Spatial Non-cooperative Target Behavior Intent Recognition Based on Data Generation and Deep Neural Networks
-
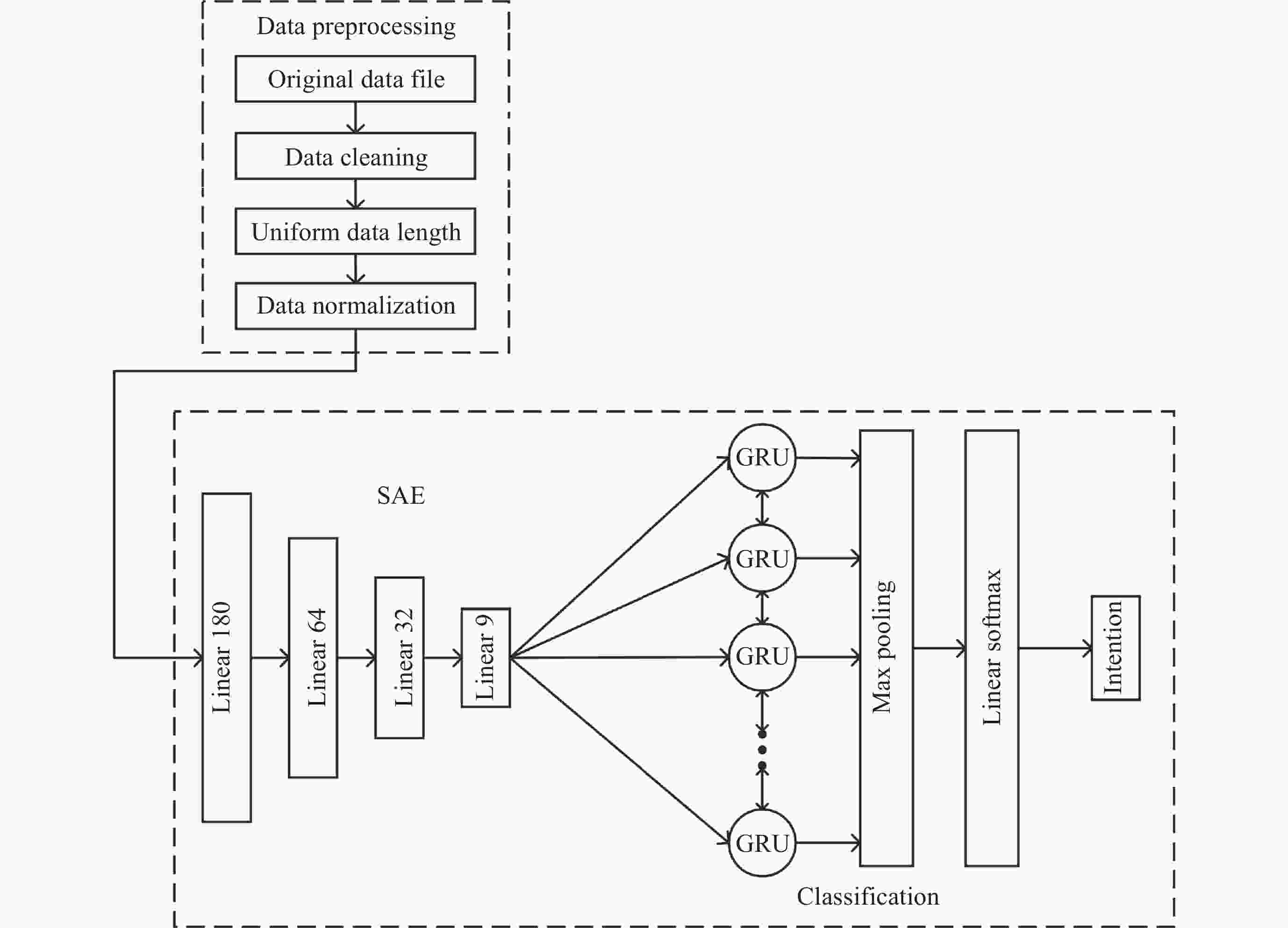
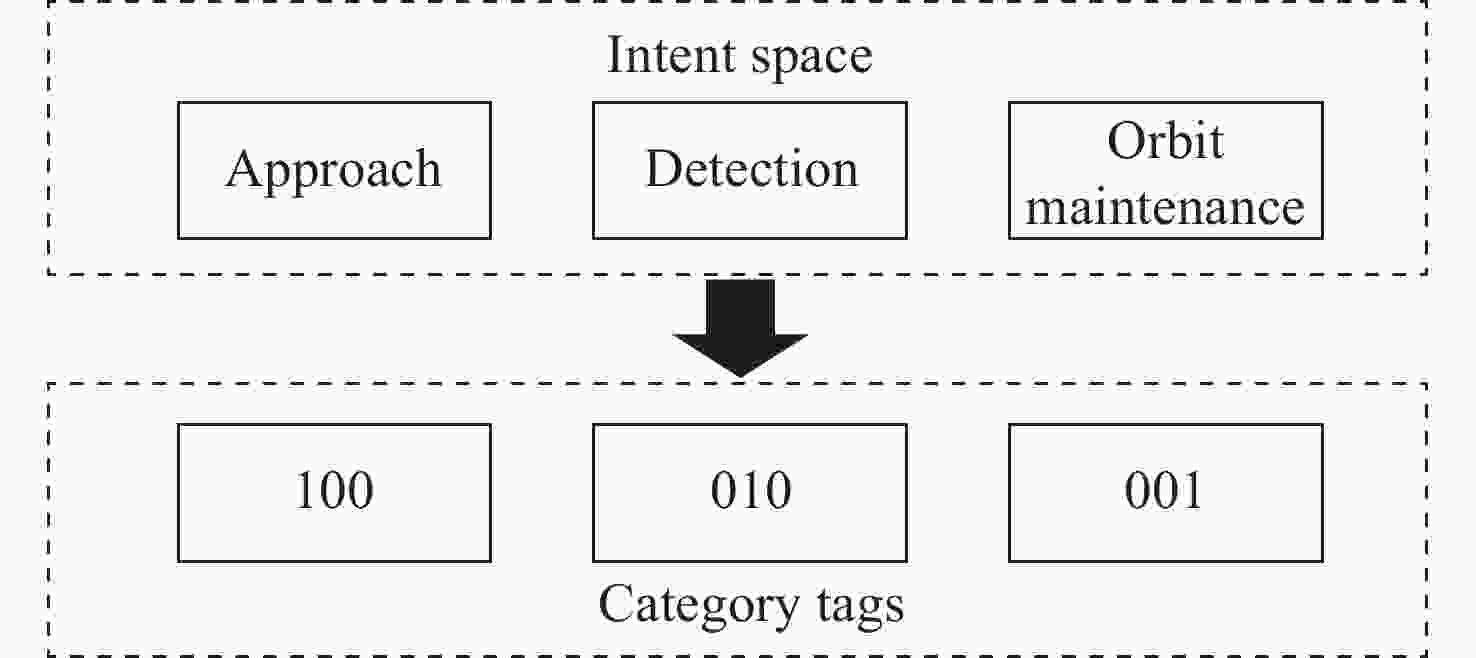
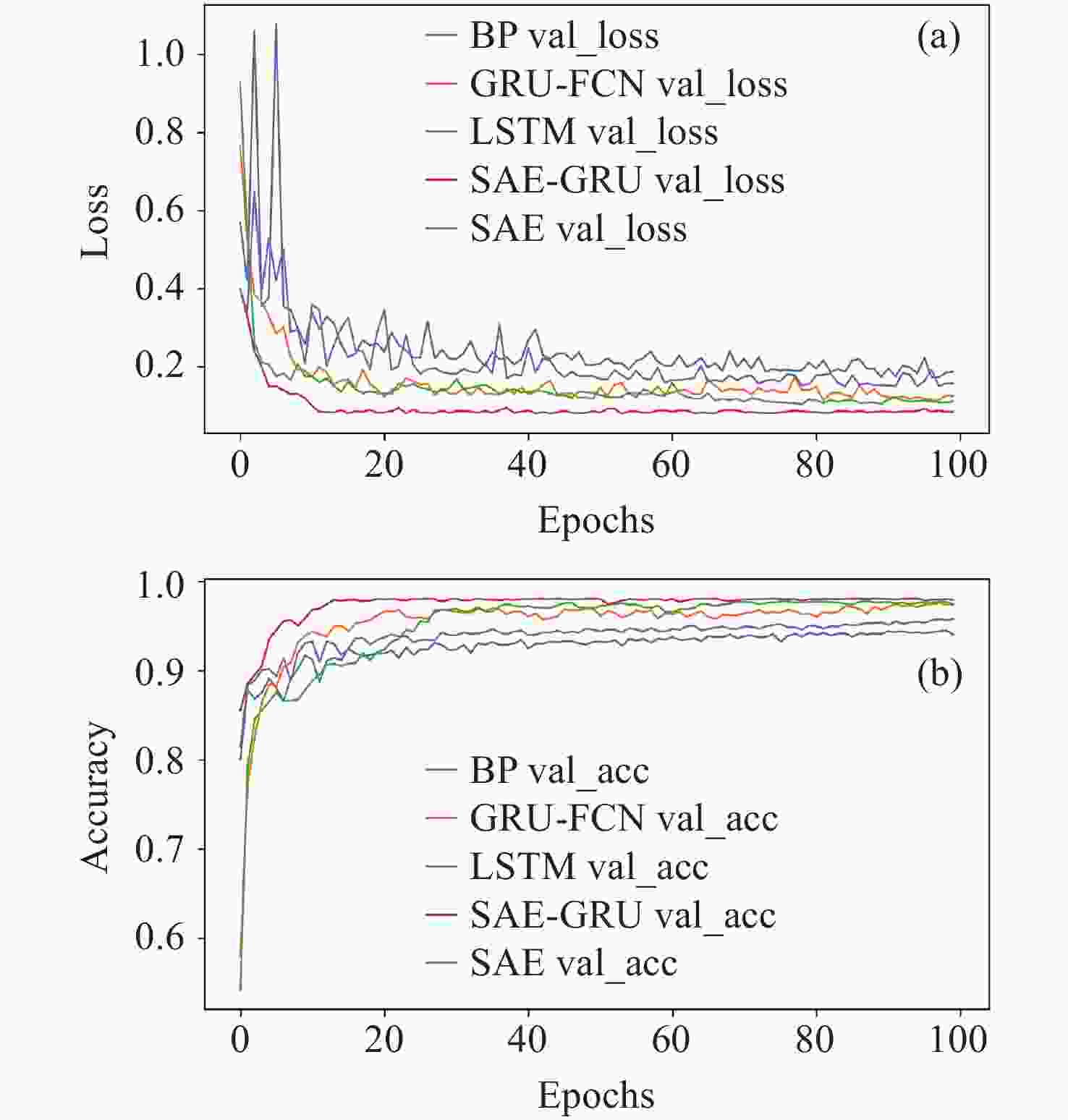
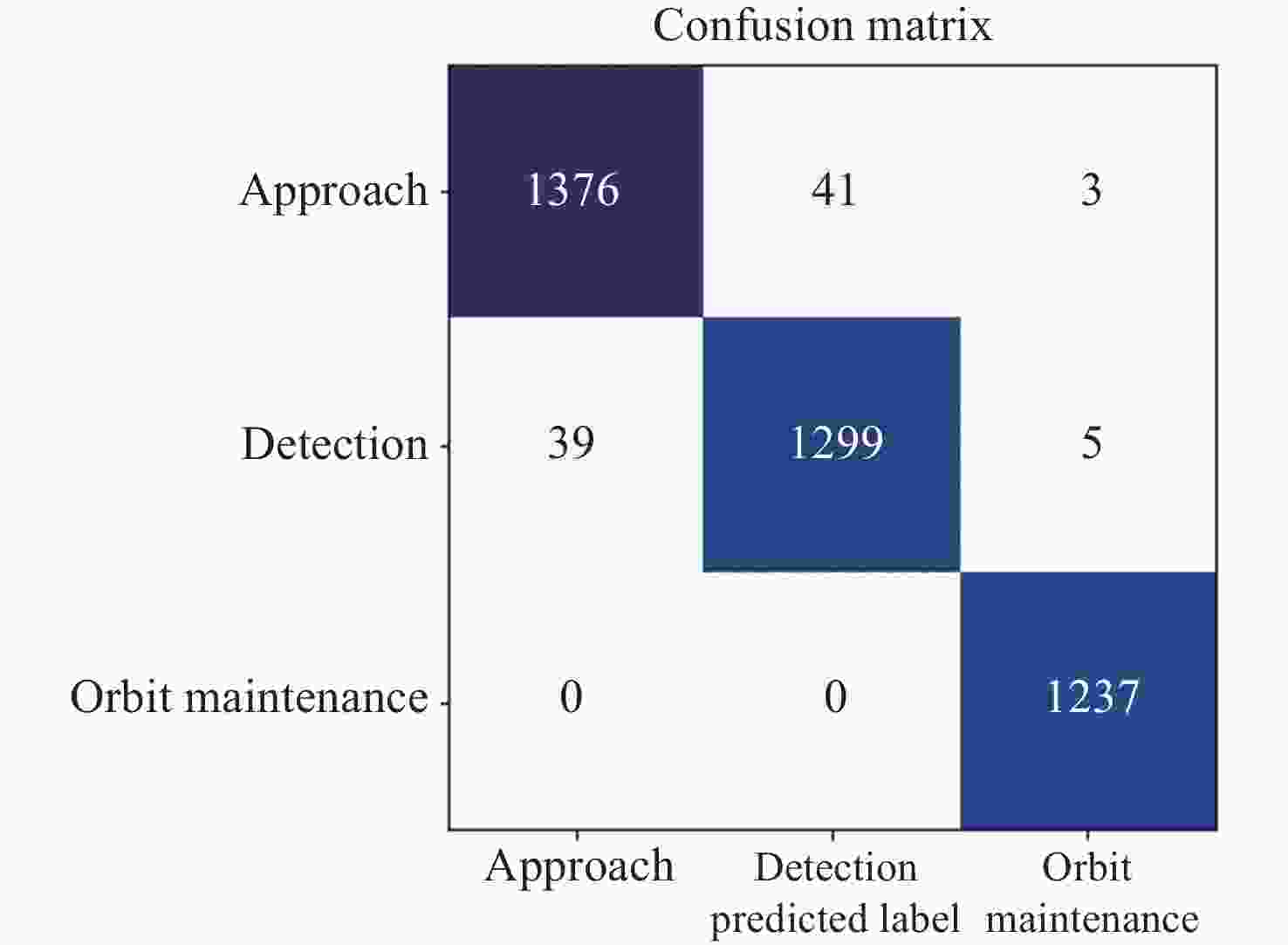
摘要: 在信息化条件下, 空间环境变得日益复杂, 空间非合作目标数量日益增长, 地面操作人员难以迅速准确地根据非合作目标的运动规律识别其意图, 因此提出基于堆叠自编码器(SAE)和门控循环网络(GRU)的空间非合作目标行为意图识别模型, 用于协助地面操作人员识别非合作目标的意图. 该模型利用自编码器对时间序列数据进行压缩, 提取其中的关键特征, 并采用GRU网络对轨迹进行分类. 由于目前尚无公开的非合作目标行为的轨道数据可供使用, 仅依靠少量已知数据难以充分训练模型. 为解决样本不足导致识别效果不佳的问题, 提出一种仿真样本生成方法, 通过仿真得到大量目标行为的轨道数据, 可用于空间非合作目标行为意图的识别. 得到仿真数据后, 将仿真数据集作为输入开展实验, 结果显示, 与仅使用长短期记忆网络(LSTM)、门控循环单元–全卷积网络(GRU-FCN)、堆叠自编码器(SAE)以及反向传播(BP)等单一模型相比, 本方法在准确率、损失值性能指标上均有显著提升, 准确率达到了97.8%.Abstract: Under the conditions of informatization, the space environment has become increasingly complex, and the number of non cooperative targets in space is growing. Ground operators find it difficult to quickly and accurately identify the intentions of non cooperative targets based on their motion patterns. Therefore, a spatial non cooperative target behavior intention recognition model based on Stacked Autoencoder (SAE) and Gated Recurrent network Unit (GRU) was proposed to assist ground operators in identifying the intention of non cooperative targets. This model utilizes an autoencoder to compress time series data, extract key features, and uses a GRU network to classify trajectories. At present, there is no publicly available orbit data for non cooperative target behavior, and it is difficult to fully train the model with only a small amount of known data. To solve the problem of poor recognition performance caused by insufficient samples, a simulation sample generation method is proposed, which obtains a large amount of target behavior trajectory data through simulation for the recognition of spatial non cooperative target behavior intentions. After the simulation data is obtained, the simulation data set is used as the input. The experimental results show that compared with the single model only using the Long and Short Term Memory network (LSTM), GRU-FCN, SAE, and Back-Propagation (BP), this method has significantly improved the accuracy and loss value performance indicators, reaching 97.8% accuracy.
-
Key words:
- Non-cooperative targets /
- Sample simulation method /
- Intent recognition /
- Deep learning
-
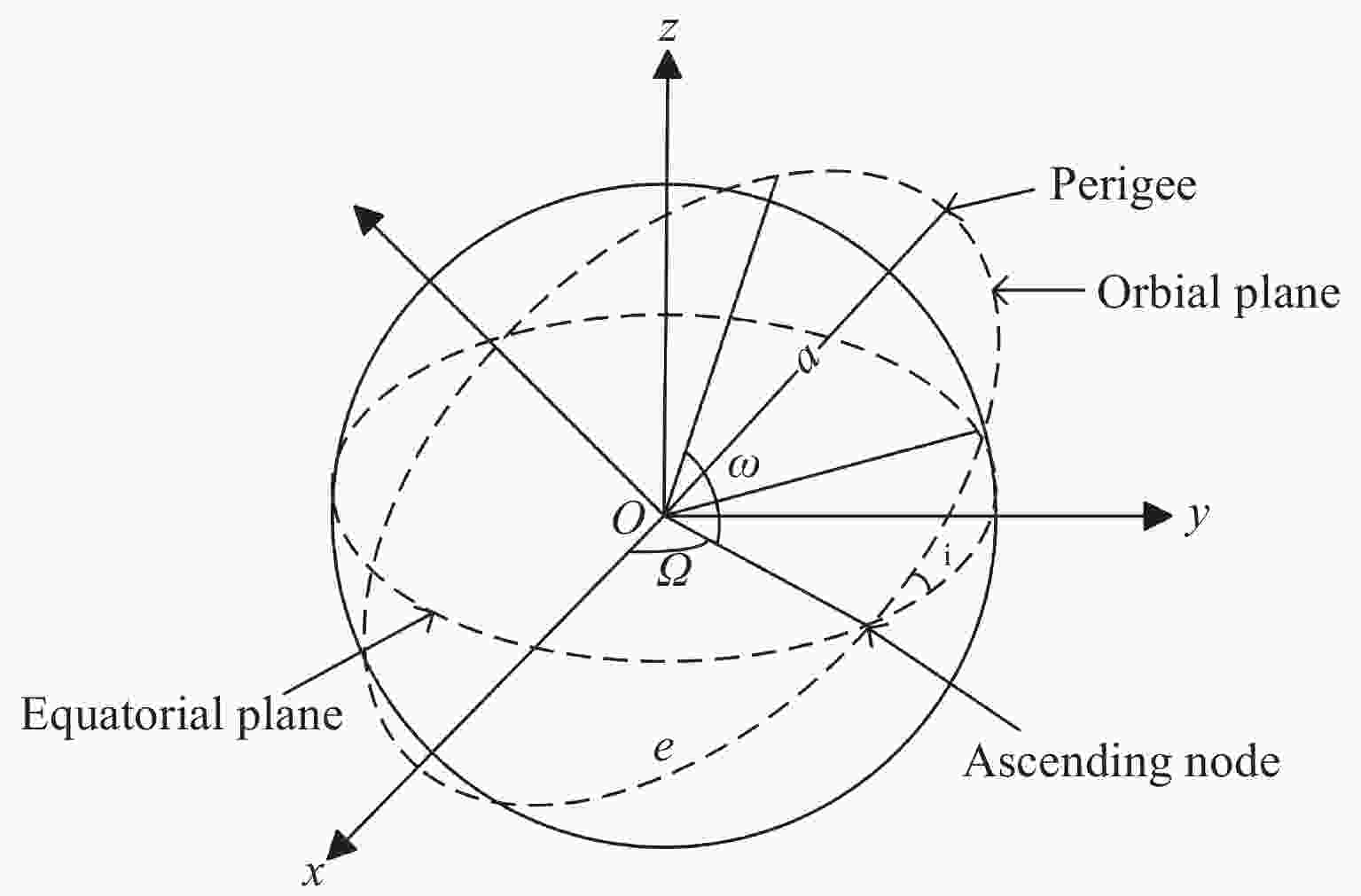
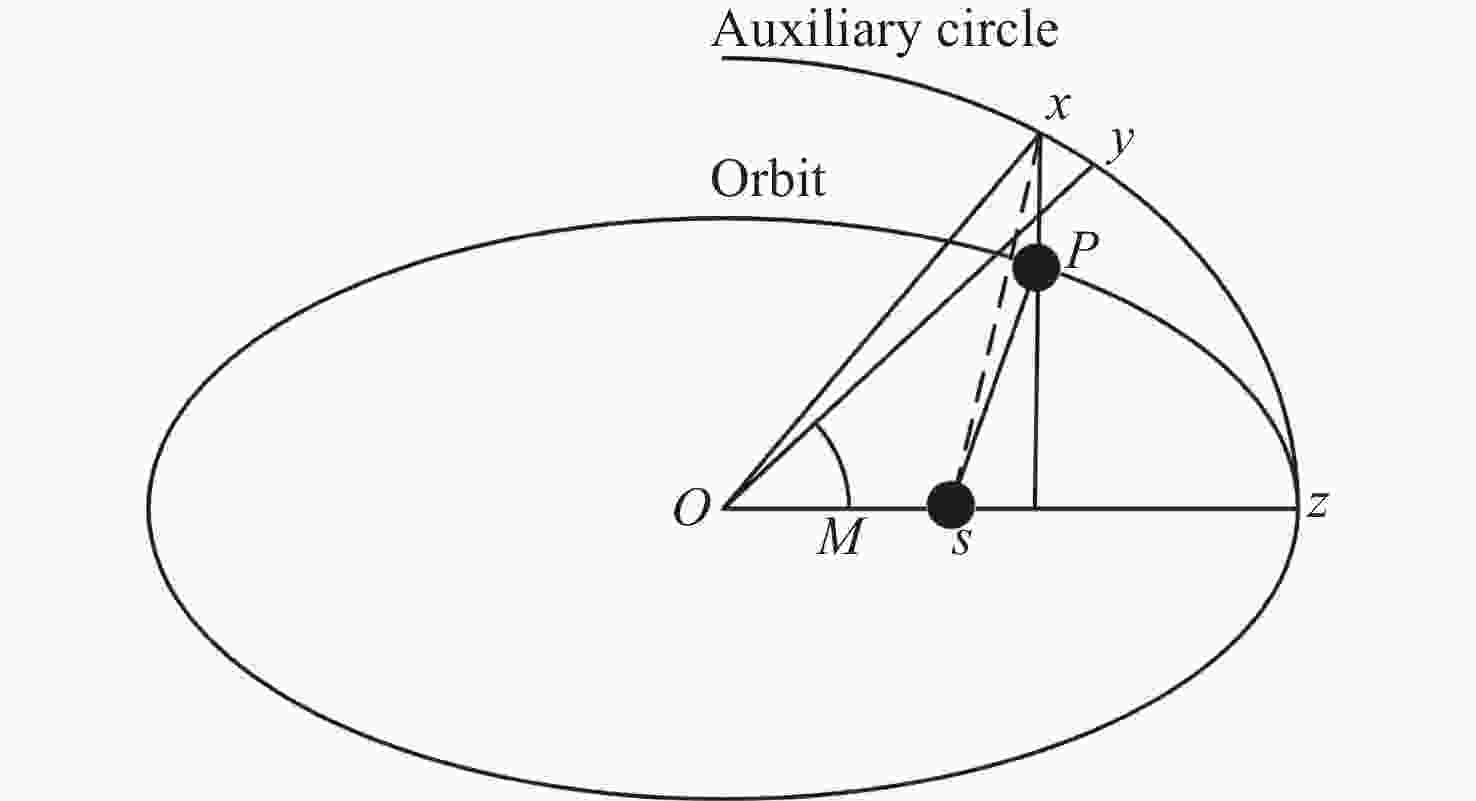
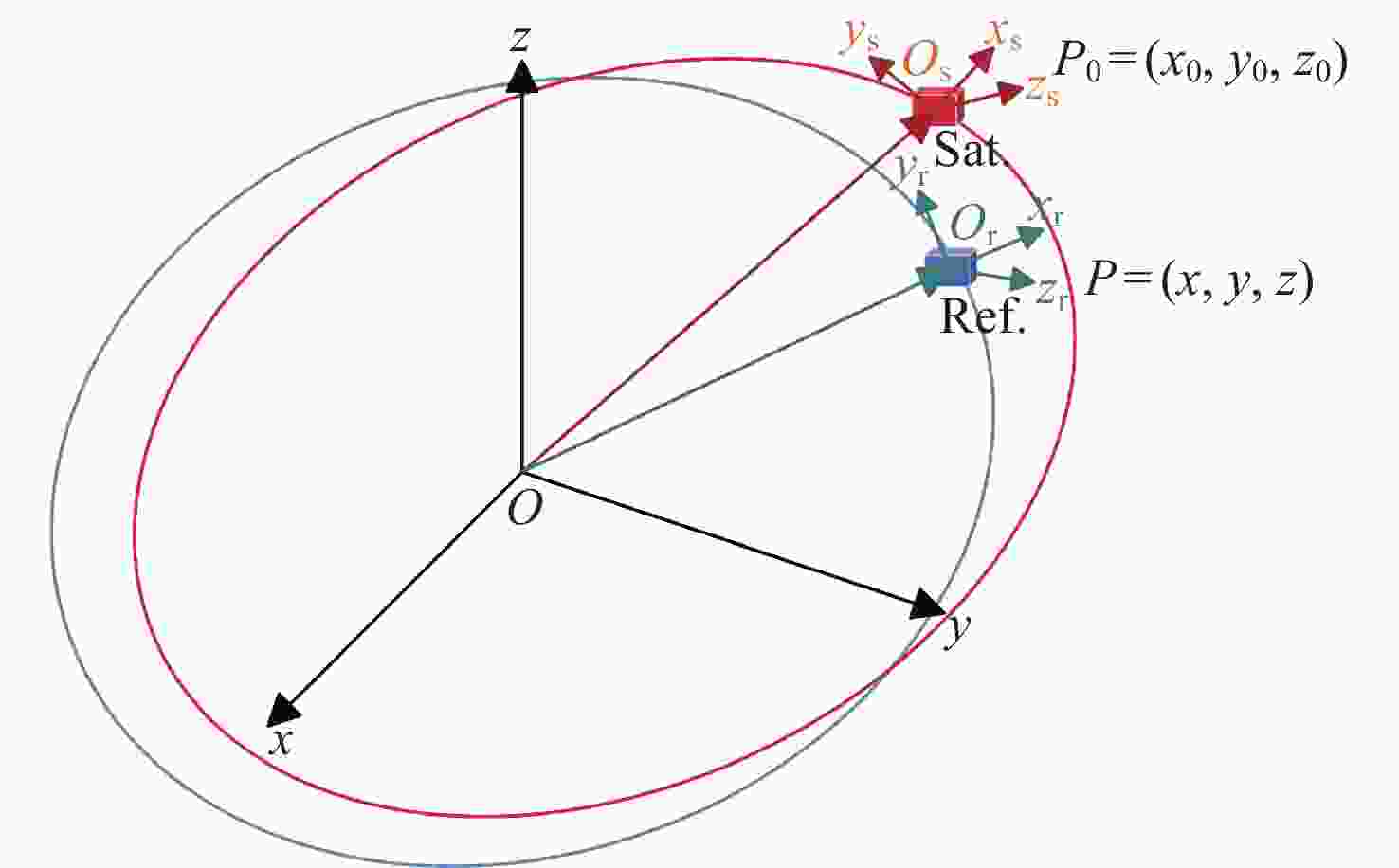
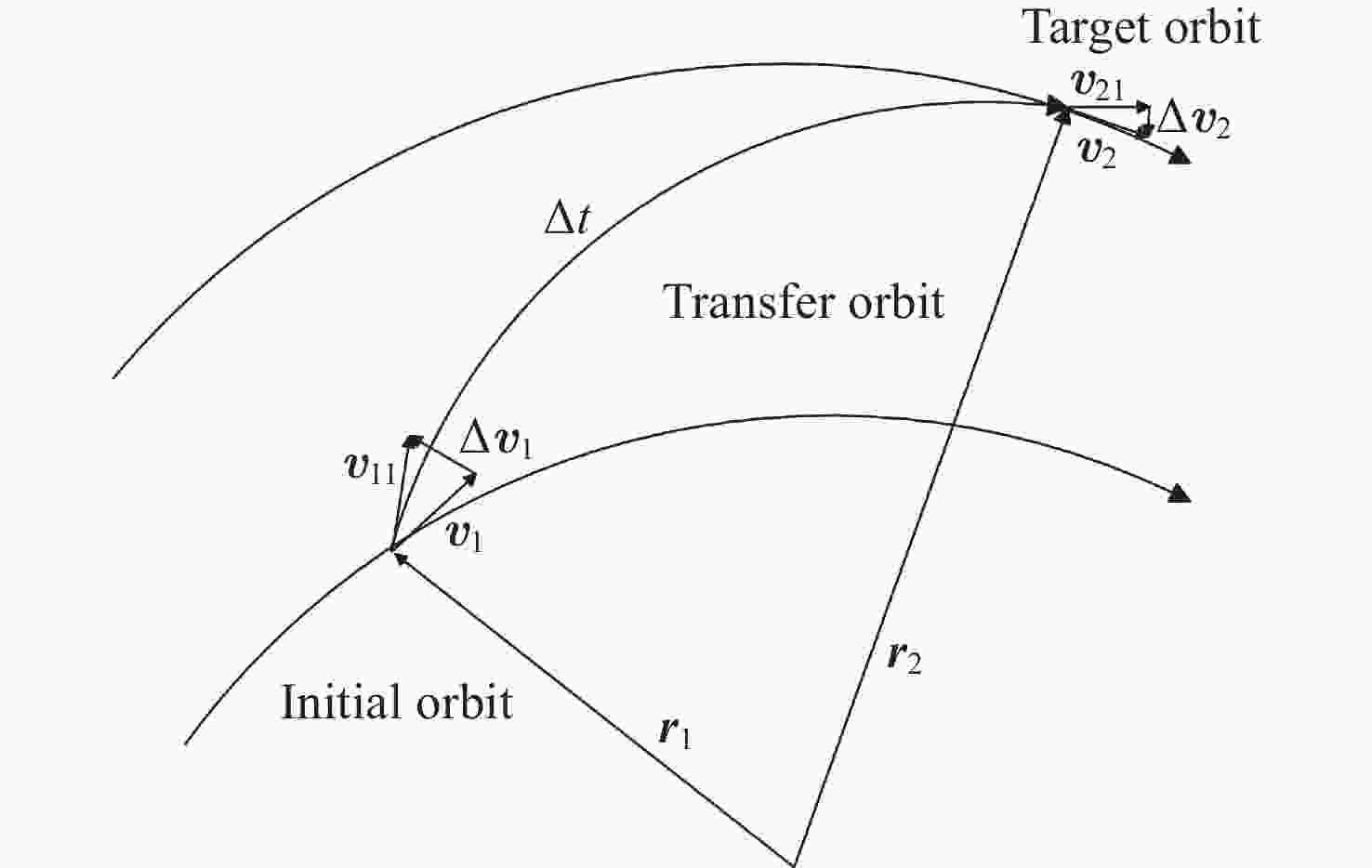
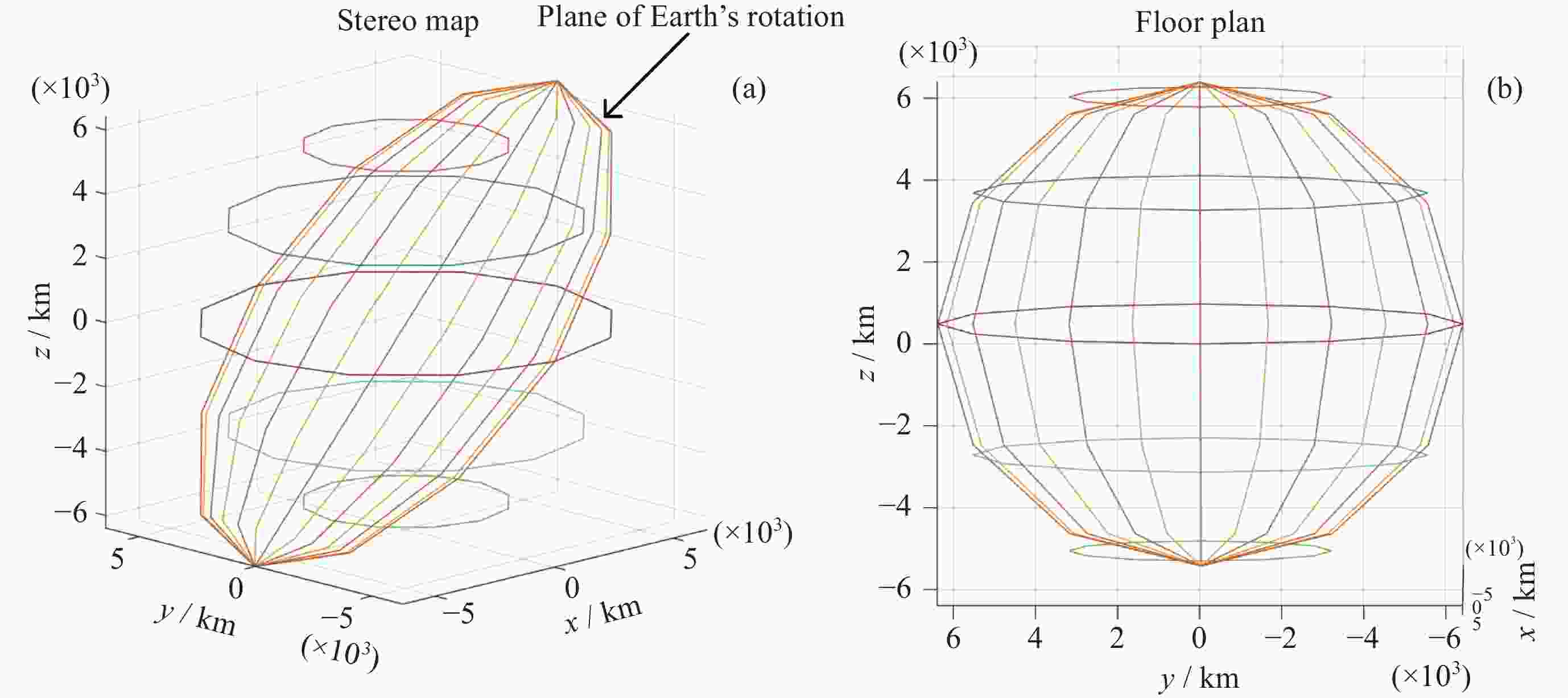
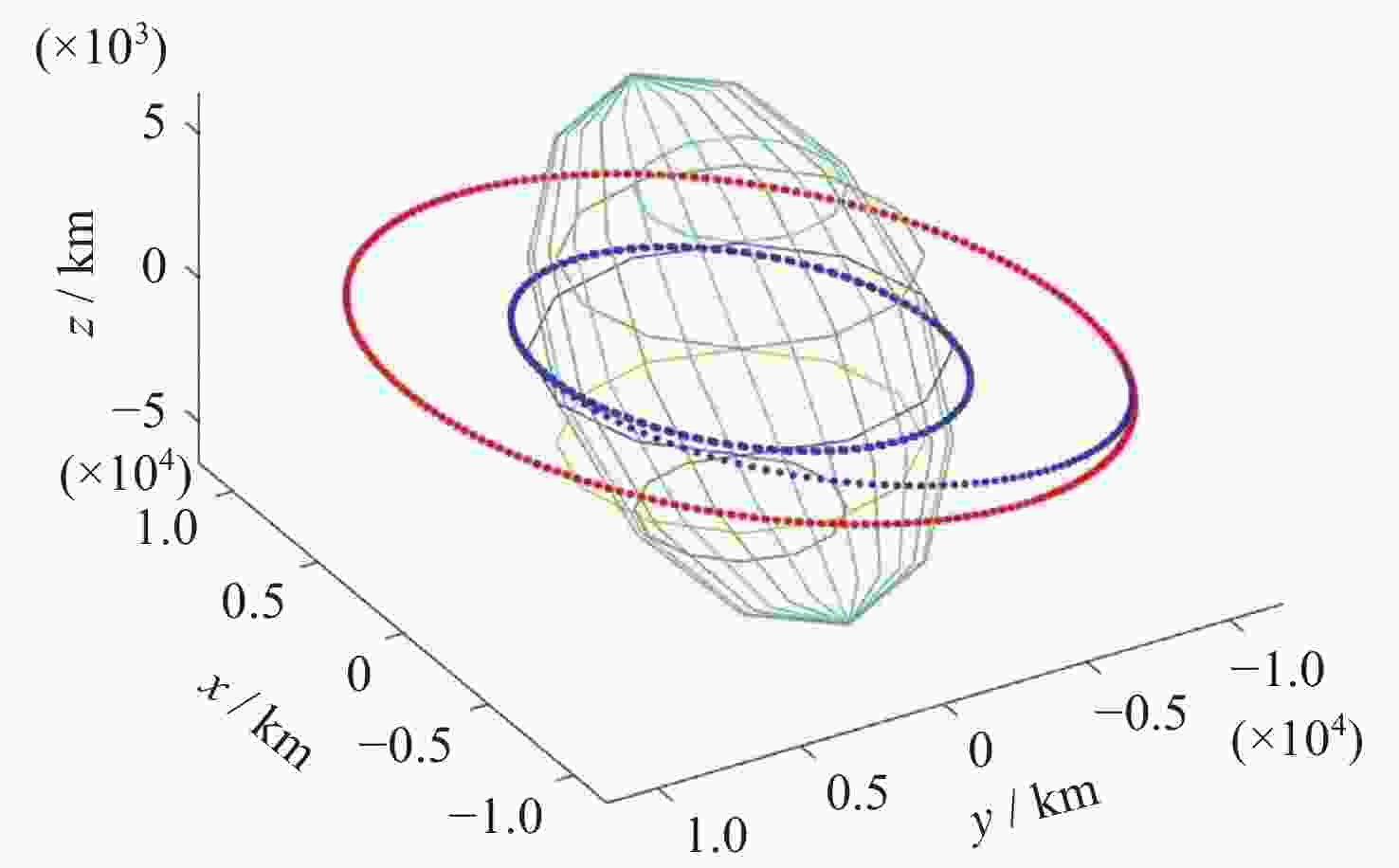
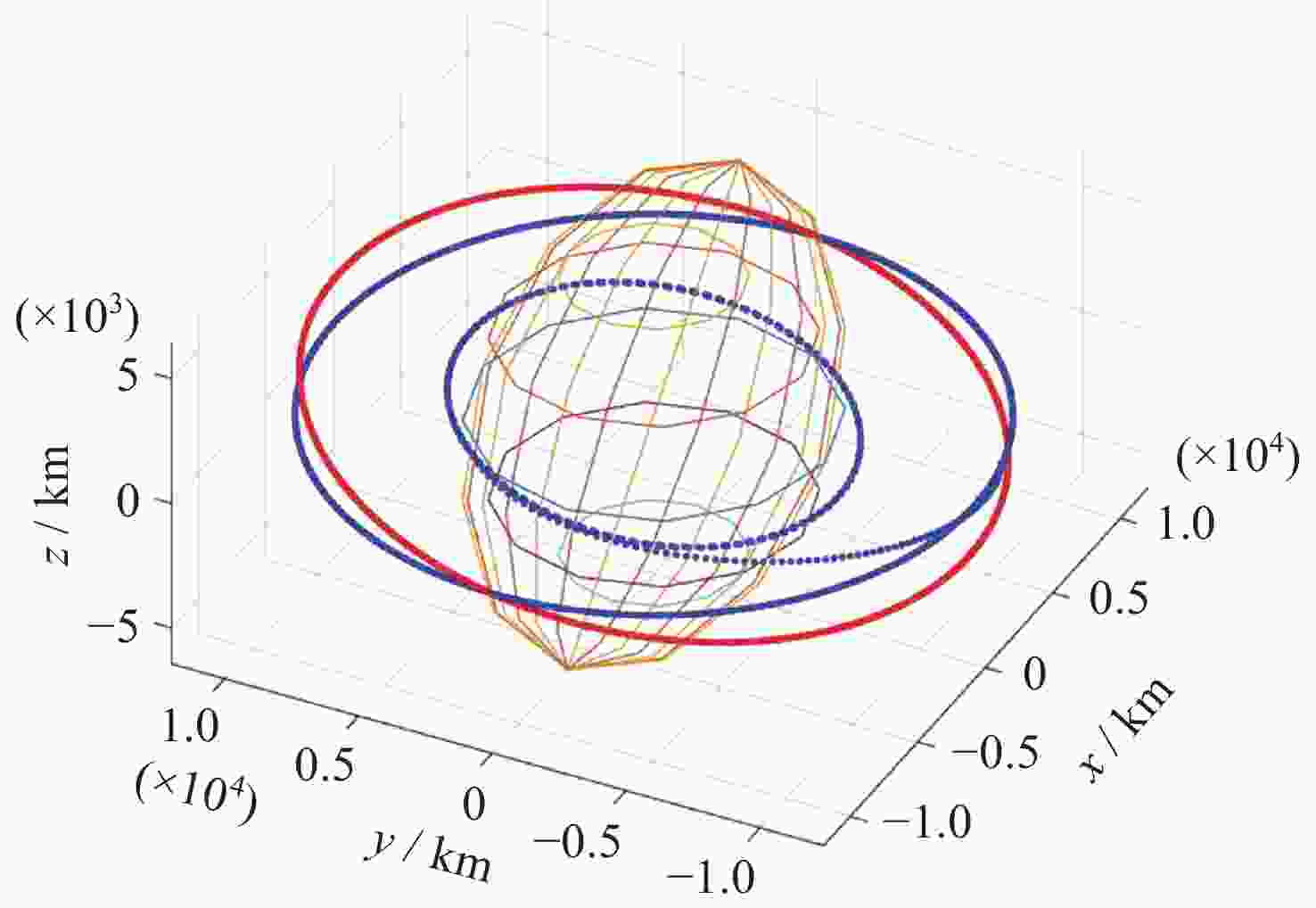
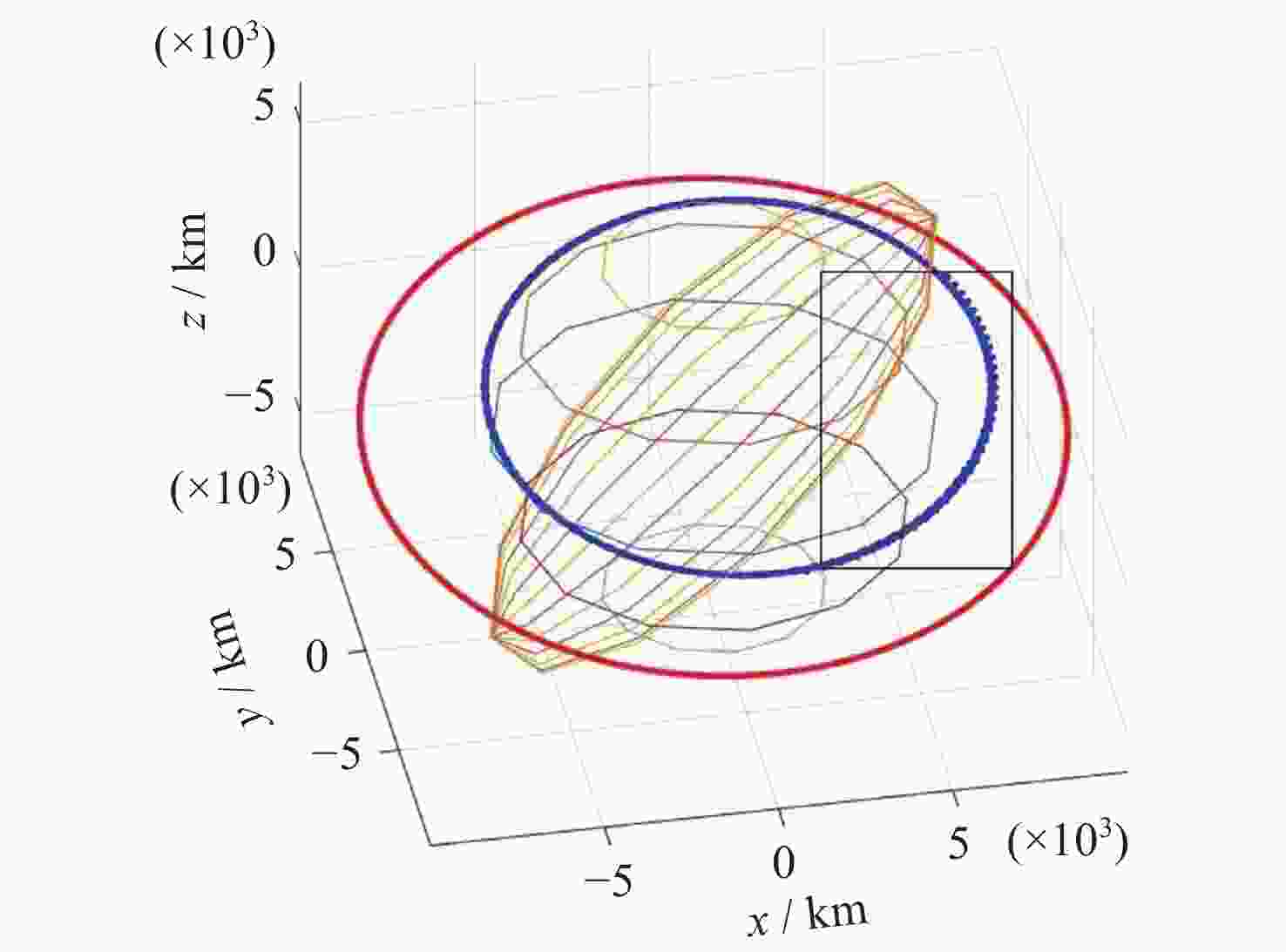
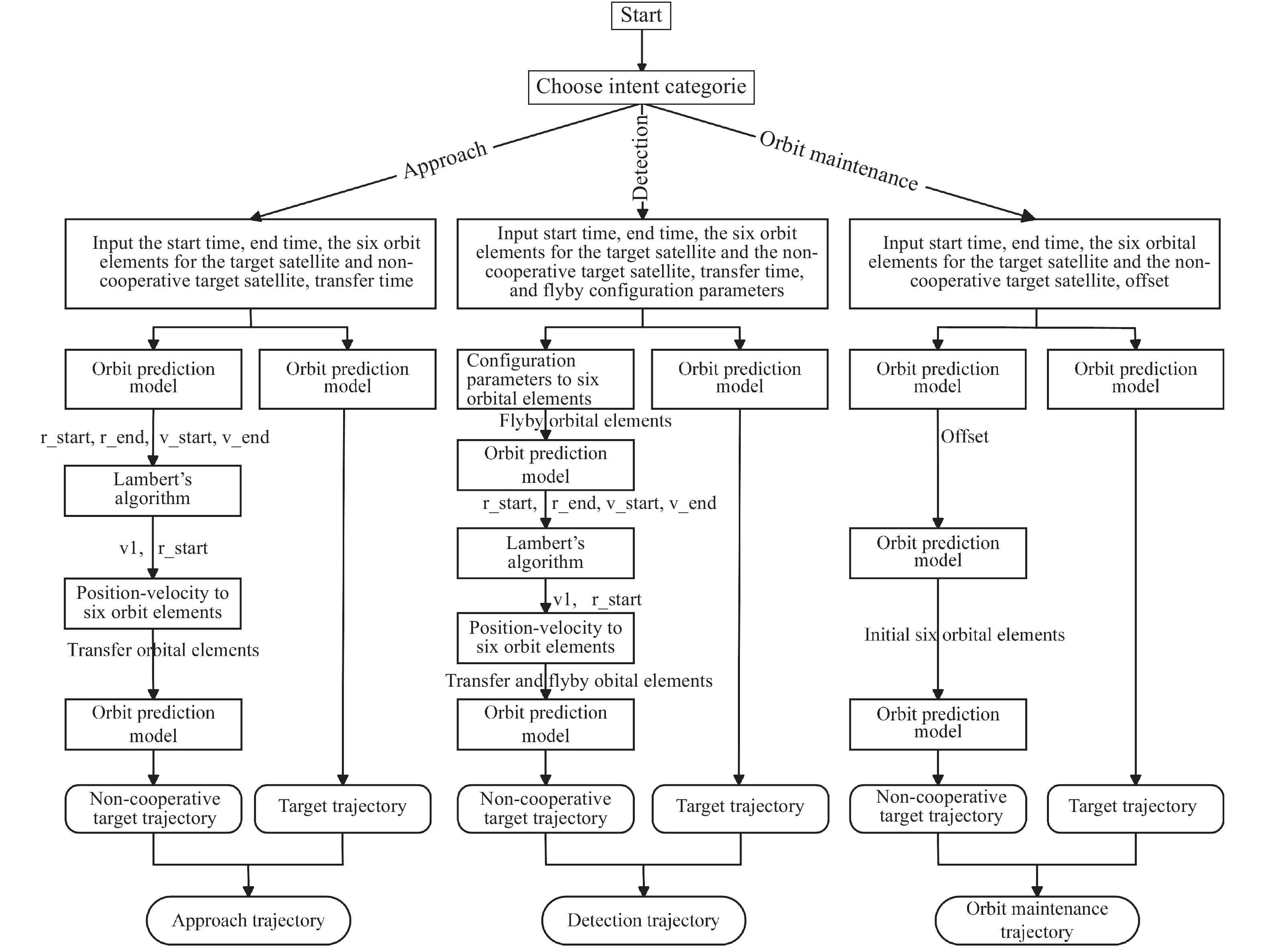
表 1 抵近意图目标星与非合作目标星轨道根数
Table 1. Orbital elements of intended target stars and non-cooperative target stars for approach intent
轨道根数 目标卫星 非合作目标卫星 Lambert转移轨道 半长轴a/km 12000 7000 9490.01 偏心率e 0 0 0.2646 轨道倾角i/(°) 10 10 10 升交点赤经Ω/(°) 0 0 2.94093 近地点幅角ω/(°) 235 235 65.2729 平近点角M/(°) 0 0 2.3429 表 2 探测意图目标卫星以及非合作目标卫星轨道根数
Table 2. Orbital elements of intended target satellites and non-cooperative target satellites for detection intent
轨道根数 目标卫星 非合作目标卫星 绕飞轨道根数 转移轨道根数 半长轴a/km 12000.5667 7000.0789 12000 9182.77 偏心率e 0 0 0 0.360 轨道倾角i/(°) 10 10 0.175 7.436 升交点赤经Ω/(°) 0 0 3.126 101.496 近地点幅角ω/(°) 235 235 321.858 339.325 平近点角M/(°) 0 0 3.142 33.034 表 3 轨道保持意图目标星与非合作目标星轨道根数
Table 3. Orbital elements of target satellites and non-cooperative target satellites for orbit maintenance intent
轨道根数 目标卫星 非合作目标卫星 偏离轨道 半长轴 a/km 14000 7333 7338 偏心率$ {{{e}}} $ 0 0.233 0.233 轨道倾角i/(°) 10 12 12 升交点赤经 Ω/(°) 0 0 360 近地点幅角 ω/(°) 235 235 234.9 平近点角M/(°) 0 0 94.97 表 4 模型超参数
Table 4. Hyperparameters of the model
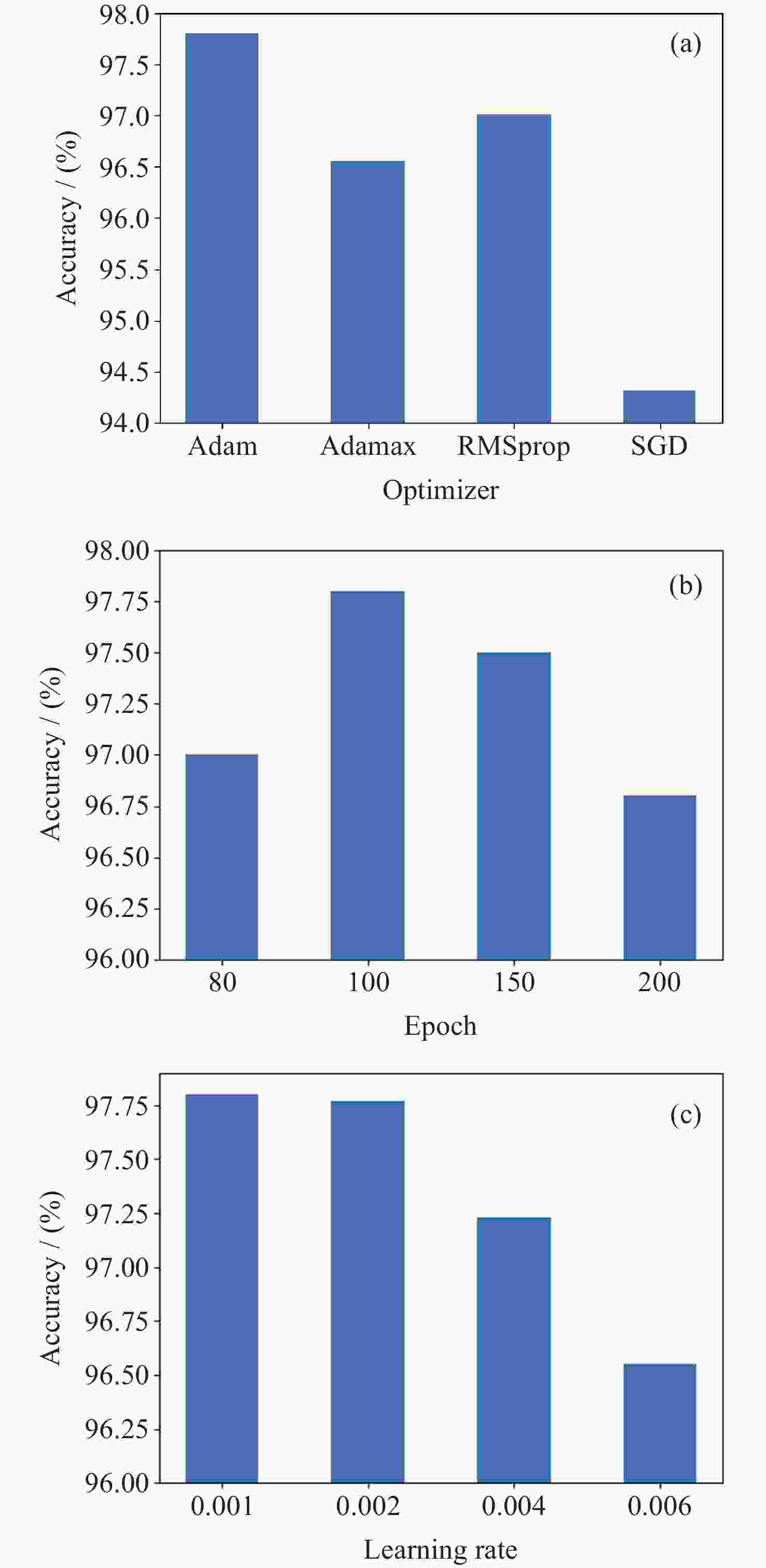
网络主要参数 值 学习率 0.001 批尺寸 128 迭代轮次 100 优化器 Adam 随机失活率/(%) 50 表 5 对比实验结果
Table 5. Comparison of experimental results
模型 训练损失 训练准确率/(%) SAE-GRU 0.0882 97.80 GRU-FCN 0.1843 94.72 LSTM 0.1775 95.34 BP 0.2342 88.89 SAE 0.2121 90.89 -
[1] JI Xiang. Study of Situation Assessment Techniques Based on Clustering and Matching[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2016 [2] 赵福均, 周志杰, 胡昌华, 等. 基于置信规则库和证据推理的空中目标意图识别方法[J]. 电光与控制, 2017, 24(8): 15-19,50 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2017.08.004ZHAO Fujun, ZHOU Zhijie, HU Changhua, et al. Aerial target intention recognition approach based on belief-rule-base and evidential reasoning[J]. Electronics Optics & Control, 2017, 24(8): 15-19,50 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2017.08.004 [3] WANG Haiwang, SHI Hongquan, LI Xiaodan. An intention recognition method based on intuitionistic fuzzy sets and Bayesian inference[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2019, 39(6): 42-45 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2019.06.011 [4] FAN Hanyang, GAO Ruiyuan, JIN Xinghua. Research on intention estimation method based on fuzzy random Bayesian networks[J]. Fire Control & Command Control, 2019, 44(7): 100-104,109 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2019.07.019 [5] 伍之前, 李登峰. 基于推理和多属性决策的空中目标攻击意图判断模型[J]. 电光与控制, 2010, 17(5): 10-13 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2010.05.003WU Zhiqian, LI Dengfeng. A model for aerial target attacking intention judgment based on reasoning and multi-attribute decision making[J]. Electronics Optics & Control, 2010, 17(5): 10-13 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2010.05.003 [6] HE Yu, CHANG Leilei, JIANG Jiang, et al. Intension identification in air defense based on belief rule base expert system under expert guidance[J]. Fire Control & Command Control, 2017, 42(9): 7-12 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2017.09.002 [7] 贾苏元, 徐金钰, 王钰. 基于自适应神经网络模糊系统(ANFIS)的空中目标意图分类[J]. 电子测量技术, 2016, 39(12): 62-66 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7300.2016.12.013JIA Suyuan, XU Jinyu, WANG Yu. Classification of air target intention based on adaptive neural network fuzzy system (ANFIS)[J]. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2016, 39(12): 62-66 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7300.2016.12.013 [8] TENG F, SONG Y F, GUO X P. Attention-TCN-BiGRU: an air target combat intention recognition model[J]. Mathematics, 2021, 9(19): 2412. doi: 10.3390/math9192412 [9] 李颖, 武君胜, 李伟刚, 等. 一种识别作战意图的层次聚合模型[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2023, 41(2): 400-408 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2023.02.018LI Ying, WU Junsheng, LI Weigang, et al. A hierarchical aggregation model for combat intention recognition[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2023, 41(2): 400-408 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2023.02.018 [10] QU C X, GUO Z C, XIA S J, et al. Intention recognition of aerial target based on deep learning[J]. Evolutionary Intelligence, 2024, 17(1): 303-311 doi: 10.1007/s12065-022-00728-9 [11] WANG Yang. Research on battlefield target identification and situation intention forecasting[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2015 [12] XIAO Q L, LIU Y N, DENG X Y, et al. A robust target intention recognition method based on dynamic Bayesian network[C]//Proceedings of the 33rd Chinese Control and Decision Conference. Kunming: IEEE, 2021: 6846-6851. DOI: 10.1109/CCDC52312.2021.9602205 [13] ZHANG C H, ZHOU Y, LI H, et al. Combat intention recognition of air targets based on 1DCNN-BiLSTM[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 134504-134516 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3337640 [14] ZHANG Y, MA W C, HUANG F H, et al. A novel air target intention recognition method based on sample reweighting and attention-Bi-GRU[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2024, 18(1): 501-504 doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2023.3319643 [15] LAI J, WANG X D, XIANG Q, et al. A semi-supervised stacked autoencoder using the pseudo label for classification tasks[J]. Entropy, 2023, 25(9): 1274 doi: 10.3390/e25091274 [16] 朱正龙, 闫野, 杨跃能. 高精度空间非合作式相对轨道状态预报[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2016, 38(3): 81-87 doi: 10.11887/j.cn.201603014ZHU Zhenglong, YAN Ye, YANG Yueneng. High-accuracy state propagation of non-cooperative relative orbit in space[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2016, 38(3): 81-87 doi: 10.11887/j.cn.201603014 [17] 徐利民, 张涛, 陶佳伟. 能量最优与燃料最优Lambert交会问题[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(9): 1888-1893XU Limin, ZHANG Tao, TAO Jiawei. Energy-optimal and fuel-optimal problems for lambert rendezvous[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(9): 1888-1893 [18] CUI Wenhao. Research on the Satellite Formation Reconfiguration and Keeping under J2 Perturbation[D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2019 [19] VALLADO A D. Fundamentals of Astrodynamics and Applications[M]. 4th ed. Hawthorne: Microcosm Press, 2013: 628-636 [20] WANG Youliang. Relative Trajectory Optimization and Control for Satellite Formation Flying[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (National Space Science Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2018 [21] LI Wenxin. Research on Modeling and Accuracy Evaluation Technology of Spacecraft Unpowered Rendezvous[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2022. DOI: 10.26944/d.cnki.gbfju.2022.002957 [22] SABOL C, MCLAUGHLIN C A, LUU K K. Meet the cluster orbits with perturbations of Keplerian elements (COWPOKE) equations[J]. Advances in the Astronautical Sciences, 2003, 114: 573-594 [23] 韩潮, 殷建丰. 基于相对轨道要素的椭圆轨道卫星相对运动研究[J]. 航空学报, 2011, 32(12): 2244-2258HAN Chao, YIN Jianfeng. Study of satellite relative motion in elliptical orbit using relative orbit elements[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2011, 32(12): 2244-2258 [24] 丁鹏, 宋亚飞. 代价敏感的空中目标意图识别方法[J]. 航空学报, 2023, 44(24): 328551 doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2023.2855DING Peng, SONG Yafei. A cost-sensitive method for aerial target intention recognition[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2023, 44(24): 328551 doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2023.2855 [25] ZHANG Shanbin. Emotional classification of short-term ECG signals using BP neural network[J]. Journal of Fujian Computer, 2024, 40(2): 11-16 doi: 10.16707/j.cnki.fjpc.2024.02.003 [26] 方华珍, 刘立, 顾青, 等. 基于轨迹预测和极限梯度提升的驾驶意图识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024: 1-9FANG Huazhen, LIU Li, GU Qing, et al. Driving intention recognition based on trajectory prediction and extreme gradient boosting[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024: 1-9 -
-





 余静 女, 国科大杭州高等研究院硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为空间非合作目标意图识别. E-mail:
余静 女, 国科大杭州高等研究院硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为空间非合作目标意图识别. E-mail: 

 下载:
下载: