Shallow-water Bathymetry Mapping from Satellite SAR Imagery Using Deep Learning with Multiple Feature Inputs
-
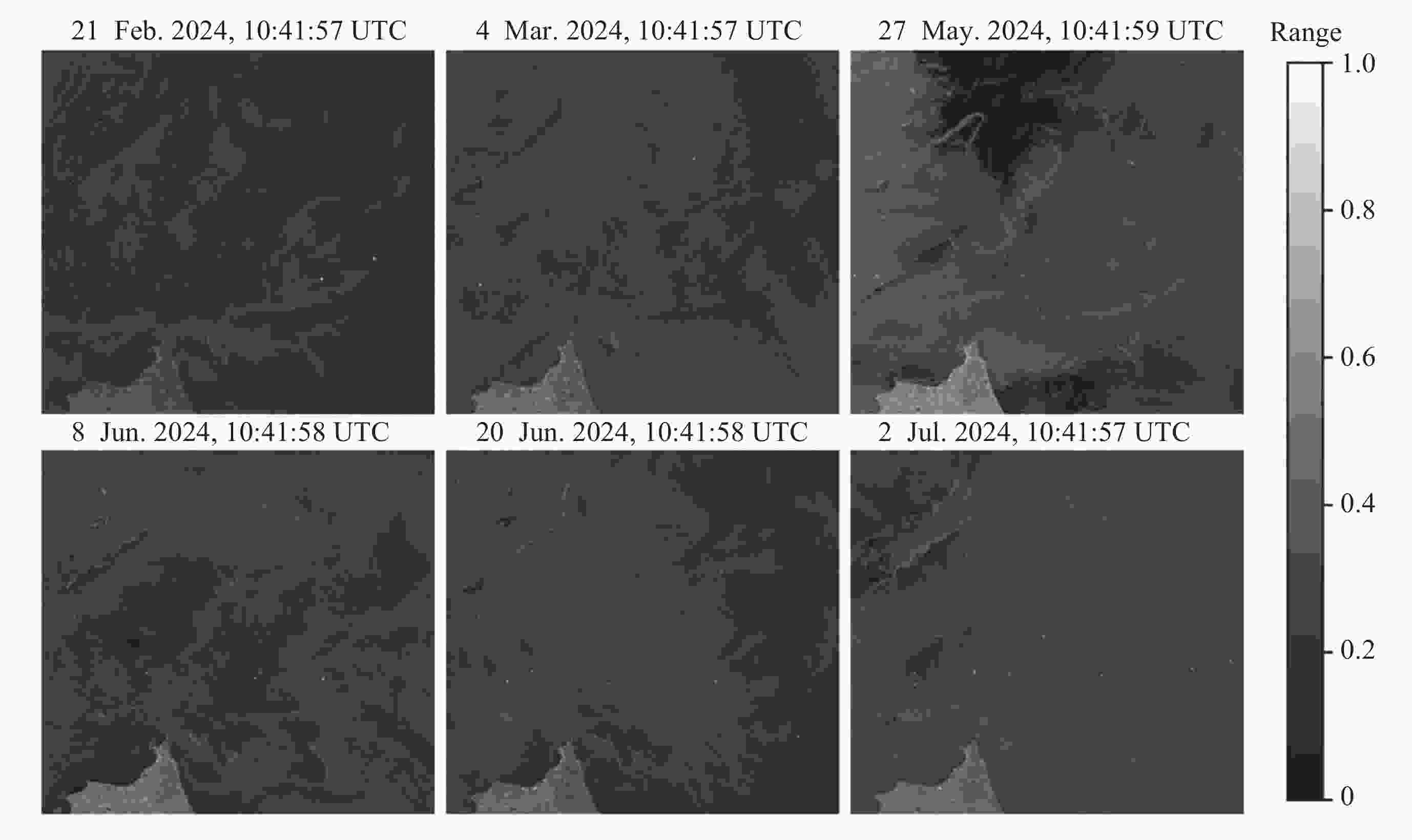
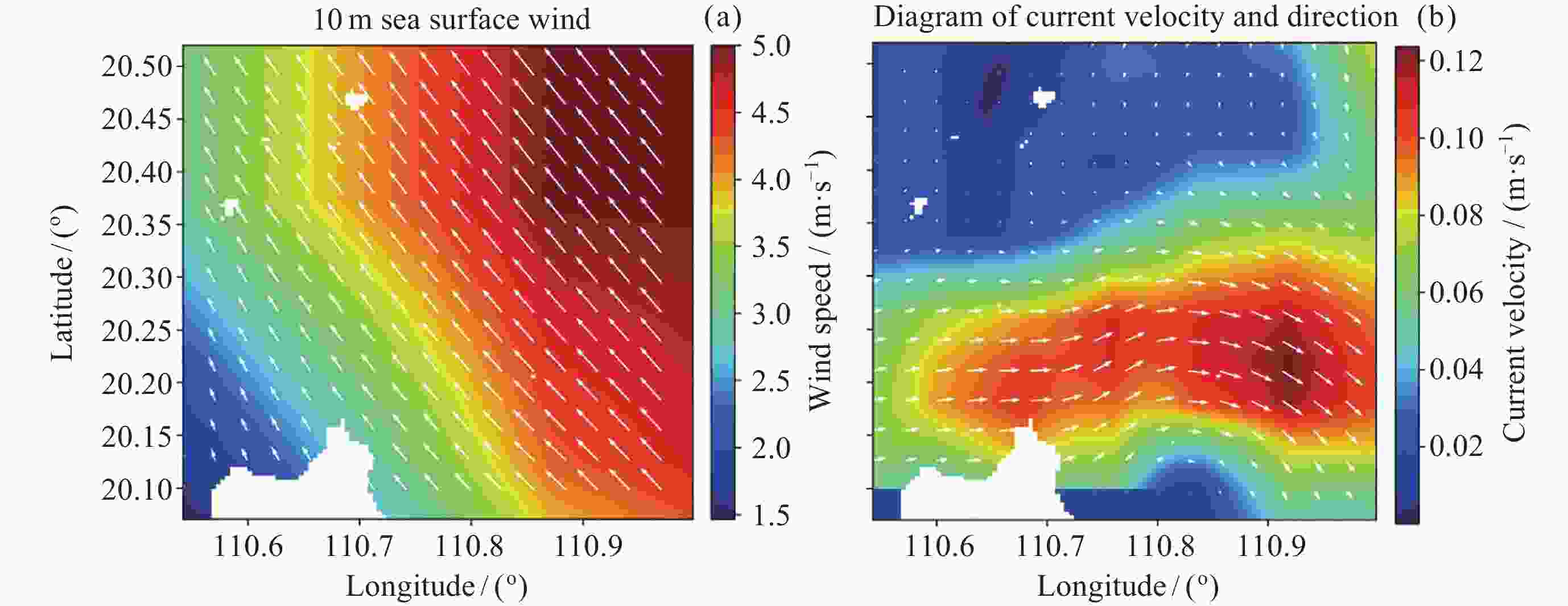
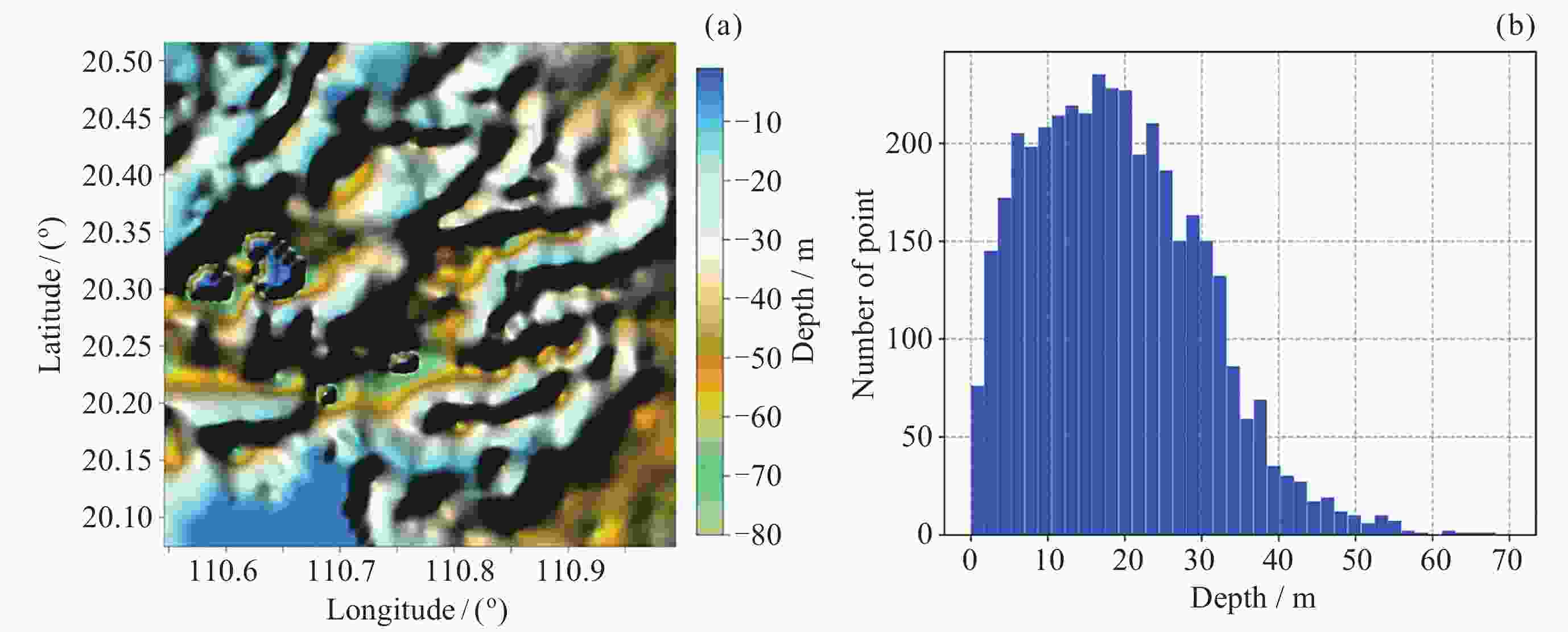
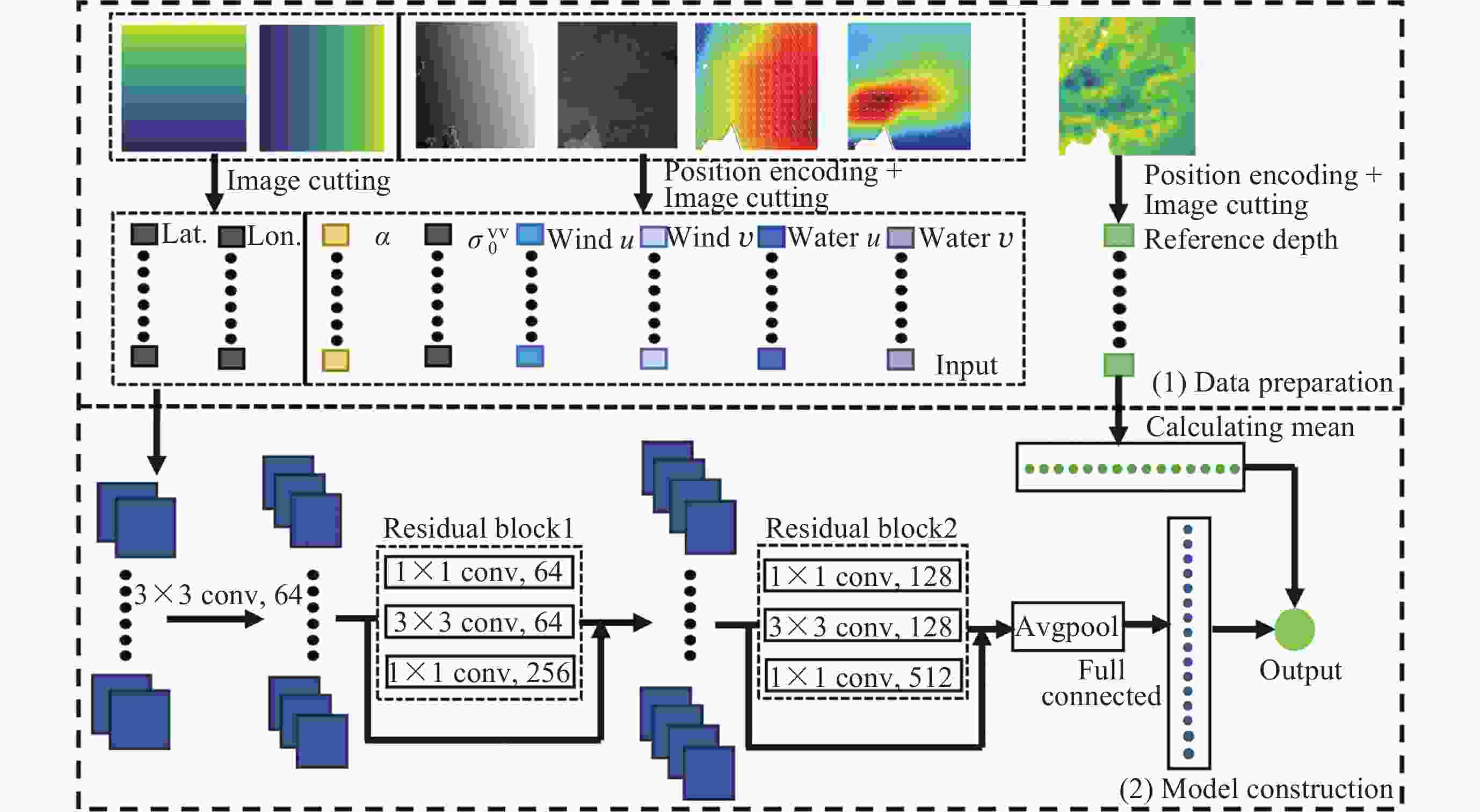
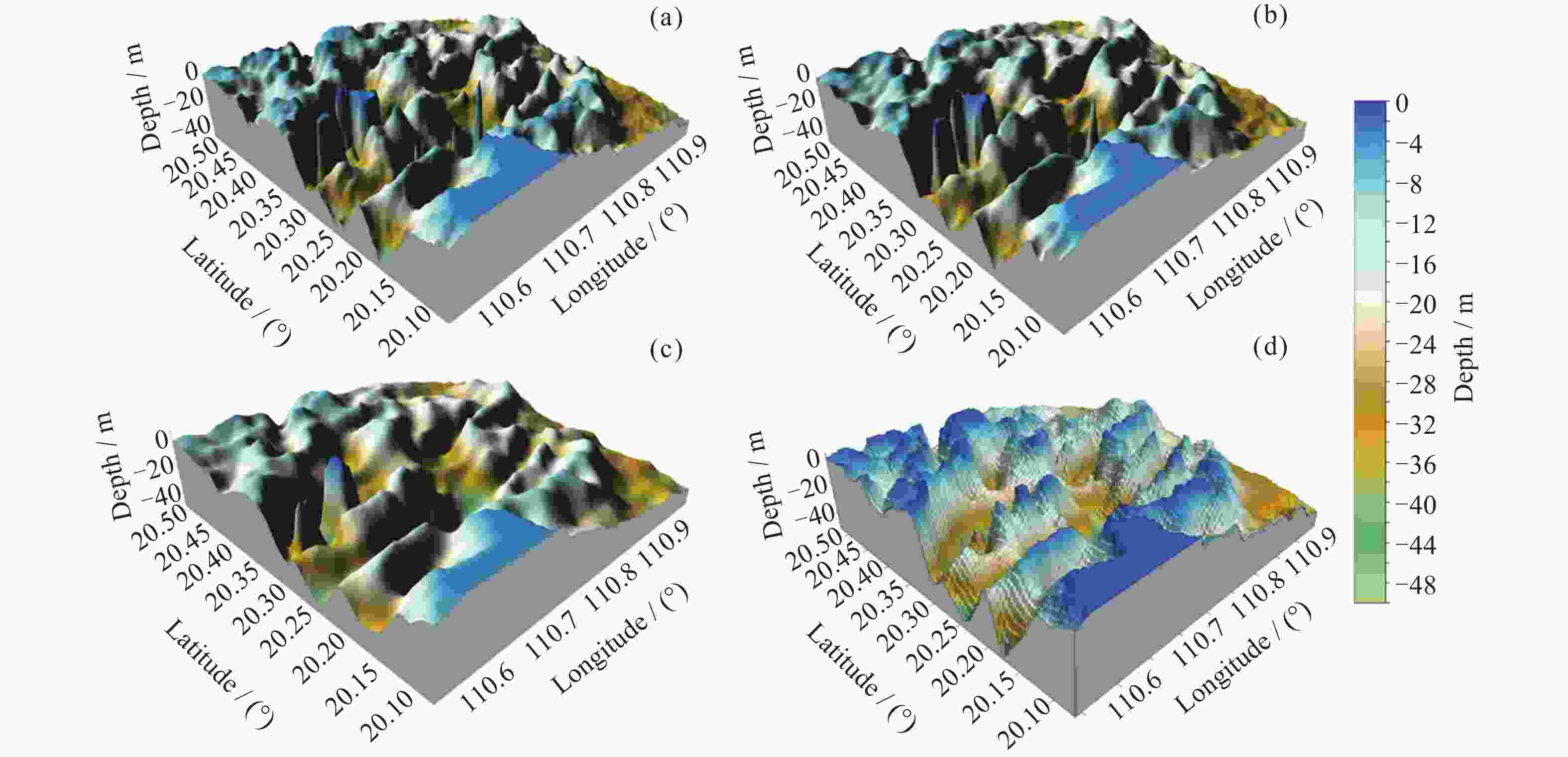
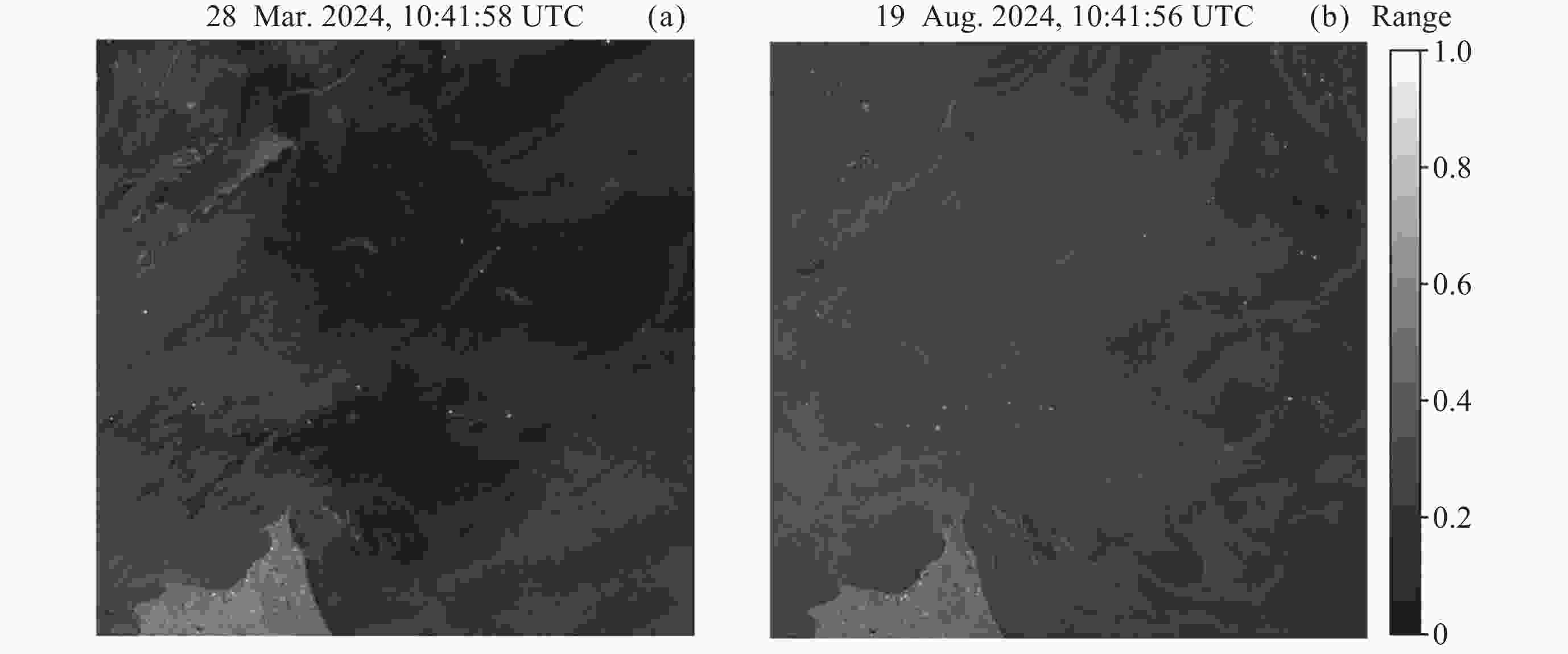
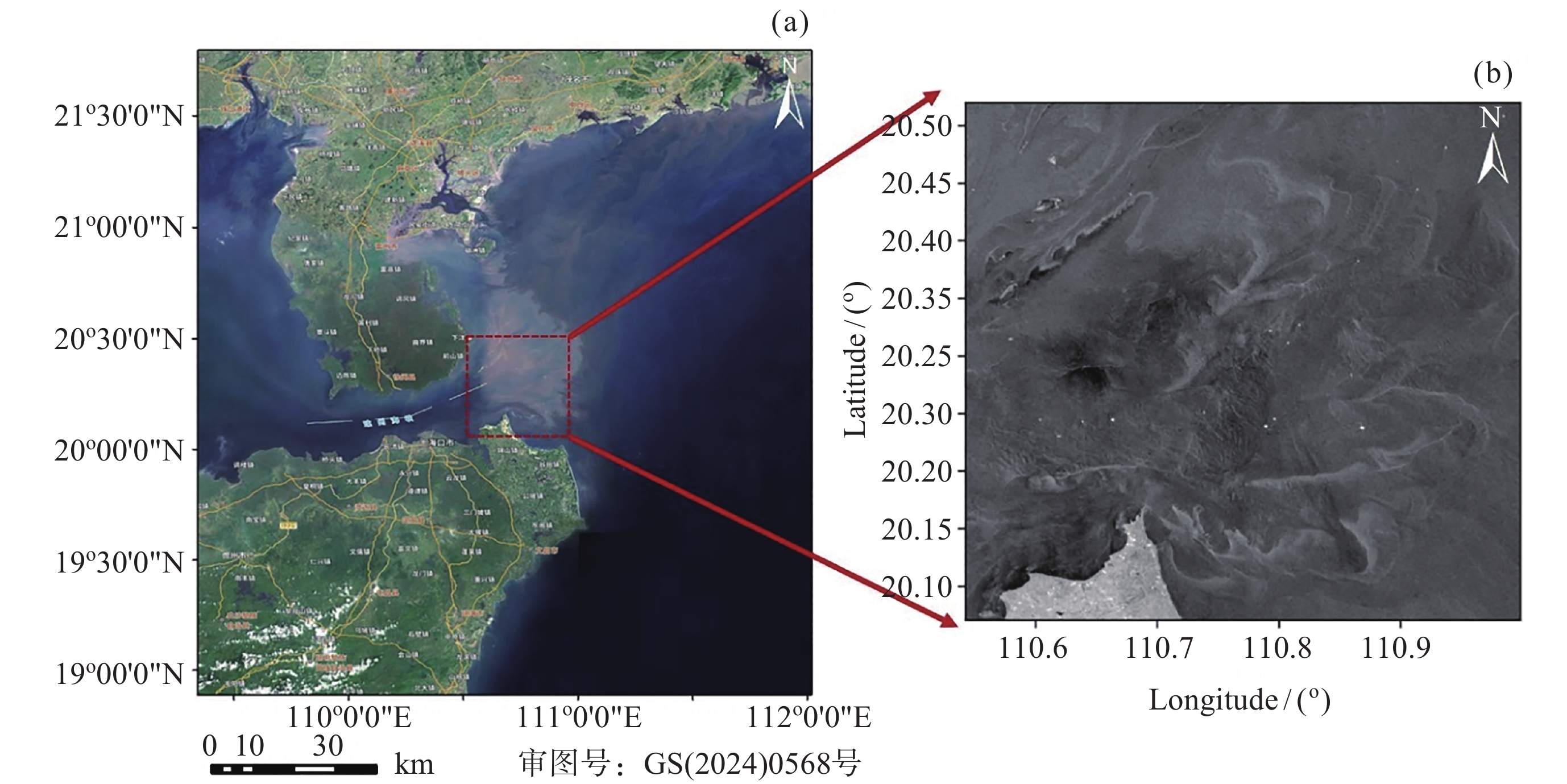
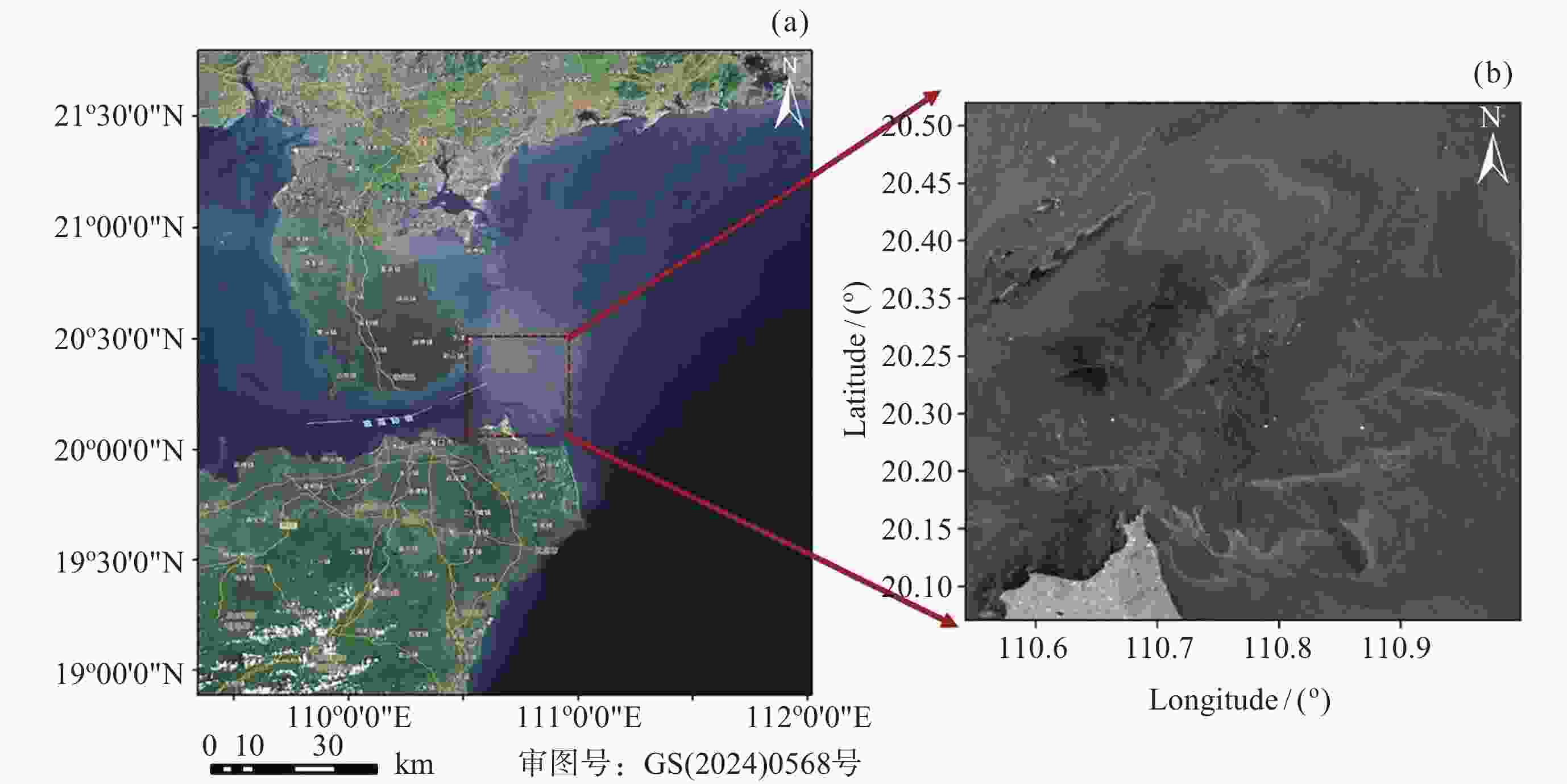
摘要: 面向浅海地形高精度反演需求, 改善光学遥感手段普遍存在的水质依赖性强和测深范围有限的问题, 研究以Sentinel-1卫星合成孔径雷达 (SAR)遥感影像为数据, 提出了一种多特征输入的深度学习浅海地形反演模型. 研究数据包括2024年中国海南岛东北部海域的6景SAR影像, 其中4景用于模型训练, 2景用于模型测试, 参考真值为ETOPO的Ice surface elevation geotiff数据. 反演模型由1个卷积层、2个BottleNeck模块和1个全连接层构成. 实验结果表明, 模型在训练集上的均方根误差和平均绝对百分比误差分别为1.57 m和6.56%, 在测试集上为1.95 m和11.55%, 水深最大探测范围为49.05 m. 此外, 对于2景不同海况条件下的影像, 其水深反演结果接近, 表明本文模型具有较好的鲁棒性, 可为浅海水下地形遥感探测提供新技术支持.Abstract: In response to the demand for high-precision shallow sea topography inversion and to improve the limitations of optical remote sensing, this study proposes a deep-learning model utilizing multiple feature inputs to inverse shallow sea topography from spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images. For the data acquisition and dataset construction, six high-resolution Sentinel-1 dual-polarization SAR images covering the waters northeast of Hainan Island of China in 2024 under different phases and sea conditions were collected, among which six images were used for model training, while the rest were used for testing. The reference depth was obtained from ETOPO. In dataset creation, SAR images are segmented into 8×8 sub-images. The model input is designed to consist of 8 feature variables, which involve the VV polarization backscattering coefficient $ {\mathrm{\sigma }}_{0}^{\mathrm{V}\mathrm{V}} $, radar incidence angle $ \theta $, geography information (latitude and longitude), and marine dynamic environmental parameters. The model output is reference depth from ETOPO with spatial consistency. The deep learning network comprises a convolutional layer, two BottleNeck modules from ResNet, and a fully connected layer. The final model performances in retrieving shallow water depth are shown as follows: For the training set, the model achieved a Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) of 1.57 m, and the average absolute percentage error is 6.56%, with the maximum detectable water depth reaching 49.05 m. The model presented with an RMSE of 1.95 m, and the average absolute percentage error is 11.55% for the testing dataset. Additionally, there is little difference between the two scenes with different temporal and sea conditions, indicating that the model is stable and robust. Thus, the proposed model was based on the brightness patterns observed in SAR imagery, which can detect shallow-water depths up to 50 m with high precision.
-
表 1 不同子图大小对2024年6月8日SAR数据的预测结果
Table 1. Predictions of different subimage sizes for SAR data on 8 June 2024
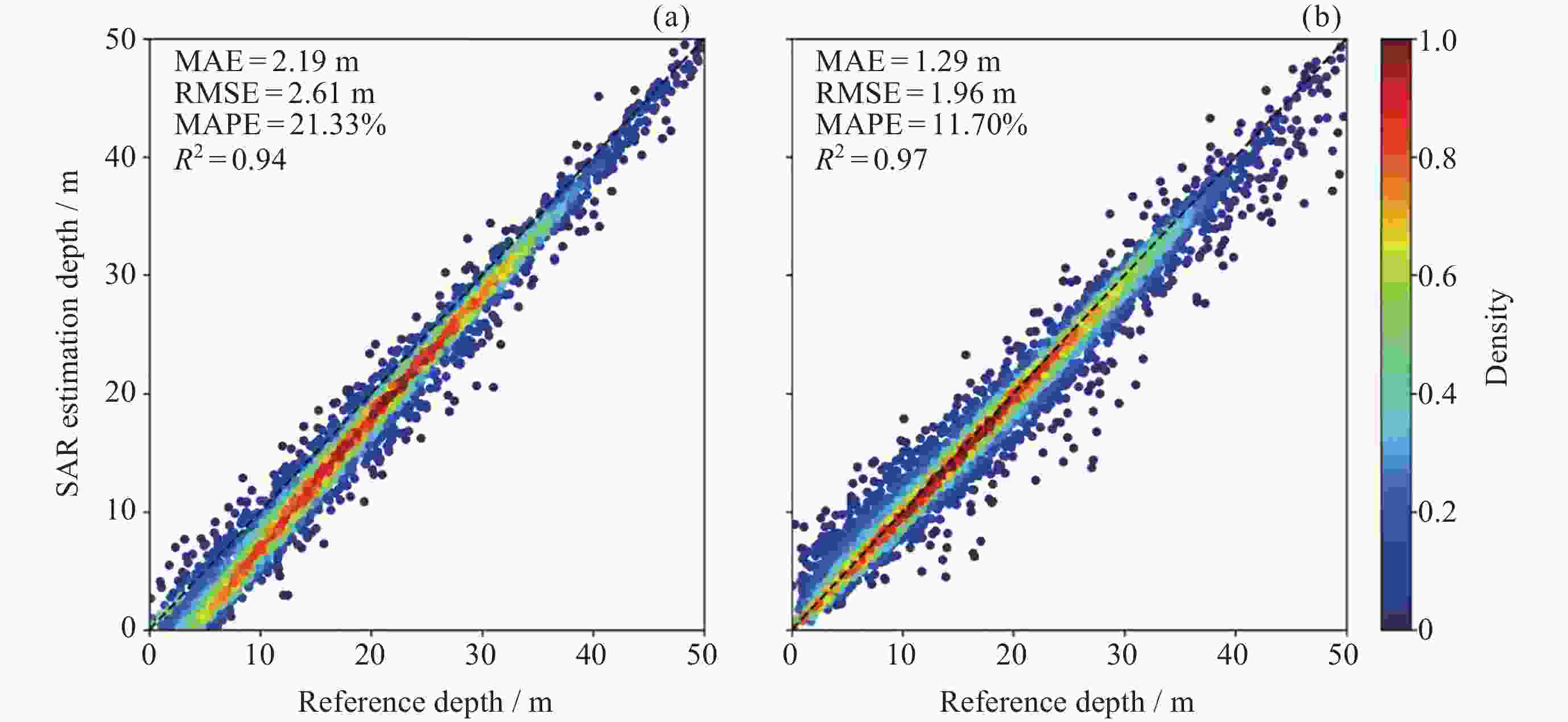
子图大小 MAE/m MAPE/(%) RMSE/m $ {R}^{2} $ 4×4 1.42 12.31 2.26 0.96 8×8 1.31 11.86 1.98 0.97 16×16 1.26 10.97 2.05 0.98 表 2 不同子图大小对2024年7月2日SAR数据的预测结果
Table 2. Predictions of different subimage sizes for SAR data on 2 July 2024
子图大小 MAE/m MAPE/(%) RMSE/m $ {R}^{2} $ 4×4 1.41 11.81 2.12 0.96 8×8 1.29 11.55 1.95 0.97 16×16 1.25 10.84 1.97 0.97 表 3 不同子图大小对2024年8月19日SAR数据的预测结果
Table 3. Predictions of different subimage sizes for SAR data on 19 August 2024
子图大小 MAE/m MAPE/(%) RMSE/m $ {R}^{2} $ 4×4 1.39 12.42 2.32 0.96 8×8 1.29 11.70 1.96 0.97 16×16 1.24 11.02 2.07 0.97 -
[1] SHEN W, CHEN M Y, WU Z Q, et al. Shallow-water bathymetry retrieval based on an improved deep learning method using GF-6 multispectral imagery in Nanshan Port waters[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2023, 16: 8550-8562 doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2023.3310166 [2] PURKIS S J, GLEASON A C R, PURKIS C R, et al. High-resolution habitat and bathymetry maps for 65, 000 sq. km of Earth’s remotest coral reefs[J]. Coral Reefs, 2019, 38(3): 467-488 [3] AI B, WEN Z, WANG Z H, et al. Convolutional neural network to retrieve water depth in marine shallow water area from remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 2888-2898 doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.2993731 [4] 崔子伟, 徐文学, 刘焱雄, 等. 机载激光测深数据获取及处理技术现状[J]. 自然资源遥感, 2023, 35(3): 1-9CUI Ziwei, XU Wenxue, LIU Yanxiong, et al. Current status of the acquisition and processing of airborne laser sounding data[J]. Remote Sensing for Natural Resources, 2023, 35(3): 1-9 [5] 李雨佳, 周晓青, 李国元, 等. 星载单光子激光雷达浅水测深技术研究进展和展望[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2022, 51(10): 20220003LI Yujia, ZHOU Xiaoqing, LI Guoyuan, et al. Progress and prospect of space-borne photon-counting lidar shallow water bathymetry technology[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2022, 51(10): 20220003 [6] SCHWARZ R, MANDLBURGER G, PFENNIGBAUER M, et al. Design and evaluation of a full-wave surface and bottom-detection algorithm for LiDAR bathymetry of very shallow waters[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2019, 150: 1-10 [7] WESTFELD P, MAAS H G, RICHTER K, et al. Analysis and correction of ocean wave pattern induced systematic coordinate errors in airborne LiDAR bathymetry[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2017, 128: 314-325 [8] HEDLEY J, ROELFSEMA C, PHINN S R. Efficient radiative transfer model inversion for remote sensing applications[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2009, 113(11): 2527-2532 [9] LIU Y M, TANG S L, DENG R R, et al. Mapping ultrahigh-spatial-resolution bathymetry for a wide range of coastal optically shallow waters without in situ bathymetric data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 4207716 [10] CAO B, DENG R R, ZHU S L. Universal algorithm for water depth refraction correction in through-water stereo remote sensing[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2020, 91: 102108 [11] LYZENGA D R. Passive remote sensing techniques for mapping water depth and bottom features[J]. Applied Optics, 1978, 17(3): 379-383 [12] 曹斌. 光学卫星影像浅海海底地形测量方法研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2018CAO Bin. A Study of Shallow Seafloor Relief Measurement Using Optical Satellite Images[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2018 [13] LAI W D, LEE Z, WANG J W, et al. A portable algorithm to retrieve bottom depth of optically shallow waters from top-of-atmosphere measurements[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2022, 2022: 9831947 [14] LIU Y M, ZHAO J, DENG R R, et al. A downscaled bathymetric mapping approach combining multitemporal Landsat-8 and high spatial resolution imagery: demonstrations from clear to turbid waters[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2021, 180: 65-81 [15] CHEN B Q, YANG Y M, XU D W, et al. A dual band algorithm for shallow water depth retrieval from high spatial resolution imagery with no ground truth[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2019, 151: 1-13 [16] XU Y, CAO B, DENG R R, et al. Bathymetry over broad geographic areas using optical high-spatial-resolution satellite remote sensing without in-situ data[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2023, 119: 103308 [17] MA S, TAO Z, YANG X F, et al. Bathymetry Retrieval From Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Data in Optical-Shallow Water[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(2): 1205-1212 [18] PACHECO A, HORTA J, LOUREIRO C, et al. Retrieval of nearshore bathymetry from Landsat 8 images: a tool for coastal monitoring in shallow waters[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2015, 159: 102-116 [19] LEGLEITER C J, OVERSTREET B T, GLENNIE C L, et al. Evaluating the capabilities of the CASI hyperspectral imaging system and Aquarius bathymetric LiDAR for measuring channel morphology in two distinct river environments[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2016, 41(3): 344-363 [20] 习晓环, 王子家, 王成. 基于ICESat-2/ATLAS数据的近海岸水深提取[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 50(7): 940-946 doi: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.22126XI Xiaohuan, WANG Zijia, WANG Cheng. Bathymetric extraction method of nearshore based on ICESat-2/ATLAS data[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2022, 50(7): 940-946 doi: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.22126 [21] 胡琪鑫, 程亮, 楚森森, 等. ICESat-2水深提取方法及其反演应用[J]. 地球物理学报, 2024, 67(3): 997-1012 doi: 10.6038/cjg2023Q0837HU Qixin, CHENG Liang, CHU Sensen, et al. Water depth extraction of ICESat-2 and application to bathymetric inversion[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2024, 67(3): 997-1012 doi: 10.6038/cjg2023Q0837 [22] 范开国, 黄韦艮, 傅斌, 等. 台湾浅滩浅海水深SAR遥感探测实例研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2012, 55(1): 310-316FAN Kaiguo, HUANG Weigen, FU Bin, et al. SAR shallow water bathymetry surveys: a case study in Taiwan Shoal[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2012, 55(1): 310-316 [23] BRUSCH S, HELD P, LEHNER S, et al. Underwater bottom topography in coastal areas from TerraSAR-X data[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2011, 32(16): 4527-4543 [24] 王小珍. 浅海典型水下地形SAR遥感成像机理和反演研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2018WANG Xiaozhen. Research on SAR Remote Sensing Imaging Mechanism and Inversion of Typical Shallow Water Topography[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2018 [25] 于祥祯, 种劲松, 洪文. 顺轨干涉SAR浅海地形成像建模及其最优雷达观测参数分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2010, 32(10): 2377-2382YU Xiangzhen, CHONG Jinsong, HONG Wen. Shallow sea topography imaging model by along-track interferometric SAR and its optimal radar parameters analysis[J]. Journal of Electronics :Times New Roman;">& Information Technology, 2010, 32(10): 2377-2382 [26] ALPERS W, HENNINGS I. A theory of the imaging mechanism of underwater bottom topography by real and synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1984, 89(C6): 10529-10546 [27] BIAN X L, SHAO Y, WANG S A, et al. Shallow water depth retrieval from multitemporal sentinel-1 SAR data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(9): 2991-3000 doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2851845 [28] YUAN Y L, HUA F, PAN Z D, et al. LAGFD-WAM numerical wave model——I. basic physical model[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1991, 10(4): 483-488 [29] ZHANG S S, LIU B, LI X F, et al. Automatic extraction of internal wave signature from multiple satellite sensors based on deep convolutional neural networks[C]//IGARSS 2020 - 2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Waikoloa: IEEE, 2020: 5717-5720 [30] WANG J, ZHANG H G, YANG J S, et al. A new mapping method of underwater bottom topography in the shallow sea by using SAR images[C]//Remote Sensing of the Ocean, Sea Ice, Coastal Waters, and Large Water Regions 2016. Edinburgh: SPIE Remote Sensing, 2016 [31] 范开国. 基于海面微波成像仿真M4S软件的SAR浅海地形遥感探测[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2009FAN Kaiguo. Shallow water bathymetry surveys by SAR based on M4S for simulations of microwave imaging oceanic surface[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2009 [32] LI D F, ZHAO Z Q. Facet-based hybrid method for electromagnetic scattering from shallow water waves modulated by submarine topography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 2004314 [33] HUANG L Y, MENG J M, FAN C Q, et al. Shallow sea topography detection from multi-source SAR satellites: a case study of Dazhou Island in China[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(20): 5184 [34] BIAN X L, SHAO Y, TIAN W, et al. Underwater topography detection in coastal areas using fully polarimetric SAR data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(6): 560 [35] PEREIRA P, BAPTISTA P, CUNHA T, et al. Estimation of the nearshore bathymetry from high temporal resolution Sentinel-1A C-band SAR data - a case study[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2019, 223: 166-178 [36] 荣飞成, 孟俊敏, 纪永刚. 基于SAR子孔径图像的浅海水下地形探测[J]. 遥测遥控, 2024, 45(1): 106-115RONG Feicheng, MENG Junmin, JI Yonggang. Shallow sea underwater topography detection based on SAR subaperture image[J]. Journal of Telemetry, Tracking and Command, 2024, 45(1): 106-115 [37] 房超, 汪胜, 刘桂红, 等. 基于SAR卫星观测的北极冰涡时空分布特征[J]. 空间科学学报, 2023, 43(6): 1125-1134 doi: 10.11728/cjss2023.06.2023-0088FANG Chao, WANG Sheng, LIU Guihong, et al. Spatio-temporal distribution characteristics of arctic ice eddies based on SAR satellite observations[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2023, 43(6): 1125-1134 doi: 10.11728/cjss2023.06.2023-0088 [38] 任诗鹤, 韩焱红, 李竞时, 等. 基于U-Net的海洋锋智能检测模型[J]. 空间科学学报, 2023, 43(6): 1091-1099 doi: 10.11728/cjss2023.06.2023-0097REN Shihe, HAN Yanhong, LI Jingshi, et al. Oceanic front detection model based on U-Net network[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2023, 43(6): 1091-1099 doi: 10.11728/cjss2023.06.2023-0097 [39] LEE S, KIM D J, LI C L, et al. A new model for high-accuracy monitoring of water level changes via enhanced water boundary detection and reliability-based weighting averaging[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2024, 313: 114360 doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2024.114360 [40] YANG H Y, FANG C, WANG S, et al. On the ambiguity removal of wind direction derived from space-borne SAR imagery using deep learning[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2024, 308: 114202 doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2024.114202 [41] YUROVSKY Y Y, KUDRYAVTSEV V N, YUROVSKAYA M V, et al. Tropical cyclone signatures in SAR ocean radial Doppler Velocity[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2024, 311: 114251 [42] ZHAO X N, WANG D Q, XU H L, et al. Water deep mapping from HJ-1B satellite data by a deep network model in the sea area of Pearl River Estuary, China[J]. Open Geosciences, 2021, 13(1): 782-795 [43] WU Z Q, MAO Z H, SHEN W, et al. Satellite-derived bathymetry based on machine learning models and an updated quasi-analytical algorithm approach[J]. Optics Express, 2022, 30(10): 16773-16793 doi: 10.1364/OE.456094 [44] KALOOP M R, El-DIASTY M, HU J W, et al. Hybrid artificial neural networks for modeling shallow-water bathymetry via satellite imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5403811 [45] ZHONG J, SUN J, LAI Z L, et al. Nearshore bathymetry from ICESat-2 LiDAR and Sentinel-2 imagery datasets using deep learning approach[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(17): 4229 doi: 10.3390/rs14174229 [46] LI X F, YANG X F, ZHENG Q N, et al. Deep-water bathymetric features imaged by spaceborne SAR in the Gulf Stream region[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2010, 37: L19603 -
-




 崔宜德 男, 2001年12月出生于山东省德州市, 现为中国科学院空天信息创新研究院在读博士研究生, 主要研究方向为基于SAR观测的浅海水下地形研究. E-mail:
崔宜德 男, 2001年12月出生于山东省德州市, 现为中国科学院空天信息创新研究院在读博士研究生, 主要研究方向为基于SAR观测的浅海水下地形研究. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: