Application of Improved Model Based on LSTM in Ionospheric TEC Forecast
-
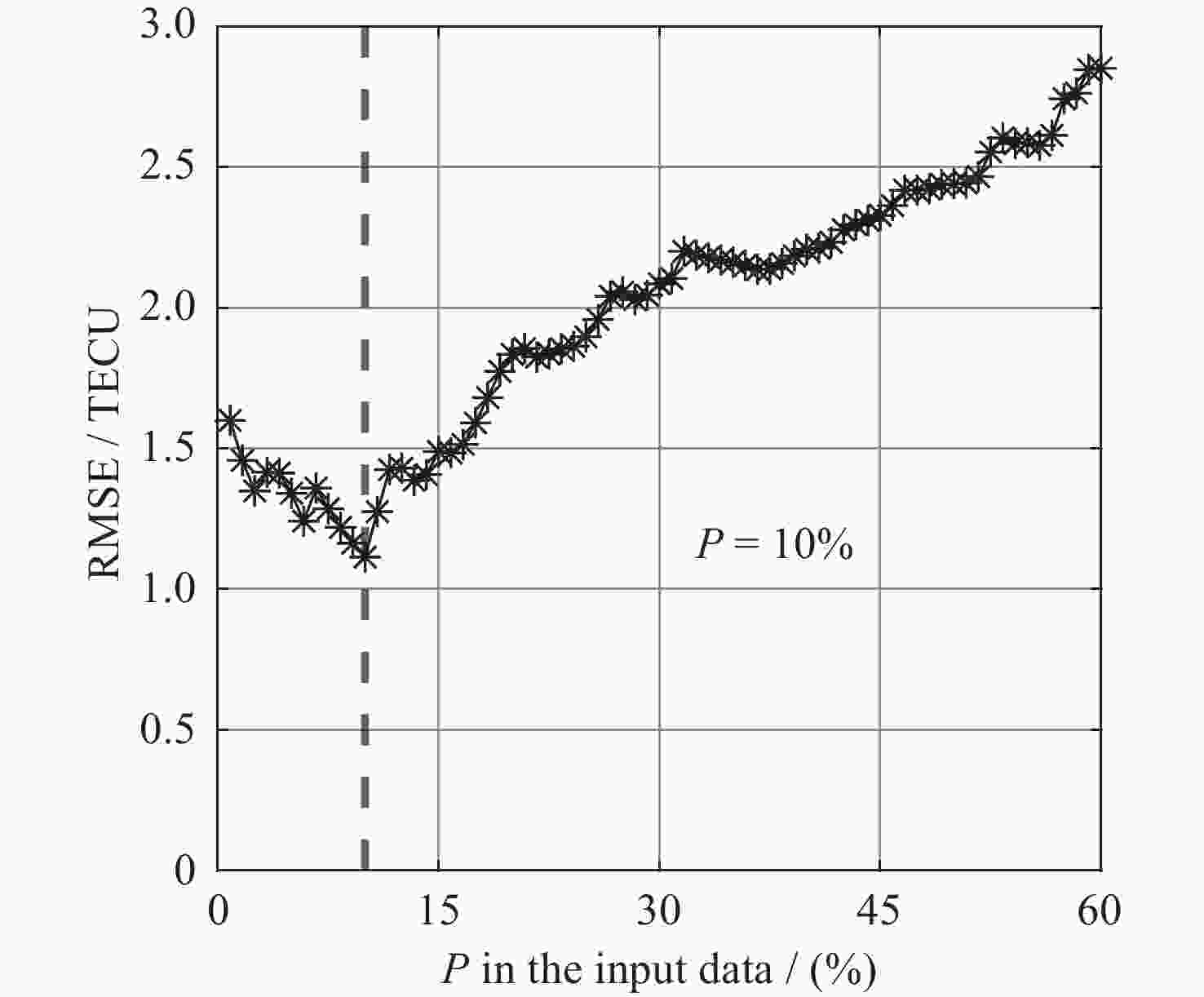
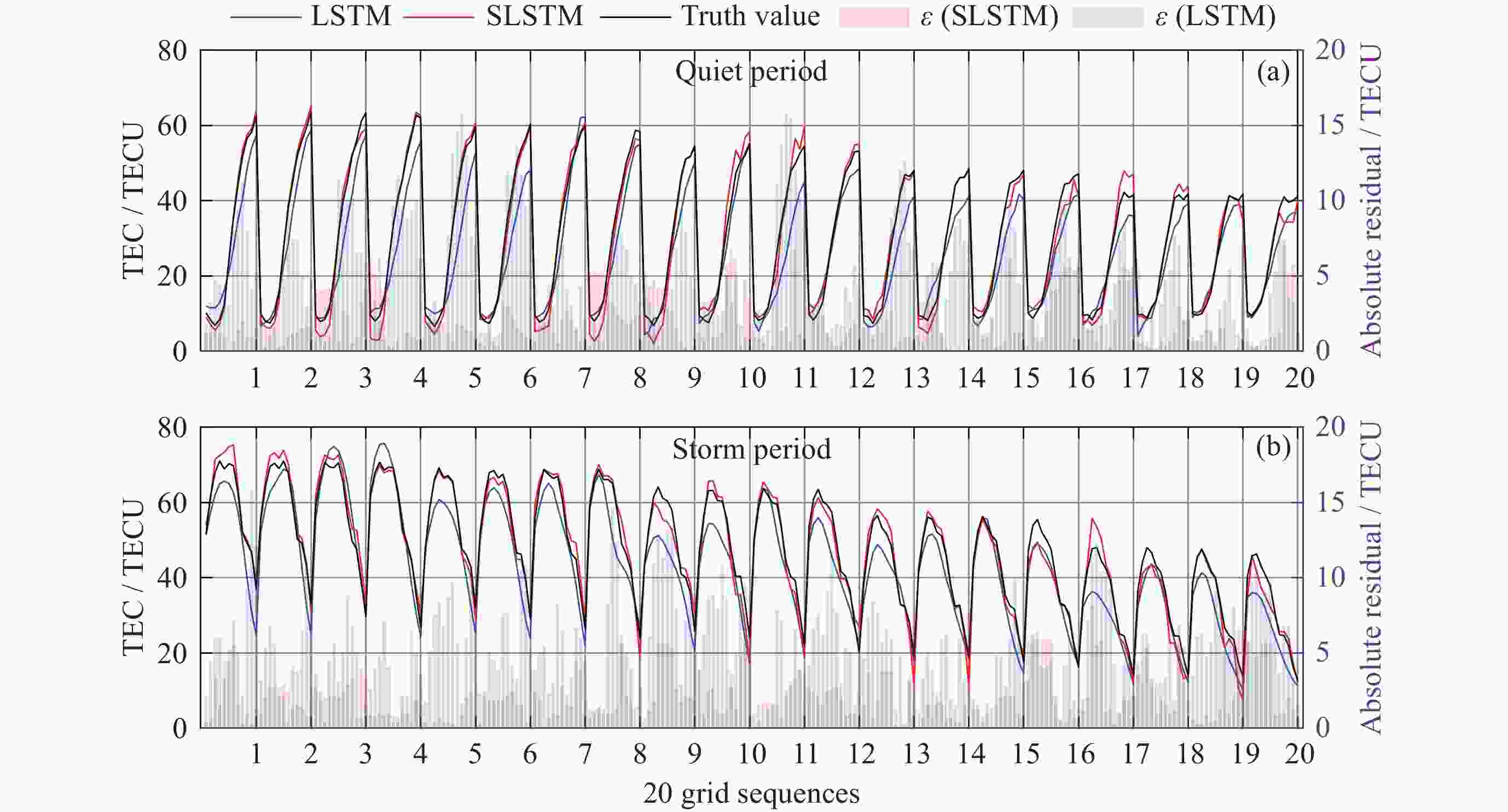
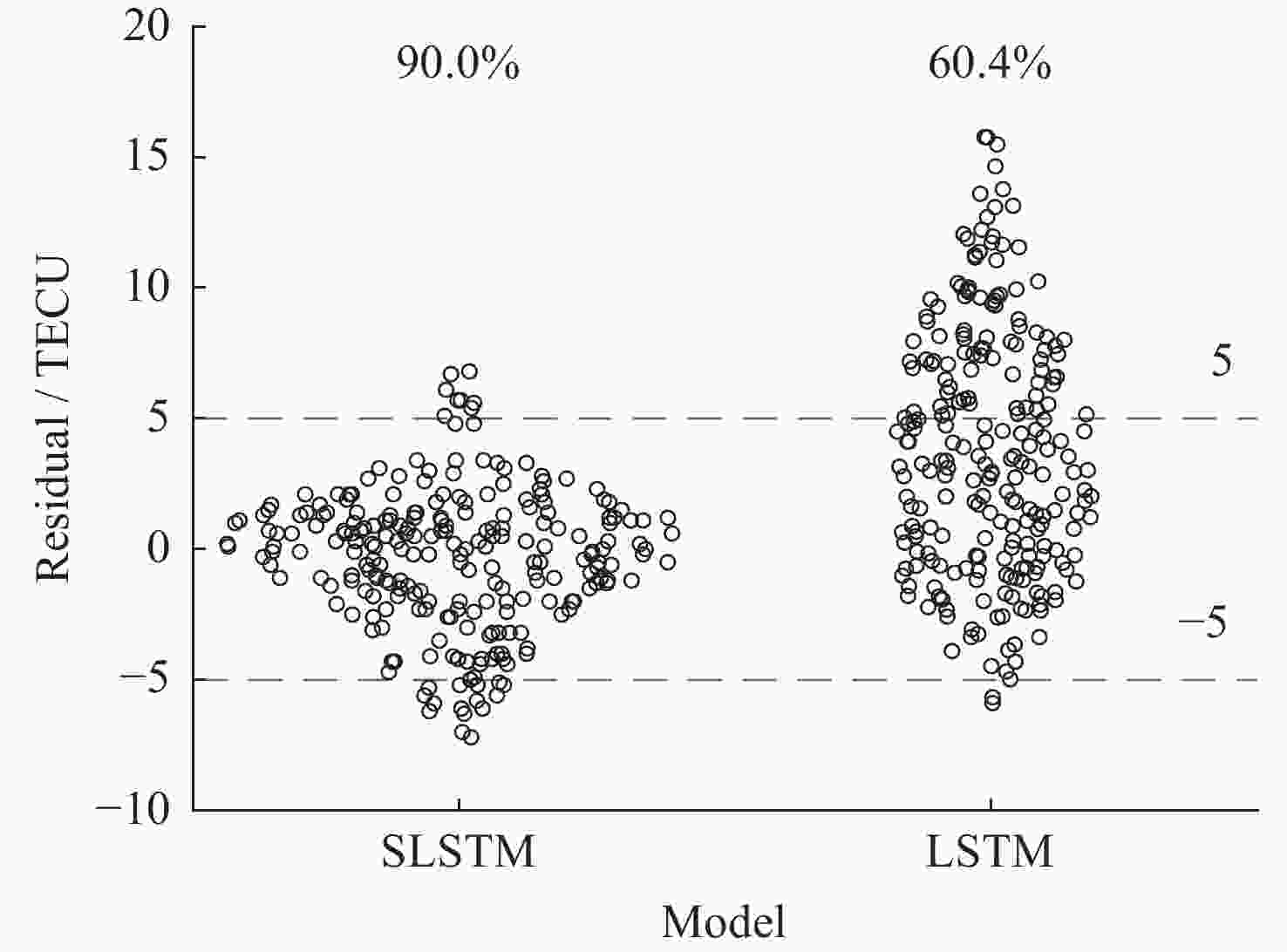
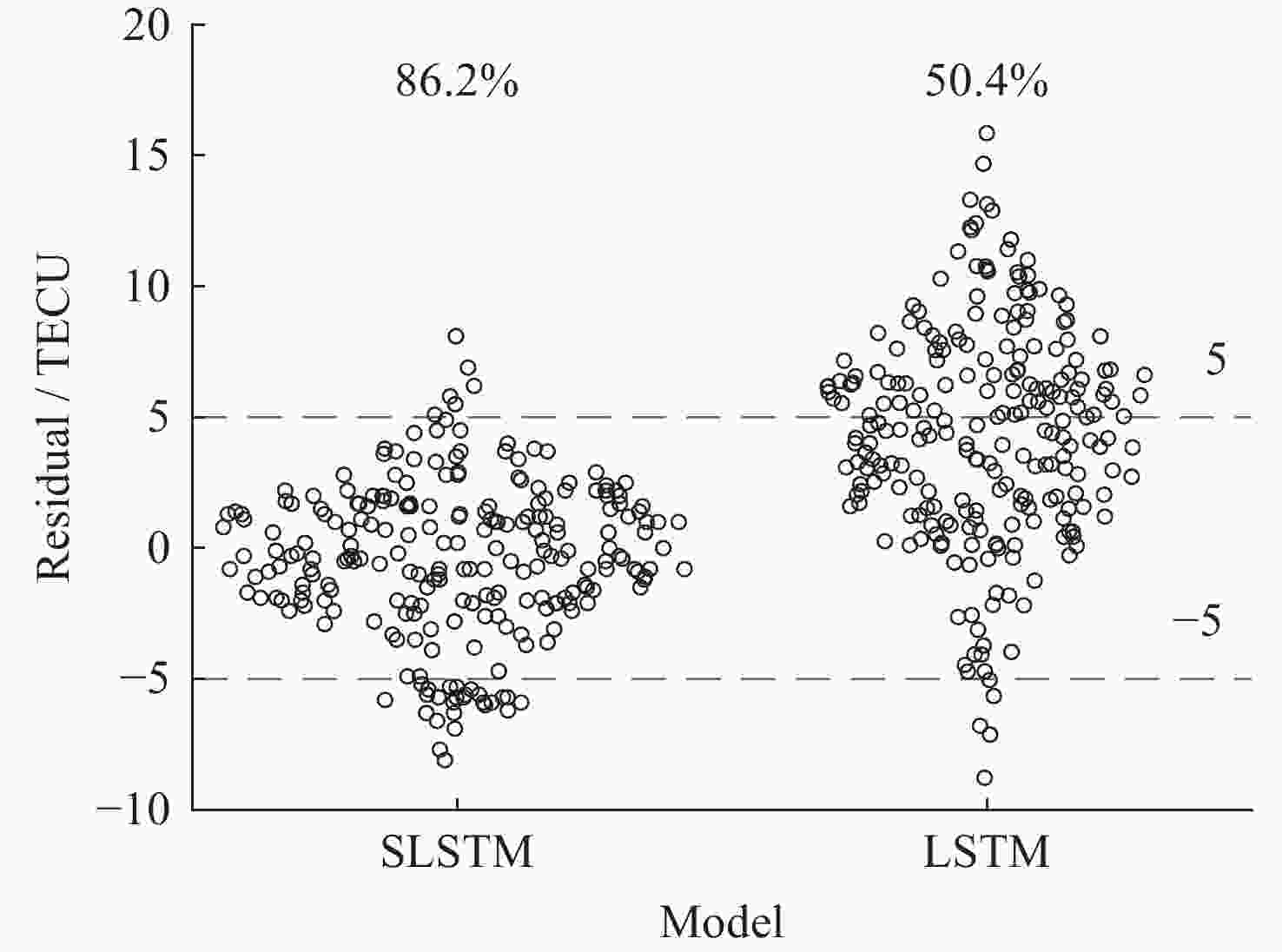
摘要: 电离层延迟是全球卫星导航定位中重要的误差源之一, 提高电离层总电子含量(Total Electron Content, TEC)预报精度对改善卫星导航定位精度极其重要. 本文联合滑动窗口(Sliding Window)和长短时记忆(Long-Short-Term Memory, LSTM)神经网络, 以滑动窗口算法对输入序列数据集不断更新并测试不同输入序列长度对应模型的精度, 最后以预测值来更新输入数据序列的最后10%, 进而构建TEC预报模型SLSTM (Sliding Window on Long-Short-Term Memory). 验证结果表明, 该模型在平静期和磁暴期预测残差绝对值小于5 TECU的比例均达85%以上, 较传统LSTM模型对应值占比增加了49%, 71%, 均方根误差(RMSE)低31%, 35%; 其预报结果的平均绝对误差(MAE)减少25%, 32%; SLSTM模型预测结果的RMSE均值、MAE均值均比传统LSTM模型、BP模型小.Abstract: Ionospheric delay is one of the most important sources of error in global satellite navigation and positioning. Improving the prediction accuracy of ionospheric Total Electron Content (TEC) is very important to improve the positioning accuracy of satellite navigation. In this paper, we combine sliding window and Long-Short-Term Memory (LSTM) neural network, and use sliding window algorithm to continuously update the input time series data set. We tested the accuracy of the models corresponding to different input sequence lengths and recorded them, and found that the accuracy of the last 10% of the input data series was the best when the predicted value was updated. Finally, we used the sliding window method to update the last 10% of the input data series with the predicted value to build the TEC prediction model. The newly constructed model, traditional LSTM model and BP model are used to predict the same TEC time series data, and Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), absolute residual error and Mean Absolute Error (MAE) are used to evaluate the accuracy of the model prediction results, and verify the prediction performance of the new model. The experimental results show that the proportion of residual absolute value less than 5 TECU predicted by the newly constructed model SLSTM (Sliding Window on Long-Short-Term Memory) in both the calm period and the magnetic storm period exceeds 85%, and the proportion of predicted residual absolute value less than 5 TECU corresponding to the traditional LSTM model increases by 49% and 71%. On the other hand, compared with the traditional LSTM model, the root-mean-square error of the new model is reduced by 31% and 35%, respectively, and the average absolute error is reduced by 25% and 32%, respectively. In addition, we can also see that the RMSE mean values and MAE mean values of SLSTM model are smaller than those of traditional LSTM model and BP model.
-
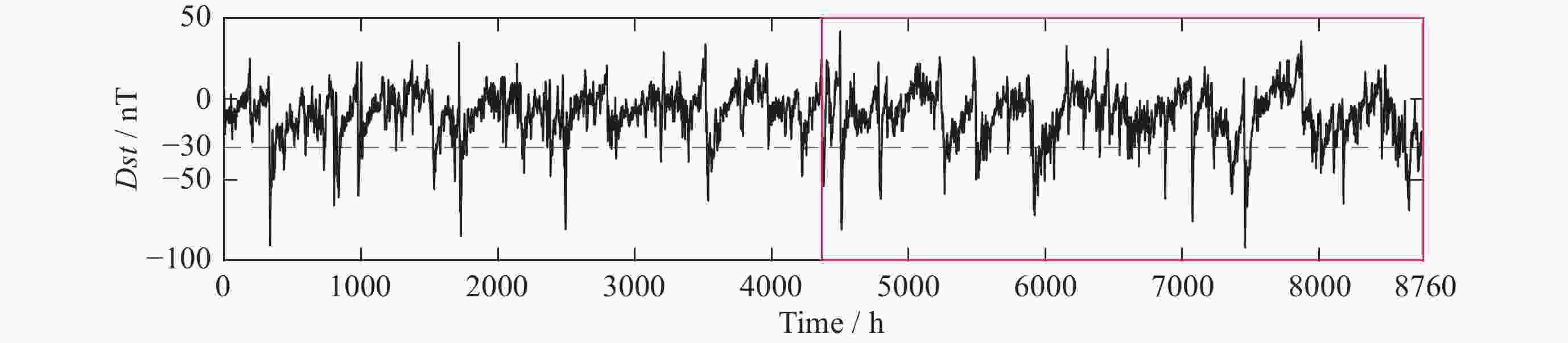
表 1 Dst指数对应地磁活动强度
Table 1. Intensity of geomagnetic activity corresponding to the Dst index
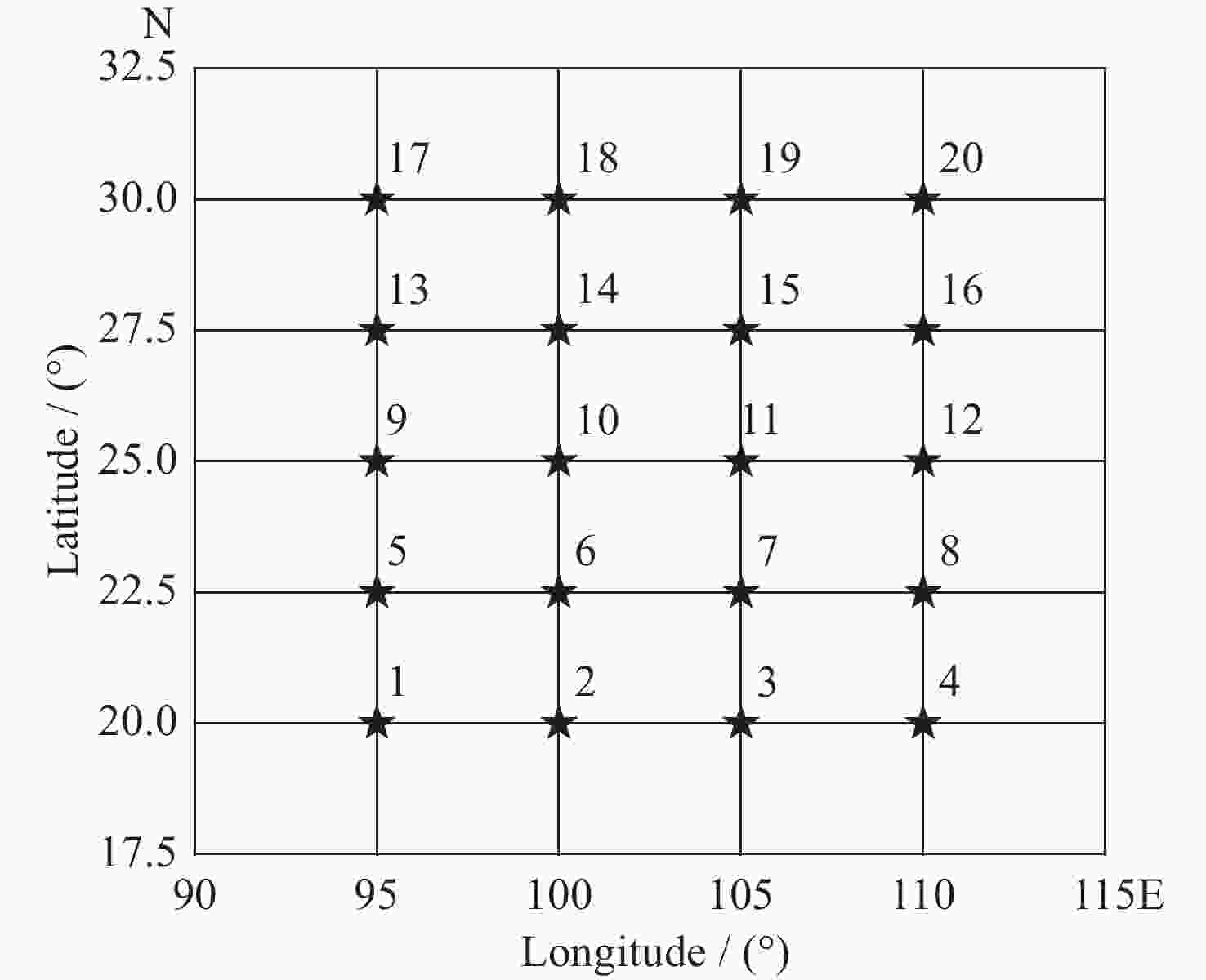
Dst /nT ≤ –100 (–100, –50] (–50, –30] > –30 地磁活动强度 强 中 弱 平静 表 2 SLSTM/LSTM模型对20个格网预测结果的MAE (单位: TECU)
Table 2. MAE of SLSTM/LSTM model for prediction results of 20 grids (Unit: TECU)
纬度/(º)N 经度/(º)E (平静期) 经度/(º)E (磁暴期) 95 100 105 110 95 100 105 110 30 2.9/2 1.0/1.8 1.4/2.4 2.0/2.4 2.7/3.4 3.5/3.8 2.1/2.6 2.8/2.8 27.5 1.6/2.1 1.4/3.3 1.6/2.4 3.3/2.8 2.7/3.4 1.6/2.9 1.6/2.6 3.5/2.9 25 2.6/3.2 3.4/2.3 2.2/3.2 1.6/4.6 3.3/3.6 3.2/3.4 2.1/2.8 2.4/3.9 22.5 1.6/3.1 1.5/2.5 2.1/1.9 3.4/2.6 1.1/4.1 1.7/2.3 2.2/2.7 2.1/3.3 20 1.1/4 1.5/3 2.8/3.0 2.2/4 2.2/5.7 2.0/3.8 2.9/3.3 1.2/4 均值 2.1/2.8 2.3/3.4 表 3 SLSTM/LSTM模型对20个格网预测结果的RMSE (单位: TECU)
Table 3. RMSE of SLSTM/LSTM model for prediction results of 20 grids (Unit: TECU)
纬度/(º)N经度/(º)E (平静期) 经度/(º)E (磁暴期) 95 100 105 110 95 100 105 110 30 3.5/2.5 1.3/2.3 2.4/2.7 3.1/2.8 3.6/4.3 4.0/4.6 3.1/3.4 3.6/3.7 27.5 1.9/2.4 2.1/3.7 2.2/3.3 3.8/3.7 3.4/4.5 2.5/3.3 1.7/3.2 4.3/4.1 25 3.2/3.7 4.0/3.2 3.2/4 1.9/5.5 3.8/4.5 3.7/4.3 2.3/3.5 2.8/4.9 22.5 1.7/3.8 1.7/3.5 2.5/2.4 3.7/3.4 1.5/5.2 1.8/3.1 2.6/3.7 2.7/4.1 20 1.2/4.7 1.6/4.3 3.1/4 3.2/5.1 2.8/7.1 2.1/4.8 3.0/4.6 1.4/5.2 均值 2.5/3.6 2.8/4.3 表 4 SLSTM, LSTM, BP模型对4个格网预测结果的RMSE均值和MAE均值(单位: TECU)
Table 4. RMSE and MAE mean values by SLSTM, LSTM and BP models for the prediction results of four grids (Unit: TECU)
模型 RMSE均值 MAE均值 平静期 磁暴期 下半年 平静期 磁暴期 下半年 SLSTM 2.7 2.8 2.7 2.0 2.2 2.1 LSTM 3.7 5.0 3.8 3.1 4.0 3.3 BP 3.7 5.1 4.0 3.3 4.2 3.6 -
[1] YAO Y B, LIU L, KONG J, et al. Global ionospheric modeling based on multi-GNSS, satellite altimetry, and Formosat-3/COSMIC data[J]. GPS Solutions, 2018, 22(4): 104 doi: 10.1007/s10291-018-0770-6 [2] YUAN Yunbin, LI Min, HUO Xingliang, et al. Research on performance of BeiDou global broadcast ionospheric delay correction model (BDGIM) of BDS-3[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2021, 50(4): 436-447 (袁运斌, 李敏, 霍星亮, 等. 北斗三号全球导航卫星系统全球广播电离层延迟修正模型(BDGIM)应用性能评估[J]. 测绘学报, 2021, 50(4): 436-447YUAN Yunbin, LI Min, HUO Xingliang, et al. Research on performance of BeiDou global broadcast ionospheric delay correction model (BDGIM) of BDS-3[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2021, 50(4): 436-447 [3] ZHU Wei, REN Xiaodong, ZHANG Xiaohong. Performance of PPP-RTK enhanced by slant ionospheric model based on reference stations with different latitudes and distances[J/OL]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, (2024-06-22). https://doi.org/10.13203/j.whugis20230476 [4] CHENG Huhua, ZHAN Caiju, ZHAO Liang, et al. Accuracy analysis of IRI2016 international reference ionosphere at altitude of 60~100 km[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2020, 49(1): 42-54 (程胡华, 詹彩菊, 赵亮, 等. IRI2016参考电离层模型在高度60~100 km的精度分析[J]. 测绘学报, 2020, 49(1): 42-54CHENG Huhua, ZHAN Caiju, ZHAO Liang, et al. Accuracy analysis of IRI2016 international reference ionosphere at altitude of 60~100 km[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2020, 49(1): 42-54 [5] QIAO J D, LIU Y, FAN Z Q, et al. Ionospheric TEC data assimilation based on Gauss–Markov Kalman filter[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2021, 68(10): 4189-4204 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2021.08.004 [6] CHEN Yutian, LIU Lilong, LIU Zhongliu, et al. Analysis of the influence of latitude factors on seasonal time series TEC short-term forecast model[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2018, 38(6): 581-586 (陈雨田, 刘立龙, 刘中流, 等. 纬度因素对季节性时序TEC短期预报模型的影响分析[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2018, 38(6): 581-586CHEN Yutian, LIU Lilong, LIU Zhongliu, et al. Analysis of the influence of latitude factors on seasonal time series TEC short-term forecast model[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2018, 38(6): 581-586 [7] YIN Ping, YAN Xiaopeng, NING Zehao. A combined forecasting method of ionospheric tomography TEC based on LSTM and IRI model[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2022, 37(5): 852-861 (尹萍, 闫晓鹏, 宁泽浩. 一种基于LSTM与IRI模型的电离层层析TEC组合预测方法[J]. 电波科学学报, 2022, 37(5): 852-861YIN Ping, YAN Xiaopeng, NING Zehao. A combined forecasting method of ionospheric tomography TEC based on LSTM and IRI model[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2022, 37(5): 852-861 [8] ZHANG Fubin, ZHOU Chen, WANG Cheng, et al. Global ionospheric TEC prediction based on deep learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2021, 36(4): 553-561 (张富彬, 周晨, 王成, 等. 基于深度学习的全球电离层TEC预测[J]. 电波科学学报, 2021, 36(4): 553-561ZHANG Fubin, ZHOU Chen, WANG Cheng, et al. Global ionospheric TEC prediction based on deep learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2021, 36(4): 553-561 [9] TANG R X, ZENG F T, CHEN Z, et al. The comparison of predicting storm-time ionospheric TEC by three methods: ARIMA, LSTM, and Seq2Seq[J]. Atmosphere, 2020, 11(4): 316 doi: 10.3390/atmos11040316 [10] TANG Siyu, HUANG Zhi. Prediction of ionospheric total electron content based on causal convolutional and LSTM network[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2022, 42(3): 357-365 (唐丝语, 黄智. 基于因果卷积与LSTM网络的电离层总电子含量预报[J]. 空间科学学报, 2022, 42(3): 357-365 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.03.210401042TANG Siyu, HUANG Zhi. Prediction of ionospheric total electron content based on causal convolutional and LSTM network[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2022, 42(3): 357-365 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.03.210401042 [11] XIE T, DAI Z Q, ZHU X W, et al. LSTM-based short-term ionospheric TEC forecast model and positioning accuracy analysis[J]. GPS Solutions, 2023, 27(2): 66 doi: 10.1007/s10291-023-01406-8 [12] HOCHREITER S, SCHMIDHUBER J. Long short-term memory[J]. Neural computation, 1997, 9(8): 1735-1780 doi: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735 [13] LIU Weifeng, HUANG Jiang, DENG Baichang, et al. Calculation analysis of ionospheric irregularity zonal drift velocity in Guangzhou based on GPS measurements[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2012, 32(1): 48-54 (刘伟峰, 黄江, 邓柏昌, 等. 基于GPS的广州地区电离层不规则体纬向漂移速度计算分析[J]. 空间科学学报, 2012, 32(1): 48-54 doi: 10.11728/cjss2012.01.048LIU Weifeng, HUANG Jiang, DENG Baichang, et al. Calculation analysis of ionospheric irregularity zonal drift velocity in Guangzhou based on GPS measurements[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2012, 32(1): 48-54 doi: 10.11728/cjss2012.01.048 [14] KAREVAN Z, SUYKENS J A K. Transductive LSTM for time-series prediction: an application to weather forecasting[J]. Neural Networks, 2020, 125: 1-9 doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2019.12.030 [15] HAO Yichen, XIE Xinyu, DING Jiaqi, et al. Spatiotemporal prediction method for the transient multiphase flow field via graph neural network[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2024, 45(9): 1761-1769 (郝祎琛, 谢心喻, 丁家琦, 等. 瞬态多相流场图神经网络时空预测方法研究[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2024, 45(9): 1761-1769HAO Yichen, XIE Xinyu, DING Jiaqi, et al. Spatiotemporal prediction method for the transient multiphase flow field via graph neural network[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2024, 45(9): 1761-1769 [16] ZHAO Xinyao. Beidou/Accelerometer Fusion Dynamic Analysis and Early Warning[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture, 2023 [17] XIE Ting, CHEN Biyan, KUANG Cuilin. Study of ionospheric anomaly detection method combining PCA and sliding time window[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2021, 41(10): 1085-1094 (谢婷, 陈必焰, 匡翠林. 结合PCA和滑动时窗的电离层异常探测方法研究[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2021, 41(10): 1085-1094XIE Ting, CHEN Biyan, KUANG Cuilin. Study of ionospheric anomaly detection method combining PCA and sliding time window[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2021, 41(10): 1085-1094 [18] TANG Wang, MA Shangchang, LI Cheng. LSTM ground temperature prediction method based on sliding window[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science :Times New Roman;">& Technology Edition), 2021, 48(3): 377-384 (唐旺, 马尚昌, 李程. 基于滑动窗口的LSTM地温预测方法[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 48(3): 377-384TANG Wang, MA Shangchang, LI Cheng. LSTM ground temperature prediction method based on sliding window[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2021, 48(3): 377-384 [19] ZHANG X H, REN X D, WU F B, et al. Short-term prediction of ionospheric TEC based on ARIMA model[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geoinformation Science, 2019, 2(1): 9-16 [20] LIU Lilong, CHEN Yutian, LI Junyu, et al. Short-term prediction and applicability analysis of regional ionospheric total electron content in active period[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(12): 1757-1764 (刘立龙, 陈雨田, 黎峻宇, 等. 活跃期区域电离层总电子短期预报及适用性分析[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2019, 44(12): 1757-1764LIU Lilong, CHEN Yutian, LI Junyu, et al. Short-term prediction and applicability analysis of regional ionospheric total electron content in active period[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(12): 1757-1764 [21] DUNCAN R A. The equatorial F-region of the ionosphere[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Terrestrial Physics, 1960, 18(2/3): 89-100 [22] GONZALEZ W D, JOSELYN J A, KAMIDE Y, et al. What is a geomagnetic storm?[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1994, 99(A4): 5771-5792 doi: 10.1029/93JA02867 [23] REN X D, YANG P X, MEI D K, et al. Global ionospheric TEC forecasting for geomagnetic storm time using a deep learning-based multi-model ensemble method[J]. Space Weather, 2023, 21(3): e2022SW003231 doi: 10.1029/2022SW003231 [24] MUHAMMAD A, KÜLAHCI F. A semi-supervised total electron content anomaly detection method using LSTM-auto-encoder[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2022, 241: 105979 doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2022.105979 [25] SHI S S, ZHANG K F, SHI J Q, et al. Modeling TEC maps over China using particle swarm optimization neural networks and long-term ground-based GPS, COSMIC, and Fengyun data[J]. Space Weather, 2023, 21(4): e2022SW003357 doi: 10.1029/2022SW003357 [26] ZHANG L, WANG F L, SUN T, et al. A constrained optimization method based on BP neural network[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2018, 29(2): 413-421 doi: 10.1007/s00521-016-2455-9 [27] XIONG Bo, LI Xiaolin, WANG Yuqing, et al. Prediction of ionospheric TEC over China based on long and short-term memory neural network[J]. Chinese Journal Geophysics, 2022, 65(7): 2365-2377 (熊波, 李肖霖, 王宇晴, 等. 基于长短时记忆神经网络的中国地区电离层TEC预测[J]. 地球物理学报, 2022, 65(7): 2365-2377XIONG Bo, LI Xiaolin, WANG Yuqing, et al. Prediction of ionospheric TEC over China based on long and short-term memory neural network[J]. Chinese Journal Geophysics, 2022, 65(7): 2365-2377 -
-




 黄灿 女, 1997年6月出生于广西壮族自治区钦州市, 桂林理工大学测绘地理信息学院在读硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为电离层参数预测方法. E-mail:
黄灿 女, 1997年6月出生于广西壮族自治区钦州市, 桂林理工大学测绘地理信息学院在读硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为电离层参数预测方法. E-mail: 

 下载:
下载: