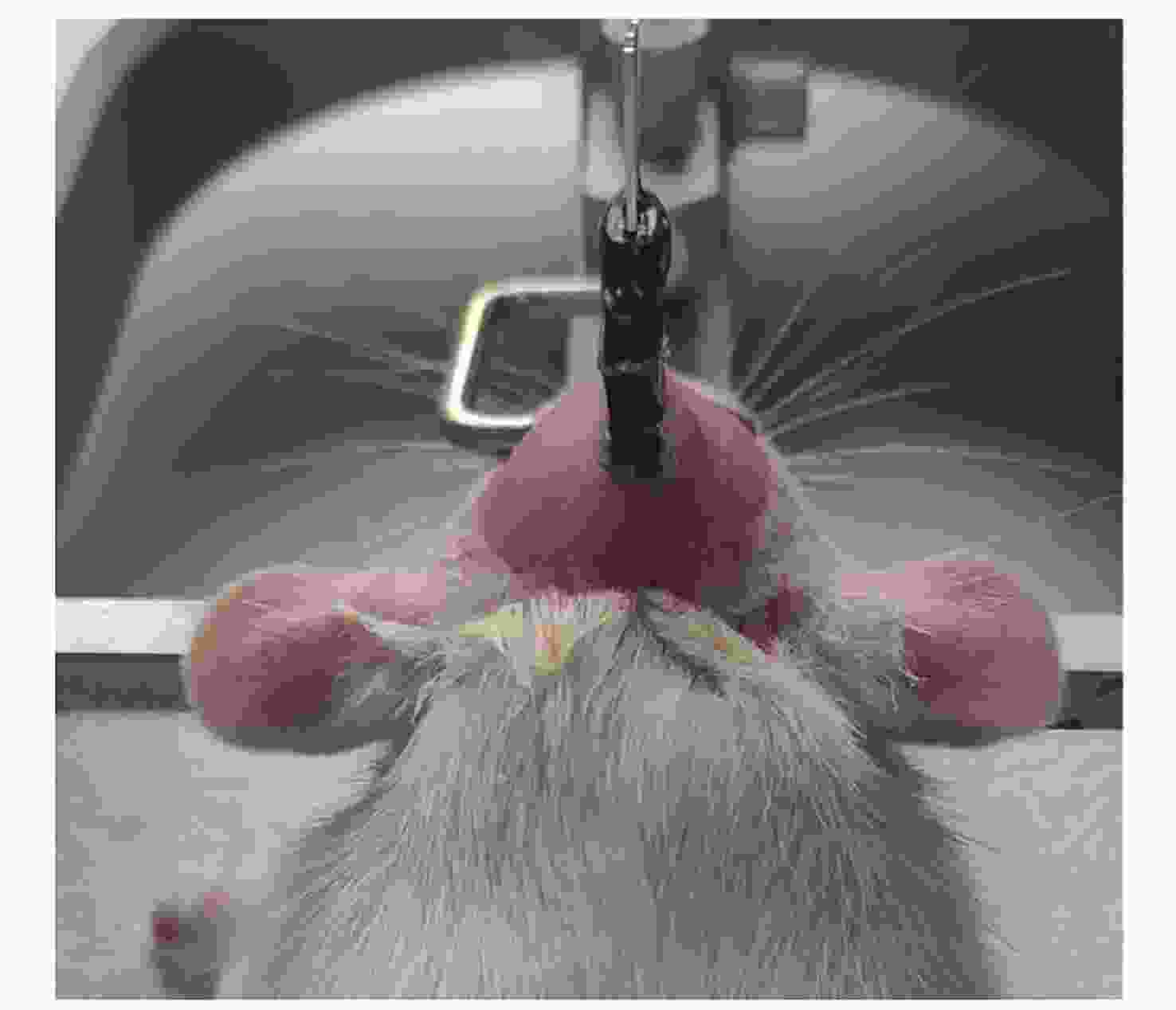
Effects of Radiation and Simulated Weightlessness on Rat EEG and Its Mechanism
-
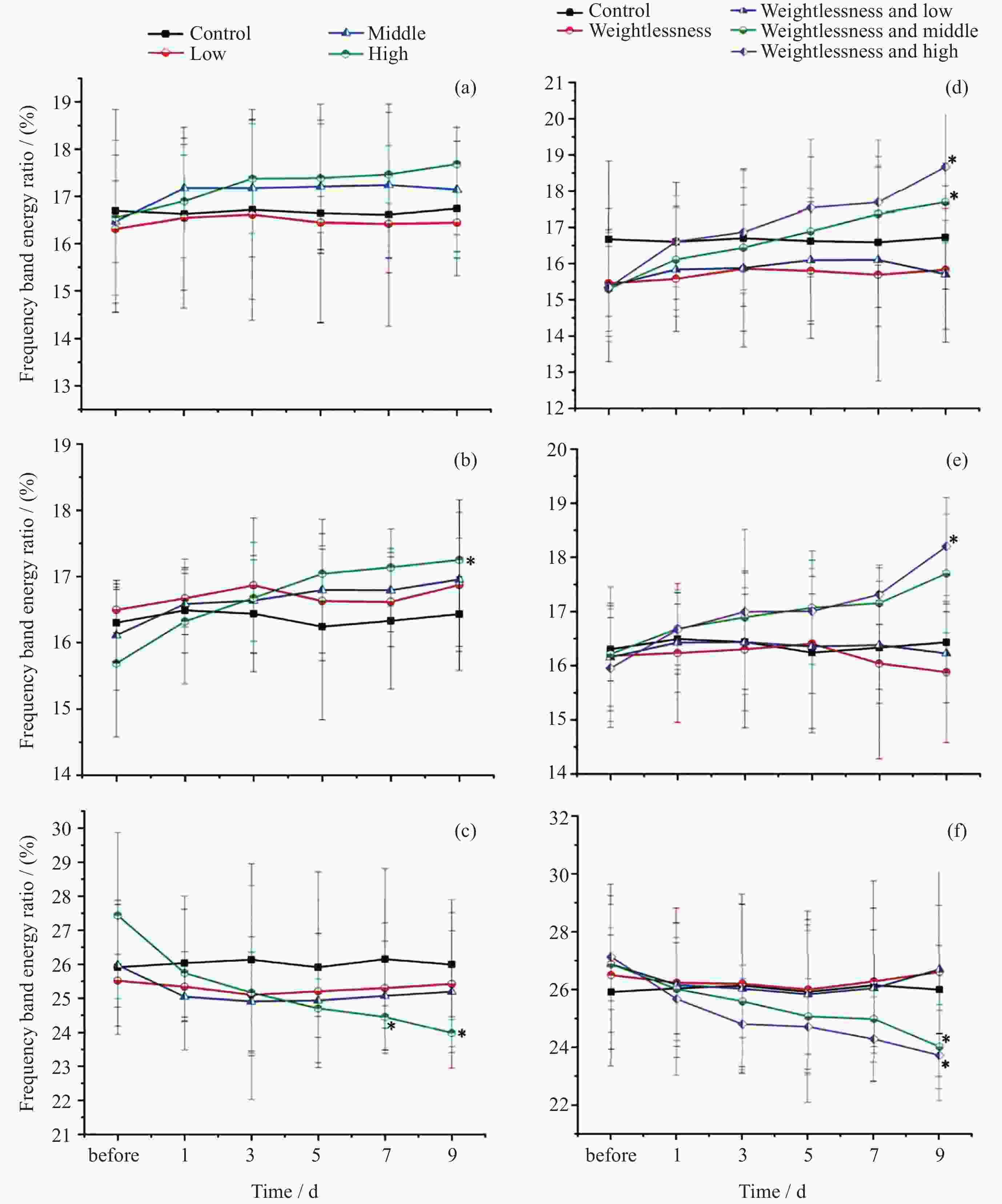
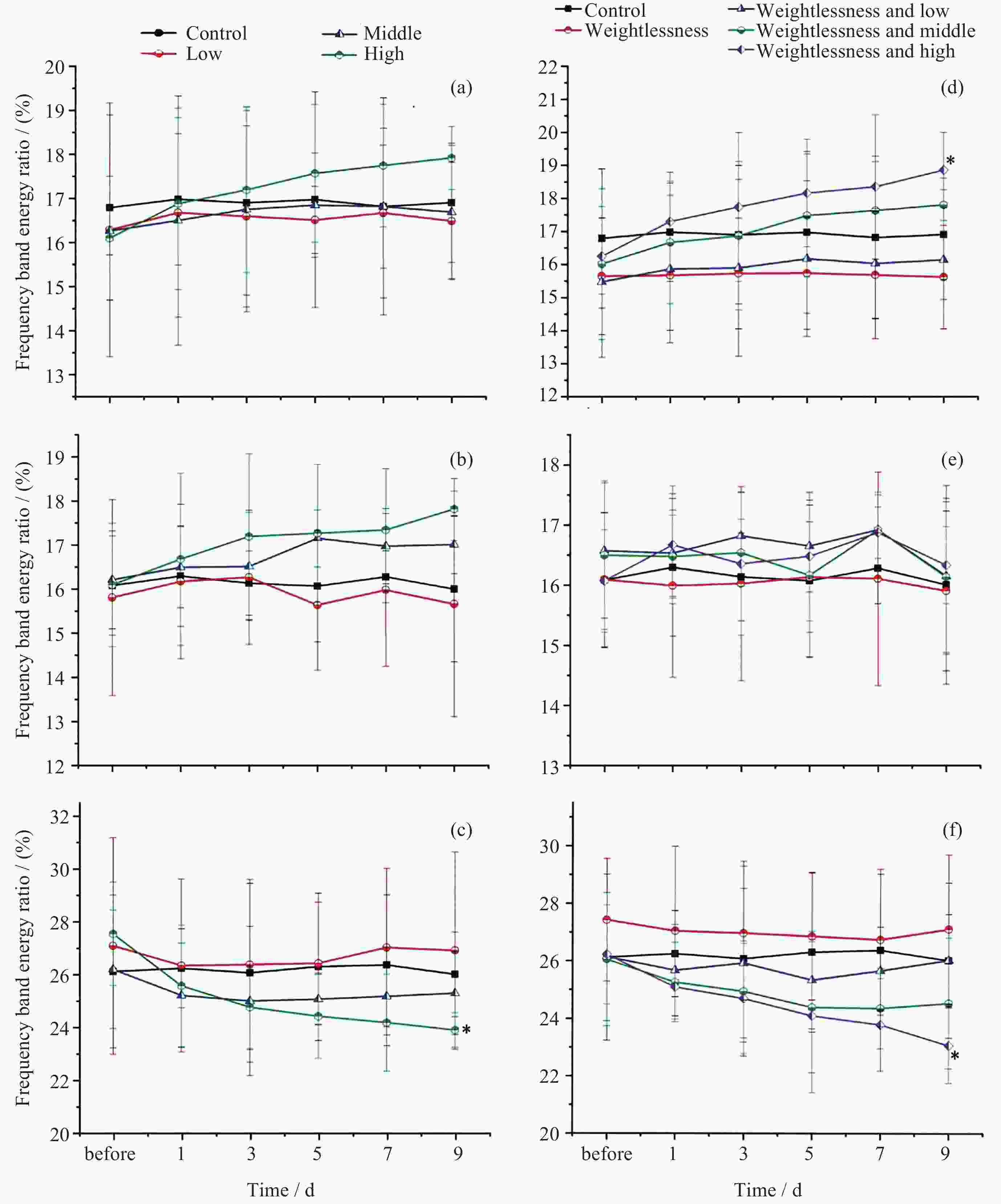
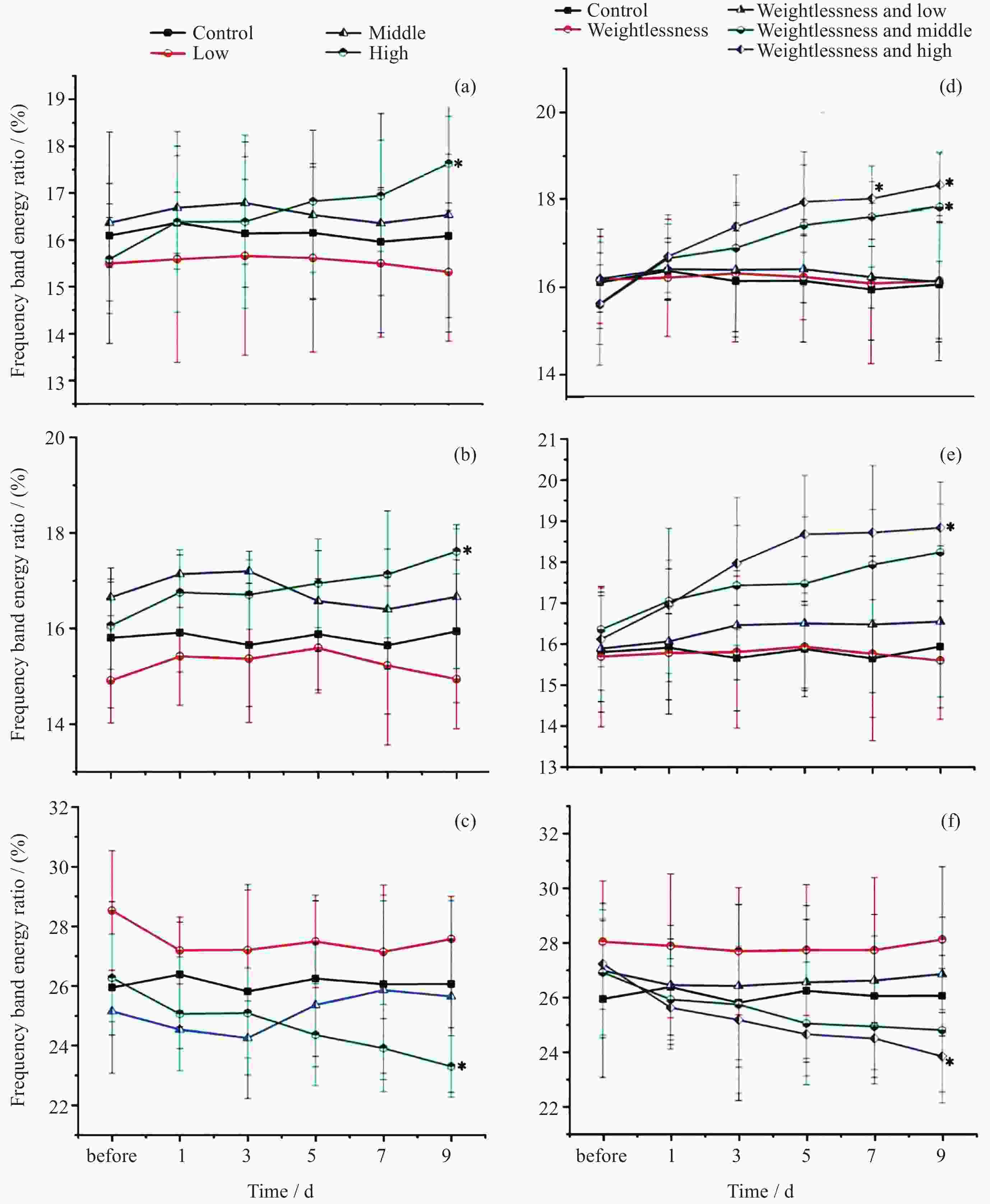
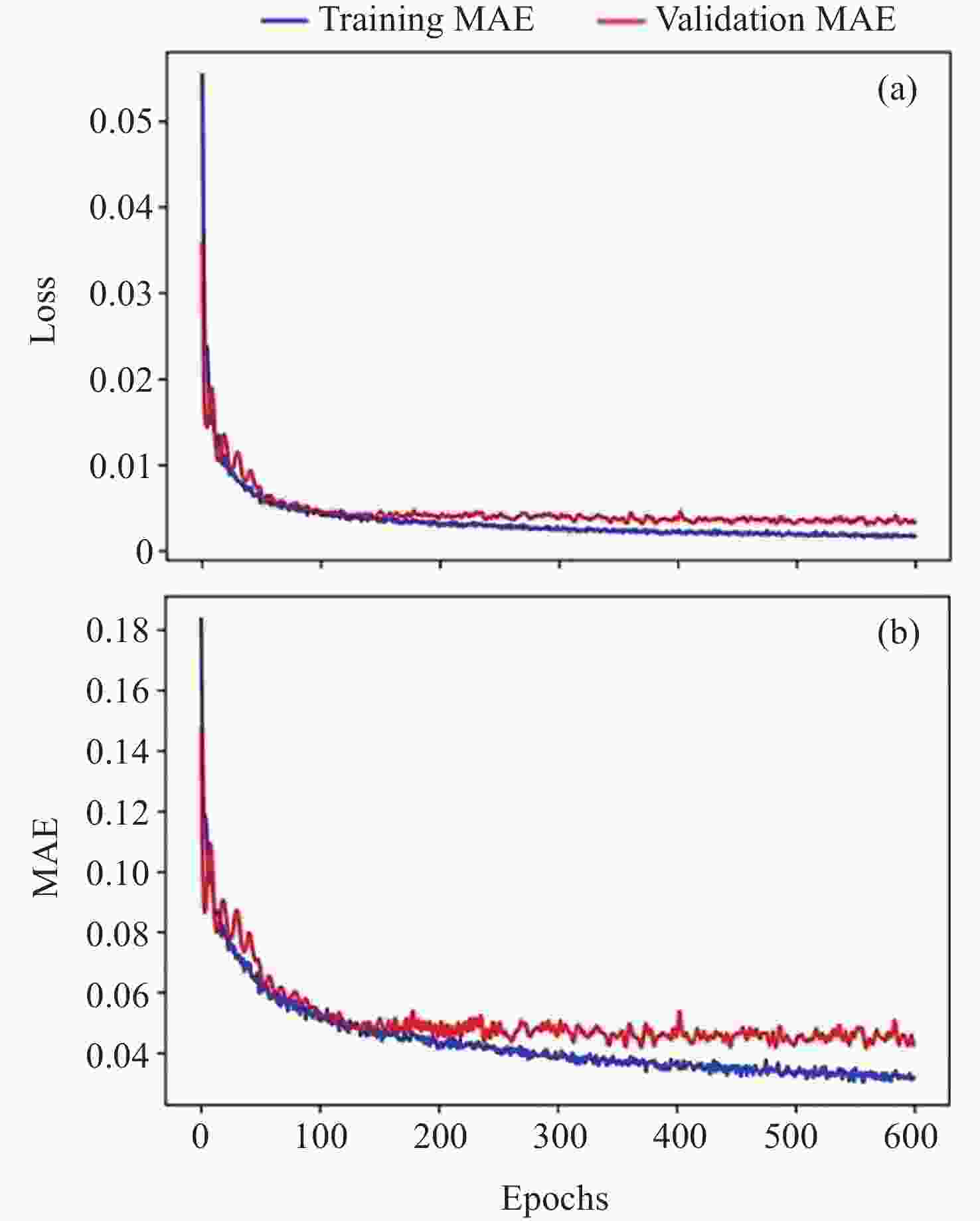
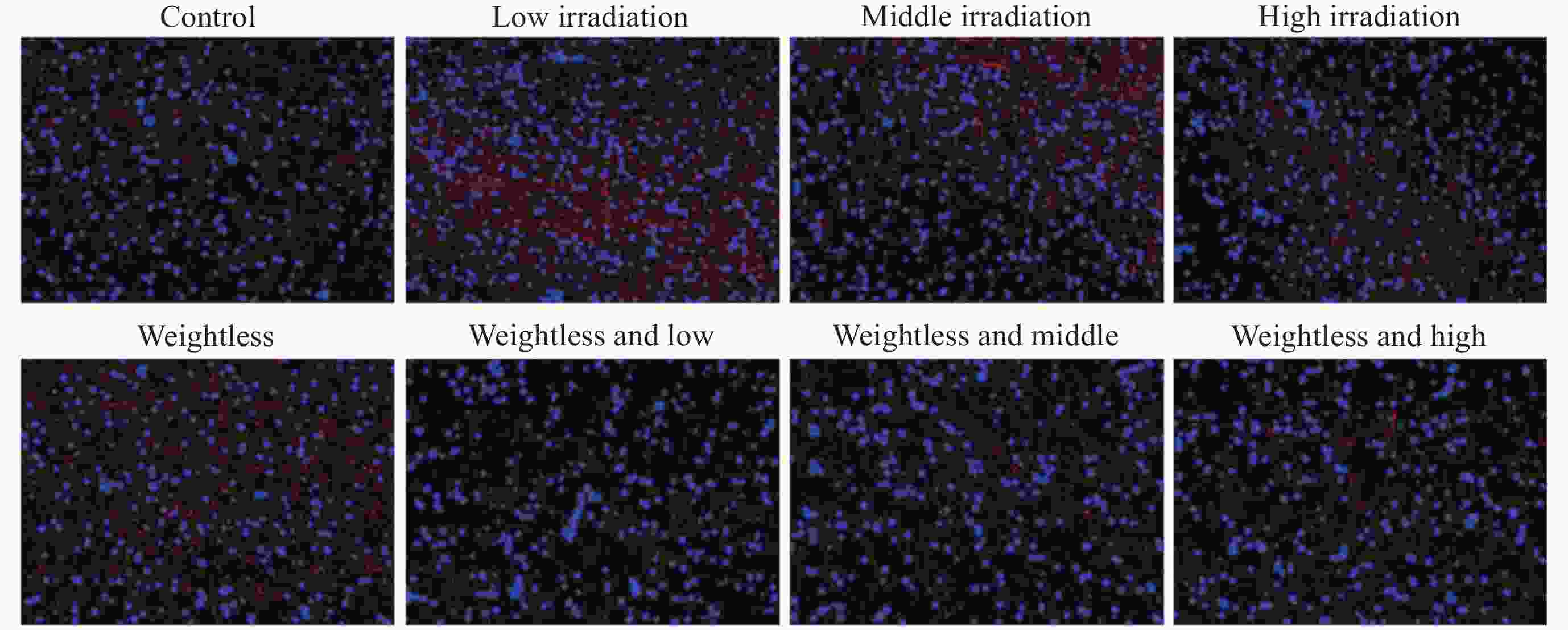
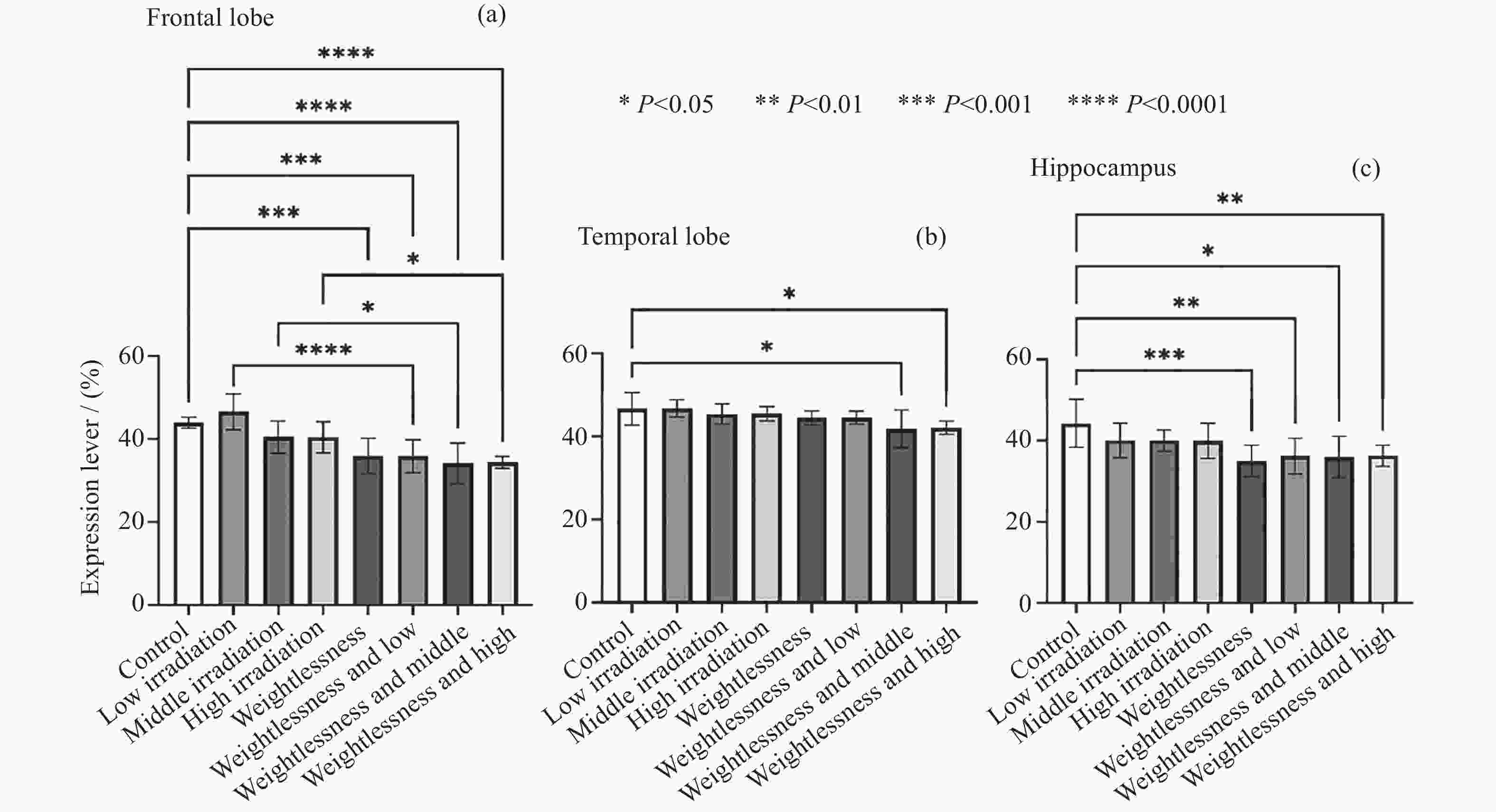
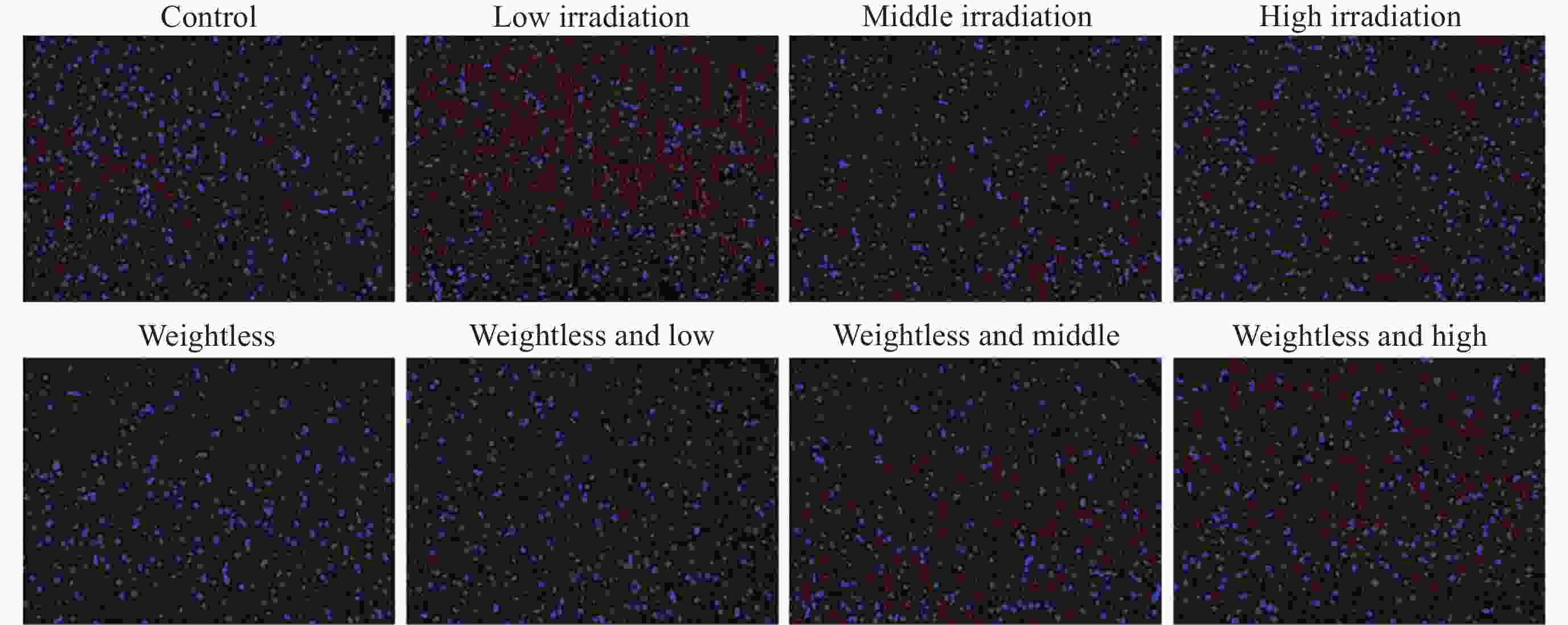
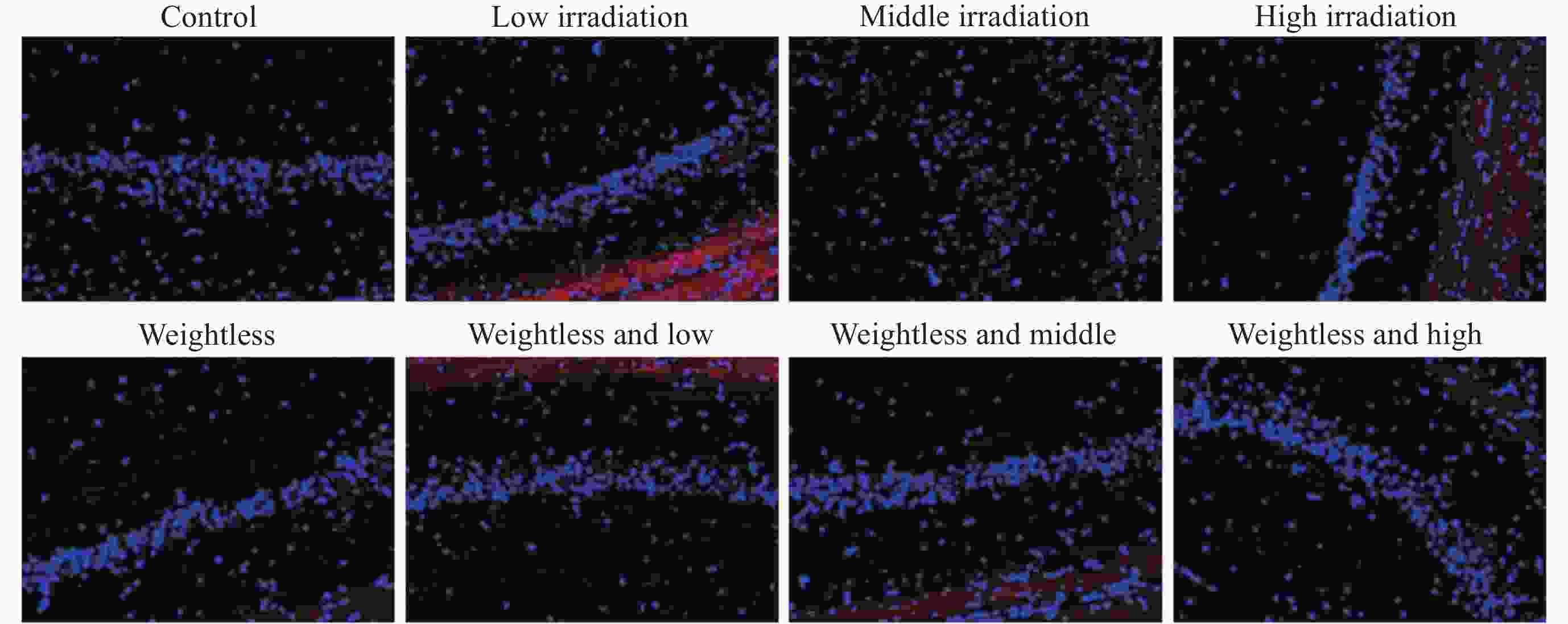
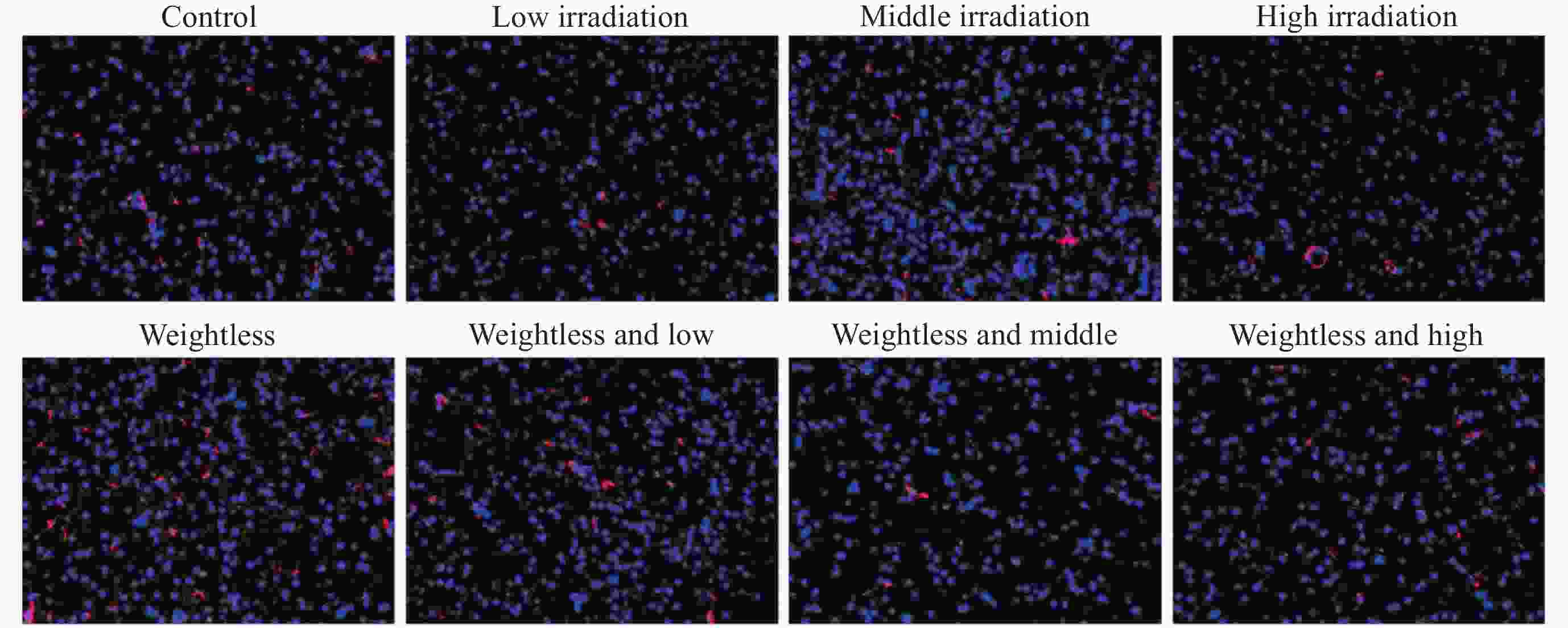
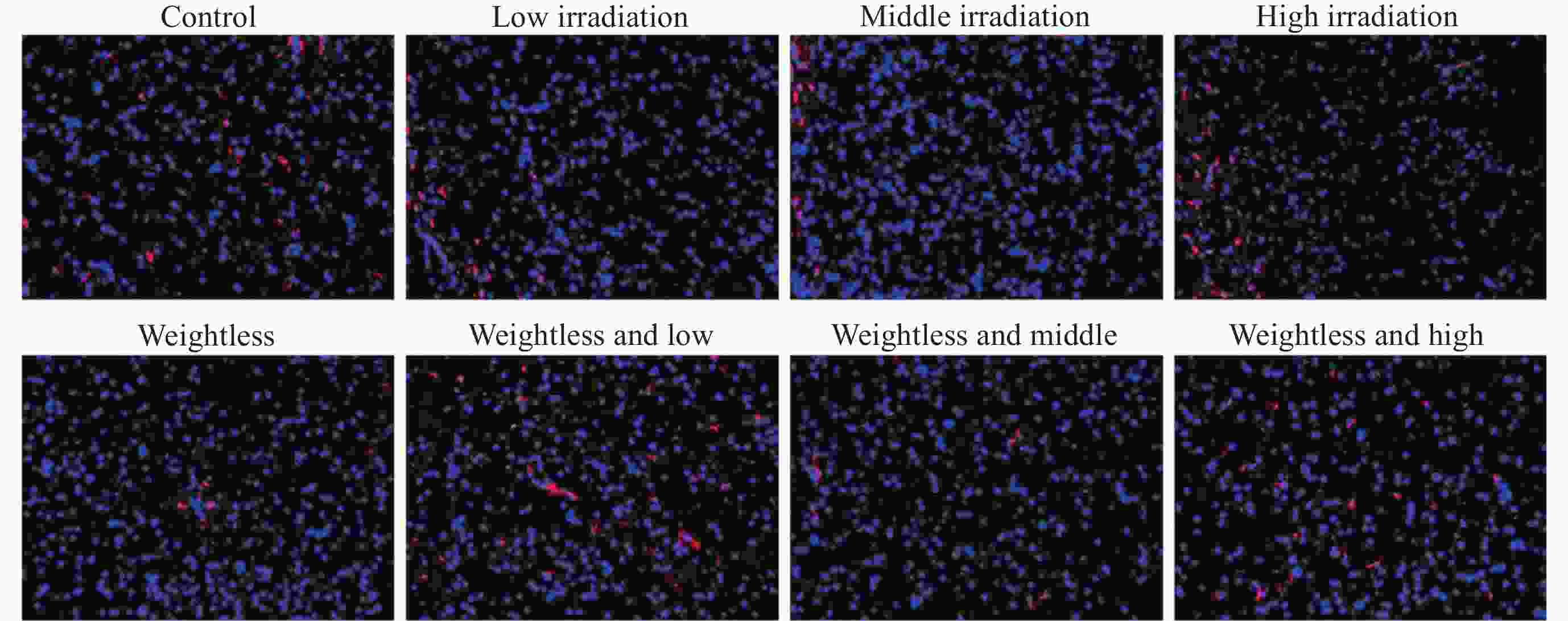
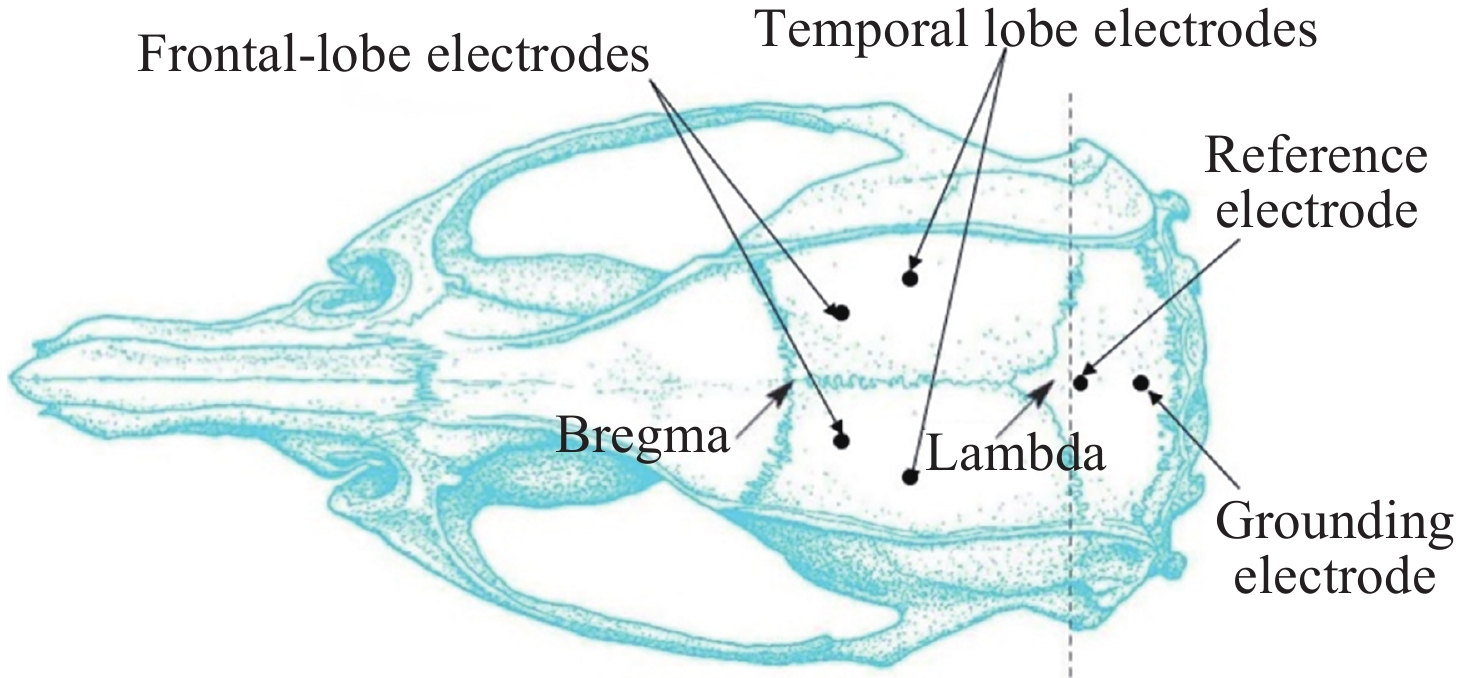
摘要: 通过生物电信号评估辐射与失重对脑的影响, 并揭示其影响规律与损伤机制, 为空间环境风险评估与防护技术研究提供参考. 以SD大鼠为对象, 设立不同实验组. 采集并分析大鼠脑电信号频谱变化, 利用神经网络模型识别脑电信号异常. 同时检测大鼠脑部特定区域的蛋白质表达量变化, 以探讨损伤机制. 辐射组与失重辐射复合组大鼠脑电信号出现慢波化, 复合作用影响显著, 神经网络模型能有效识别异常信号. 辐射与失重导致大鼠脑部髓鞘受损, 相关蛋白表达量出现变化, 提示胶质细胞激活. 辐射与失重对大鼠脑电信号有明显影响, 复合作用效果更为显著, 这可能与髓鞘受损及胶质细胞激活有关. 本研究为空间环境下的风险评估与防护技术提供了重要参考.Abstract: This article aims to assess the impact of radiation and weightlessness on the brain, specifically through the analysis of bioelectrical signals. Our goal is to elucidate the patterns and mechanisms underlying the effects of radiation, weightlessness, and their combined influence on Electroencephalogram (EEG) signals. This understanding will serve as a crucial reference for risk assessment and protective technology research in space environments. A comprehensive study was conducted utilizing SD rats as the experimental subjects. The eight different experimental groups were established to analyze EEG signals and automatically detect abnormal brain signals caused by radiation or weightlessness exposure.To delve deeper into the underlying biological mechanisms, the expression levels of Myelin Basic Protein (MBP), Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein (GFAP), and ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1 (IBA1) were examined in specific brain regions, such as the frontal lobe, temporal lobe, and hippocampus. The study found that rats exposed to radiation alone or in combination with weightlessness showed a marked slow-wave EEG pattern, with the combined effect being more significant, indicating an enhanced effect. The neural network model accurately distinguished normal from abnormal EEG signals. The decrease of MBP and increase of GFAP and IBA1 were observed in the combined radiation-weightlessness groups, suggesting myelin damage and activation of astrocytes and microglias. The study reveals the effects of radiation and weightlessness on brain signals, showing that radiation alone induces slow-wave EEG patterns, and the combination with weightlessness exacerbates these patterns. The mechanism involves myelin sheath damage and glial cell activation. This understanding is crucial for assessing risks and developing protective measures in space, laying the groundwork for future research to improve astronaut safety and well-being.
-
Key words:
- Gamma ray /
- Weightlessness /
- Electroencephalogram (EEG) /
- Neural network /
- Proteins
-
表 1 不同模型对大鼠脑电自动识别的准确度
Table 1. Accuracy of automatic recognition of rat EEG with different models
Machine learning model Recognition accuracy K-nearest neighbors 0.6166 Logistic regression 0.2195 Random forest 0.8502 Neural networks 0.9029 -
[1] GARRETT-BAKELMAN F E, DARSHI M, GREEN S J, et al. The NASA twins study: a multidimensional analysis of a year-long human spaceflight[J]. Science, 2019, 364(6436): eaau8650 doi: 10.1126/science.aau8650 [2] TU D N, BASNER M, SMITH M G, et al. Dynamic ensemble prediction of cognitive performance in spaceflight[J]. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12(1): 11032 doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-14456-8 [3] DEMERTZI A, VAN OMBERGEN A, TOMILOVSKAYA E, et al. Cortical reorganization in an astronaut’s brain after long-duration spaceflight[J]. Brain Structure and Function, 2015, 221(5): 2873-2876 [4] ALGEDA F R, ELTAHAWY N A, SHEDID S M, et al. The impact of gamma-radiation on the cerebral- and cerebellar- cortex of male rats' brain[J]. Brain Research Bulletin, 2022, 186: 136-142 doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2022.05.011 [5] ZHANG J Y, HU B, CHEN W J, et al. Quantitative EEG and its correlation with cardiovascular, cognition and mood state: an integrated study in simulated microgravity[J]. Microgravity Science and Technology, 2014, 26(6): 401-418 doi: 10.1007/s12217-014-9388-7 [6] CUCINOTTA F A. Review of NASA approach to space radiation risk assessments for mars exploration[J]. Health Physics, 2015, 108(2): 131-142 doi: 10.1097/HP.0000000000000255 [7] LIU L R, LIU J C, BAO J S, et al. Interaction of microglia and astrocytes in the neurovascular unit[J]. Frontiers in Immunology, 2020, 11: 1024 doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01024 [8] LISJAK M, POTOKAR M, ZOREC R, et al. Indirect role of AQP4b and AQP4d isoforms in dynamics of astrocyte volume and orthogonal arrays of particles[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(3): 735 doi: 10.3390/cells9030735 [9] STRÁDI A, SZABÓ J, INOZEMTSEV K O, et al. Comparative radiation measurements in the Russian segment of the International Space Station by applying passive dosimeters[J]. Radiation Measurements, 2017, 106: 267-272 doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2017.01.018 [10] LI S Q, SONG Q Y, WU B, et al. Structural damage to the rat eye following long-term simulated weightlessness[J]. Experimental Eye Research, 2022, 223: 109200 doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2022.109200 [11] ZHANG M Y, LIU D, WANG Q S, et al. Detection of alertness-related EEG signals based on decision fused BP neural network[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2022, 74: 103479 doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2022.103479 [12] 黄迪. 细胞焦亡介导X射线和安罗替尼协同治疗食管鳞状细胞癌的作用机制研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2023HUANG Di. The Role and Mechanism of Pyroptosis in X-ray Andanlotinib Therapy for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma[D]. Ji’nan: Shandong University, 2023 [13] ANDREWS H L, BRACE K C. Terminal phenomena associated with massive doses of X-rays[J]. American Journal of Physiology-Legacy Content, 1953, 175(1): 138-140 doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1953.175.1.138 [14] MCFARLAND W L, LEVIN S G. Electroencephalographic responses to 2500 Rads of whole-body gamma-neutron radiation in the monkey Macaca mulatta[J]. Radiation Research, 1974, 58: 60-73 doi: 10.2307/3573949 [15] LOGANOVSKY K N, YURYEV K L. EEG patterns in persons exposed to ionizing radiation as a result of the Chernobyl accident: part 1: conventional EEG analysis[J]. The Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 2001, 13(4): 441-458 doi: 10.1176/jnp.13.4.441 [16] SPIRONELLI C, BUSENELLO J, ANGRILLI A. Supine posture inhibits cortical activity: evidence from Delta and Alpha EEG bands[J]. Neuropsychologia, 2016, 89: 125-131 doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2016.06.015 [17] CHOI J W, JEONG M H, HER S J, et al. Abnormal sleep delta rhythm and interregional phase synchrony in patients with restless legs syndrome and their reversal by dopamine agonist treatment[J]. Journal of Clinical Neurology, 2017, 13(4): 340-350 doi: 10.3988/jcn.2017.13.4.340 [18] LIN C T, KING J T, CHUANG C H, et al. Exploring the brain responses to driving fatigue through simultaneous EEG and fNIRS measurements[J]. International Journal of Neural Systems, 2020, 30(1): 1950018 doi: 10.1142/S0129065719500187 [19] WASCHER E, RASCH B, SÄNGER J, et al. Frontal theta activity reflects distinct aspects of mental fatigue[J]. Biological Psychology, 2014, 96: 57-65 doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2013.11.010 [20] CAVINESS J N, UTIANSKI R L, HENTZ J G, et al. Differential spectral quantitative electroencephalography patterns between control and Parkinson’s disease cohorts[J]. European Journal of Neurology, 2016, 23(2): 387-392 doi: 10.1111/ene.12878 [21] GERAEDTS V J, BOON L I, MARINUS J, et al. Clinical correlates of quantitative EEG in Parkinson disease: a systematic review[J]. Neurology, 2018, 91(19): 871-883 doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000006473 [22] D'ATRI A, SCARPELLI S, GORGONI M, et al. EEG alterations during wake and sleep in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease[J]. iScience, 2021, 24(4): 102386 doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102386 [23] SARMAH R J, KUNDU S. Stable layers of pure myelin basic protein (MBP): structure, morphology and hysteresis behaviors[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2023, 662: 130973 doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2023.130973 [24] GOYAL H, SINGH N, GURJAR O P, et al. Radiation induced demyelination in cervical spinal cord of the head and neck cancer patients after receiving radiotherapy[J]. Journal of Biomedical Physics and Engineering, 2019, 10(1): 1-6 [25] CHEN Q H, YUAN F F, DU L L et al. The clinical analysis of 26 patients with acute demyelinating encephalopathy[J]. Journal of Brain and Nervous Diseases, 2013, 21(1): 4-6 [26] DEANTONI M, BAILLET M, HAMMAD G, et al. Association between sleep slow-wave activity and in-vivo estimates of myelin in healthy young men[J]. NeuroImage, 2023, 272: 120045 doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2023.120045 [27] AKIYAMA K, TANAKA R, SATO M, et al. Cognitive dysfunction and histological findings in adult rats one year after whole brain irradiation[J]. Neurologia Medico-Chirurgica, 2001, 41(12): 590-598 doi: 10.2176/nmc.41.590 [28] PIAO J, MAJOR T, AUYEUNG G, et al. Human embryonic stem cell-derived oligodendrocyte progenitors remyelinate the brain and rescue behavioral deficits following radiation[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2015, 16(2): 198-210 doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2015.01.004 [29] XIONG W F, QIU S J, WANG H Z, et al. 1H‐MR spectroscopy and diffusion tensor imaging of normal‐appearing temporal white matter in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma after irradiation: Initial experience[J]. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2013, 37(1): 101-108 doi: 10.1002/jmri.23788 [30] LOWE M C, MONEY K M, MATTHEWS E, et al. Case of autoimmune GFAP astrocytopathy with eosinophils in the cerebrospinal fluid[J]. Journal of Neuroimmunology, 2023, 385: 578249 doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2023.578249 [31] COLANGELO A M, CIRILLO G, LAVITRANO M L, et al. Targeting reactive astrogliosis by novel biotechnological strategies[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2012, 30(1): 261-271 doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.06.016 [32] NAGHIEH P, DELAVAR A, AMIRI M, et al. Astrocyte’s self-repairing characteristics improve working memory in spiking neuronal networks[J]. Iscience, 2023, 26(12): 108241 doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108241 [33] MURGAS P, GODOY B, VON BERNHARDI R. Aβ potentiates inflammatory activation of glial cells induced by scavenger receptor ligands and inflammatory mediators in culture[J]. Neurotoxicity Research, 2012, 22(1): 69-78 doi: 10.1007/s12640-011-9306-3 [34] GARBER C, VASEK M J, VOLLMER L L, et al. Astrocytes decrease adult neurogenesis during virus-induced memory dysfunction via IL-1[J]. Nature Immunology, 2018, 19(2): 151-161 doi: 10.1038/s41590-017-0021-y [35] FOLEY J, BLUTSTEIN T, LEE S, et al. Astrocytic IP3/Ca2+ signaling modulates theta rhythm and REM sleep[J]. Frontiers in Neural Circuits, 2017, 11: 3 [36] LEE H S, GHETTI A, PINTO-DUARTE A, et al. Astrocytes contribute to gamma oscillations and recognition memory[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2014, 111(32): E3343-E3352 [37] KENKHUIS B, SOMARAKIS A, KLEINDOUWEL L R T, et al. Co-expression patterns of microglia markers Iba1, TMEM119 and P2RY12 in Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Neurobiology of Disease, 2022, 167: 105684 doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2022.105684 [38] GUO S R, WANG H, YIN Y F. Microglia polarization from M1 to M2 in neurodegenerative diseases[J]. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 2022, 14: 815347 doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.815347 [39] WANG H X, LIU C, HAN M, et al. TRAM1 promotes microglia M1 polarization[J]. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 2016, 58(2): 287-296 doi: 10.1007/s12031-015-0678-3 [40] WU J, DING D H, LI Q Q, et al. Lipoxin A4 regulates lipopolysaccharide-induced BV2 microglial activation and differentiation via the notch signaling pathway[J]. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, 2019, 13: 19 doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00019 [41] GAVILANES A W D, GANTERT M, STRACKX E, et al. Increased EEG delta frequency corresponds to chorioamnionitis-related brain injury[J]. Frontiers in Bioscience (Scholar Edition), 2010, 2(2): 432-438 [42] GRIGOROVSKY V, BARDAKJIAN B L. Neuro-glial network model of postictal generalized EEG suppression (PGES)[C]//2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC). Honolulu, HI, USA: IEEE, 2018: 2044-2047 -
-





 丰俊东 女, 1978年12月出生于黑龙江省哈尔滨市, 现为南京航空航天大学核科学与技术系副教授, 硕士生导师, 主要研究方向为辐射风险评估与防护技术研究等. E-mail:
丰俊东 女, 1978年12月出生于黑龙江省哈尔滨市, 现为南京航空航天大学核科学与技术系副教授, 硕士生导师, 主要研究方向为辐射风险评估与防护技术研究等. E-mail: 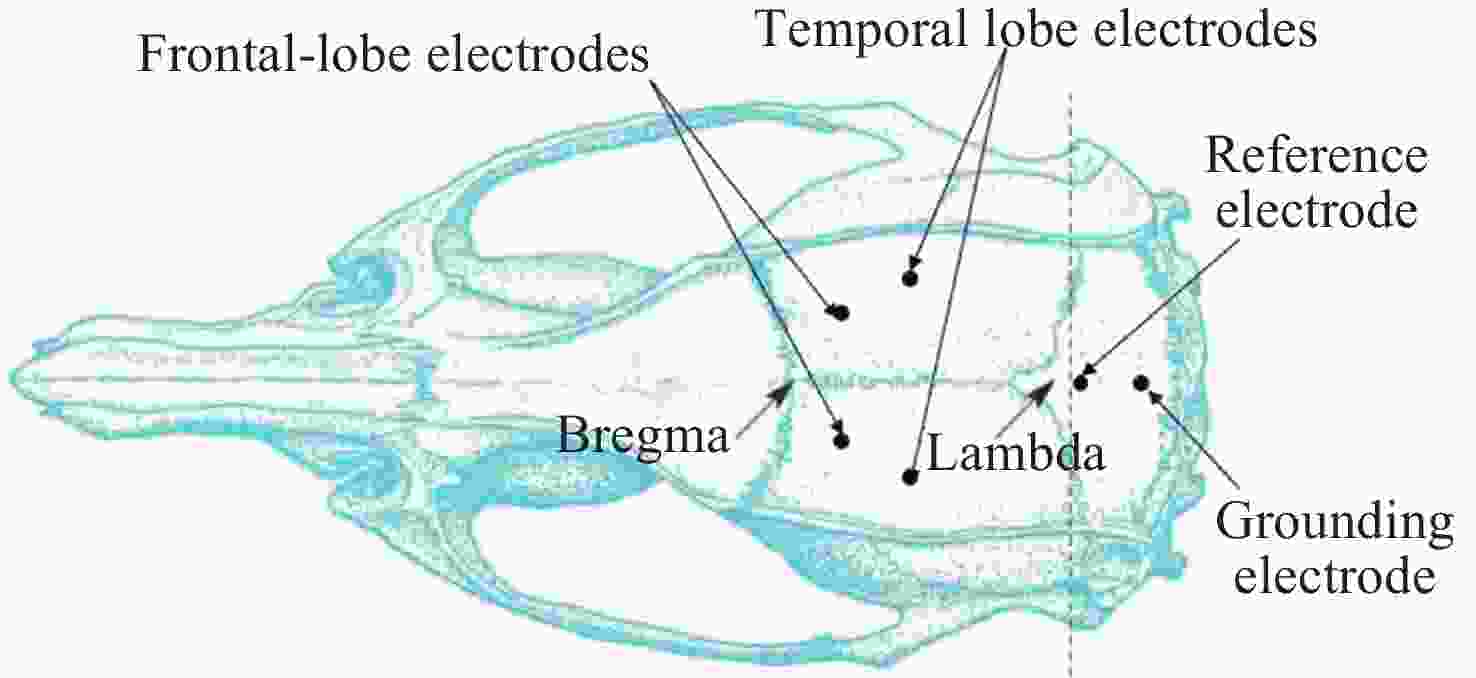
 下载:
下载: