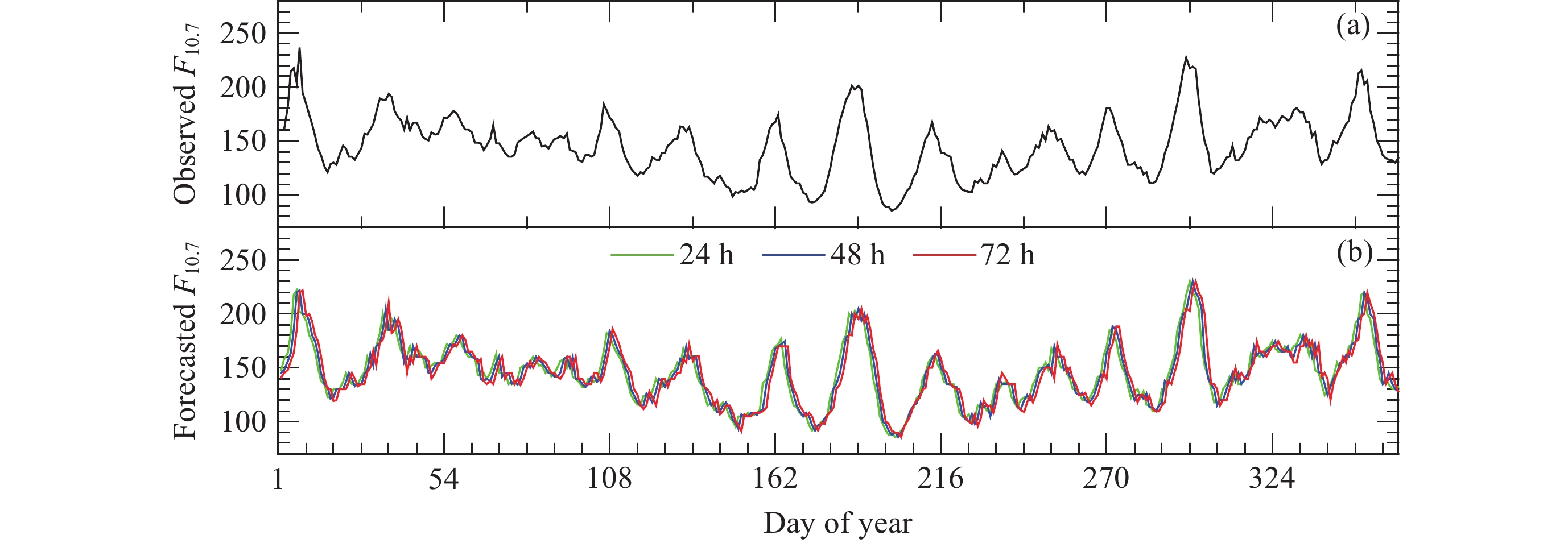
| [1] |
ROEMER M, FRAMKE W, SCHUCHARDT K G H. Solar EUV and decimetric indices and thermospheric models[J]. Advances in Space Research, 1983, 3(1): 75-82 doi: 10.1016/0273-1177(83)90208-9
|
| [2] |
HEDIN A E. Correlations between thermospheric density and temperature, solar EUV flux, and 10.7-cm flux variations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1984, 89(A11): 9828-9834 doi: 10.1029/JA089iA11p09828
|
| [3] |
刘芳, 蔡立锋, 孙先伟, 等. 空间环境参数预报数据在轨控策略中的融合应用[J]. 无线电工程, 2019, 49(4): 314-318 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2019.04.10LIU Fang, CAI Lifeng, SUN Xianwei, et al. Fusion application of prediction data for space environmental parameters in orbit control strategy[J]. Radio Engineering, 2019, 49(4): 314-318 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2019.04.10
|
| [4] |
张育林, 陈小前, 闫野, 译. 空间环境及其对航天器的影响[M]. 北京: 中国宇航出版社, 2011PISACANE V L. The Space Environment and its Effects on Space Systems[M]. Virginia: American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2008
|
| [5] |
林元章. 太阳物理导论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2000LIN Yuanzhang. Introduction of Solar Physics[M]. Beijing: China Science Press, 2000
|
| [6] |
王劲松, 吕建永. 空间天气[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2009WANG Jingsong, LÜ Jianyong. Space Weather[M]. Beiing: China Meteorological Press, 2009
|
| [7] |
张效信, 杜丹, 郭建广. 空间天气定量预报模式[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2016ZHANG Xiaoxin, DU Dan, GUO Jianguang. Quantitative Forecasting Model of Space Weather[M]. Beijng: China Meteorological Press, 2016
|
| [8] |
雷久侯, 李若曦, 任德馨, 等. 热层大气密度反演与建模研究进展[J]. 地球与行星物理论评, 2023, 54(4): 434-454LEI Jiuhou, LI Ruoxi, REN Dexin, et al. Recent progress on the retrieval and modeling of thermosphere mass density[J]. Reviews of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, 2023, 54(4): 434-454
|
| [9] |
BRUINSMA S, FORBES J M, NEREM R S, et al. Thermosphere density response to the 20–21 November 2003 solar and geomagnetic storm from CHAMP and GRACE accelerometer data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2006, 111(A6): A06303
|
| [10] |
LEI J H, THAYER J P, LU G, et al. Rapid recovery of thermosphere density during the October 2003 geomagnetic storms[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2011, 116(A3): A03306
|
| [11] |
LEI J H, BURNS A G, THAYER J P, et al. Overcooling in the upper thermosphere during the recovery phase of the 2003 October storms[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2012, 117(A3): A03314
|
| [12] |
LIU R, LÜHR H, DOORNBOS E, et al. Thermospheric mass density variations during geomagnetic storms and a prediction model based on the merging electric field[J]. Annales Geophysicae, 2010, 28(9): 1633-1645 doi: 10.5194/angeo-28-1633-2010
|
| [13] |
LIU R, MA S Y, LÜHR H. Predicting storm-time thermospheric mass density variations at CHAMP and GRACE altitudes[J]. Annales Geophysicae, 2011, 29(3): 443-453 doi: 10.5194/angeo-29-443-2011
|
| [14] |
LÜHR H, ROTHER M, KÖHLER W, et al. Thermospheric up-welling in the cusp region: evidence from CHAMP observations[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2004, 31(6): L06805
|
| [15] |
SUTTON E K, FORBES J M, NEREM R S. Global thermospheric neutral density and wind response to the severe 2003 geomagnetic storms from CHAMP accelerometer data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2005, 110(A9): A09S40
|
| [16] |
刘振兴. 太空物理学[M]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学出版社, 2005LIU Zhenxing. Space Physics[M]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology Press, 2005
|
| [17] |
张桂清, 王家龙. 北京天文台太阳活动预报新方案的检验和与旧方案及WWA预报效果的比对[J]. 地球物理学报, 1994, 9: 42-47ZHANG Guiqing, WANG Jialong. Verification on new scheme of predicting x-ray flares in BAO and comparison with predicting effectiveness of old scheme and WWA[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 1994, 9: 42-47
|
| [18] |
CROWN M D. Validation of the NOAA space weather prediction center’s solar flare forecasting look-up table and forecaster-issued probabilities[J]. Space Weather, 2012, 10(6): S06006
|
| [19] |
DEVOS A, VERBEECK C, ROBBRECHT E. Verification of space weather forecasting at the regional warning center in Belgium[J]. Journal of Space Weather and Space Climate, 2014, 4: A29 doi: 10.1051/swsc/2014025
|
| [20] |
SHARPE M A, MURRAY S A. Verification of space weather forecasts issued by the met office space weather operations centre[J]. Space Weather, 2017, 15(10): 1383-1395 doi: 10.1002/2017SW001683
|
| [21] |
ZHONG Q Z, WANG J J, MENG X J, et al. Prediction model for solar energetic proton events: analysis and verification[J]. Space Weather, 2017, 17(5): 709-726
|
| [22] |
中国气象局. QX/T 295-2015 空间天气短期预报检验方法[S]. 北京: 中国气象出版社, 2015China Meteorological Administration. QX/T 295-2015 Verification methods for short-term space weather forecast[S]. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 2015
|
| [23] |
The conceptual approach). New York: USA Springer, 1997 (吴喜之, 程博, 柳林旭, 等译. 统计学(基本概念和方法). 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000GUDMUND R I, MARY G. Statistics
|
| [24] |
BERDYUGINA S V, USOSKIN I G. Active longitudes in sunspot activity: century scale persistence[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2003, 405(3): 1121-1128
|
| [25] |
USOSKIN I G, BERDYUGINA S V, POUTANEN J. Preferred sunspot longitudes: non-axisymmetry and differential rotation[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2005, 441(1): 347-352
|
| [26] |
ZHANG L Y, CUI Y M, HE H, et al. Longitudinal distribution of major solar flares during 1975-2005[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2007, 40(7): 970-975 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2006.12.052
|
| [27] |
ZHANG L Y, WANG H N, DU Z L, et al. Long-term behavior of active longitudes for solar X-ray flares[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2007, 471(2): 711-716
|
| [28] |
ZHANG L Y, WANG H N, DU Z L. Prediction of solar active longitudes[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2008, 484(2): 523-527
|
| [29] |
ZHANG L, MURSULA K, USOSKIN I, et al. Global analysis of active longitudes of solar X-ray flares[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2011, 73(2/3): 258-263
|
| [30] |
CHEN A Q, WANG J X, LI J W, et al. Statistical properties of superactive regions during solar cycles 19-23[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2011, 534: A47
|
| [31] |
BIESECKER D A, WEBB D F, ST CYR O C. STEREO space weather and the space weather beacon[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2008, 136(1/2/3/4): 45-65
|
| [32] |
PESNELL W D, THOMPSON B J, CHAMBERLIN P C. The solar dynamics observatory (SDO)[J]. Solar Physics, 2012, 275(1/2): 3-15
|
| [33] |
SCHOU J, SCHERRER P H, BUSH R I, et al. Design and ground calibration of the Helioseismic and Magnetic ima- ger (HMI) instrument on the Solar dynamics observatory (SDO)[J]. Solar Physics, 2012, 275(1/2): 229-259
|
| [34] |
罗冰显, 刘四清, 钟秋珍, 等. 冕洞特征参数与重现型地磁暴关系的统计研究[J]. 空间科学学报, 2007, 27(2): 117-124 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-6124.2007.02.005LUO Bingxian, LIU Siqing, ZHONG Qiuzhen, et al. Primary study about the relationships between coronal holes’ parameters and the correlative geomagnetic disturbances[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2007, 27(2): 117-124 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-6124.2007.02.005
|
| [35] |
卜萱, 罗冰显, 刘四清, 等. 冕洞特征参数与地磁暴强度及发生时间统计[J]. 空间科学学报, 2020, 40(1): 9-19 doi: 10.11728/cjss2020.01.009BU Xuan, LUO Bingxian, LIU Siqing, et al. Statistical study between characteristic parameters of coronal holes and intensity/time of geomagnetic storms[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2020, 40(1): 9-19 doi: 10.11728/cjss2020.01.009
|
| [36] |
高扬, 吕建永, 王明, 等. 基于深度学习的太阳F10.7辐射通量的短期预报研究[J]. 天文学报, 2022, 63(1): 104-114GAO Yang, LÜ Jianyong, WANG Ming, et al. Short-term prediction of solar F10.7 radiation flux based on deep learning[J]. Acta Astronomica Sinica, 2022, 63(1): 104-114
|
| [37] |
HUANG X, WANG H N, XU L, et al. Deep learning based solar flare forecasting model. I. Results for line-of-sight magnetograms[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2018, 856(1): 7 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/aaae00
|
| [38] |
ZHENG Y F, LI X B, WANG X S. Solar flare prediction with the hybrid deep convolutional neural network[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2019, 885(1): 73 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/ab46bd
|
| [39] |
LI X B, ZHENG Y F, WANG X S, et al. Predicting solar flares using a novel deep convolutional neural network[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2020, 891(1): 10 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/ab6d04
|
| [40] |
BHATTACHARJEE S, ALSHEHHI R, DHURI D B, et al. Supervised convolutional neural networks for classification of flaring and nonflaring active regions using line-of-sight magnetograms[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2020, 898(2): 98 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/ab9c29
|
| [41] |
CHEN A Q, YE Q, WANG J X. Flare index prediction with machine learning algorithms[J]. Solar Physics, 2021, 296(10): 150 doi: 10.1007/s11207-021-01895-1
|
| [42] |
LIU S X, XU L, ZHAO Z R, et al. Deep learning based solar flare forecasting model. II. Influence of image resolution[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2022, 941(1): 20 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/ac99dc
|
| [43] |
LI M, CUI Y M, LUO B X, et al. Deep neural networks of solar flare forecasting for complex active regions[J]. Fron tiers in Astronomy and Space Sciences, 2023, 10: 1177550 doi: 10.3389/fspas.2023.1177550
|
| [44] |
温靖, 钟秋珍, 刘四清. 太阳10.7 cm射电流量中期预报模型研究(II)[J]. 空间科学学报, 2010, 30(3): 198-204 doi: 10.11728/cjss2010.03.198WEN Jing, ZHONG Qiuzhen, LIU Siqing. Model research of 10.7 cm solar radio flux 27-day forecast (II)[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2010, 30(3): 198-204 doi: 10.11728/cjss2010.03.198
|
| [45] |
LEI L, ZHONG Q, WANG J, et al. The mid-term forecast method of F10.7 based on extreme ultraviolet images[J]. Advances in Astronomy, 2019, 2019: 5604092
|
| [46] |
HENNEY C J, TOUSSAIN W A, WHITE S M, et al. Forecasting F10.7 with solar magnetic flux transport modeling[J]. Space Weather, 2012, 10(2): S02011
|





 陈安芹 女, 1980年1月出生于山东省昌乐县, 现为国家卫星气象中心(国家空间天气监测预警中心)高级工程师、首席预报员, 主要研究方向为太阳活动区特征、空间天气预报等. E-mail:
陈安芹 女, 1980年1月出生于山东省昌乐县, 现为国家卫星气象中心(国家空间天气监测预警中心)高级工程师、首席预报员, 主要研究方向为太阳活动区特征、空间天气预报等. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: