基于LSTM Spatio-temporal Transformer的电离层TEC预测模型
doi: 10.11728/cjss2025.05.2024-0117 cstr: 32142.14.cjss.2024-0117
Ionospheric TEC Prediction Model Based on LSTM Spatio-temporal Transformer
-
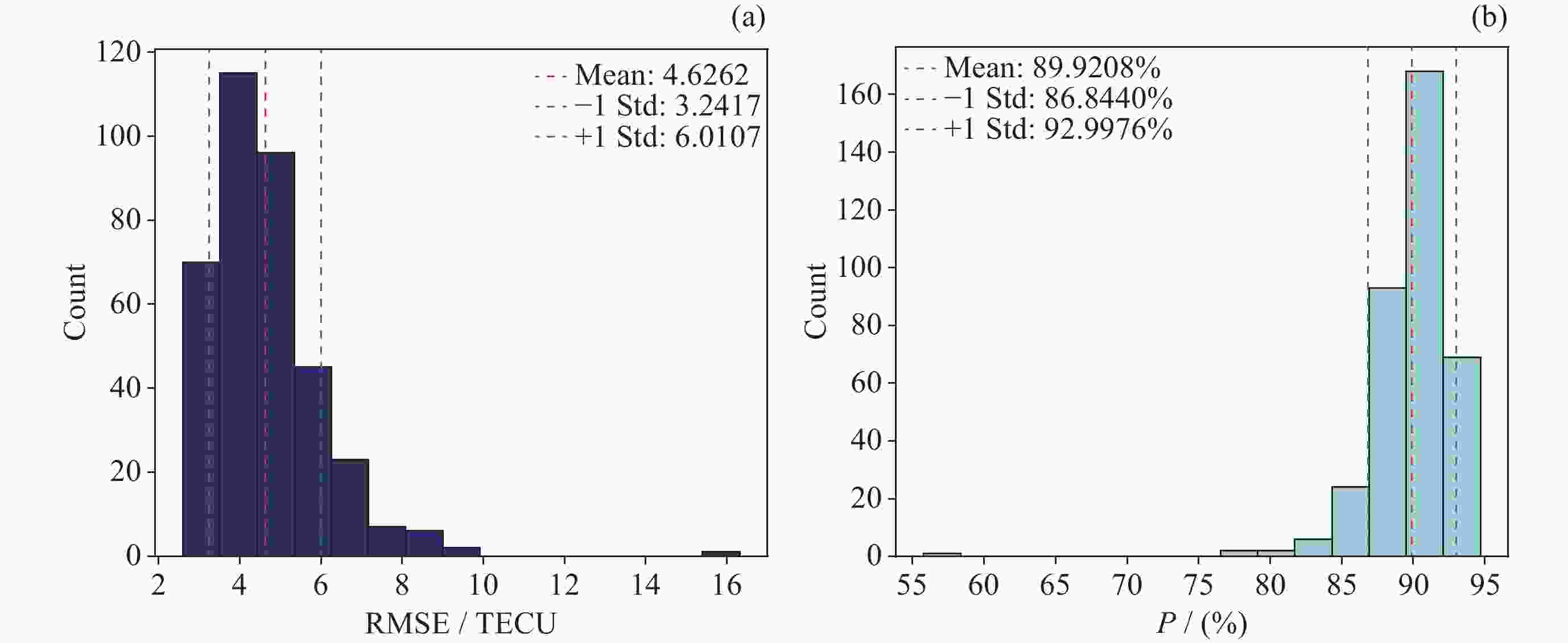
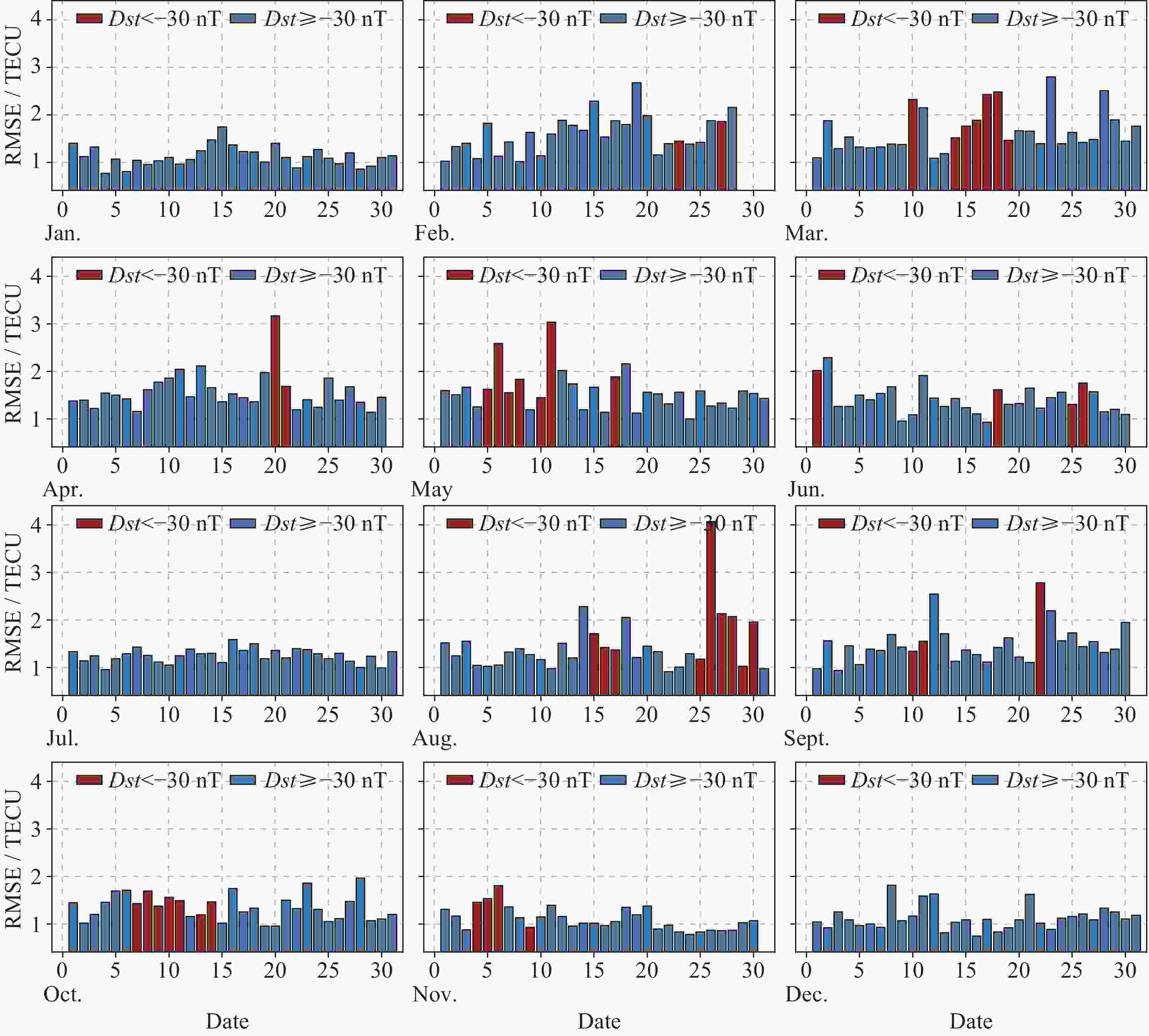
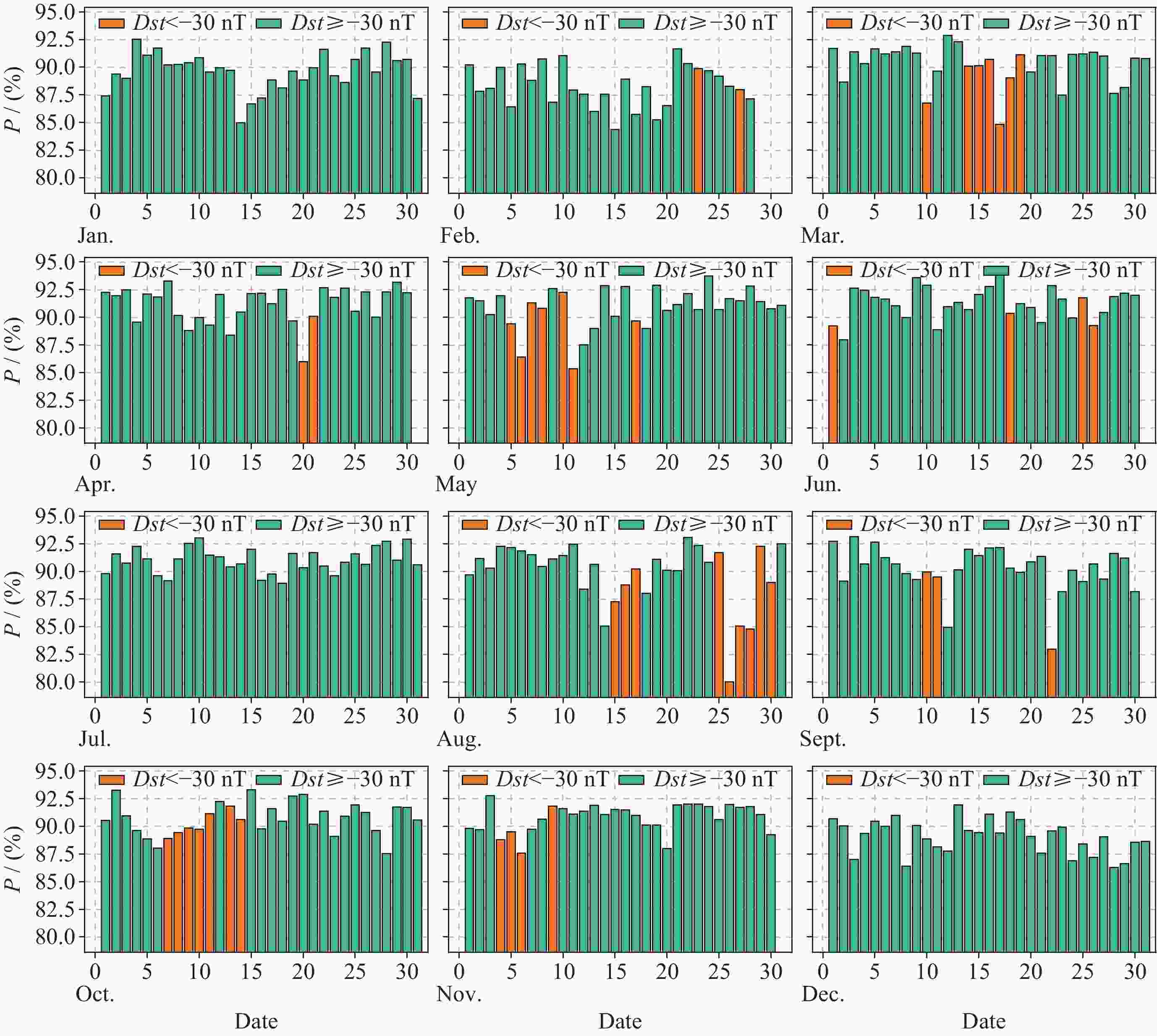
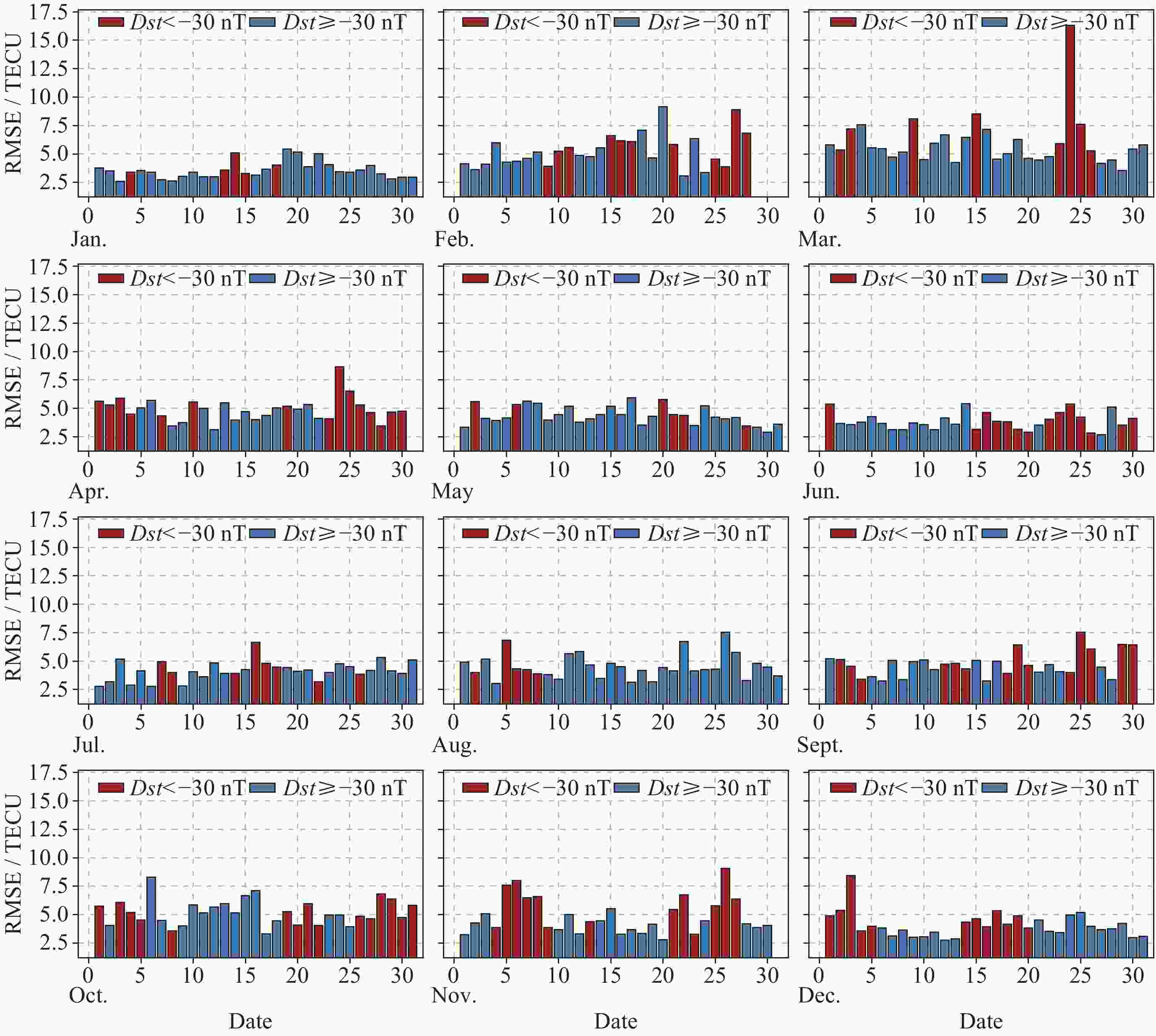
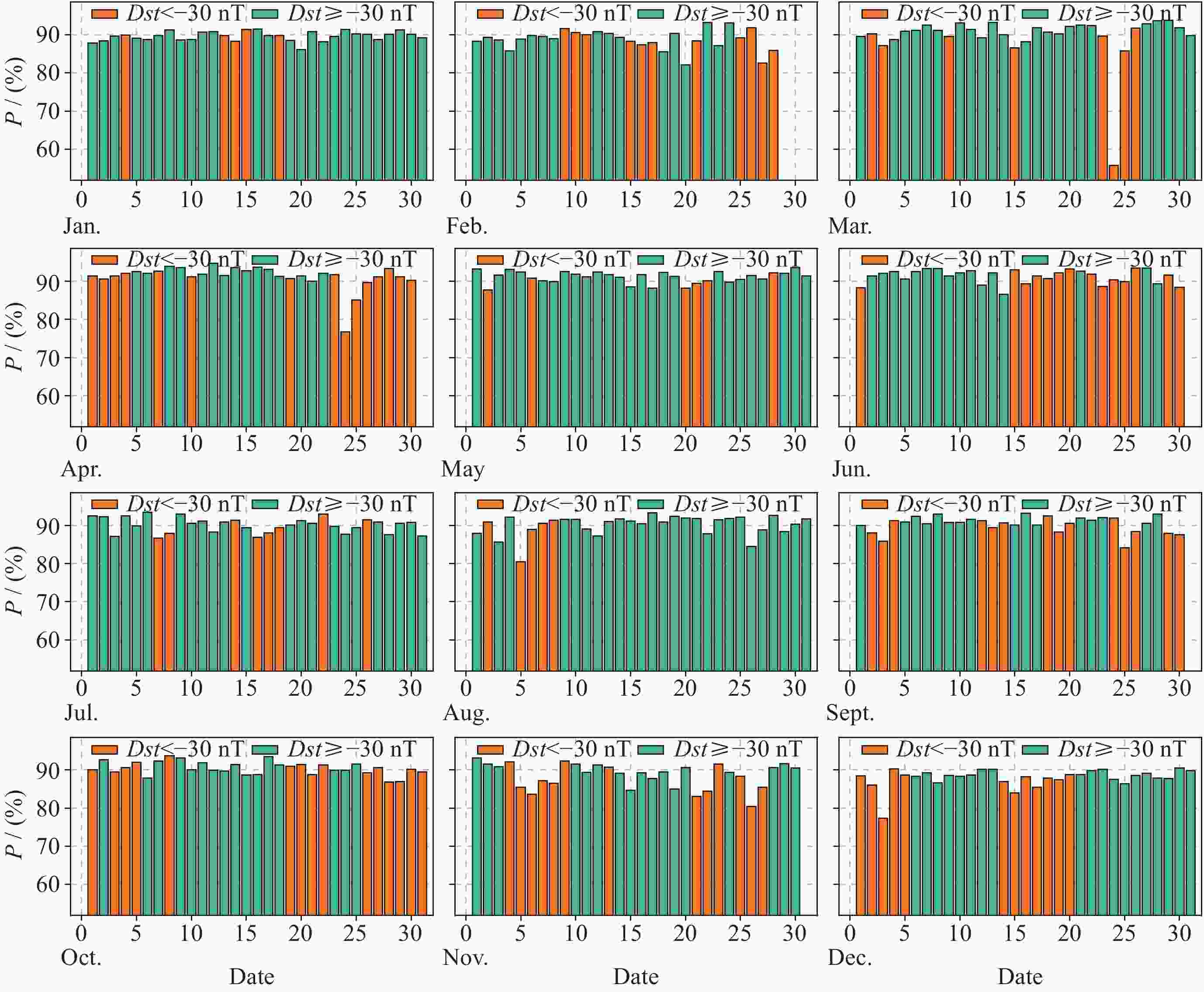
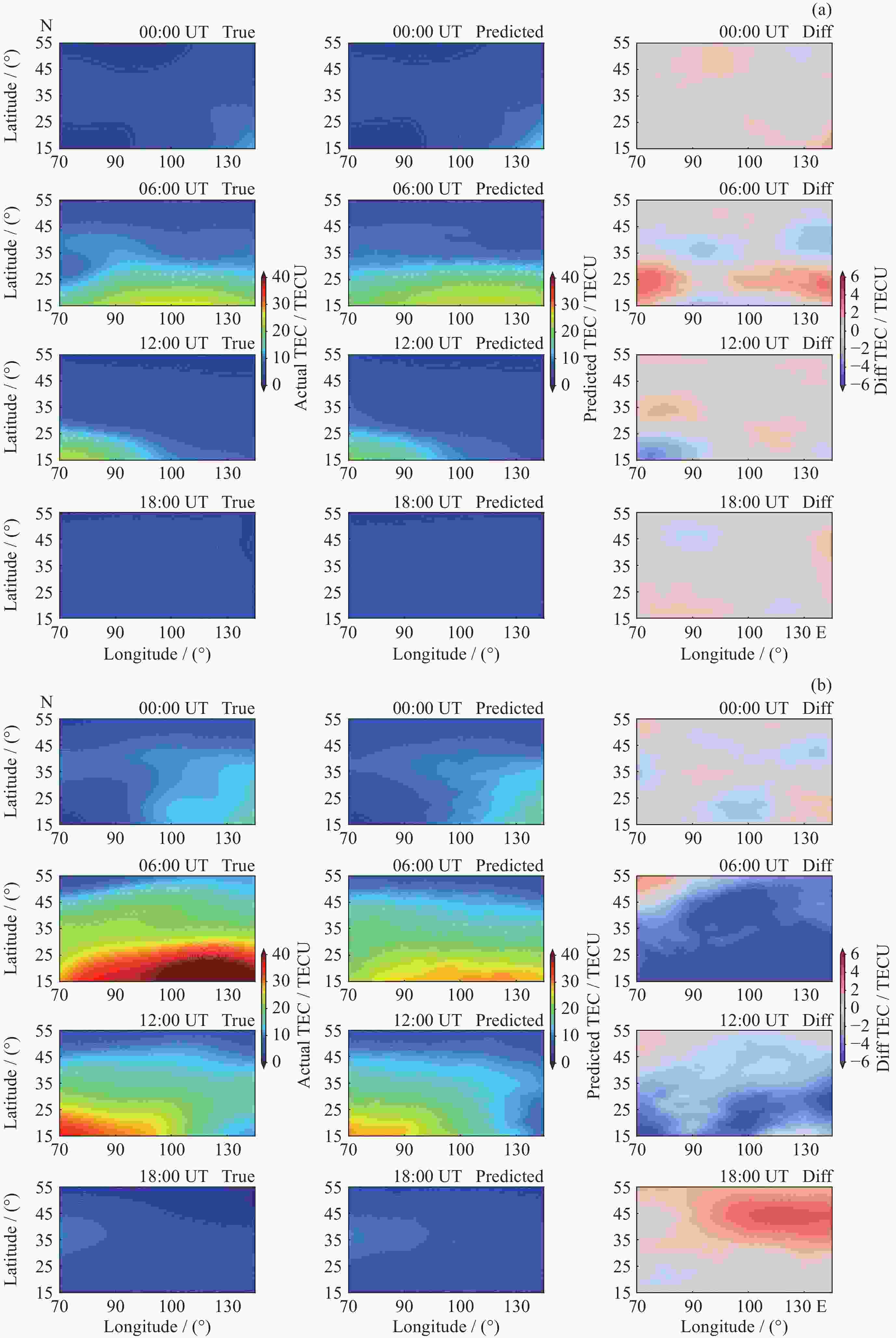
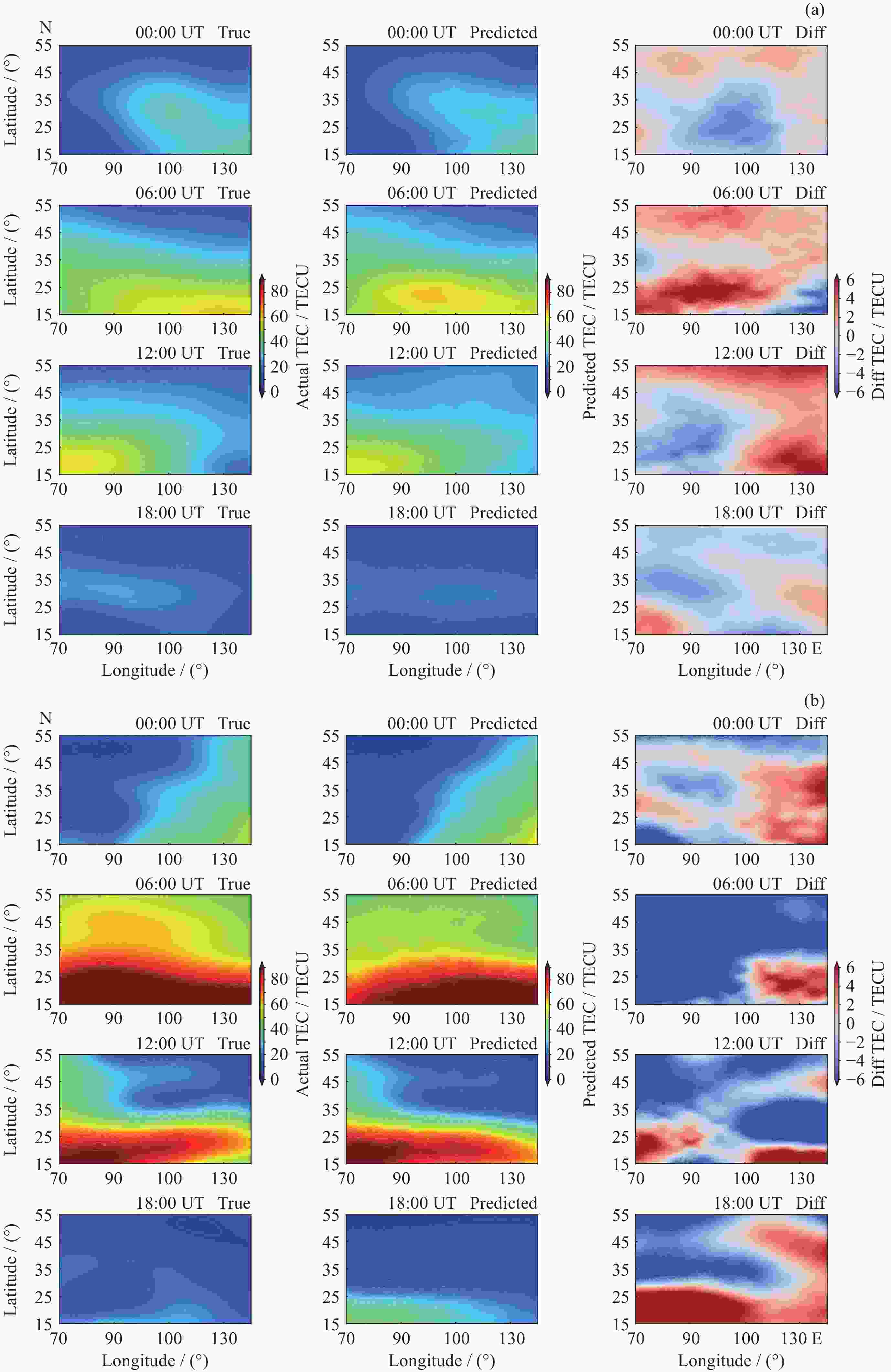
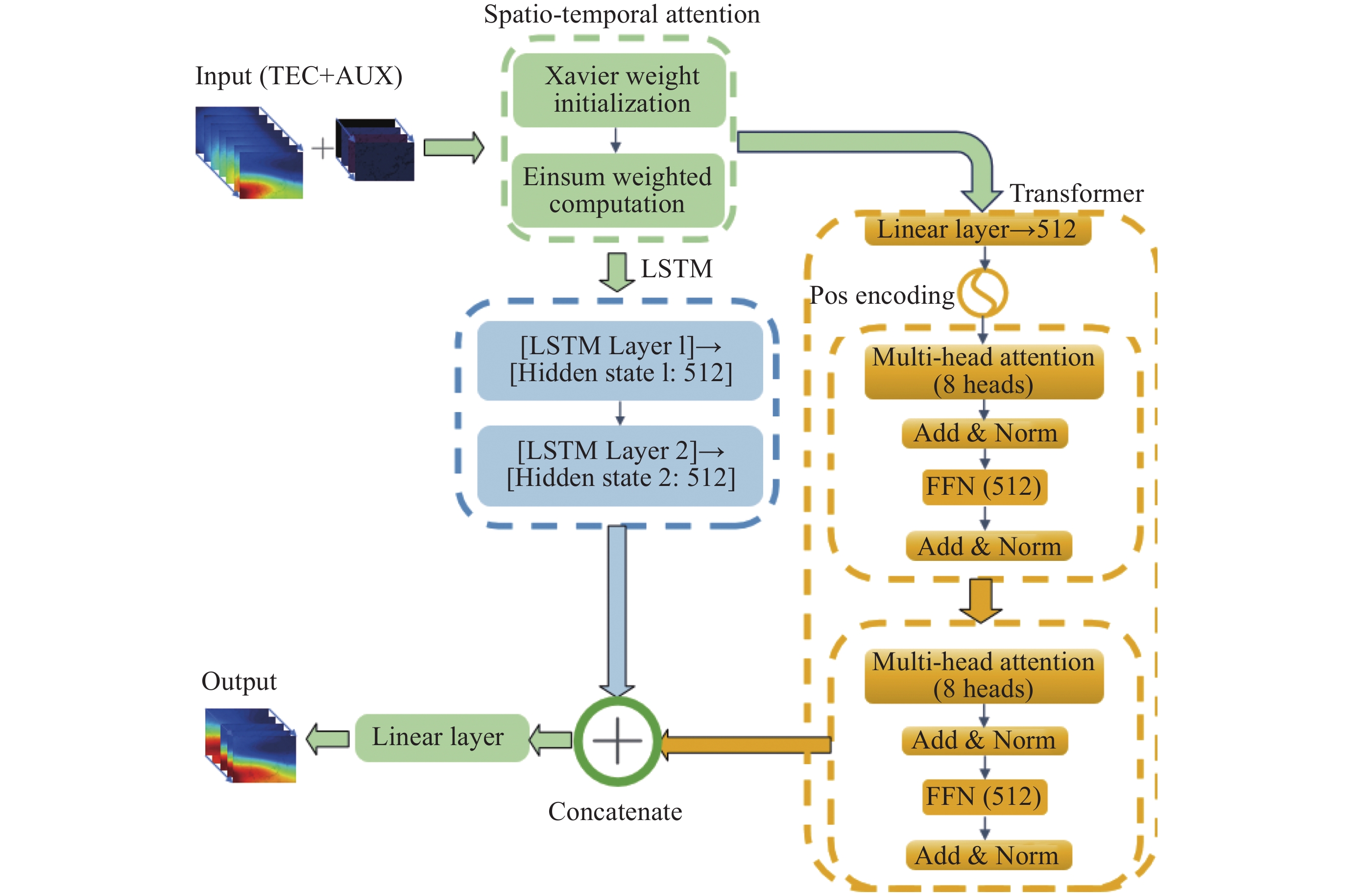
摘要: 电离层总电子含量(TEC)是研究电离层时空变化的重要参数. 本文提出一种结合时空Transformer (STT)与长短期记忆网络(LSTM), 并引入时空注意力机制的电离层TEC组合预测模型(LSTM-STT). 利用2000-2023年国际GNSS服务欧洲定轨中心(CODE)提供的中国及其周边地区的TEC数据, 时间范围覆盖8766 d, 采用滑动窗口方法对数据进行处理, 模型以前48 h的TEC数据以及辅助参数作为输入, 用于预测后24 h的TEC数据, 据此构建了8764个样本. 为验证模型性能, 分别在2018年(太阳活动低年)和2023年(太阳活动高年)开展实验进行预测分析. 研究结果表明, 模型在2018年测试集上全部样本的均方根误差(RMSE)均值为1.3981 TECU, 相对精度均值为90.2524%; 在2023年测试集上全部样本的RMSE均值为4.6262 TECU, 相对精度均值为89.9208%, 说明模型在不同太阳活动状态下均表现出良好的预测性能.
-
关键词:
- 电离层TEC /
- 时空Transformer /
- 长短期记忆网络 /
- 预测模型
Abstract: The ionosphere is a major source of error for satellite navigation, communication, and other applications, and the Total Electron Content (TEC) of the ionosphere is an important parameter for studying the temporal and spatial variations of the ionosphere, and it is extremely important to accurately predict the ionospheric TEC under different space weather conditions. Existing prediction models, when using auxiliary parameters such as solar activity and geomagnetic activity to improve the performance of ionospheric TEC prediction models, treat the auxiliary parameters as global covariates, ignoring the fact that the auxiliary parameters, although having the same value at each location, have different effects on the ionospheric TEC. To solve this problem, a combined ionospheric TEC prediction model (LSTM-STT) is proposed in this paper, which combines the Space-Time Transformer (STT) with the Long-Short-Term Memory (LSTM) and introduces the space-time attention mechanism. The model adopts the TEC data of China and its surrounding areas from 2000 to 2023 provided by the Center for Orbit Determination in Europe (CODE) of the International GNSS Service organization (IGS), with a time range of 8766 days, and the data are processed by the sliding window method, and the model takes the TEC data of the first 48 hours and the auxiliary parameters as inputs, and the TEC data of the last 24 hours after the prediction are constructed with 8764 samples. A total of 8764 samples were constructed. To verify the performance of the model, experimental prediction analyses were conducted in 2018 (a low solar activity year) and 2023 (a high solar activity year). The results show that the model has an average root mean square error of 1.3981 TECU and an average relative accuracy of 90.2524% on the 2018 test set, and an average root mean square error of 4.6262 TECU and an average relative accuracy of 89.9208% on the 2023 test set, which indicates that the model has good prediction performance.-
Key words:
- Ionospheric TEC /
- Spatio-temporal transformer /
- LSTM /
- Prediction model
-
表 1 以太阳活动低年(2018年)作为测试集的划分策略
Table 1. Segmentation strategy with a low solar activity year (2018) as the test set
名称 训练集 验证集 测试集 时间范围 2000-2016年, 2019-2023年 2017年 2018年 样本数量 8034 365 365 表 2 以太阳活动高年(2023年)作为测试集的划分策略
Table 2. Segmentation strategy with a high solar activity year (2023) as the test set
名称 训练集 验证集 测试集 时间范围 2000-2021年 2022年 2023年 样本数量 8034 365 365 -
[1] XIONG Nianlu, TANG Cunchen, LI Xingjian. Introduction to Ionospheric Physics[M]. Wuhan: Wuhan University Press, 1999 (熊年禄, 唐存琛, 李行健. 电离层物理概论[M]. 武汉: 武汉大学出版社, 1999XIONG Nianlu, TANG Cunchen, LI Xingjian. Introduction to Ionospheric Physics[M]. Wuhan: Wuhan University Press, 1999 [2] LIU Shuqiong, GAO Xin, LI Changchun. Prediction models of ionospheric TEC by EEMD and radial basis function neural network[J]. Engineering of Surveying and Mapping, 2020, 29(3): 15-19 (刘淑琼, 高鑫, 李长春. EEMD-RBF神经网络的电离层TEC预报模型[J]. 测绘工程, 2020, 29(3): 15-19 doi: 10.19349/j.cnki.issn1006-7949.2020.03.004LIU Shuqiong, GAO Xin, LI Changchun. Prediction models of ionospheric TEC by EEMD and radial basis function neural network[J]. Engineering of Surveying and Mapping, 2020, 29(3): 15-19 doi: 10.19349/j.cnki.issn1006-7949.2020.03.004 [3] HU Wenquan. Application of improved model based on RBF neural network in ionospheric TEC prediction[J]. Geomatics :Times New Roman;">& Spatial Information Technology, 2023, 46(8): 164-167 (胡文权. 基于RBF神经网络的改进模型在电离层TEC预报中的应用[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息, 2023, 46(8): 164-167 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2023.08.044HU Wenquan. Application of improved model based on RBF neural network in ionospheric TEC prediction[J]. Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology, 2023, 46(8): 164-167 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2023.08.044 [4] TANG Jun, LI Yinjian, ZHONG Zhengyu, et al. Prediction model of ionospheric TEC by EOF and LSTM neural network[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2021, 41(9): 911-915,944 (汤俊, 李垠健, 钟正宇, 等. EOF-LSTM神经网络的电离层TEC预报模型[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2021, 41(9): 911-915,944 doi: 10.14075/j.jgg.2021.09.005TANG Jun, LI Yinjian, ZHONG Zhengyu, et al. Prediction model of ionospheric TEC by EOF and LSTM neural network[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2021, 41(9): 911-915,944 doi: 10.14075/j.jgg.2021.09.005 [5] TANG Jun, GAO Xin. Prediction models of Ionospheric TEC by MEEMD and Elman recurrent neural network[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2020, 40(4): 395-399 (汤俊, 高鑫. MEEMD-Elman神经网络的电离层TEC预报模型[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2020, 40(4): 395-399 doi: 10.14075/j.jgg.2020.04.014TANG Jun, GAO Xin. Prediction models of Ionospheric TEC by MEEMD and Elman recurrent neural network[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2020, 40(4): 395-399 doi: 10.14075/j.jgg.2020.04.014 [6] NI Yude, YAN Miaoyu, LIU Ruihua. Short-term prediction of ionospheric TEC based on DOA-BP neural network[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2024, 45(4): 328707 (倪育德, 闫苗玉, 刘瑞华. 基于DOA-BP神经网络的电离层TEC短期预测[J]. 航空学报, 2024, 45(4): 328707 doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2023.28707NI Yude, YAN Miaoyu, LIU Ruihua. Short-term prediction of ionospheric TEC based on DOA-BP neural network[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2024, 45(4): 328707 doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2023.28707 [7] TANG Jun, ZHONG Zhengyu, DING Mingfei, et al. A prediction model of ionospheric TEC in China based on Elman neural network improved by Particle Swarm Optimization algorithm[J/OL]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 1-15[2024-12-03]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1676.TN.20230403.1808.005.html (汤俊, 钟正宇, 丁明飞, 等. 利用粒子群算法改进Elman神经网络的中国区域电离层TEC预报[J/OL]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 1-15[2024-12-03]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1676.TN.20230403.1808.005.htmlTANG Jun, ZHONG Zhengyu, DING Mingfei, et al. A prediction model of ionospheric TEC in China based on Elman neural network improved by Particle Swarm Optimization algorithm[J/OL]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 1-15[2024-12-03]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1676.TN.20230403.1808.005.html [8] YUAN Yuhuan, XIA Guozhen, ZHANG Xinmiao, et al. Synthesis-style auto-correlationbased transformer: A learner on ionospheric TEC series forecasting[J/OL]. Space Weather, 2023, 21, e2023SW003472. https://doi.org/10.1029/2023SW003472 [9] YUAN Tianjiao, CHEN Yanhong, LIU Siqing, et al. Prediction model for ionospheric total electron content based on deep learning recurrent neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2018, 38(1): 48-57 (袁天娇, 陈艳红, 刘四清, 等. 基于深度学习递归神经网络的电离层总电子含量经验预报模型[J]. 空间科学学报, 2018, 38(1): 48-57 doi: 10.11728/cjss2018.01.048YUAN Tianjiao, CHEN Yanhong, LIU Siqing, et al. Prediction model for ionospheric total electron content based on deep learning recurrent neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2018, 38(1): 48-57 doi: 10.11728/cjss2018.01.048 [10] ZHANG Fubin, ZHOU Chen, WANG Cheng, et al. Global ionospheric TEC prediction based on deep learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2021, 36(4): 553-561 (张富彬, 周晨, 王成, 等. 基于深度学习的全球电离层TEC预测[J]. 电波科学学报, 2021, 36(4): 553-561 doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2020051101ZHANG Fubin, ZHOU Chen, WANG Cheng, et al. Global ionospheric TEC prediction based on deep learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2021, 36(4): 553-561 doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2020051101 [11] REN X C, ZHAO B Q, REN Z P, et al. Deep learning‐based prediction of global ionospheric TEC during storm periods: Mixed CNN‐BiLSTM method[J]. Space Weather, 2024, 22(7): e2024SW003877 doi: 10.1029/2024SW003877 [12] YIN Ping, YAN Xiaopeng, NING Zehao. A combined forecasting method of ionospheric tomography TEC based on LSTM and IRI model[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2022, 37(5): 852-861 (尹萍, 闫晓鹏, 宁泽浩. 一种基于LSTM与IRI模型的电离层层析TEC组合预测方法[J]. 电波科学学报, 2022, 37(5): 852-861 doi: 10.12265/j.cjors.2021271YIN Ping, YAN Xiaopeng, NING Zehao. A combined forecasting method of ionospheric tomography TEC based on LSTM and IRI model[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2022, 37(5): 852-861 doi: 10.12265/j.cjors.2021271 [13] LIU Haijun, LEI Dongxing, YUAN Jing, et al. Ionospheric TEC prediction based on Attention-LSTM[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2024, 67(2): 439-451 (刘海军, 雷东兴, 袁静, 等. 基于注意力机制LSTM的电离层TEC预测[J]. 地球物理学报, 2024, 67(2): 439-451 doi: 10.6038/cjg2022Q0603LIU Haijun, LEI Dongxing, YUAN Jing, et al. Ionospheric TEC prediction based on Attention-LSTM[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2024, 67(2): 439-451 doi: 10.6038/cjg2022Q0603 [14] SHIH C Y, LIN C Y T, LIN S Y, et al. Forecasting of global ionosphere maps with multi-day lead time using Transformer-based neural networks[J]. Space Weather, 2024, 22(2): e2023SW003579 doi: 10.1029/2023SW003579 [15] YIN Mengting, ZOU Ziming, ZHONG Jia. A prediction model of the grid point ionospheric TEC[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2021, 41(4): 568-579 (殷梦婷, 邹自明, 钟佳. 一种电离层TEC格点预测模型[J]. 空间科学学报, 2021, 41(4): 568-579 doi: 10.11728/cjss2021.04.568YIN Mengting, ZOU Ziming, ZHONG Jia. A prediction model of the grid point ionospheric TEC[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2021, 41(4): 568-579 doi: 10.11728/cjss2021.04.568 [16] TANG J, ZHONG Z Y, HU J C, et al. Forecasting regional Ionospheric TEC maps over china using BiConvGRU deep learning[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(13): 3405 doi: 10.3390/rs15133405 [17] REN X D, YANG P X, MEI D K, et al. Global ionospheric TEC forecasting for geomagnetic storm time using a deep learning-based multi-model ensemble method[J]. Space Weather, 2023, 21(3): e2022SW003231 doi: 10.1029/2022SW003231 [18] LI Yongtao, LI Jianwen, DAI Taogao, et al. Influence of solar activity on ionospheric TEC change[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2018, 38(6): 847-854 (李涌涛, 李建文, 代桃高, 等. 太阳活动对电离层TEC变化影响分析[J]. 空间科学学报, 2018, 38(6): 847-854 doi: 10.11728/cjss2018.06.847LI Yongtao, LI Jianwen, DAI Taogao, et al. Influence of solar activity on ionospheric TEC change[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2018, 38(6): 847-854 doi: 10.11728/cjss2018.06.847 [19] ZHAO Haishan, YANG Li, XU Shiyi. Analysis of ionospheric TEC variation characteristics in solar activity years[J]. Journal of Navigation and Positioning, 2017, 5(1): 24-30 (赵海山, 杨力, 徐世依. 太阳活动高低年电离层TEC变化特性分析[J]. 导航定位学报, 2017, 5(1): 24-30 doi: 10.16547/j.cnki.10-1096.20170106ZHAO Haishan, YANG Li, XU Shiyi. Analysis of ionospheric TEC variation characteristics in solar activity years[J]. Journal of Navigation and Positioning, 2017, 5(1): 24-30 doi: 10.16547/j.cnki.10-1096.20170106 [20] AN Yuzhu, ZHANG Ren, WANG Weimin, et al. Correlation analysis between sunspot and TEC[J]. Journal of PLA University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2012, 13(5): 571-576 (安玉柱, 张韧, 王伟民, 等. 太阳黑子数与电离层TEC的相关性分析[J]. 解放军理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 13(5): 571-576AN Yuzhu, ZHANG Ren, WANG Weimin, et al. Correlation analysis between sunspot and TEC[J]. Journal of PLA University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2012, 13(5): 571-576 [21] LIU Libo, WAN Weixing, CHEN Yiding, et al. Solar activity effects of the ionosphere: A brief review[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2011, 56(12): 1202-1211 (刘立波, 万卫星, 陈一定, 等. 电离层与太阳活动性关系[J]. 科学通报, 2011, 56(7): 477-487. DOI: 10.1007/s11434-010-04226-9LIU Libo, WAN Weixing, CHEN Yiding, et al. Solar activity effects of the ionosphere: A brief review[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2011, 56(12): 1202-1211 [22] China Meteorological Administration. QX/T 239-2014 Levels of geomagnetic activity[S]. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 2014 (中国气象局. QX/T 239-2014 地磁活动水平分级[S]. 北京: 中国气象出版社, 2014China Meteorological Administration. QX/T 239-2014 Levels of geomagnetic activity[S]. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 2014 [23] LIAO Wenti, CHEN Zhou, ZHAO Yuxin, et al. Short- and medium-term forecasting of global ionospheric TEC map based on hybrid model LSTM-DNN[J]. Spacecraft Environment Engineering, 2021, 38(3): 281-286 (廖文梯, 陈洲, 赵瑜馨, 等. 利用混合模型LSTM-DNN进行全球电离层TEC map的中短期预报[J]. 航天器环境工程, 2021, 38(3): 281-286 doi: 10.12126/see.2021.03.007LIAO Wenti, CHEN Zhou, ZHAO Yuxin, et al. Short- and medium-term forecasting of global ionospheric TEC map based on hybrid model LSTM-DNN[J]. Spacecraft Environment Engineering, 2021, 38(3): 281-286 doi: 10.12126/see.2021.03.007 -
-




 王朝钰 男, 1998年出生于湖北省鄂州市, 硕士研究生, 研究方向为卫星导航技术、电离层遥感遥测成像, 深度学习, 智能布粮装置. E-mail:
王朝钰 男, 1998年出生于湖北省鄂州市, 硕士研究生, 研究方向为卫星导航技术、电离层遥感遥测成像, 深度学习, 智能布粮装置. E-mail: 

 下载:
下载: