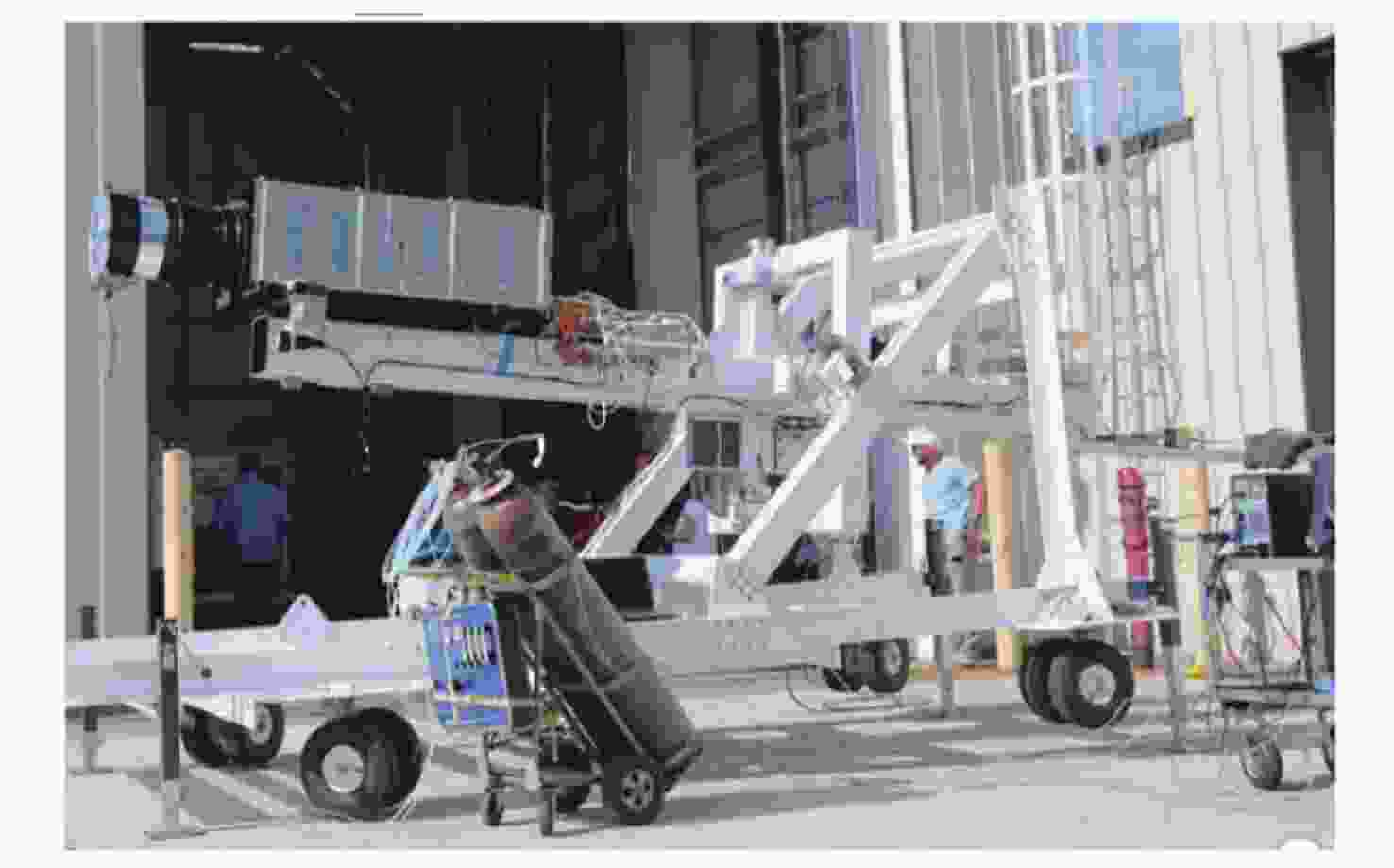
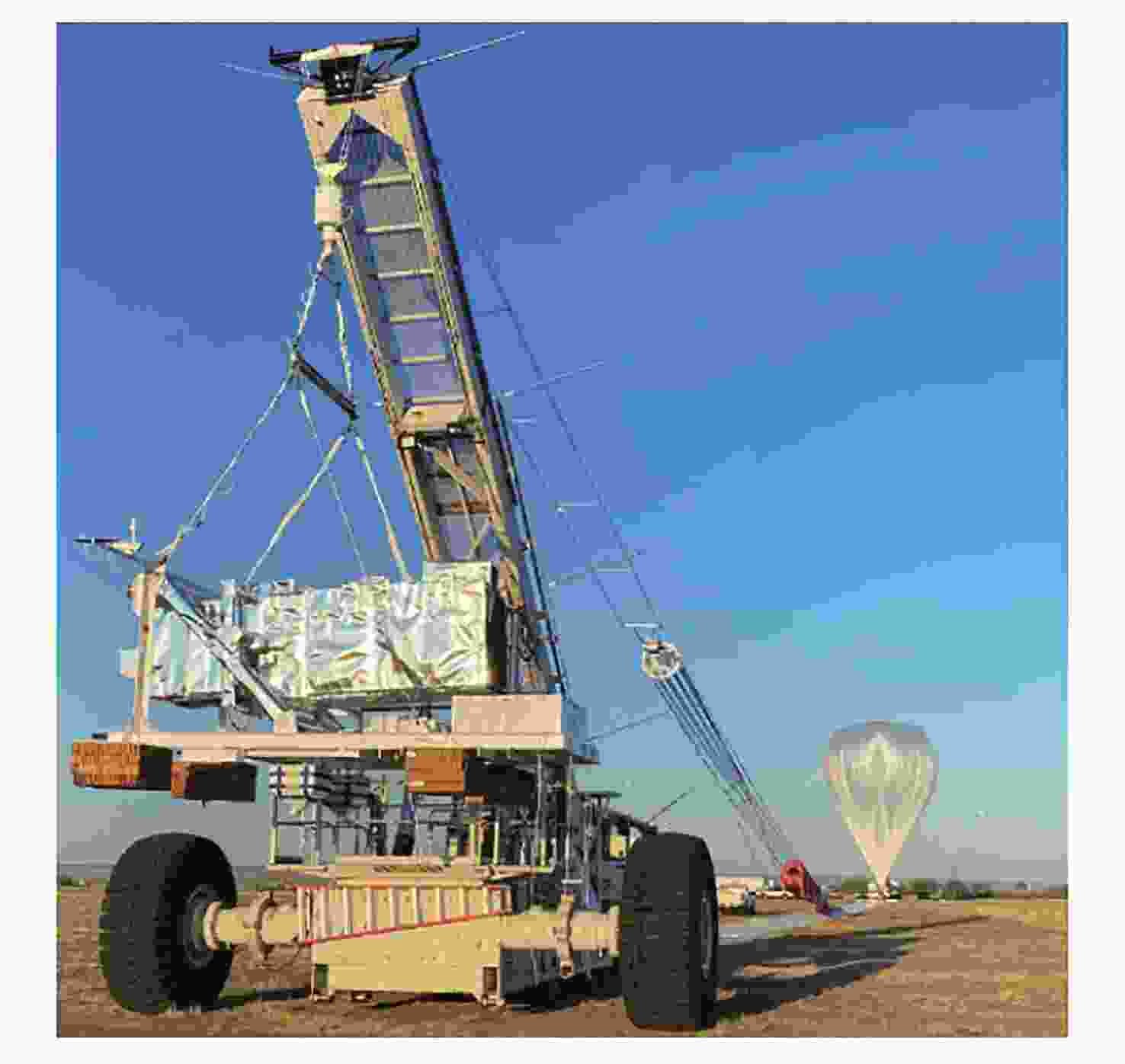
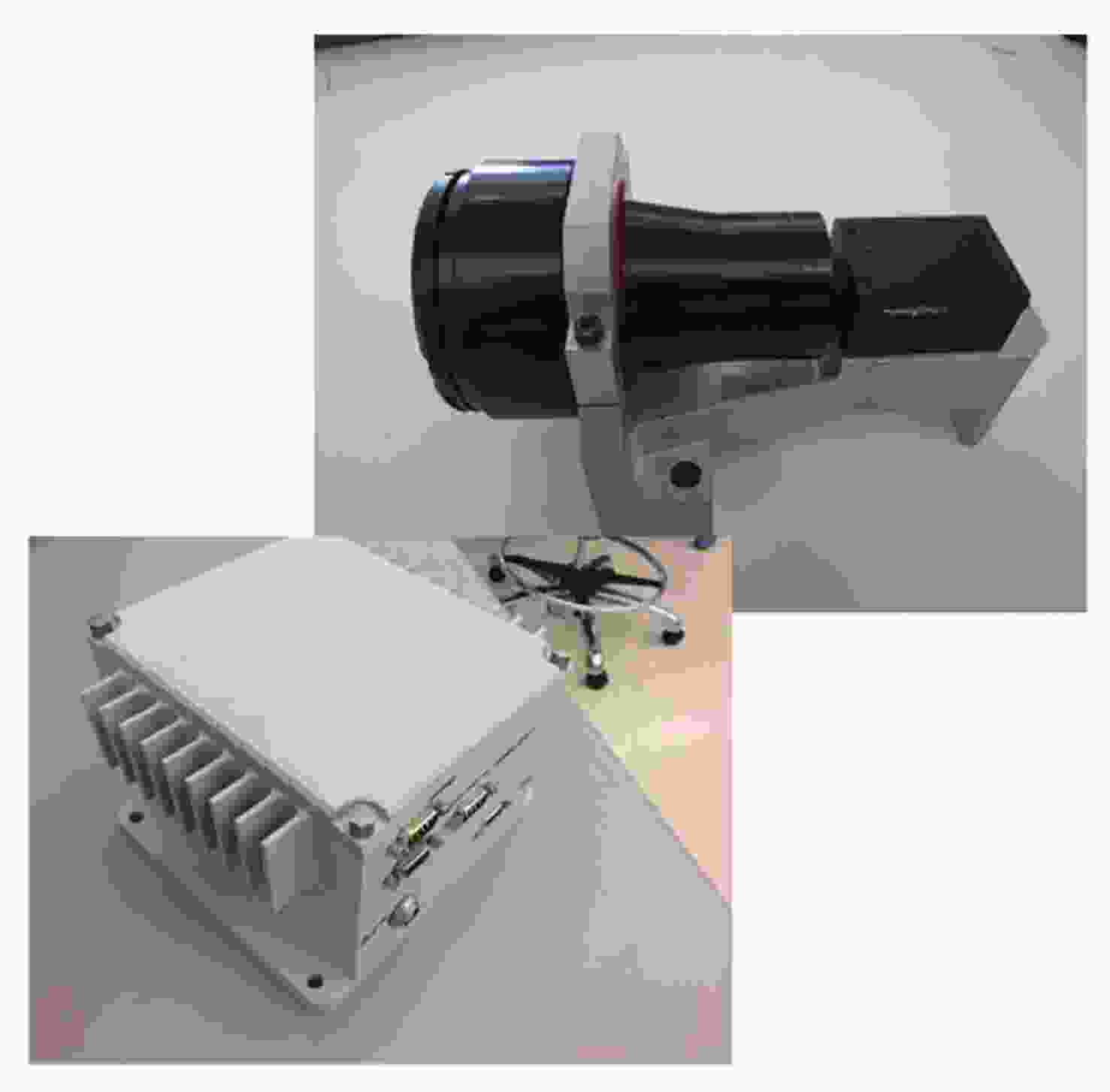
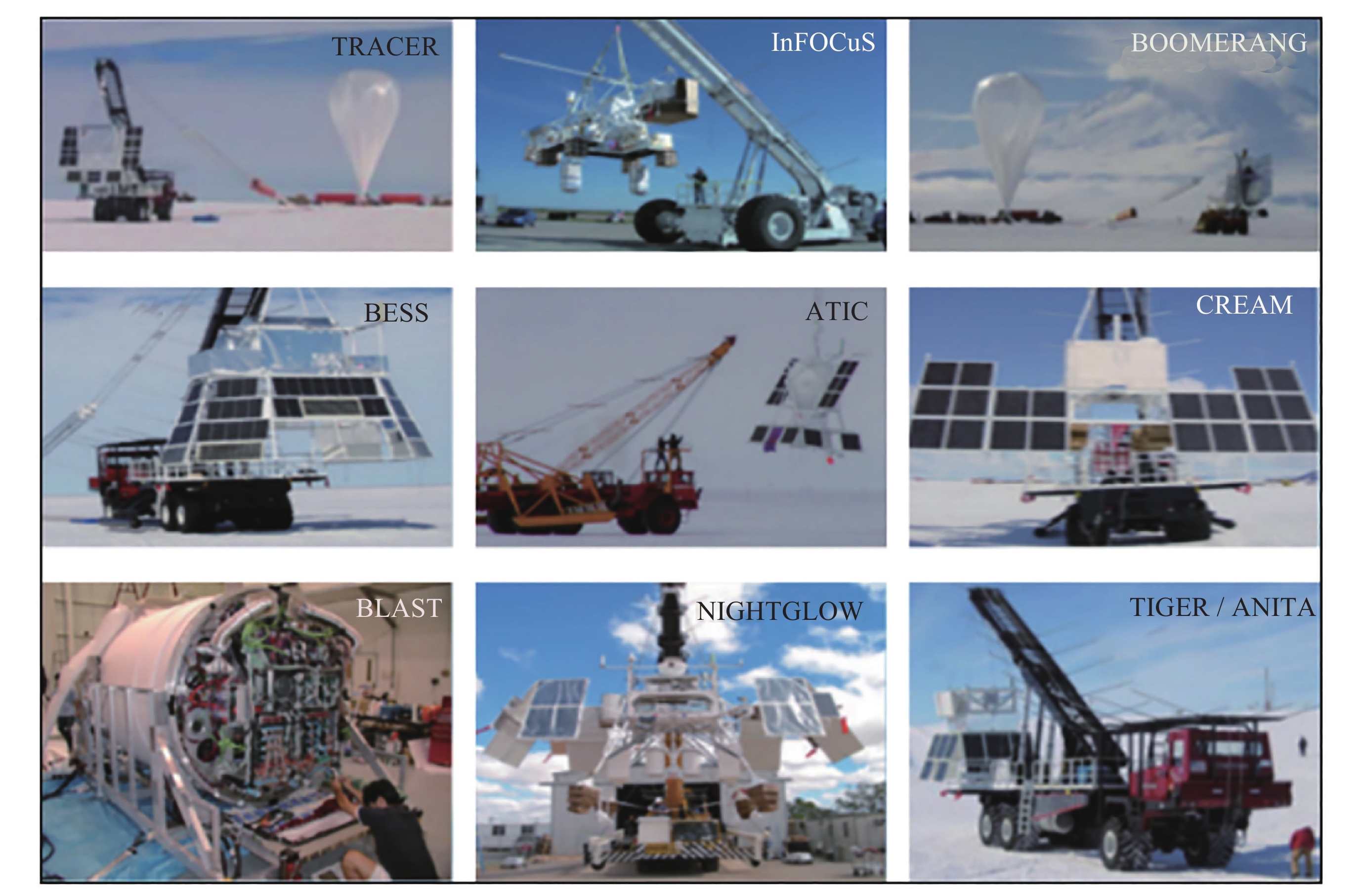
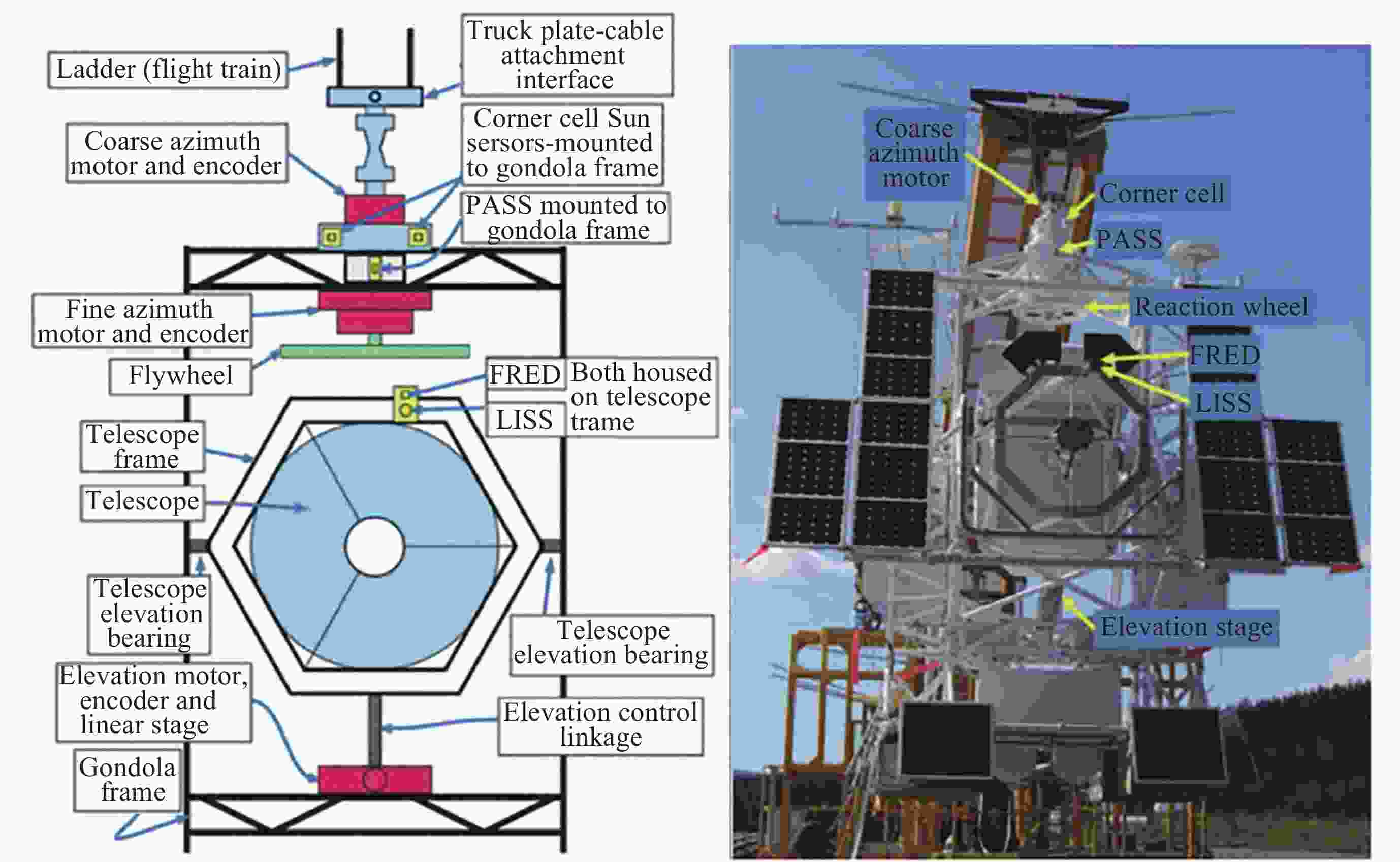
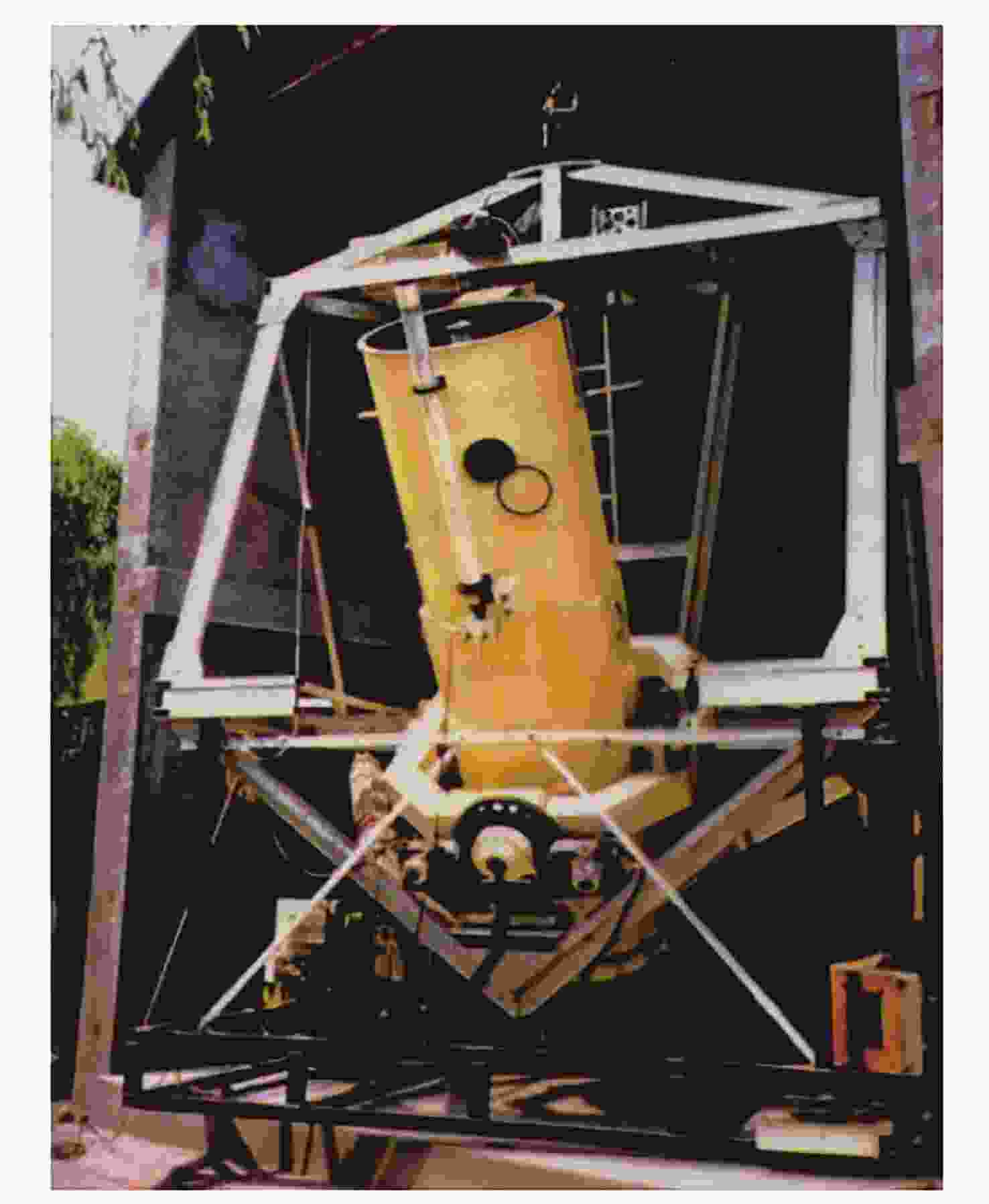
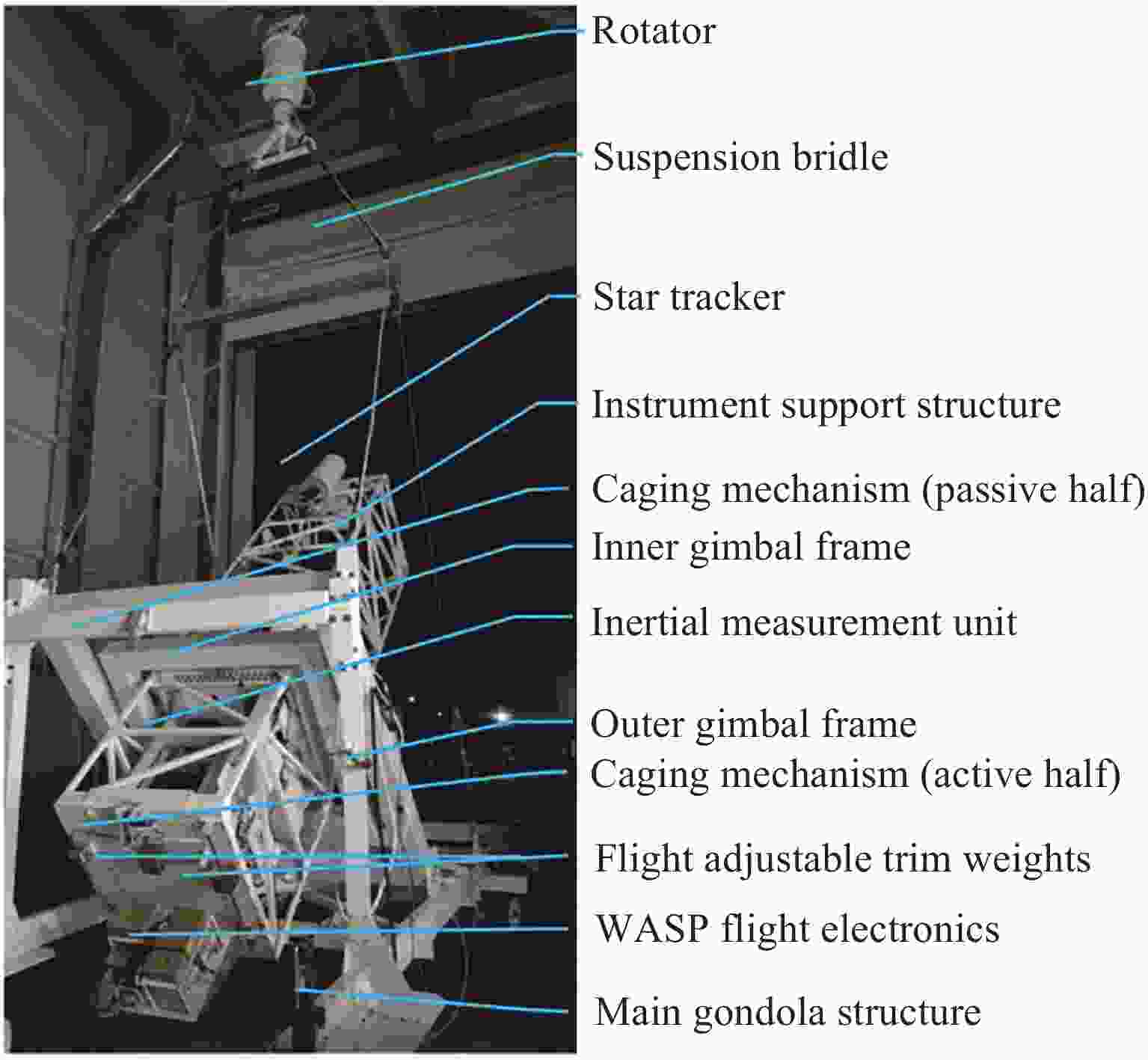
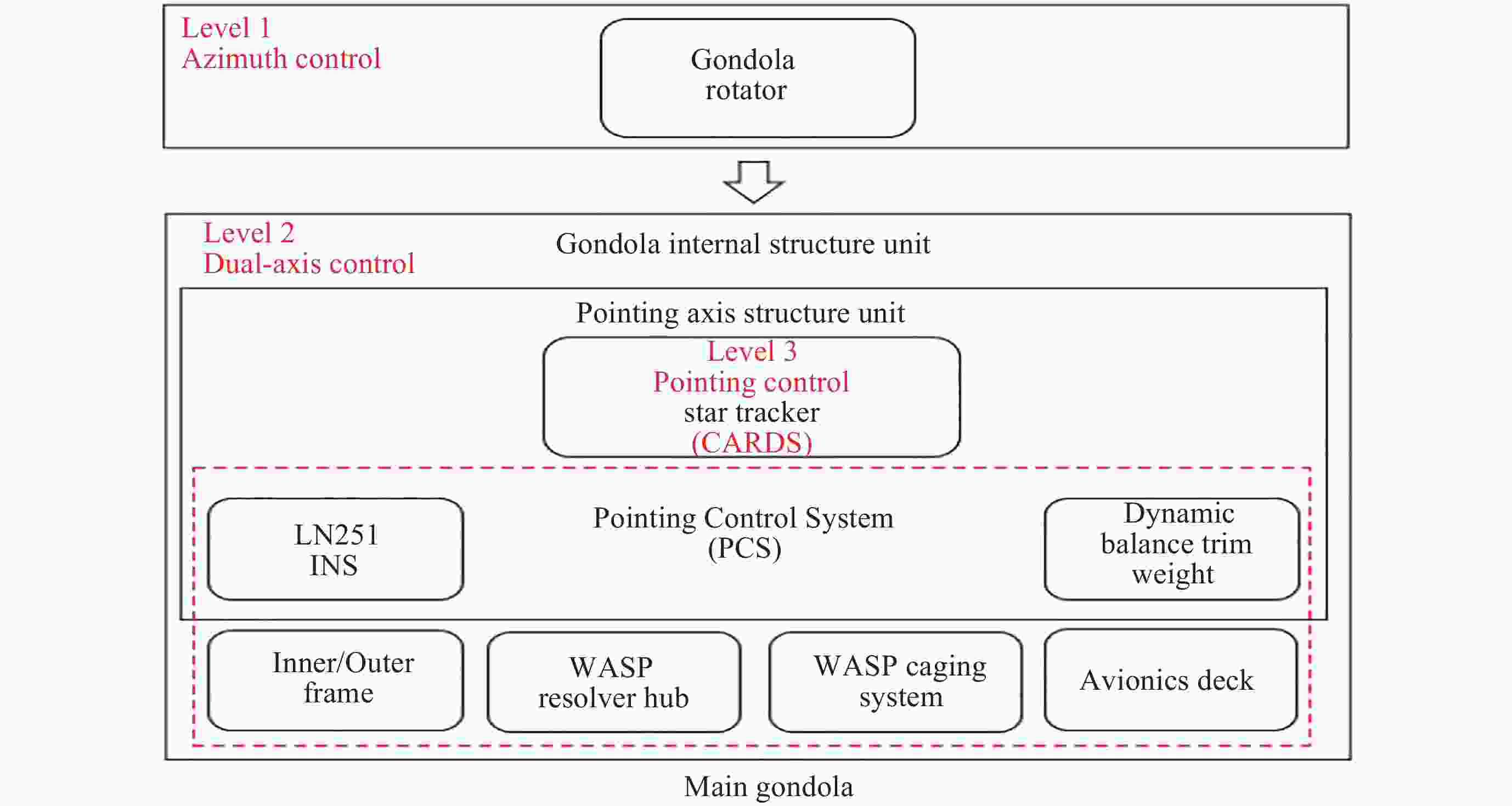
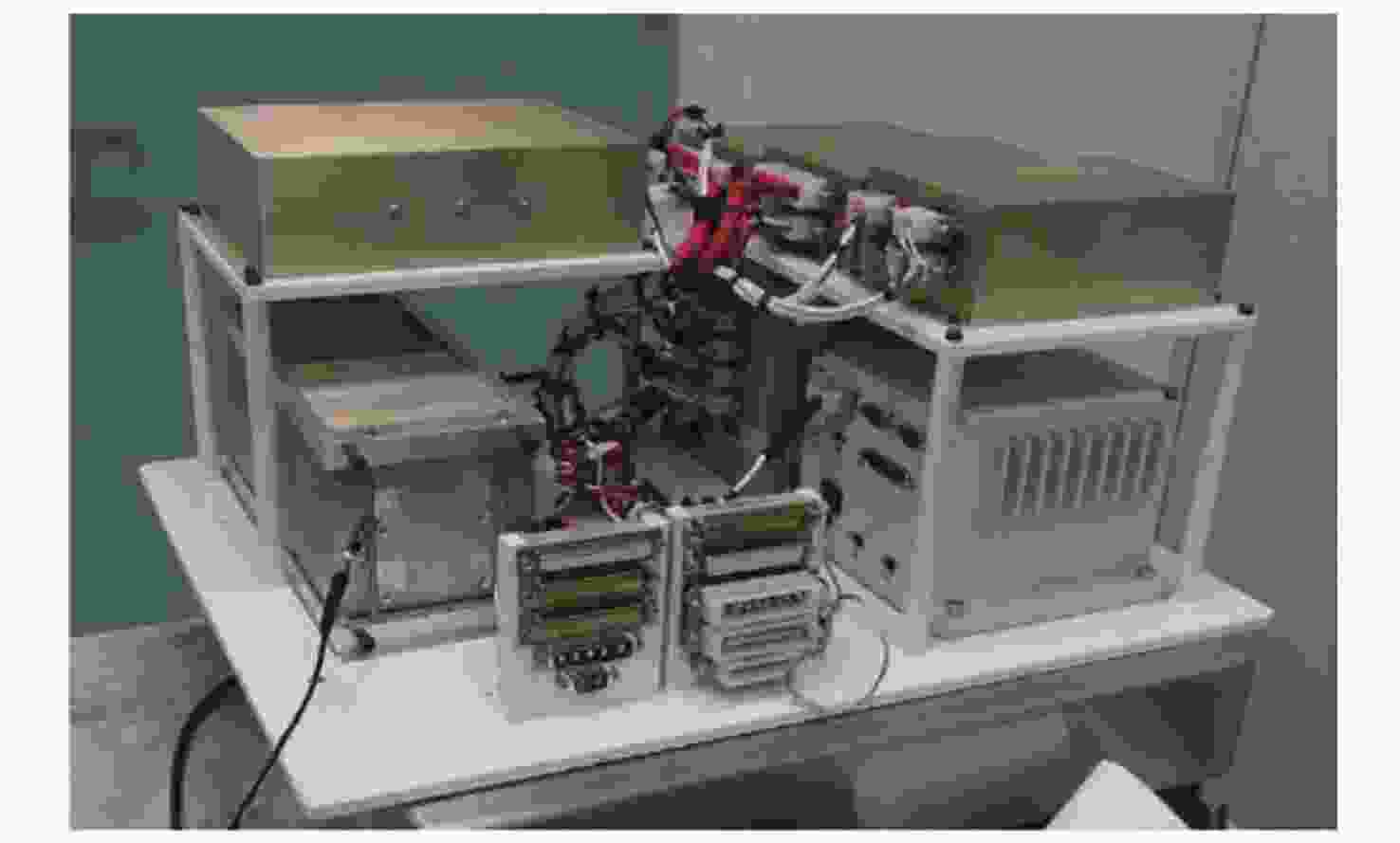
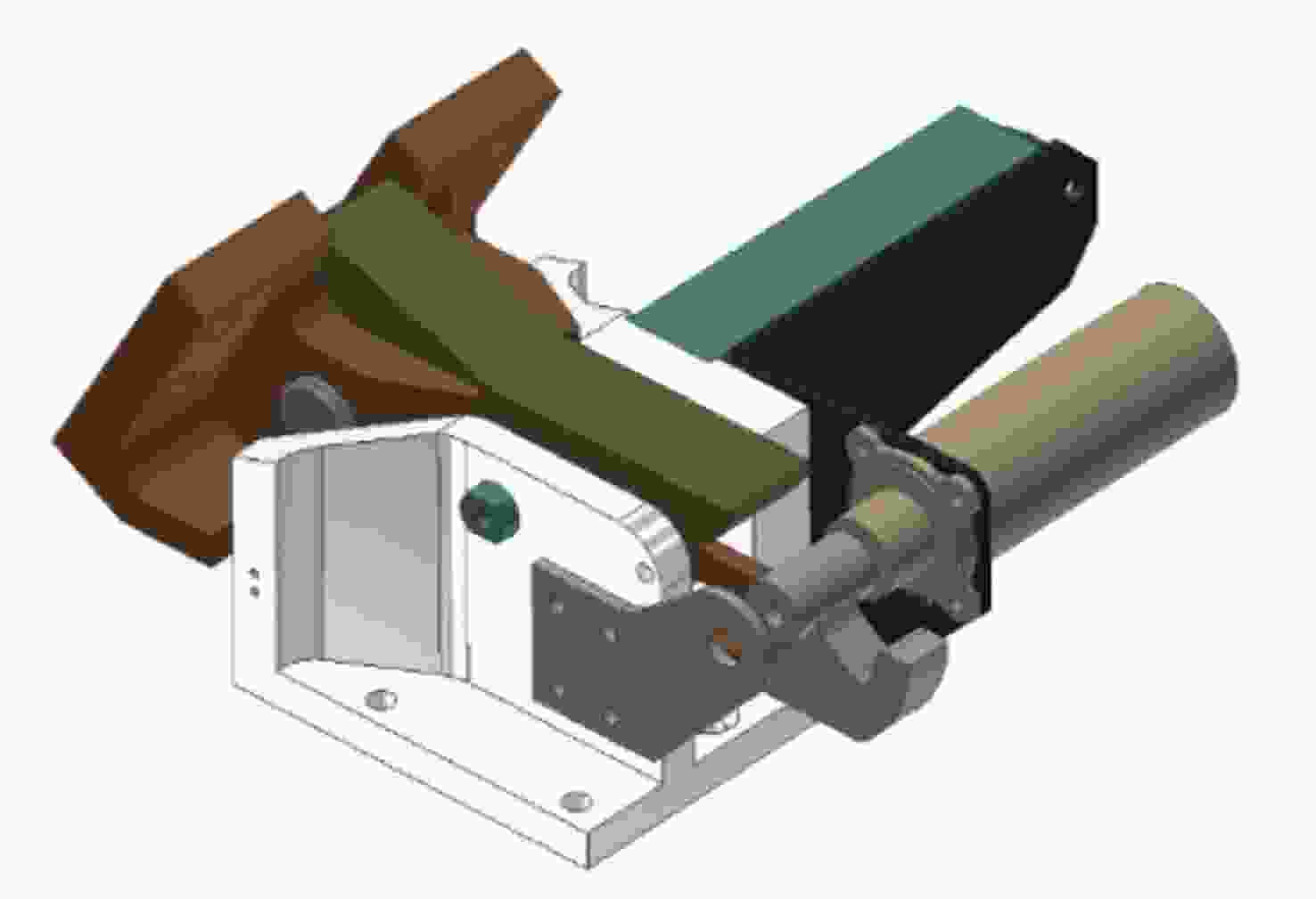
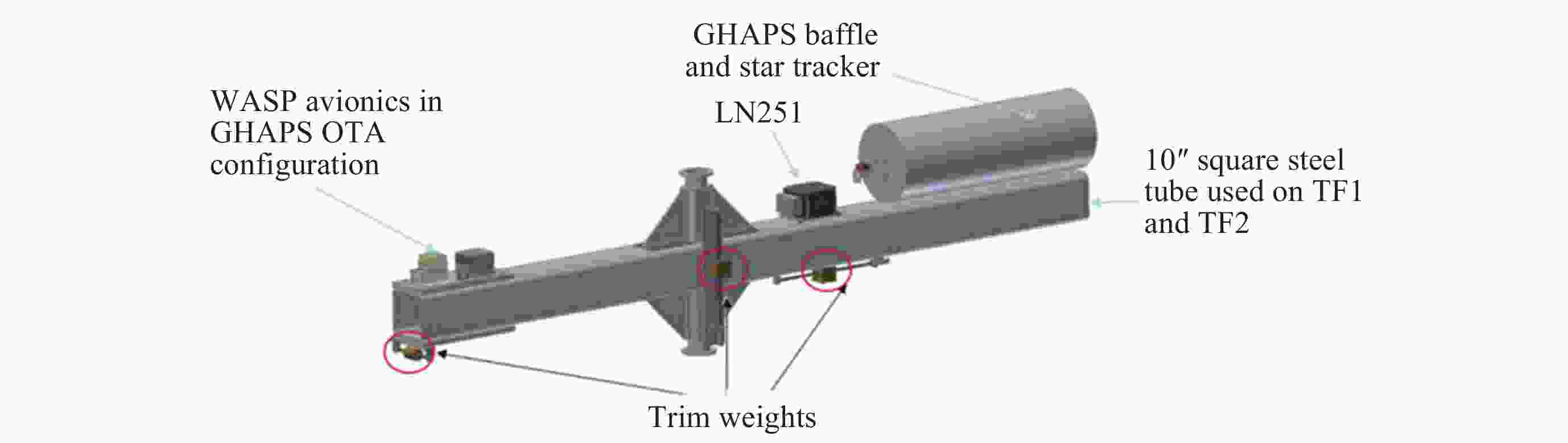
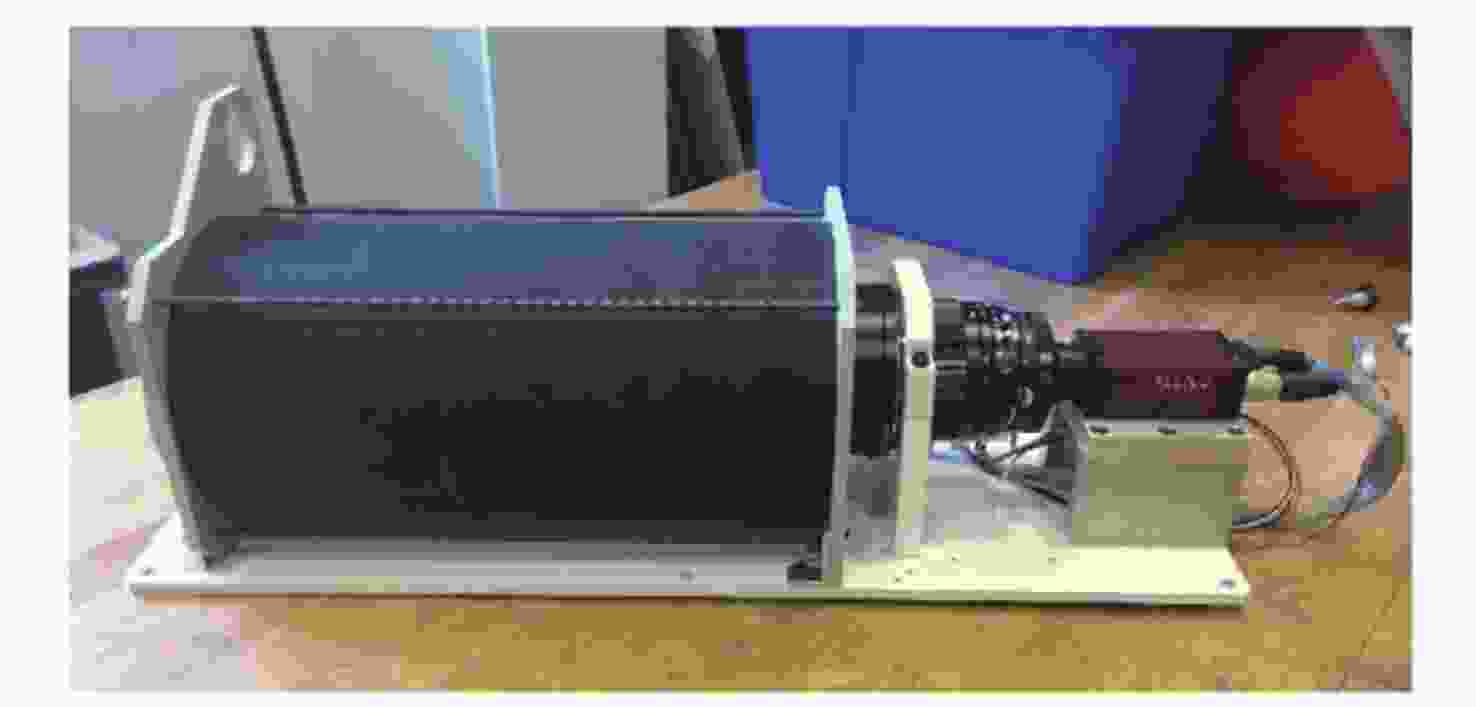
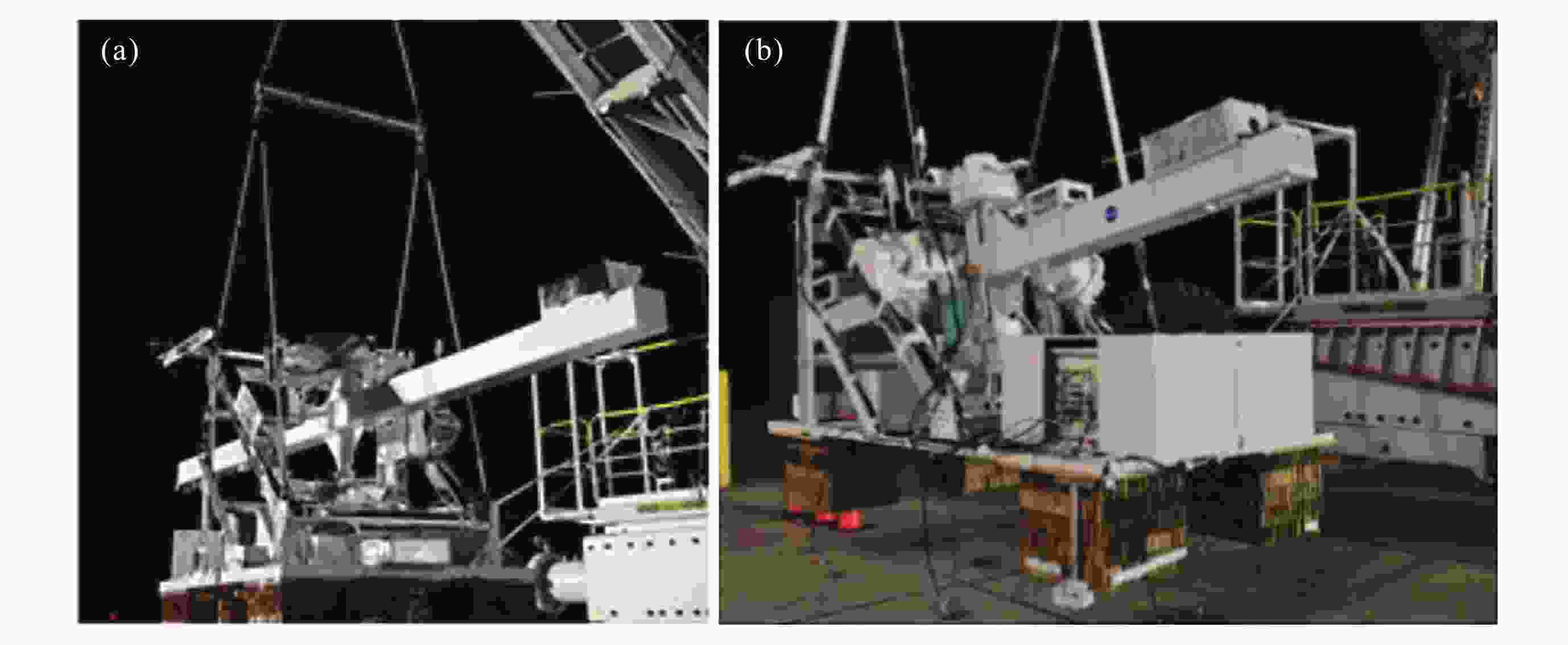
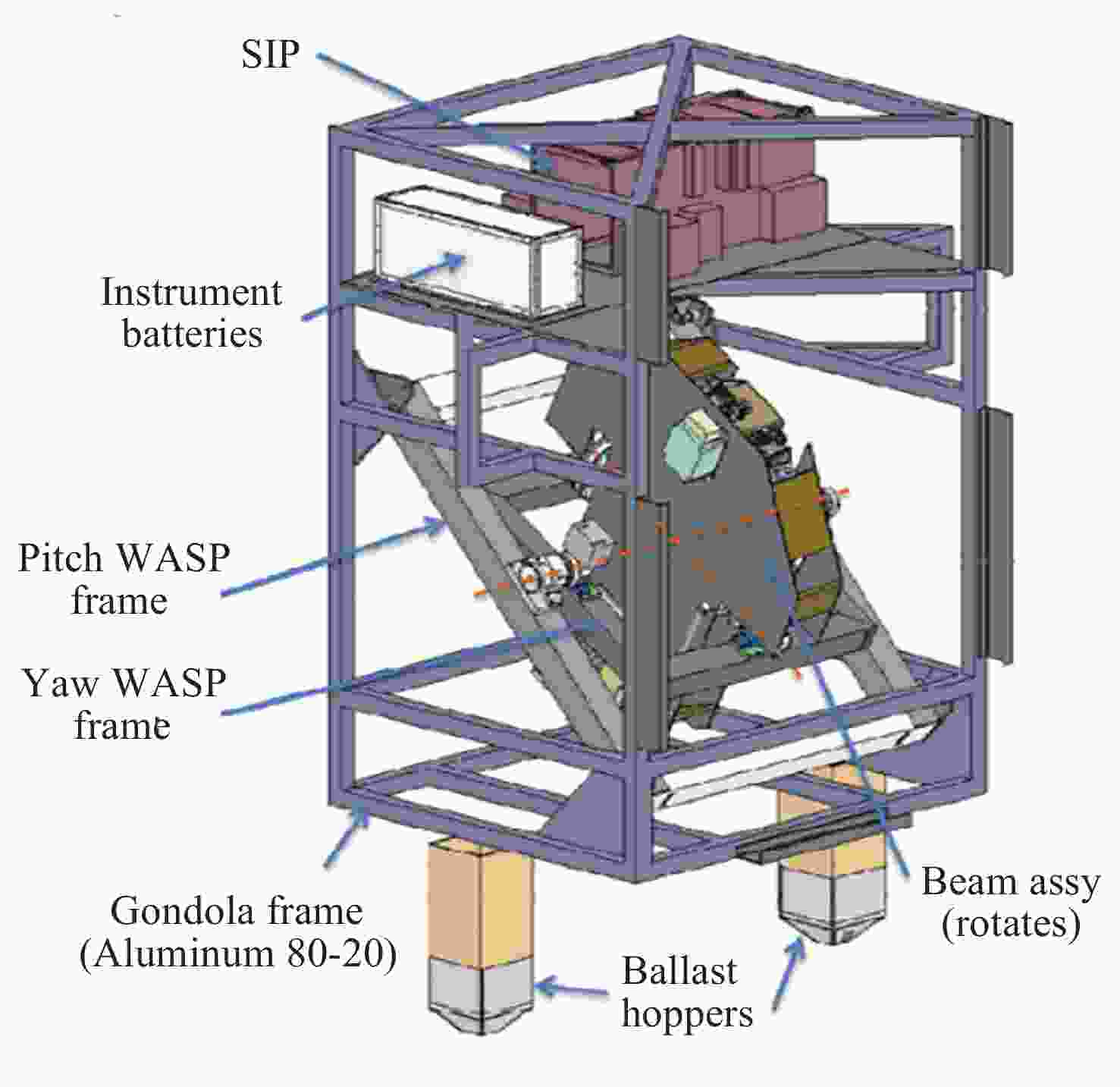
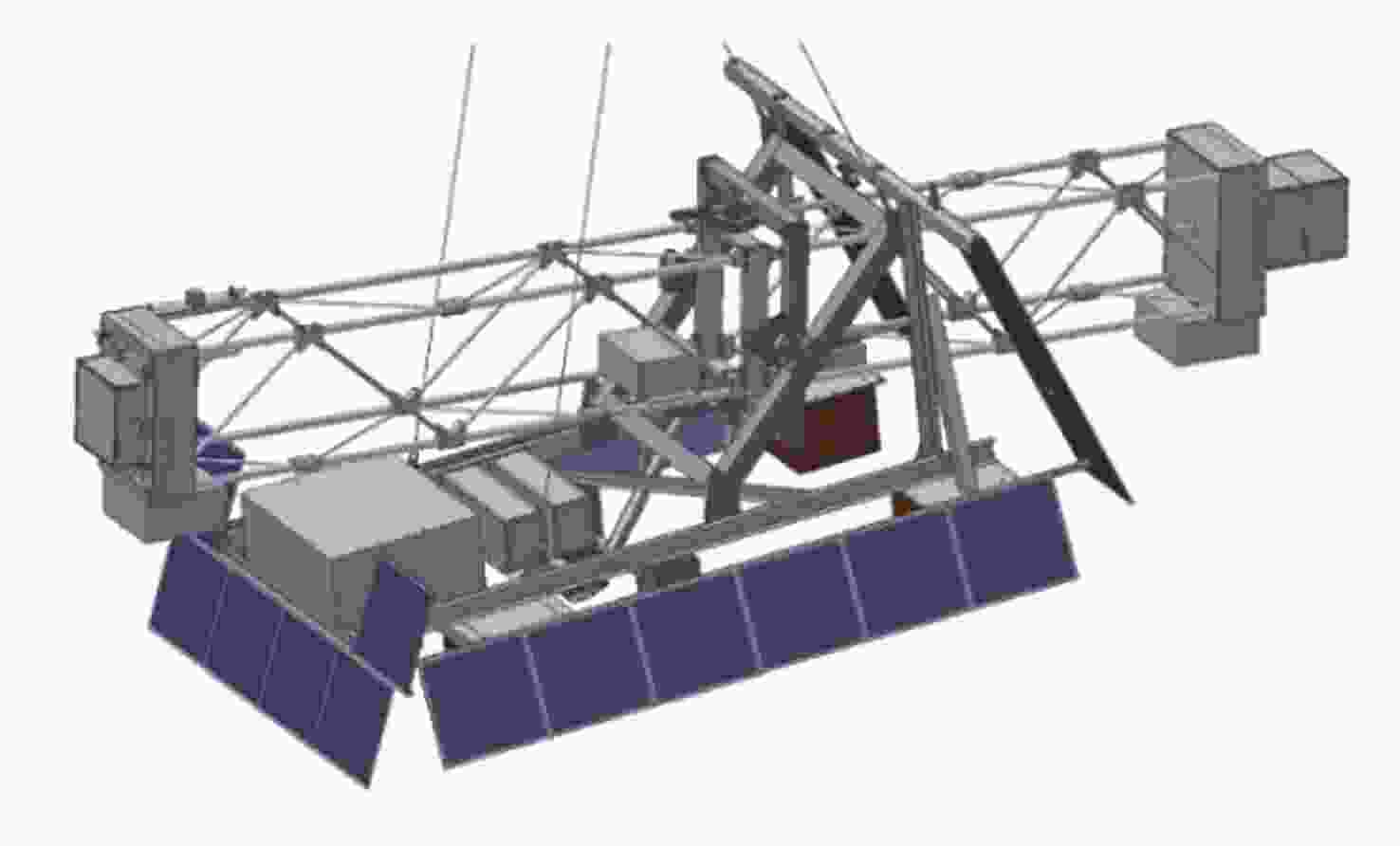
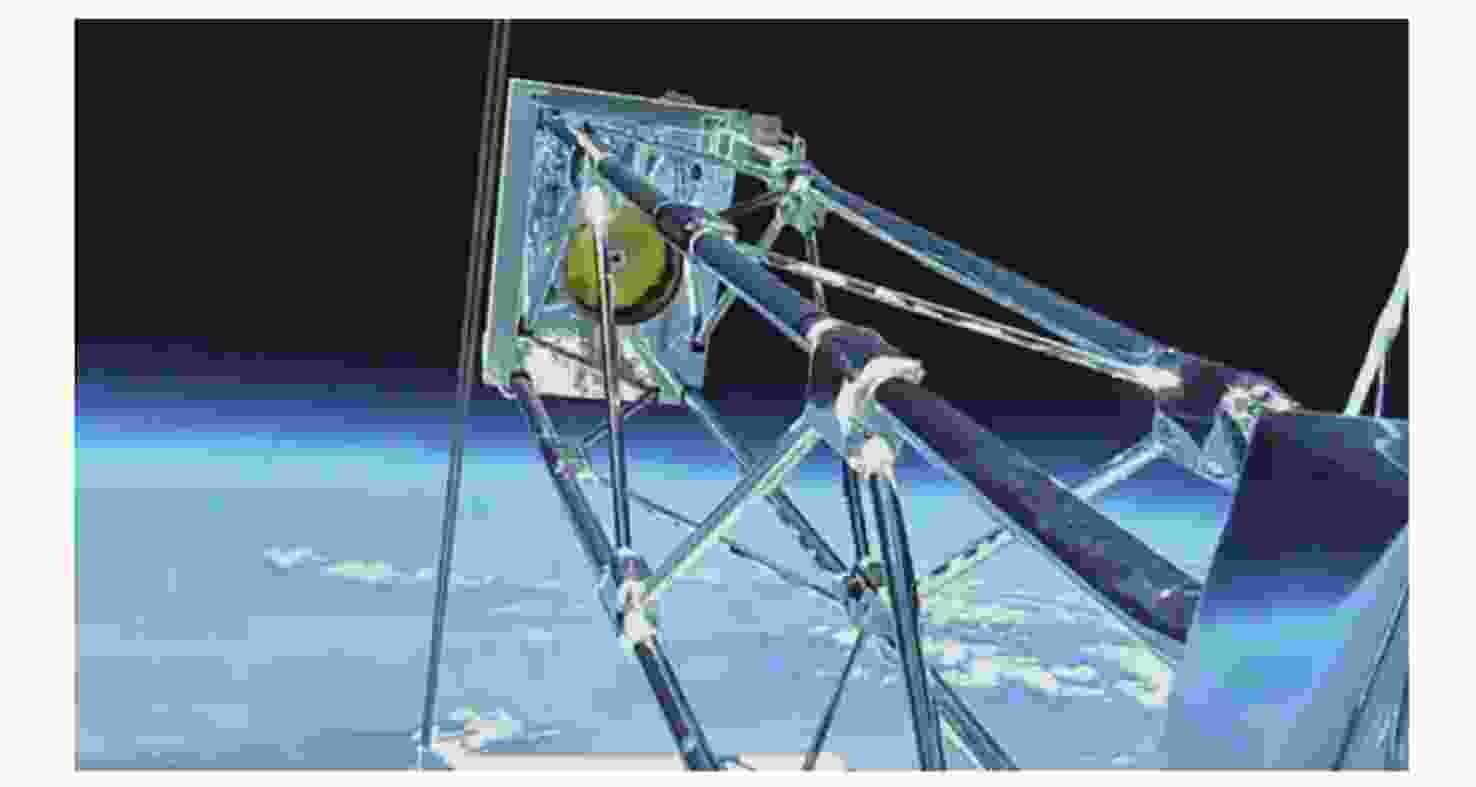
Arc Second Pointing System of Near Space Observatories WASP
-
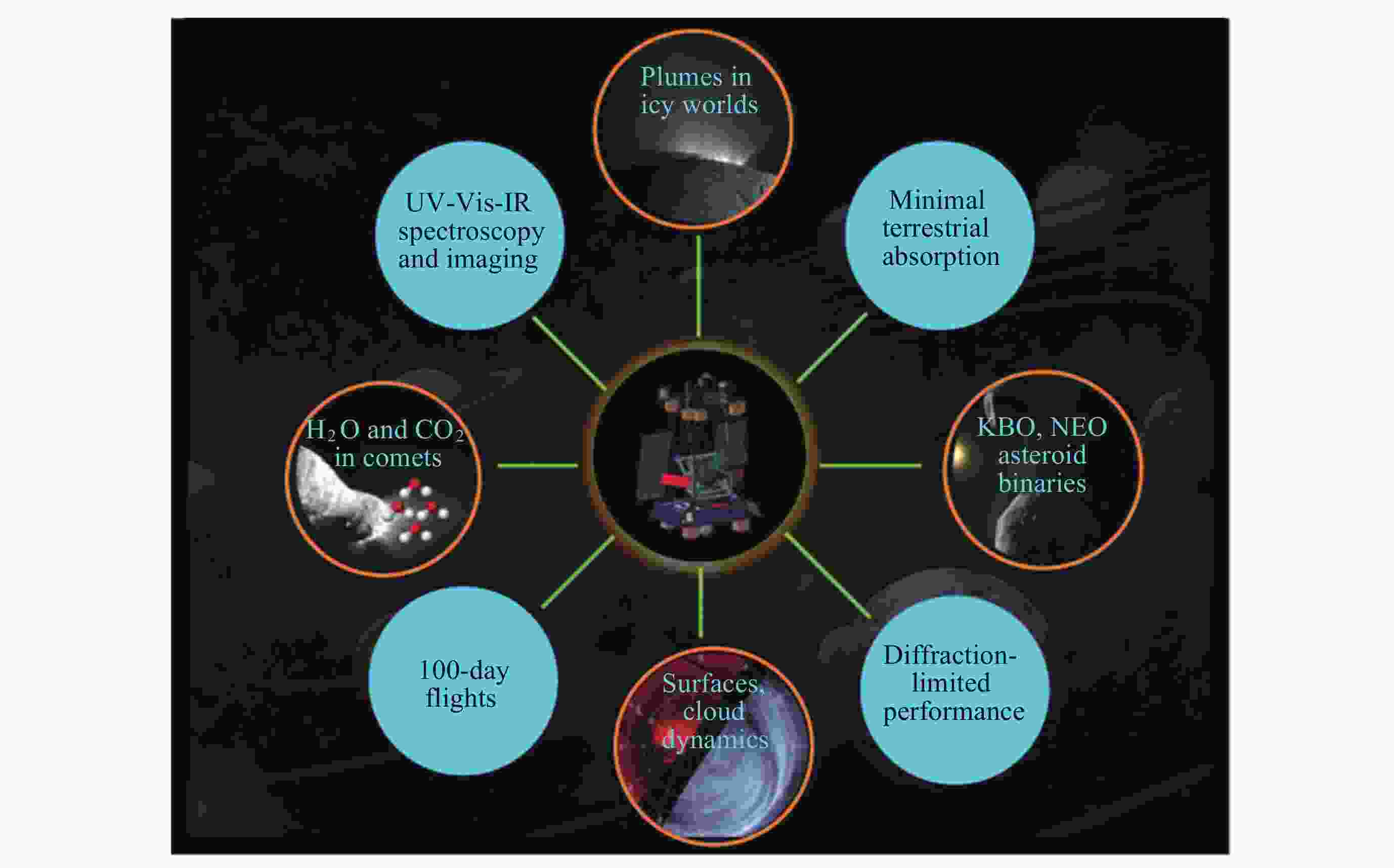
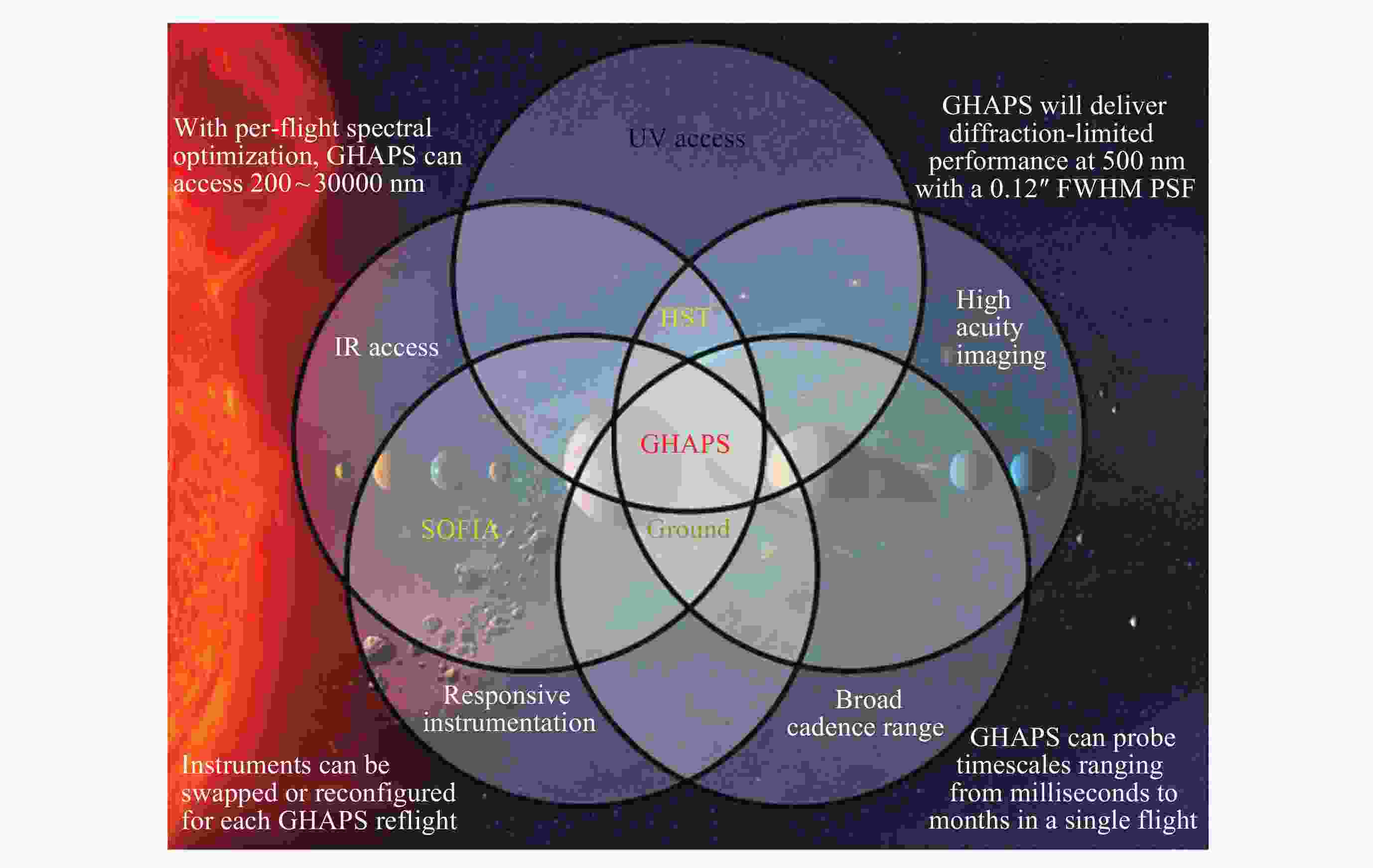
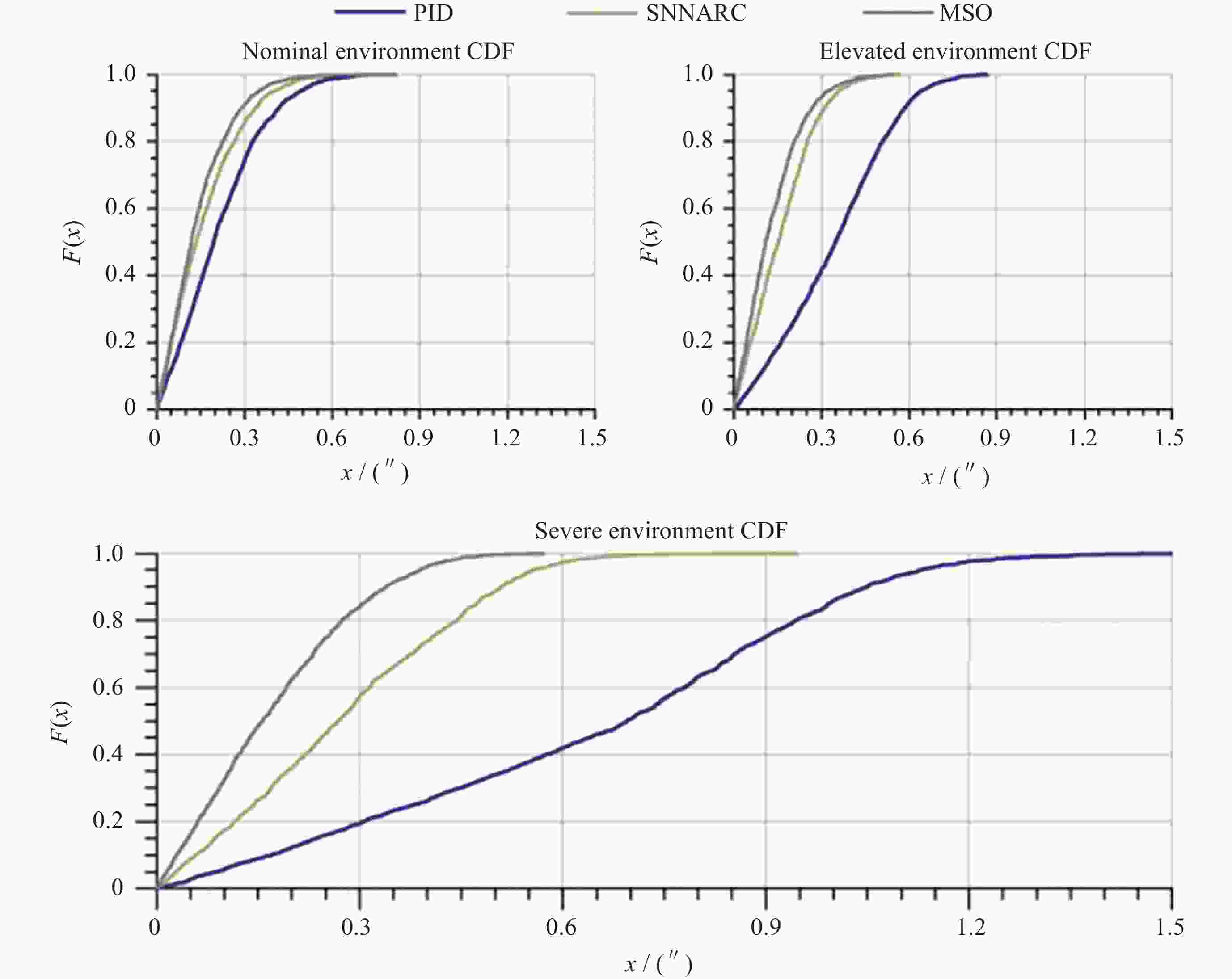
摘要: WASP (Wallops Arc Second Pointer)是由美国国家航空航天局(NASA)开发的一种临近空间天文台亚角秒级指向系统, 旨在构建可适配多类科学载荷的临近空间天文观测平台. WASP系统由指向控制系统(PCS)和星跟踪器子系统(CARDS)组成, 该系统结合精密机械和电子组件, 辅以超压气球技术, 能在临近空间执行长时飞行任务, 同时保持亚角秒级的指向精度. WASP系统的灵活性和标准化设计使其能够适配多种科学载荷, 满足不同的任务需求. 在空间科学领域, WASP系统的应用不仅拓宽了高空科学气球的研究范围, 也为临近空间天文台的建设提供了创新方案, 推动了对临近空间的探索. WASP系统的成功试飞和应用, 为其在行星科学、天体物理学和地球观测等领域的应用奠定了基础, 也为中国临近空间科学的发展提供了可靠的参考.Abstract: The Wallops Arc Second Pointer (WASP), developed by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) in response to the challenge of sub-arcsecond-level pointing stability for high-altitude scientific balloon platforms during long-duration observational missions, is a near-space observatory-grade sub-arcsecond pointing system designed to establish a multi-payload-compatible near-space astronomical observation platform. Comprising a Pointing Control System (PCS) and a star tracker subsystem (Camera Attitude Reference Determination System, CARDS), WASP serves as the core technology for achieving high-precision fine-pointing control in near-space environments. By integrating precision mechanical and electronic components with super-pressure balloon technology, the system enables extended-duration missions in near-space while maintaining sub-arcsecond-level pointing accuracy. Its modular design and standardized interfaces allow seamless adaptation to diverse scientific payloads, fulfilling varied mission requirements. To transition early-stage ground-test hardware and software from laboratory settings to real-world flight conditions, the WASP team collaborated with multiple research groups to conduct five successive test flights. These flights validated the system's technical methodologies and performance capabilities while enabling further optimizations based on operational mission requirements. Following the completion of WASP’s development phase, the system has engaged in scientific collaborations with numerous research teams, producing notable achievements. Since 2014, WASP has supported missions including the X-Calibur hard X-ray polarimeter, BITSE (Balloon-borne Investigation of Temperature and Speed of Electrons in the corona), PICTURE-C (Planetary Imaging Concept Testbed Using a Recoverable Experiment-Coronagraph), SuperHERO (Super High-Energy Resolution Observatory), and XL-Calibur, yielding groundbreaking scientific results across astrophysics and planetary science domains. In the field of space science, WASP not only expands the research scope of high-altitude balloon platforms but also provides innovative solutions for constructing near-space observatories, advancing the exploration of near-space environments. The successful test flights and operational deployments of WASP have laid a foundation for its applications in planetary science, astrophysics, and Earth observation, while offering a reliable reference for the development of near-space science in China.
-
表 1 5次试飞测试中的优化内容
Table 1. Optimizations made during 5 test flights
优化点 具体作用 试飞阶段 集成星追踪器 集成星追踪器到控制系统, 提高了指向精度和稳定性 技术验证飞行 电子设备位置调整 将航电甲板从外部框架移动到模拟望远镜上, 优化重量分布和空间利用 技术验证飞行 WASP轮毂编码器 在WASP轮毂上增加角度位置编码器, 提高了角度测量的精度 技术验证飞行 目标跟踪方案 在控制软件中实施新的定位方案, 主动补偿滚动角度扰动, 提高了扫描操作 的准确性 搭载科研仪器试飞 机械结构 修改冷却器的安装方式以提高隔离性, 并增加加强件以减少结构偏转 搭载科研仪器试飞 集成CARDS子系统 提供低成本系统, 为WASP控制系统提供姿态输入 搭载科研仪器试飞 集成三轴光纤陀螺仪 提供位置和加速度输出给WASP飞行计算机, 用于控制系统算法 搭载科研仪器试飞 动态平衡系统组件 使用动态平衡组件在飞行中补偿指向结构平衡的变化 搭载科研仪器试飞 自锁机构 提供冗余方法释放和锁定指向结构 搭载科研仪器试飞 集成星跟踪器 具有飞行中对齐目标和自主对准的能力 搭载科研仪器试飞 表 2 中国科学院临近空间球载天文台姿控吊舱研制目标
Table 2. Development objectives of the attitude control gondola for the near-space balloon-borne observatory by the Chinese Academy of Sciences
指向目标 应用场景 指向精度要求 对星定向 天文观测 ≤20″ 对日定向 太阳能电池标定 ≤0.3° -
[1] 黄宛宁, 张晓军, 李智斌, 等. 临近空间科学技术的发展现状及应用前景[J]. 科技导报, 2019, 37(21): 46-62HUANG Wanning, ZHANG Xiaojun, LI Zhibin, et al. Development status and application prospect of near space science and technology[J]. Science Technology Review, 2019, 37(21): 46-62 [2] SMITH-PIERCE M C, CHAROENBOONVIVAT Y C, SHUKLA D, et al. High altitude aerodynamic reflectors to counter climate change[C]//2018 Applied Aerodynamics Conference. New York: AIAA, 2018 [3] STREETMAN B J. Attitude tracking control simulating the Hubble Space Telescope[C]//Proceedings of the AIAA Guidance, Control, and Dynamics Conference. Reston: American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2003 [4] SMITH R L, JOHNSON T K, DAVIS M J, et al. High-altitude balloon platforms for optical imaging: System design and feasibility analysis[J]. Journal of Astronomical Telescopes, Instruments, and Systems, 2010, 6(2): 023001 [5] 黄宛宁, 李智斌, 张钊, 等. 2019年临近空间科学技术热点回眸[J]. 科技导报, 2020, 38(1): 38-46HUANG Wanning, LI Zhibin, ZHANG Zhao, et al. Summary of hot spots of near space vehicles in 2019[J]. Science :Times New Roman;">& Technology Review, 2020, 38(1): 38-46 [6] 李智斌, 黄宛宁, 张钊, 等. 2020年临近空间科技热点回眸[J]. 科技导报, 2021, 39(1): 54-68LI Zhibin, HUANG Wanning, ZHANG Zhao, et al. Summary of the hot spots of near space science and technology in 2020[J]. Science Technology Review, 2021, 39(1): 54-68 [7] 顾逸东. 关于空间科学发展的一些思考[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2022, 37(8): 1031-1049GU Yidong. Thoughts on space science development[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2022, 37(8): 1031-1049 [8] 王赤, 时蓬, 宋婷婷, 等. 远航2050: 欧洲空间科学规划及启示[J]. 科技导报, 2022, 40(4): 6-15WANG Chi, SHI Peng, SONG Tingting, et al. Voyage 2050: ESA Science’s Long-term plane and enlightenment[J]. Science Technology Review, 2022, 40(4): 6-15 [9] FAIRBROTHER D A. The NASA balloon program - positioning for the future[C]//AIAA Balloon Systems Conference. Dallas, TX: American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2015 [10] 祝榕辰, 王生. 超压气球研究与发展现状[C]//第二十四届全国空间探测学术交流会论文摘要集. 西安: 中国空间科学学会, 2011ZHU Rongchen, WANG Sheng. Research and development status of superpressure balloons[C]//Summary of Papers at the 24th National Space Exploration Academic Exchange Conference. Xi’an: Chinese Society of Space Sciences, 2011 [11] 祝榕辰, 王生, 杨燕初, 等. 南瓜型超压气球球体设计与地面试验[C]//第四届高分辨率对地观测学术年会论文集. 北京: 中国科学院高分辨率对地观测系统重大专项管理办公室, 2017ZHU Rongchen, WANG Sheng, YANG Yanchu, et al. Design and ground experiments of pumpkin shaped overpressure balloon spheres[C]//Proceedings of the 4th High Resolution Earth Observation Academic Annual Conference. Beijing: Office of Major Special Management of High Resolution Earth Observation Systems, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017 [12] YAJIMA N. A new design and fabrication approach for pressurized balloon[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2000, 26(9): 1357-1360 doi: 10.1016/S0273-1177(00)00060-0 [13] DEWEESE K D, WARD P R. Demonstration of a balloon borne arc-second pointer design[C]//36th COSPAR Scientific Assembly. Beijing: NTRS, 2006 [14] WARD P R, DEWEESE K. Arc-Second Pointer for Balloon-Borne Astronomical Instrument[R]. Greenbelt: NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, 2004. NASA-CR-2004-213153 [15] STUCHLIK D. The wallops Arc second pointer-a balloon borne fine pointing system[C]//AIAA Balloon Systems Conference. Dallas: AIAA, 2015 [16] STUCHLIK D. The NASA Wallops Arc-Second Pointer (WASP) system for precision pointing of scientific balloon instruments and telescopes[C]//AIAA Balloon Systems Conference. Denver: AIAA, 2017 [17] SMITH I S JR. Advancements in NASA balloon research and development[J]. Advances in Space Research, 1996, 17(9): 37-44 doi: 10.1016/0273-1177(95)00674-4 [18] FAIRBROTHER D A. 2017 NASA balloon program update[C]//AIAA Balloon Systems Conference. Denver, Colorado: American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2017 [19] YAJIMA N, KOGAJI S, HASHINO K. Research on the Direction Control System of a Balloon-Borne Telescope[R]. Tsukuba: Mechanical Engineering Laboratory, AIST, 1986. MEL Technical Report 86-015 [20] 叶祥明. 大型球载望远镜高精度姿态控制及指向技术研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院北京天文台, 1999YE Xiangming. Study on High-accuracy Attitude Control and Pointing Technology of A Large Balloon-borne Solar Telescope[D]. Beijing: National Astronomical Observatories, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 1999 [21] PASCALE E, ADE P A R, BOCK J J, et al. The balloon-borne large aperture submillimeter telescope: BLAST[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2008, 681(1): 400 doi: 10.1086/588541 [22] 张伟, 袁朝辉, 章卫国, 等. 平流层球载系统方位控制仿真与试验研究[J]. 计算机仿真, 2009, 26(8): 37-40 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2009.08.010ZHANG Wei, YUAN Zhaohui, ZHANG Weiguo, et al. Simulation and experiment study of attitude control for stratospheric balloon-borne gondola system[J]. Computer Simulation, 2009, 26(8): 37-40 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2009.08.010 [23] 何琳琳, 刘兆瑜, 窦满锋, 等. 高空气球吊篮方位控制的反作用飞轮系统[J]. 微特电机, 2007, 35(8): 36-38,41 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7018.2007.08.013HE Linlin, LIU Zhaoyu, DOU Manfeng, et al. Research on the reaction wheel control system in the azimuth control of nacelle[J]. Small :Times New Roman;">& Special Electrical Machines, 2007, 35(8): 36-38,41 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7018.2007.08.013 [24] 刘艳霄, 宋腾飞, 张涛, 等. 欧洲球载太阳望远镜SUNRISE及相关研究成果简介[J]. 天文研究与技术, 2021, 18(3): 314-336LIU Yanxiao, SONG Tengfei, ZHANG Tao, et al. Overview of balloon-borne solar telescope-SUNRISE[J]. Astronomical Research :Times New Roman;">& Technology, 2021, 18(3): 314-336 [25] 王鸿辉, 袁朝辉, 何长安. 球载吊篮方位控制综合解耦器设计[C]//第三十二届中国控制会议论文集(D卷). 西安: 中国自动化学会控制理论专业委员会, 中国系统工程学会, 2013: 5222-5226WANG Honghui, YUAN Zhaohui, HE Chang’an. Design of comprehensive decoupler for balloon-borne Gondola’s Azimuth control[C]//Proceedings of the 32nd Chinese Control Conference (D Volume). Xi’an: Technical Committee on Control Theory, Chinese Association of Automation, Systems Engineering Society of China, 2013: 5222-5226 [26] SHOJI Y, TAGUCHI M, NAKANO T, et al. FUJIN-2: Balloon borne telescope for optical observation of planets[J]. Transactions of the Japan Society for Aeronautical and Space Sciences, Aerospace Technology Japan, 2016, 14(ists30): 95-102 [27] YE X, YAJIMA N, AI G, et al. Attitude control and high precision pointing control system of a large balloon borne solar telescope[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2000, 26(9): 1419-1422 doi: 10.1016/S0273-1177(00)00076-4 [28] HANAGUD A, SIMPSON J, LANZI R, et al. A solar pointing system for the long duration balloon missions[C]//International Balloon Technology Conference. San Francisco: AIAA, 2012 [29] KOPP G, SMITH P, BELTING C, et al. Radiometric flight results from the HyperSpectral imager for climate science (HySICS)[J]. Geoscientific Instrumentation, Methods and Data Systems, 2017, 6(1): 169-191 doi: 10.5194/gi-6-169-2017 [30] HURFORD T A, MANDELL A M, REDDY V, et al. Observatory for planetary investigations from the stratosphere[J]. Earth and Space Science, 2015, 2(4): 171-184 [31] KISLAT F, BEHESHTIPOUR B, DOWKONTT P, et al. Design of the telescope truss and gondola for the balloon-borne X-ray polarimeter X-Calibur[J]. Journal of Astronomical Instrumentation, 2017, 6(2): 1740008 doi: 10.1142/S2251171717400086 [32] ABARR Q, BEHESHTIPOUR B, BEILICKE M, et al. Performance of the X-Calibur hard X-ray polarimetry mission during its 2018/19 long-duration balloon flight[J]. Astroparticle Physics, 2022, 143: 102749 doi: 10.1016/j.astropartphys.2022.102749 [33] ABARR Q, AWAKI H, BARING M G, et al. XL-Calibur -- a second-generation balloon-borne hard X-ray polarimetry mission[J]. Astroparticle Physics, 2021, 126: 102529 [34] GONG Q, GOPALSWAMY N, NEWMARK J. Innovative Compact Coronagraph Approach for Balloon-borne Investigation of Temperature and Speed of Electrons in the Corona (BITSE)[C]//Astronomical Optics: Design, Manufacture, and Test of Space and Ground Systems II. San Diego, United States: SPIE, 2019: 111160F [35] GOPALSWAMY N, NEWMARK J, YASHIRO S, et al. The Balloon-borne Investigation of Temperature and Speed of Electrons in the corona (BITSE): mission description and preliminary results[J]. Solar Physics, 2021, 296(1): 15 doi: 10.1007/s11207-020-01751-8 [36] COOK T, CAHOY K, CHAKRABARTI S, et al. Planetary imaging concept testbed using a recoverable experiment–coronagraph (PICTURE C)[J]. Journal of Astronomical Telescopes, Instruments, and Systems, 2015, 1(4): 044001 doi: 10.1117/1.JATIS.1.4.044001 [37] MENDILLO C B, HEWAWASAM K, HOWE G A, et al. Decoupling the image-plane and low-order wavefront sensors for the PICTURE-C coronagraph[C]//Proceedings Volume 11117, Techniques and Instrumentation for Detection of Exoplanets IX. San Diego: SPIE, 2019 [38] MENDILLO C B, HEWAWASAM K, MARTEL J, et al. Balloon flight demonstration of coronagraph focal plane wavefront correction with PICTURE-C[J]. Journal of Astronomical Telescopes, Instruments, and Systems, 2023, 9(2): 025005 [39] MENDILLO C B, HEWAWASAM K, MARTEL J, et al. The PICTURE-C exoplanetary imaging balloon mission: second flight results and the transition to a new mission, PICTURE-D[C]//Proceedings Volume 12680, Techniques and Instrumentation for Detection of Exoplanets XI. San Diego: SPIE, 2023 [40] GASKIN J, APPLE J, CHAVIS K S, et al. High energy replicated optics to explore the sun: hard X-ray balloon-borne telescope[C]//2013 IEEE Aerospace Conference. Big Sky, MT: IEEE, 2013: 1-11 [41] GASKIN J, ELSNER R, RAMSEY B, et al. SuperHERO: Design of a new hard-X-ray focusing telescope[C]//2015 IEEE Aerospace Conference. Big Sky, MT: IEEE, 2015: 1-15 [42] YOUNG R. Overview of the Gondola for High Altitude Planetary Science (GHAPS)[R]. Greenbelt: International Society for Optical Engineering, 2016 [43] LEWIS M, JUERGENS J R, ARETSKIN-HARITON E, et al. Gondola for High Altitude Planetary Science (GHAPS) Guide System Trade Study[R]. Pasadena: NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory, 2020 [44] UDINSKI E P, LANZI R J. Wallops Arc-Second Pointing (WASP) System[R]. Athens: NASA, 2023 [45] HEATWOLE S H, CRAIG S D, CASTELLUCCI K J, et al. Low-Cost Star Tracker Development for Suborbital and Small Satellite Platforms[R]. Greenbelt: NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, 2019 [46] GALCHENKO P, PERNICKA H. Neural network attitude control system design for the wallops arc-second pointer[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2022, 45(7): 1365-1370 doi: 10.2514/1.G006465 [47] 马俊, 朱猛, 王才喜, 等. 临近空间光电探测技术与发展展望[J]. 空天技术, 2022(2): 85-96MA Jun, ZHU Meng, WANG Caixi, et al. Technology and development prospect of electro-optical detection in near space[J]. Aerospace Technology, 2022(2): 85-96 -
-




 崔钰琅 男, 2001年1月出生于重庆市江北区, 现为中国科学院空天信息创新研究院硕士研究生, 飞行器设计专业. E-mail:
崔钰琅 男, 2001年1月出生于重庆市江北区, 现为中国科学院空天信息创新研究院硕士研究生, 飞行器设计专业. E-mail: 
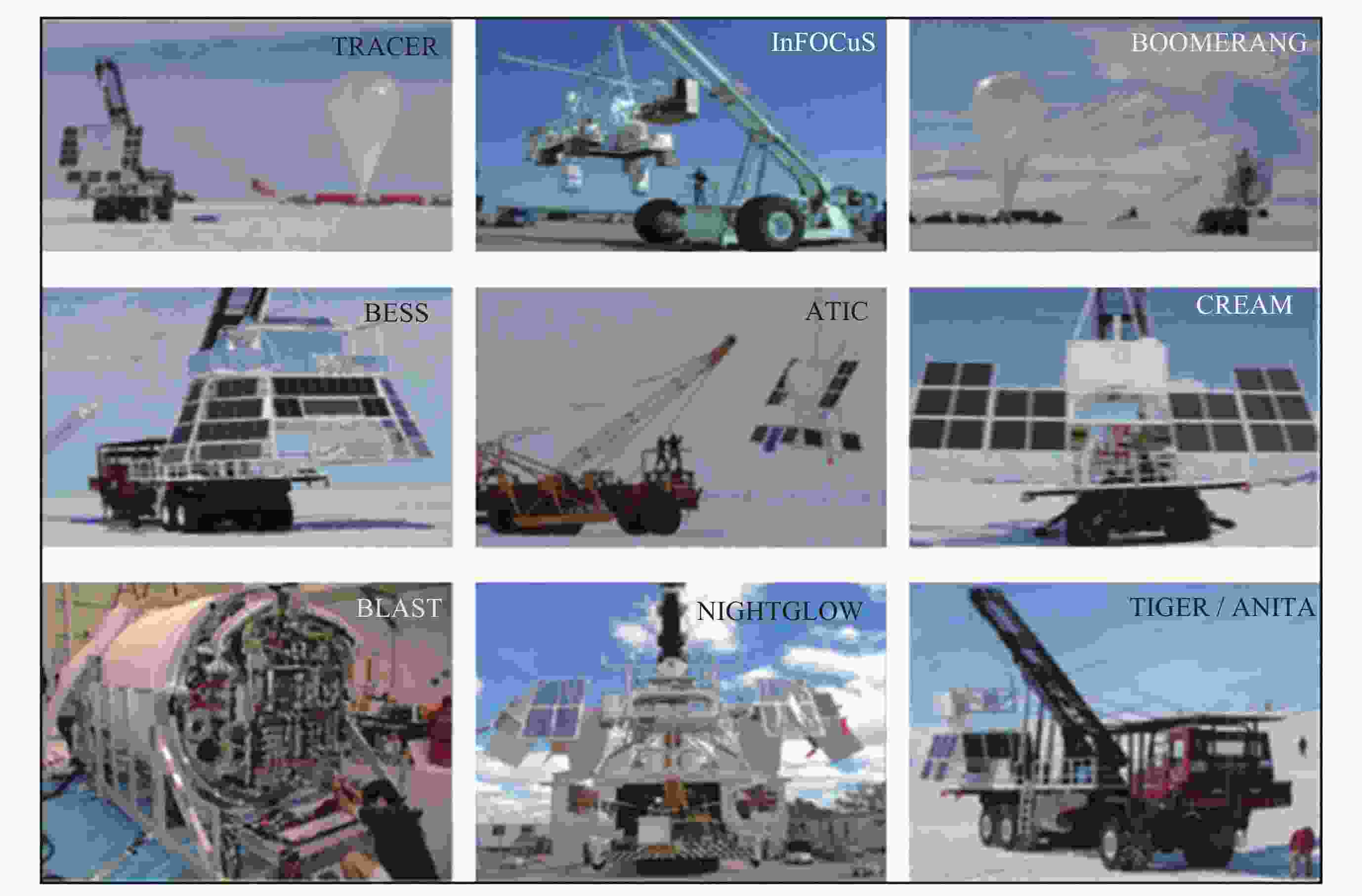

 下载:
下载: