Standard Dataset of Ionospheric Equatorial Plasma Bubbles over Southern China Based on Airglow Observations
-
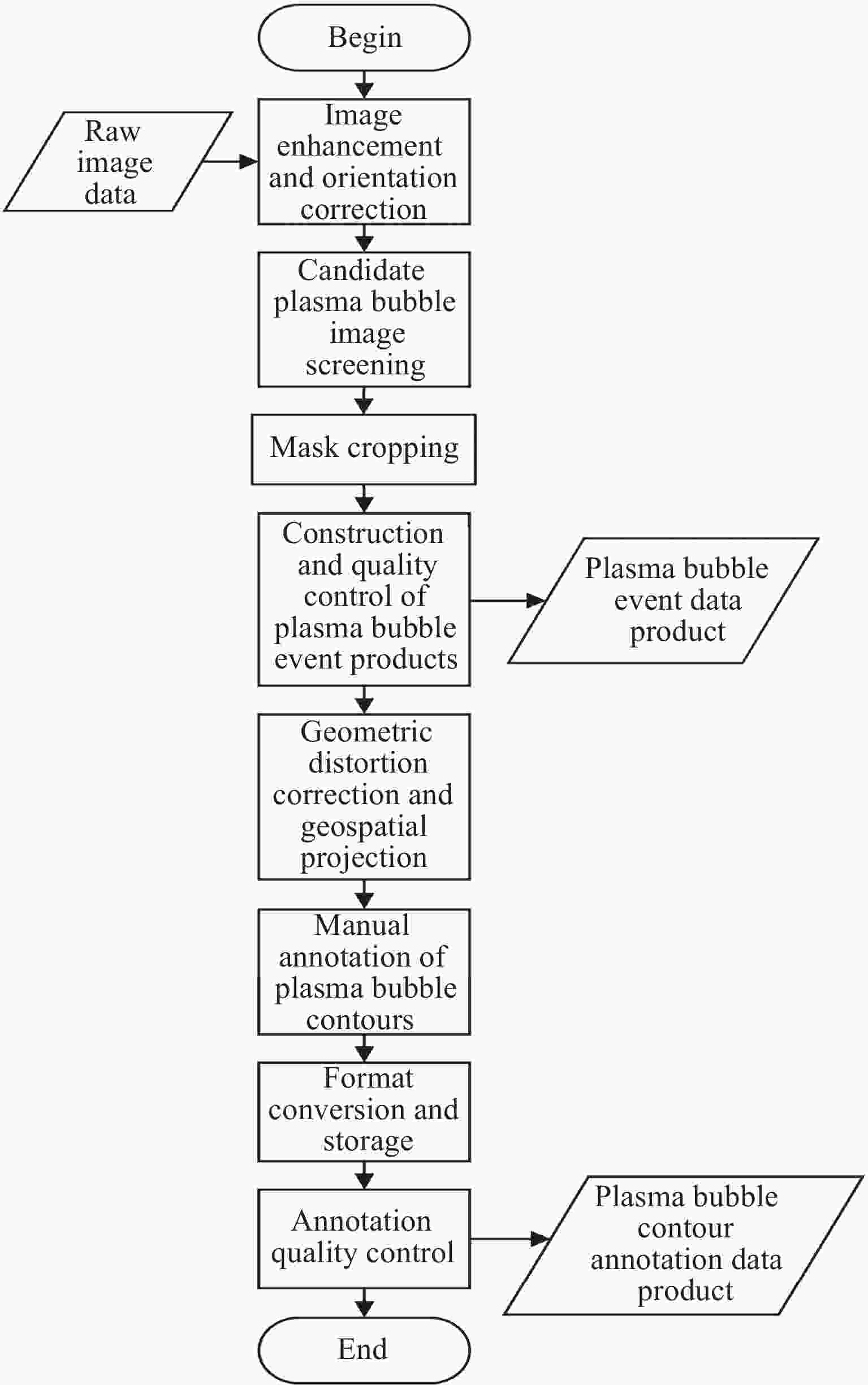
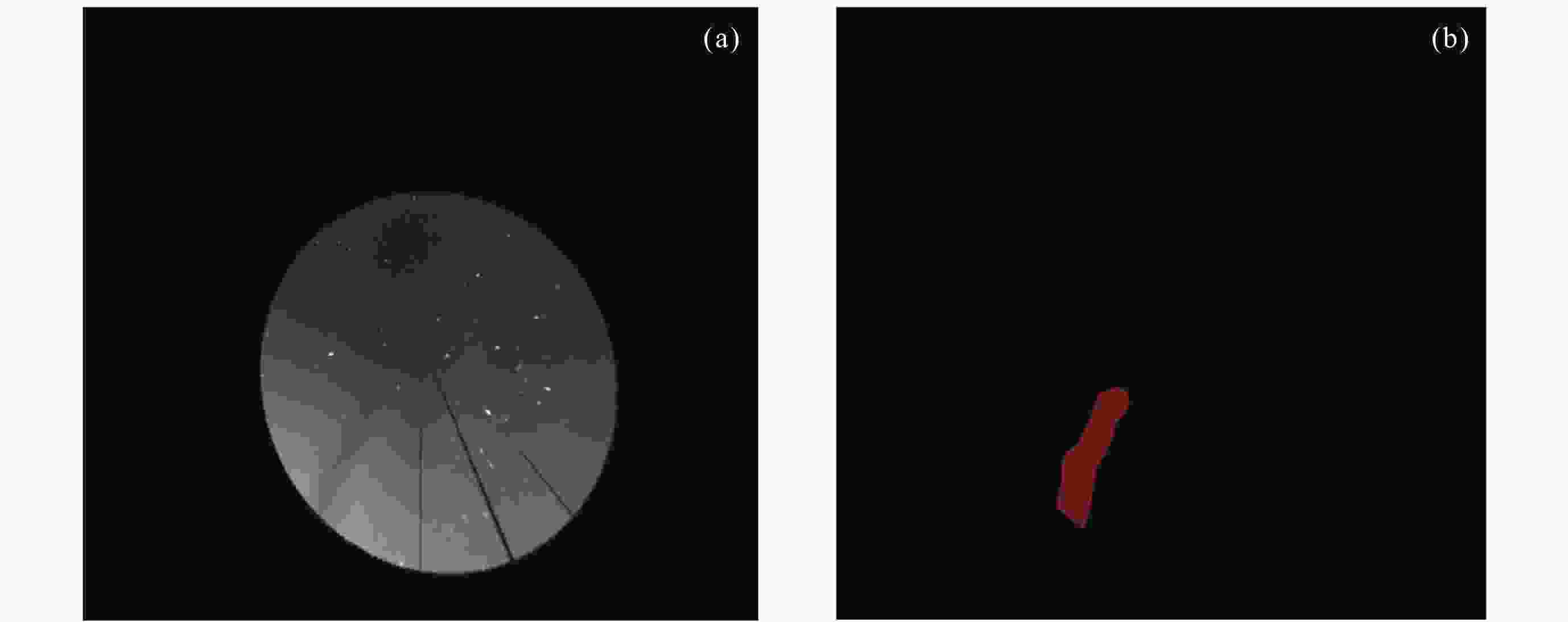
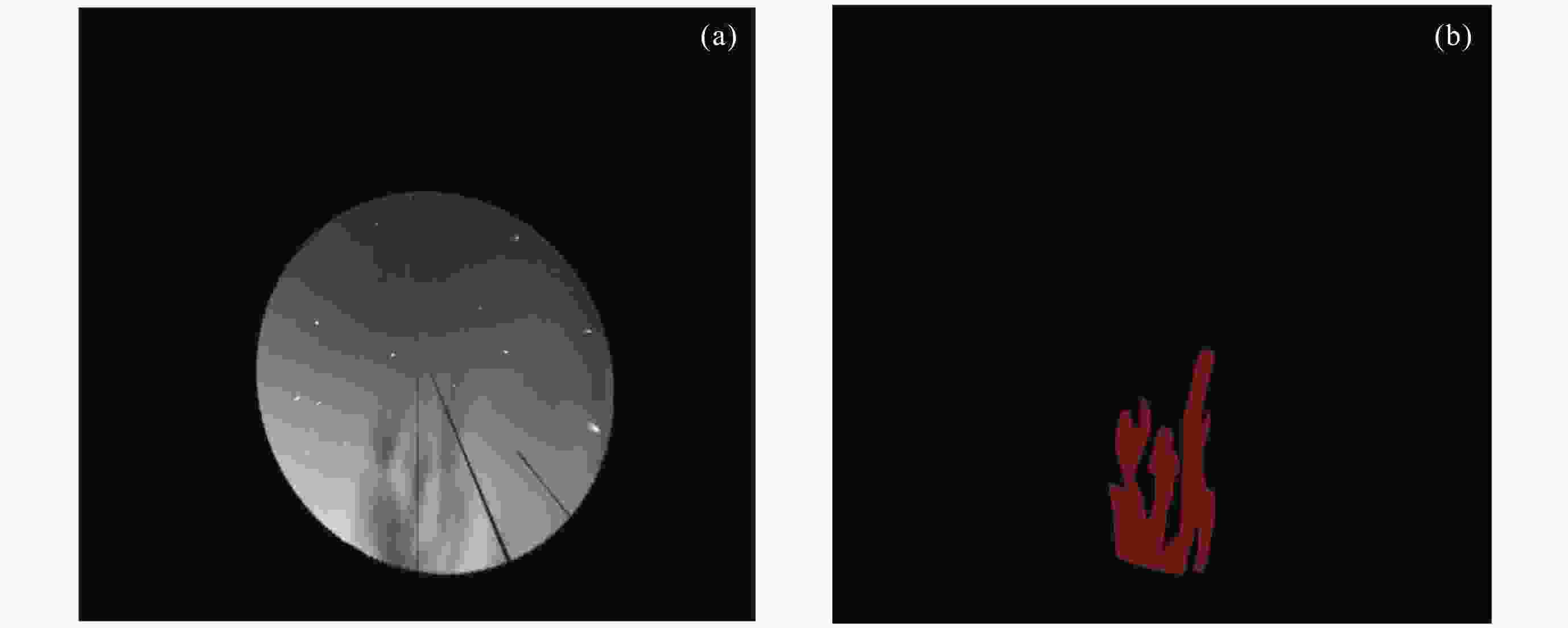
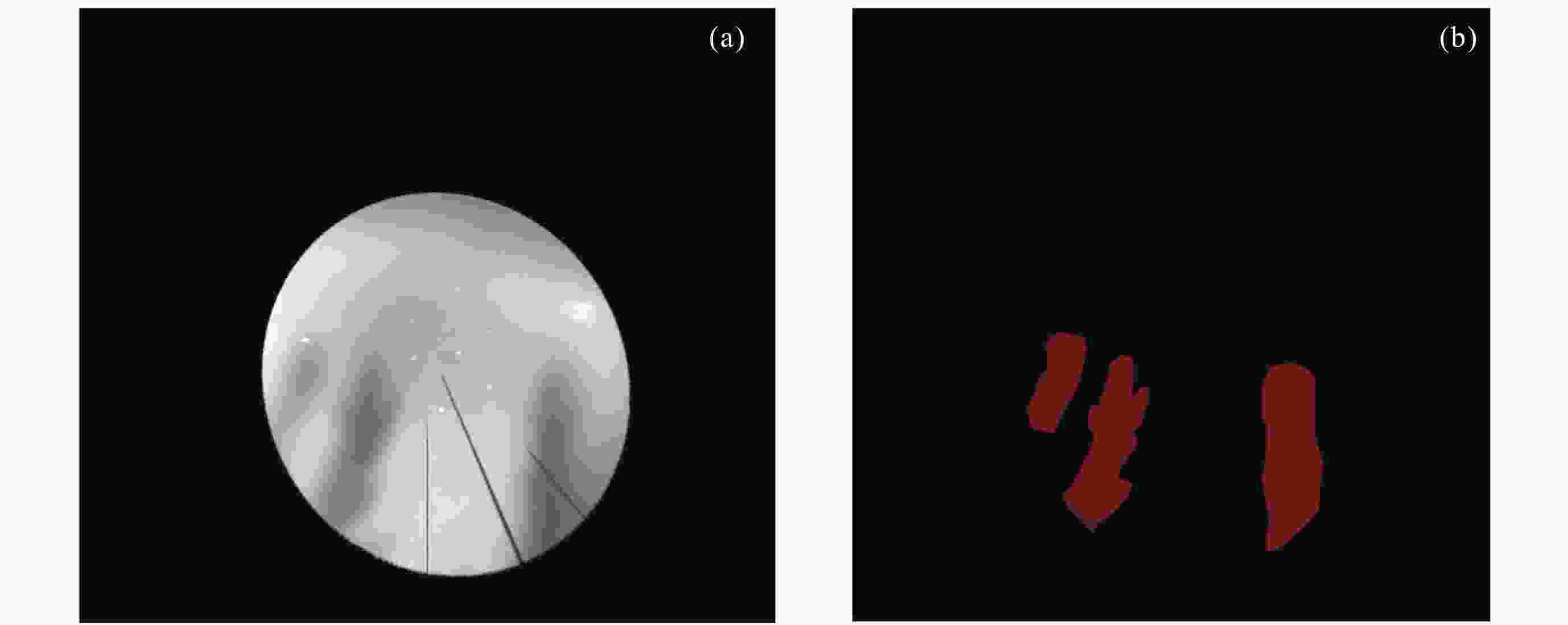
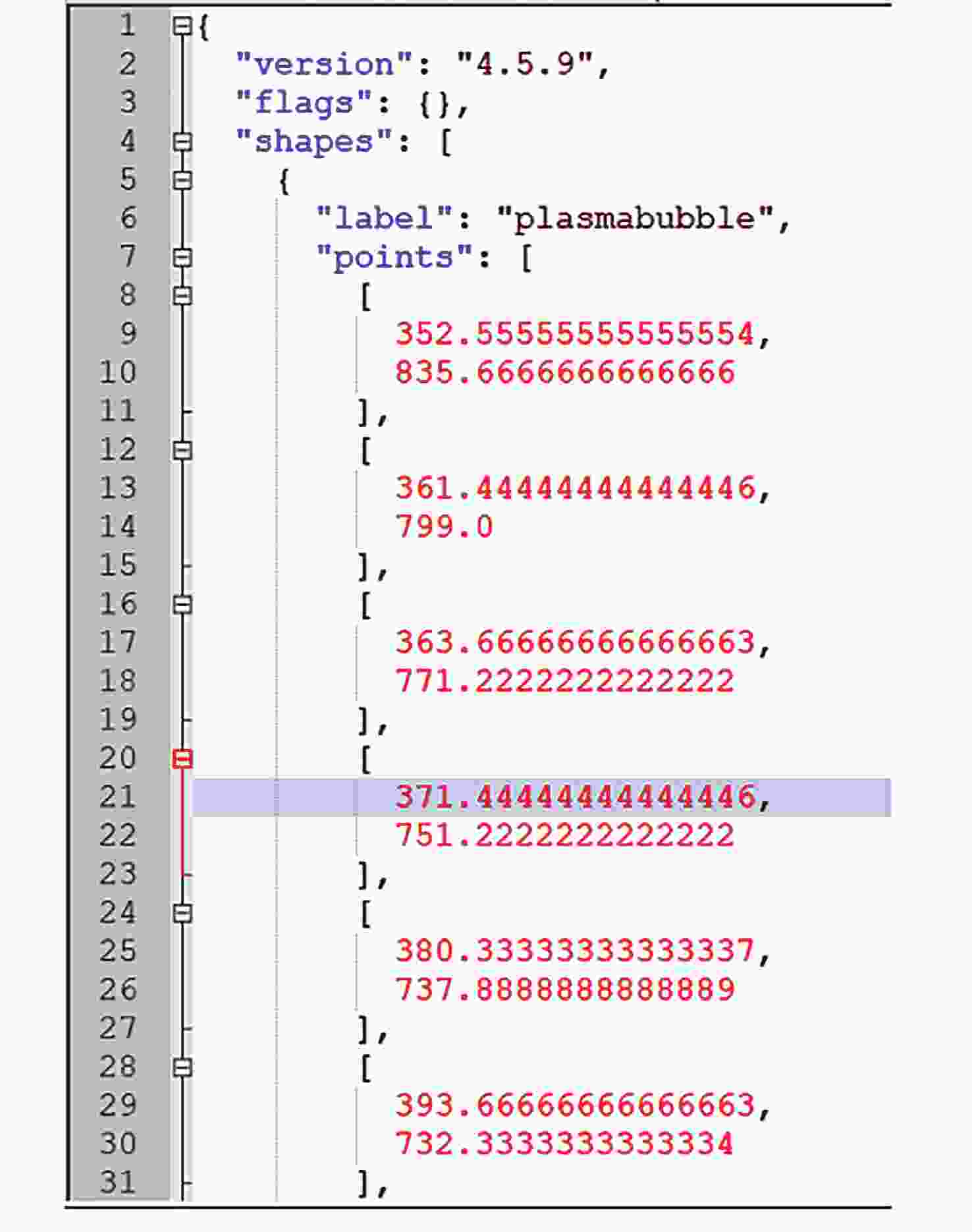
摘要: 研究构建了首个基于气辉观测的电离层等离子体泡标准数据集, 包含等离子体泡事件数据与精确轮廓标注数据. 该数据集源自云南曲靖站630 nm波段气辉成像仪历时一个完整太阳活动周(2012-2022年)的连续观测, 所有原始数据均经过图像增强、方位校正、几何畸变校正及地理坐标投影等标准化预处理, 并由专家团队完成等离子体泡事件识别及轮廓标注. 该数据集的时间分辨率高达3 min, 系统收录了不同太阳活动强度下的等离子体泡事件样本, 涵盖I形与Y形等多种典型形态. 本数据集为开发高精度监督式人工智能算法提供了高质量基准数据, 有助于促进基于气辉成像的电离层等离子体泡自动化检测与形态演化研究.Abstract: Airglow imaging observations, with their high spatiotemporal resolution and large-scale continuous monitoring capability, provide a crucial approach to studying the fine horizontal structures and evolutionary characteristics of ionospheric equatorial plasma bubbles. However, the current lack of high-quality, professionally annotated plasma bubble datasets severely restricts the application of supervised Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms in this field. To address this issue, this study constructs the first standardized dataset of ionospheric plasma bubbles based on airglow observations, including plasma bubble event data products and precise contour annotation data products. The dataset is derived from continuous observations over a full solar activity cycle (2012-2022) by a 630 nm band airglow imager at the Qujing Station in Yunnan, China. All raw data underwent standardized preprocessing, including image enhancement, azimuth correction, geometric distortion correction, and geographic coordinate projection. Expert teams then performed plasma bubble event identification and contour annotation. With a high temporal resolution of 3 minutes, the dataset systematically documents plasma bubble events under varying solar activity intensities, covering multiple typical morphologies such as shaped I- and Y-shaped structures. This dataset provides high-quality benchmark data for developing high-precision supervised AI algorithms, facilitating automated detection and morphological evolution research of ionospheric plasma bubbles based on airglow imaging.
-
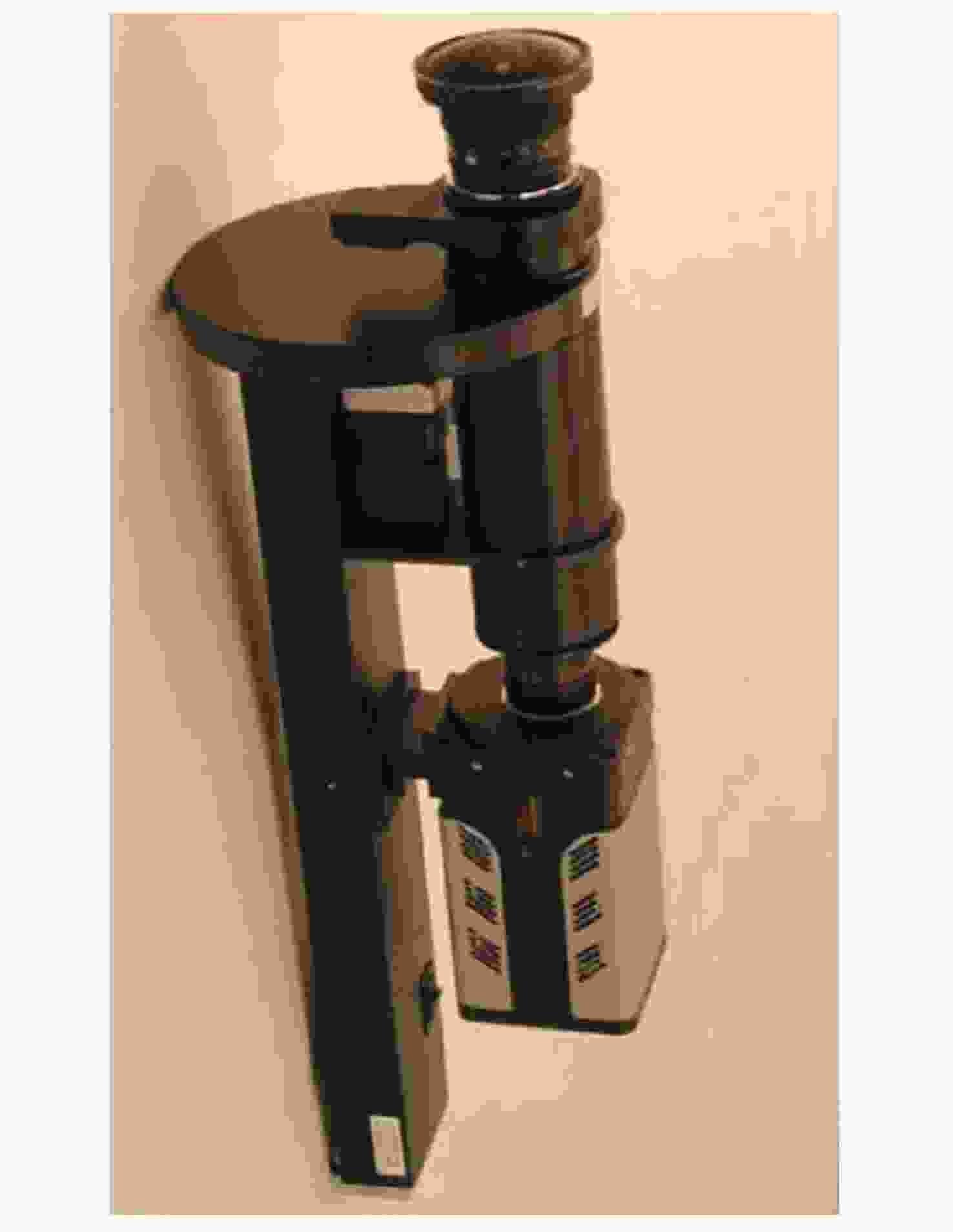
图 2 全天空气辉成像仪实物[21]
Figure 2. Picture of the all-sky airglow imager
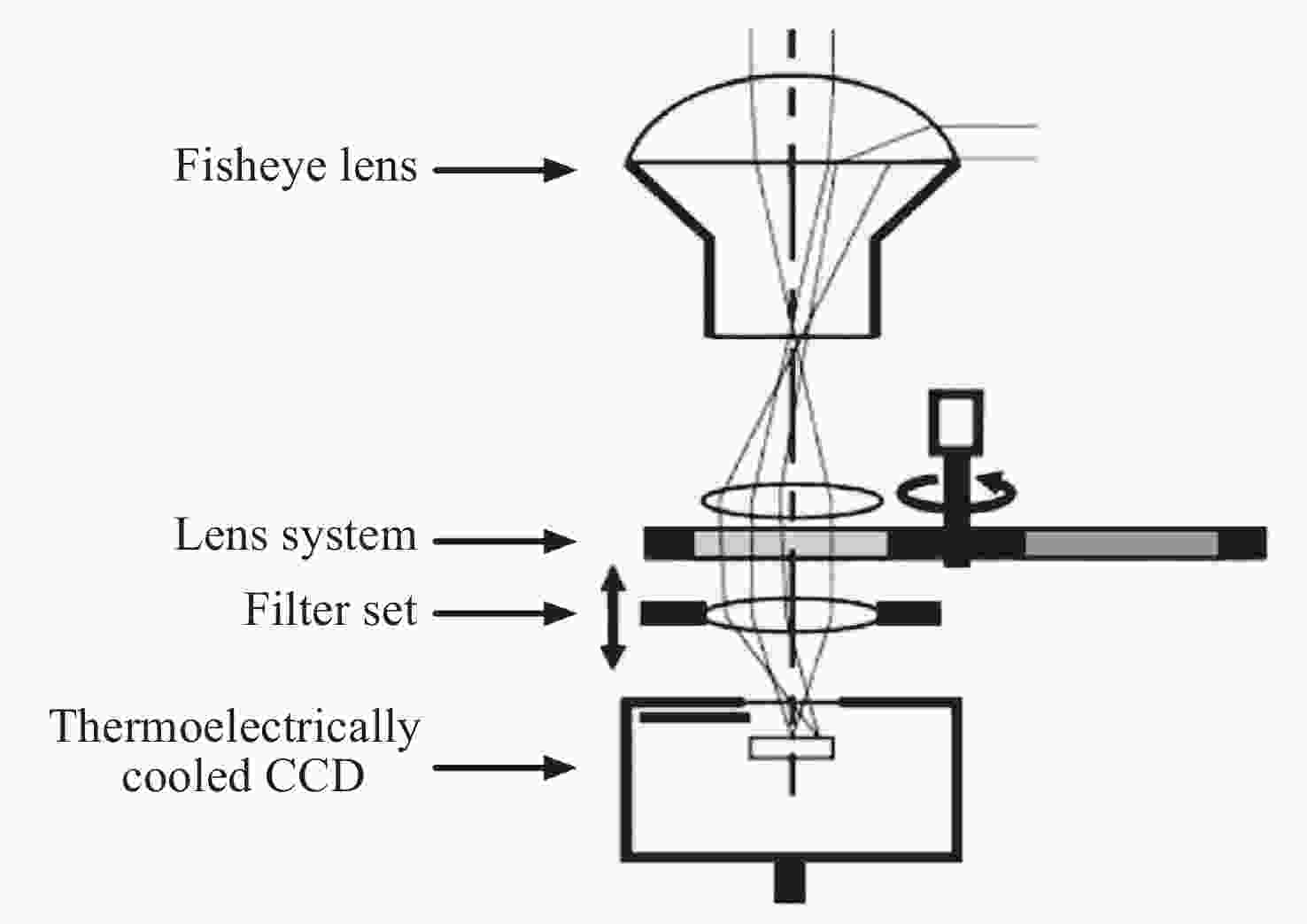
图 3 全天空气辉成像仪内部结构[21]
Figure 3. All-sky airglow imager internal structure
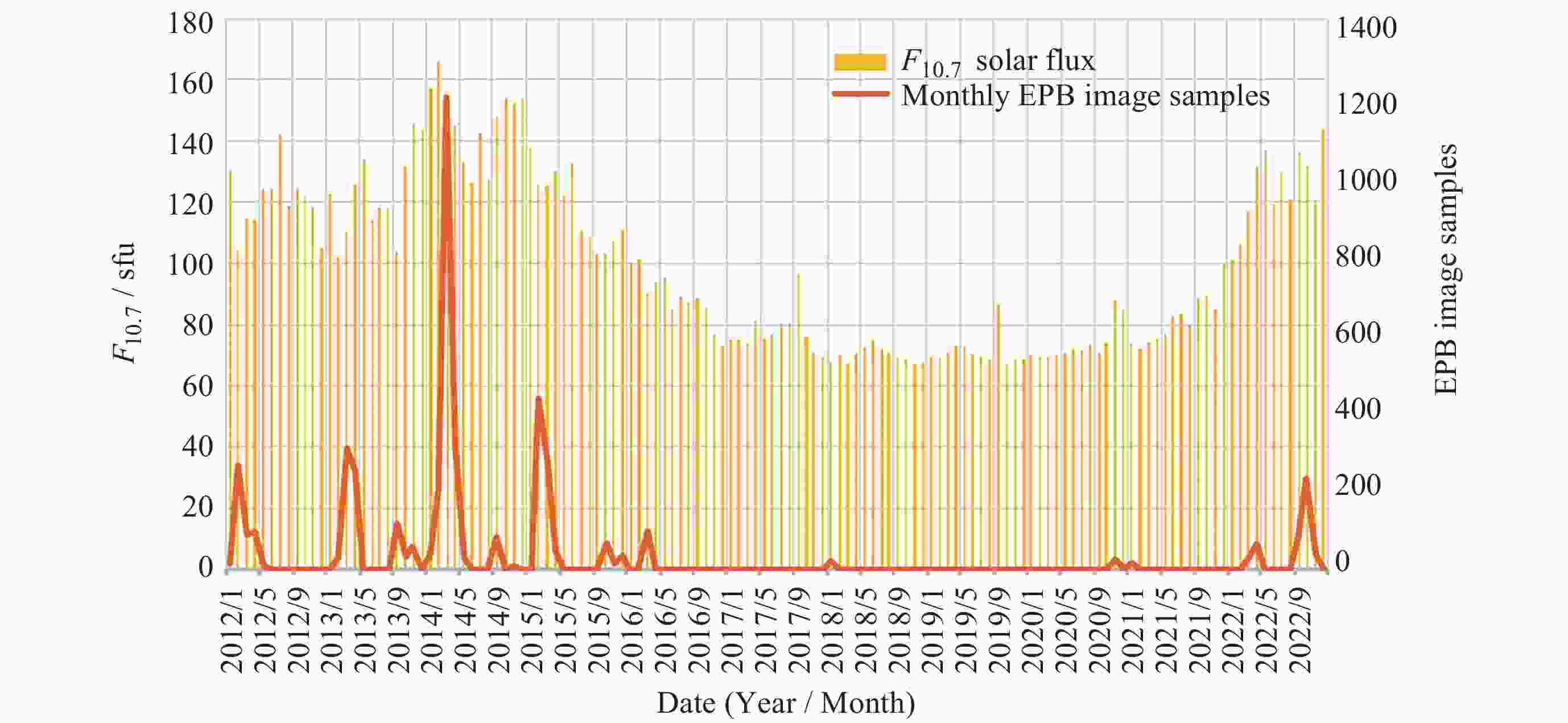
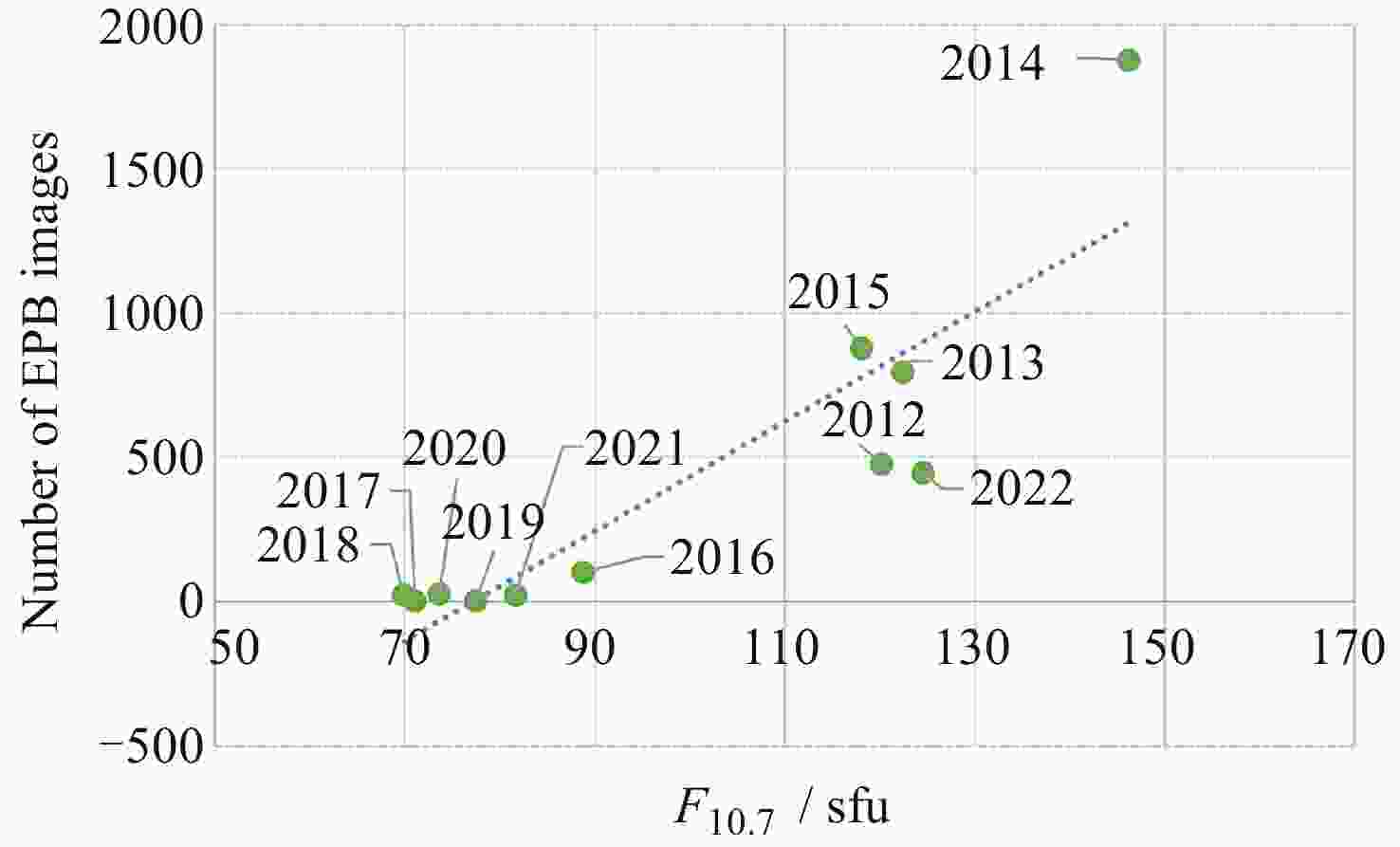
图 12 等离子体泡样本逐年逐月分布与太阳活动水平的关系[25]
Figure 12. Relationship between interannual and monthly distributions of plasma bubble samples and solar activity levels
表 1 曲靖台站不同年份观测夜晚与气辉观测图像及等离子体泡样本分布
Table 1. Distribution of observation nights, airglow observation images and plasma bubble samples at Qujing Station in different years
Year Observation nights Clear nights Images Good quality images EPB images 2012 291 108 43389 13639 474 2013 347 132 58441 16012 799 2014 357 145 68662 18066 1893 2015 360 121 75368 19112 889 2016 323 112 65849 18012 99 2017 341 110 71820 17739 0 2018 313 129 64227 19510 21 2019 294 133 60604 18701 0 2020 313 134 62052 17150 25 2021 363 135 77322 20012 20 2022 355 133 75641 20124 444 Total 3657 1392 723375 198077 4664 -
[1] OTT E. Theory of Rayleigh-Taylor bubbles in the equatorial ionosphere[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1978, 83(A5): 2066-2070 doi: 10.1029/JA083iA05p02066 [2] WEBER E J, BUCHAU J, EATHER R H, et al. North-south aligned equatorial airglow depletions[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1978, 83(A2): 712 doi: 10.1029/JA083iA02p00712 [3] KELLEY M C. The Earth’s Ionosphere: Plasma Physics and Electrodynamics, Second Edition[M]. Boston: Academic Press, c2009. Hardback ISBN: 9780120884254 [4] AGGSON T L, LAAKSO H, MAYNARD N C, et al. In situ observations of bifurcation of equatorial ionospheric plasma depletions[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1996, 101(A3): 5125-5132 doi: 10.1029/95ja03837 [5] IMOÇIN E, INYURT S, TEMUÇIN H, et al. Investigation of equatorial plasma bubble irregularities under different geomagnetic conditions during the equinoxes and the occurrence of plasma bubble suppression[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2020, 177: 341-350 doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2020.08.007 [6] WOODMAN R F, LA HOZ C. Radar observations of F region equatorial irregularities[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1976, 81(31): 5447-5466 doi: 10.1029/JA081i031p05447 [7] WOODMAN R F. Spread F-an old equatorial aeronomy problem finally resolved[J]. Annales Geophysicae, 2009, 27(5): 1915-1934 doi: 10.5194/angeo-27-1915-2009 [8] MENDILLO M, BAUMGARDNER J. Airglow characteristics of equatorial plasma depletions[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1982, 87(A9): 7641-7652 doi: 10.1029/JA087iA09p07641 [9] SAHAI Y, FAGUNDES P R, BITTENCOURT J A. Transequatorial F-region ionospheric plasma bubbles: solar cycle effects[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2000, 62(15): 1377-1383 doi: 10.1016/S1364-6826(00)00179-6 [10] KELLEY M C, MAKELA J J, LEDVINA B M, et al. Observations of equatorial spread-F from Haleakala, Hawaii[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2002, 29(20): 2003 doi: 10.1029/2002GL015509 [11] MAKELA J J, LEDVINA B M, KELLEY M C, et al. Analysis of the seasonal variations of equatorial plasma bubble occurrence observed from Haleakala, Hawaii[J]. Annales Geophysicae, 2004, 22(9): 3109-3121 doi: 10.5194/angeo-22-3109-2004 [12] TAORI A, SINDHYA A. Measurements of equatorial plasma depletion velocity using 630 nm airglow imaging over a low-latitude Indian station[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2014, 119(1): 396-401 doi: 10.1002/2013JA019465 [13] NARAYANAN V L, GURUBARAN S, SHINY M B B, et al. Some new insights of the characteristics of equatorial plasma bubbles obtained from Indian region[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2017, 156: 80 doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2017.03.006 [14] WANG C. New chains of space weather monitoring stations in China[J]. Space Weather, 2010, 8(8): S08001 doi: 10.1029/2010SW000603 [15] LI Q Z, XU J Y, GUSMAN A R, et al. Upper-atmosphere responses to the 2022 Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai volcanic eruption via acoustic gravity waves and air-sea interaction[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2024, 24(14): 8343-8361 doi: 10.5194/acp-24-8343-2024 [16] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84-90 doi: 10.1145/3065386 [17] SMIRNOV E A, TIMOSHENKO D M, ANDRIANOV S N. Comparison of regularization methods for ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. AASRI Procedia, 2014, 6: 89-94 doi: 10.1016/j.aasri.2014.05.013 [18] LIU L, OUYANG W L, WANG X G, et al. Deep learning for generic object detection: a survey[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2020, 128(2): 261-318 doi: 10.1007/s11263-019-01247-4 [19] LAI C, XU J Y, YUE J, et al. Automatic extraction of gravity waves from all-sky airglow image based on machine learning[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(13): 1516 doi: 10.3390/rs11131516 [20] LAI C, XU J Y, LIN Z S, et al. Statistical characteristics of nighttime medium-scale traveling ionospheric disturbances from 10-years of airglow observation by the machine learning method[J]. Space Weather, 2023, 21(5): e2023SW- 003430 doi: 10.1029/2023SW003430 [21] SUN Longchang. Study on Low- and Mid-Latitudinal Ionospheric Irregularity Based on Ground-Based and Satellite Observations[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (National Space Science Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2017: 47-48 [22] GARCIA F J, TAYLOR M J, KELLEY M C. Two-dimensional spectral analysis of mesospheric airglow image data[J]. Applied Optics, 1997, 36(29): 7374-7385 doi: 10.1364/AO.36.007374 [23] HUANG C Y, BURKE W J, MACHUZAK J S, et al. Equatorial plasma bubbles observed by DMSP satellites during a full solar cycle: toward a global climatology[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2002, 107(A12): 1434 doi: 10.1029/2002JA009452 [24] WU K, XU J Y, ZHU Y J, et al. Occurrence characteristics of branching structures in equatorial plasma bubbles: a statistical study based on all-sky imagers in China[J]. Earth and Planetary Physics, 2021, 5(5): 407-415 doi: 10.26464/epp2021044 [25] ZHONG J, ZOU Z M, WU K, et al. Automatic detection and feature extraction of equatorial plasma bubbles from all-sky airglow image based on machine learning[J]. Space Weather, 2025, 23(5): e2025SW004336 doi: 10.1029/2025SW004336 [26] HAASE J S, DAUTERMANN T, TAYLOR M J, et al. Propagation of plasma bubbles observed in Brazil from GPS and airglow data[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2011, 47(10): 1758-1776 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2010.09.025 -
-





 钟佳 男, 1987年出生, 博士, 中国科学院国家空间科学中心项目高级工程师, 主要研究方向为空间天气数据挖掘与机器学习建模、科学可视化技术. E-mail:
钟佳 男, 1987年出生, 博士, 中国科学院国家空间科学中心项目高级工程师, 主要研究方向为空间天气数据挖掘与机器学习建模、科学可视化技术. E-mail:  邹自明 男, 1971年出生, 博士, 中国科学院国家空间科学中心研究员、国家空间科学数据中心主任、中国科学院大学博士生导师, 长期从事空间科学与数据科学交叉领域研究. E-mail:
邹自明 男, 1971年出生, 博士, 中国科学院国家空间科学中心研究员、国家空间科学数据中心主任、中国科学院大学博士生导师, 长期从事空间科学与数据科学交叉领域研究. E-mail:  徐寄遥 男, 1959年出生, 博士, 中国科学院国家空间科学中心研究员、博士生导师, 国家杰出青年基金获得者, 现任国家重大科技基础设施“空间环境地基综合监测网——子午工程II期”总工程师. 长期从事中高层大气物理学研究. E-mail:
徐寄遥 男, 1959年出生, 博士, 中国科学院国家空间科学中心研究员、博士生导师, 国家杰出青年基金获得者, 现任国家重大科技基础设施“空间环境地基综合监测网——子午工程II期”总工程师. 长期从事中高层大气物理学研究. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: