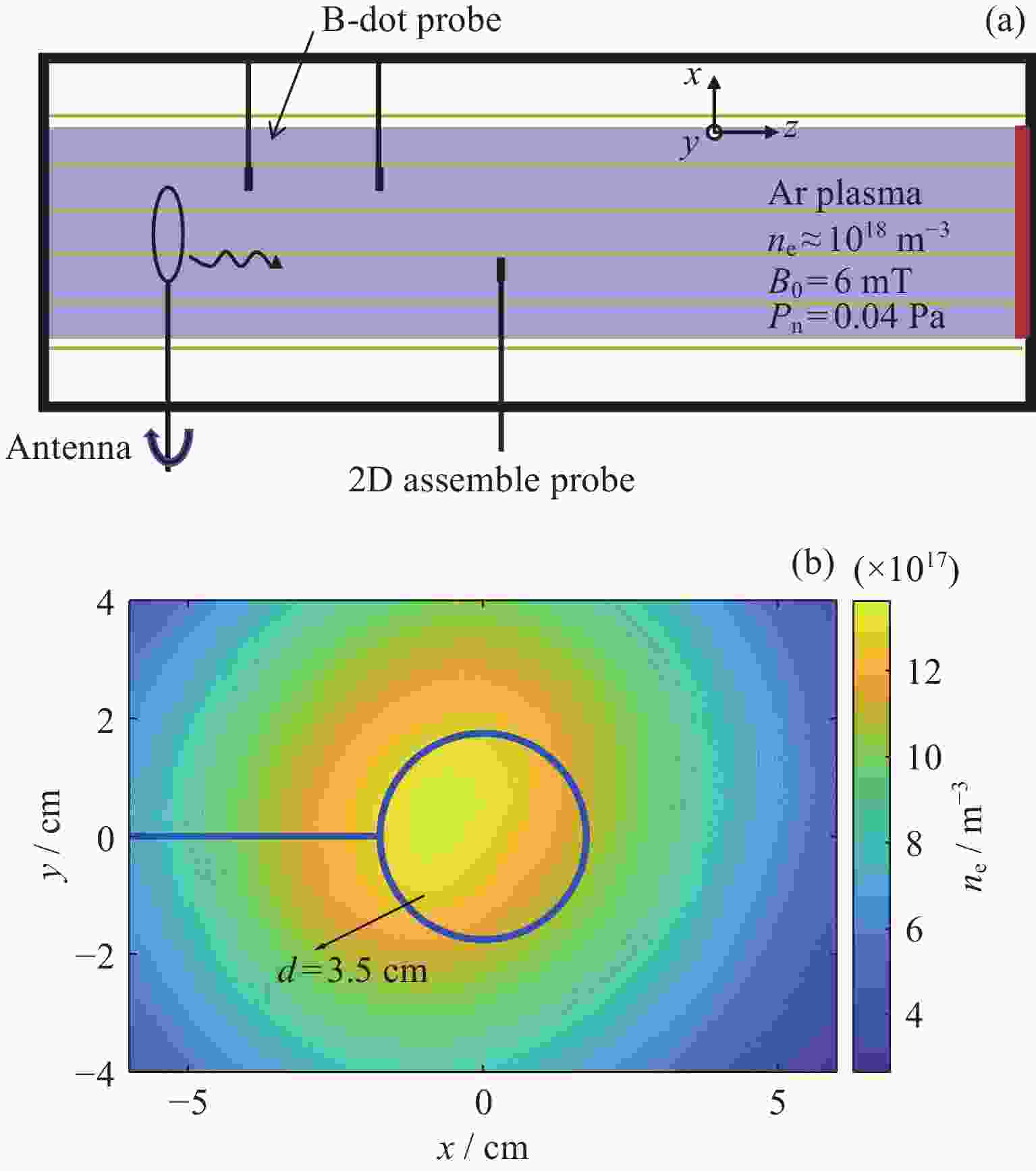
Experimental Study on the Properties of Helicon Mode Whistler Waves
-
摘要: 哨声波是地球内磁层中常见的一种等离子体波动, 其不仅可以加速电子到相对论能量, 还可散射电子沉降到大气层形成弥散极光. 哨声波是一支右旋偏振波, 在空间等离子体中其等相位面通常被认为是一个平面. 近年来, 地面等离子体实验正在成为研究哨声波激发和传播的一种重要手段. 本文在中国科学技术大学线性磁化等离子体装置(KLMP)上开展了磁环天线激发波动的实验, 并利用3D磁探针测量了波动磁场的演化信息. 测量结果发现, 磁环天线激发了一种等相位面为螺旋状的右旋偏振波动, 根据天线设置的不同, 螺旋波模数分别为m=0和m=1. 通过计算波动的波长和频率, 确定这种螺旋波满足哨声波的色散关系, 为进一步在等离子体实验装置中研究哨声波打下了基础.Abstract: Whistler waves, as common plasma waves, play an important role in the Earth’s inner magnetosphere. Through the interaction of whistler waves and particles, some electrons can be accelerated to relativistic energy, and another part of the electrons are scattered into the loss cone and settled into the atmosphere to form diffuse auroras. The whistler wave is a right-handed polarized wave whose equiphase plane is usually considered to be a plane in space plasma. In recent years, ground plasma experiments are becoming an important means to study the excitation and propagation of whistler waves. In the Keda Linear Magnetized Plasma device (KLMP) at the University of Science and Technology of China, a magnetic loop antenna is used to excite plasma waves and a 3D magnetic probe is used to measure the evolution of wave magnetic field. The measurement results show that the antenna has excited a right-handed polarization wave with a helical equiphase plane. The helicon waves modules are m=0 and m=1 according to different antenna settings. By calculating the wavelength and frequency of the waves, it is confirmed that the helicon waves can satisfy the dispersion relation of whistler waves, laying the foundation for further research on whistler waves in plasma experimental devices.
-
Key words:
- Ground plasma experiments /
- Whistler waves /
- Helicon waves /
- Magnetic field measurement
-
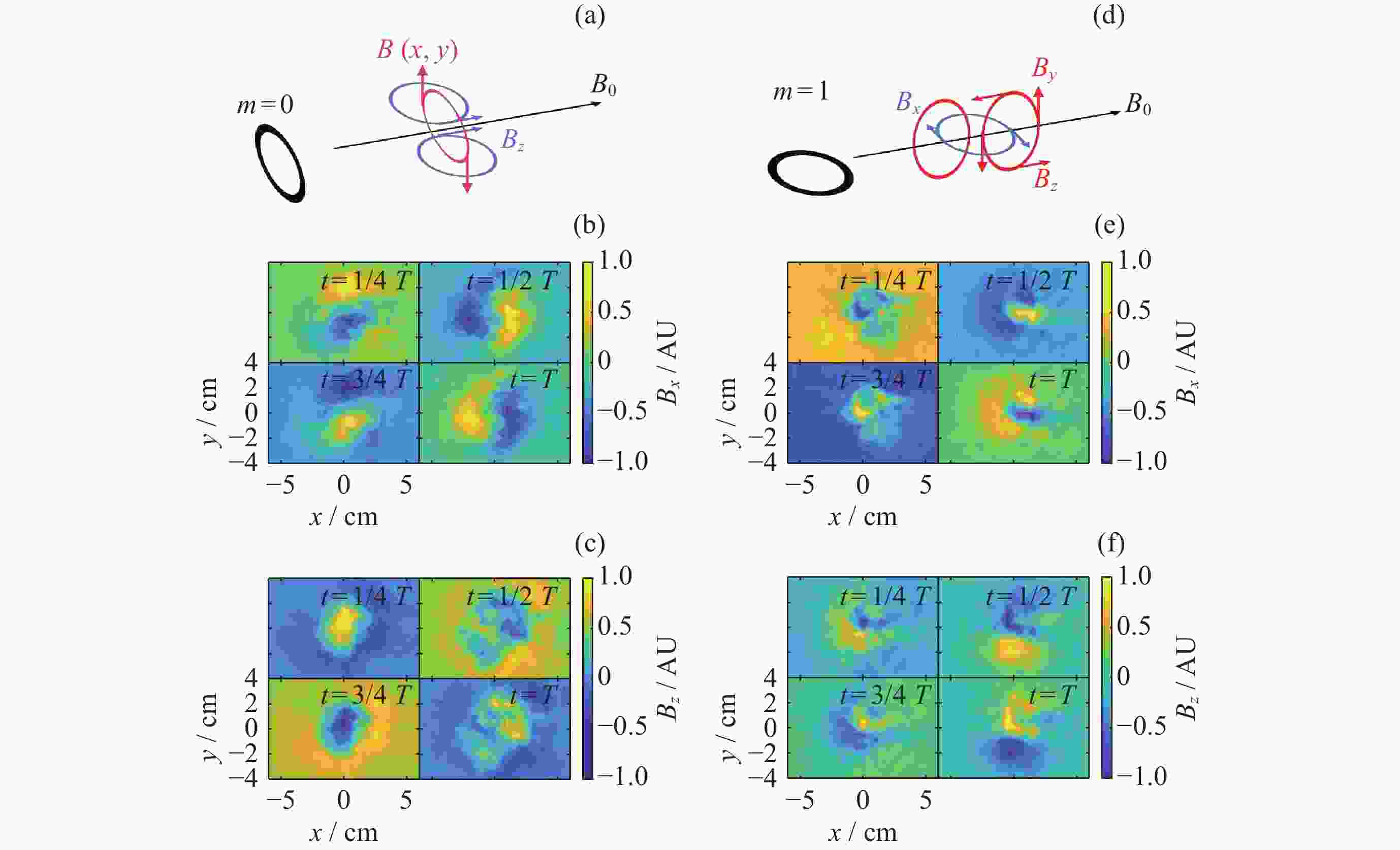
图 2 螺旋波磁场及xy平面内磁场测量结果. (a)~(c) m=0螺旋波, (d)~(f) m=1螺旋波, (a)(d)磁场, (b)(e) x方向磁场分量Bx随时间的变化, (c)(f) z方向磁场分量Bz随时间的变化
Figure 2. Magnetic field diagram of the helicon waves and the magnetic field measurement results in the xy plane. (a)~(c) m=0 helicon waves, and (d)~(f) m=1 helicon waves. (a) and (d) are the magnetic field diagram, (b) and (e) are the change of Bx with time, (c) and (f) are the change of Bz with time
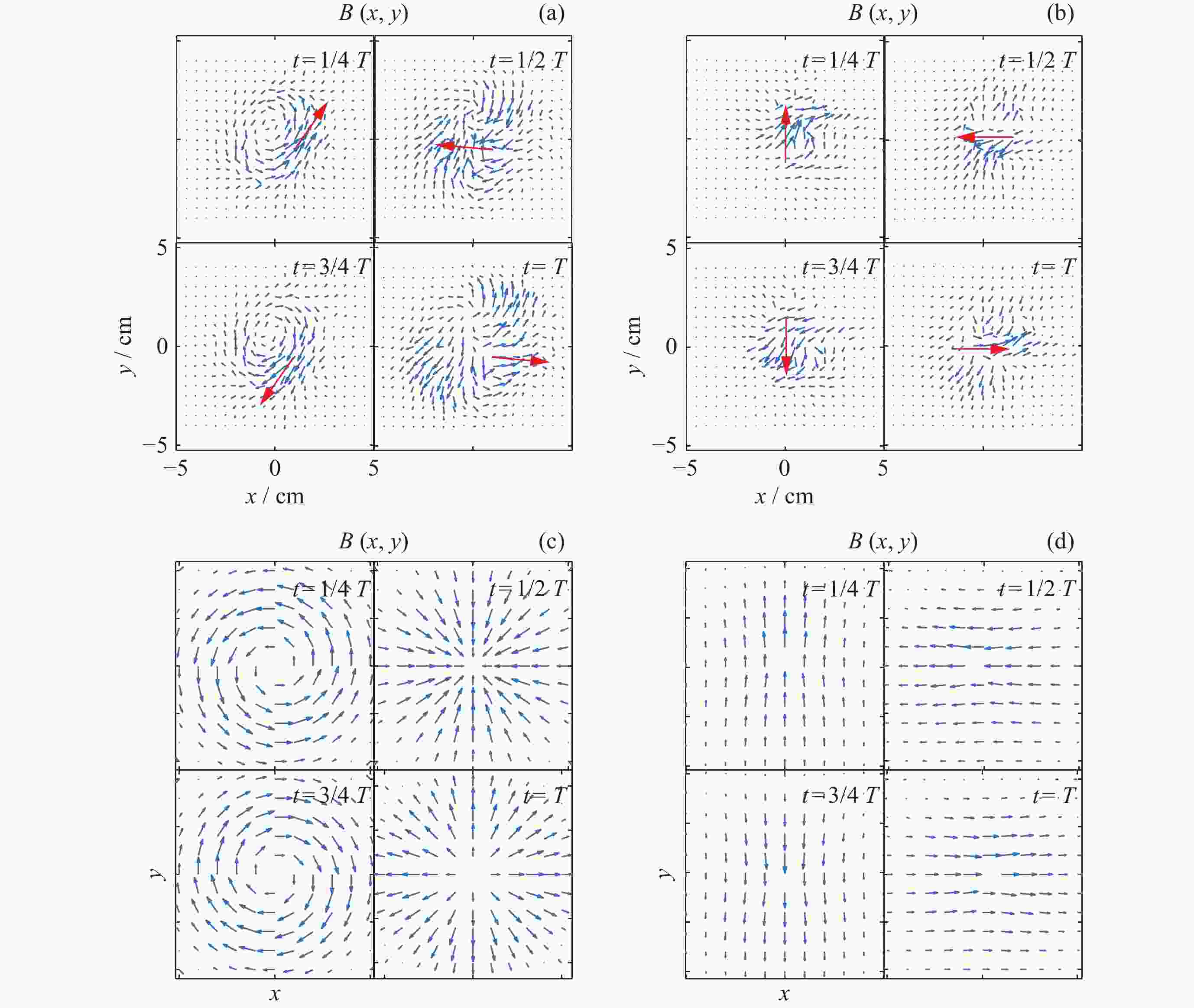
图 3 xy平面内螺旋波磁场矢量随时间的变化. (a) m=0实验测量结果, (b) m=1实验测量结果, (c) m=0理论模型, (d) m=1理论模型
Figure 3. Variation of magnetic field vector of helicon waves in xy plane with time. (a) m=0 experimental measurement results, (b) m=1 experimental measurement results, (c) m=0 theoretical model, (b) m=1 theoretical model
-
[1] STENZEL R L. Whistler waves in space and laboratory plasmas[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1999, 104(A7): 14379-14395 doi: 10.1029/1998JA900120 [2] LI W, THORNE R M, BORTNIK J, et al. Typical properties of rising and falling tone chorus waves[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2011, 38(14): L14103 [3] KHOTYAINTSEV Y V, CULLY C M, VAIVADS A, et al. Plasma jet braking: energy dissipation and nonadiabatic electrons[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2011, 106(16): 165001 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.106.165001 [4] ZHANG X, ANGELOPOULOS V, ARTEMYEV A V, et al. Whistler and electron firehose instability control of electron distributions in and around dipolarizing flux bundles[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2018, 45(18): 9380-9389 doi: 10.1029/2018GL079613 [5] WILDER F D, ERGUN R E, GOODRICH K A, et al. Observations of whistler mode waves with nonlinear parallel electric fields near the dayside magnetic reconnection separatrix by the Magnetospheric Multiscale mission[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2016, 43(12): 5909-5917 doi: 10.1002/2016GL069473 [6] CONTEL O L, RETINÒ A, BREUILLARD H, et al. Whistler mode waves and Hall fields detected by MMS during a dayside magnetopause crossing[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2016, 43(12): 5943-5952 doi: 10.1002/2016GL068968 [7] WILSON III L B, SIBECK D G, BRENEMAN A W, et al. Quantified energy dissipation rates in the terrestrial bow shock: 1. Analysis techniques and methodology[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2014, 119(8): 6455-6474 doi: 10.1002/2014JA019929 [8] TONG Y G, VASKO I Y, ARTEMYEV A V, et al. Statistical study of whistler waves in the solar wind at 1 au[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2019, 878(1): 41 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/ab1f05 [9] BORTNIK J, CHEN L, LI W, et al. Modeling the evolution of chorus waves into plasmaspheric hiss[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2011, 116(A8): A08221 [10] LI W, THORNE R M, BORTNIK J, et al. Characteristics of hiss-like and discrete whistler-mode emissions[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2012, 39(18): L18106 [11] MEREDITH N P, HORNE R B, GLAUERT S A, et al. Slot region electron loss timescales due to plasmaspheric hiss and lightning-generated whistlers[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2007, 112(A8): A08214 [12] SU Z P, XIAO F L, ZHENG H N, et al. STEERB: a three-dimensional code for storm-time evolution of electron radiation belt[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2010, 115(A9): A09208 [13] NI B B, BORTNIK J, THORNE R M, et al. Resonant scattering and resultant pitch angle evolution of relativistic electrons by plasmaspheric hiss[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2013, 118(12): 7740-7751 doi: 10.1002/2013JA019260 [14] LYONS L R, THORNE R M, KENNEL C F. Pitch-angle diffusion of radiation belt electrons within the plasmasphere[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1972, 77(19): 3455-3474 doi: 10.1029/JA077i019p03455 [15] ABEL B, THORNE R M. Electron scattering loss in Earth’s inner magnetosphere: 1. Dominant physical processes[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1998, 103(A2): 2385-2396 doi: 10.1029/97JA02919 [16] LAM M M, HORNE R B, MEREDITH N P, et al. Origin of energetic electron precipitation >30 keV into the atmosphere[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2010, 115(A4): 2009JA014619 doi: 10.1029/2009JA014619 [17] THORNE R M, NI B B, TAO X, et al. Scattering by chorus waves as the dominant cause of diffuse auroral precipitation[J]. Nature, 2010, 467(7318): 943-946 doi: 10.1038/nature09467 [18] KASAHARA S, MIYOSHI Y, YOKOTA S, et al. Pulsating aurora from electron scattering by chorus waves[J]. Nature, 2018, 554(7692): 337-340 doi: 10.1038/nature25505 [19] URRUTIA J M, STENZEL R L. Helicons in uniform fields. I. Wave diagnostics with hodograms[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2018, 25(3): 032111 doi: 10.1063/1.5017625 [20] STENZEL R L. Whistler waves with angular momentum in space and laboratory plasmas and their counterparts in free space[J]. Advances in Physics: X, 2016, 1(4): 687-710 doi: 10.1080/23746149.2016.1240017 [21] CHEN F F. Helicon discharges and sources: a review[J]. Plasma Sources Science and Technology, 2015, 24(1): 014001 doi: 10.1088/0963-0252/24/1/014001 [22] STENZEL R L, URRUTIA J M. Helicons in Unbounded Plasmas[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2015, 114(20): 205005 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.114.205005 [23] KLOZENBERG J P, MCNAMARA B, THONEMANN P C. The dispersion and attenuation of helicon waves in a uniform cylindrical plasma[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1965, 21(3): 545-563 doi: 10.1017/S0022112065000320 [24] STENZEL R L, URRUTIA J M. Comparison of electric dipole and magnetic loop antennas for exciting whistler modes[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2016, 23(8): 082120 doi: 10.1063/1.4960666 [25] STENZEL R L. Whistler modes excited by magnetic antennas: a review[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2019, 26(8): 080501 doi: 10.1063/1.5097852 [26] KE Y G, CHEN L J, GAO X L, et al. Whistler-mode waves trapped by density irregularities in the Earth’s magnetosphere[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2021, 48(7): e2020GL092305 doi: 10.1029/2020GL092305 [27] CHEN R, GAO X L, LU Q M, et al. In situ observations of whistler-mode chorus waves guided by density ducts[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(4): e2020JA028814 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028814 -
-





 唐磊 男, 2001年11月出生于四川省达州市, 现为中国科学技术大学地球与空间科学学院硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为实验室等离子体中的哨声波现象. E-mail:
唐磊 男, 2001年11月出生于四川省达州市, 现为中国科学技术大学地球与空间科学学院硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为实验室等离子体中的哨声波现象. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: