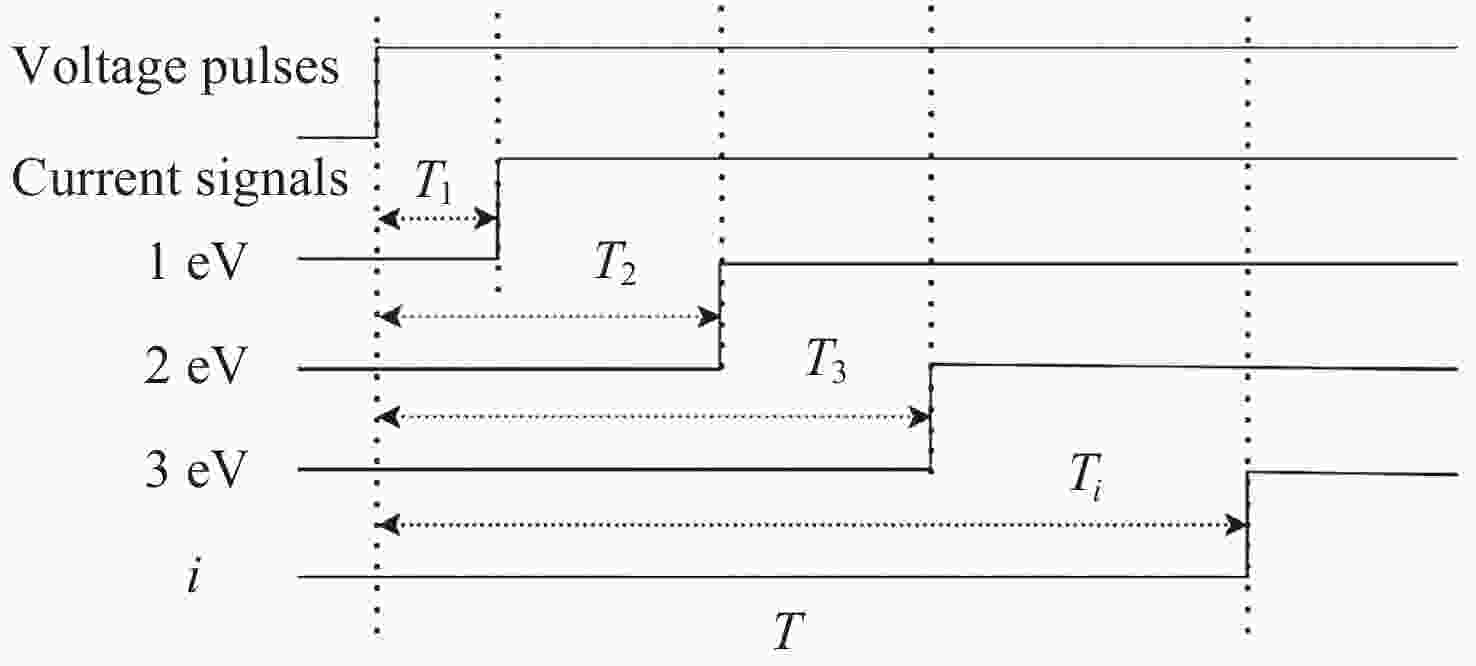
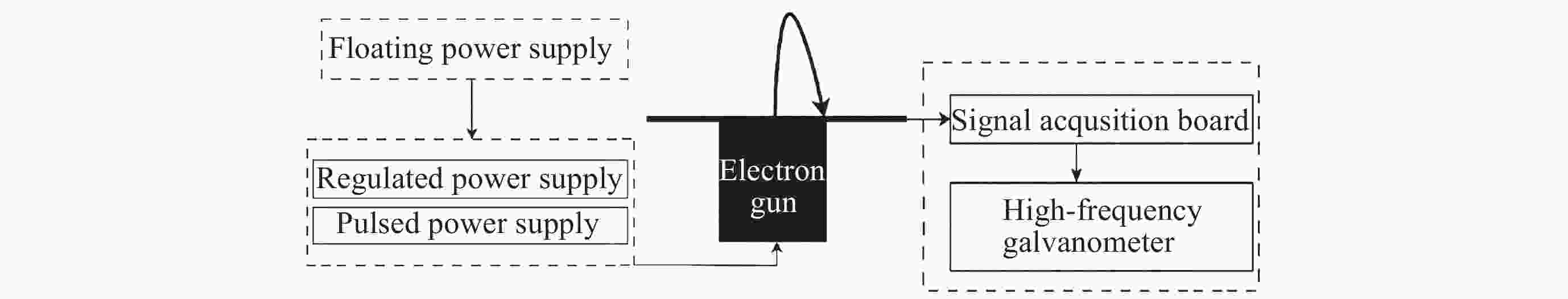
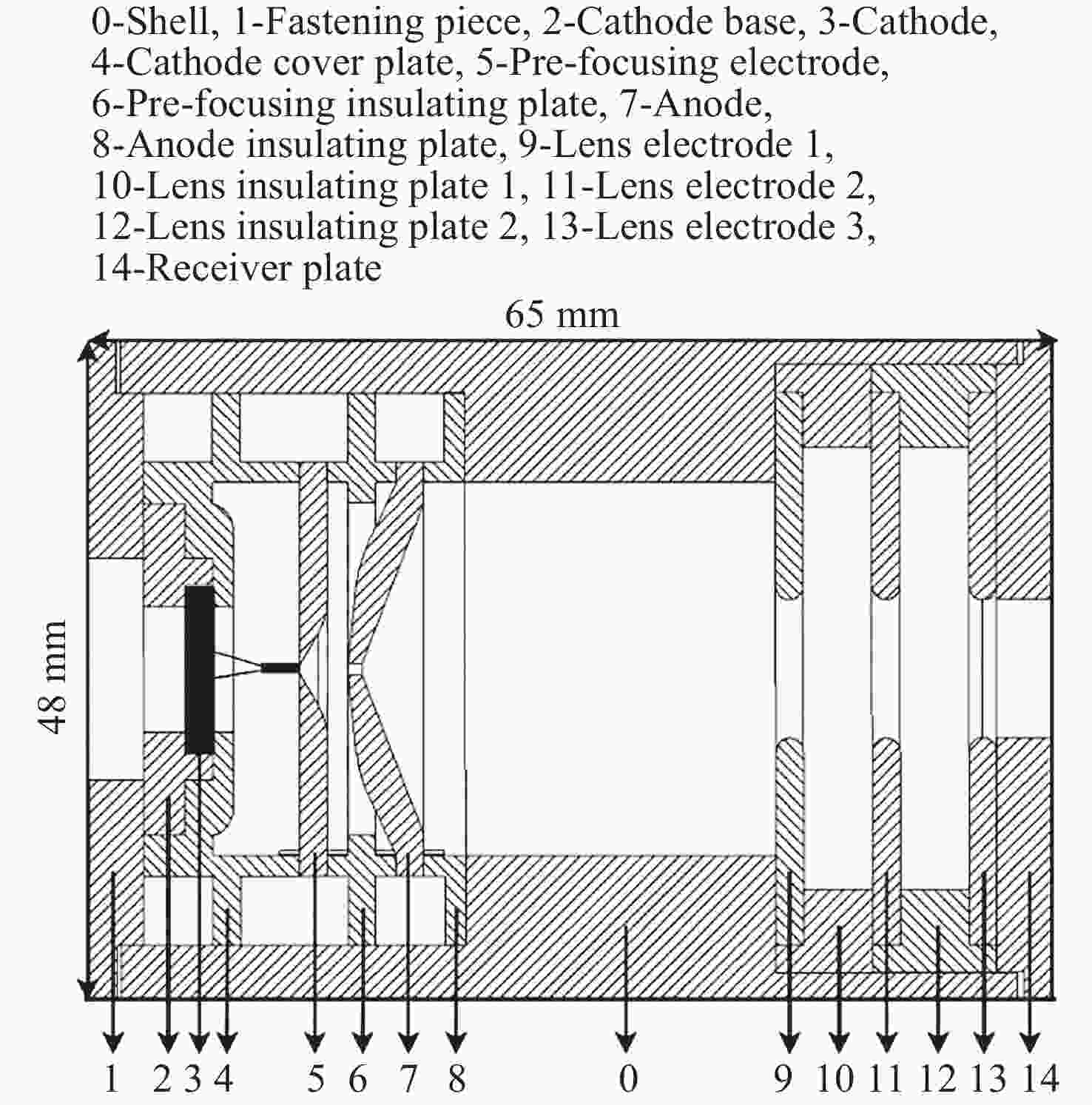
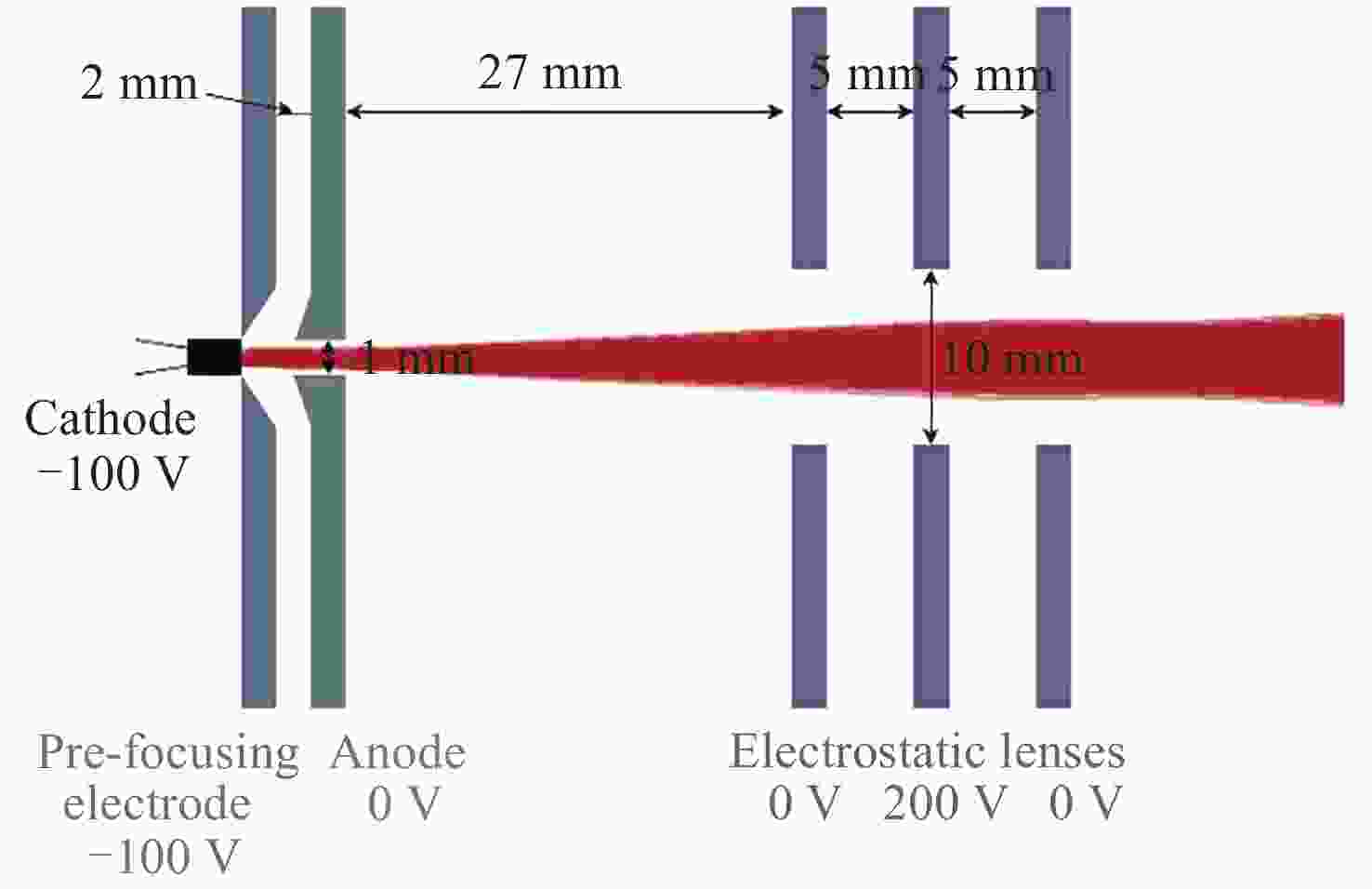
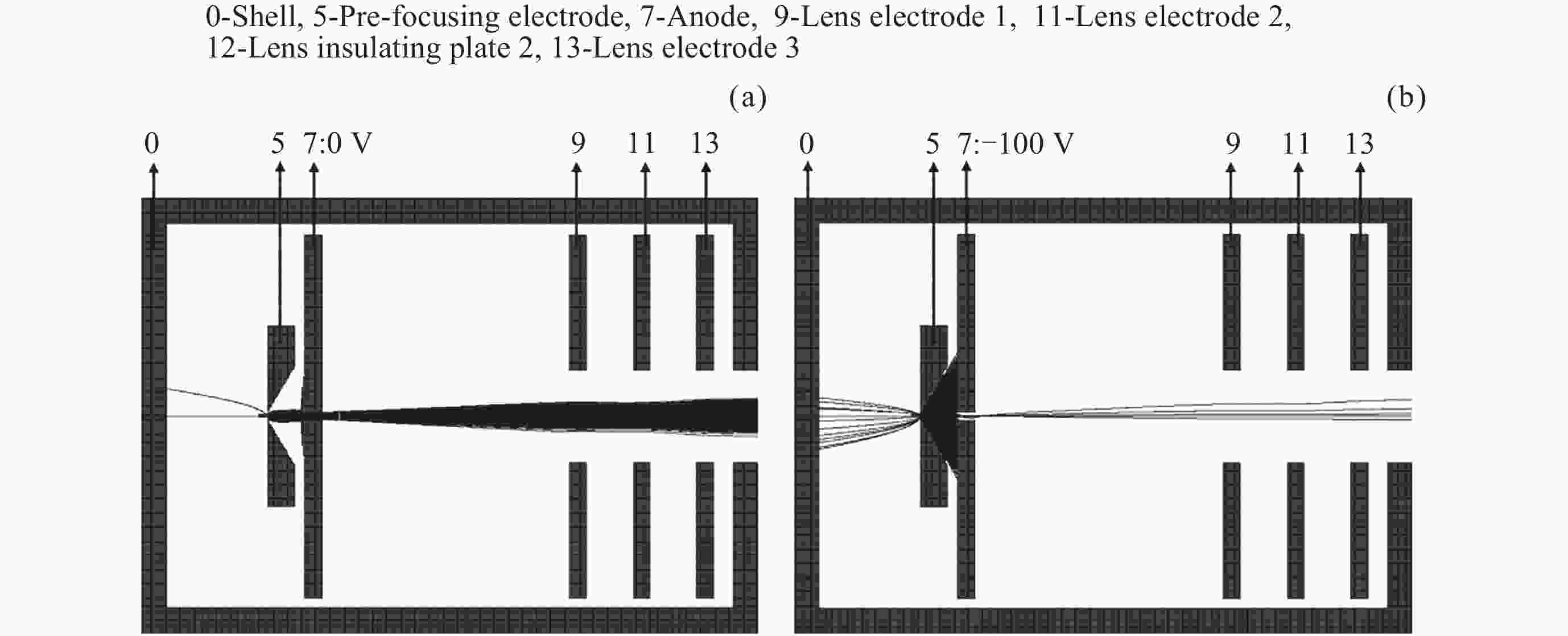
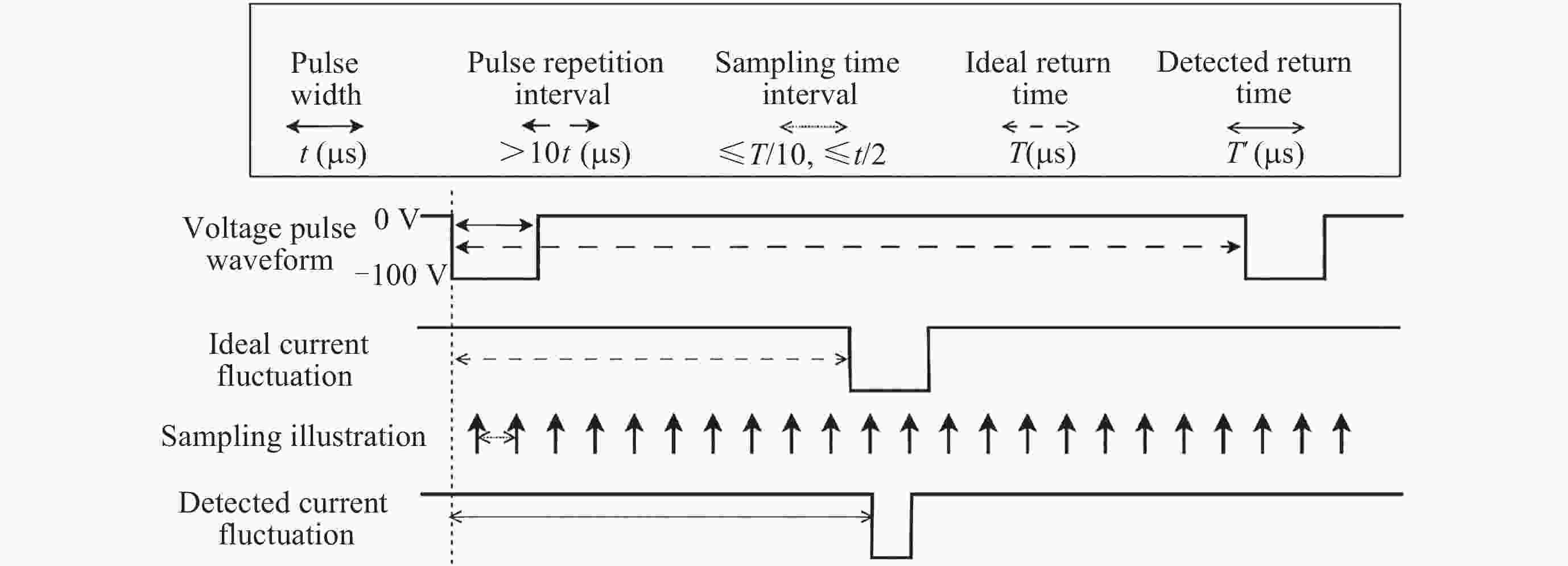
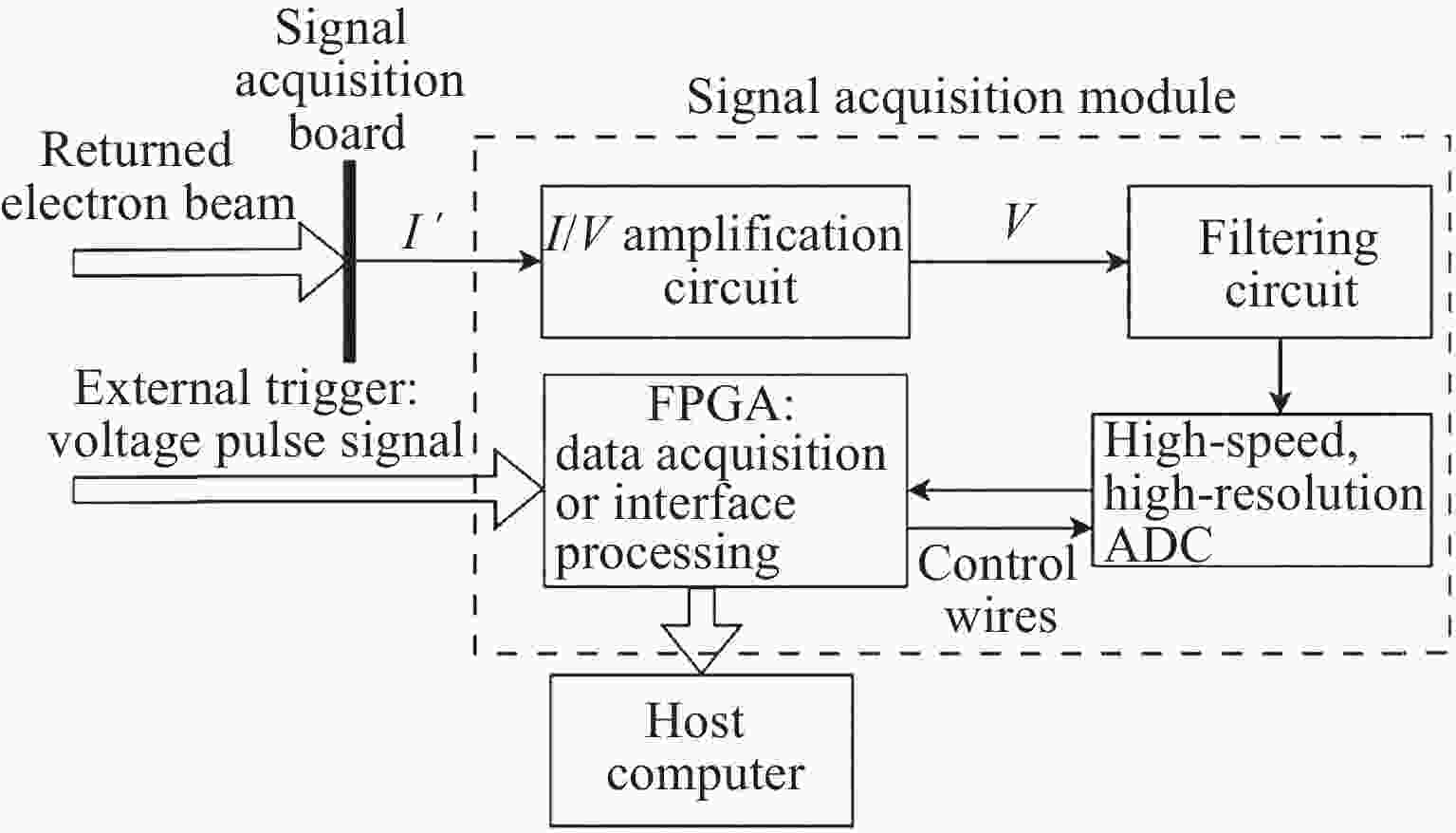
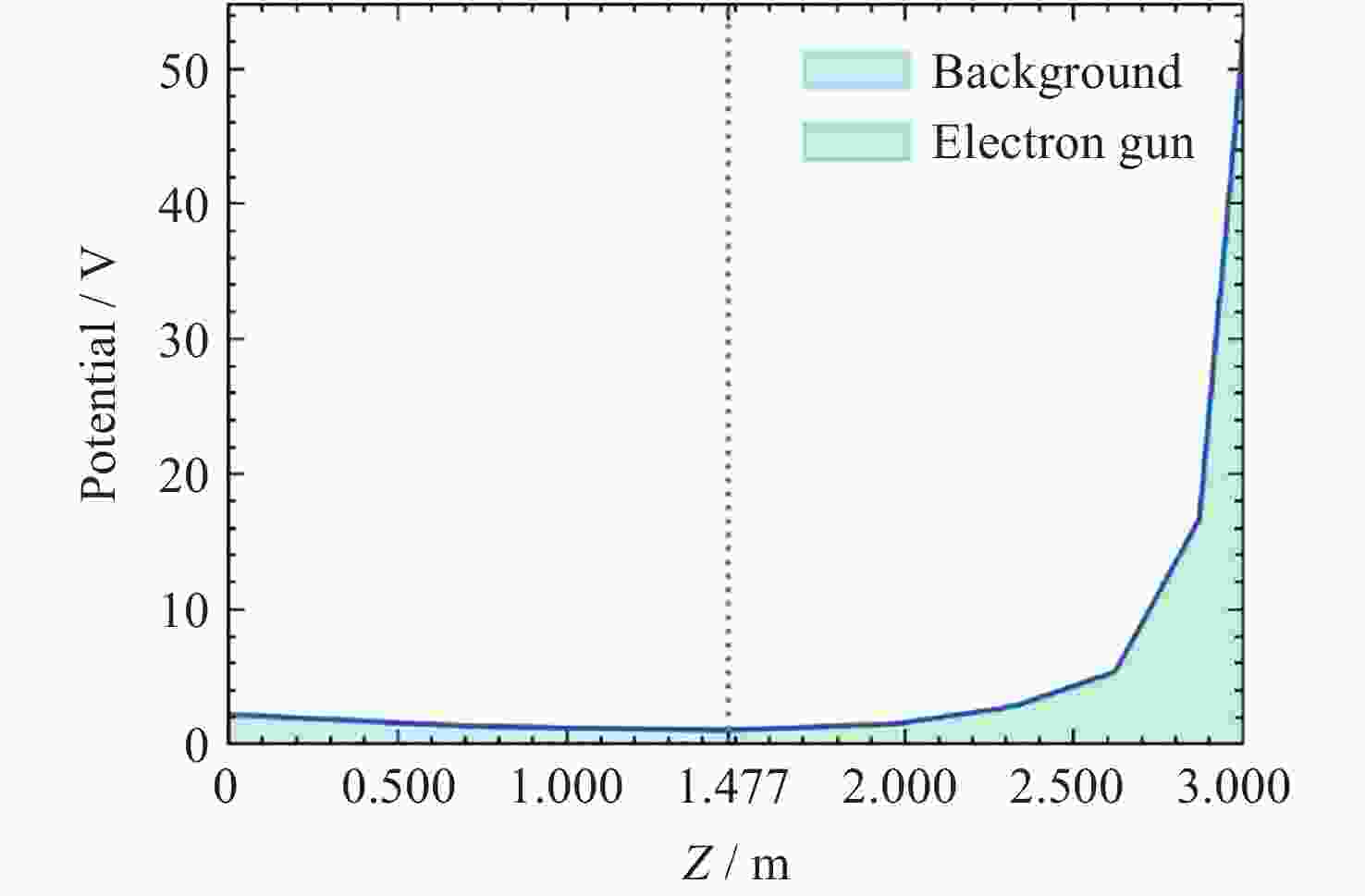
Return-type Electron-based Lunar Surface Electric Field Detection Technology
-
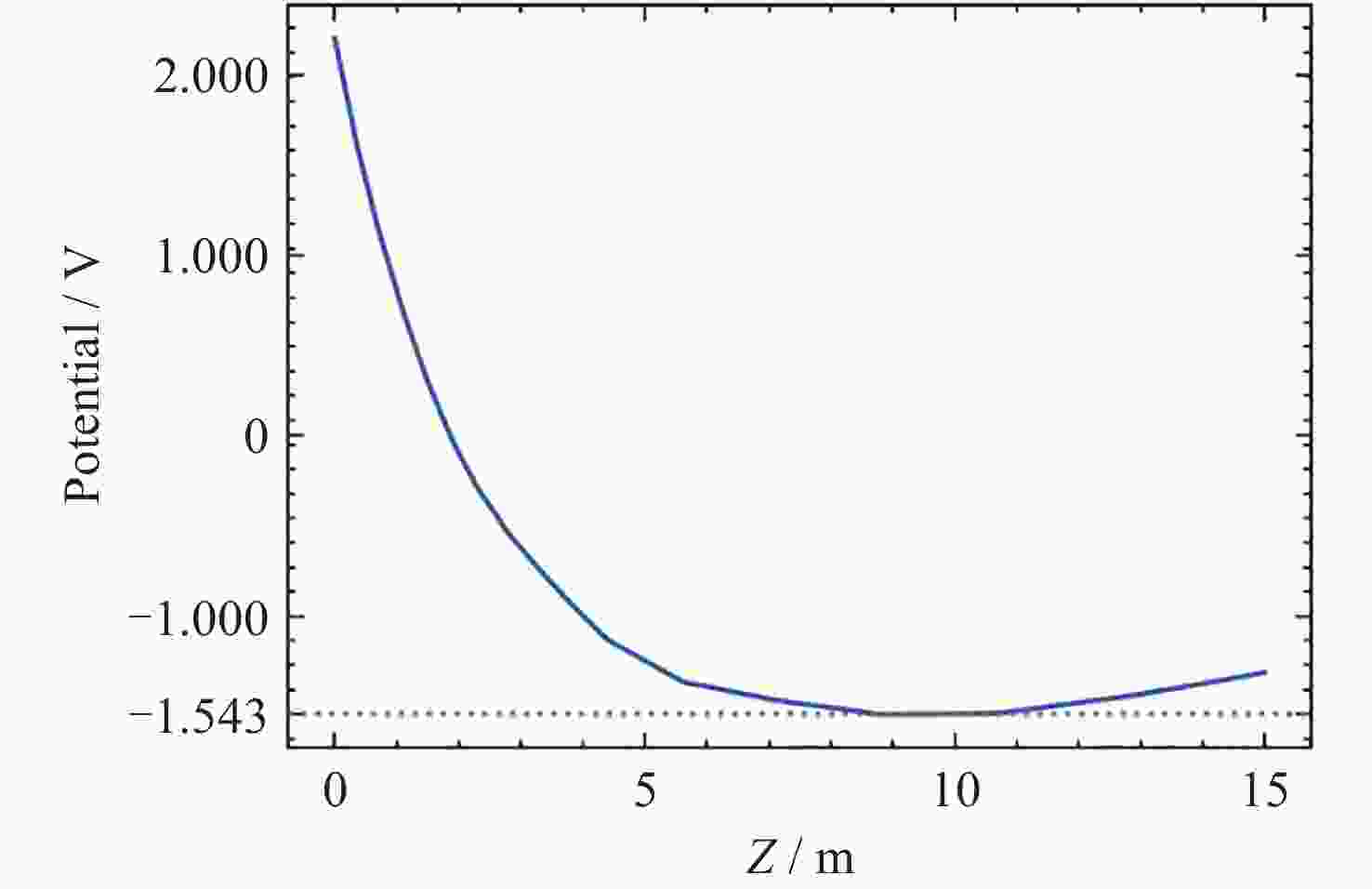
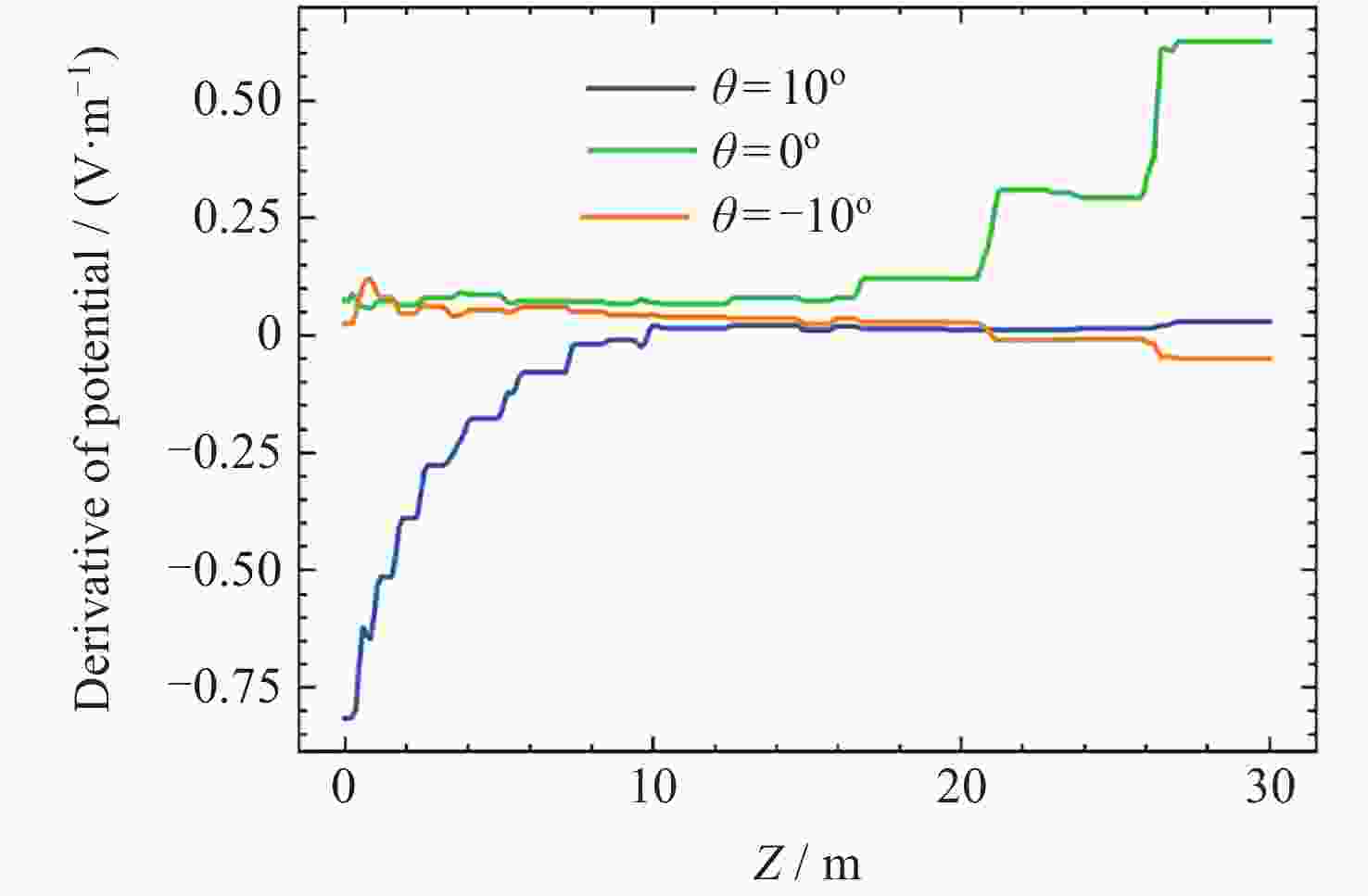
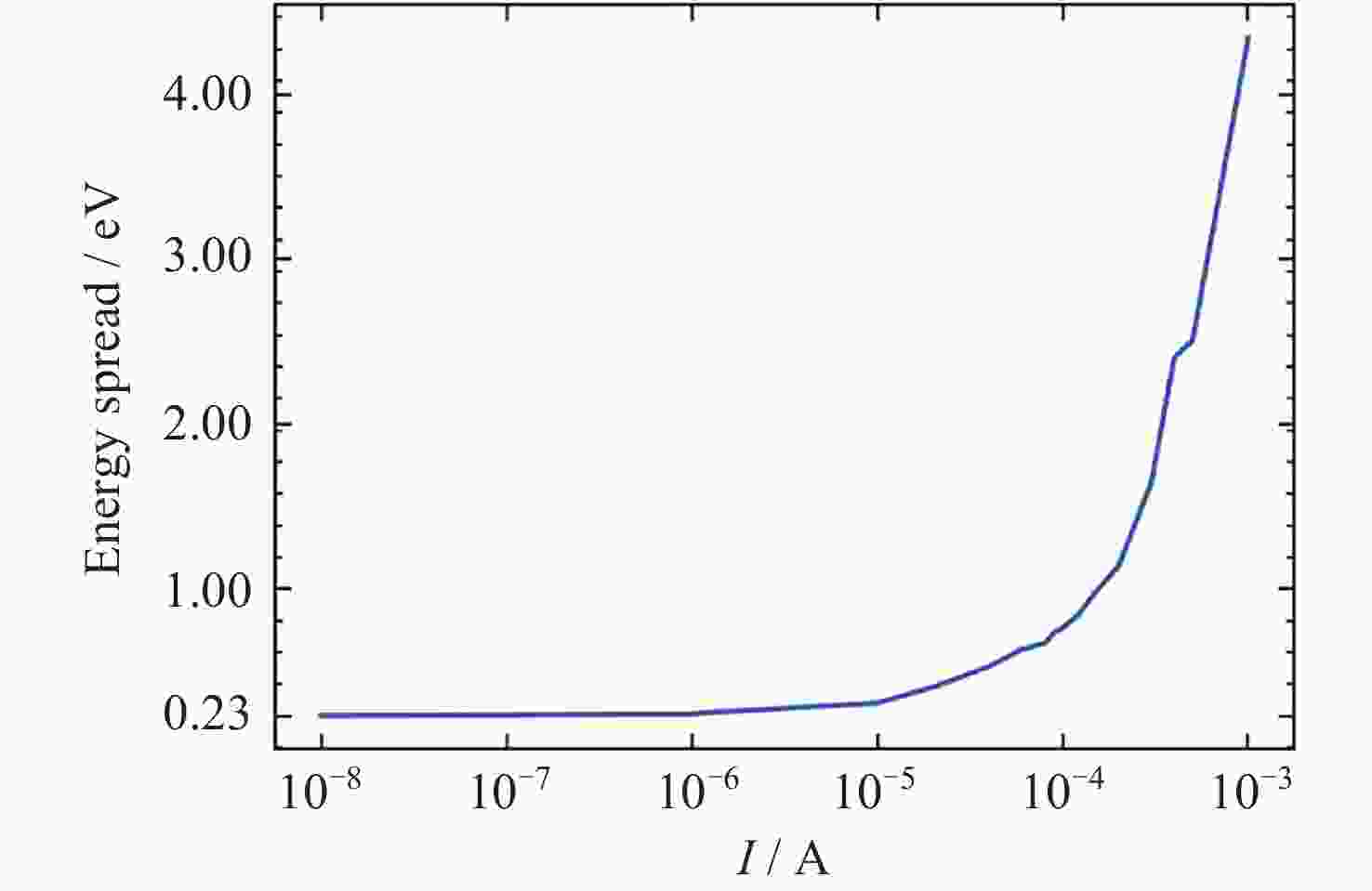
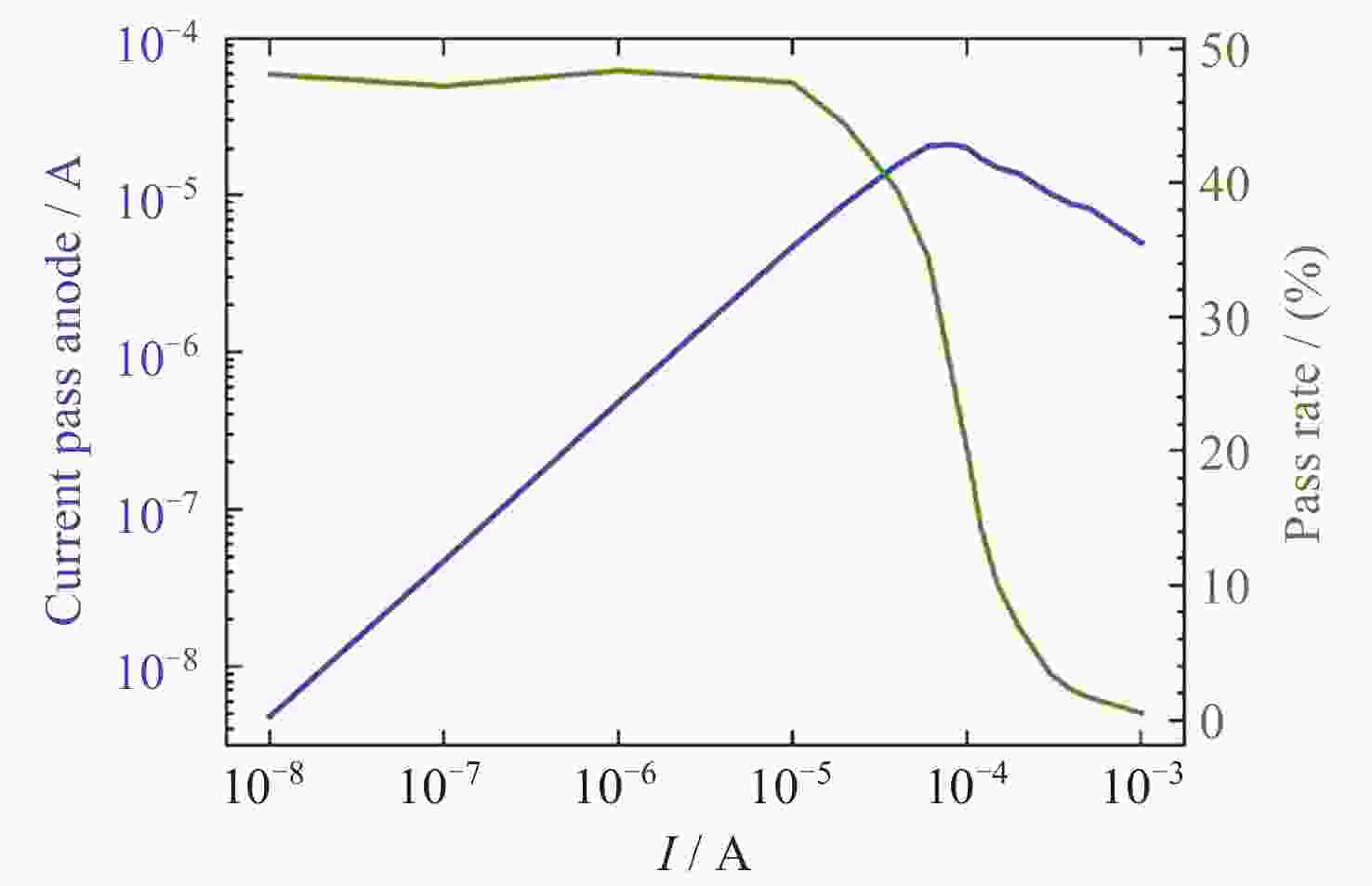
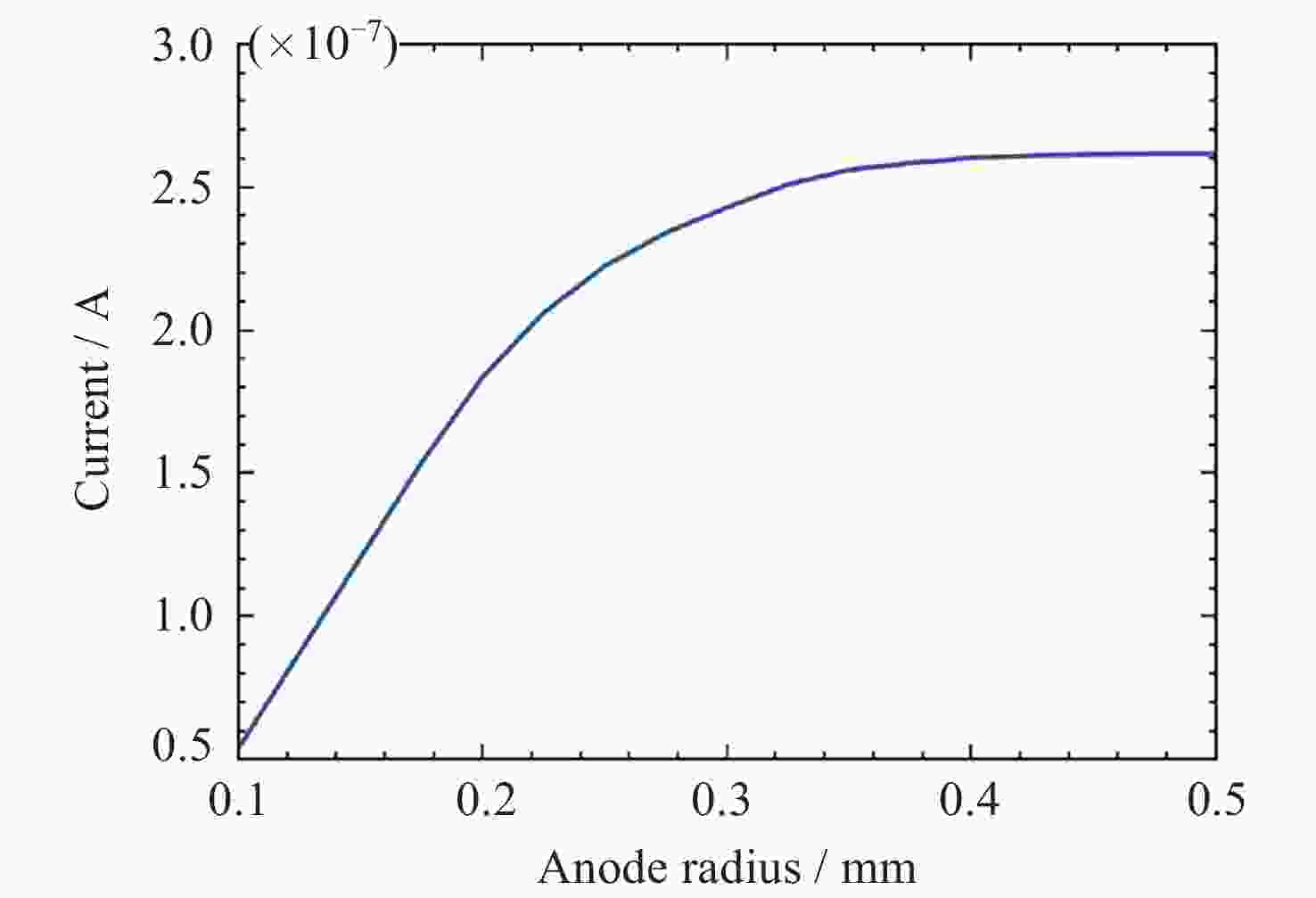
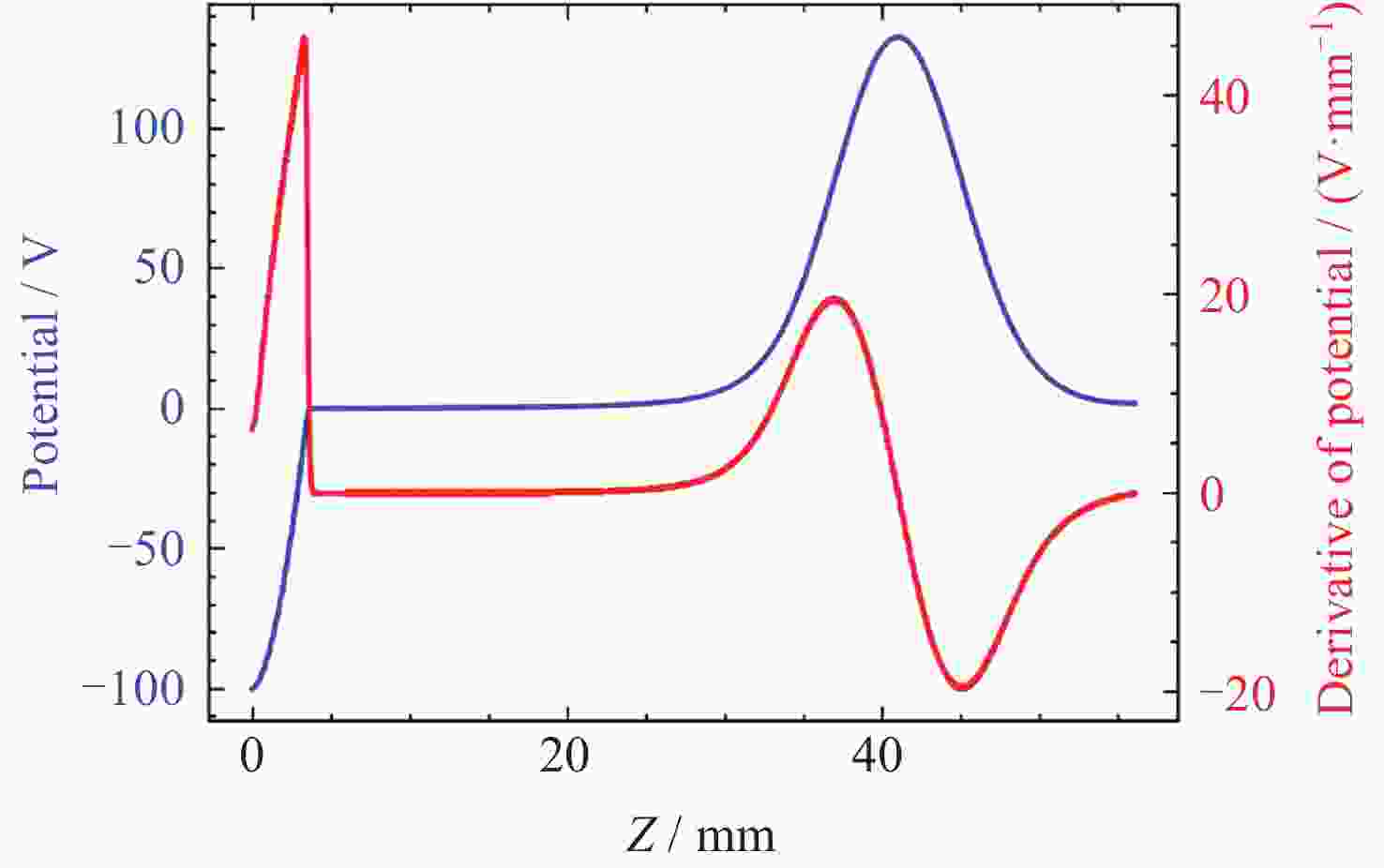
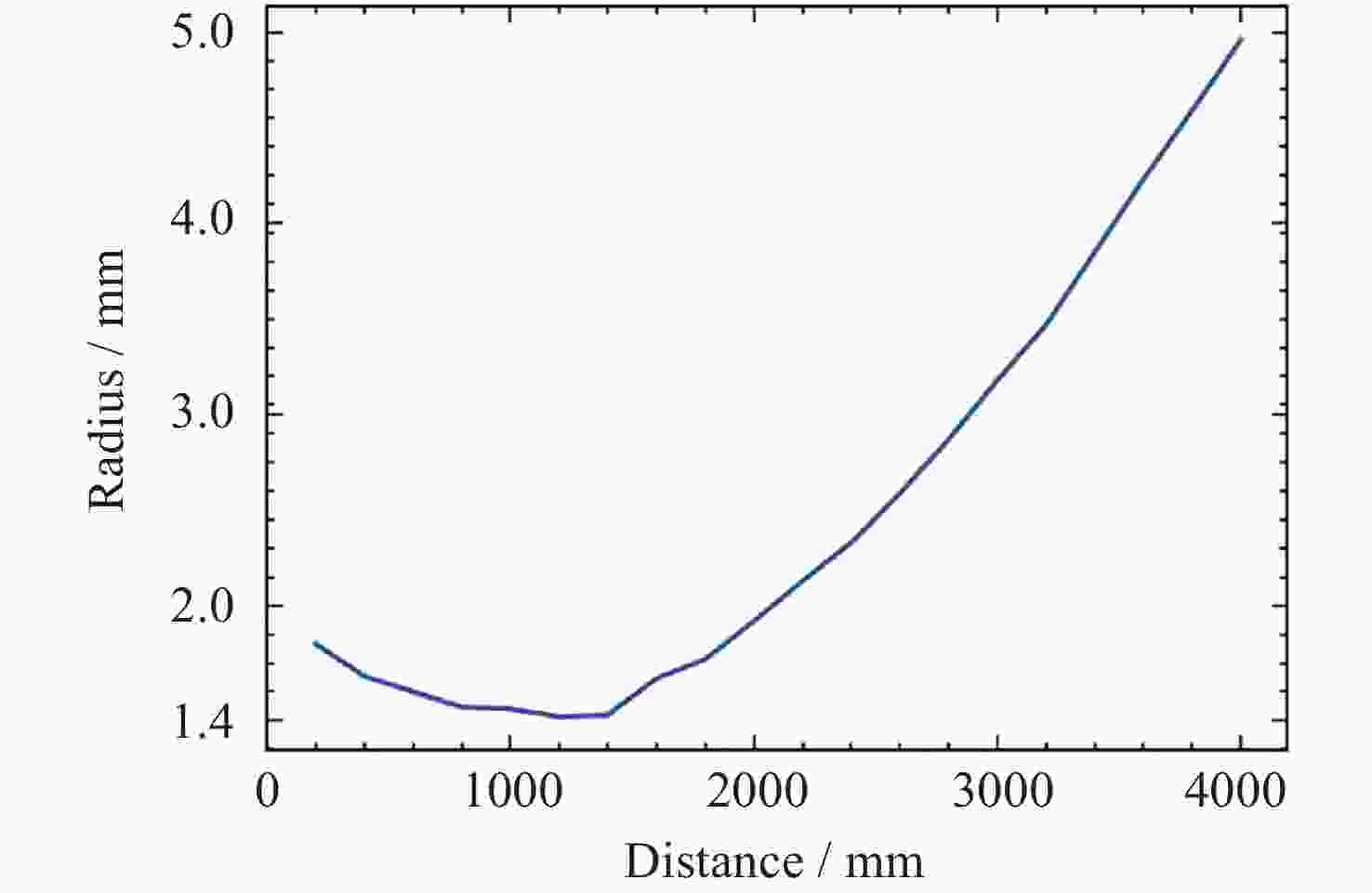
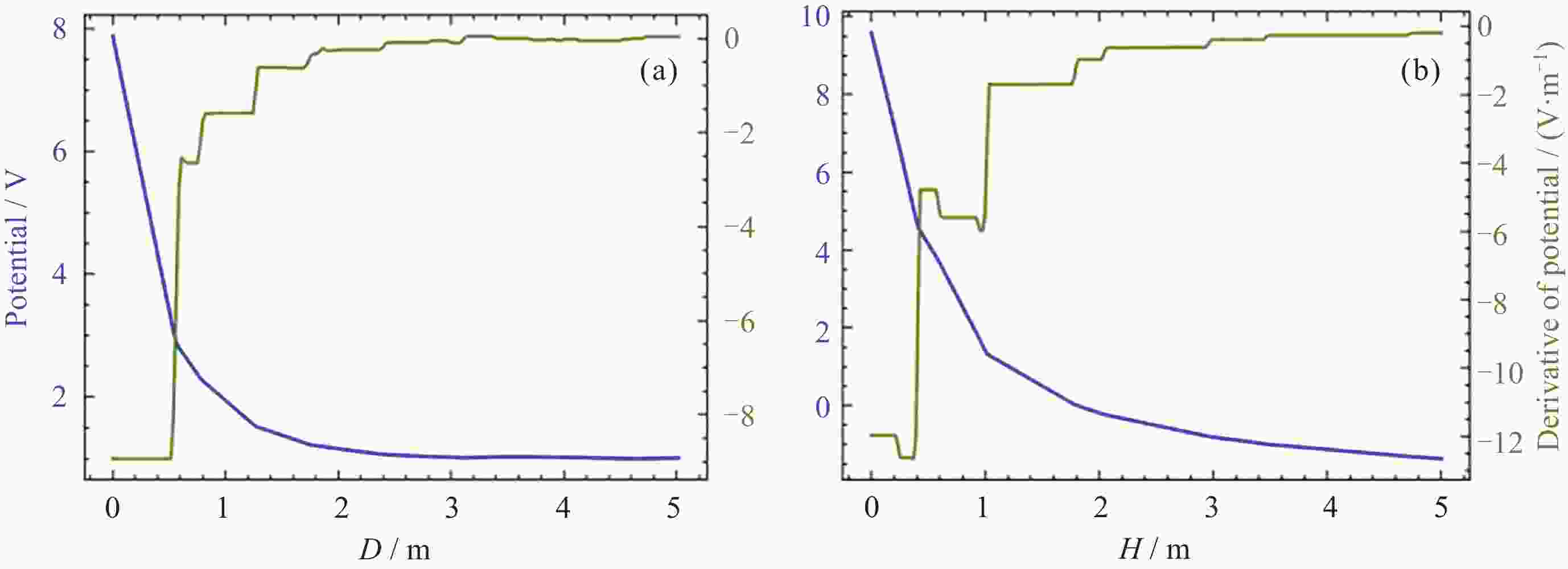
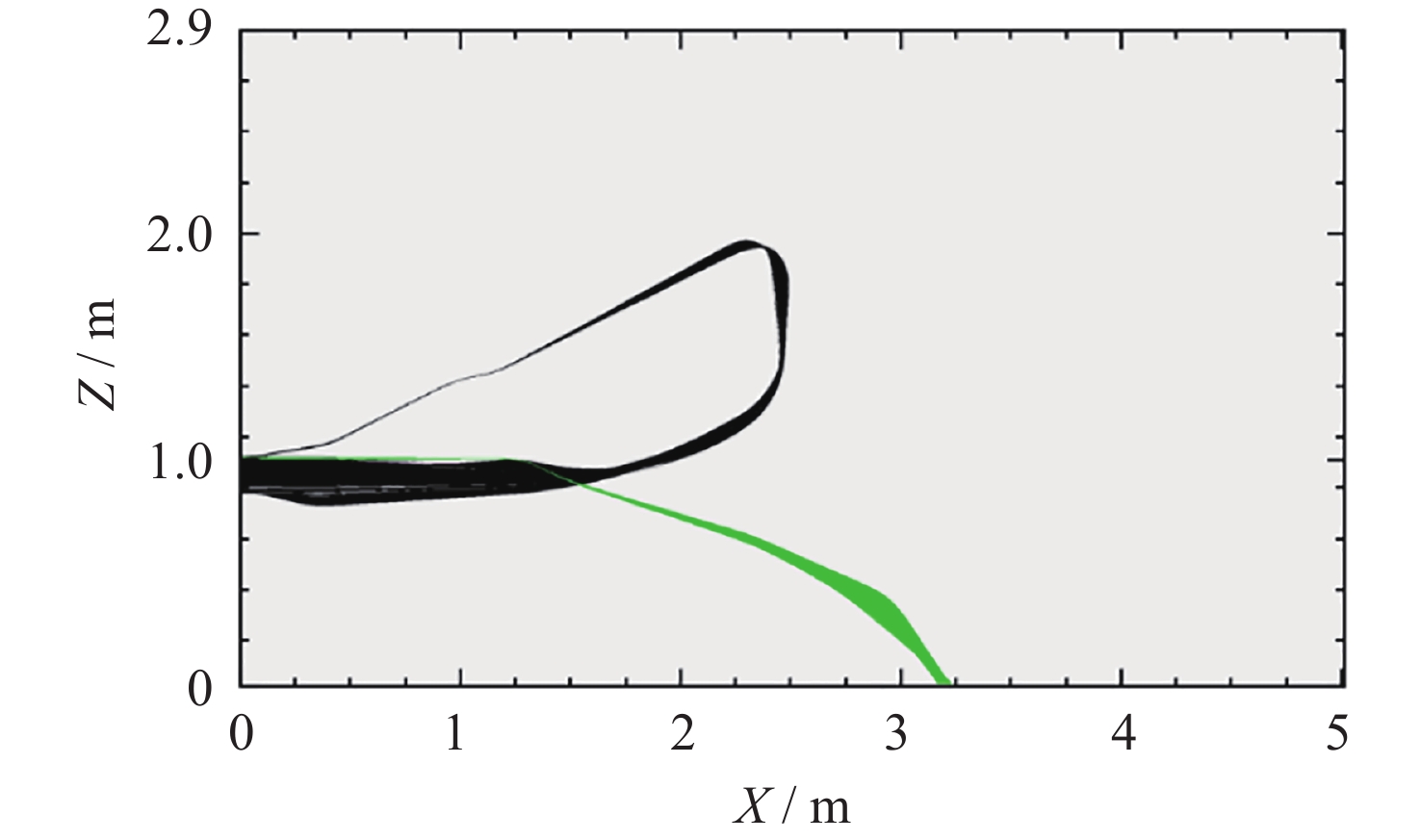
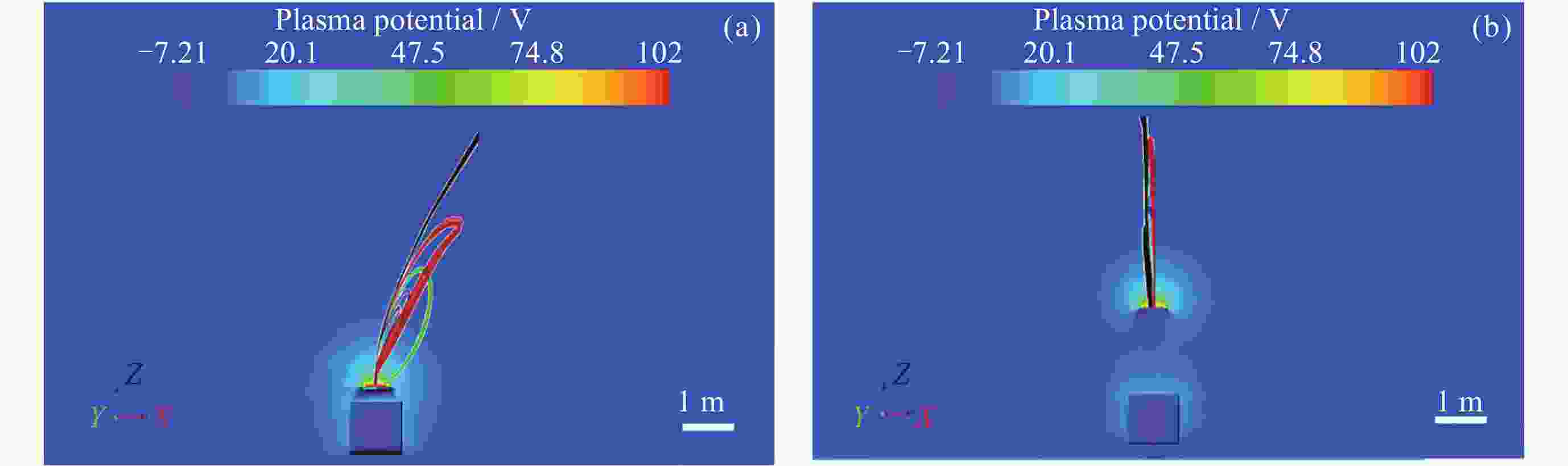
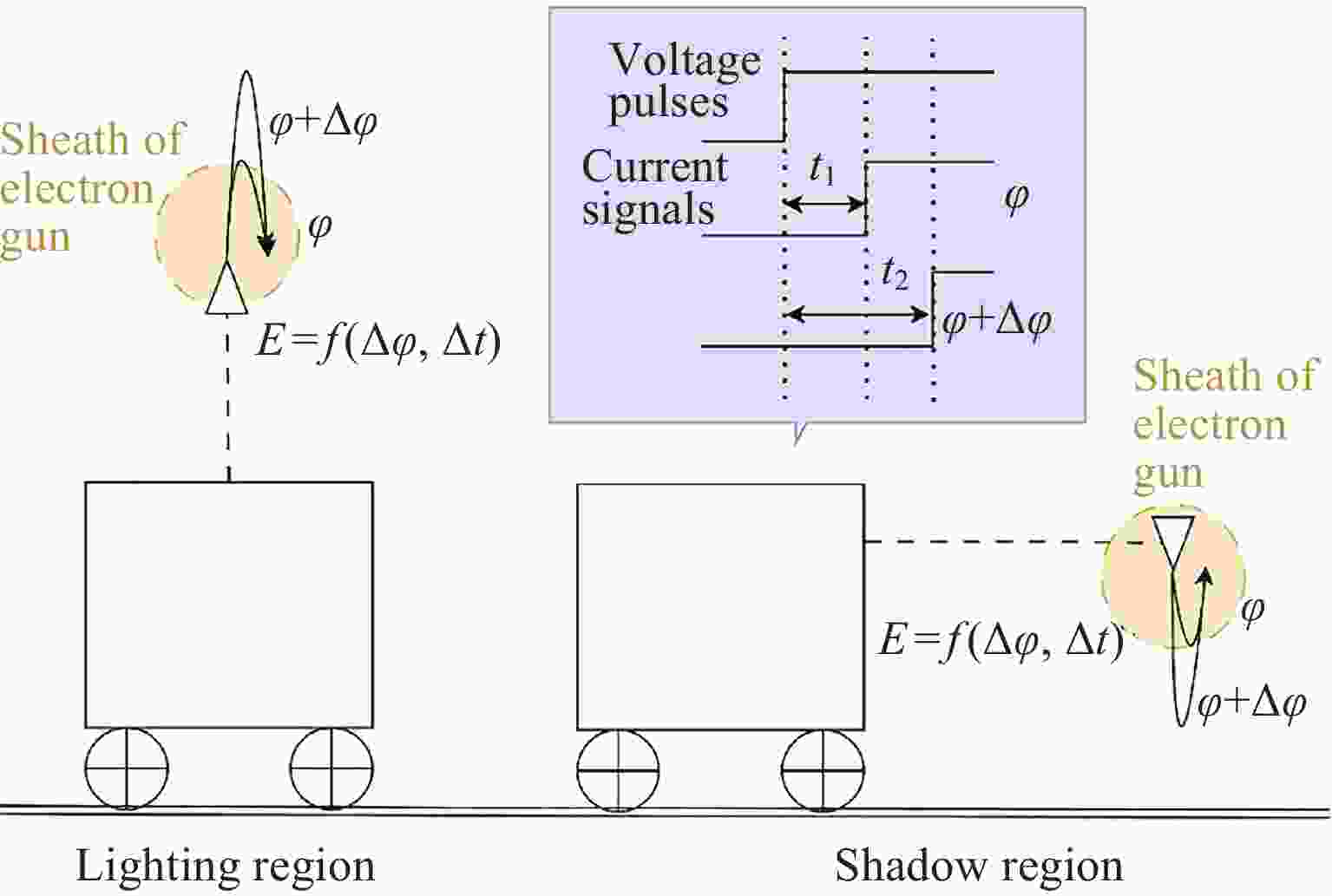
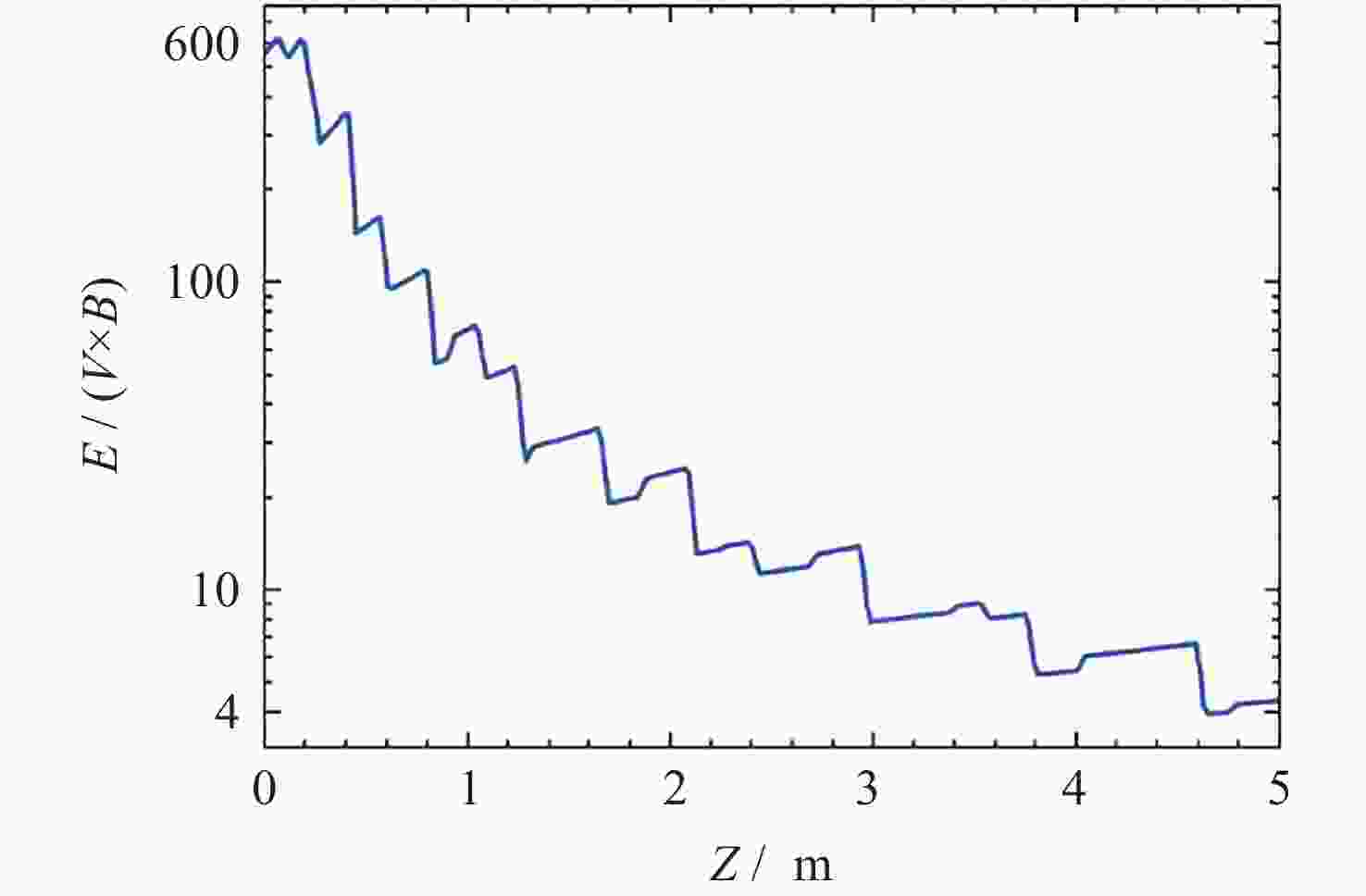
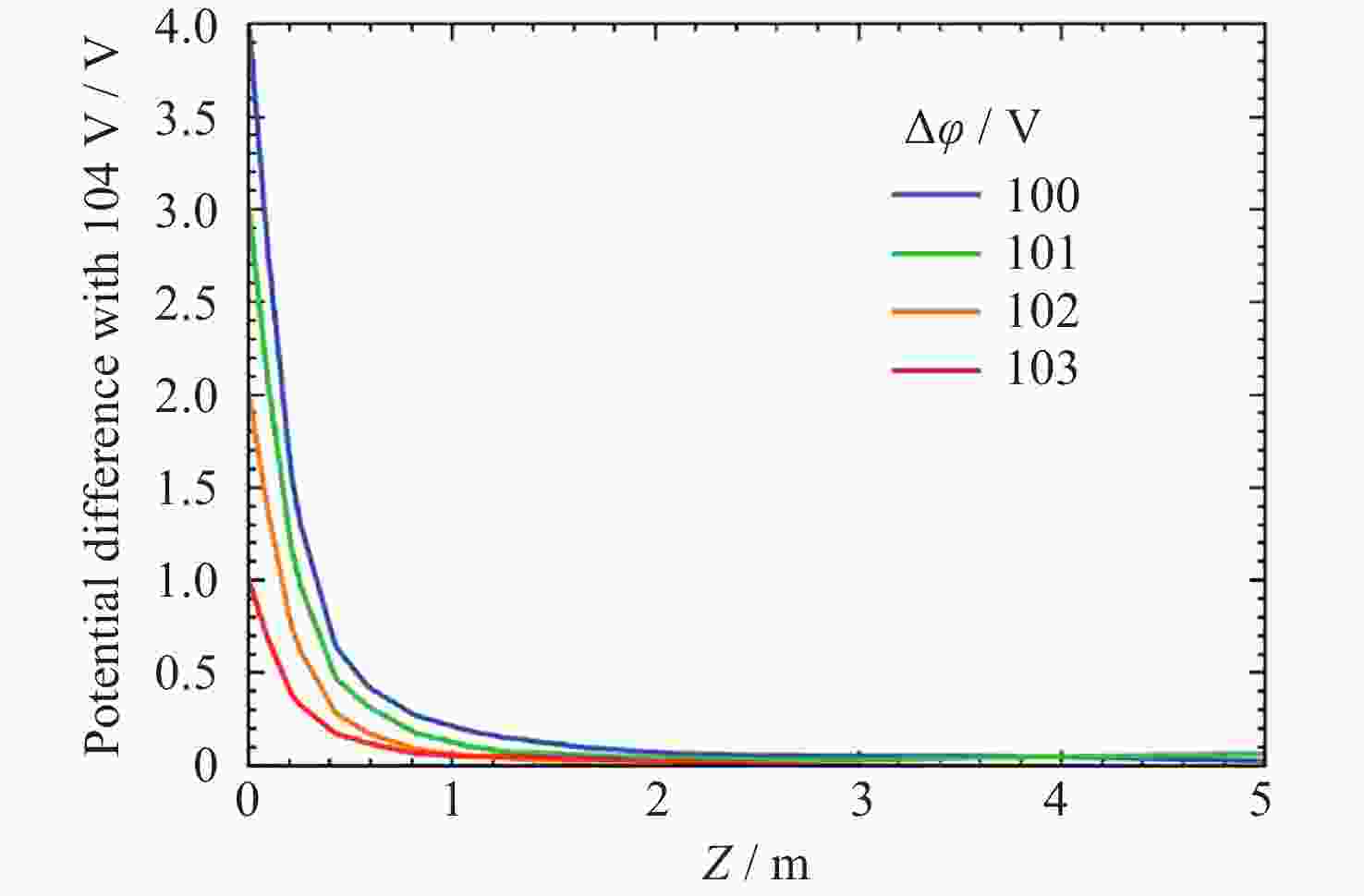
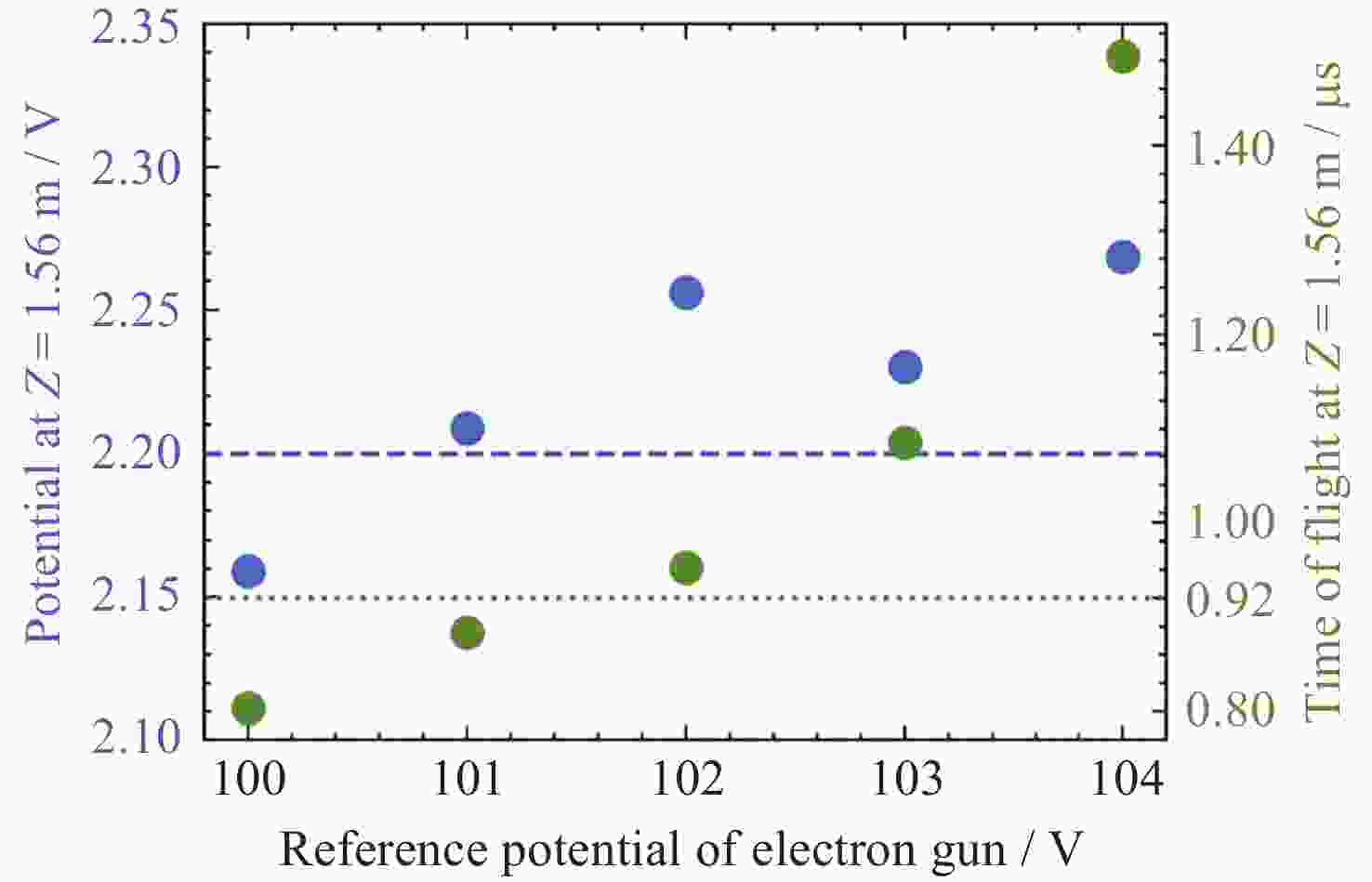
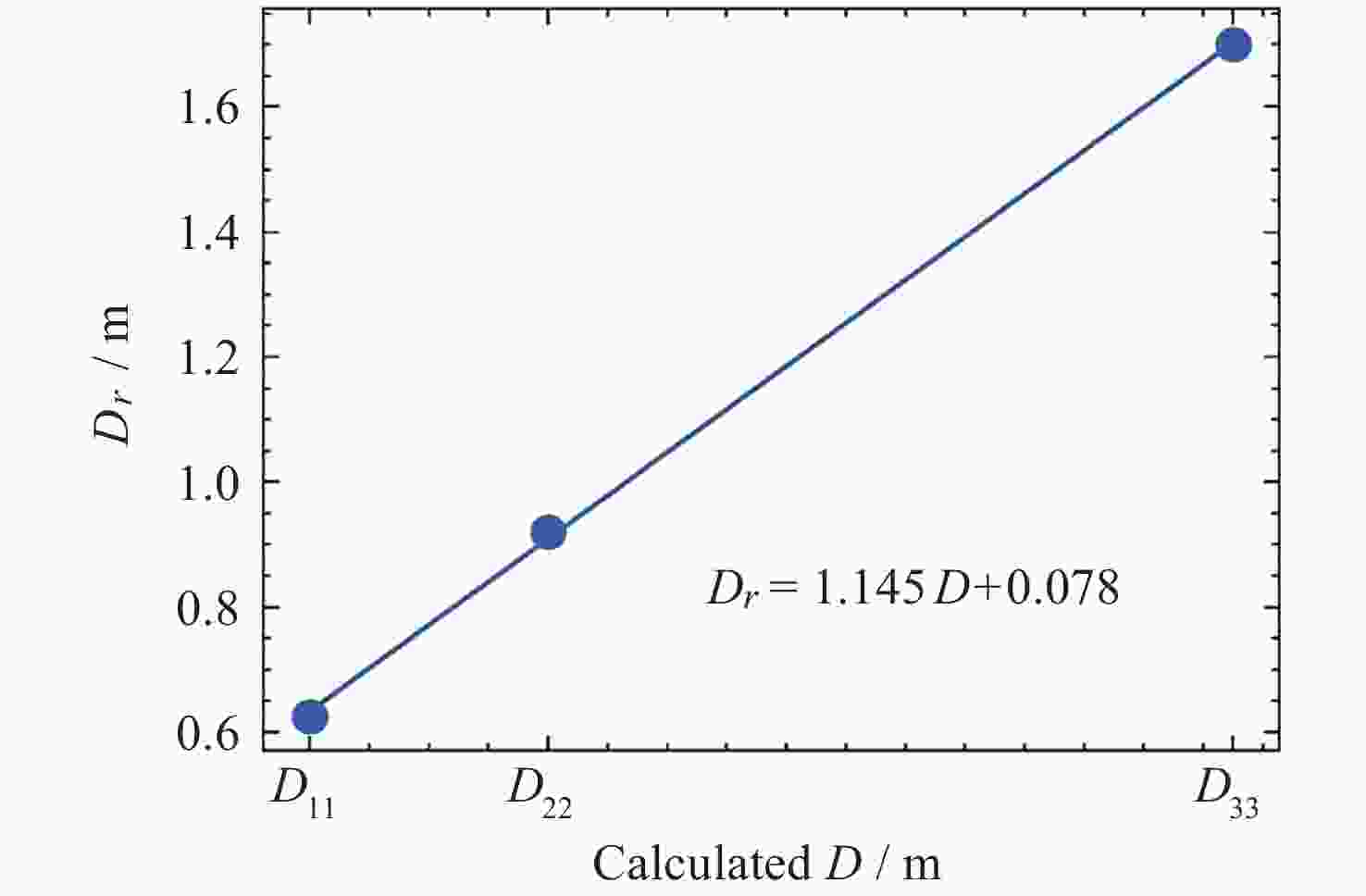
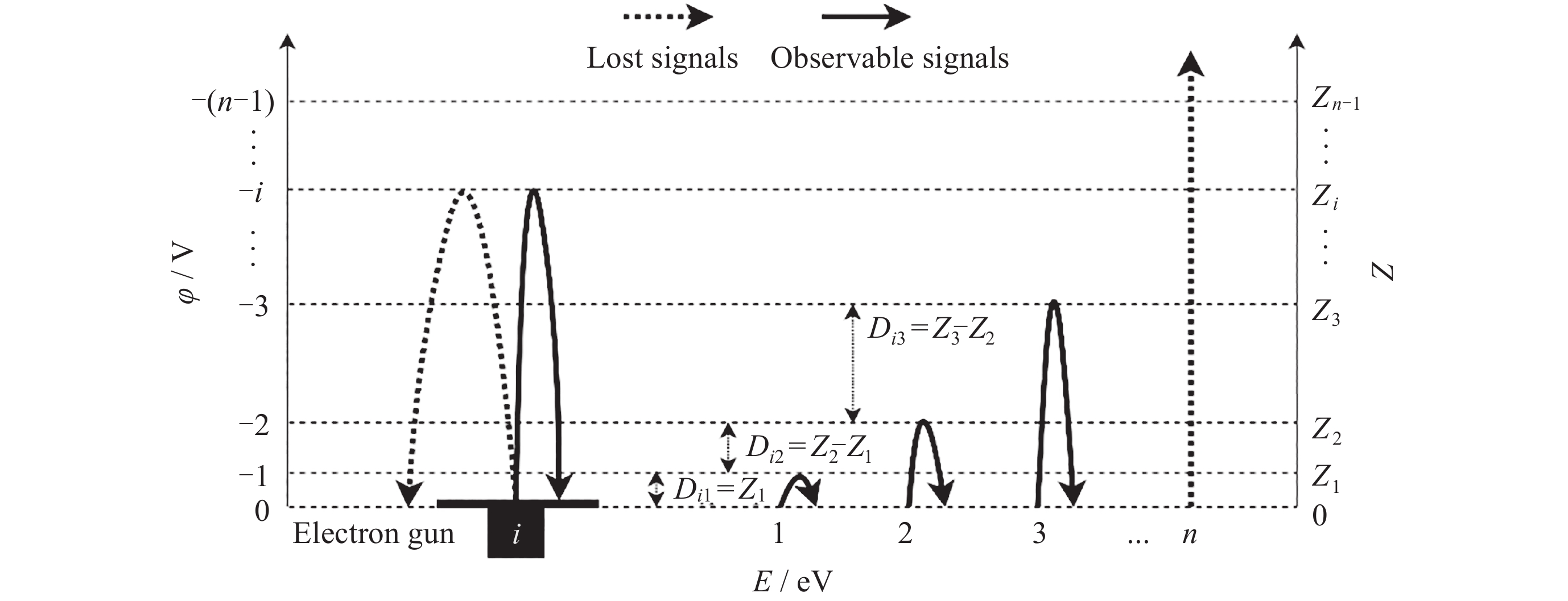
摘要: 提出了一种原位探测月表电场的新技术及相应计算方法, 以满足探测南极月面电场环境特性的需求. 根据仿真结果, 月表电场精细测量需要低能散、高电流的平行电子束发射能力, 设计的低能层流电子枪在10–8~10–5 A的发射电流下, 能散<0.4 eV, 且随发射电流减弱而降低; 通过控制发射电流、调整阳极孔径, 可对电流进行调控; 采用pierce电子枪的阴阳极结构和静电透镜对电子束的平行度进行进一步控制, 仿真显示10–7 A电子束的扩散效果较弱, 各方面性能符合探测需求. 此外, 构建通过电子束返回时间测量垂直电场的探测方式, 模拟验证月表光照区向上发射电子束时相应的电场计算结果可反映背景电场, 返回电子式月表电场探测技术达到了执行月表电场测量所需的要求.Abstract: This study aims to propose an active, on-site, high-resolution lunar surface electric field detection technology along with corresponding computational methods, to meet the requirements of exploring the comprehensive characteristics of the lunar surface environment, and helps understanding the interaction between the Moon and solar wind. According to the simulation results, precise measurement of lunar surface electric fields demands electron emission capabilities with low energy spread, relatively high current, and parallel electron beams. Preliminary system parameters with the capability of receiving return current signals have been designed, including system parameters for voltage stabilization, pulse power supply modules, and signal acquisition modules. Referring to the simulation results, the low-energy laminar flow electron gun designed in this study exhibits an energy spread of <0.4 eV at emission currents ranging from 10–8 to 10–5 A, with the energy spread decreasing as the emission current weakens. Control of emission current is achieved by regulating the initial current of the thermionic cathode, employing a cathode-anode structure like Pierce electron gun and adjusting the anode aperture. Additional control over beam parallelism is achieved using an electrostatic lens. Simulation verifies that the 10–7 A electron beam exhibits minimal diffusion within a 4 m working distance, meeting the requirements for accurate detection of lunar surface electric fields. The paper proposes and simulates the measurement of lunar electric fields by emitting electron beams upwards in the lunar illuminated region. The simulation and calculation results of lunar vertical electric fields show a linear relationship, verifying the feasibility of the detection plan, with the influence of background magnetic fields being negligible. The feasibility of actively adjusting the electron gun reference potential to expand the electron beam range to (–100, +100) V has also been proposed and verified. According to simulation analysis, our return-type electron-based lunar surface electric field detection technology, along with the designed and manufactured low-energy electron gun, can meet the requirements for mobile, non-contact detection of vertical electric fields on the surface of the lunar South Pole.
-
表 1 性能参数
Table 1. Performance parameters
Potential range/
VElectric field range/
(V⋅m–1)Electric field resolution/
(V⋅m–1)(–100, +100) (0.5, 5) ≤0.5 -
[1] STUBBS T J, HALEKAS J S, FARRELL W M, et al. Lunar surface charging: a global perspective using lunar prospector data[M]//KRUEGER H, GRAPS A. Workshop on Dust in Planetary Systems. Kauai, Hawaii: ADS, 2007: 181-184 [2] HALEKAS J S, MITCHELL D L, LIN R P, et al. Evidence for negative charging of the lunar surface in shadow[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2002, 29(10): 1435 [3] HALEKAS J S, ANGELOPOULOS V, SIBECK D G, et al. First results from ARTEMIS, a new two-spacecraft lunar mission: counter-streaming plasma populations in the lunar wake[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2011, 165(1/2/3/4): 93-107 [4] KATO M, HARADA Y, XU S S, et al. Modeling photoelectron and auger electron emission from the sunlit lunar surface: a comparison with ARTEMIS observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2023, 128(10): e2023JA031707 doi: 10.1029/2023JA031707 [5] 刘沐明, 冯永勇. 太阳风离子在月面的反射过程及对月面电场的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(理学版), 2018, 56(6): 1513-1520LIU Muming, FENG Yongyong. Reflection of solar wind ions on lunar surface and its influence on lunar surface electric field[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Science Edition), 2018, 56(6): 1513-1520 [6] 谢良海, 张爱兵, 李磊, 等. 嫦娥四号能量中性原子观测揭示太阳风与月面相互作用新特征[J]. 空间科学学报, 2022, 42(1): 11-24 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.01.20220113XIE Lianghai, ZHANG Aibing, LI Lei, et al. Chang’E-4 energetic neutral atom observation reveals new features about the solar wind-moon interaction[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2022, 42(1): 11-24 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.01.20220113 [7] FENNER M A, FREEMAN J W JR, HILLS H K. The electric potential of the lunar surface[J]. Proceedings of the Fourth Lunar Science Conference, 1973, 3: 2877-2887 [8] DE B R, CRISWELL D R. Intense localized photoelectric charging in the lunar sunset terminator region, 1. Development of potentials and fields[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research (1896-1977), 1977, 82(7): 999-1004 [9] LI L, ZHANG Y T, ZHOU B, et al. Lunar surface potential and electric field[J]. Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2019, 19(6): 77 doi: 10.1088/1674-4527/19/6/77 [10] LUND D, HE X M, HAN D R. Kinetic particle simulations of plasma charging at lunar craters under severe conditions[J]. Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 2023, 60(4): 1176-1187 doi: 10.2514/1.A35622 [11] 甘红, 李雄耀, 魏广飞. 嫦娥四号着陆区织女陨坑电场环境数值模拟[J]. 空间科学学报, 2020, 40(2): 250-263 doi: 10.11728/cjss2020.02.250GAN Hong, LI Xiongyao, WEI Guangfei. Electric fields distribution of Zhinyu crater in Chang’E-4 landing area[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2020, 40(2): 250-263 doi: 10.11728/cjss2020.02.250 [12] JARVINEN R, ALHO M, KALLIO E, et al. On vertical electric fields at lunar magnetic anomalies[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2014, 41(7): 2243-2249 doi: 10.1002/2014GL059788 [13] XU S S, POPPE A R, HALEKAS J S, et al. Mapping the lunar wake potential structure with ARTEMIS data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2019, 124(5): 3360-3377 doi: 10.1029/2019JA026536 [14] YU D Y, SUN Z Z, ZHANG H. Future prospects of lunar lander technology[M]//YU D Y, SUN Z Z, ZHANG H. Technology of Lunar Soft Lander. Singapore: Springer, 2021: 551-555 [15] PASCHMANN G, MELZNER F, FRENZEL R, et al. The electron drift instrument for cluster[J]. Space Science Reviews, 1997, 79(1): 233-269 [16] 余后满, 饶炜, 张益源, 等. “嫦娥七号”探测器任务综述[J]. 深空探测学报(中英文), 2023, 10(6): 567-576YU Houman, RAO Wei, ZHANG Yiyuan, et al. Mission analysis and spacecraft design of Chang’E-7[J]. Journal of Deep Space Exploration, 2023, 10(6): 567-576 [17] 吴伟, 刘超, 张贤国, 等. 一种低能量远焦距电子枪技术[J]. 空间科学学报, 2023, 43(1): 144-155 doi: 10.11728/cjss2023.01.220208013WU Wei, LIU Chao, ZHANG Xianguo, et al. Research on a low energy Tele-focus electron gun[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2023, 43(1): 144-155 doi: 10.11728/cjss2023.01.220208013 [18] KUYATT C E. Electrostatic lenses[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 1978, 49(4): 551 doi: 10.1063/1.1135432 [19] JACKSON T L, FARRELL W M, ZIMMERMAN M I. Rover wheel charging on the lunar surface[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2015, 55(6): 1710-1720 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2014.12.027 [20] 程彬杰, 刘学东, 唐天同, 等. 电子束中Boersch效应的实验研究[J]. 真空科学与技术, 1998, 18(5): 364-368CHENG Binjie, LIU Xuedong, TANG Tiantong, et al. Experimental studies of the Boersch effect of electron beams[J]. Vacuum Science and Technology (China), 1998, 18(5): 364-368 [21] SHIMIZU R, ONODA H, HASHIMOTO H, et al. Oxygen-enhanced thermionic emission pattern of hemispherical single-crystal LaB6[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1984, 55(5): 1379-1387 doi: 10.1063/1.333228 [22] DYAL P, PARKIN C W, DAILY W D. Magnetism and the interior of the Moon[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1974, 12(4): 568-591 doi: 10.1029/RG012i004p00568 -
-




 金菲凡 女, 1999年8月出生于上海市, 现于中国科学院大学(中国科学院国家空间科学中心)攻读硕士学位, 主要研究方向为月球电场环境探测技术. E-mail:
金菲凡 女, 1999年8月出生于上海市, 现于中国科学院大学(中国科学院国家空间科学中心)攻读硕士学位, 主要研究方向为月球电场环境探测技术. E-mail:  刘超 男, 1981年3月出生于河南省周口市, 现为中国科学院国家空间科学中心正高级工程师, 博士生导师, 主要从事空间环境及等离子体就位探测技术的研究. E-mail:
刘超 男, 1981年3月出生于河南省周口市, 现为中国科学院国家空间科学中心正高级工程师, 博士生导师, 主要从事空间环境及等离子体就位探测技术的研究. E-mail: 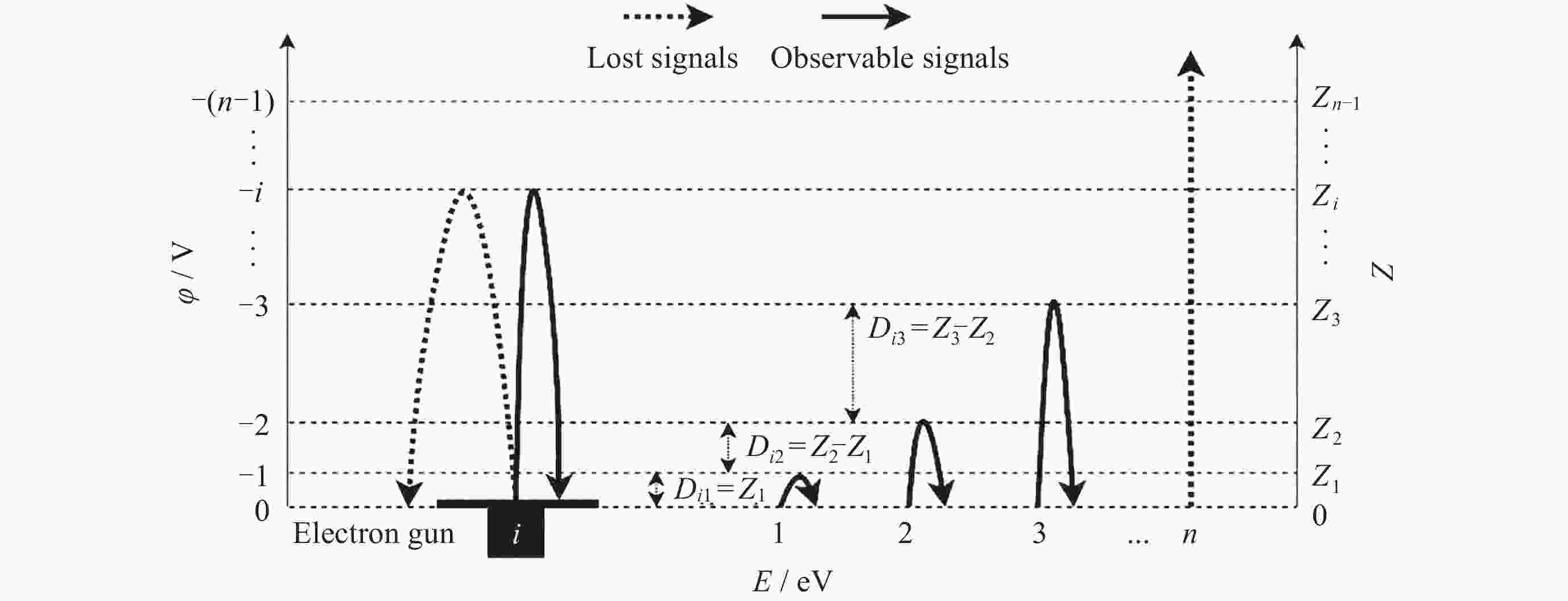
 下载:
下载: