Video Super-resolution Method for Spacecraft Approaching and Detecting Asteroids
-
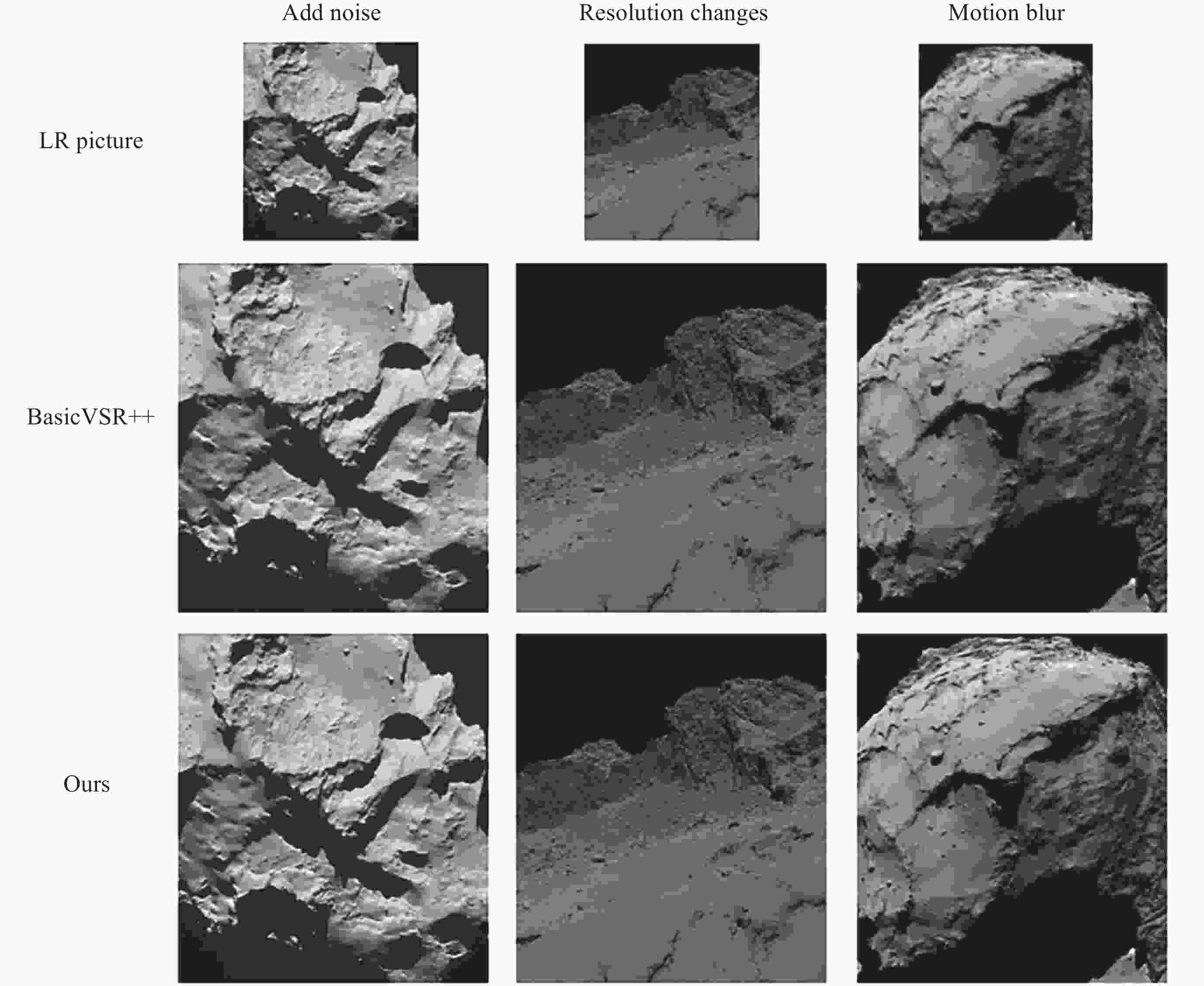
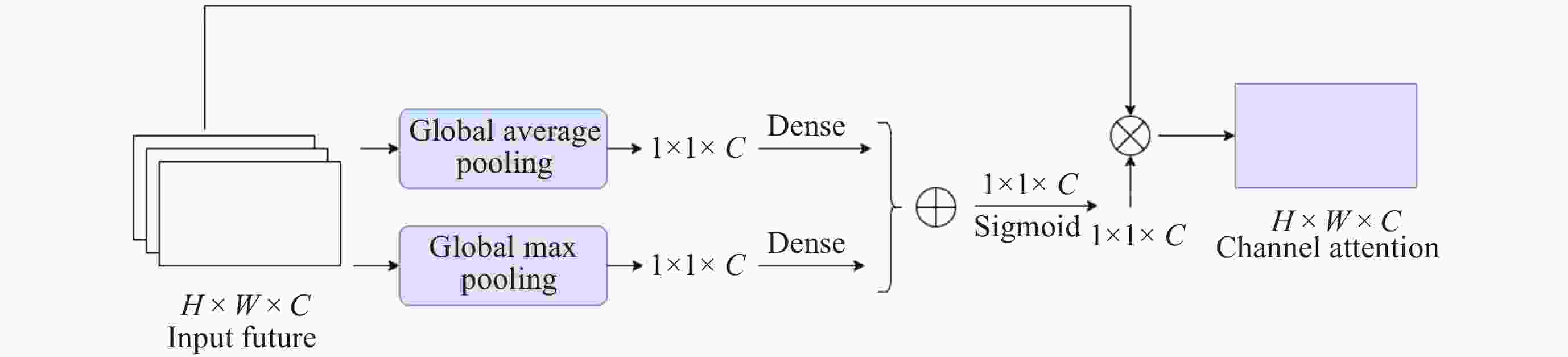
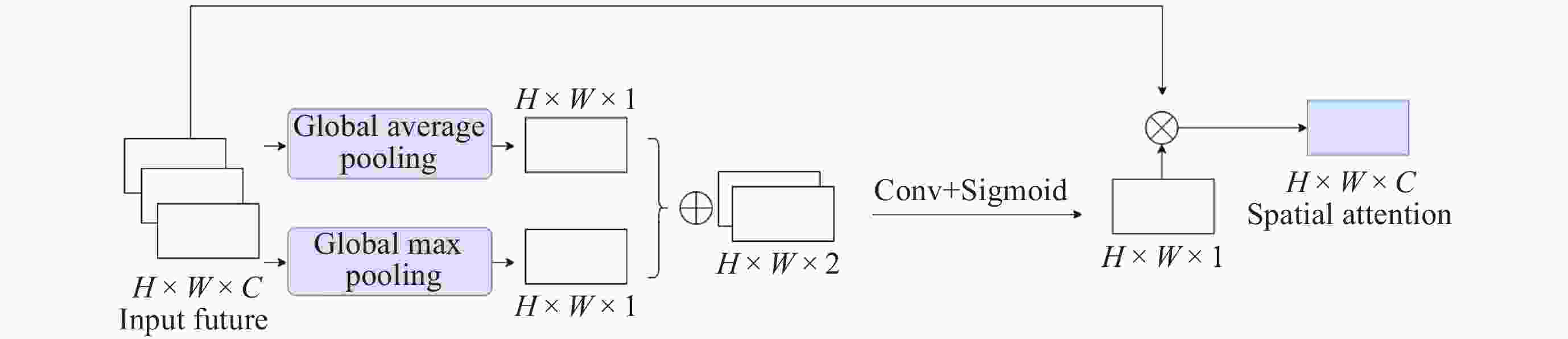
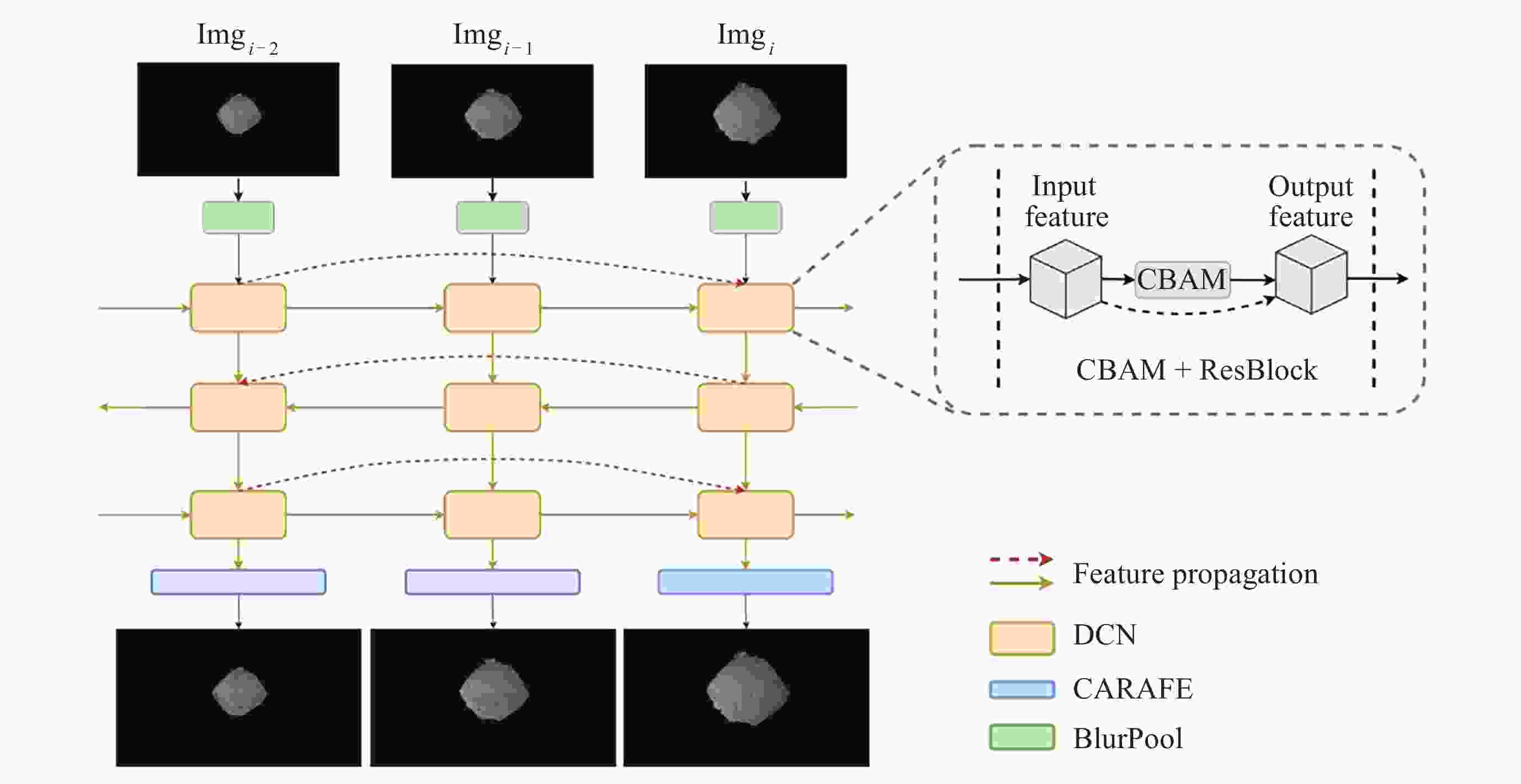
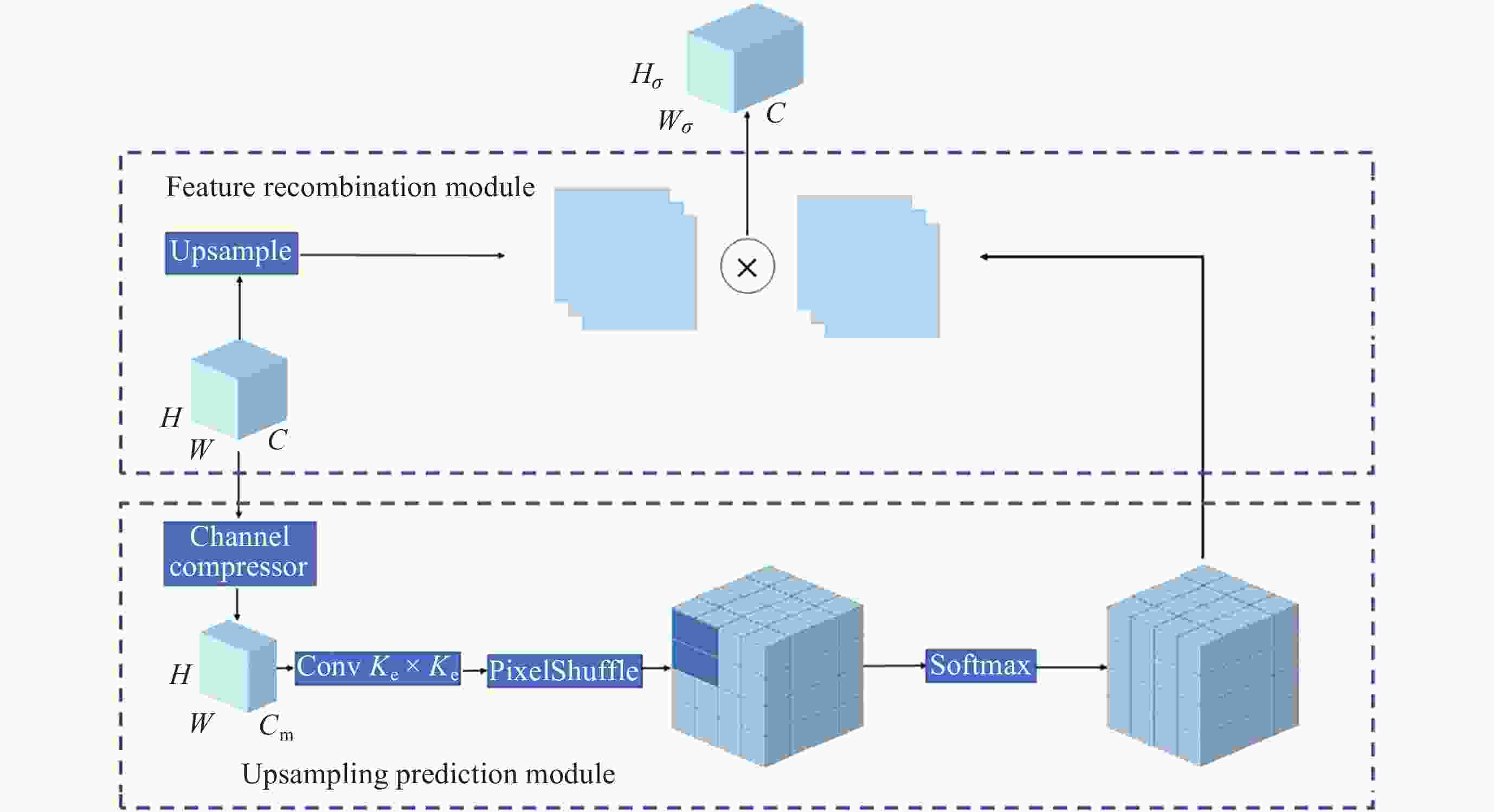
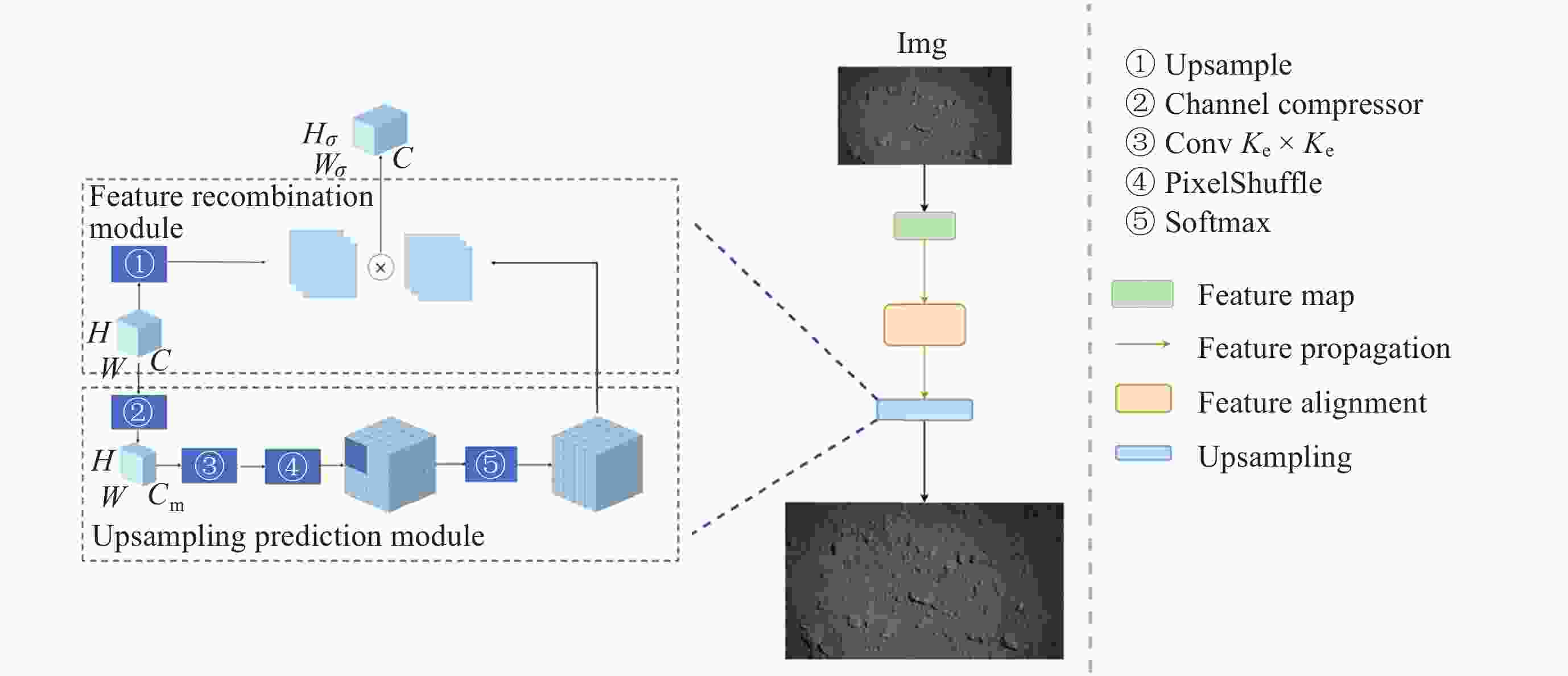
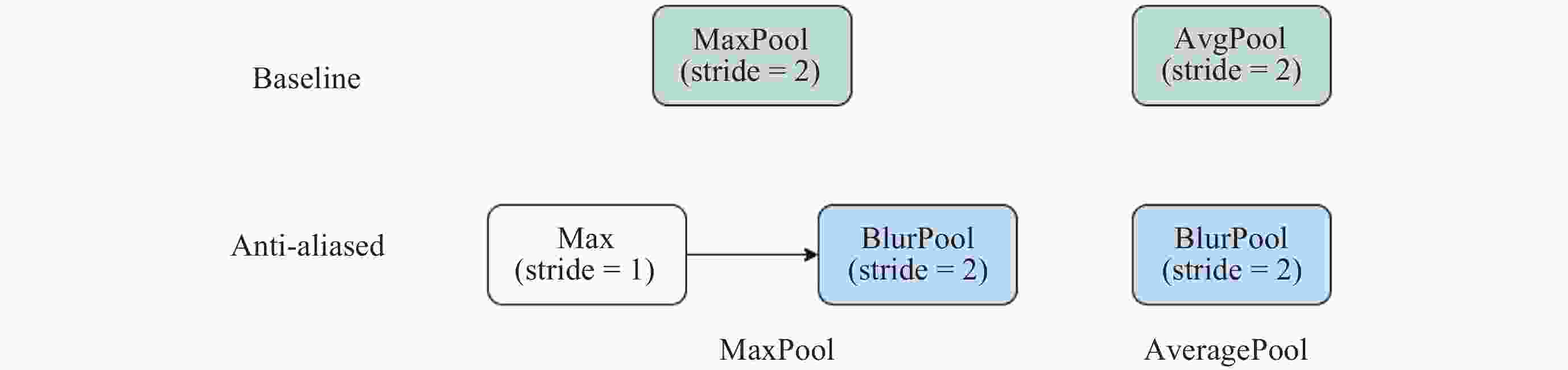
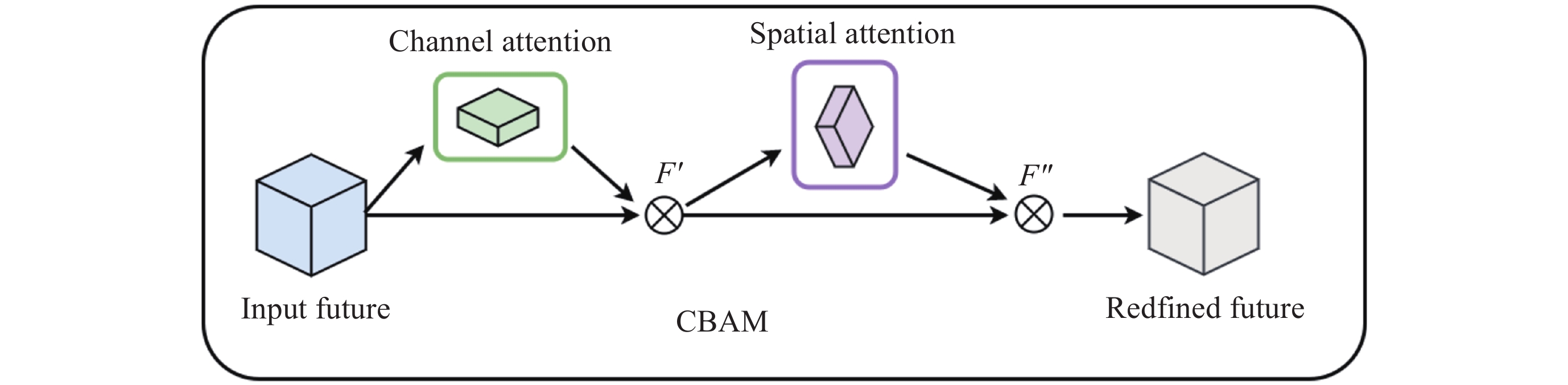
摘要: 针对抵近探测中平台运动、抖动导致的动态图像序列模糊及分辨率低的问题, 提出了一种基于BasicVSR++的视频超分辨方法. 通过引入空间和通道注意力机制强化细节特征提取, 结合共享投射权重、多组机制和采样点调制优化对齐模块, 弥补正则卷积在长距离依赖与自适应空间聚集的不足. 采用下采样与低通滤波器结合的方式, 减少高频成分, 提升抗图像抖动鲁棒性, 同时引入新上采样模块, 通过融合局部与全局特征生成自适应上采样核, 进一步扩展感受野, 以更好地恢复全局结构并重建细节. 仿真实验结果显示, 本文提出的方法在峰值信噪比(PSNR)和结构相似性(SSIM)指标上, 分别比原始方法提高了2.2%和2.1%, 验证了本文方法在抵近探测图像序列超分辨率重建质量提升方面的有效性.Abstract: In the imaging process of approach detection, dynamic image sequences often have problems such as image blur and insufficient resolution due to platform movement and jitter. This paper studies the super-resolution of image sequences in the process of approach detection and proposes a video super-resolution method based on BasicVSR++. By introducing spatial and channel attention mechanisms to enhance the model’s ability to extract detail features, combined with shared projection weights, multi-group mechanisms and sampling point modulation, the effect of the alignment module is improved. While improving the network feature extraction capability, it makes up for the shortcomings of regular convolution in long-distance dependency and adaptive spatial aggregation. At the same time, downsampling is combined with a low-pass filter to reduce the high-frequency components of the image, which improves the robustness of the model to slight image jitter. In addition, a new upsampling module is introduced to combine local and global features, generate an adaptive upsampling kernel to expand the receptive field, and better restore the global structure and reconstruct details. The simulation experimental results show that the proposed method improves the Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) and Structural Similarity (SSIM) indicators by 2.2% and 2.1% respectively compared with the original method, which proves the effectiveness of the method proposed in this paper in improving the quality super-resolution reconstruction of the image sequence in close proximity.
-
表 1 网络训练所用网络配置条件
Table 1. Configuration conditions used for network training
软硬件配置 型号/版本号 CPU Intel Core i7-12700 GPU NVIDIA RTX 3080 内存 12 GB 软件环境 Python3.9, CUDA12.1, Pytorch1.7.1 表 2 多干扰因素下模型成像指标对比
Table 2. Comparison of model imaging indicators under multiple interference factors
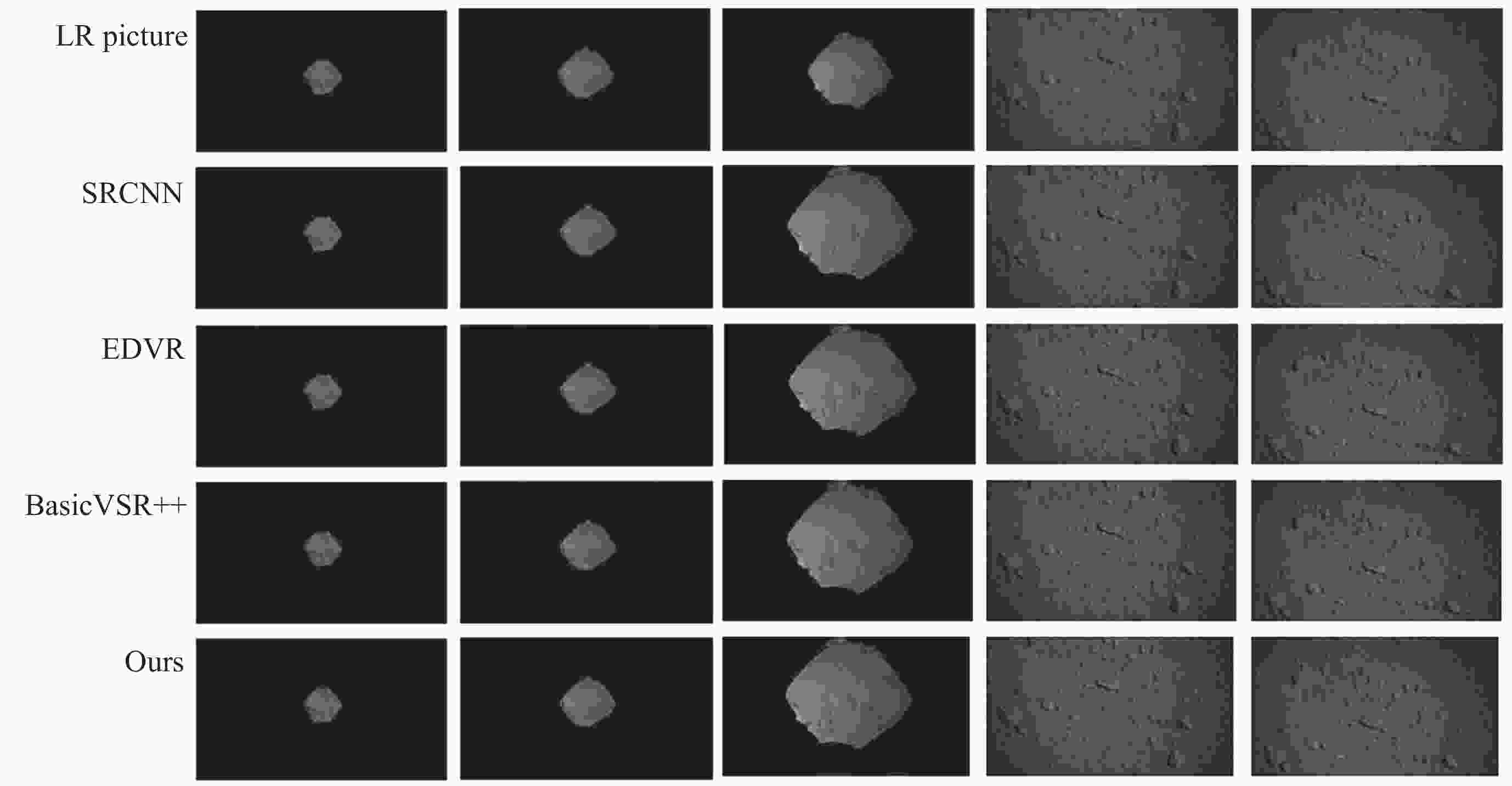
Metrics Bicubic SRCNN TOFlow EDVR RSDN BasicVSR++ Ours Add noise SSIM 0.8684 0.8654 0.8748 0.8912 0.8954 0.9008 0.9171 PSNR 28.61 29.54 29.67 30.69 30.95 31.28 31.82 Resolution changes SSIM 0.8625 0.8751 0.8779 0.8852 0.8952 0.9010 0.9173 PSNR 28.93 29.10 29.79 30.65 31.04 31.30 31.83 Motion blur SSIM 0.8586 0.8693 0.8767 0.8792 0.8972 0.9011 0.9174 PSNR 28.27 28.98 29.15 30.12 30.84 31.31 31.81 表 3 模型消融实验结果
Table 3. Model ablation test results
Test No. CBAM CARAFE IDCN BlurPool PSNR/dB SSIM 1 × × × × 31.39 0.9019 2 √ × × × 31.51 0.9085 3 √ √ × × 31.72 0.9126 4 √ √ √ × 31.86 0.9176 5 √ √ √ √ 31.91 0.9181 注 符号√表示该实验组包含该模块, 符号×表示未包含该模块. -
[1] DONG C, LOY C C, HE K M, et al. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(2): 295-307 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2439281 [2] KIM J, LEE J K, LEE K M. Accurate image super-resolution using very deepconvolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. LasVegas: IEEE, 2016: 1646-1654 [3] YANG J C, HUANG T. Image super-resolution: Historical overview and future challenges[M]//MILANFAR P. Super-Resolution Imaging. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2017: 1-34 [4] LIU H Y, RUAN Z B, ZHAO P, et al. Video super-resolution based on deep learning: a comprehensive survey[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2022, 55(8): 5981-6035 doi: 10.1007/s10462-022-10147-y [5] LEPCHA D C, GOYAL B, DOGRA A, et al. Image super-resolution: a comprehensive review, recent trends, challenges and applications[J]. Information Fusion, 2022, 91: 230-260 doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2022.10.007 [6] HA V K, REN J C, XU X Y, et al. Deep learning based single image super-resolution: A survey[C]//9th Advances in Brain Inspired Cognitive Systems. Cham: Springer, 2018: 106-119 [7] WANG Z H, CHEN J, HOI S C H. Deep learning for image super-resolution: A survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(10): 3365-3387 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2020.2982166 [8] JENEFA A, KURIAKOSE B M, EDWARD N V, et al. EDSR: Empowering super-resolution algorithms with high-quality DIV2K images[J]. Intelligent Decision Technologies, 2023, 17(4): 1249-1263 doi: 10.3233/IDT-230218 [9] NAGANO Y, KIKUTA Y. SRGAN for super-resolving low-resolution food images[C]//Proceedings of the Joint Workshop on Multimedia for Cooking and Eating Activities and Multimedia Assisted Dietary Management. New York: ACM, 2018: 33-37 [10] WANG X T, CHAN K C K, YU K, et al. EDVR: Video restoration with enhanced deformable convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Long Beach: IEEE, 2019: 1954-1963 [11] TIAN Y P, ZHANG Y L, FU Y, et al. TDAN: Temporally-Deformable Alignment Network for video super-resolution[C]//Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle: IEEE, 2020: 3357-3366 [12] GOPALAKRISHNAN S, CHOUDHURY A. A “deep” review of video super-resolution[J]. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2024, 129: 117175 doi: 10.1016/j.image.2024.117175 [13] CHAN K C K, ZHOU S C, XU X Y, et al. BasicVSR++: Improving video super-resolution with enhanced propagation and alignment[C]//Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New Orleans: IEEE, 2022: 5962-5971 [14] RABINOWITZ D L. Detection of Earth-approaching asteroids in near real time[J]. Astronomical Journal, 1991, 101(4): 1518-1529 doi: 10.1086/115785 [15] NIU Z Y, ZHONG G A, YU H. A review on the attention mechanism of deep learning[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 452: 48-62 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.03.091 [16] GUO M H, XU T X, LIU J J, et al. Attention mechanisms in computer vision: a survey[J]. Computational Visual Media, 2022, 8(3): 331-368 doi: 10.1007/s41095-022-0271-y [17] SOYDANER D. Attention mechanism in neural networks: where it comes and where it goes[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2022, 34(16): 13371-13385 doi: 10.1007/s00521-022-07366-3 [18] HU J, SHEN L, SUN G, et al. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City: IEEE, 2018: 7132-7141 [19] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]//Proceedings of the 15th European Conference. Cham: Springer, 2018: 3-19 [20] WEN W L, REN W Q, SHI Y H, et al. Video super-resolution via a spatio-temporal alignment network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 1761-1773 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2022.3146625 [21] SHI S W, GU J J, XIE L B, et al. Rethinking alignment in video super-resolution transformers[C]//Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans: Curran Associates Inc., 2022: 2615 [22] CABALLERO J, LEDIG C, AITKEN A, et al. Real-time video super-resolution with spatio-temporal networks and motion compensation[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu: IEEE, 2017: 2848-2857 [23] WANG L G, GUO Y L, LIN Z P, et al. Learning for video super-resolution through HR optical flow estimation[C]//14th Asian Conference on Computer Vision. Cham: Springer, 2019: 514-529 [24] XUE T F, CHEN B A, WU J J, et al. Video enhancement with task-oriented flow[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2019, 127(8): 1106-1125 doi: 10.1007/s11263-018-01144-2 [25] SAJJADI M S M, VEMULAPALLI R, BROWN M. Frame-recurrent video super-resolution[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City: IEEE, 2018: 6626-6634 [26] JO Y, OH S W, KANG J, et al. Deep video super-resolution network using dynamic upsampling filters without explicit motion compensation[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City: IEEE, 2018: 3224-3232 [27] HASSANIN M, ANWAR S, RADWAN I, et al. Visual attention methods in deep learning: An in-depth survey[J]. Information Fusion, 2024, 108: 102417 doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2024.102417 [28] CORDONNIER J B, LOUKAS A, JAGGI M. On the relationship between self-attention and convolutional layers[C]//International Conference on Learning Representations. Addis Ababa: OpenReview. net, 2019 [29] ZHU X Z, HU H, LIN S, et al. Deformable convNets v2: More deformable, better results[C]//Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach: IEEE, 2019: 9300-9308 [30] Wang H, Su D, Liu C, et al. Deformable Non-Local Network for VideoSuper-Resolution[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 177734-177744 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2958030 [31] YING X Y, WANG L G, WANG Y Q, et al. Deformable 3D convolution for video super-resolution[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2020, 27: 1500-1504 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2020.3013518 [32] WANG W, DAI J, CHEN Z, et al. InternImage: Exploring large-scale vision foundation models with deformable convolutions[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Vancouver: IEEE, 2023: 14408-14419. [33] XIONG Y W, LI Z Q, CHEN Y T, et al. Efficient deformable convNets: Rethinking dynamic and sparse operator for vision applications[C]//Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle: IEEE, 2024: 5652-5661 [34] SHI W Z, CABALLERO J, HUSZÁR F, et al. Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network[C]//Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas: IEEE, 2016: 1874-1883 [35] WANG J Q, CHEN K, XU R, et al. CARAFE: Content-aware reassembly of features[C]//Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul: IEEE, 2019: 3007-3016 [36] ZHANG R. Making convolutional networks shift-invariant again[C]//Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning. Long Beach: PMLR, 2019: 7324-7334 [37] AZULAY A, WEISS Y. Why do deep convolutional networks generalize so poorly to small image transformations[OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1805.12177, 2018. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1805.12177 [38] WEISS K, KHOSHGOFTAAR T M, WANG D D. A survey of transfer learning[J]. Journal of Big Data, 2016, 3: (1): 1-40 -
-




 陈宇涵 男, 现就读于中国科学院国家空间科学中心, 硕士研究生, 专业为计算机技术. 主要研究方向为图像处理技术. E-mail:
陈宇涵 男, 现就读于中国科学院国家空间科学中心, 硕士研究生, 专业为计算机技术. 主要研究方向为图像处理技术. E-mail: 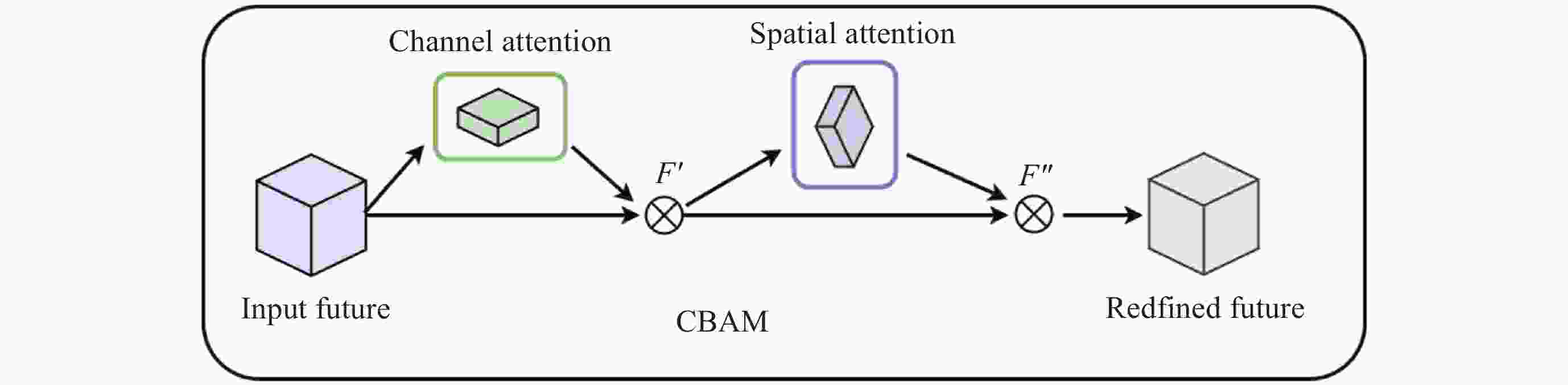
 下载:
下载: