Comparative Analysis of Four Neural Network Methods for TEC Modeling during Ionospheric Magnetic Storms
-
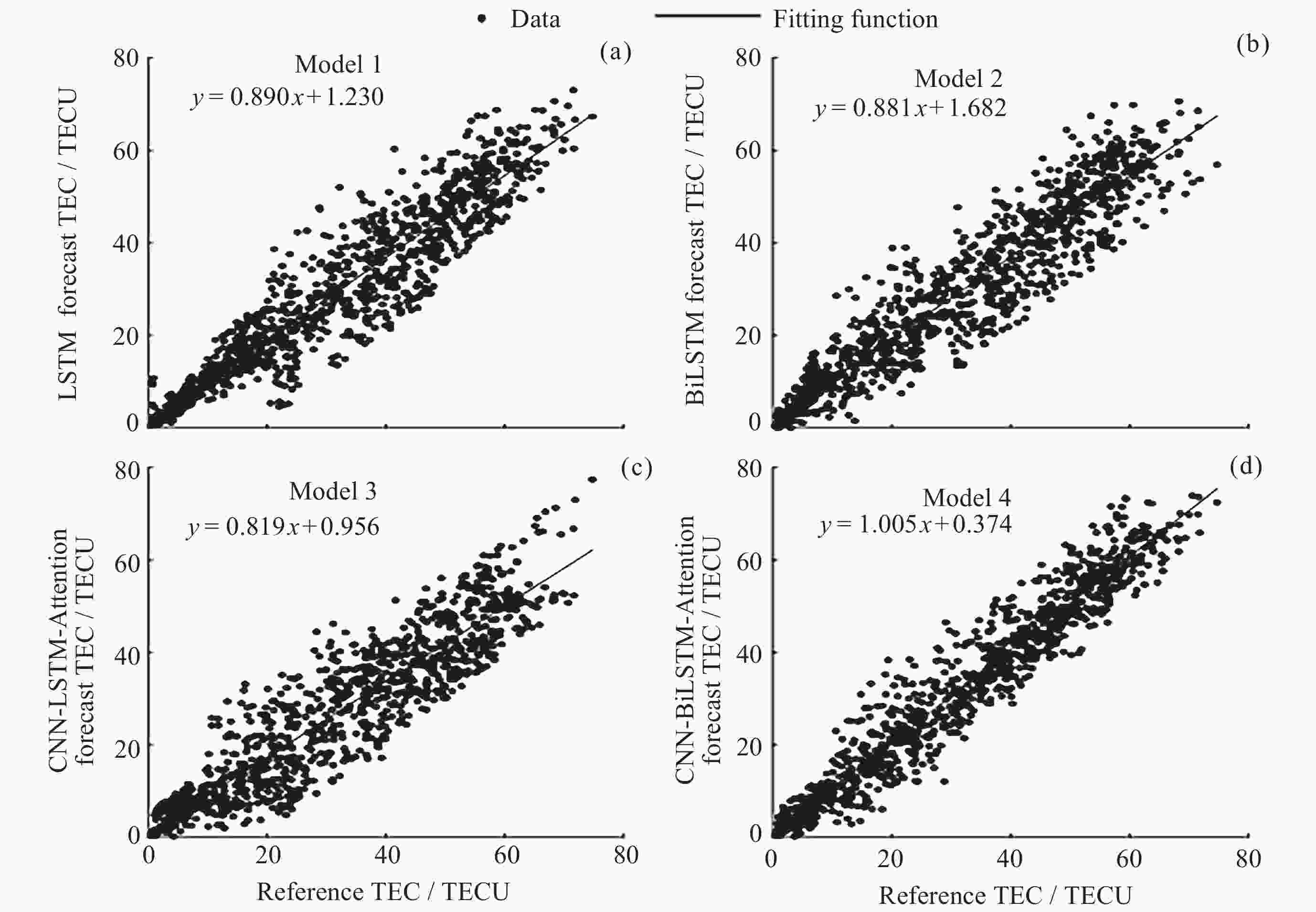
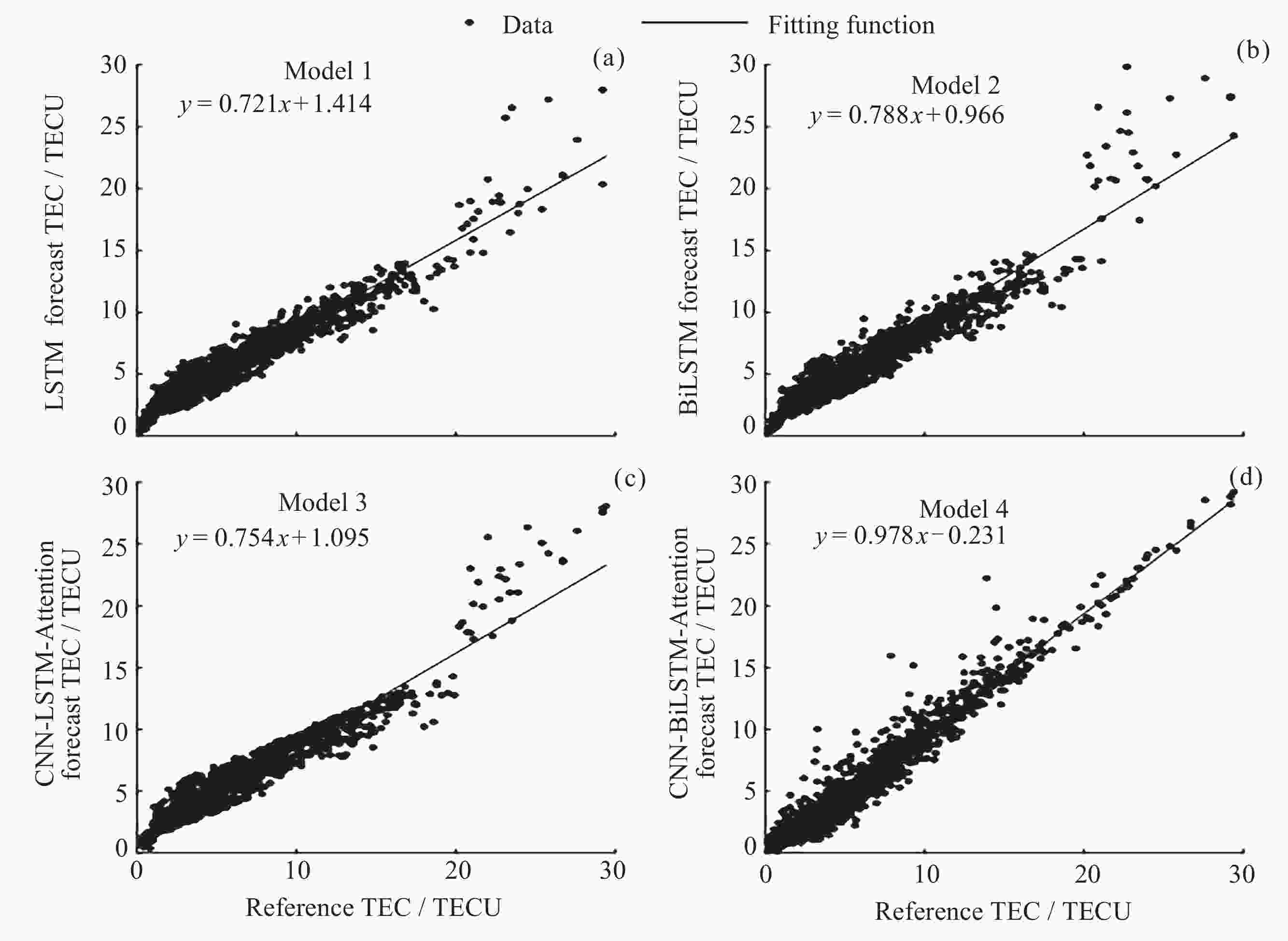
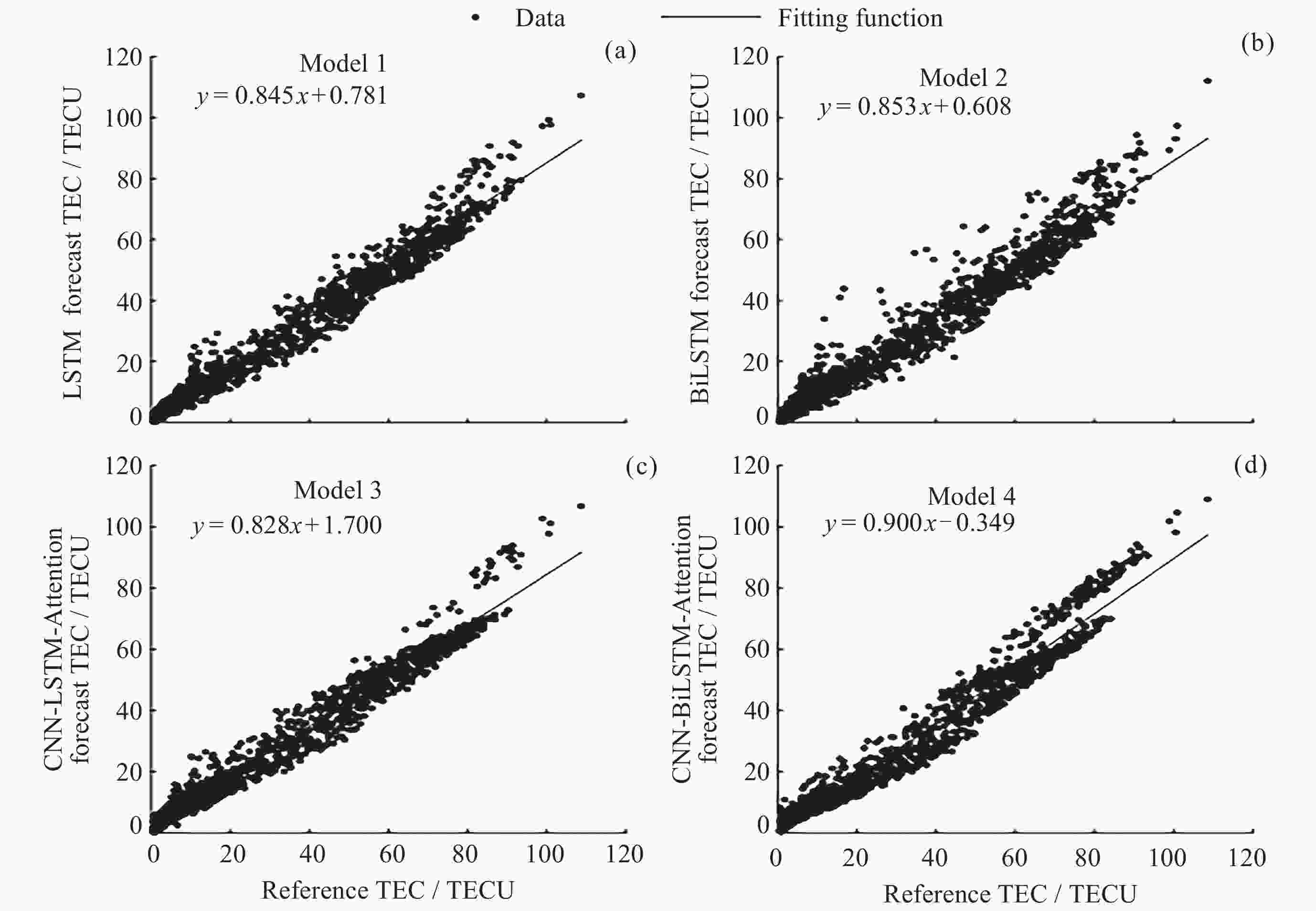
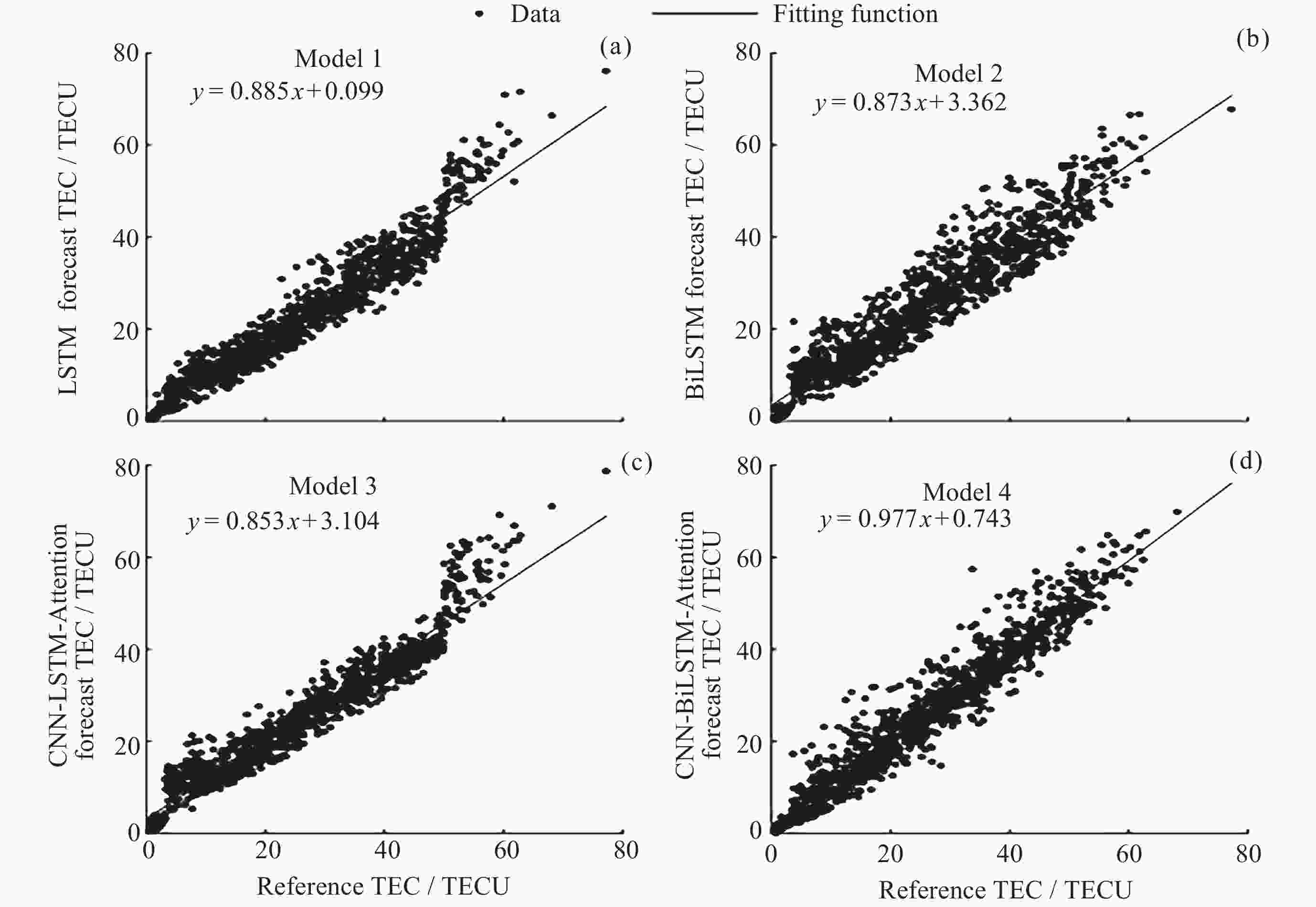
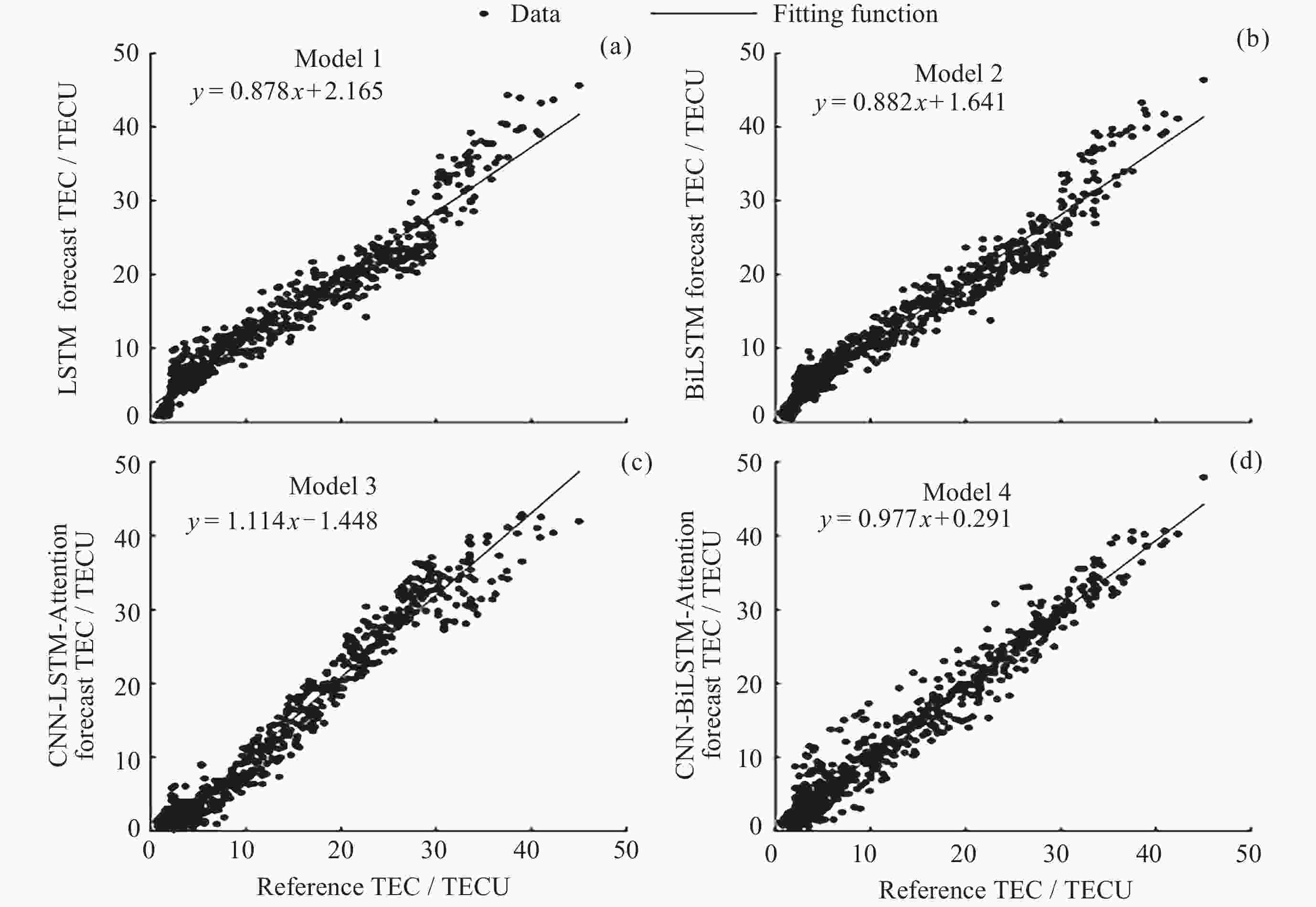
摘要: 电离层总电子含量(TEC)是描述电离层的重要参数, 然而电离层经验模型对于磁暴期TEC的预测精度不够理想. 针对这个问题, 使用LSTM、BiLSTM、结合注意力机制的卷积神经网络–长短期记忆(CNN-LSTM-Attention)以及结合注意力机制的卷积神经网络–双向长短期记忆(CNN-BiLSTM-Attention)神经网络模型进行电离层TEC预报的研究. 根据Dst ≤ –30 nT的标准, 确定了2004-2022年发生磁暴的时间段. 在此基础上, 结合多种时空参数(UTS与UTC, SA与AA, CHS与SHS), 得到了4种适用于磁暴期TEC的预测模型. 利用2023年磁暴期的TEC对四种模型的精度和可靠性进行验证. 结果表明, CNN-BiLSTM-Attention模型的预测效果明显优于其他三种模型, 其绝对平均误差(MAE)为0.882~5.270 TECU, 均方根误差(RMSE)为1.175~6.983 TECU, 且预测结果与参考值之间存在较强的相关性, 决定系数(R2)均在0.7以上. 此外, 该模型拟合函数的斜率整体上最接近于1, 同样优于其他三种模型的拟合效果.Abstract: The Total Electron Content (TEC) of the ionosphere is an important parameter for describing the ionosphere activities, and much research has been done for the accurate methods for the ionospheric TEC prediction. However, the prediction accuracy of ionospheric empirical models for TEC during geomagnetic storms is still not ideal. To address this issue, this paper aims to assess the performance of ionospheric TEC predicting methods, which involve the LSTM, the BiLSTM, the Convolutional Neural Network-Long Short-Term Memory combined with Attention mechanism (CNN-LSTM-Attention), and the Convolutional Neural Network-Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory combined with Attention mechanism (CNN-BiLSTM-Attention). At first, the geomagnetic storm periods are identified by comparing with the threshold of Dst index (≤–30 nT), during the years from 2004 to 2022. Then, four neural network models for the ionospheric TEC prediction are formed, through the combinations of multiple spatiotemporal parameters, such as UTS, UTC, SA, AA, CHS, and SHS. Finally, the accuracy and reliability of the four neural network models are assessed using the reference TEC dataset collected during geomagnetic storms in 2023, and three statistical index, Mean Absolute Error (MAE), The Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), and coefficient of determination R2, are utilized. The results show that, the performance of the CNN-BiLSTM-Attention model is superior to the other three models, with MAE ranging from 0.882 to 5.270 TECU, RMSE between 1.175 and 6.983 TECU, and R2 values exceeding 0.7. In order to better describe the difference between the predicted values and the reference values, the scatter plots of two datasets are plotted for the fitting of linear regression equations. The slope of fitted function from CNN-BiLSTM-Attention model is very close to the ideal value 1, also indicating a better performance compared to the other models.
-
表 1 Dst指数与地磁活动关系
Table 1. Relationship between Dst index and geomagnetic activity
Dst 指数/nT 地磁情况 Dst > –30 地磁平静期 –50 < Dst ≤ –30 微小磁暴 –100 < Dst ≤ –50 中等磁暴 –200 < Dst ≤ –100 大磁暴 Dst ≤ –200 特大磁暴 表 2 低纬度测站模型预测TEC的精度统计
Table 2. Accuracy of model prediction TEC at low latitude stations
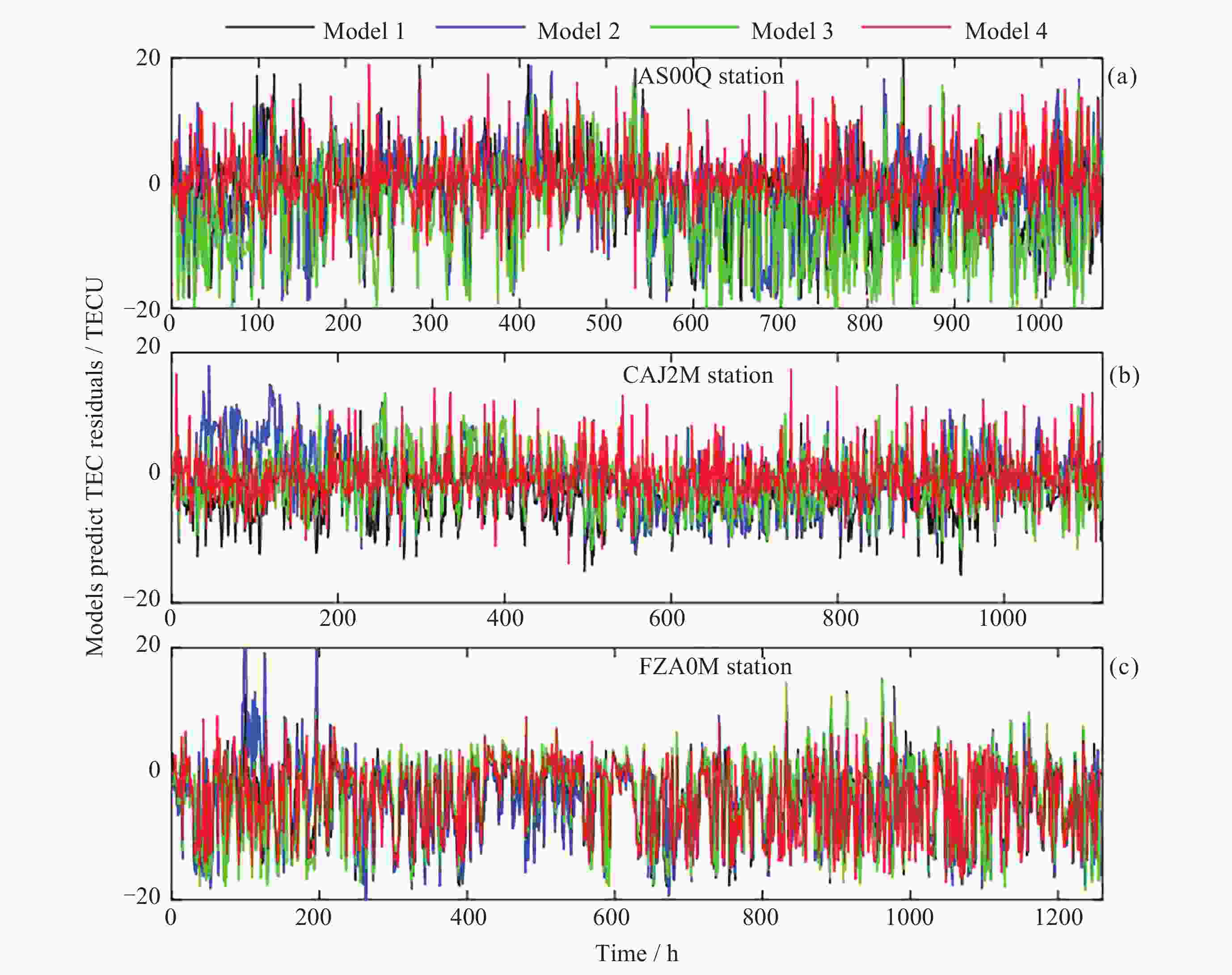
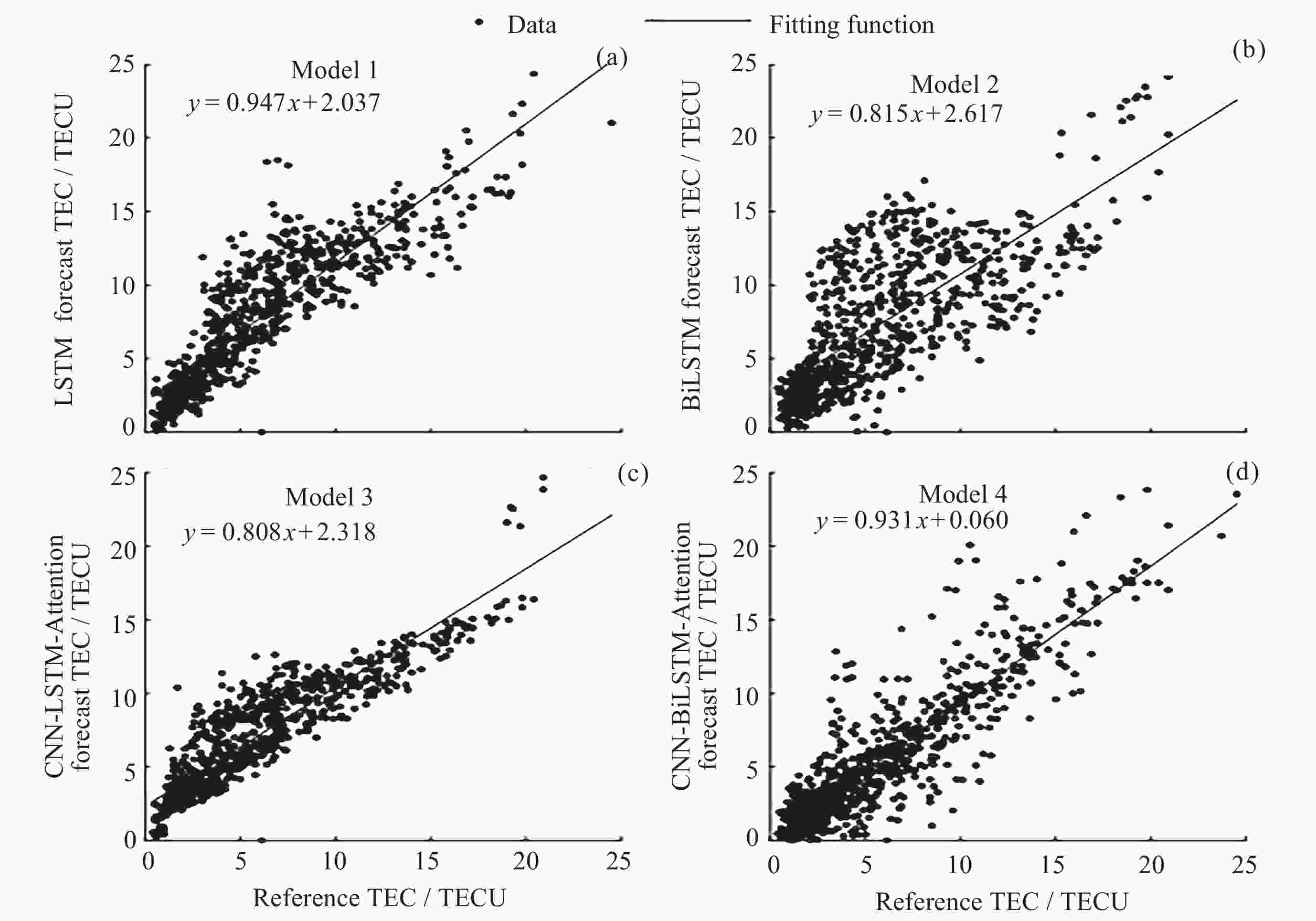
站点 评价指标 LSTM BiLSTM CNN-LSTM-Attention CNN-BiLSTM-Attention AS00Q站 MAE/TECU 5.013 5.257 6.725 3.637 RMSE/TECU 6.856 7.014 8.756 5.013 R2 0.871 0.865 0.790 0.931 CAJ2M站 MAE/TECU 4.126 4.304 3.666 3.303 RMSE/TECU 5.124 5.472 4.604 4.116 R2 0.888 0.890 0.917 0.931 FZA0M站 MAE/TECU 5.809 6.156 5.931 5.270 RMSE/TECU 7.602 7.976 7.695 6.983 R2 0.920 0.912 0.918 0.932 表 3 中纬度测站模型预测TEC的精度统计
Table 3. Accuracy of model prediction TEC at middle latitude stations
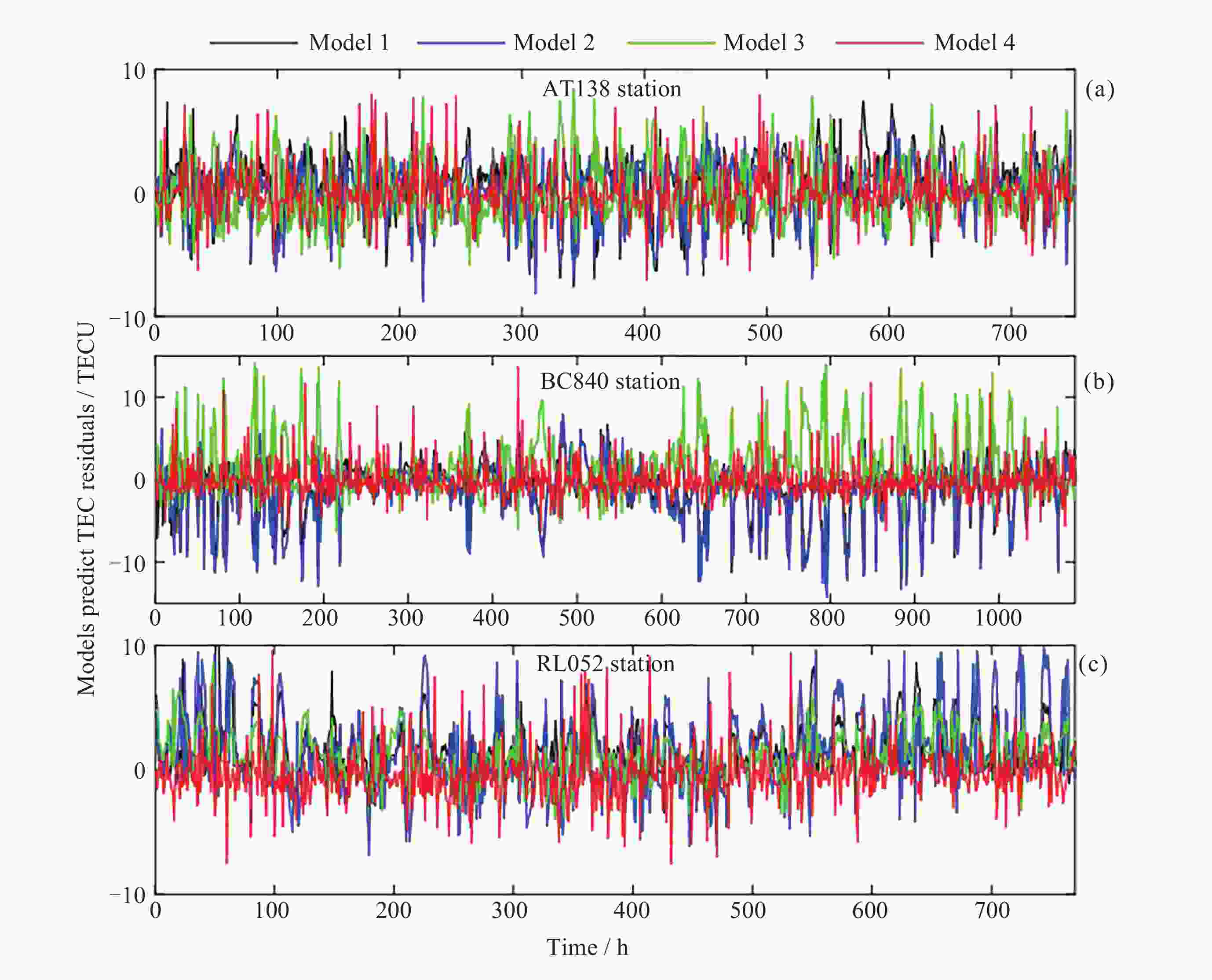
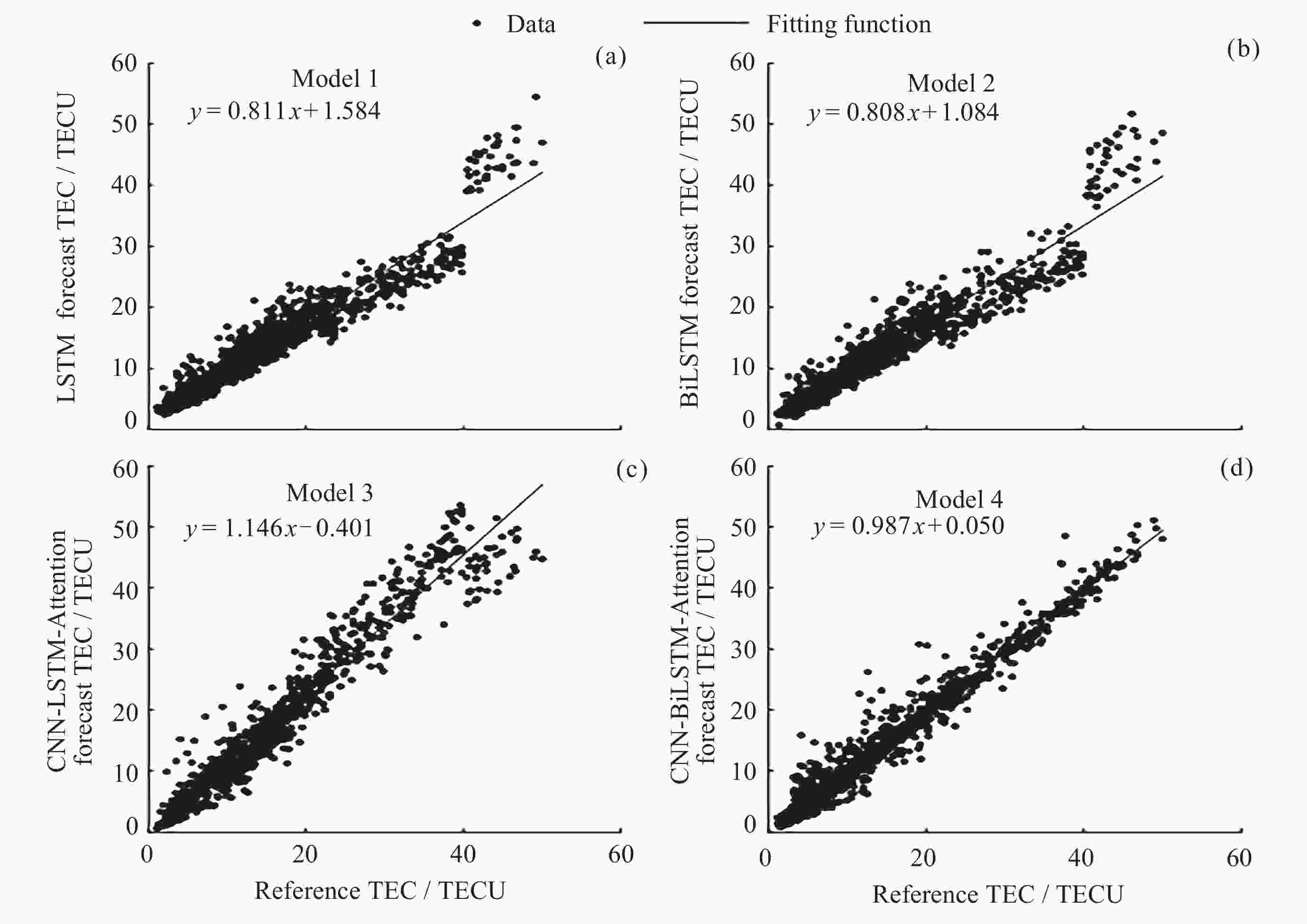
站点 评价指标 LSTM BiLSTM CNN-LSTM-Attention CNN-BiLSTM-Attention AT138站 MAE/TECU 2.150 1.896 2.001 1.482 RMSE/TECU 2.672 2.399 2.528 2.132 R2 0.938 0.950 0.945 0.961 BC840站 MAE/TECU 2.385 2.856 2.533 1.494 RMSE/TECU 3.522 3.832 3.752 2.158 R2 0.897 0.878 0.883 0.961 RL052站 MAE/TECU 2.082 3.702 1.774 1.529 RMSE/TECU 2.778 5..089 2.284 2.177 R2 0.617 0.363 0.759 0.765 表 4 高纬度测站模型预测TEC的精度统计
Table 4. Accuracy of model prediction TEC at high latitude stations
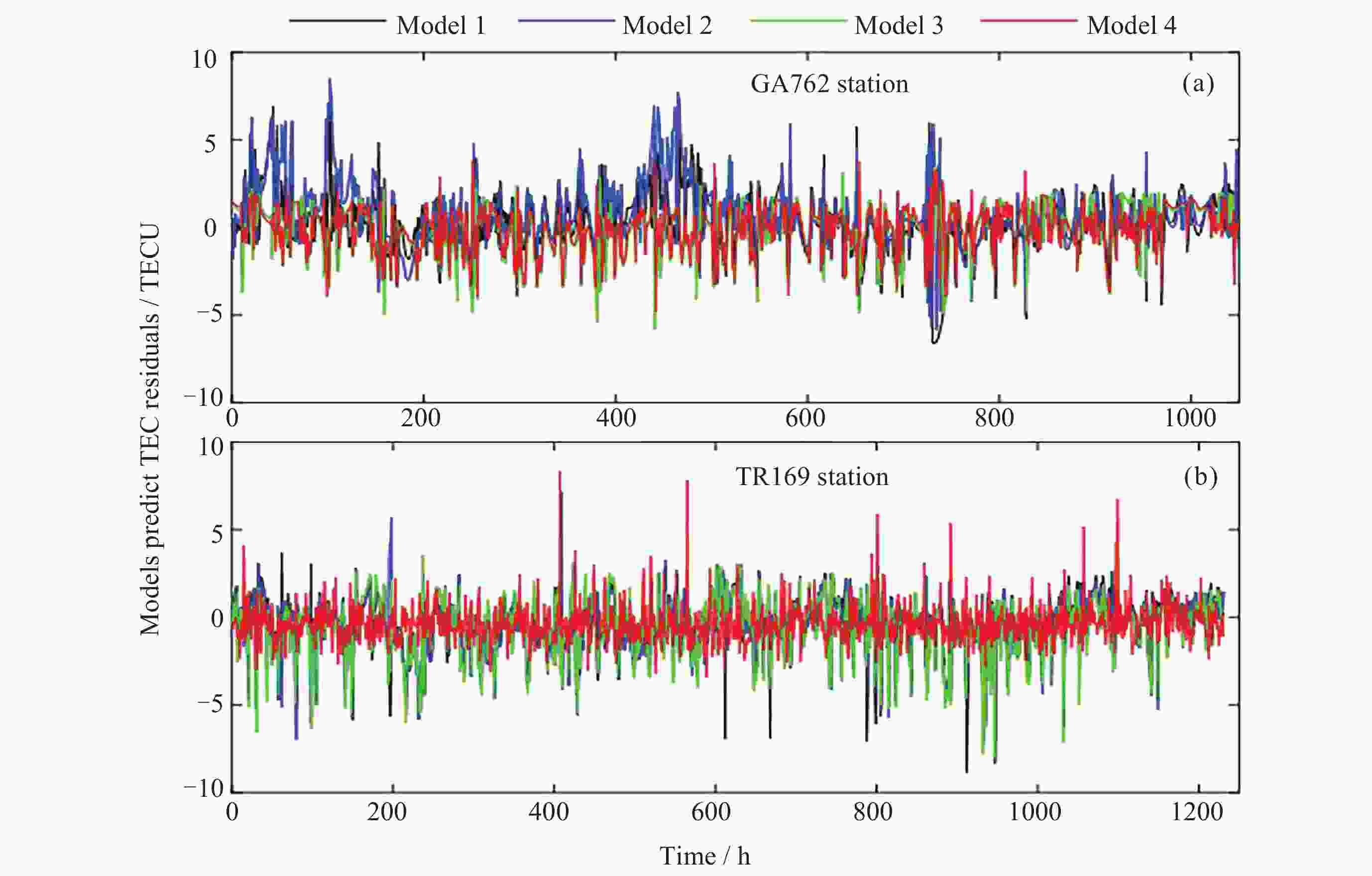
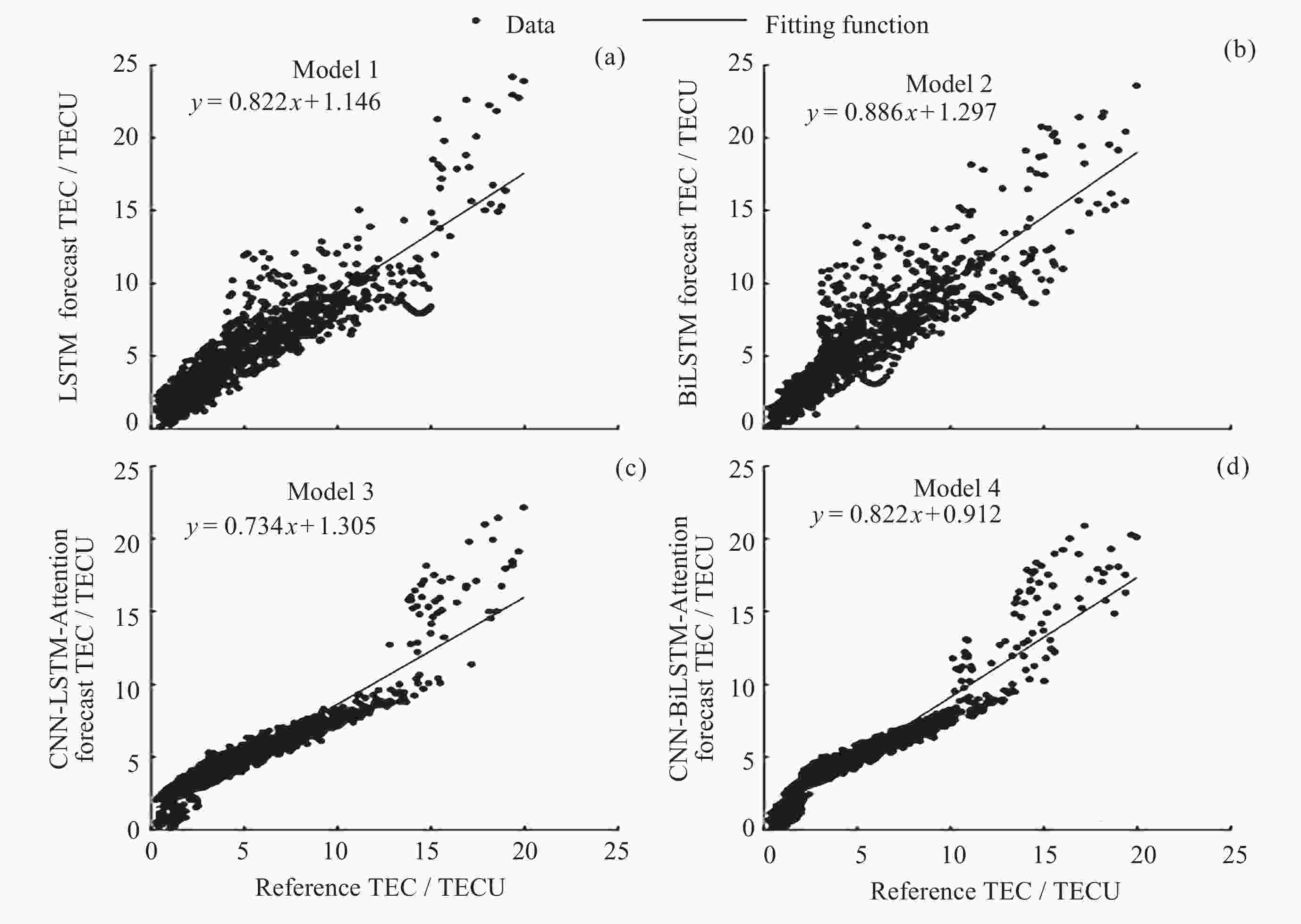
站点 评价指标 LSTM BiLSTM CNN-LSTM-Attention CNN-BiLSTM-Attention GA762站 MAE/TECU 1.291 1.472 1.116 1.033 RMSE/TECU 1.765 2.069 1.489 1.341 R2 0.790 0.711 0.850 0.883 TR169站 MAE/TECU 1.288 1.233 1.254 0.882 RMSE/TECU 1.750 1.678 1.709 1.175 R2 0.868 0.878 0.874 0.940 -
[1] YUAN Yunbin. Study on Theories and Methods of Correcting Ionospheric Delay and Monitoring Ionosphere Based on GPS[D]. Wuhan: Institute of Geodesy and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2002 [2] YUAN Yunbin, HUO Xingliang, ZHANG Baocheng. Research progress of precise models and correction for GNSS ionospheric delay in China over recent years[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2017, 46(10): 1364-1378 (袁运斌, 霍星亮, 张宝成. 近年来我国GNSS电离层延迟精确建模及修正研究进展[J]. 测绘学报, 2017, 46(10): 1364-1378 doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170349YUAN Yunbin, HUO Xingliang, ZHANG Baocheng. Research progress of precise models and correction for GNSS ionospheric delay in China over recent years[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2017, 46(10): 1364-1378 doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170349 [3] HAN Xihao, ZHENG Shuaiyong, YANG Jianlei, et al. Status and development of the ionospheric error correction techniques in satellite navigation[J]. GNSS World of China, 2024, 49(2): 111-126 (韩喜豪, 郑帅勇, 杨建雷, 等. 卫星导航中电离层误差校正技术现状与发展[J]. 全球定位系统, 2024, 49(2): 111-126 doi: 10.12265/j.gnss.2023105HAN Xihao, ZHENG Shuaiyong, YANG Jianlei, et al. Status and development of the ionospheric error correction techniques in satellite navigation[J]. GNSS World of China, 2024, 49(2): 111-126 doi: 10.12265/j.gnss.2023105 [4] ZhANG Ting. Study on Empirical Model of Ionospheric TEC Based on Multi-Source Data[D]. Zibo: Shandong University of Technology, 2023 [5] ZHANG B B, WANG Z T, SHEN Y, et al. Evaluation of f0F2 and hmF2 parameters of IRI-2016 model in different latitudes over China under high and low solar activity years[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(4): 860 doi: 10.3390/rs14040860 [6] FENG J D, ZHANG Y B, LI W, et al. Analysis of ionospheric TEC response to solar and geomagnetic activities at different solar activity stages[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2023, 71(5): 2225-2239 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2022.10.032 [7] TANG Siyu, HUANG Zhi. Prediction of ionospheric total electron content based on causal convolutional and LSTM network[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2022, 42(3): 357-365 (唐丝语, 黄智. 基于因果卷积与LSTM网络的电离层总电子含量预报[J]. 空间科学学报, 2022, 42(3): 357-365 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.03.210401042TANG Siyu, HUANG Zhi. Prediction of ionospheric total electron content based on causal convolutional and LSTM network[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2022, 42(3): 357-365 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.03.210401042 [8] TANG Jun, ZHONG Zhengyu, LI Yinjian, et al. Short-term prediction model of ionospheric TEC based on SSA-Elman neural network[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2022, 42(4): 378-383 (汤俊, 钟正宇, 李垠健, 等. 基于SSA-Elman神经网络的电离层TEC短期预报模型[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2022, 42(4): 378-383TANG Jun, ZHONG Zhengyu, LI Yinjian, et al. Short-term prediction model of ionospheric TEC based on SSA-Elman neural network[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2022, 42(4): 378-383 [9] LIU Haijun, LEI Dongxing, YUAN Jing, et al. Ionospheric TEC prediction based on Attention-LSTM[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2024, 67(2): 439-451 (刘海军, 雷东兴, 袁静, 等. 基于注意力机制LSTM的电离层TEC预测[J]. 地球物理学报, 2024, 67(2): 439-451 doi: 10.6038/cjg2022Q0603LIU Haijun, LEI Dongxing, YUAN Jing, et al. Ionospheric TEC prediction based on Attention-LSTM[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2024, 67(2): 439-451 doi: 10.6038/cjg2022Q0603 [10] WU Han, HUANG Ling, LIU Lilong, et al. Short term prediction model of ionospheric TEC based on SSA-LSTM[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2022, 42(6): 626-630,654 (吴晗, 黄玲, 刘立龙, 等. 基于SSA-LSTM的短期电离层TEC组合预报模型[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2022, 42(6): 626-630,654WU Han, HUANG Ling, LIU Lilong, et al. Short term prediction model of ionospheric TEC based on SSA-LSTM[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2022, 42(6): 626-630,654 [11] TANG J, LI Y J, DING M F, et al. An ionospheric TEC forecasting model based on a CNN-LSTM-Attention mechanism neural network[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(10): 2433 doi: 10.3390/rs14102433 [12] CHEN Jianghe, XIONG Pan, WU Haochen, et al. A multi-parameter fusion forecast model of ionospheric TEC in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region[J]. Earthquake, 2024, 44(2): 12-32 (陈江河, 熊攀, 武浩琛, 等. 京津冀区域电离层TEC多参数融合预测模型[J]. 地震, 2024, 44(2): 12-32 doi: 10.12196/j.issn.1000-3274.2024.02.002CHEN Jianghe, XIONG Pan, WU Haochen, et al. A multi-parameter fusion forecast model of ionospheric TEC in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region[J]. Earthquake, 2024, 44(2): 12-32 doi: 10.12196/j.issn.1000-3274.2024.02.002 [13] MA Bin, HUANG Ling, WU Han, et al. Study on the NeuralProphet forecast TEC model over China during the severe geomagnetic storm in March 2015[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2024, 67(2): 452-460 (马彬, 黄玲, 吴晗, 等. 2015年3月特大磁暴期间中国区域电离层TEC NeuralProphet预报模型研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2024, 67(2): 452-460 doi: 10.6038/cjg2023R0225MA Bin, HUANG Ling, WU Han, et al. Study on the NeuralProphet forecast TEC model over China during the severe geomagnetic storm in March 2015[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2024, 67(2): 452-460 doi: 10.6038/cjg2023R0225 [14] YANG Mo, WANG Jing. A spatial-temporal attention based BiLSTM for stock index prediction[J]. Operations Research and Management Science, 2023, 32(8): 174-180 (杨蓦, 王静. 基于时空注意力机制的双向长短期记忆神经网络的股指预测研究[J]. 运筹与管理, 2023, 32(8): 174-180YANG Mo, WANG Jing. A spatial-temporal attention based BiLSTM for stock index prediction[J]. Operations Research and Management Science, 2023, 32(8): 174-180 [15] YANG Zixing. Research on Short-Term Wind Power Prediction Based on Hybrid CNN-BiLSTM-AM Model[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2023 [16] ZHANG Zhenchao. Remote Sensing Image Based on Convolutional Neural Network Model Scene Classification Research[D]. Ganzhou: Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, 2022 (张振超. 基于卷积神经网络模型的遥感影像场景分类研究[D]. 赣州: 江西理工大学, 2022ZHANG Zhenchao. Remote Sensing Image Based on Convolutional Neural Network Model Scene Classification Research[D]. Ganzhou: Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, 2022 [17] LIU Libo, CHEN Yiding, ZHANG Ruilong, et al. Some investigations of ionospheric diurnal variation[J]. Reviews of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, 2021, 52(6): 647-661 [18] ZHANG Ting, ZHAO Qingxin, ZHONG Huixin, et al. Accuracy analysis of IRI 2016 model in ocean and land areas[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2021, 46(9): 14-33 (张亭, 赵庆鑫, 钟慧鑫, 等. 国际参考电离层2016模型在陆海区域的精度分析[J]. 测绘科学, 2021, 46(9): 14-33ZHANG Ting, ZHAO Qingxin, ZHONG Huixin, et al. Accuracy analysis of IRI 2016 model in ocean and land areas[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2021, 46(9): 14-33 [19] SONG Rui. Modeling Ionospheric f0F2 in China and Its Research on Application[D]. Beijing: Institute of Earthquake Forecasting, China Earthquake Administration, 2018 [20] GUO Qijia, YAO Yibin, ZHOU Yongjiang. PM2.5 random forest prediction model incorporating GNSS meteorological parameters[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2021, 46(4): 37-42,56 -
-




 朱佳豪 男, 2000年生, 河南商丘人, 现为江苏师范大学地理测绘与城乡规划学院电子信息专业硕士研究生. E-mail:
朱佳豪 男, 2000年生, 河南商丘人, 现为江苏师范大学地理测绘与城乡规划学院电子信息专业硕士研究生. E-mail: 

 下载:
下载: