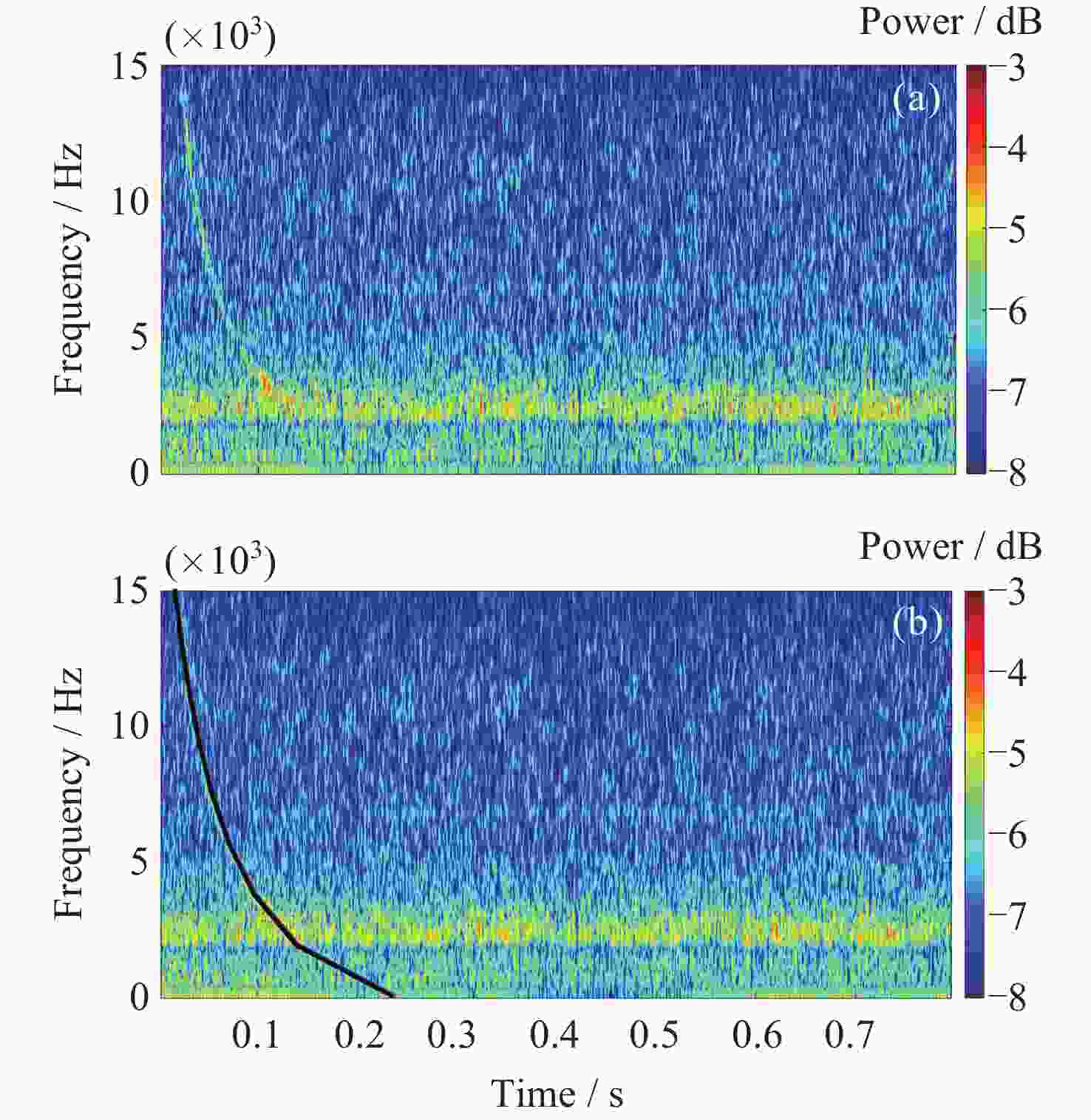
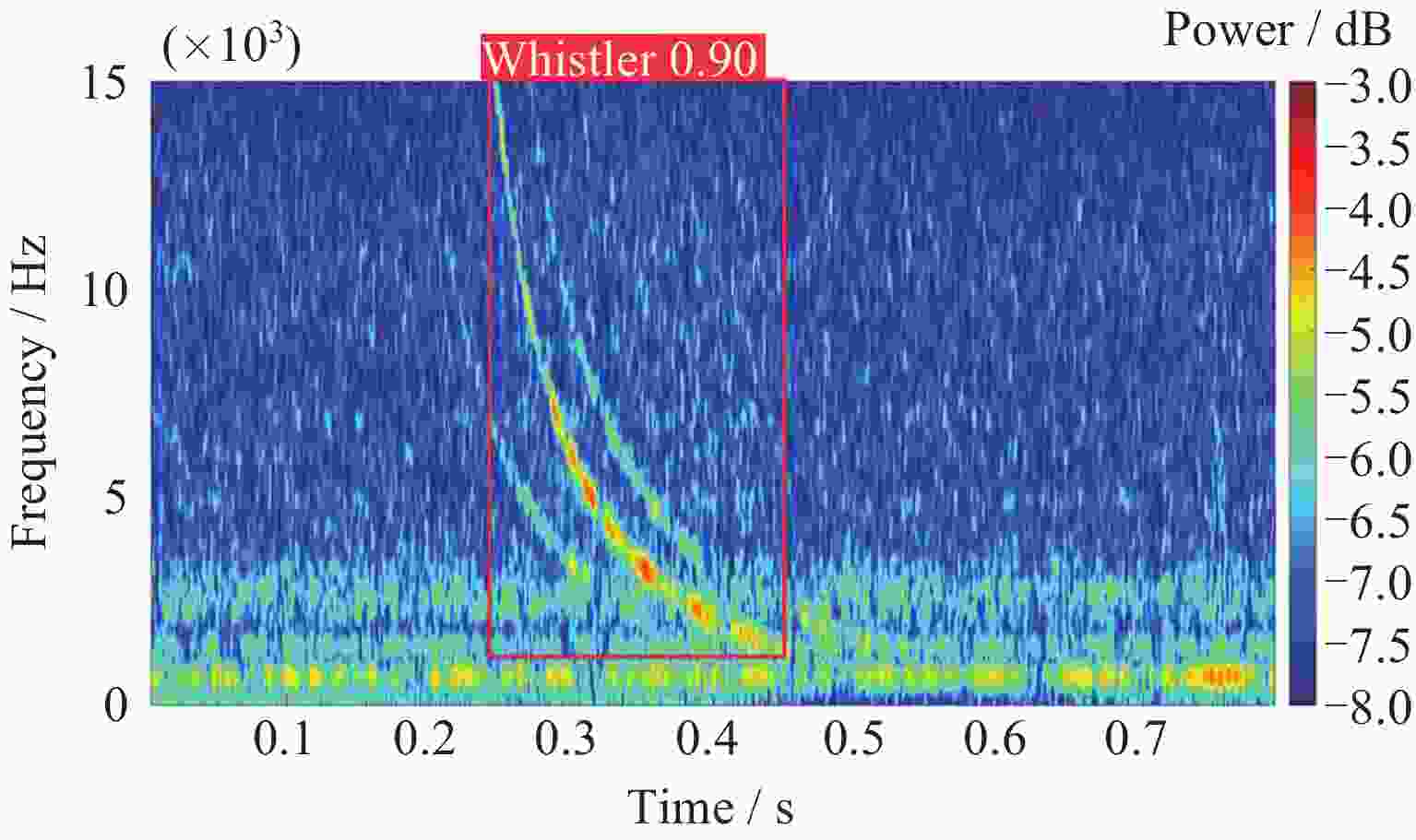
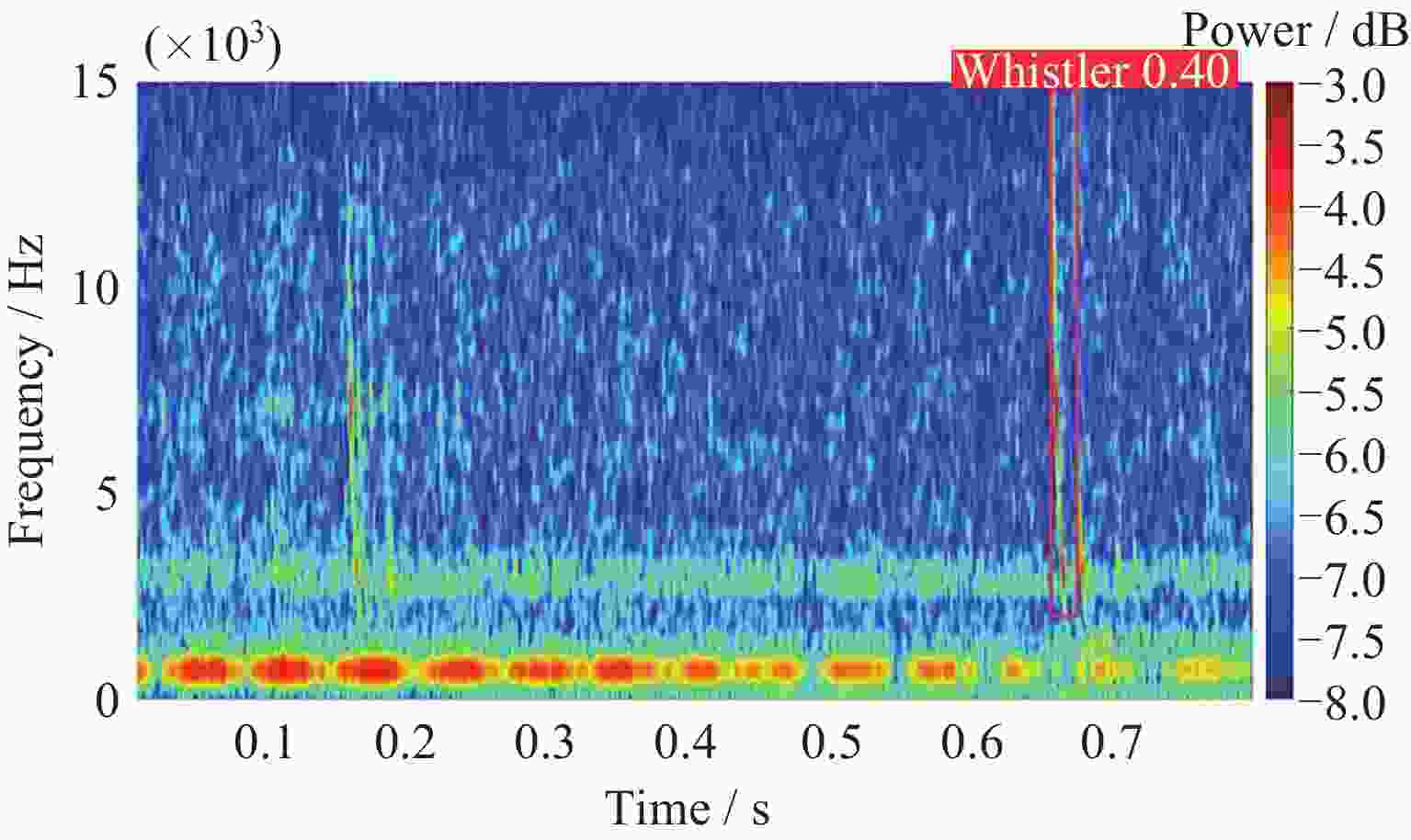
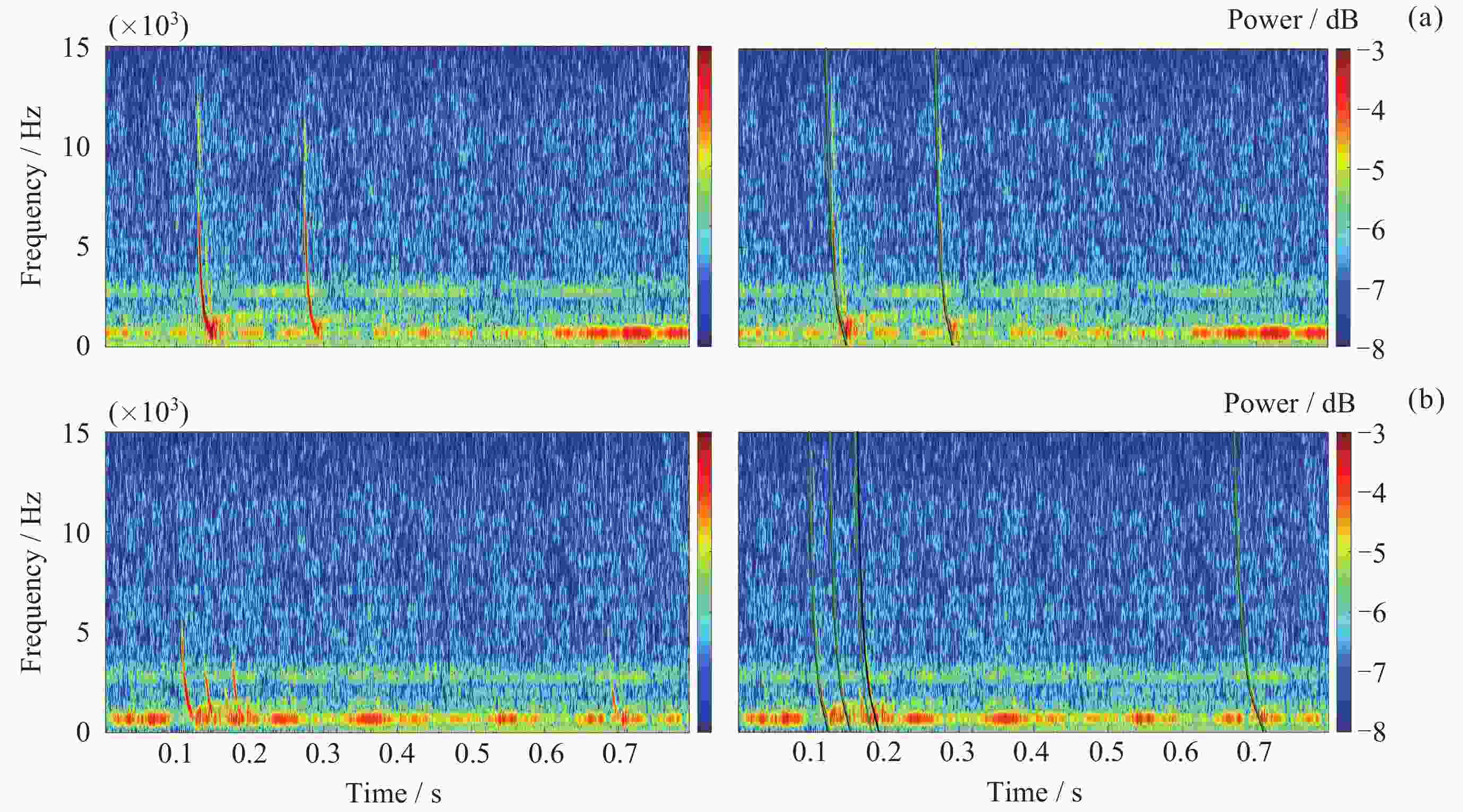
Fast and Robust Automatic Extraction Method for the Lightning Whistler Scattering Coefficient of the Zhangheng Satellite
-
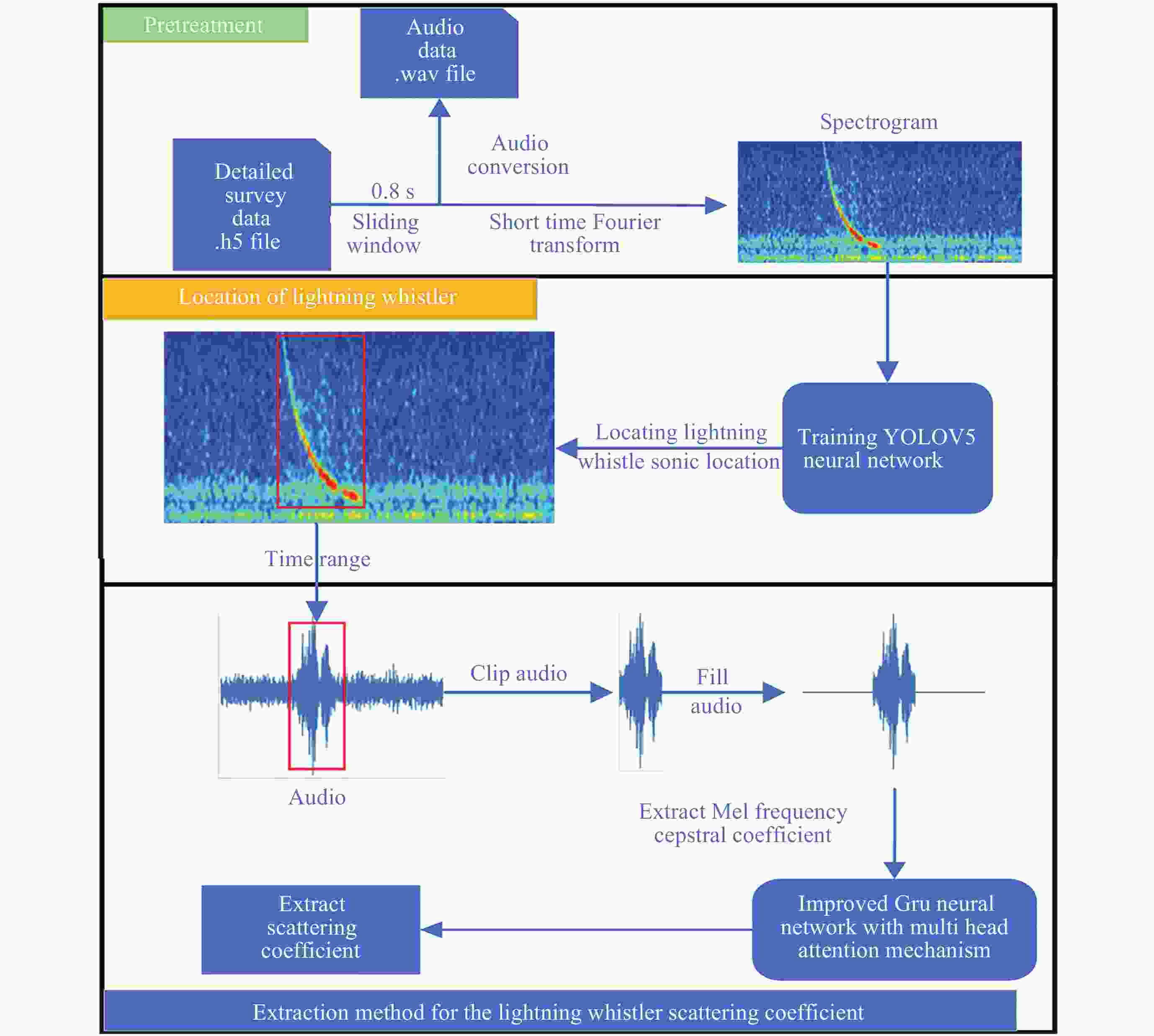
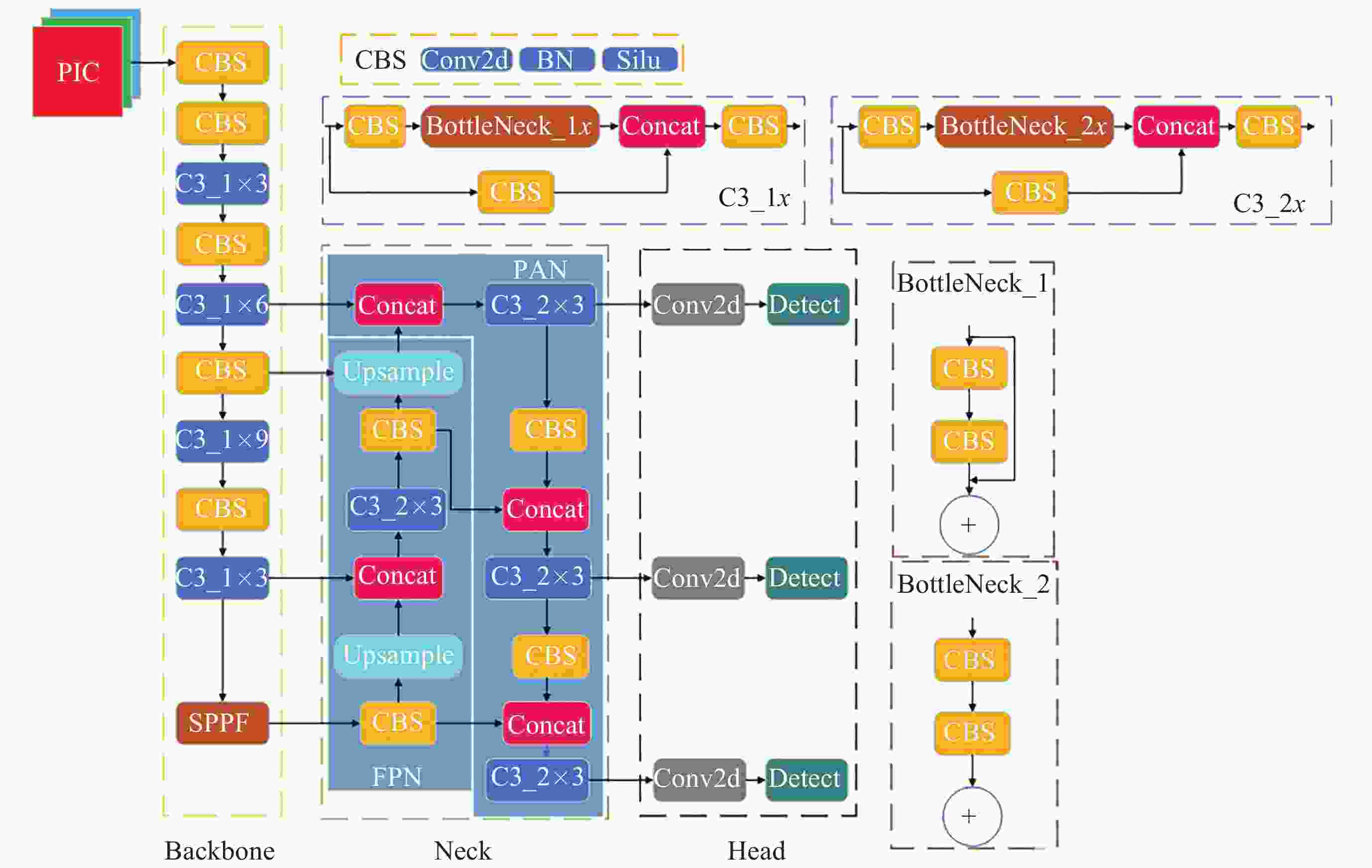
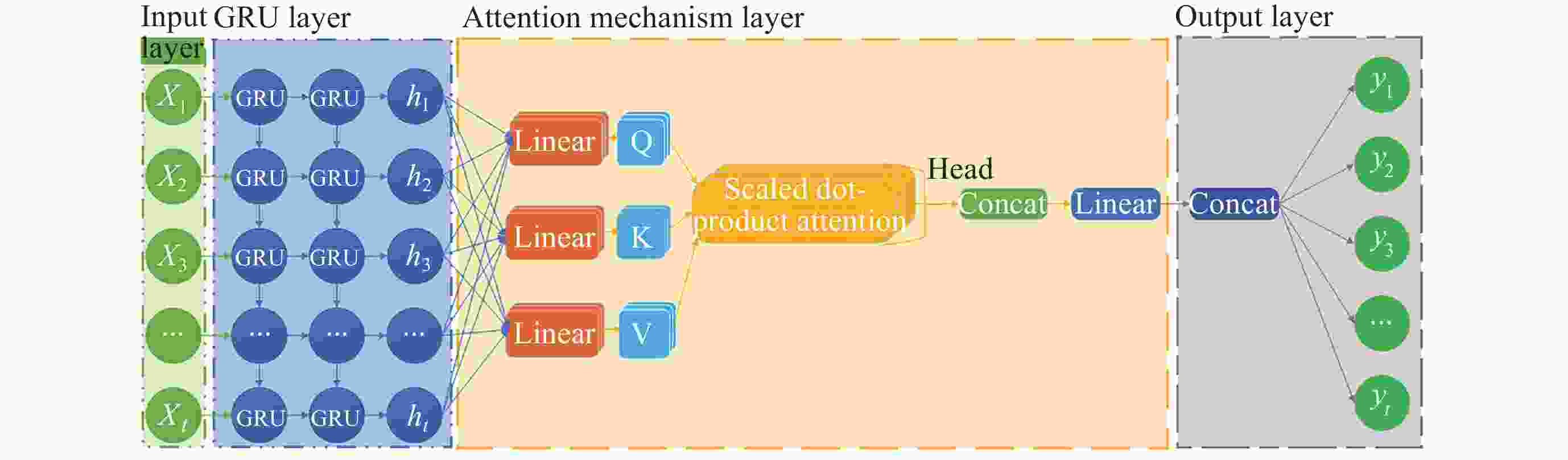
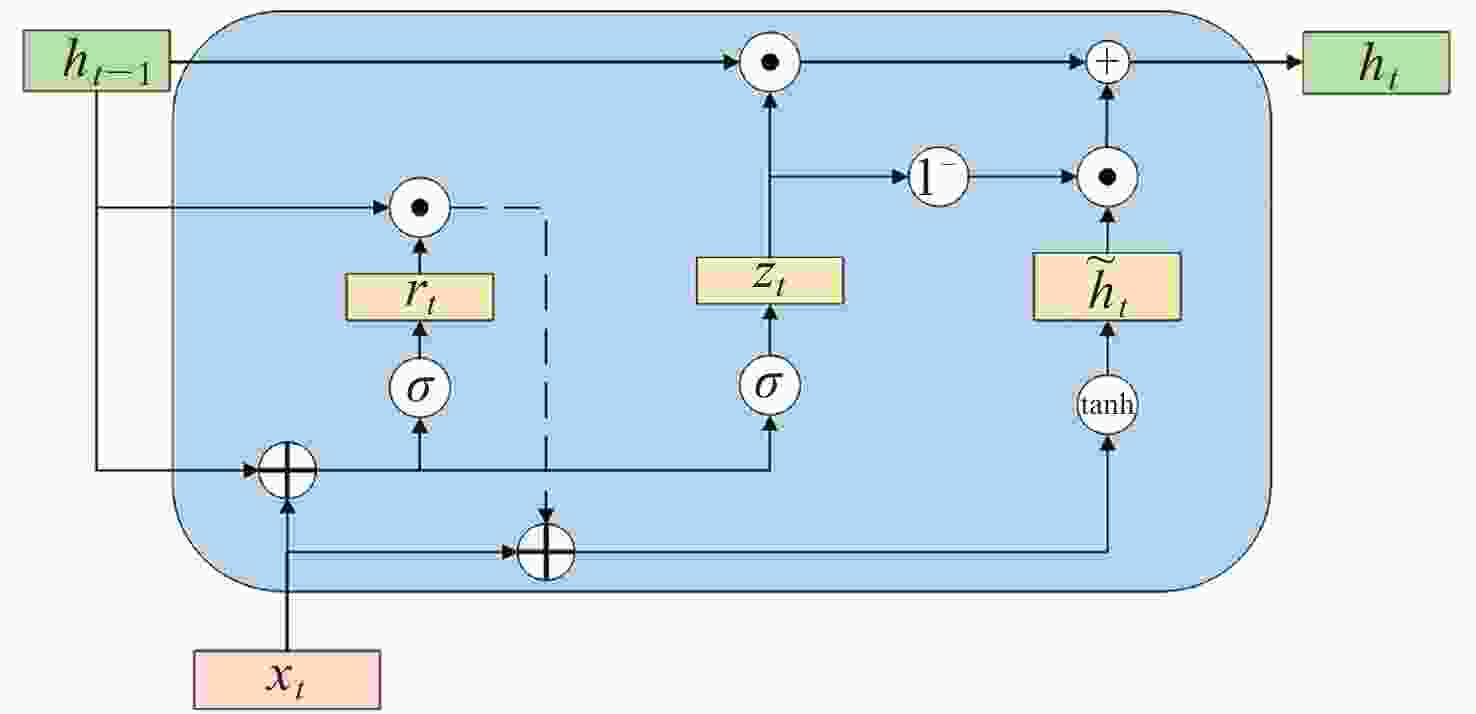
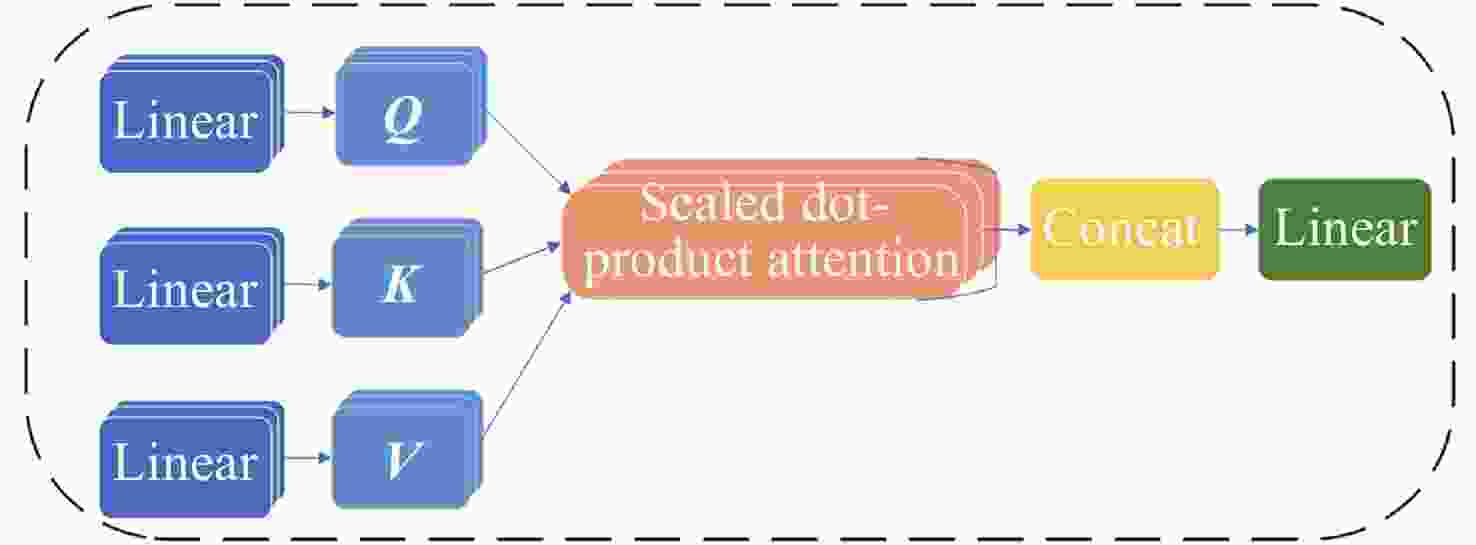
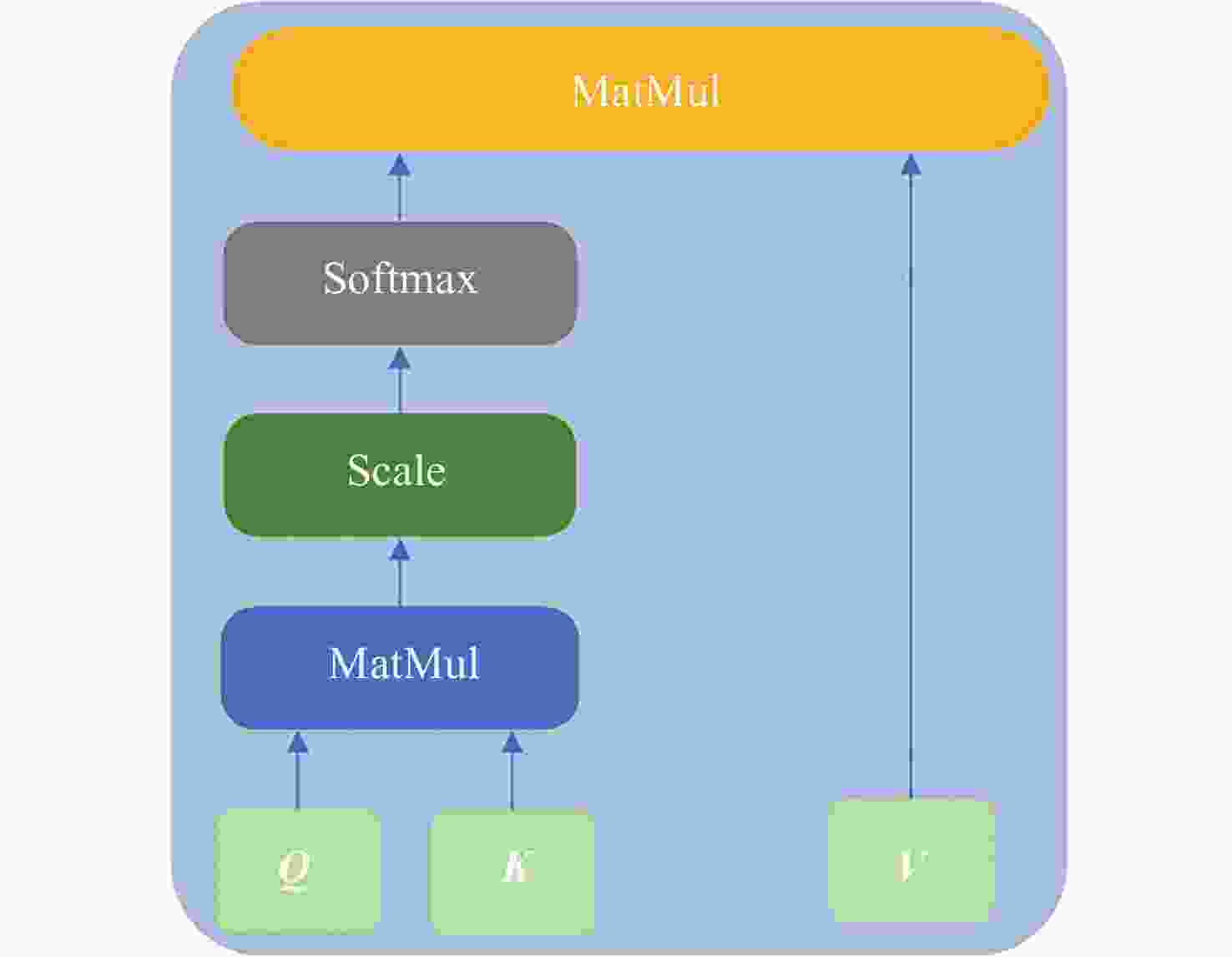
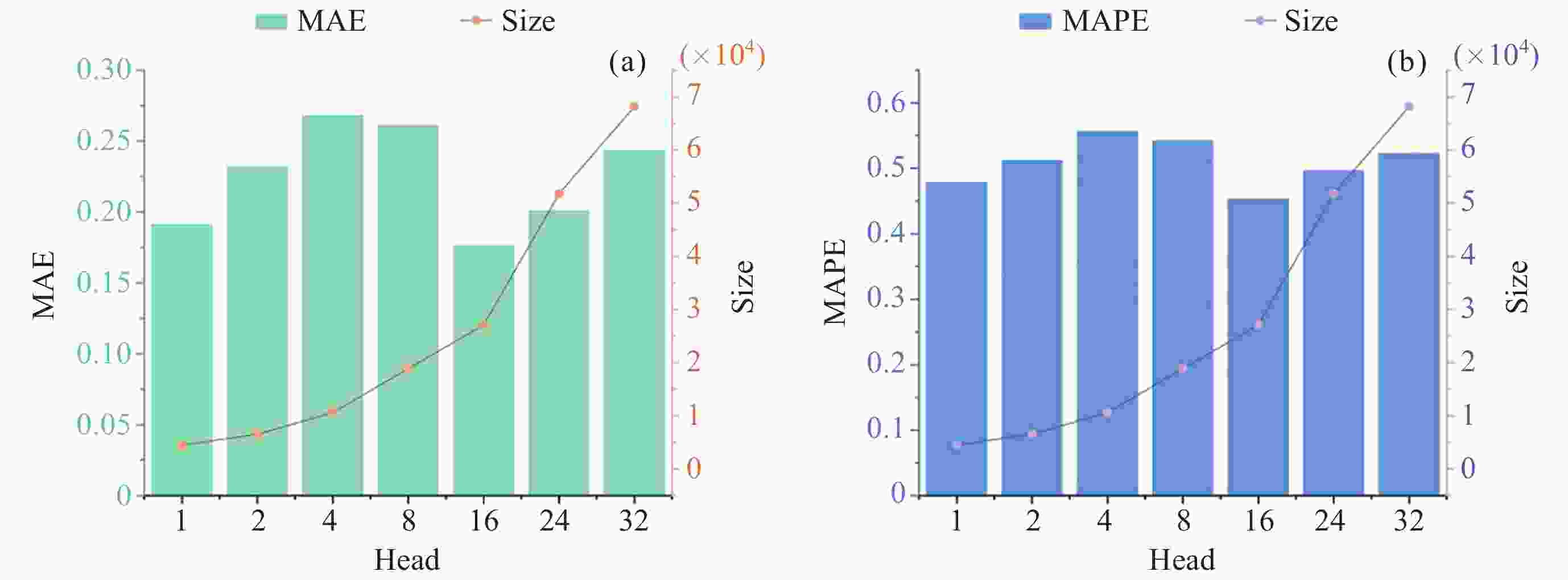
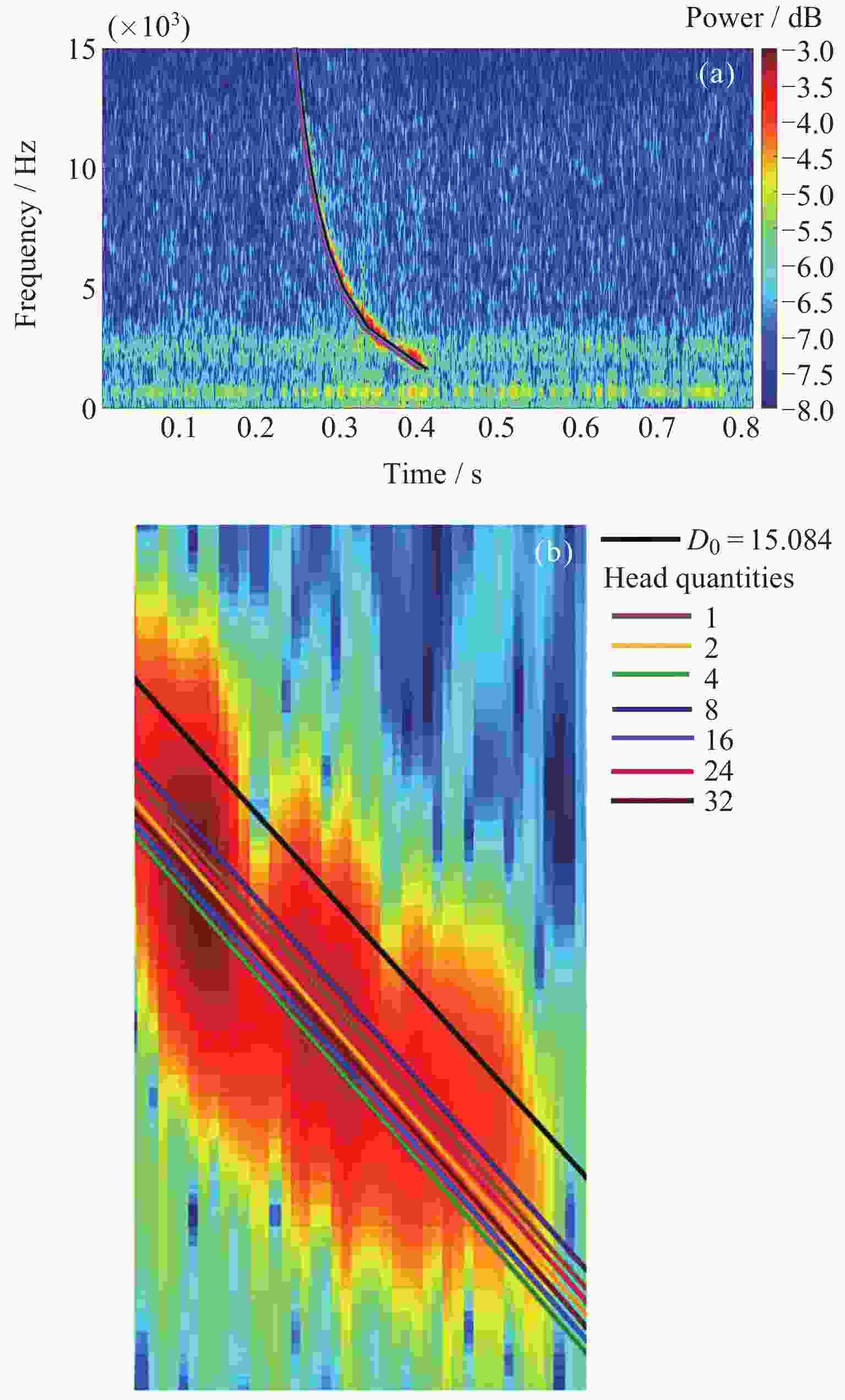
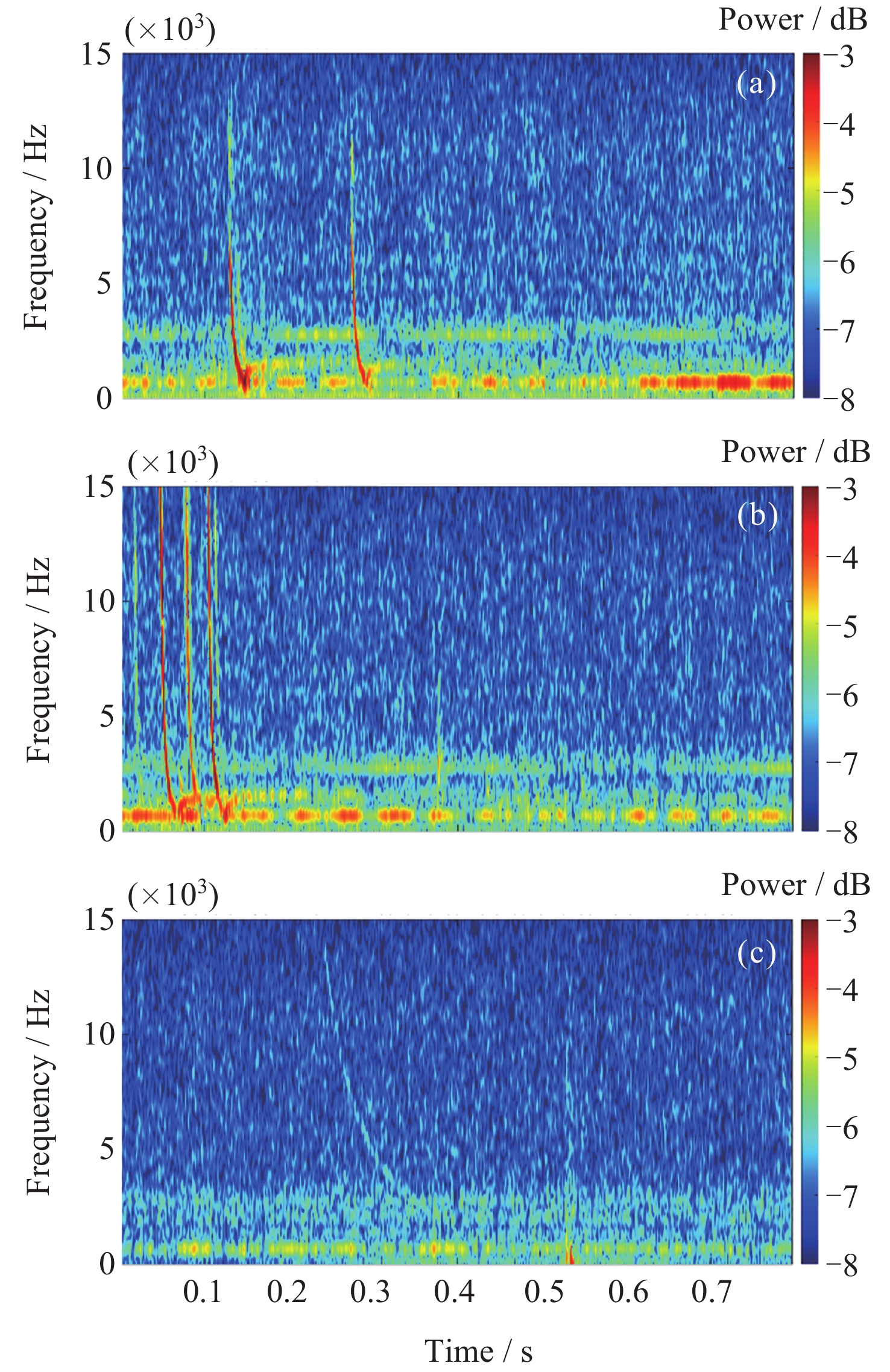
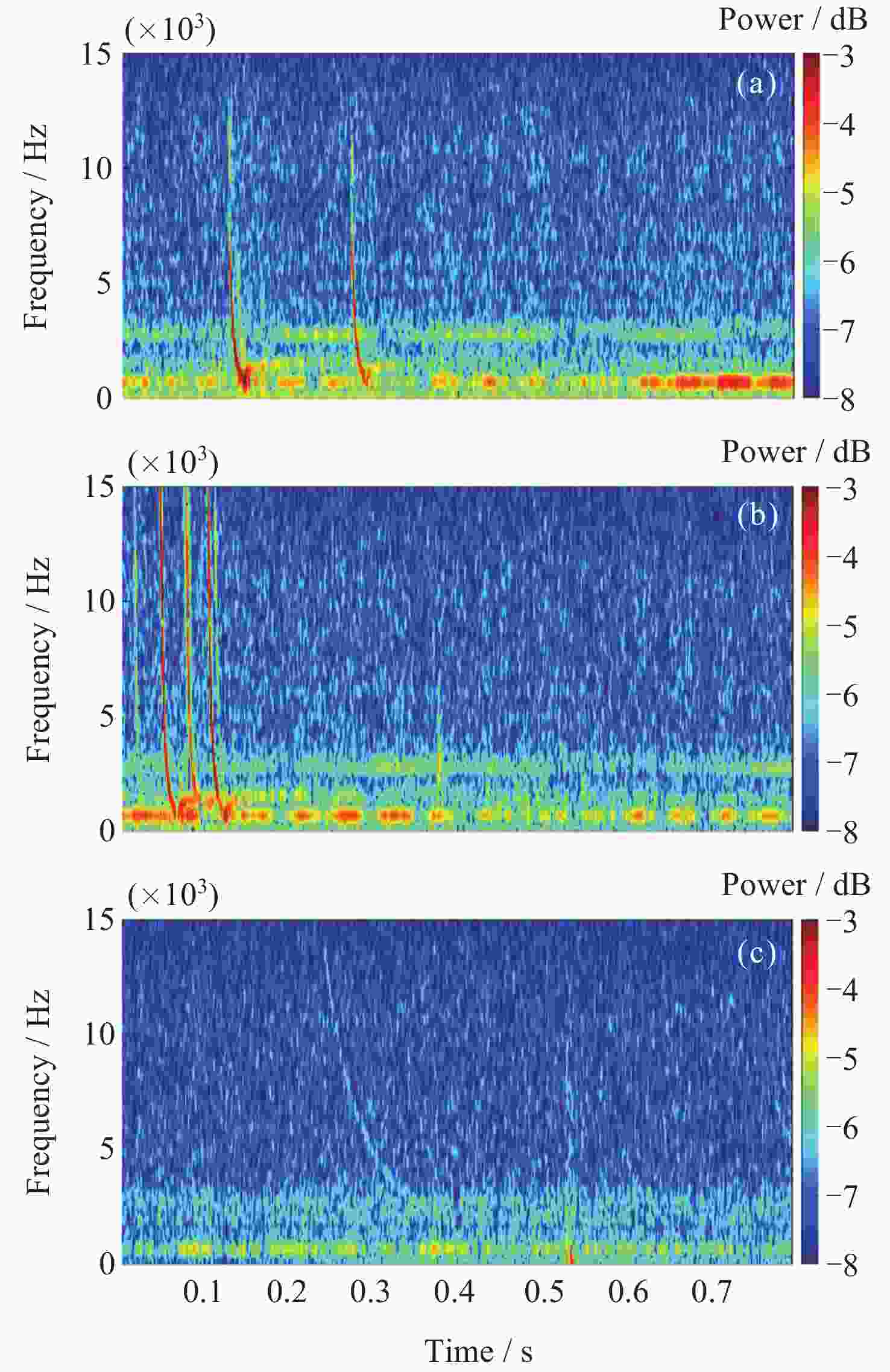
摘要: 张衡卫星日产数据高达20 GByte, 人工方法已经无法满足海量数据提取的需求. 提出了一种快速稳健的闪电哨声波散射系数自动提取方法. 将原始数据转换为时频图和音频文件; 针对时频图, 创建YOLOV5神经网络自动定位闪电哨声波, 输出其时频位置信息; 根据其时频位置信息截取对应音频文件得到含有闪电哨声波的音频数据, 并用零将其填充为0.8 s的音频片段; 提取音频片段的梅尔频率倒谱系数, 将其输入多头注意力机制改进的门控循环网络, 自动提取闪电哨声波散射系数. 将该方法应用于2020年2月的数据集, 得到如下结果: 其平均绝对误差和平均绝对百分比误差为0.453和0.176, 相比文献[
1 ]方法降低了70%和 46%. 每段数据平均处理时间为0.074 s, 相比文献[1 ]方法降低了92%. 本文提出的自动音频分析方法, 可较为准确和快速地提取闪电哨声波的散射系数.-
关键词:
- 张衡卫星 /
- GRU神经网络 /
- YOLOV5神经网络 /
- 闪电哨声波 /
- 散射系数
Abstract: The daily production data of the Zhangheng satellite can reach up to 20 GB, rendering manual methods inadequate for handling such massive data demands. This paper proposes a rapid and robust Lightning Whistle Scattering Coefficient Automatic Extraction Method (LWSC-AEM). Firstly, detailed data from the Search Coil Magnetometer (SCM) of the Zhangheng satellite is extracted using a sliding window of 0.8 seconds, which is then transformed into time-frequency plots and audio files. Secondly, a YOLOV5 neural network is employed to automatically locate LW in the time-frequency plots and output their time-frequency position information. Subsequently, the corresponding audio data containing Lightning Whistlers is extracted based on this time-frequency position information from the files, and zero-padded to form audio segments of 0.8 seconds. Finally, the Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs) of the audio segments are extracted and fed into a Gate Recurrent Unit (GRU) improved with a multi-head attention mechanism to automatically extract the LW scattering coefficient. Applying this method to the data from the VLF band of the SCM payload of the Zhangheng satellite in February 2020 yields the following results: the average absolute error and average absolute percentage error are 0.453 and 0.176 respectively. Compared to the method by Ref. [1 ], the average absolute error is reduced by 1.079, a decrease of 70%, and the average absolute percentage error is reduced by 0.148, a decrease of 46%. The average processing time per data segment is 0.074 seconds, which is a reduction of 0.826 seconds, or 92%, compared to the method by Ref. [1 ], which processed each data segment on average. The automatic extraction method for lightning whistler wave scattering coefficients proposed in this paper can quickly and accurately extract these coefficients. -
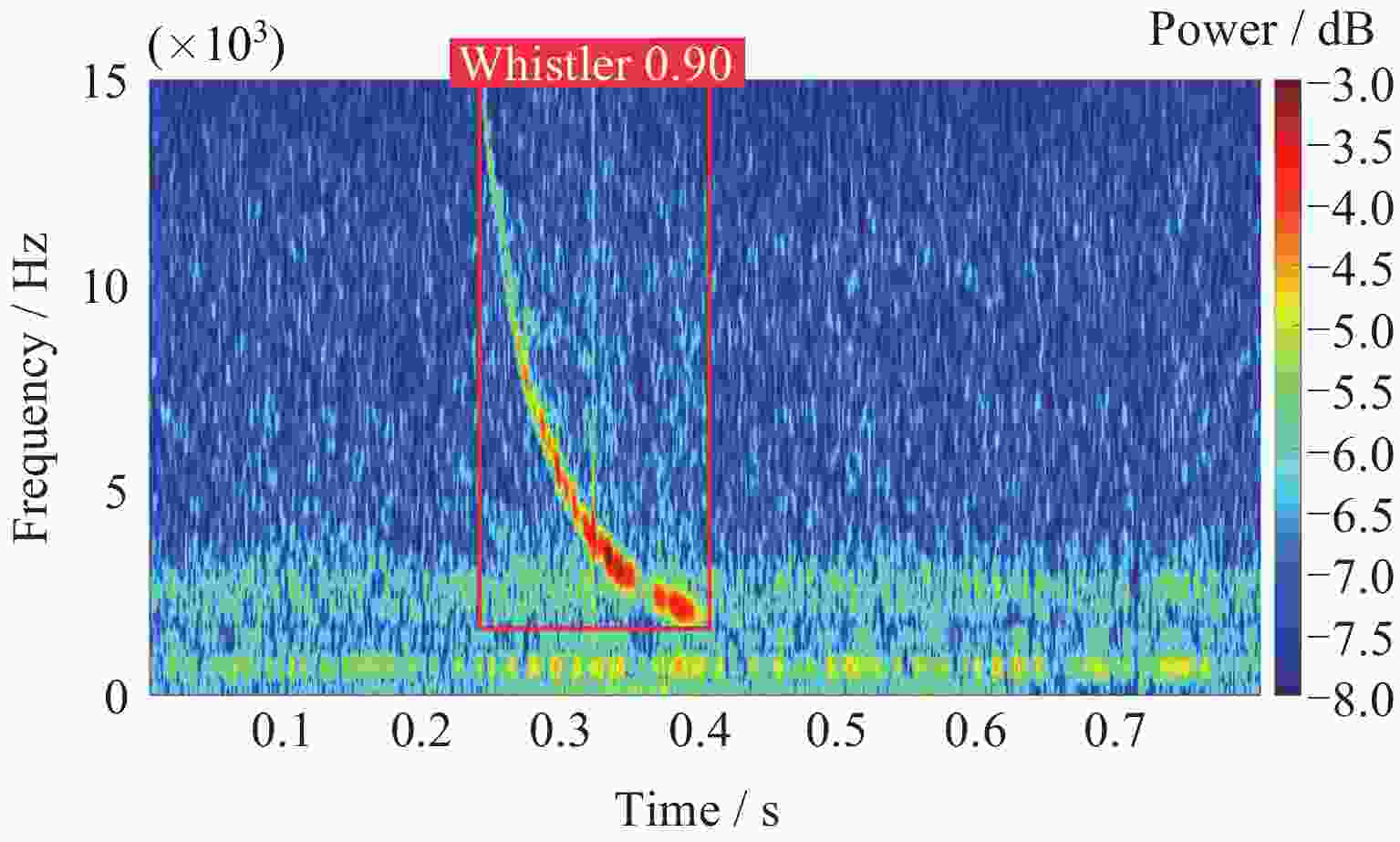
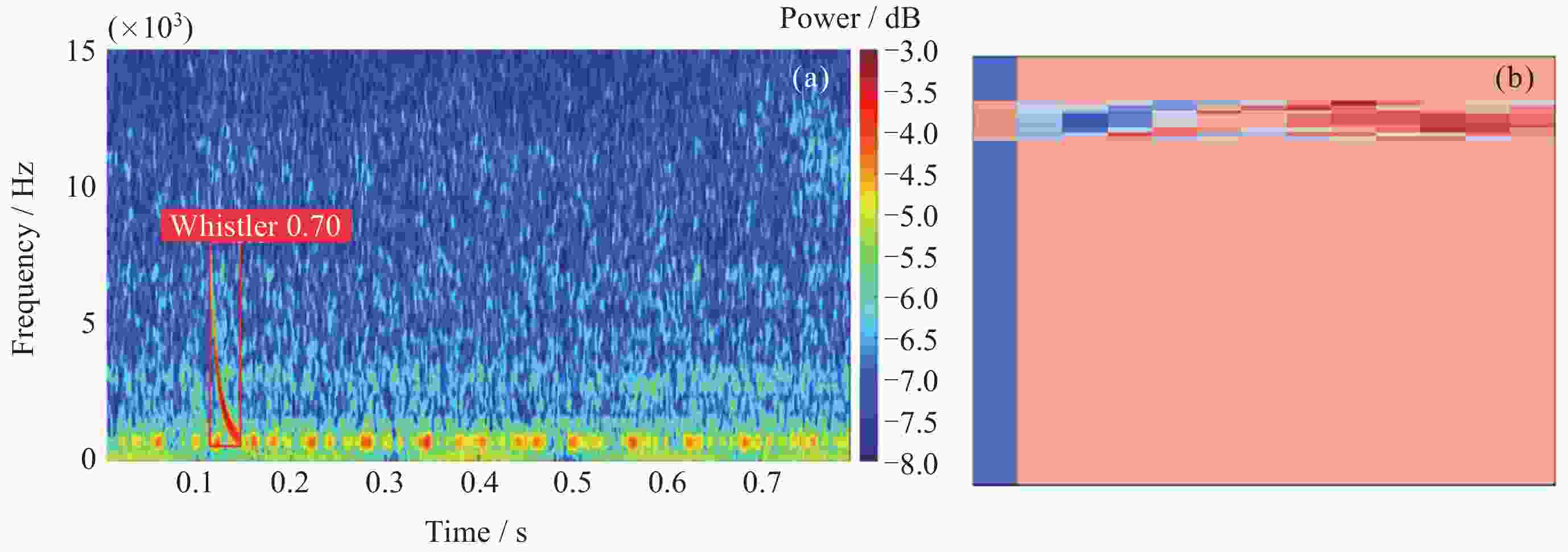
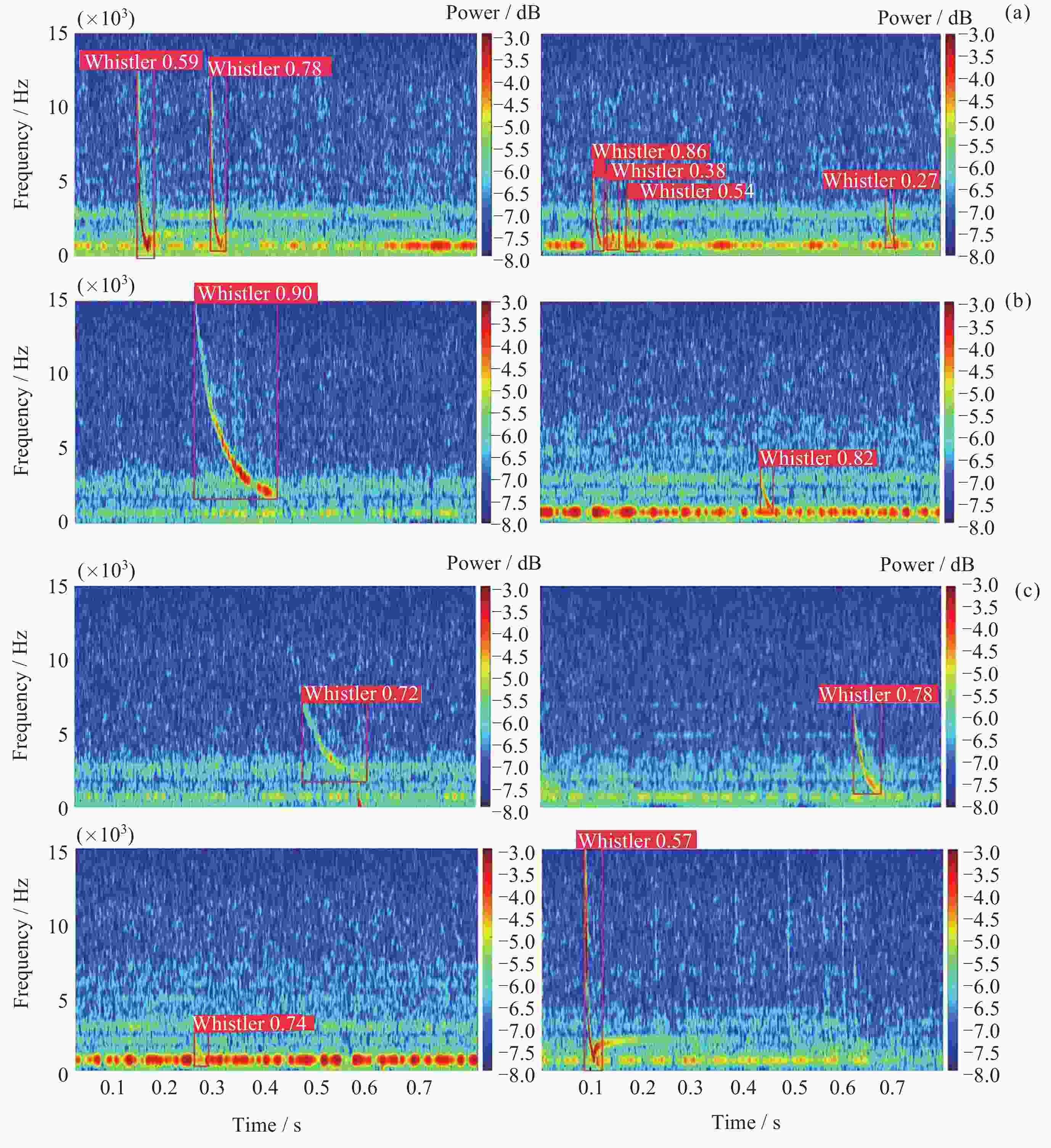
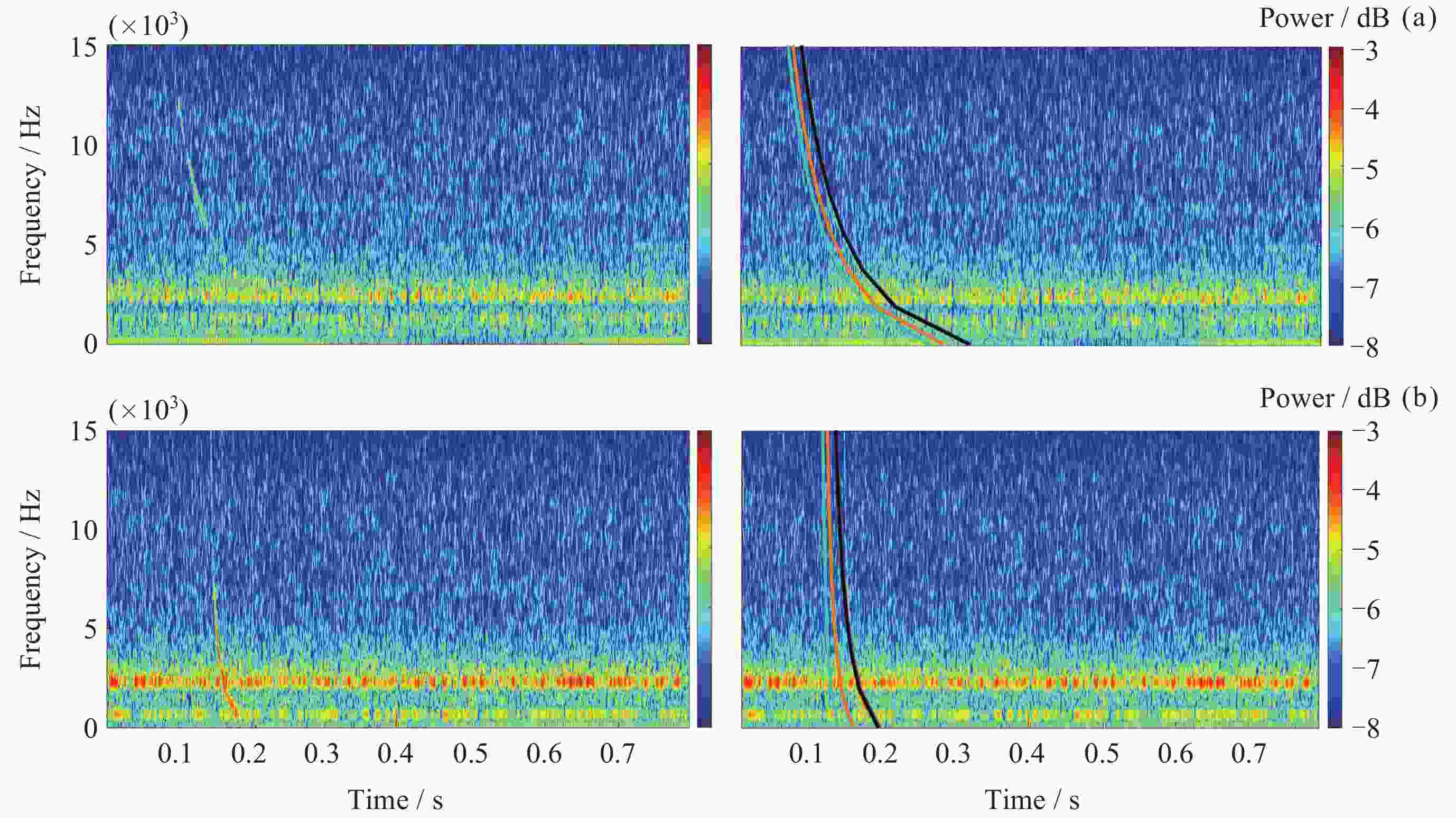
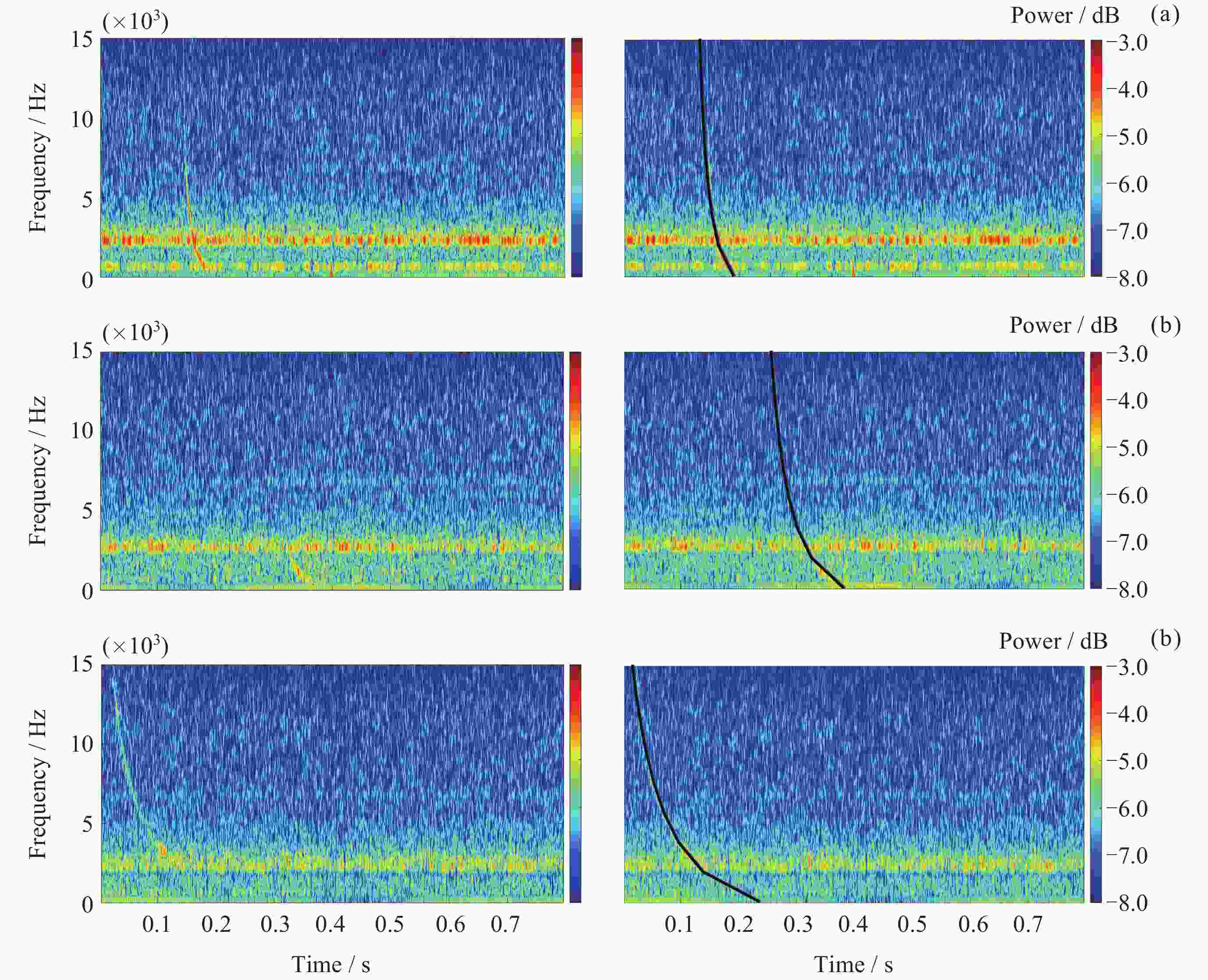
表 1 闪电哨声波识别结果
Table 1. Lightning whistle localization outcome
算法名称 P/(%) R/(%) YOLOV5 91.8 93.4 表 2 散射系数提取结果
Table 2. Scattering coefficient extraction results
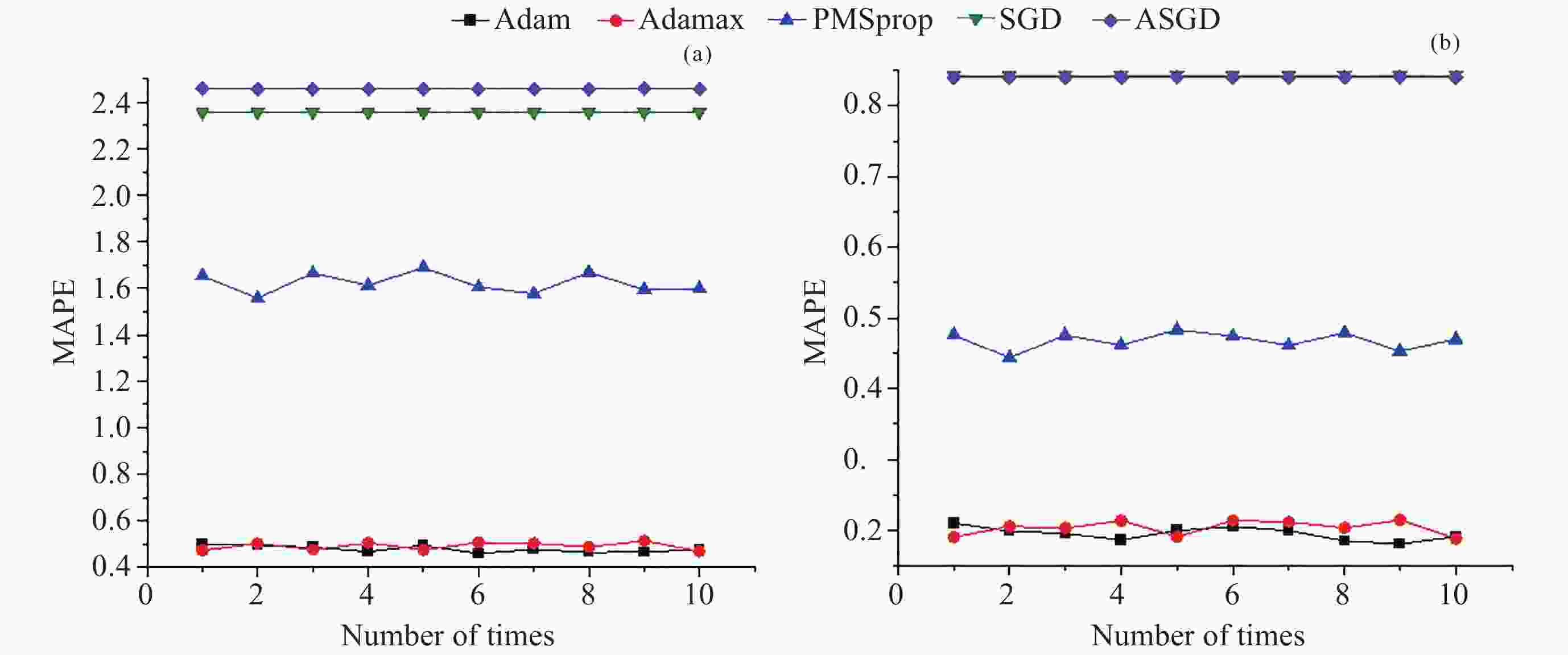
性能指标 $ \mathrm{M}\mathrm{A}\mathrm{E} $ $ \mathrm{M}\mathrm{A}\mathrm{P}\mathrm{E} $ 人工方法 - - GRU-MHA 0.453 0.176 GRU-WH 2.361 0.876 Unet-WH 1.532 0.324 表 3 散射系数提取时间情况
Table 3. Scattering coefficient extraction time
性能指标 AET/s 人工方法 360 LWSC-AEM 0.074 Unet-WH 0.9 -
[1] FENG Xiaokang, YUAN Jing, WANG Qiao, et al. Automatic extraction of physical parameters of lightning whistler recorded by search coil magnetometer onboard ZhangHeng Satellite[J/OL]. Progress in Geophysics, 2023, 38(6): 2373-2391 [2] CHEN Y P, NI B B, GU X D, et al. First observations of low latitude whistlers using WHU ELF/VLF receiver system[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2017, 60(1): 166-174 doi: 10.1007/s11431-016-6103-5 [3] CARPENTER D L, ANDERSON R R. An ISEE/whistler model of equatorial electron density in the magnetosphere[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1992, 97(A2): 1097-1108 doi: 10.1029/91JA01548 [4] SINGH A K, VERMA U P, BHARGAWA A. Remote sensing of Mid/Upper atmosphere using ELF/VLF waves[J]. Global Journal of Science Frontier Research: A Physics and Space Science, 2018, 18(10): 10-21 [5] OIKE Y, KASAHARA Y, GOTO Y. Spatial distribution and temporal variations of occurrence frequency of lightning whistlers observed by VLF/WBA onboard Akebono[J]. Radio Science, 2014, 49(9): 753-764 doi: 10.1002/2014RS005523 [6] BAYUPATI I P A, KASAHARA Y, GOTO Y. Study of dispersion of lightning whistlers observed by Akebono satellite in the earth’s plasmasphere[J]. IEICE Transactions on Communications, 2012, E95. B(11): 3472-3479 [7] CLILVERD M A, NUNN D, LEV-TOV S J, et al. Determining the size of lightning-induced electron precipitation patches[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2002, 107(A8): SIA 10-1-SIA 10-11 [8] KISHORE A, DEO A, KUMAR S. Upper atmospheric remote sensing using ELF–VLF lightning generated tweek and whistler sferics[J]. The South Pacific Journal of Natural and Applied sciences, 2016, 34(1): 12-20 doi: 10.1071/SP16002 [9] PARROT M, PINÇON J L, SHKLYAR D. Short-fractional hop whistler rate observed by the low-altitude satellite DEMETER at the end of the solar cycle 23[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2019, 124(5): 3522-3531 doi: 10.1029/2018JA026176 [10] HORNE R B, GLAUERT S A, MEREDITH N P, et al. Space weather impacts on satellites and forecasting the Earth’s electron radiation belts with SPACECAST[J]. Space Weather, 2013, 11(4): 169-186 doi: 10.1002/swe.20023 [11] REN Y, DAI L, LI W, et al. Whistler waves driven by field-aligned streaming electrons in the near-Earth magnetotail reconnection[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2019, 46(10): 5045-5054 doi: 10.1029/2019GL083283 [12] REN Y, DAI L, WANG C, et al. Statistical characteristics in the spectrum of whistler waves near the diffusion region of dayside magnetopause reconnection[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2021, 48(1): e2020GL090816 doi: 10.1029/2020GL090816 [13] ZHOU Huaibei, XIAO Zuo, SUN Chuanli. A study of cloud-earth lightning parameters by using whistler spectrum[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 1989(1): 1-7 doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.1989.01.001 [14] 何友文. 哨声“源”的分析[J]. 空间科学学报, 1981, 1(2): 143-152 doi: 10.11728/cjss1981.02.143HE Youwen. An analysis of whistler sources[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 1981, 1(2): 143-152 doi: 10.11728/cjss1981.02.143 [15] ARTEMYEV A V, LAPSHIN N V, SIMONOV S A. Prospects of predicting the number of geese on spring migration stopover sites in Karelia[J]. The Herald of Game Management, 2014, 11(2): 249-255 [16] HU Yunpeng, ZHIMA Zeren, HUANG Jianping, et al. Algorithms and implementation of wave vector analysis tool for the electromagnetic waves recorded by the CSES satellite[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2020, 63(5): 1751-1765 doi: 10.6038/cjg2020N0405 [17] HELLIWELL R A. Whistlers and Related Ionospheric Phenomena[M]. Stanford: Stanford University Press, 1965 [18] LICHTENBERGER J, FERENCZ C, BODNÁR L, et al. Automatic whistler detector and analyzer system: automatic whistler detector[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2008, 113(A12): A12201 [19] Stanford VLF Group. Automated detection of whistlers for the TARANIS spacecraft overview of the project[EB/OL]. 2009 [20] DHARMA K S, BAYUPATI I P A, BUANA P W. Automatic lightning whistler detection using connected component labeling method[J]. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology, 2014, 66(2): 638-645 [21] KONAN O J E Y, MISHRA A K, LOTZ S. Machine learning techniques to detect and characterise whistler radio waves[OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2002.01244v1, 2020 [22] YUAN Jing, WANG Qiao, ZHANG Xuemin, et al. Advances in the automatic detection algorithms for lightning whistlers recorded by electromagnetic satellite data[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2021, 64(5): 1471-1495. DOI: 10.6038/cjg2021O0263 [23] YUAN Jing, WANG Qiao, YANG Dehe, et al. Automatic recognition algorithm of lightning whistlers observed by the Search Coil Magnetometer onboard the Zhangheng-1 Satellite[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2021, 64(11): 3905-3924. DOI: 10.6038/cjg2021O0164 [24] YUAN Jing, WANG Zijie, ZHIMA Zeren, et al. Automatic recognition algorithm of the lightning whistler waves by using speech processing technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2022, 65(3): 882-897. DOI: 10.6038/cjg2022P0365 [25] ECKERSLEY T L. Musical atmospherics[J]. Nature, 1935, 135(3403): 104-105 doi: 10.1038/135104a0 [26] DAI Jian, ZHAO Xu, LI Lianpeng, et al. Improved YOLOV5-based infrared dim-small target detection under complex background[J]. Infrared Technology, 2022, 44(5): 504-512 [27] HE Yu, TIAN Junwei, ZHANG Zhen, et al. Lightweight research of YOLOV5 target detection[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2023, 59(1): 92-99 [28] SHAO Yanhua, ZHANG Duo, CHU Hongyu, et al. A review of YOLO object detection based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Electronics :Times New Roman;">& Information Technology, 2022, 44(10): 3697-3708. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT210790 [29] PANG Cong, JIANG Yong, LIAO Chengwang, et al. Automatic recognition of natural earthquakes and artificial blasting based on the sample entropy of the Mel frequency cepstrum coefficient and support vector machine optimized by gray wolf optimization[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2022, 44(5): 1169-1175 [30] 袁正午, 肖旺辉. 改进的混合MFCC语音识别算法研究[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2009, 45(33): 108-110YUAN Zhengwu, XIAO Wanghui. Improved speech recognition algorithm based on MFCC feature[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2009, 45(33): 108-110 [31] TAN Xiangyong, HU Tianying, LIU Feng. Serial correlation test for linear models under Huber loss[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology (Natural Science), 2023, 37(8): 342-347 -
-





 韩金昇 男, 1999年1月出生于河北省唐山市, 硕士. 主要研究方向为地球观测数据智能处理与分析等领域. E-mail:
韩金昇 男, 1999年1月出生于河北省唐山市, 硕士. 主要研究方向为地球观测数据智能处理与分析等领域. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: