Comparison and Application of Simplified Calculation Methods for Spacecraft Collision Probability
-
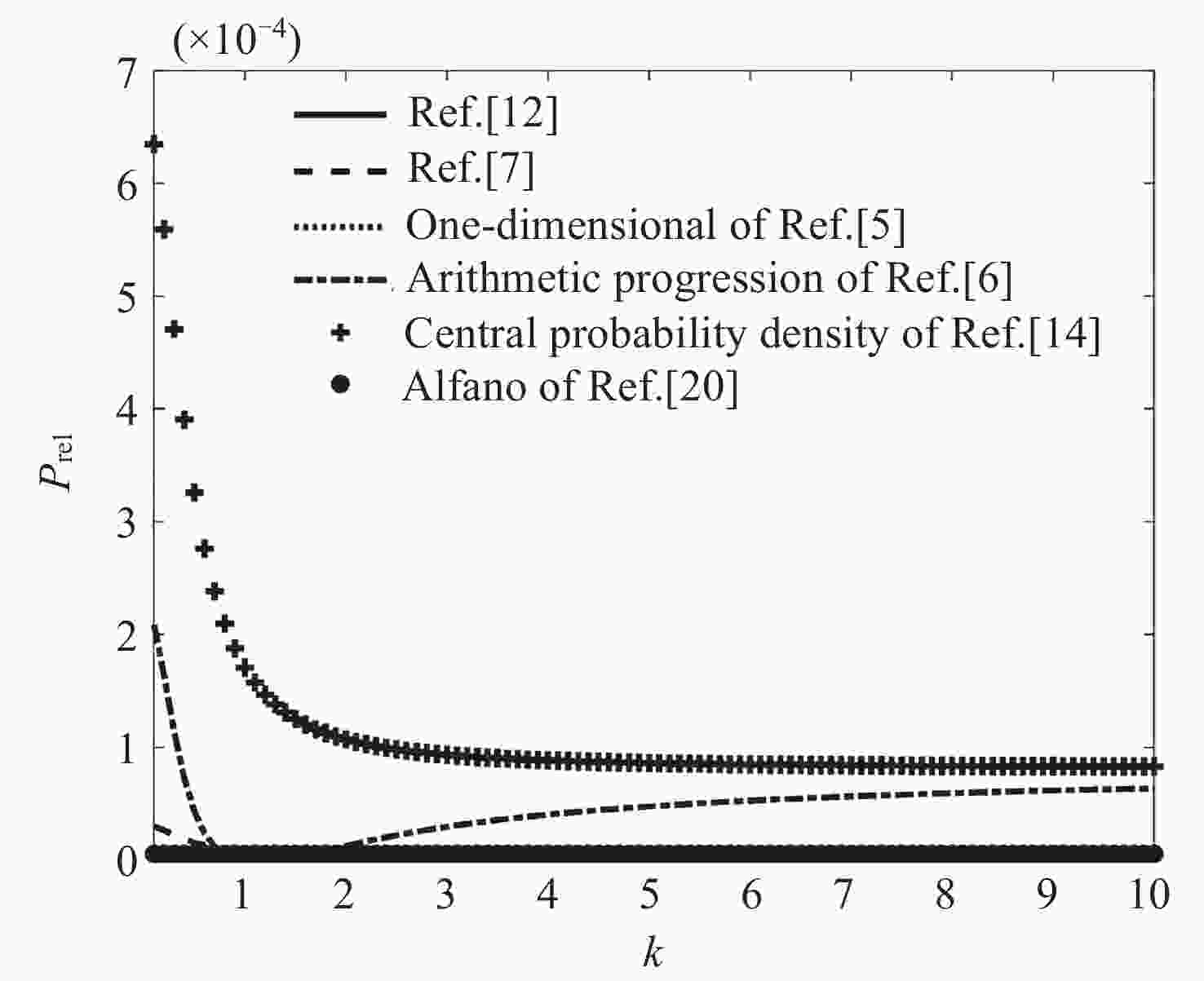
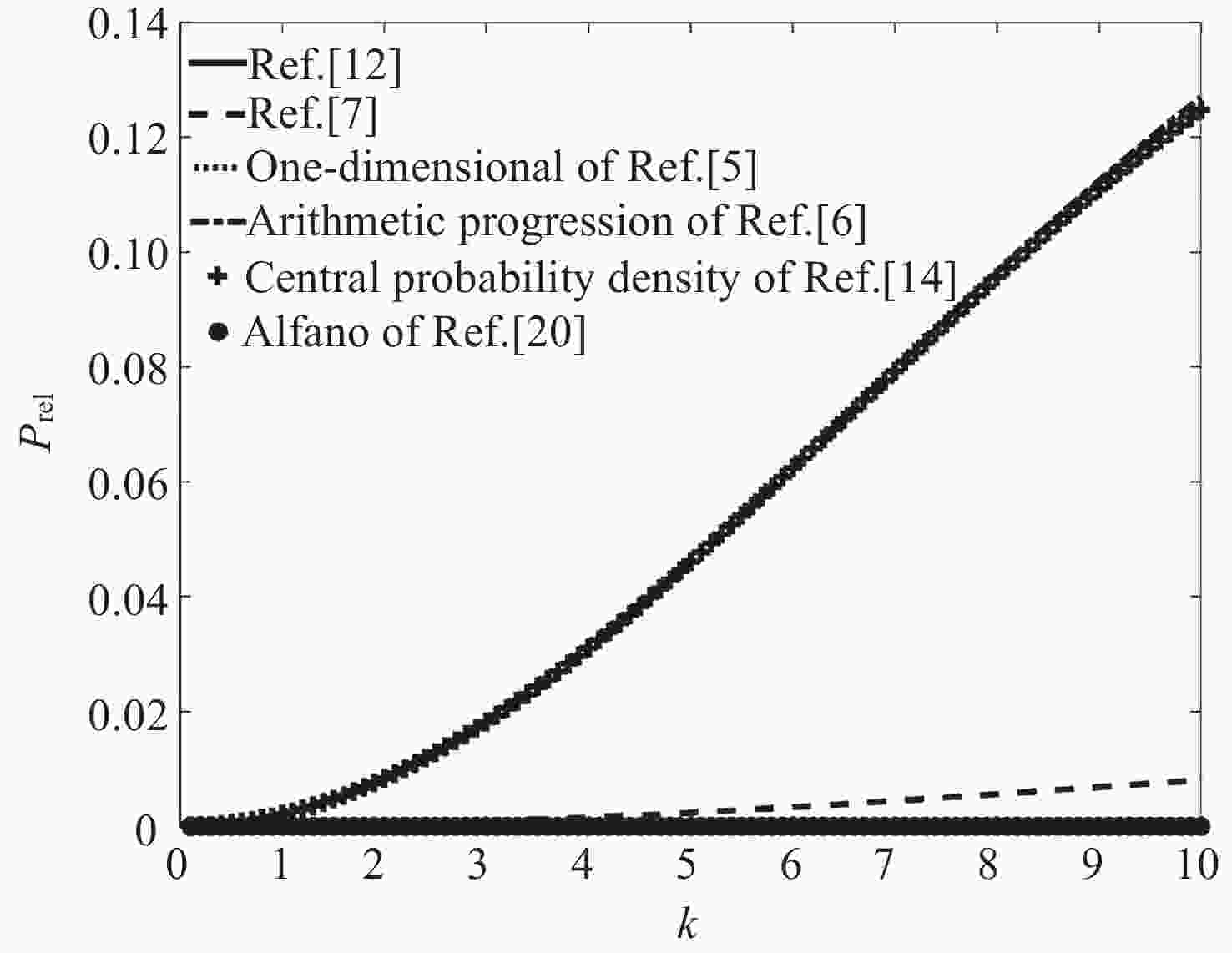
摘要: 针对空间飞行器碰撞概率问题, 基于碰撞概率的假设条件与计算原理, 对现有常见方法进行分析, 归纳每种方法在线性与非线性、空间目标是否规则等方面的适用性及特点, 通过数值计算验证了上述方法, 并从计算速度与计算精度两个维度对每种方法进行评估. 评估结果表明, 中心概率密度法的计算速度最快,曲线积分法的相对误差最小, 基于辛普森公式的二维积分方法具有较均衡的效果, 三维体积积分适用于非线性场景,蒙特卡洛法最为精准但是运算速度最慢. 综合考虑计算精度、计算速度、相对速度、相对位置关系等因素, 根据每种方法的特点提出了多种场景下较为适用的碰撞概率简化计算方法, 研究结果可以为在轨碰撞概率的计算与分析提供参考.Abstract: With the rapid increase in the number of debris and spacecraft in space, spacecraft need to assess collision risks in real time. However, due to the limited on-board software and hardware resources, there is an urgent need for a collision probability calculation method with appropriate computational load and high assessment accuracy. Aiming at the problem of spacecraft collision probability, this paper firstly explains the assumptions and calculation principles of collision probability, then summarizes and analyzes the existing common methods, summarizes the applicability and characteristics of each method in terms of linearity and nonlinearity, whether the space target is regular, etc., and finally verifies the adaptability of the above methods through numerical calculation, and evaluates each method from the two dimensions of calculation speed and calculation accuracy. The evaluation results show that the central probability density method has the fastest calculation speed. The relative error of the curve integration method is the smallest, the two-dimensional integration method based on Simpson’s formula has a relatively balanced effect. 3D volume integration is suitable for nonlinear scenes, the Monte Carlo method is the most accurate, but the slowest. Considering the factors such as calculation accuracy, calculation speed, relative velocity, and relative position relationship, this paper proposes a simplified calculation method for collision probability in various scenarios according to the characteristics of each method, and the research results can provide a reference for the calculation and analysis of on-orbit collision probability.
-
Key words:
- Collision probability /
- Covariance matrix /
- Space debris /
- Nonlinear relative motion /
- Space vehicles
-
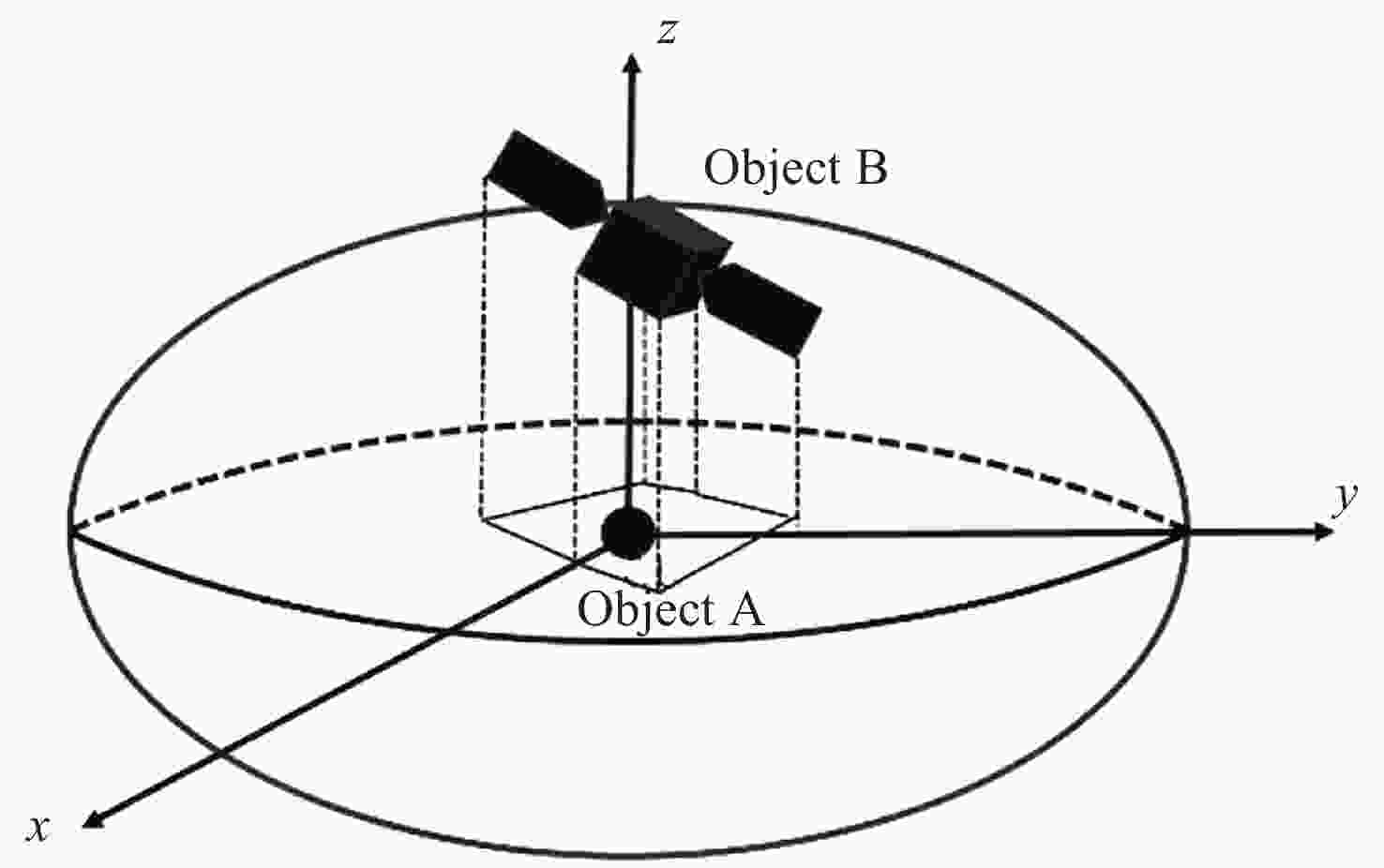
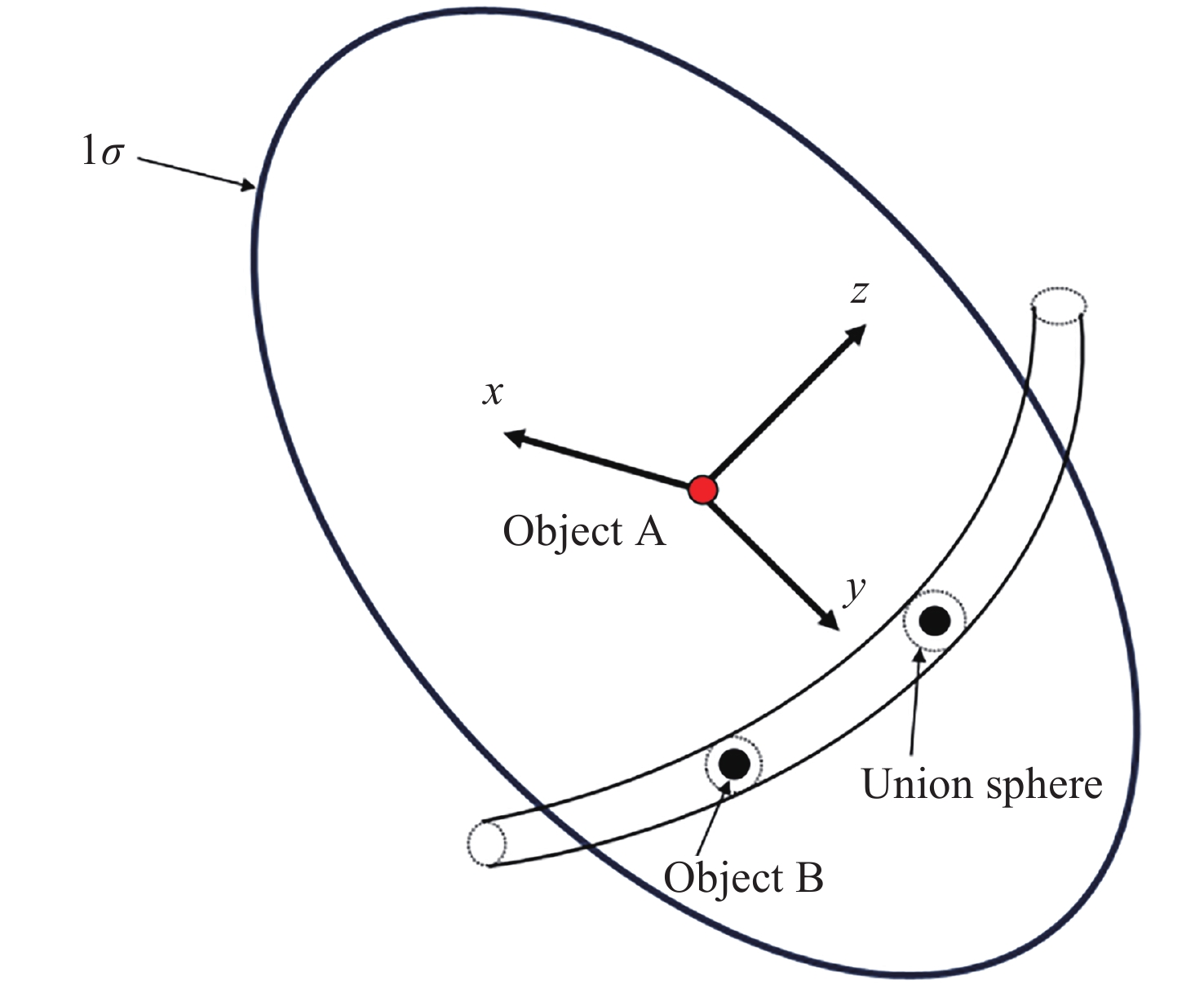
表 1 两个航天器在J2000惯性系下的初始位置速度
Table 1. Initial position velocity of two spacecraft in an inertial frame of J2000
Object x/km y/km z/km A –150.798437 1182.676987 –7143.77556 B –150.619960 1182.018386 –7143.78799 Object vx / (km·s–1) vy / (km·s–1) vz / (km·s–1) A 7.290071 –1.126282 –0.354014 B 5.915107 4.347936 0.643388 表 2 二维碰撞概率计算结果
Table 2. Calculation results of two-dimensional collision probability
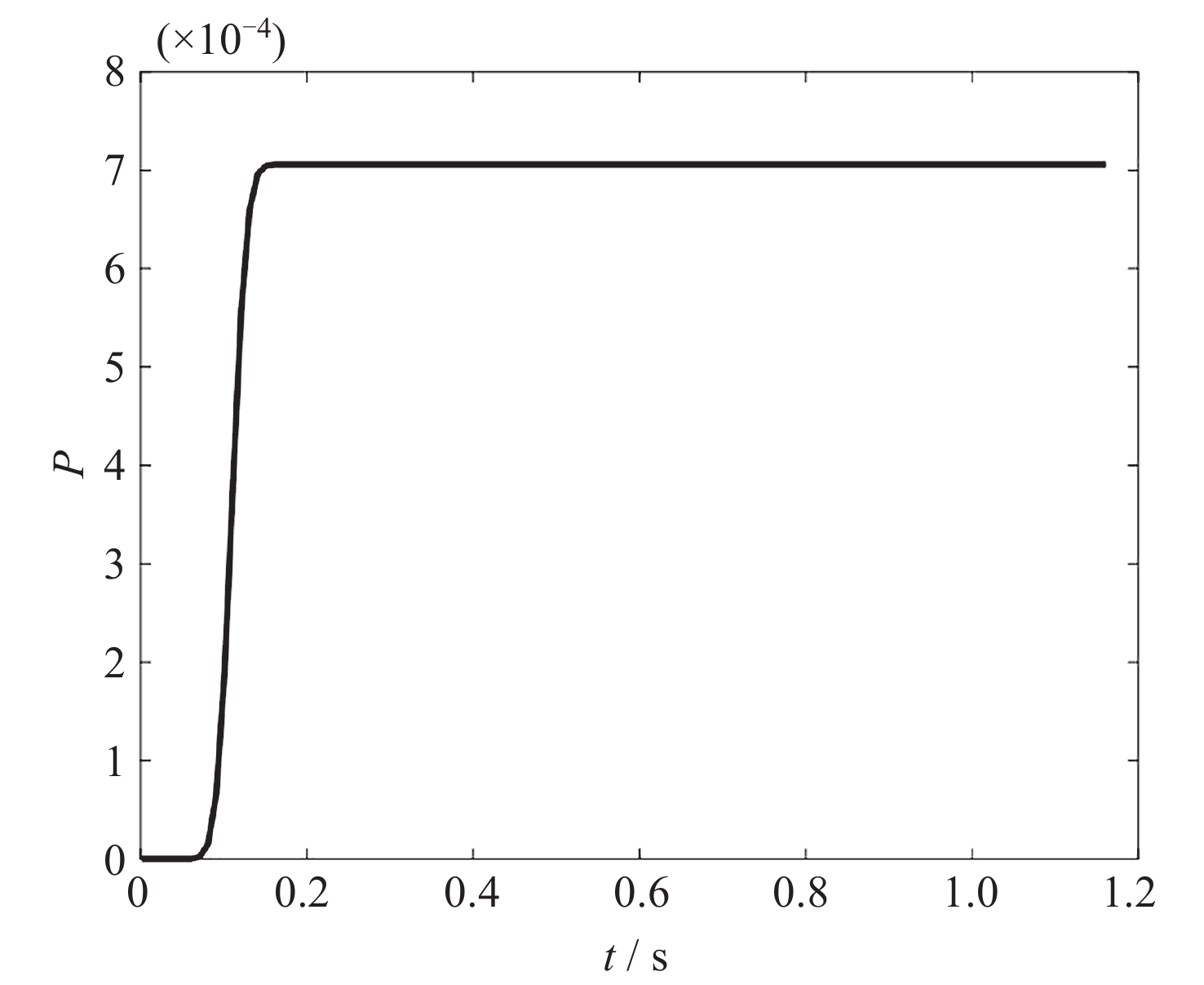
方法 碰撞概率 相对误差率 计算时间/s 二维面积积分法 $ 7.066\times {10}^{-4} $ - 0.1097 中心概率密度面积法 $ 7.051\times {10}^{-4} $ 0.0021 0.0064 一重积分法 $ 7.066\times {10}^{-4} $ $ 8.9\times {10}^{-14} $ 0.1259 级数法 $ 7.051\times {10}^{-4} $ 0.0021 0.0126 矩形域近似法 $ 7.067\times {10}^{-4} $ $ 1.00\times {10}^{-4} $ 0.0392 曲线积分法 $ 7.066\times {10}^{-4} $ $ 5.3\times {10}^{-15} $ 0.1097 辛普森公式积分法 $ 7.066\times {10}^{-4} $ $ 5.64\times {10}^{-6} $ 0.0074 表 3 蒙特卡罗方法计算结果
Table 3. Calculation results by Monte Carlo method
方法 碰撞概率 运算次数/次 计算时间/s 二维蒙特卡洛法 $ 7.068\times {10}^{-4} $ $ 1\times {10}^{10} $ 1224.6 三维蒙特卡洛法 $ 7.076\times {10}^{-4} $ $ 5\times {10}^{6} $ 67180.4 表 4 不同应用情形下碰撞概率工程适用方法
Table 4. Calculation method applicable to the collision probability under different circumstances
相遇情形 方法 同轨 体积拼接积分法 异轨 辛普森公式积分法 多目标碰撞概率计算 中心概率密度面积法 编队绕飞 体积拼接积分法、曲线积分法 合作目标 曲线积分法 非合作目标 辛普森公式积分法 高精度计算 蒙特卡洛法、体积拼接积分法 -
[1] 冯昊, 田百义, 张相宇. 巨型商业星座发展对轨道资源影响探索[J]. 空间碎片研究, 2021, 21(2): 40-45FENG Hao, TIAN Baiyi, ZHANG Xiangyu. Analysis on influence of giant commercial constellations on orbit resources[J]. Space Debris Research, 2021, 21(2): 40-45 [2] 程陶, 刘静, 王荣兰, 等. 空间碎片预警中的碰撞概率方法研究[J]. 空间科学学报, 2006, 26(6): 452-458 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-6124.2006.06.008CHENG Tao, LIU Jing, WANG Ronglan, et al. Collision probability analysis and application of cataloged space debris[J]. Chin. J. Space Sci., 2006, 26(6): 452-458 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-6124.2006.06.008 [3] LELEUX D, SPENCER R, ZIMMERMAN P, et al. Probability-based space shuttle collision avoidance[C]//SpaceOps 2002 Conference. Houston: AIAA, 2002 [4] 王继河, 张锦绣, 曹喜滨. 分布式卫星系统自主安全管理与控制研究综述[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2009, 41(5): 1-5WANG Jihe, ZHANG Jinxiu, CAO Xibin. Survey of autonomous safety operation and control for distributed satellite system[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2009, 41(5): 1-5 [5] 白显宗, 陈磊. 空间目标碰撞概率计算方法研究[J]. 宇航学报, 2008, 29(4): 1435-1442,1456 doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2008.04.063BAI Xianzong, CHEN Lei. Research on Calculational method of collision probability between space objects[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2008, 29(4): 1435-1442,1456 doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2008.04.063 [6] 白显宗, 陈磊. 基于空间压缩和无穷级数的空间碎片碰撞概率快速算法[J]. 应用数学学报, 2009, 32(2): 336-353 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-3079.2009.02.014BAI Xianzong, CHEN Lei. A rapid algorithm of space debris collision probability based on space compression and infinite series[J]. Acta Mathematicae Applicatae Sinica, 2009, 32(2): 336-353 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-3079.2009.02.014 [7] 董文朴, 任磊生, 周浩, 等. 空间目标碰撞概率的等效矩形域快速算法[J]. 宇航学报, 2020, 41(12): 1594-1600DONG Wenpu, REN Leisheng, ZHOU Hao, et al. Rapid algorithm of space objects collision probability with equivalent rectangular area[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2020, 41(12): 1594-1600 [8] 邢尧. GEO空间态势及碰撞规避可视化研究[D]. 太原: 中北大学, 2023XING Yao. Research on GEO Spatial Situation and Collision Avoidance Visualization[D]. Taiyuan: North University of China, 2023 [9] LEI Qiwei. Orbit Prediction and Collision Probability Calculation Method of Space Station Based on Intelligent Algorithm[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2022 [10] CAO Yi. Research on Energy Analysis and Control Method of Non-Cooperative Target Hovering[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2021 [11] 邢林峰, 李克行, 薛超. 空间碎片自主规避方法[J]. 空间碎片研究, 2023, 23(1): 19-23XING Linfeng, LI Kehang, XUE Chao. Autonomous space debris avoidance method[J]. Space Debris Research, 2023, 23(1): 19-23 [12] PATERA R P. Method for calculating collision probability between a satellite and a space tether[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2002, 25(5): 940-945 doi: 10.2514/2.4967 [13] MCKINLEY D. Development of a nonlinear probability of collision tool for the earth observing system[C]//AIAA/AAS Astrodynamics Specialist Conference and Exhibit. Keystone: AIAA, 2006 [14] 杨维维, 赵勇, 陈小前, 等. 航天器碰撞概率计算方法研究进展[J]. 中国空间科学技术, 2012, 32(6): 8-15 doi: 10.3780/j.issn.1000-758X.2012.06.002YANG Weiwei, ZHAO Yong, CHEN Xiaoqian, et al. Progress in calculation methods for collision probability of spacecraft[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2012, 32(6): 8-15 doi: 10.3780/j.issn.1000-758X.2012.06.002 [15] 张炜, 张荣之, 王秀红, 等. 星链卫星碰撞威胁及预警策略研究[J]. 载人航天, 2022, 28(5): 606-612ZHANG Wei, ZHANG Rongzhi, WANG Xiuhong, et al. Analysis of collision threat and collision detection strategy of starlink constellation[J]. Manned Spaceflight, 2022, 28(5): 606-612 [16] REN Shuyi. Orbital Evolution Analysis and Collision Risk Assessment for LEO Satellite Constellation[D]. Beijing: National Space Science Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2022 [17] CHAN K. Collision probability analyses for earth orbiting satellites[J]. Advances in the Astronautical Sciences, 1997, 96: 1033-1048 [18] 许晓丽, 熊永清. 非线性相对运动下空间碎片碰撞概率计算的研究[J]. 天文学报, 2011, 52(1): 73-85XU Xiaoli, XIONG Yongqing. A research on collision probability calculation of space debris for nonlinear relative motion[J]. Acta Astronomica Sinica, 2011, 52(1): 73-85 [19] CHAN F K. Short-Term vs. Long-Term Spacecraft Encounters [C]//AIAA/AAS Astrodynamics Specialist Conference and Exhibit. Providence: AIAA, 2004 [20] AKELLA M R, ALFRIEND K T. Probability of collision between space objects[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2000, 23(5): 769-772 doi: 10.2514/2.4611 -
-





 王宁 男, 2000年3月出生于山西省运城市. 现为北京控制工程研究所硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为航天器空间规避策略. E-mail:
王宁 男, 2000年3月出生于山西省运城市. 现为北京控制工程研究所硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为航天器空间规避策略. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: