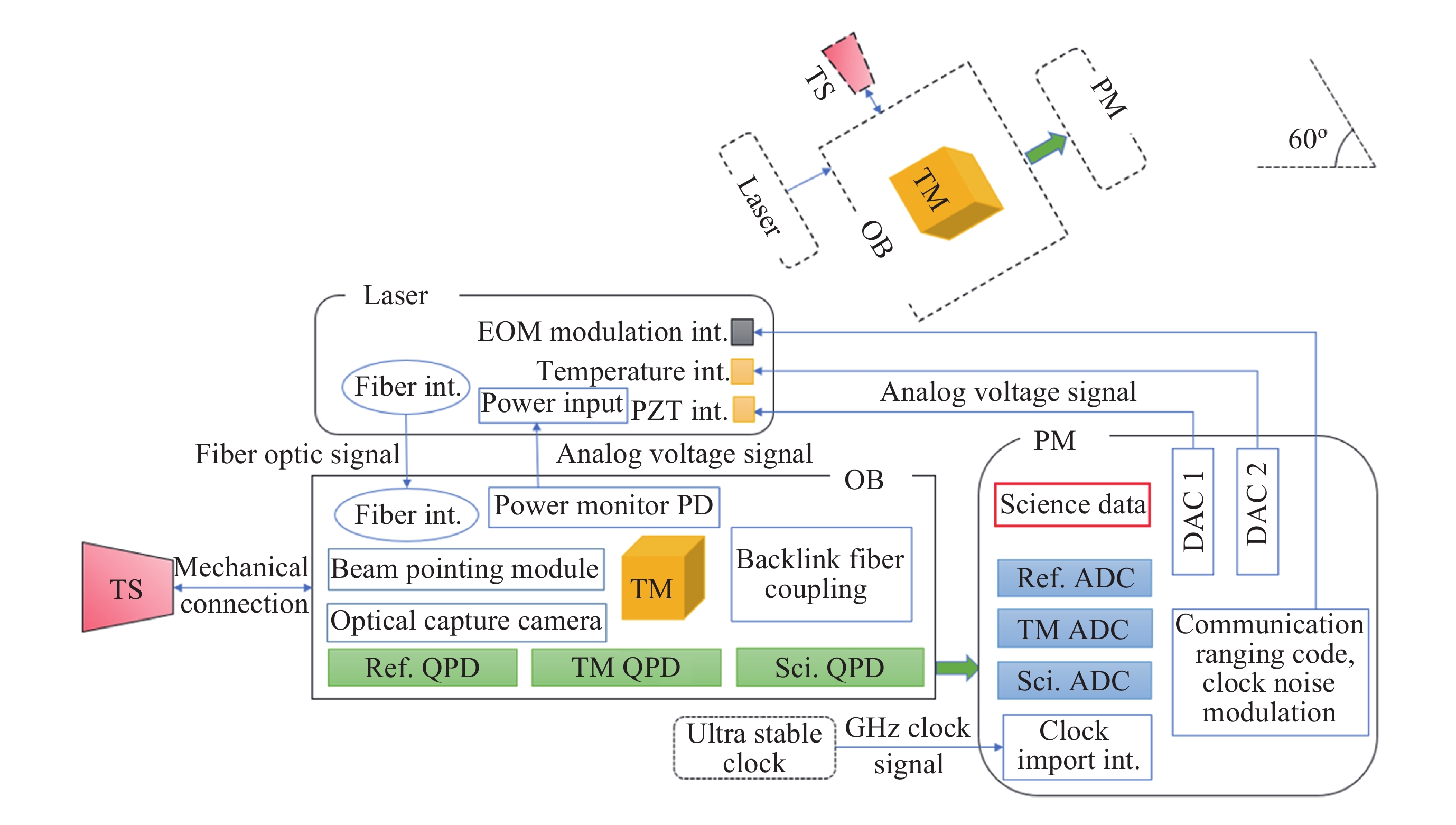
Noise and Index Decomposition of Taiji-2 Interferometer System
-
摘要: 空间引力波探测太极计划是中国科学院发起的mHz频段引力波探测任务, 由围绕太阳旋转的三颗卫星组成等边三角形, 星间距3×106 km, 通过激光差分干涉方法实现卫星间pm级位移波动测量. 作为太极计划“三步走”战略的承上启下的关键环节, 太极二号将全面验证太极计划的各项关键技术. 太极二号卫星构型与太极三号相同, 激光干涉系统作为核心测量手段, 需达到30 pm·Hz–1/2的噪声水平. 本文从顶层指标出发, 逐步分解各子系统噪声指标及关键参数, 包括激光器、干涉仪光学平台、相位计、望远镜、呼吸角补偿机构等. 研究结果可为太极二号后续工程任务的指标划分奠定理论基础.Abstract: The Taiji program for space-based gravitational wave detection is a mission initiated by the Chinese Academy of Sciences to explore gravitational waves in the mHz frequency band. It consists of three satellites orbiting the Sun in an equilateral triangle formation with an arm length of 3×106 km, employing laser interferometry to measure picometer-level displacement fluctuations between satellites. As a pivotal link in Taiji’s “three-step” development strategy, Taiji-2 will comprehensively validate all key technologies of the program. The satellite configuration of the Taiji-2 satellite shares the same configuration as Taiji-3, with its laser interferometry system requiring a noise level of 30 pm·Hz–1/2 as the core measurement technique. This paper systematically decomposes the top-level requirements into subsystem noise budgets and key parameters, including the laser system, interferometer optical bench, phasemeter, telescope, and breathing angle compensation mechanism. The research findings establish a theoretical foundation for subsequent engineering task allocation in the Taiji-2 mission.
-
表 1 太极计划顶层指标参数
Table 1. Top-level indicator parameters of the Taiji program
卫星 臂长
/m光功率/W 望远镜口径/cm 系统测距噪声/(pm·Hz–1/2) 加速度噪声/(m·s–2·Hz–1/2) Taiji-3 3×109 2~3 40 8 3×10–15 Taiji-2 3×109 2~3 40 30 3×10–14 表 2 Taiji-2干涉仪系统各功能指标参数
Table 2. Indicator parameters of Taiji-2 interferometer function
功能 参数 需求 星间测距测角 本地位移测量噪声/(pm·Hz–1/2) ≤10 本地角度测量噪声/(nrad·Hz–1/2) ≤10 星间通信
与绝对距离测量通信速率/(kbit·s–1) ≥20 距离测量精度/m ≤10 星间时钟噪声传递 噪声/(pm·Hz–1/2) ≤10 弱光锁相 噪声/(pm·Hz–1/2) ≤6 锁臂 噪声/(Hz·Hz–1/2) ≤10–4 表 3 Taiji-2测距噪声指标分解
Table 3. Indicator decomposition for ranging noise in Taiji-2
噪声类型 指标/
(pm·Hz–1/2)噪声模型 相关参数 数值 散粒噪声 6 $ {\tilde{x}}_{\mathrm{S}\mathrm{N}}=\dfrac{2\sqrt{hc}}{{\mathrm{\pi }}^{2}}\dfrac{{\lambda }^{\tfrac{3}{2}}L}{\varepsilon {D}^{2}}{{P}_{\mathrm{o}}}^{-\tfrac{1}{2}} $ Po激光输出功率/W 1.2 望远镜口径D/m 0.4 ε总光学效率 0.3 激光频率噪声
(TDI)10 ― 频率稳定度/(Hz·Hz–1/2) 30 TDI/(pm·Hz–1/2) 10 激光功率噪声 2 $ {N}_{1\mathrm{f}{\text{-}}\mathrm{R}\mathrm{I}\mathrm{N}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2\left({P}_{\mathrm{m}}+{P}_{\mathrm{r}}\right)}}{\sqrt{{\eta }_{\mathrm{h}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{t}}{P}_{m}{P}_{\mathrm{r}}}}\tilde{r}\left(1{\mathrm{f}}_{\mathrm{h}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{t}}\right)\left|\mathrm{s}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\left(\dfrac{\varphi -{\varphi }_{\mathrm{R}}}{2}\right)\right| $
$ {N}_{2\mathrm{f}{\text{-}}\mathrm{R}\mathrm{I}\mathrm{N}}=\sqrt{2}\tilde{r}\left(2{\mathrm{f}}_{\mathrm{h}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{t}}\right)\left|\mathrm{s}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\left(\varphi -{\varphi }_{\mathrm{R}}\right)\right| $MHz-RIN/Hz–1/2 10–8 $ F=\dfrac{P}{c}\left(1+\rho \right) $ mHz-RIN/Hz–1/2 10–4 光程噪声 10 ― 光学平台光程噪声/(pm·Hz–1/2) 10 TTL噪声 15 $ {\alpha }_{\mathrm{T}\mathrm{T}\mathrm{L}}=\dfrac{{{x}}_{\mathrm{T}\mathrm{T}\mathrm{L}}}{{\theta }_{\mathrm{p}}} $ 光束抖动/(rad·Hz–1/2) 3 望远镜放大倍数 100 耦合系数/(m·rad–1) 5 超前指向噪声 5 ― 机构光程噪声/(pm·Hz–1/2) 5 相位测量噪声 5 ― 探测器等效光功率噪声、相位计测相
噪声、相位计模拟前端噪声/(pm·Hz–1/2)5 时钟噪声 10 $ {\tilde{\phi }}_{\mathrm{U}\mathrm{S}\mathrm{O}}=2\mathrm{\pi } {\tilde{t}}_{\mathrm{U}\mathrm{S}\mathrm{O}} {f}_{\mathrm{h}} $ 计时误差/(s·Hz–1/2) 4×10–13 差分频率/MHz 5~25 望远镜稳定性噪声 10 ― ― ― 激光指向噪声 10 $ \tilde{x}=\dfrac{\mathrm{\pi }d{D}^{2}}{2{\lambda }^{2}}{\theta }_{\mathrm{d}\mathrm{c}}{\tilde{\theta }}_{\mathrm{p}} $ 望远镜镜面平整度@1064 nm λ/20 指向静态偏差/nrad 30 指向抖动/(nrad·Hz–1/2) 30 杂散光 5 $ \Delta \varphi =-\sqrt{\dfrac{{P}_{\mathrm{s}}}{{P}_{\mathrm{o}}}}\Delta {\varphi }_{\mathrm{s}} $ 杂散光功率/nW 1 参考光功率/μW 100 结构稳定性/(nm·Hz–1/2) 1 呼吸角补偿光程噪声 5 ― ― ― 其他噪声 5 ― ― ― 总噪声 ― ― 总噪声值/(pm·Hz–1/2) 29.8 -
[1] LUO Z R, WANG Y, WU Y L, et al. The Taiji program: a concise overview[J]. Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics, 2021, 2021(5): 05A108 doi: 10.1093/ptep/ptaa083 [2] 吴岳良, 胡文瑞, 王建宇, 等. 空间引力波探测综述与拟解决的科学问题[J]. 空间科学学报, 2023, 43(4): 589-599 doi: 10.11728/cjss2023.04.yg08WU Yueliang, HU Wenrui, WANG Jianyu, et al. Review and scientific objectives of spaceborne gravitational wave detection missions[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2023, 43(4): 589-599 doi: 10.11728/cjss2023.04.yg08 [3] GONG Y G, LUO J, WANG B. Concepts and status of Chinese space gravitational wave detection projects[J]. Nature Astronomy, 2021, 5(9): 881-889 doi: 10.1038/s41550-021-01480-3 [4] LUO J, CHEN L S, DUAN H Z, et al. TianQin: a space-borne gravitational wave detector[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2016, 33(3): 035010 doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/33/3/035010 [5] The Taiji Scientific Collaboration. China’s first step towards probing the expanding universe and the nature of gravity using a space borne gravitational wave antenna[J]. Communications Physics, 2021, 4(1): 34 doi: 10.1038/s42005-021-00529-z [6] LIU H S, LUO Z R, SHA W, et al. In-orbit performance of the laser interferometer of Taiji-1 experimental satellite[J]. International Journal of Modern Physics A, 2021, 36(11n12): 2140004 doi: 10.1142/S0217751X21400042 [7] The Taiji Scientific Collaboration. The pilot of Taiji program — from the ground to Taiji-2[J]. International Journal of Modern Physics A, 2021, 36(11/12): 2012001 [8] LUO Z R, ZHANG M, WANG J Y, et al. Progress of Taiji-2 Project[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2024, 44(4): 674-676 doi: 10.11728/cjss2024.04.2024-yg14 [9] 王娟, 齐克奇, 王少鑫, 等. 面向空间引力波探测的激光干涉技术研究进展及展望[J]. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学, 2024, 54(7): 270405WANG Juan, QI Keqi, WANG Shaoxin, et al. Advance and prospect in the study of laser interferometrytechnology for space gravitational wave detection[J]. Scientia Sinica Physica, Mechanica :Times New Roman;">& Astronomica, 2024, 54(7): 270405 [10] 高瑞弘, 刘河山, 罗子人, 等. 太极计划激光指向调控方案介绍[J]. 中国光学, 2019, 12(3): 425-431 doi: 10.3788/co.20191203.0425GAO Ruihong, LIU Heshan, LUO Ziren, et al. Introduction of laser pointing scheme in the Taiji program[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(3): 425-431 doi: 10.3788/co.20191203.0425 [11] 刘河山, 高瑞弘, 罗子人, 等. 空间引力波探测中的绝对距离测量及通信技术[J]. 中国光学, 2019, 12(3): 486-492 doi: 10.3788/co.20191203.0486LIU Heshan, GAO Ruihong, LUO Ziren, et al. Laser ranging and data communication for space gravitational wave detection[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(3): 486-492 doi: 10.3788/co.20191203.0486 [12] CHEN P Q, ZHANG Y B, DENG R J, et al. Experimental demonstration of bi-directional laser ranging and data communication for space gravitational wave detection[J]. Results in Physics, 2024, 65: 107985 doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2024.107985 [13] 江强, 董鹏, 刘河山, 等. 太极计划时钟噪声传递的地面原理验证[J]. 中国光学(中英文), 2023, 16(6): 1394-1403 doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0012JIANG Qiang, DONG Peng, LIU Heshan, et al. Ground-based principle verification of clock noisetransfer for the Taiji program[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(6): 1394-1403 doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0012 [14] 王晨, 高雪荣, 齐克奇, 等. 太极计划的弱光锁相地面实验验证及噪声分析[J]. 中国激光, 2025, 52(11): 1101004 doi: 10.3788/CJL241485WANG Chen, GAO Xuerong, QI Keqi, et al. Weak light phase-locked ground-based experimantal validation and noise analysis of the Taiji projecet[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2025, 52(11): 1101004 doi: 10.3788/CJL241485 [15] BARKE S. Inter-Spacecraft Frequency Distribution for Future Gravitational Wave Observatories[D]. Hannover: Leibniz Universität Hannover, 2015 [16] ZHAN Z H, LUO Y X, YEH H C, et al. Development of a space-compatible packaging system for an integrated monolithic ultra-stable optical reference[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2024, 95(10): 104505 doi: 10.1063/5.0224636 [17] 刘宇, 张玉珠, 彭晓东, 等. 激光频率波动对空间引力波探测激光干涉测量的影响分析[J]. 空间科学学报, 2025, 45(1): 179-188 doi: 10.11728/cjss2025.01.2024-0020LIU Yu, ZHANG Yuzhu, PENG Xiaodong, et al. Analysis of the influence and importance of laser frequency fluctuation on laser interference simulation system for space gravitational wave detection[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2025, 45(1): 179-188 doi: 10.11728/cjss2025.01.2024-0020 [18] ZHANG J F, YANG Z, MA X S, et al. Inter-spacecraft offset frequency setting strategy in the Taiji program[J]. Applied Optics, 2022, 61(3): 837-843 doi: 10.1364/AO.442583 [19] ZHANG J F, MA X S, ZHAO M Y, et al. Advanced inter-spacecraft offset frequency setting strategy for the Taiji program based on a two-stage optimization algorithm[J]. Applied Optics, 2023, 62(16): 4370-4380 doi: 10.1364/AO.487809 [20] FAN X, FAYER S E, MYERS T G, et al. Switchable damping for a one-particle oscillator[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2021, 92(2): 023201 doi: 10.1063/5.0038005 [21] HUARCAYA V, ÁLVAREZ M D, PENKERT D, et al. 2×10–13 Fractional laser-frequency stability with a 7-cm unequal-arm Mach-Zehnder interferometer[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2023, 20(2): 024078 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.20.024078 [22] GHOSH S, SANJUAN J, MUELLER G. Arm locking performance with the new LISA design[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2022, 39(11): 115009 doi: 10.1088/1361-6382/ac69a4 [23] YAMAMOTO K, BYKOV I, REINHARDT J N, et al. Experimental end-to-end demonstration of intersatellite absolute ranging for the laser interferometer space antenna[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2024, 22(5): 054020 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.22.054020 [24] WISSEL L, WITTCHEN A, SCHWARZE T S, et al. Relative-intensity-noise coupling in heterodyne interferometers[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2022, 17(2): 024025 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.17.024025 [25] WISSEL L, HARTWIG O, BAYLE J B, et al. Influence of laser relative-intensity noise on the laser interferometer space antenna[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2023, 20(1): 014016 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.20.014016 [26] WISSEL L, HEWITSON M, HEINZEL G. Measuring the impact of laser relative intensity noise on heterodyne interferometers using differential wavefront sensing[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2024, 22(4): 044048 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.22.044048 [27] LUO Z R, GUO Z K, JIN G, et al. A brief analysis to Taiji: science and technology[J]. Results in Physics, 2020, 16: 102918 doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2019.102918 [28] REID M M, HAUGHIAN K, CUMMING A V, et al. Temperature dependence of the thermal conductivity of hydroxide catalysis bonds between silicon substrates[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2023, 40(24): 245006 doi: 10.1088/1361-6382/ad0923 [29] LOHDE A, VOIGT D, GERBERDING O. Dual balanced readout for scattered light noise mitigation in Michelson interferometers[J]. Physical Review D, 2025, 111(2): 022004 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevD.111.022004 [30] ROHR M J, AST S, GERBERDING O, et al. Fiber backscatter under increasing exposure to ionizing radiation[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(23): 34894-34903 doi: 10.1364/OE.404139 [31] 言立慧, 刘河山, 边星, 等. 太极计划中的测温电桥激励源设计与验证[J]. 空间科学学报, 2025, 45(3): 1-10YAN Lihui, LIU Heshan, BIAN Xing, et al. Design and verification of temperature measurement bridge excitation source in the Taiji Program[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2025, 45(3): 1-10 [32] ROBERTSON D I, FITZSIMONS E D, KILLOW C J, et al. Automated precision alignment of optical components for hydroxide catalysis bonding[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(22): 28323-28334 doi: 10.1364/OE.26.028323 [33] MANGANO V, VAN VEGGEL A A, DOUGLAS R, et al. Determination of the refractive index and thickness of a hydroxide-catalysis bond between fused silica from reflectivity measurements[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(4): 3196-3213 doi: 10.1364/OE.25.003196 [34] SCHUSTER S, TRÖBS M, WANNER G, et al. Experimental demonstration of reduced tilt-to-length coupling by a two-lens imaging system[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(10): 10466-10475 doi: 10.1364/OE.24.010466 [35] ARMANO M, AUDLEY H, BAIRD J, et al. Tilt-to-length coupling in LISA Pathfinder: a data analysis[J]. Physical Review D, 2023, 108(10): 102003 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevD.108.102003 [36] SALLUSTI M, GATH P, WEISE D, et al. LISA system design highlights[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2009, 26(9): 094015 doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/26/9/094015 [37] 梁浴榕. 外差激光干涉仪中的高精度相位测量研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2013LIANG Yurong. Hign Precision Phase Measurement for Heterofyne Laser Interferomter[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2013 [38] YANG R, LIU H S, LUO Z R. Optimization design of decimation filter for the phasemeter in the space gravitational wave detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2024, 73: 7006508 [39] 李卓, 郑建华, 李明涛, 等. 太阳系天体引力对空间引力波探测日心编队构型的影响分析[J]. 空间科学学报, 2021, 41(3): 457-466 doi: 10.11728/cjss2021.03.457LI Zhuo, ZHENG Jianhua, LI Mingtao, et al. Analysis of celestial gravity influence on heliocentric formation flying of gravitational wave observatory[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2021, 41(3): 457-466 doi: 10.11728/cjss2021.03.457 [40] 许茗洋, 谈玉杰, 邵成刚. 空间引力波探测中的时钟噪声抑制技术研究进展[J]. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学, 2025, 55(3): 230409XU Mingyang, TAN Yujie, SHAO Chenggang. Research progress on clock noise suppression technique for space-borne gravitational wave detection[J]. Scientia Sinica Physica, Mechanica :Times New Roman;">& Astronomica, 2025, 55(3): 230409 [41] SANZ I E, HESKE A, LIVAS J C. A telescope for LISA – the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna[J]. Advanced Optical Technologies, 2018, 7(6): 395-400 doi: 10.1515/aot-2018-0044 [42] SASSO C P, MANA G, MOTTINI S. Telescope jitters and phase noise in the LISA interferometer[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(12): 16855-16870 doi: 10.1364/OE.27.016855 [43] JERSEY K, ZHANG Y Q, HARLEY-TROCHIMCZYK I, et al. Design, fabrication, and testing of an optical truss interferometer for the LISA telescope[C]//Design, Manufacture, and Test of Space and Ground Systems III. San Diego: SPIE, 2021 [44] BENDER P L. Wavefront distortion and beam pointing for LISA[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2005, 22(10): S339-S346 doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/22/10/027 [45] Team L S. LISA Pre-Phase A Report[R]. Noordwijk: ESTEC, 1998 [46] TRÖBS M, 'ARCIO L D, BARKE S, et al. Testing the LISA optical bench[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Space Optics. Ajaccio: ESA, 2012 [47] NOFRARIAS M, MARÍN A F G, LOBO A, et al. Thermal diagnostic of the optical window on board LISA Pathfinder[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2007, 24(20): 5103-5121 doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/24/20/012 [48] PACZKOWSKI S, GIUSTERI R, HEWITSON M, et al. Postprocessing subtraction of tilt-to-length noise in LISA[J]. Physical Review D, 2022, 106(4): 042005 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevD.106.042005 -
-




 刘河山 男, 1988年出生于安徽阜阳, 博士, 副研究员, 2015年于中国科学院大学获得博士学位, 研究领域涉及激光干涉测距、高精度相位测量、精密指向控制、激光锁相等. E-mail:
刘河山 男, 1988年出生于安徽阜阳, 博士, 副研究员, 2015年于中国科学院大学获得博士学位, 研究领域涉及激光干涉测距、高精度相位测量、精密指向控制、激光锁相等. E-mail: 
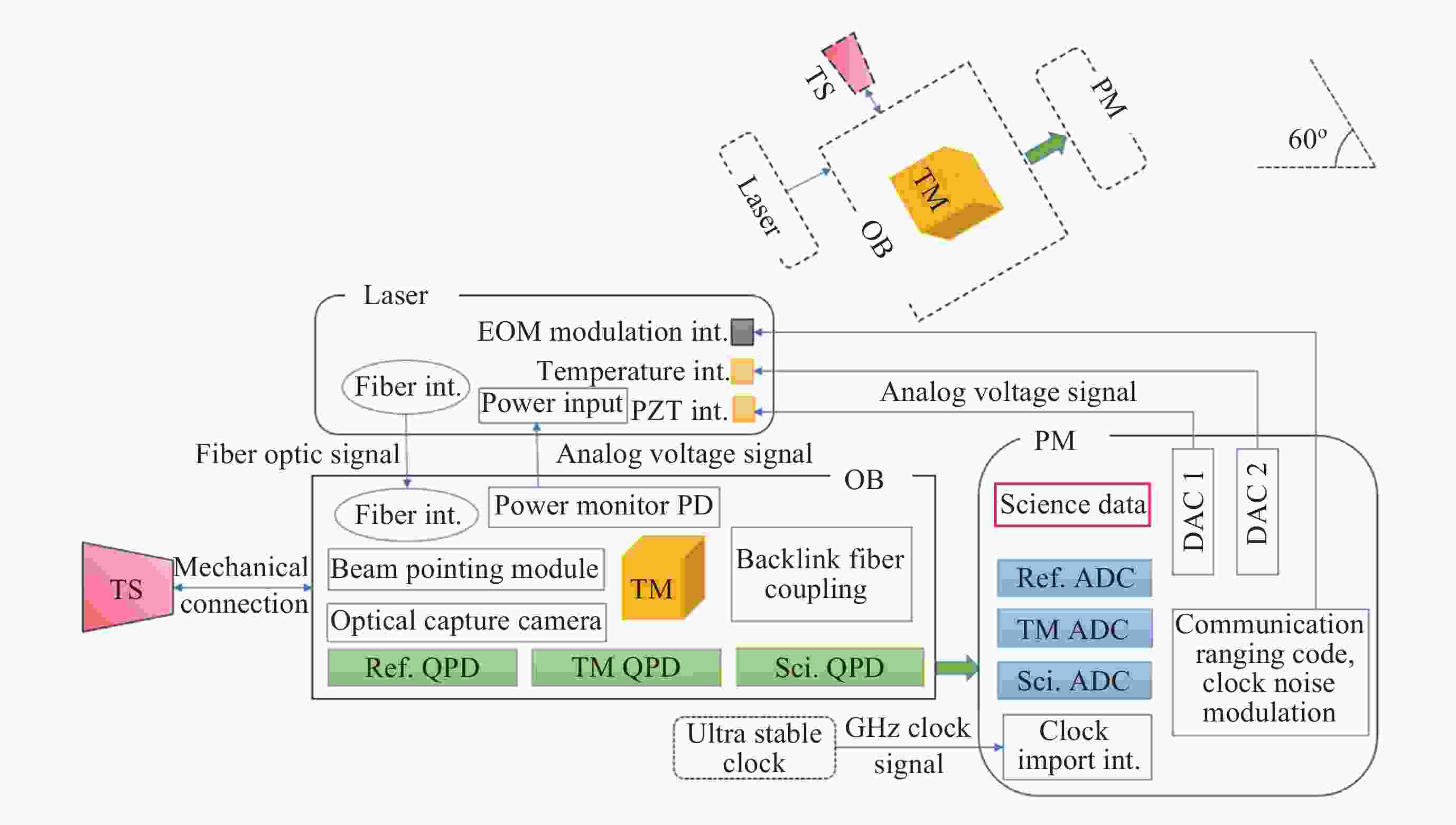
 下载:
下载: